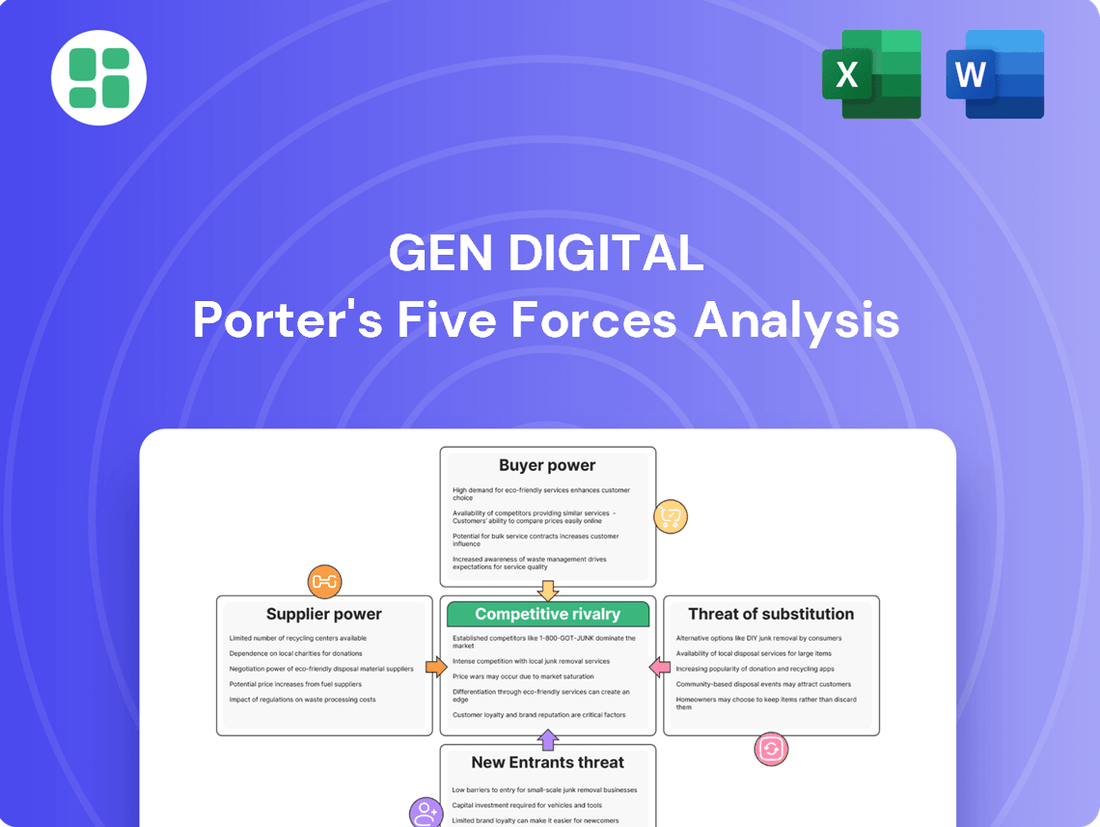
Gen Digital Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Gen Digital Bundle
Gen Digital operates in a dynamic tech landscape where understanding competitive forces is crucial. Our analysis delves into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the cybersecurity sector. This snapshot offers a glimpse into the pressures shaping Gen Digital's market position.
The complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis unlocks a deeper understanding of Gen Digital's strategic environment, providing actionable intelligence on each force. Gain the insights needed to navigate this competitive terrain and make informed strategic decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration for Gen Digital is relatively low because the essential building blocks for cybersecurity software, like development tools and cloud services, are widely available from numerous providers. This broad availability limits the leverage any single supplier can exert.
While specialized threat intelligence feeds are important, Gen Digital's substantial size and significant investment in internal research and development capabilities mean it doesn't have to depend heavily on any one external source for crucial technology or proprietary information. This internal strength acts as a buffer against supplier power.
Furthermore, Gen Digital's ownership of a diverse range of well-known brands, such as Norton, Avast, and Avira, allows it to spread its resource needs across various areas, reducing its overall reliance on any particular external supplier for its intellectual property or technological advancements.
Switching costs for Gen Digital to change suppliers are generally low for common IT infrastructure and software. This is because many components are standardized, making it easier to find alternatives. For instance, readily available cloud services and modular software architectures reduce the complexity and expense of transitioning between vendors.
While migrating extensive datasets or integrating entirely new core technologies might present some initial costs, the overall barriers remain manageable. The modular design prevalent in contemporary software and cloud solutions significantly lowers these integration hurdles, allowing for greater supplier flexibility.
This inherent flexibility empowers Gen Digital to negotiate favorable terms with its suppliers. By not being heavily reliant on a single provider, the company can effectively avoid being locked into unfavorable contracts or pricing structures, thereby strengthening its bargaining position.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Gen Digital's consumer cybersecurity market is quite low. Companies that could potentially supply Gen Digital, like cloud service providers or component manufacturers, generally don't possess the established consumer brand trust, extensive distribution networks, or direct customer engagement that Gen Digital has built. Their primary business focus remains elsewhere, making a costly move into direct competition with Gen Digital an improbable strategy.
Importance of Supplier Inputs to Gen Digital's Business
While Gen Digital relies on various suppliers for components and services, its bargaining power is somewhat mitigated by its own robust internal capabilities. For instance, its significant investment in AI-driven solutions, as highlighted by its AI-first strategy for its cyber safety platform, means it's not entirely dependent on external AI development frameworks. This internal expertise reduces the critical nature of any single specialized input.
Gen Digital's extensive user base also plays a role in lessening supplier leverage. The vast amounts of data collected from millions of users fuel its own research and development, particularly in areas like threat intelligence. This self-sufficiency in data collection for innovation diminishes the reliance on external providers for core product enhancement, thereby limiting supplier power.
- Internal AI Development: Gen Digital's AI-first strategy for its cyber safety platform showcases substantial in-house AI capabilities, reducing reliance on external specialized AI frameworks.
- Data-Driven Innovation: A vast user base provides extensive data for internal R&D, particularly in threat intelligence, lessening dependence on external data suppliers.
- Strategic Partnerships: While specific suppliers for niche components might hold some leverage, Gen Digital's overall strategy focuses on building internal strengths, which can counter supplier power.
Availability of Substitute Inputs for Gen Digital
Gen Digital benefits from a wide availability of substitute inputs for its operations, significantly weakening supplier bargaining power. In the software industry, numerous tools and platforms can fulfill similar functions. This allows Gen Digital to readily switch suppliers if one becomes too demanding or unreliable, preventing any single supplier from exerting undue influence.
For instance, in the realm of cloud computing services, which are crucial for software companies, Gen Digital has multiple major providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) to choose from. The competitive landscape among these providers means they are incentivized to offer favorable terms to attract and retain large clients like Gen Digital, further limiting their individual bargaining leverage.
- Wide Availability of Substitutes: The software industry, where Gen Digital operates, is characterized by a broad array of tools and platforms that can perform comparable functions.
- Reduced Supplier Dependence: This abundance of alternatives means Gen Digital is not reliant on any single supplier, mitigating the risk of price hikes or supply disruptions.
- Competitive Cloud Services: Major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP compete fiercely, offering Gen Digital favorable terms and limiting the bargaining power of individual cloud infrastructure suppliers.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: The ease with which Gen Digital can switch inputs significantly diminishes the bargaining power of its suppliers.
Gen Digital's bargaining power with suppliers is strong due to the availability of numerous alternatives for essential components and services. The company's significant investment in internal R&D, including its AI-first strategy, further reduces its dependence on external specialized providers. This strategic focus on self-sufficiency, coupled with a vast user base that fuels internal data analysis for innovation, significantly limits the leverage individual suppliers can exert.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Gen Digital's market is low, as potential suppliers like cloud providers lack the established consumer trust and distribution networks. This overall dynamic allows Gen Digital to negotiate favorable terms and avoid unfavorable contracts, reinforcing its advantageous position.
| Factor | Assessment for Gen Digital | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Low; many providers for development tools and cloud services. | Weakens supplier power. |
| Importance of Input | Reduced reliance on single external sources due to internal R&D and diverse brand portfolio. | Weakens supplier power. |
| Switching Costs | Generally low for standard IT infrastructure and software components. | Weakens supplier power. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Low; potential suppliers lack established consumer brands and distribution. | Weakens supplier power. |
| Availability of Substitutes | High; numerous tools and platforms can fulfill similar functions. | Weakens supplier power. |
What is included in the product
Gen Digital's Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its cybersecurity market, evaluating threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the rivalry among existing players.
Instantly identify and prioritize competitive threats with a visual, easy-to-understand overview of all five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Gen Digital's consumer base, which includes individuals and families, generally shows a moderate to high degree of price sensitivity. This is largely due to the crowded cybersecurity market, where many alternative solutions, including free antivirus software, are readily available.
While consumers may have some loyalty to established brands like Norton and Avast, their purchasing decisions are often influenced by factors such as perceived value, the feature sets offered, and the overall pricing strategy. For instance, a 2023 survey indicated that over 60% of consumers consider price a primary factor when choosing software subscriptions.
Therefore, Gen Digital faces the challenge of offering premium cybersecurity products while remaining competitive on price to retain its substantial paying customer segment. This balance is crucial for sustained growth in a market where switching costs for consumers are relatively low.
The availability of numerous substitute products, such as Microsoft Defender built into operating systems and free antivirus software, significantly boosts customer bargaining power. This wide array of alternatives means consumers can easily switch if Gen Digital's pricing or features aren't competitive, compelling the company to constantly enhance its value proposition. For instance, in 2024, the cybersecurity market saw continued growth in free and freemium security solutions, putting pressure on paid providers like Gen Digital to demonstrate superior features and support.
Switching costs for customers moving between cybersecurity providers are generally quite low. For instance, a user can typically uninstall one antivirus program and install another with minimal effort. This ease of transition means customers are not heavily locked into a particular provider.
While there might be a slight inconvenience in reconfiguring settings or familiarizing oneself with a new user interface, these are usually minor hurdles. For example, a 2024 survey indicated that over 70% of consumers consider ease of installation a key factor when choosing software, underscoring the low barrier to switching.
These low switching costs empower customers, as they can readily explore and adopt more affordable or feature-rich alternatives. This dynamic puts pressure on cybersecurity companies to continually innovate and offer competitive pricing to retain their customer base.
Customer Information and Awareness
Customers today are incredibly well-informed, especially in the cybersecurity space. They can easily access online reviews, read tech publications, and learn from personal experiences, giving them a significant advantage when choosing solutions. This heightened awareness means companies like Gen Digital must be exceptionally clear about what makes their cyber safety and identity protection services stand out from the competition. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 70% of consumers research product reviews extensively before making a purchase in the tech sector.
This customer intelligence directly impacts Gen Digital's bargaining power. When consumers understand the threat landscape and the various protective measures available, they can more effectively compare offerings and negotiate for better value. They are less likely to be swayed by marketing alone and more inclined to seek out solutions that demonstrably meet their specific needs, potentially driving down prices or demanding enhanced features.
- Informed Consumer Base: A significant majority of consumers now conduct thorough online research before purchasing technology products, impacting pricing and feature demands.
- Value Proposition Clarity: Gen Digital faces pressure to clearly communicate the unique benefits of its cyber safety and identity protection services to a knowledgeable audience.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Customers can easily compare Gen Digital's offerings against competitors, increasing their leverage in price and service negotiations.
- Demand for Transparency: Increased customer awareness fuels a demand for transparent pricing and clear explanations of service efficacy.
Customer Base Size and Concentration
Gen Digital benefits from an enormous and geographically spread customer base. With over 65 million paid users and close to 500 million total users globally, the company's revenue is not reliant on any single entity.
This vast customer distribution significantly dilutes individual customer bargaining power. The sheer volume of users across more than 150 countries means that even large corporate clients represent a small fraction of Gen Digital's overall revenue, limiting their ability to demand concessions.
- Customer Base: Over 65 million paid customers.
- Total User Reach: Nearly 500 million users worldwide.
- Geographic Spread: Operations in over 150 countries.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: Diversified revenue reduces individual customer leverage.
Gen Digital's large, geographically dispersed customer base, exceeding 65 million paid users and nearly 500 million total users globally, significantly limits individual customer bargaining power. This broad reach, spanning over 150 countries, means no single customer or small group can heavily influence pricing or terms. The company's revenue is diversified, reducing reliance on any particular segment, which strengthens Gen Digital's position against individual customer demands.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Gen Digital |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Base Size | Over 65 million paid users, nearly 500 million total users worldwide. | Lowers individual customer bargaining power due to scale. |
| Geographic Diversification | Operations in over 150 countries. | Further dilutes any single customer's influence on overall strategy. |
| Revenue Diversification | Revenue not reliant on any single customer or region. | Increases Gen Digital's resilience and reduces susceptibility to customer pressure. |
Full Version Awaits
Gen Digital Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Gen Digital Porter's Five Forces analysis, providing a thorough examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate access to this professionally prepared strategic tool.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Gen Digital competes in a crowded consumer cybersecurity space, facing numerous rivals. This market includes long-standing companies like NortonLifeLock and Bitdefender, alongside newer, innovative firms. The acquisition of Avast by Gen Digital in 2022, for instance, consolidated market share but also highlighted the ongoing consolidation and competition within the sector.
The competitive landscape is further intensified by the presence of tech giants. Microsoft, with its Windows Defender, offers integrated security solutions directly to billions of users, posing a significant challenge to standalone cybersecurity providers. This broad reach means Gen Digital must constantly innovate to differentiate its offerings beyond basic protection.
The cybersecurity industry is booming, with projections indicating continued strong growth. This expansion is largely fueled by the increasing sophistication of cyber threats and the widespread integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) by both malicious actors and security providers. For instance, the global cybersecurity market was valued at approximately $214.9 billion in 2023 and is forecast to reach $370.4 billion by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.5%.
This rapid industry growth creates a fertile ground for intense competition. Companies like Gen Digital are heavily investing in AI-powered solutions to enhance their offerings and secure market share. This arms race in AI development means that staying ahead requires constant innovation and significant R&D expenditure, intensifying rivalry among established players and emerging startups alike.
In the competitive cybersecurity landscape, product differentiation is a constant challenge. Many solutions offer similar core functionalities, making it difficult for companies like Gen Digital to truly stand out. This is where a strong focus on innovation becomes paramount.
Gen Digital is actively pursuing differentiation through its integrated 'Cyber Safety' platform. This approach aims to offer a holistic solution, combining device security, online privacy, and identity protection. The recent acquisition of MoneyLion further expands this by incorporating financial wellness, creating a more comprehensive value proposition for consumers.
Continuous innovation is key to maintaining this edge. Gen Digital is investing in areas like AI-powered threat detection, which can proactively identify and neutralize emerging cyber threats. Enhancing the user experience also plays a significant role, making complex security features more accessible and user-friendly for a broader audience.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for consumers in the cybersecurity sector are generally low, which means customers can readily move between different providers. This ease of switching significantly fuels competitive rivalry among companies like Gen Digital.
The low friction in switching compels cybersecurity firms to focus heavily on retaining existing customers. Strategies such as implementing subscription-based models and offering enhanced value-added services are crucial for maintaining customer loyalty. For instance, Gen Digital reported that its subscription revenue, a key driver of recurring customer relationships, grew by 10% in the fiscal year 2024, reaching $2.3 billion.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers can easily compare and switch between cybersecurity solutions, increasing competitive pressure.
- Customer Retention Focus: Companies invest in strategies like subscription models and value-added services to keep customers.
- Subscription Revenue Growth: Gen Digital's fiscal year 2024 subscription revenue reached $2.3 billion, highlighting the importance of this retention strategy.
High Exit Barriers
High exit barriers significantly contribute to the intense competitive rivalry within the cybersecurity sector. Companies often have substantial investments in specialized fixed assets, including extensive research and development (R&D) infrastructure and proprietary intellectual property. For example, in 2024, cybersecurity firms continued to pour billions into R&D to stay ahead of evolving threats, making it economically challenging to divest these specialized assets.
The deep entrenchment of established brand recognition also acts as a formidable barrier. Once a cybersecurity company builds trust and a reputation for reliability, it's difficult and costly to disassociate from that identity. This commitment to their existing market position means firms are more inclined to fight for market share rather than seek an exit, thereby sustaining a highly competitive environment.
- Significant R&D Investment: Cybersecurity firms consistently invest heavily in R&D, with global spending projected to exceed $200 billion in 2024, creating specialized, hard-to-liquidate assets.
- Intellectual Property Value: Patents and proprietary algorithms represent valuable but often non-transferable assets, locking companies into the market.
- Brand Equity: Established cybersecurity brands have significant customer loyalty, making it difficult for companies to exit without losing substantial value.
- Specialized Workforce: The need for highly skilled cybersecurity professionals means companies have invested in human capital that is difficult to redeploy elsewhere.
Gen Digital faces intense rivalry due to low customer switching costs, forcing a strong focus on retention and value-added services. The company's fiscal year 2024 saw subscription revenue climb to $2.3 billion, underscoring the success of this strategy in a market where customers can easily move between providers.
High exit barriers, including substantial R&D investments and strong brand equity, further fuel this rivalry. Companies are compelled to remain and compete fiercely rather than exit, especially given the billions invested globally in cybersecurity R&D during 2024.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Gen Digital |
|---|---|---|
| Rival Firms | Numerous competitors, including tech giants like Microsoft and specialized cybersecurity firms. | Requires continuous innovation and differentiation to capture market share. |
| Switching Costs | Generally low for consumers, allowing easy migration between providers. | Intensifies competition and necessitates strong customer retention strategies. |
| Exit Barriers | High due to significant R&D, intellectual property, and brand recognition. | Encourages companies to remain and compete aggressively, sustaining rivalry. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
A significant threat of substitution for Gen Digital's offerings comes from widely available free security software and the built-in security features of operating systems. For instance, Microsoft Defender, integrated into Windows, provides a baseline level of protection that many consumers find adequate for their everyday use. This accessibility of free or bundled security solutions directly competes with Gen Digital's paid premium services, potentially limiting customer willingness to upgrade.
Users adopting safer online behaviors, like using strong passwords and being wary of suspicious links, can act as a behavioral substitute for some cybersecurity software. This increased user caution can lessen the perceived necessity for extensive paid solutions.
For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 75% of internet users reported actively practicing safer online habits, a notable increase from previous years. This growing user diligence directly impacts the demand for certain cybersecurity products.
Consumers can opt for standalone privacy and identity protection tools, bypassing Gen Digital's integrated cyber safety suites. For instance, the VPN market alone is projected to reach $7.17 billion by 2024, with numerous providers offering specialized services that can substitute for components of Gen Digital's broader offerings.
Hardware-Based Security Solutions
The increasing integration of robust security features directly into hardware devices by manufacturers presents a notable threat of substitutes for software-based security solutions. This trend, where devices offer pre-emptive, hardware-level protection, can diminish the perceived need for certain software layers. For instance, advancements in secure enclaves and trusted platform modules (TPMs) are becoming more common across a range of consumer electronics and business hardware.
This hardware-centric approach can be particularly impactful as it offers a foundational security layer that is often more difficult to compromise than software alone. By embedding security at the chip level, manufacturers are creating devices that are inherently more resistant to certain types of attacks. This directly challenges the market share and value proposition of standalone software security products.
- Hardware-based security features are increasingly being built into new devices, potentially reducing reliance on software.
- This trend offers a foundational security layer that can be more resilient to cyber threats.
- The perceived necessity for some software-based security solutions may decline as hardware capabilities advance.
Emergence of Niche or AI-Native Security Tools
The rapid evolution of artificial intelligence presents a significant threat of substitutes for Gen Digital. Highly specialized AI-native security tools are emerging, often available at low or no cost, that can outperform broad security suites in addressing specific threat vectors. For instance, AI-powered anomaly detection tools, while not a direct replacement for Gen Digital's entire offering, could substitute for specific endpoint monitoring functionalities if they prove more efficient or accurate in identifying novel threats.
This fragmentation of the security market by niche AI solutions could erode Gen Digital's market share for individual services. Consider the growing availability of open-source AI security frameworks that developers can readily adapt. In 2024, the cybersecurity market saw continued investment in AI-driven solutions, with companies like CrowdStrike and SentinelOne heavily leveraging AI for threat detection, demonstrating the trend towards specialized, AI-native capabilities.
- AI-Native Tools: Specialized AI solutions targeting specific cybersecurity needs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Potential for free or low-cost alternatives to broad security suites.
- Market Fragmentation: Niche AI tools could chip away at Gen Digital's market for specific functionalities.
- Competitive Landscape: Major cybersecurity players are heavily investing in AI, indicating a strong market shift.
The threat of substitutes for Gen Digital is significant, driven by readily available free security software and built-in operating system protections. For instance, Microsoft Defender offers a baseline security that many users find sufficient, directly competing with Gen Digital's premium paid services. Furthermore, consumers can opt for specialized standalone tools, such as VPNs, which are projected to reach $7.17 billion in market value by 2024, thereby substituting for certain aspects of Gen Digital's broader cybersecurity suites.
Entrants Threaten
The cybersecurity market, particularly for consumers, thrives on established brand recognition and deep-seated trust. Gen Digital has cultivated this through its portfolio of well-known brands, including Norton, Avast, and LifeLock, which are synonymous with digital security for millions.
Newcomers to this space face a formidable challenge in replicating the trust and brand equity that Gen Digital already commands. Consumers in the cybersecurity sector often prioritize proven reliability and a strong reputation, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction without significant investment in building credibility.
Developing cutting-edge cybersecurity solutions, especially those leveraging advanced AI for threat intelligence, demands significant capital for research and development. For instance, major players in the cybersecurity space often invest hundreds of millions of dollars annually in R&D. This high barrier to entry, driven by the need for substantial upfront investment, deters many potential new competitors from entering the market and challenging established firms like Gen Digital.
Gen Digital leverages a robust network of distribution channels, encompassing direct online sales, strategic alliances with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and a significant footprint in physical retail. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, Gen Digital reported strong performance driven by its direct-to-consumer offerings and OEM partnerships, which are crucial for pre-installing its software solutions on new devices.
New competitors face a substantial hurdle in replicating this established infrastructure. Building comparable direct sales capabilities or securing OEM agreements requires significant capital investment and time, often spanning several years. This difficulty in accessing established distribution networks acts as a potent deterrent for potential new entrants seeking to gain market share in the cybersecurity and digital safety landscape.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
The threat of new entrants in the cybersecurity sector is significantly mitigated by the substantial economies of scale enjoyed by established players like Gen Digital. With a user base exceeding 500 million, Gen Digital leverages this scale for highly efficient threat intelligence gathering, data processing, and customer support. This operational efficiency translates into lower per-unit costs, a barrier that new entrants struggle to overcome.
Furthermore, the experience curve plays a crucial role. Years of dealing with evolving cyber threats have allowed Gen Digital to refine its algorithms, detection methods, and response protocols. This accumulated expertise, embedded in their technology and operational processes, creates a knowledge advantage that is difficult and time-consuming for newcomers to replicate, thus heightening the barrier to entry.
- Economies of Scale: Gen Digital's 500 million+ users enable significant cost advantages in data processing and threat intelligence.
- Experience Curve: Decades of operational experience have honed Gen Digital's cybersecurity solutions, creating a knowledge moat.
- Capital Requirements: The substantial investment needed for advanced R&D and global infrastructure deters smaller competitors.
- Brand Loyalty and Switching Costs: Existing customer relationships and the complexity of migrating security systems create loyalty, making it hard for new entrants to gain traction.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
The cybersecurity and data privacy landscape is continually shaped by evolving regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). New entrants face significant challenges in navigating these complex compliance requirements, which demand substantial investment in time and resources. For instance, achieving compliance with GDPR can cost businesses upwards of $10,000 to $50,000 annually, depending on their size and data processing activities.
Established firms like Gen Digital have already invested in robust infrastructure and developed in-house expertise to manage these regulatory demands efficiently. This existing framework provides a significant advantage, allowing them to adapt more readily to new compliance mandates without the substantial upfront costs and learning curves that new entrants must overcome.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating a patchwork of global and regional data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA requires specialized legal and technical knowledge.
- Compliance Costs: Implementing necessary security measures, audits, and legal counsel for compliance can represent a substantial barrier to entry, potentially costing tens of thousands of dollars annually.
- Established Infrastructure: Gen Digital's existing compliance frameworks and dedicated teams reduce the incremental cost and time for adhering to new regulations compared to a startup.
The threat of new entrants for Gen Digital is considerably low due to high capital requirements for research and development, particularly in AI-driven threat intelligence, where major players invest hundreds of millions annually. Furthermore, established distribution networks, including OEM partnerships crucial for pre-installing software, represent a significant hurdle for newcomers to replicate. The need for substantial upfront investment in both technology and market access deters many potential competitors from entering the cybersecurity space.
Economies of scale and the experience curve also act as strong deterrents. Gen Digital's user base of over 500 million facilitates efficient data processing and threat intelligence, leading to lower per-unit costs that new entrants cannot easily match. Decades of refining algorithms and response protocols have created a knowledge advantage that is time-consuming and costly for new companies to build, effectively raising the barrier to entry.
Navigating complex and evolving regulations like GDPR and CCPA presents another significant challenge. While Gen Digital has established infrastructure for compliance, new entrants face substantial costs, potentially tens of thousands of dollars annually, for legal counsel, audits, and implementing necessary security measures. This regulatory complexity and associated costs further limit the threat of new entrants.
| Factor | Impact on Gen Digital | Barrier for New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements (R&D) | Enables advanced AI threat intelligence | Very High; requires hundreds of millions in annual investment |
| Distribution Networks | Strong OEM and direct-to-consumer presence | Very High; costly and time-consuming to establish |
| Economies of Scale (500M+ Users) | Lower per-unit costs in data processing and support | High; difficult to achieve comparable efficiency |
| Experience Curve | Refined algorithms and response protocols | High; requires years of operational data and refinement |
| Regulatory Compliance | Existing infrastructure and expertise | High; significant annual costs ($10k-$50k+) for legal and technical measures |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Gen Digital Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from official company filings, investor relations materials, and reputable industry analysis reports to comprehensively assess competitive dynamics.