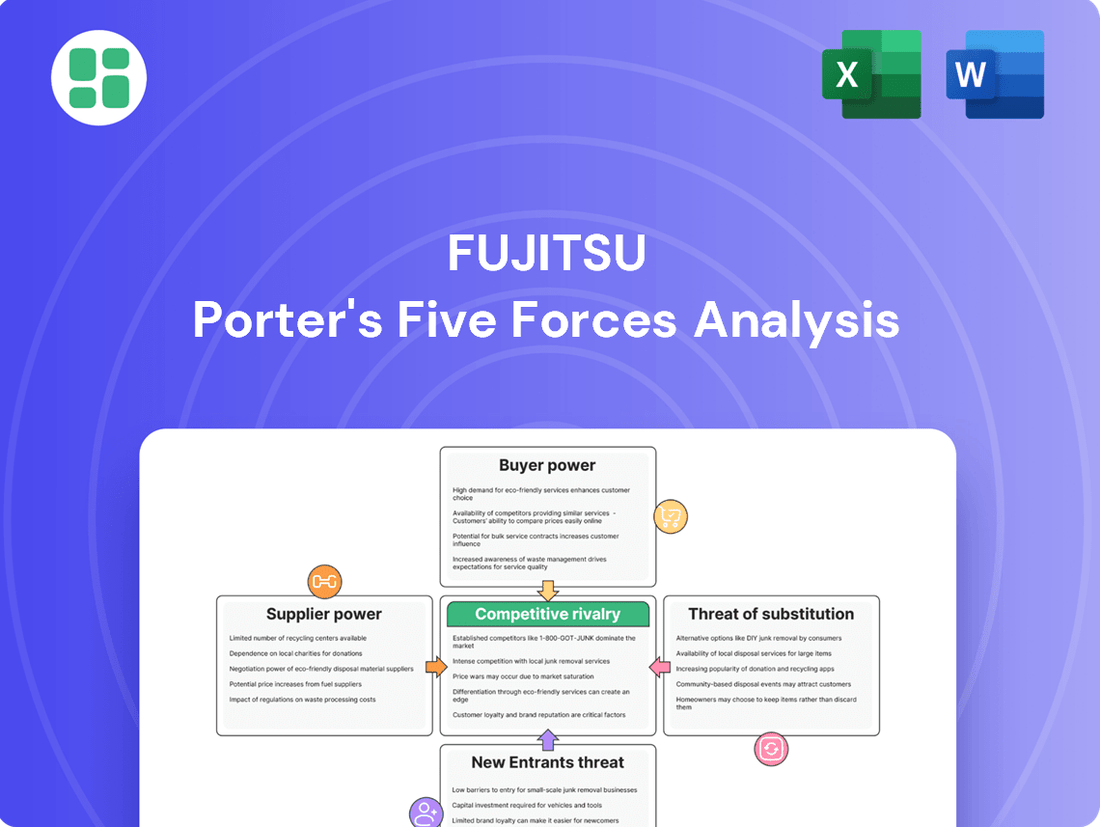
Fujitsu Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Fujitsu Bundle
Fujitsu operates in a dynamic tech landscape where the threat of new entrants is moderate, while the bargaining power of buyers can be significant due to readily available alternatives. Understanding these pressures is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis delves deeper, revealing the intensity of each force impacting Fujitsu, from intense rivalry to the growing threat of substitutes. Unlock actionable insights to navigate Fujitsu's competitive terrain and drive informed business decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Fujitsu's reliance on highly specialized components like advanced microprocessors and microelectronics places significant bargaining power in the hands of its limited suppliers. For instance, the semiconductor industry, a key area for Fujitsu, is characterized by a few dominant players controlling the production of cutting-edge chips. In 2024, the global semiconductor market was valued at over $600 billion, with a substantial portion concentrated among a handful of manufacturers, giving them considerable leverage.
This dependency means suppliers can dictate terms, potentially increasing prices or impacting delivery schedules, which directly affects Fujitsu's manufacturing costs and operational efficiency. The ability of Fujitsu to secure long-term supply agreements or invest in in-house R&D for critical components is vital to counter this supplier influence.
Suppliers of operating systems, enterprise software, and specialized development tools wield significant influence due to their proprietary technologies and strict licensing agreements. For Fujitsu, whose business heavily relies on sophisticated IT solutions and software development, any increase in licensing fees or less favorable contract terms from major software providers can directly affect its profit margins and the overall competitiveness of its service offerings.
In 2024, the global software market continued its upward trajectory, with enterprise software licensing remaining a substantial cost for technology firms like Fujitsu. Companies that develop critical operating systems and specialized development tools often operate with high switching costs for their clients, reinforcing their bargaining power. Fujitsu's strategy to mitigate this involves fostering strategic alliances with key software vendors and investing in its own internal software development capabilities to reduce reliance on external, potentially costly, licensing.
The availability of highly skilled professionals in specialized fields such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and cybersecurity directly influences Fujitsu's supplier power. These human resources are absolutely vital for Fujitsu's ability to innovate and deliver its services effectively.
A scarcity of such specialized talent can lead to increased labor expenses and delays in project execution, especially within fast-paced digital transformation sectors. For instance, the global demand for AI specialists outstripped supply significantly in 2024, with reports indicating a shortage of over 2 million AI professionals worldwide.
Fujitsu's proactive approach includes substantial investments in reskilling initiatives and comprehensive talent development programs, aiming to mitigate the impact of this talent scarcity and secure a competitive edge.
Proprietary Technology and IP
Suppliers possessing unique technologies or significant intellectual property (IP) for essential hardware or software components can wield substantial leverage. Fujitsu's reliance on advanced technology for its offerings necessitates careful management of these supplier relationships to mitigate dependency and secure favorable pricing. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key supplier area, saw continued consolidation, potentially increasing the bargaining power of remaining dominant players.
Fujitsu's strategy to counter this involves actively diversifying its technology partnerships. By collaborating with providers like AWS for cloud services and Oracle for database solutions, Fujitsu can create alternative sourcing options, thereby balancing the power dynamics. This approach is crucial as Fujitsu aims to integrate best-in-class technologies across its portfolio, from quantum-inspired computing to advanced AI solutions.
- Proprietary Technology: Suppliers with unique technological innovations can command higher prices and dictate terms.
- Intellectual Property (IP): Patents and exclusive rights over critical components grant suppliers significant influence.
- Fujitsu's Mitigation: Diversifying partnerships with entities like AWS and Oracle helps reduce reliance on any single technology supplier.
- Market Context (2024): Trends like semiconductor industry consolidation can amplify supplier bargaining power, making strategic sourcing paramount for Fujitsu.
Global Supply Chain Disruptions
Global supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by events like the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions, significantly amplify the bargaining power of suppliers. For Fujitsu, this means increased costs for essential components and raw materials. For instance, the semiconductor shortage that began in 2020 continued to impact various industries throughout 2021 and 2022, with lead times extending significantly and prices rising. This scarcity grants suppliers leverage to dictate terms and pricing, directly affecting Fujitsu's operational costs and product availability.
Fujitsu's extensive global footprint, while a strength, also exposes it to a wider range of potential disruptions. Extreme weather events, trade policy shifts, or regional conflicts can create localized or widespread shortages, empowering suppliers in affected areas. The company must therefore prioritize supply chain resilience. Strategies such as multi-sourcing, diversifying supplier bases across different geographic regions, and robust inventory management are crucial to mitigate these risks and maintain operational continuity.
The impact of these disruptions on Fujitsu's bargaining power of suppliers can be quantified by observing price trends for key inputs. For example, reports from early 2024 indicated continued volatility in the prices of certain electronic components due to ongoing supply-demand imbalances. Fujitsu's ability to negotiate favorable terms is directly challenged when suppliers face limited competition or overwhelming demand, forcing them to absorb higher costs or pass them on to customers.
- Increased component costs: The global semiconductor shortage saw prices for certain chips increase by 10-30% in 2021-2022.
- Extended lead times: Delivery times for critical electronic components stretched from weeks to months, impacting production schedules.
- Geopolitical impact: Regional conflicts can disrupt logistics and access to raw materials, giving suppliers in unaffected areas greater leverage.
- Need for diversified sourcing: Companies like Fujitsu are actively seeking to reduce reliance on single suppliers or regions to build resilience.
The bargaining power of Fujitsu's suppliers is substantial, particularly those providing highly specialized components and proprietary software. This leverage stems from limited supplier options, high switching costs for Fujitsu, and the critical nature of these inputs for its advanced technology solutions.
In 2024, the global semiconductor market, a key supplier area for Fujitsu, remained concentrated among a few dominant players, valued at over $600 billion. This concentration allows these suppliers to influence pricing and delivery terms, directly impacting Fujitsu's manufacturing costs and operational efficiency.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Power | Fujitsu's Mitigation Strategies | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semiconductors & Microelectronics | Limited number of dominant manufacturers, proprietary technology | Diversifying technology partnerships, investing in R&D | Market valued over $600 billion, ongoing consolidation |
| Software & Operating Systems | Proprietary technology, strict licensing, high switching costs | Strategic alliances with vendors, in-house development | Enterprise software licensing remains a significant cost |
| Specialized Talent (AI, Quantum) | Scarcity of skilled professionals, high demand | Investment in reskilling and talent development programs | Shortage of over 2 million AI professionals globally |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive landscape for Fujitsu by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the technology sector.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Fujitsu's large enterprise and government clients wield considerable bargaining power. These clients, often purchasing in massive volumes, can negotiate favorable terms, demand tailored solutions, and insist on rigorous service level agreements. For instance, a significant portion of Fujitsu's revenue is derived from these large contracts, making their demands impactful.
This leverage stems from the sheer scale of their commitments and their capacity to switch providers if their needs aren't met. Fujitsu actively works to strengthen customer relationships and deliver superior value to retain these crucial accounts, recognizing that customer loyalty in this segment is hard-won.
For commoditized products like PCs and standard servers, customers can readily switch to rivals if prices are lower or features are marginally better. This dynamic makes customers very sensitive to price, compelling Fujitsu to compete fiercely on cost and fundamental features in these areas. In 2023, the global PC market saw shipments decline by 14.8% year-over-year, highlighting intense price competition.
In the IT sector, particularly for major corporations, customers possess extensive knowledge regarding market pricing, available alternatives, and what competitors offer. This readily available information significantly strengthens their negotiating position, directly impacting Fujitsu's profit margins.
Fujitsu counters this by highlighting its proprietary intellectual property and specialized services, such as advanced AI solutions, to set its products and services apart. This focus on differentiation aims to reduce price sensitivity and justify premium pricing, as seen in the growing demand for specialized cloud and AI services, which saw significant investment in 2024.
Demand for Integrated Solutions
Customers are increasingly looking for complete IT packages that work together smoothly, rather than just individual pieces of technology. This means they want hardware, software, and services to all connect seamlessly, giving them more say in how projects are shaped and what level of complexity is involved. Fujitsu must demonstrate its ability to provide these end-to-end solutions and showcase its strong skills in putting different systems together.
Fujitsu's Uvance portfolio directly addresses this shift by offering integrated solutions designed to meet the complex needs of modern businesses. For instance, in 2024, the global market for integrated IT solutions saw significant growth, with many enterprises prioritizing vendors capable of delivering holistic digital transformation strategies.
- Demand for integrated solutions Customers expect seamless functionality across hardware, software, and services, influencing project scope and complexity.
- Fujitsu's response The Uvance offerings are specifically designed to meet this demand for end-to-end IT capabilities.
- Market trend The global market for integrated IT solutions experienced substantial growth in 2024, highlighting customer preference for comprehensive vendor offerings.
Threat of In-house IT Development
For very large enterprises or government bodies, the option to develop IT solutions internally, particularly for critical but non-core functions, presents a significant bargaining power. This capability acts as a natural cap on the prices Fujitsu can command for its services, especially in custom software development and ongoing maintenance.
This threat is particularly relevant as organizations increasingly seek greater control over their IT infrastructure and data. For instance, in 2024, many large corporations are investing heavily in building out their internal cloud capabilities, reducing reliance on external vendors for foundational IT services.
Fujitsu’s strategy to counter this involves highlighting its specialized expertise, advanced technological capabilities, and the scalability that often surpasses what in-house teams can realistically achieve, especially when considering the total cost of ownership and the speed to market.
The bargaining power of customers in this context can be seen in:
- Potential for cost savings: Large clients may estimate significant cost reductions by bringing IT development in-house, influencing their negotiation stance.
- Desire for greater control: The ability to dictate development priorities and maintain direct oversight of sensitive data can be a strong motivator for in-house solutions.
- Access to specialized skills: While Fujitsu offers expertise, clients might believe they can acquire or develop niche skills internally for specific, long-term projects.
Customers, especially large enterprises and government entities, possess substantial bargaining power due to their significant purchasing volumes and ability to negotiate favorable terms. This leverage is amplified by their capacity to switch providers if their specific needs, including tailored solutions and stringent service level agreements, are not met. For commoditized offerings, price sensitivity is high, forcing Fujitsu into competitive pricing strategies. In 2023, the global PC market, a segment with high customer price sensitivity, experienced a notable 14.8% year-over-year decline in shipments.
The trend towards integrated IT solutions, where clients expect seamless hardware, software, and service integration, further enhances customer influence by dictating project scope and complexity. Fujitsu's Uvance portfolio directly addresses this by offering end-to-end capabilities, a strategy that aligns with the substantial growth observed in the integrated IT solutions market during 2024. Furthermore, the option for large clients to develop IT solutions internally, particularly for non-core functions, acts as a ceiling on Fujitsu's pricing power, especially as firms invest more in internal cloud capabilities, as seen in 2024.
| Customer Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on Fujitsu | Supporting Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| High Volume Purchases | Enables negotiation of lower prices and better terms. | Large enterprise and government contracts form a significant revenue base. |
| Switching Costs (Low for Commoditized Products) | Increases price sensitivity and competition. | Global PC market shipments declined 14.8% in 2023, indicating intense price competition. |
| Demand for Integrated Solutions | Requires Fujitsu to offer comprehensive, end-to-end IT packages. | Global integrated IT solutions market saw significant growth in 2024. |
| Potential for In-House Development | Limits pricing power for custom or ongoing services. | Increased investment in internal cloud capabilities by large corporations in 2024. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Fujitsu Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Fujitsu Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of the competitive landscape within the IT services industry. You're seeing the exact, professionally formatted document that will be instantly available for download upon purchase. This ensures you receive a ready-to-use, comprehensive analysis without any surprises or placeholder content.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The IT sector is a battlefield, with titans like IBM, Dell, HP, Microsoft, AWS, Google, and Huawei constantly vying for dominance. This intense competition, especially in areas like cloud computing and AI, forces companies like Fujitsu to compete fiercely on price, innovation, and market share.
In 2024, the global IT services market, a key area for Fujitsu, was projected to reach over $1.3 trillion, highlighting the sheer scale and competitive intensity. These global giants often possess vast resources, allowing them to invest heavily in research and development, further intensifying the pressure on Fujitsu to maintain its edge.
The IT sector, a key battleground for Fujitsu, is defined by relentless technological evolution, particularly in AI, cloud, and cybersecurity. This constant churn necessitates substantial R&D investment, driving rapid product and service updates and potentially shortening lifecycles.
Fujitsu's strategic emphasis on AI and digital transformation directly addresses this intense competitive pressure. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, Fujitsu allocated a significant portion of its revenue to R&D, a crucial investment to maintain its edge in these fast-moving technological frontiers and to counter rivals who are similarly pushing innovation boundaries.
In mature markets such as PCs and servers, Fujitsu faces intense price competition, which naturally squeezes profit margins. This pressure extends to services, where basic cloud infrastructure and IT support can become commoditized, sparking price wars among providers.
Fujitsu's strategic pivot towards Fujitsu Uvance is designed to counter this by emphasizing high-value, differentiated services and solutions. This approach aims to move the company away from competing solely on price, seeking to capture greater value through innovation and specialized offerings.
Market Segmentation and Niche Specialization
While the IT services industry is generally competitive, Fujitsu distinguishes itself by focusing on specific market segments and specialized areas. For instance, in the public sector, Fujitsu's long-standing relationships and deep understanding of government requirements provide a significant advantage. Similarly, in manufacturing, their tailored solutions address the unique needs of production environments.
Fujitsu's competitive edge is further amplified by its strong regional presence and industry-specific knowledge. In 2024, their deep roots in Japan, a key market, allow them to offer highly localized support and solutions. This regional strength, combined with expertise in emerging technologies like quantum computing and advanced AI applications, enables them to carve out profitable niches.
- Segment Focus: Fujitsu excels in public sector and manufacturing IT solutions, leveraging deep industry knowledge.
- Niche Specialization: The company actively competes in high-growth areas such as quantum computing and specific AI applications.
- Regional Strength: Fujitsu maintains a significant competitive advantage in its home market of Japan, with strong regional operations.
Global Expansion and Regional Strengths
Fujitsu faces intense competition as rivals aggressively expand globally and bolster their regional strengths. While Fujitsu holds a dominant position in Japan, achieving profitable international growth and effectively challenging deeply rooted competitors in markets like North America and Europe remains a significant hurdle.
The company's ability to compete is directly impacted by the market share and strategic maneuvers of global IT giants. For instance, in 2024, major competitors continued to invest heavily in cloud infrastructure and AI capabilities, areas where Fujitsu is also focusing its efforts. This global push means Fujitsu must not only innovate but also execute its expansion strategies flawlessly to gain traction in diverse economic landscapes.
- Global Footprint Expansion: Competitors are actively increasing their presence in key international markets, often through acquisitions and organic growth.
- Regional Dominance: Established players in North America and Europe possess strong brand recognition and extensive customer networks, making market entry challenging for Fujitsu.
- Strategic Alliances: Partnerships, such as Fujitsu's collaboration with Amazon Web Services (AWS), are crucial for expanding global reach and offering integrated solutions.
Competitive rivalry within the IT sector is exceptionally fierce, with Fujitsu contending against global powerhouses like IBM, Dell, and Microsoft. This intense landscape, particularly in high-growth areas such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence, compels Fujitsu to constantly innovate and compete on price and service quality to maintain its market position.
The sheer scale of investment by competitors in R&D, often exceeding Fujitsu's allocations, creates a significant challenge. For example, in 2024, many leading IT firms reported R&D spending in the tens of billions of dollars, a stark contrast to Fujitsu's fiscal year 2023 R&D investments, which, while substantial, are a smaller absolute figure.
Fujitsu's strategy to focus on specialized areas like public sector and manufacturing IT solutions, coupled with its strong regional presence in Japan, helps mitigate some of this direct rivalry. However, the global push by competitors to expand their reach and offer comprehensive digital transformation services means Fujitsu must continually refine its value proposition to stand out.
The commoditization of basic IT services, especially in mature markets like PCs and servers, intensifies price wars. Fujitsu's pivot to higher-value offerings under Fujitsu Uvance aims to escape this commoditization, but success hinges on effectively differentiating its advanced solutions and services against a backdrop of aggressive pricing by larger rivals.
| Competitor | Key Market Focus | 2024 R&D Investment (Est.) |
|---|---|---|
| IBM | Hybrid Cloud, AI, Consulting | $7 Billion+ |
| Dell Technologies | PCs, Servers, IT Infrastructure | $2 Billion+ |
| Microsoft | Cloud (Azure), AI, Software | $25 Billion+ |
| Fujitsu | Digital Transformation, AI, Cloud Services | $1.5 Billion+ (FY23) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing adoption of cloud-native solutions and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) presents a substantial threat to Fujitsu's established on-premise hardware and software revenue streams. Businesses are increasingly shifting towards cloud environments, diminishing the demand for physical servers and on-site IT infrastructure management.
This trend is evident in the global cloud computing market, which was projected to reach over $1.35 trillion in 2024, demonstrating a significant shift away from traditional on-premise solutions. Fujitsu's strategic response includes forging partnerships with major cloud providers and expanding its own cloud service offerings to remain competitive in this evolving landscape.
The rise of mature and widely adopted open-source software (OSS) presents a significant threat of substitution for Fujitsu's proprietary offerings. These cost-effective alternatives allow businesses to develop tailored solutions without incurring licensing fees, directly challenging traditional IT vendors like Fujitsu.
For instance, the global open-source software market was valued at approximately $22.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong shift towards these alternatives. Fujitsu must highlight its unique value proposition through superior functionality, robust support, and seamless integration capabilities to counter this trend and retain its competitive edge in the software and services sectors.
The rise of in-house development and citizen development platforms presents a significant threat of substitution for Fujitsu's IT services. Many organizations are leveraging low-code/no-code solutions to build custom applications internally, especially for less complex digital transformation initiatives. For instance, in 2023, Gartner predicted that by 2025, the number of active citizen developers in large enterprises would grow by 40% compared to 2022, underscoring this trend.
This shift means Fujitsu needs to clearly articulate the value proposition of its specialized expertise for intricate, large-scale projects that go beyond the capabilities of these internal development tools. While citizen development democratizes application creation, it often falls short when dealing with complex integrations, robust security requirements, or mission-critical systems where Fujitsu's deep technical knowledge and experience are essential differentiators.
Emerging Technologies as Substitutes
New and disruptive technologies represent a significant threat of substitution for Fujitsu's current offerings. Advanced AI agents, for instance, could automate tasks currently requiring human IT support or complex software, thereby offering an alternative solution for businesses. While quantum computing's impact is more long-term, its potential to revolutionize data processing could render some of Fujitsu's current high-performance computing solutions less relevant.
Fujitsu is actively addressing this threat by investing in these emerging areas. For example, their Fujitsu Kozuchi AI service aims to provide cutting-edge AI capabilities, positioning them to lead rather than be displaced by these technological shifts. This proactive approach is crucial in a rapidly evolving IT landscape where innovation can quickly create viable substitutes.
- AI Automation: Technologies like advanced AI agents can automate IT support and software functions, directly substituting traditional service models.
- Quantum Computing's Potential: While still developing, quantum computing could eventually offer superior solutions for complex computational problems, impacting high-performance computing markets.
- Edge Computing Impact: The rise of edge computing might shift processing power away from centralized data centers, potentially altering demand for certain Fujitsu infrastructure services.
- Fujitsu's Strategic Investments: Fujitsu's commitment to R&D in AI and other advanced technologies, such as their Kozuchi AI service, demonstrates a strategy to mitigate substitution risks.
Managed Services and Outsourcing
Companies looking to manage IT costs often turn to outsourcing and managed services. This presents a significant threat of substitutes for integrated solutions offered by companies like Fujitsu. For instance, the global IT outsourcing market was valued at approximately $374 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $500 billion by 2027, indicating strong demand for these alternative solutions.
These specialized providers can offer cost-effective alternatives for specific IT functions, such as cloud management, cybersecurity, or data analytics. This necessitates Fujitsu to consistently highlight its unique value proposition, emphasizing the benefits of its comprehensive, secure, and industry-specific expertise over piecemeal service offerings.
- Cost Efficiency: Outsourcing can reduce capital expenditure on IT infrastructure and personnel.
- Specialized Expertise: Niche providers often possess deeper expertise in specific IT domains.
- Scalability: Managed services allow businesses to scale IT resources up or down more easily.
- Focus on Core Business: Outsourcing frees up internal resources to concentrate on primary business objectives.
The increasing adoption of cloud-native solutions and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) presents a substantial threat to Fujitsu's established on-premise hardware and software revenue streams. Businesses are increasingly shifting towards cloud environments, diminishing the demand for physical servers and on-site IT infrastructure management. This trend is evident in the global cloud computing market, which was projected to reach over $1.35 trillion in 2024, demonstrating a significant shift away from traditional on-premise solutions.
The rise of mature and widely adopted open-source software (OSS) presents a significant threat of substitution for Fujitsu's proprietary offerings. These cost-effective alternatives allow businesses to develop tailored solutions without incurring licensing fees, directly challenging traditional IT vendors like Fujitsu. For instance, the global open-source software market was valued at approximately $22.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong shift towards these alternatives.
New and disruptive technologies, such as advanced AI agents, can automate tasks currently requiring human IT support or complex software, thereby offering an alternative solution for businesses. Fujitsu is actively addressing this threat by investing in these emerging areas, for example, their Fujitsu Kozuchi AI service aims to provide cutting-edge AI capabilities, positioning them to lead rather than be displaced by these technological shifts.
Companies looking to manage IT costs often turn to outsourcing and managed services, presenting a significant threat of substitutes for integrated solutions offered by companies like Fujitsu. The global IT outsourcing market was valued at approximately $374 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $500 billion by 2027, indicating strong demand for these alternative solutions.
| Substitute Category | Market Size (2023/2024 Estimate) | Growth Projection | Impact on Fujitsu |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Computing (SaaS/IaaS/PaaS) | >$1.35 Trillion (2024) | Continued strong growth | Reduces demand for on-premise hardware/software |
| Open-Source Software (OSS) | ~$22.5 Billion (2023) | Substantial growth | Challenges proprietary software revenue |
| AI Automation & Citizen Development | N/A (Emerging/Growing) | Rapid adoption | Automates IT support and internal development, reducing need for external services |
| IT Outsourcing & Managed Services | ~$374 Billion (2023) | Projected >$500 Billion by 2027 | Offers cost-effective alternatives for specific IT functions |
Entrants Threaten
The IT sector, particularly areas like advanced AI and hardware, demands massive upfront investment. For instance, developing cutting-edge semiconductors or sophisticated AI algorithms requires billions in research and development, alongside the construction of specialized facilities. This financial hurdle significantly deters new companies from entering, especially those without substantial backing.
Fujitsu's significant R&D expenditures, often in the billions of dollars annually, and its extensive global infrastructure create a formidable barrier. In 2023, Fujitsu reported R&D expenses of approximately ¥380 billion (around $2.6 billion USD), underscoring its commitment to innovation and its ability to absorb the high costs associated with technological advancement.
Established technology giants like Fujitsu leverage significant economies of scale. This means they can produce goods and services at a lower per-unit cost due to their massive production volumes. For instance, in 2024, Fujitsu's global supply chain operations likely benefited from bulk purchasing discounts on components, a privilege not easily matched by a new entrant.
Furthermore, economies of scope allow Fujitsu to spread the costs of research and development, marketing, and customer support across a wide range of products and services. This diversification makes it challenging for newcomers to offer a comparable breadth of solutions and support without incurring prohibitive initial investments, thereby creating a substantial barrier to entry.
Fujitsu benefits from a deeply ingrained brand reputation and strong customer loyalty, especially among large enterprise and government sectors. These clients prioritize reliability, security, and a history of successful partnerships, making it difficult for newcomers to penetrate. Building this level of trust, a cornerstone of Fujitsu's 'trust in society through innovation' ethos, is a formidable barrier.
Access to Distribution Channels and Global Reach
New entrants face significant hurdles in replicating Fujitsu's established global sales, service, and support infrastructure. Building a comparable network requires immense capital investment and time, making it a formidable barrier to entry. For instance, in 2024, the cost of establishing a comprehensive international IT service and support presence can easily run into billions of dollars, a scale that deters most newcomers.
Fujitsu's extensive global reach, cultivated over decades, provides a distinct competitive advantage. New companies often struggle to achieve the same level of market penetration and customer accessibility. While some may initially target niche markets or leverage strategic partnerships, scaling these operations to match Fujitsu's worldwide capabilities presents a substantial long-term challenge.
Consider the difficulty of securing prime distribution channels. Fujitsu's long-standing relationships with major retailers, IT service providers, and enterprise clients worldwide are not easily disrupted. New entrants must find alternative, often less efficient, pathways to market, which can limit their initial sales volume and brand visibility. In 2023, for example, securing shelf space or preferred vendor status with large enterprise clients often depended on proven track records and extensive support capabilities that emerging companies lack.
- High Capital Investment: Replicating Fujitsu's global infrastructure demands billions in investment for sales, service, and support networks.
- Established Relationships: Fujitsu benefits from decades of cultivated relationships with key distributors and enterprise clients.
- Scalability Challenges: New entrants relying on niche markets face significant hurdles in scaling to compete with Fujitsu's global operational capacity.
- Distribution Channel Access: Gaining access to established distribution channels is a major obstacle for new players attempting to reach a broad customer base.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
The IT industry, especially in sensitive areas like government, finance, and healthcare, is heavily regulated. These regulations often cover data privacy, cybersecurity, and operational standards. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and similar frameworks globally impose stringent data handling requirements.
Navigating these complex and evolving regulatory landscapes presents a substantial barrier for new companies seeking to enter the market. Established players like Fujitsu have already invested in and developed robust compliance frameworks and expertise, giving them a significant advantage.
- Regulatory Burden: New entrants must dedicate substantial resources to understand and comply with diverse regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and various national cybersecurity mandates.
- Compliance Costs: The financial outlay for achieving and maintaining compliance, including audits and certifications, can be prohibitive for startups.
- Established Infrastructure: Fujitsu, having operated for decades, possesses pre-existing compliant systems and processes, reducing the incremental cost of adhering to new or existing rules.
The threat of new entrants for Fujitsu is generally low due to significant barriers. High capital requirements for R&D and infrastructure, coupled with established brand loyalty and deep customer relationships, make market entry challenging. Furthermore, extensive global networks and regulatory compliance add further layers of difficulty for potential competitors.
Fujitsu's substantial R&D investments, exceeding ¥380 billion (approximately $2.6 billion USD) in 2023, create a high barrier. New entrants would need comparable funding to innovate and compete effectively. Additionally, navigating complex global regulations, such as GDPR, requires significant investment in compliance frameworks, a cost already absorbed by established players like Fujitsu.
Access to established distribution channels and the difficulty in replicating Fujitsu's decades-long customer relationships present formidable obstacles. For instance, securing preferred vendor status with large enterprise clients in 2024 often hinges on proven track records and robust support capabilities, which new companies typically lack.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Fujitsu's Advantage | Example Data (Illustrative) |
| Capital Investment | High costs for R&D, manufacturing, and global infrastructure. | Prohibitive for most startups. | Decades of accumulated capital and operational scale. | 2023 R&D spend: ~¥380 billion ($2.6B USD). |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Established trust and long-term partnerships with enterprise clients. | Difficult to penetrate established markets. | Strong reputation for reliability and security. | High retention rates in key sectors (e.g., government, finance). |
| Economies of Scale & Scope | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volume and cost spreading across diverse products. | Inability to match competitive pricing. | Efficient global supply chain and diversified product portfolio. | 2024 bulk purchasing discounts on components. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to data privacy, cybersecurity, and operational standards. | Significant resource and time commitment. | Existing compliant systems and expertise. | Compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and national cybersecurity mandates. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Fujitsu Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from company annual reports, financial statements, and investor presentations. We also incorporate insights from reputable industry research firms and market intelligence platforms to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.