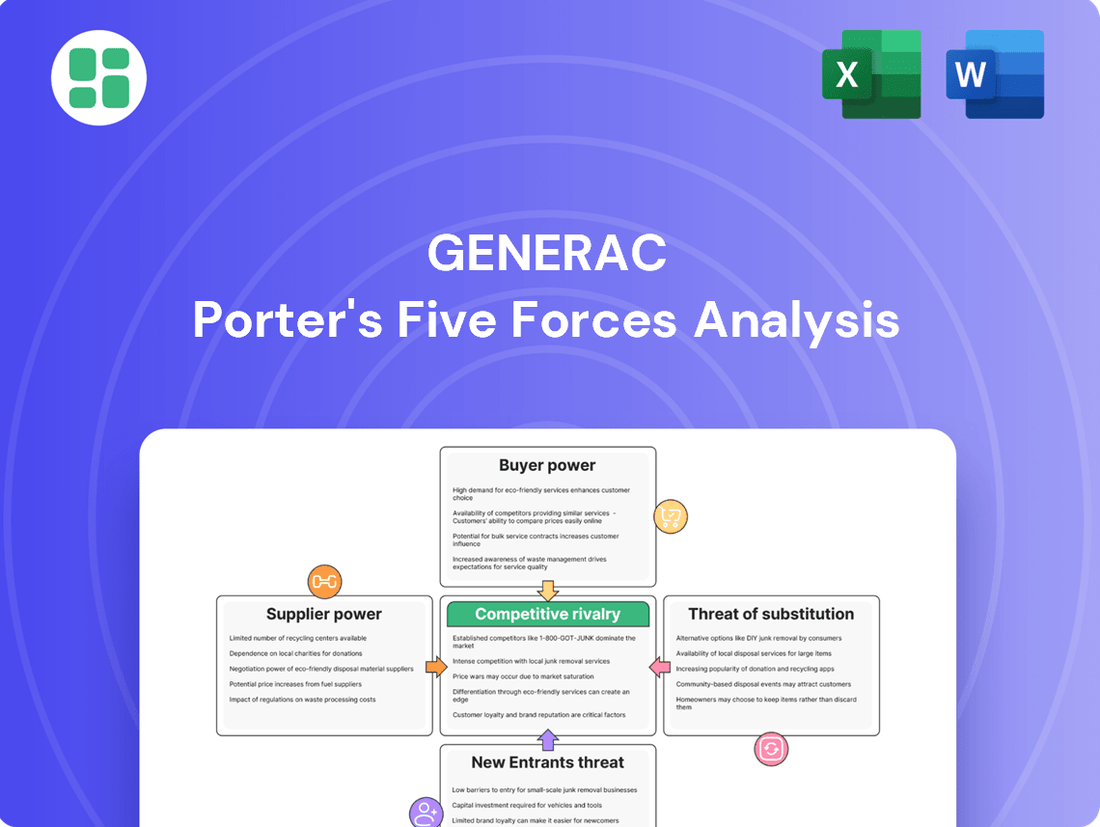
Generac Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Generac Bundle
Generac's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the intense rivalry among existing players to the significant bargaining power of its suppliers. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate this market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Generac’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Generac relies on a diverse supply chain for crucial parts like engines, electronic controls, steel, and copper. Supplier concentration becomes a key factor; if a small number of companies control the supply of essential components, they gain considerable leverage. This is especially true for specialized parts needed for power generation and energy storage systems, where Generac might have fewer alternatives.
Generac faces considerable switching costs when changing suppliers for critical components. The process often necessitates significant re-engineering of their products, investment in new tooling, and rigorous re-qualification of parts. This complexity directly enhances the bargaining power of their existing suppliers.
For instance, if Generac relies on a supplier for a highly integrated control system or a proprietary engine technology, the expense and time required to find and implement an alternative could be prohibitive. This dependency means suppliers offering such specialized solutions can command higher prices or more favorable terms, as Generac would experience substantial disruption and financial impact from a supplier shift.
Generac's reliance on suppliers offering highly specialized or proprietary components, like advanced battery cells for its energy storage solutions or unique engine technologies, significantly bolsters supplier bargaining power. For instance, a supplier of a critical, patented generator control module that no other firm produces grants them considerable leverage. This exclusivity means Generac has limited alternatives, potentially leading to higher input costs and longer lead times for product development in 2024.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Generac's market, essentially becoming competitors, can diminish Generac's bargaining power. This means if a key component supplier, for instance, decided it could profitably manufacture and sell Generac's generators or related energy systems directly, it would create a new competitive pressure.
While this forward integration is a theoretical risk, the significant capital investment required and the intricate knowledge of end-user markets for power generation solutions make it a less likely or immediate concern for most of Generac's suppliers. For example, the specialized manufacturing processes and distribution networks needed for residential standby generators are substantial barriers. In 2023, Generac's revenue was approximately $3.7 billion, indicating the scale of operations a supplier would need to replicate.
- Forward Integration Risk: Suppliers moving into Generac's product space directly reduces Generac's leverage.
- Capital Intensity Barrier: The substantial financial resources needed to enter Generac's markets limits supplier appetite for forward integration.
- Market Complexity: Understanding and navigating the diverse customer base and regulatory landscape for energy solutions is a significant hurdle for potential supplier competitors.
Importance of Generac to Supplier's Business
Generac's substantial purchasing volume significantly diminishes the bargaining power of its suppliers. When Generac accounts for a large percentage of a supplier's total sales, that supplier has a strong incentive to keep Generac satisfied, thus limiting their ability to demand higher prices or less favorable terms. For instance, if a key component supplier derives over 20% of its revenue from Generac, they are less likely to risk that relationship by pushing for unfavorable contract changes.
Conversely, Generac's position as a relatively small customer for highly diversified suppliers can shift leverage. If a supplier serves numerous large clients, Generac's business might represent a minor portion of their overall revenue, potentially giving that supplier more room to negotiate terms that benefit them. However, Generac's status as a leading global manufacturer of power generation equipment does provide some counterbalance to this dynamic, as their consistent demand and market presence are attractive to many suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers is further influenced by the availability of alternative suppliers for Generac. If Generac can easily switch to another provider for critical components without significant disruption or cost, the current supplier's leverage is weakened. This is particularly true for standardized parts where multiple manufacturers exist. For example, in 2024, the market for certain electrical components saw increased competition, which would generally reduce supplier power.
- Generac's scale as a major buyer reduces supplier leverage.
- Supplier dependency on Generac revenue limits their negotiation power.
- Generac's ability to source from multiple suppliers mitigates supplier power.
- The availability of alternative suppliers for Generac is a key factor in supplier bargaining power.
Generac's bargaining power with suppliers is moderated by its significant purchasing volume, which can reduce supplier leverage if Generac represents a substantial portion of their sales. However, for highly diversified suppliers, Generac's business might be a smaller fraction, potentially increasing supplier negotiation strength. The availability of alternative suppliers for critical components, especially standardized ones, is a key factor in limiting supplier power, as seen with increased competition in electrical components in 2024.
The bargaining power of Generac's suppliers is influenced by the concentration of suppliers for critical components; fewer suppliers mean more leverage for them. Generac faces high switching costs for specialized parts, such as proprietary engine technologies or integrated control systems, which strengthens supplier power. For instance, a supplier of a patented generator control module in 2024 would have considerable leverage due to Generac's limited alternatives, potentially increasing input costs.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Generac Context |
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases power | Key for specialized parts like engines and controls |
| Switching Costs | High costs increase power | Significant for re-engineering and re-qualification of parts |
| Availability of Alternatives | More alternatives decrease power | Strong for standardized components, weaker for proprietary ones |
| Purchasing Volume | High volume decreases power | Generac's scale can influence supplier behavior |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping Generac's market, examining rivalry, buyer and supplier power, new entrants, and substitutes to illuminate strategic opportunities and threats.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a dynamic visualization of all five forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Generac's customer base is quite varied, ranging from individual homeowners to large commercial and industrial operations. This diversity means price sensitivity isn't uniform across the board. Homeowners buying generators for their homes might be more swayed by upfront costs, especially for non-essential upgrades.
However, commercial and industrial clients often look beyond the initial price tag. For them, factors like long-term reliability, maintenance costs, and the overall cost of ownership tend to be more critical. This means they are less likely to be solely driven by the lowest price.
In 2024, Generac saw robust sales in its residential product lines. This performance suggests that despite potential price considerations for homeowners, the demand for their solutions remained strong, highlighting the value proposition beyond just the sticker price.
Customers considering Generac's products have a variety of alternatives, ranging from relying on the traditional power grid to exploring other generator brands or even entirely different energy solutions like solar-only systems. This wide array of choices significantly enhances the bargaining power of customers. If Generac's pricing is perceived as too high or its product features fall short of competitive offerings, customers can readily switch to a substitute, putting pressure on Generac to remain competitive.
Generac's buyer concentration is a key factor in customer bargaining power. If a few large entities, like major distributors or significant industrial clients, account for a substantial portion of Generac's sales, their ability to negotiate better terms increases. This is particularly relevant for Generac's commercial and industrial product lines, where order volumes are typically much larger than for residential sales.
However, Generac's extensive dealer network helps to mitigate this risk. By having numerous independent dealers across various regions, Generac diversifies its customer base, reducing reliance on any single buyer. This broad distribution model naturally dilutes the individual bargaining power of smaller or even moderately sized customers.
For instance, while specific customer concentration data for 2024 isn't publicly detailed, Generac's strategy of expanding its residential product offerings and its vast network of over 7,000 dealers in North America alone suggests a deliberate effort to avoid over-dependence on a few large buyers.
Switching Costs for Customers
The cost for customers to switch away from Generac can be quite significant. Once a Generac system is installed, moving to a competitor often means incurring new installation fees, dealing with potential compatibility problems with existing setups, and a learning curve for a new product. These financial and practical hurdles effectively lower the bargaining power customers wield.
Generac actively works to enhance customer loyalty and reduce the likelihood of switching. By developing an integrated ecosystem of products and services, they aim to create a sticky environment where customers are more inclined to stay within the Generac family. This strategy is designed to increase customer lock-in, making it less appealing to explore alternative solutions.
- High Installation Costs: Replacing a Generac generator or related equipment can cost thousands of dollars in new installation, especially for whole-home standby units.
- Compatibility Challenges: Existing Generac accessories, control panels, or monitoring systems may not seamlessly integrate with competitor products, necessitating further investment.
- Learning Curve: Users familiar with Generac's interface and operation may face a period of adjustment and potential inefficiency when learning a new system.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers, particularly in the commercial and industrial sectors, are increasingly well-informed. This allows them to readily compare pricing, features, and user feedback for various power generation solutions. In 2024, the accessibility of online reviews and detailed product specifications significantly amplified this trend.
This heightened market transparency empowers buyers, enabling them to negotiate more favorable terms with suppliers like Generac. They can leverage readily available data to push for better pricing and service agreements. For instance, a large construction firm might use aggregated performance data from multiple Generac competitors to secure a discount on a fleet purchase.
- Informed Buyers: Customers can easily access and compare product specifications, pricing, and performance reviews online, reducing information asymmetry.
- Negotiating Power: Increased transparency allows customers to leverage competitive offerings to negotiate better terms and pricing.
- Brand Differentiation: Generac's established brand reputation and its robust dealer network serve as crucial counterbalances to customer bargaining power by fostering loyalty and trust.
Generac's customer bargaining power is influenced by several factors, including the availability of substitutes and the cost for customers to switch. The wide array of alternative power solutions available means customers can easily shift to competitors if Generac's offerings are not perceived as competitive, thus exerting pressure on pricing and features.
The significant costs associated with switching, such as new installation and potential compatibility issues, act as a deterrent for customers, thereby reducing their bargaining power. Generac's efforts to build customer loyalty through integrated product ecosystems further lock in customers, diminishing their inclination to switch and negotiate aggressively.
In 2024, Generac's strong residential sales indicate that while price is a consideration, the overall value proposition, including reliability and brand trust, resonated with homeowners. For larger commercial clients, the focus remains on total cost of ownership, making them less susceptible to minor price fluctuations but more sensitive to long-term performance and service agreements.
The increasing market transparency, fueled by readily available online information and reviews in 2024, has empowered customers to make more informed comparisons. This allows them to negotiate more effectively, leveraging competitive data to secure better terms, though Generac's established brand and dealer network provide a counterbalance.
Full Version Awaits
Generac Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the exact Generac Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape within the generator industry. You're looking at the actual, fully formatted document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this precise file, allowing for immediate strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Generac operates in a crowded power generation and energy technology market. The field includes major industrial players such as Cummins and Kohler, alongside innovative energy storage specialists like Enphase Energy. This broad spectrum of domestic and international competitors significantly heightens the competitive rivalry Generac faces.
The overall growth rate of the backup power and energy technology market significantly impacts competitive rivalry. While the residential generator market experienced robust growth, driven by increasing power outages and a heightened demand for energy resilience, the commercial and industrial segments have encountered some softness. For instance, Generac reported a 14% increase in net sales for its residential power segment in the first quarter of 2024, contrasting with a slight decline in its commercial and industrial segment during the same period.
Generac stands out by focusing on innovation and reliability, developing a growing range of energy solutions that now include smart home integration and energy storage. This strategy helps them avoid direct price wars, though rivals are also pushing similar tech, making continuous differentiation crucial.
In 2024, Generac continued to bolster its product differentiation. For instance, they launched updated generator models and expanded their energy storage offerings, aiming to capture market share through advanced features and integrated systems. This commitment to new product development is key in a market where competitors are also actively innovating.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in the power generation equipment sector, including substantial investments in specialized manufacturing facilities and long-term customer contracts, can trap companies in the market even when profits are low. This scenario intensifies competitive rivalry as firms are compelled to stay and fight for market share, rather than exit gracefully. Generac, for instance, operates in a capital-intensive industry where the cost of shutting down or repurposing specialized production lines can be prohibitively high.
The significant capital outlay for advanced manufacturing, research and development, and global distribution networks creates a substantial hurdle for companies considering departure. For example, the development of new generator technologies often requires multi-year R&D cycles and extensive testing, locking in capital. This financial commitment makes exiting the market a difficult and costly decision, thereby sustaining pressure among existing players.
- High Fixed Asset Investments: Generac's manufacturing plants and specialized machinery represent significant fixed assets that are difficult to liquidate or redeploy, increasing exit costs.
- Specialized Manufacturing Facilities: The need for highly specialized equipment and processes in generator production means these facilities have limited alternative uses, raising exit barriers.
- Long-Term Contracts and Commitments: Existing service agreements, warranties, and supply chain commitments can obligate companies to remain operational for extended periods, even if market conditions deteriorate.
- Brand Reputation and Customer Relationships: The established brand equity and deep customer relationships built over years are assets that companies are reluctant to abandon, further discouraging exit.
Brand Identity and Loyalty
Generac’s robust brand identity, especially in the home standby generator sector, creates a significant barrier to entry. Its strong market presence means many consumers automatically associate Generac with generators, fostering a high degree of brand loyalty. This makes it challenging for competitors to chip away at Generac's established customer base.
This brand loyalty is further solidified by accolades such as being named America's Most Trusted Home Generator Brand in 2024. Such recognition directly translates into a competitive advantage, as consumers are more likely to choose a brand they trust and perceive as reliable, even when faced with alternative options.
- Brand Recognition: Generac is often the go-to name for home generators.
- Customer Loyalty: Established trust makes customers less likely to switch.
- Market Synonymousness: The brand is nearly interchangeable with the product category for many consumers.
- 2024 Recognition: Named America's Most Trusted Home Generator Brand, reinforcing its strong market perception.
Generac faces intense competition from established players like Kohler and Cummins, as well as emerging energy storage specialists such as Enphase Energy. This diverse competitive landscape, encompassing both large industrial firms and innovative technology companies, significantly amplifies the rivalry within the power generation and energy technology sectors.
The market's growth trajectory directly influences the intensity of competition. While the residential generator market saw strong demand in early 2024, with Generac reporting a 14% increase in its residential power segment sales in Q1 2024, the commercial and industrial segments experienced some slowdown. This uneven growth means companies are fiercely vying for dominance in the more robust residential sector.
Generac's strategy of focusing on innovation and reliability, particularly in smart home integration and energy storage, helps it navigate this competitive environment. However, rivals are also investing heavily in similar technologies, making continuous product differentiation and technological advancement critical for maintaining market position.
High exit barriers, stemming from substantial investments in specialized manufacturing and R&D, force companies to remain competitive even in challenging conditions. Generac's commitment to advanced manufacturing and its extensive distribution networks create significant capital lock-in, ensuring that existing players remain actively engaged in competing for market share.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Improvements in grid reliability represent a potential substitute threat to Generac's core business. If the national power grid becomes significantly more resilient, leading to fewer and shorter power outages, the demand for backup generators could diminish. This would directly impact the market for Generac's products.
However, current trends suggest this threat may be limited. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. experienced a notable number of significant weather events, contributing to widespread power disruptions. Furthermore, projections for rising energy costs in 2024 and beyond indicate that consumers and businesses will likely continue to seek ways to mitigate the impact of grid instability and high electricity prices, thereby supporting demand for backup power solutions.
Standalone battery energy storage systems, particularly when integrated with solar power, present a compelling, quiet, and emission-free alternative to traditional generators for backup power and energy independence. Generac is actively competing in this space with its own PWRcell energy storage systems.
However, the broader energy storage market is rapidly expanding, with numerous other companies offering battery solutions that directly substitute for generator functions, potentially impacting Generac's market share in backup power applications.
The increasing adoption of energy-efficient appliances and smart home energy management systems presents a significant threat of substitution for Generac. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy reported that ENERGY STAR certified appliances use, on average, 9% less energy than their standard counterparts, a trend expected to accelerate. This reduction in overall energy consumption can diminish the perceived need for substantial backup power solutions like generators, as households require less power during outages.
Furthermore, widespread participation in demand-side management (DSM) programs, often incentivized by utility companies, can further curb energy demand. These programs encourage consumers to reduce their electricity usage during peak hours, effectively smoothing out demand curves and lessening reliance on backup power. While Generac has ventured into smart home technology, a substantial societal shift toward energy conservation could directly impact the market size for their core generator products.
Microgrids and Distributed Generation (Non-Generac)
The increasing adoption of community microgrids and distributed energy resources not reliant on Generac's core generator technology poses a significant threat of substitutes. These systems, often featuring solar panels coupled with battery storage, offer localized energy solutions and a pathway to energy independence, bypassing the need for traditional fossil fuel-based generators. For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy reported that by the end of 2023, over 300 microgrid projects were operational or in development across the nation, many of which are centered around renewable energy sources and advanced storage, not Generac's traditional offerings.
These alternative solutions cater to a growing demand for resilient and sustainable energy, directly competing with Generac's established market. The trend is amplified by supportive government policies and declining costs for renewable technologies. For example, the U.S. solar market saw installations grow by 40% in 2023 compared to 2022, according to the Solar Energy Industries Association, indicating a robust and expanding substitute market. Generac is actively addressing this by investing in broader energy technology solutions, including battery storage and smart grid integration, to remain competitive.
- Growing Market Share of Non-Generator Solutions: The U.S. microgrid market is projected to reach $20 billion by 2028, with a significant portion driven by renewable energy and storage, representing a direct substitute.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in solar efficiency and battery storage density are making these substitutes increasingly cost-effective and attractive alternatives to traditional backup power.
- Policy Support: Federal and state incentives for renewable energy and grid modernization further bolster the appeal and adoption of these non-Generac distributed generation systems.
- Generac's Strategic Response: Generac's investments in technologies like PWRcell (home battery storage) and its participation in grid services demonstrate an effort to counter the threat of substitutes by expanding its own distributed energy portfolio.
Alternative Fuel Technologies
While Generac's core business relies on combustion engines, the increasing viability of alternative power generation technologies presents a potential substitute threat. Advanced fuel cells, for instance, offer a non-combustion-based approach to backup power, currently occupying niche markets but with the potential for broader adoption driven by technological progress and sustainability initiatives. For example, the global fuel cell market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a developing competitive landscape.
These emerging technologies could eventually offer comparable reliability and performance to traditional generators, albeit through different means. Generac's strategic focus on evolving towards more sustainable energy solutions, including exploring hydrogen fuel cell technology, directly addresses this long-term substitute threat by aiming to remain at the forefront of energy innovation.
- Fuel Cell Market Growth: The fuel cell market is expected to expand, potentially offering alternatives to traditional generators.
- Technological Advancement: Innovations in fuel cell technology could make them more competitive substitutes in the future.
- Generac's Strategy: Generac is actively investing in sustainable energy solutions to counter this evolving threat.
The threat of substitutes for Generac's generator business is multifaceted, encompassing improvements in grid reliability, the rise of battery storage, energy efficiency, and microgrids. While Generac competes in the battery storage market with its PWRcell systems, the broader energy storage sector is expanding rapidly with numerous players. The U.S. Department of Energy reported that ENERGY STAR certified appliances use approximately 9% less energy, a trend that could reduce the need for extensive backup power.
Community microgrids and distributed energy resources, often powered by solar and battery storage, offer localized energy independence and directly compete with traditional generators. By the end of 2023, over 300 microgrid projects were operational or in development across the U.S., many leveraging renewables. The U.S. solar market saw a 40% installation growth in 2023, highlighting the increasing appeal of these substitute solutions.
| Substitute Technology | Key Characteristic | Market Trend/Data | Impact on Generac |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improved Grid Reliability | Reduced frequency/duration of outages | U.S. grid resilience is a focus, but significant weather events in 2023 caused widespread outages. | Could decrease demand for backup generators. |
| Battery Energy Storage (e.g., PWRcell) | Quiet, emission-free backup; energy independence | Rapidly expanding market with many competitors. | Direct competition; Generac is a participant but faces market share pressure. |
| Energy Efficiency & Smart Home Management | Reduced overall energy consumption | ENERGY STAR appliances use ~9% less energy; growing adoption of demand-side management programs. | Diminishes the perceived need for large backup power solutions. |
| Microgrids & Distributed Energy Resources | Localized, resilient energy solutions | Over 300 U.S. microgrid projects by end of 2023; 40% growth in U.S. solar installations in 2023. | Bypasses traditional generators, offering alternative energy independence. |
| Fuel Cells | Non-combustion power generation | Global fuel cell market valued at ~$2.5 billion in 2023; projected growth. | Emerging alternative with potential for future competition. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the power generation and energy technology sector, particularly in manufacturing generators and sophisticated energy solutions, demands significant upfront capital. This includes substantial investments in research and development, establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and building robust distribution channels.
These high capital requirements create a formidable barrier for potential new competitors. For instance, the average cost to build a new, medium-sized generator manufacturing facility can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, not to mention the ongoing R&D expenses needed to stay competitive in areas like battery storage and smart grid technology.
Generac enjoys significant economies of scale in its manufacturing, procurement, and distribution processes. This allows the company to produce its products at a lower cost per unit compared to smaller or emerging competitors. For instance, in 2023, Generac reported net sales of $3.7 billion, indicating a substantial volume of production that drives down per-unit costs.
New entrants would find it challenging to match Generac's cost efficiencies, making it difficult to compete effectively on price. The sheer scale of Generac's operations, coupled with its established supply chain and distribution network, creates a substantial barrier to entry that new companies would struggle to overcome in the near term.
Generac benefits from strong brand loyalty, making it difficult for newcomers to capture market share. This loyalty is built on years of reliable performance and customer trust.
The company’s extensive distribution network, boasting 9,100 authorized residential dealers by late 2024, presents a formidable barrier. Replicating this reach requires substantial time, capital, and strategic partnerships, significantly deterring potential new entrants.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
Generac's strong portfolio of patents and proprietary technology significantly raises the barrier to entry for new competitors. Their innovations in generator design, energy storage solutions, and smart home connectivity require substantial research and development investment for any newcomer to replicate. For instance, Generac's ongoing product development, including advancements in hybrid power systems, further solidifies their technological lead.
The threat of new entrants is mitigated by Generac's established intellectual property.
- Proprietary Technology: Generac possesses unique technologies in generator engineering and smart home integration.
- Patent Protection: Numerous patents safeguard Generac's product designs and operational processes.
- R&D Investment: The significant R&D expenditure required to match Generac's technological capabilities deters potential new entrants.
- Innovation Pipeline: Continuous new product launches demonstrate Generac's commitment to maintaining a technological edge.
Regulatory Hurdles and Safety Standards
The power generation industry is heavily regulated, with new entrants facing significant compliance challenges. These include meeting strict emissions standards, adhering to complex electrical codes, and obtaining various product certifications. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continued to enforce stringent rules on emissions from stationary sources, requiring substantial investment in pollution control technology for any new generator manufacturer.
Navigating these regulatory hurdles is a time-consuming and expensive process. Companies must invest in research and development to ensure their products meet evolving environmental and safety mandates. The cost of compliance, including testing, documentation, and potential retrofitting, can deter smaller or less capitalized new entrants, thereby reinforcing the barrier to entry.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants in the power generation sector often face upfront costs exceeding millions of dollars to meet EPA emissions standards and other safety certifications.
- Time to Market: Obtaining necessary approvals and certifications can add 1-3 years to a product's development cycle, delaying revenue generation.
- Evolving Standards: Continuous updates to safety and environmental regulations necessitate ongoing investment and adaptation, posing a persistent challenge for new market participants.
The threat of new entrants into Generac's market remains relatively low. High capital requirements for manufacturing and R&D, coupled with Generac's established economies of scale and brand loyalty, create significant barriers.
Furthermore, Generac's extensive dealer network and robust patent portfolio deter potential competitors. Navigating stringent regulatory compliance, such as EPA emissions standards, also adds considerable cost and time, further limiting new entrants.
By late 2024, Generac's 9,100 authorized residential dealers underscore the difficulty new companies face in establishing a comparable distribution reach.
The company’s substantial net sales of $3.7 billion in 2023 highlight the scale advantages that new entrants would struggle to match, impacting their ability to compete on price.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Generac Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse data sources, including Generac's annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We also incorporate industry-specific market research reports and data from reputable financial news outlets to capture the competitive landscape.