Freund Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Freund Bundle
Porter's Five Forces Analysis is a powerful framework that dissects the competitive landscape of any industry, revealing the underlying forces that shape profitability. By understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitutes, businesses can identify strategic advantages and potential pitfalls.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Freund’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The pharmaceutical machinery and excipients sectors often depend on highly specialized components and raw materials. When a small number of suppliers control the market for essential inputs, they gain considerable leverage over Freund Corporation, especially when viable alternatives are scarce. This is especially relevant for sophisticated electronic parts, high-precision engineering materials, or distinct chemical compounds used in excipients.
High switching costs for Freund significantly bolster the bargaining power of its suppliers. In the pharmaceutical industry, these costs are particularly substantial, encompassing re-tooling manufacturing equipment, re-validating complex production processes, and re-qualifying new raw materials to meet stringent regulatory standards. For instance, the average cost for a pharmaceutical company to switch a key raw material supplier can range from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars, factoring in the extensive validation and testing required.
If suppliers can credibly threaten to move into manufacturing pharmaceutical machinery or excipients themselves, their bargaining power over Freund significantly increases. This forward integration would enable them to directly compete with Freund, potentially restricting Freund's access to critical components or driving up their costs.
For instance, a major supplier of a unique chemical compound used in Freund's patented drug formulation could potentially develop their own finished drug product. In 2024, the pharmaceutical excipient market was valued at approximately $10.5 billion, with significant consolidation occurring, suggesting some large players might have the capital and expertise to consider such a move.
However, the highly specialized nature of Freund's end products, requiring extensive R&D and regulatory approval, makes this forward integration less likely for many raw material suppliers. The barriers to entry in developing and marketing a finished pharmaceutical product are substantial, often requiring billions in investment and years of clinical trials.
Importance of Freund as a Customer
Freund Corporation's position as a customer significantly shapes the bargaining power of its suppliers. When Freund accounts for a substantial portion of a supplier's sales, that supplier is more inclined to offer competitive pricing and favorable contract terms to retain Freund's business. For instance, if Freund represents over 15% of a key component supplier's annual revenue, that supplier's leverage diminishes considerably.
Conversely, if Freund is a minor client for a supplier, the supplier holds greater power. This is because the loss of Freund's business would have a negligible impact on the supplier's overall financial health. In such scenarios, suppliers are less likely to concede on price increases or other contractual demands, knowing that Freund has fewer alternatives or that switching suppliers would be costly.
The concentration of suppliers also plays a role. If Freund relies on a few suppliers for critical inputs, those suppliers gain more leverage. However, if Freund can source from a diverse and competitive supplier base, its bargaining power increases. For example, in 2024, Freund's strategic diversification of its electronics component suppliers from 5 to 12 providers reduced the average supplier revenue concentration from 20% to 8% for those specific components.
- Supplier Dependence: Freund's revenue contribution to its suppliers directly impacts their willingness to negotiate.
- Customer Size: Larger orders from Freund can translate into greater supplier concessions.
- Supplier Market Share: If a supplier has a dominant market share for a product Freund needs, their bargaining power is elevated.
- Switching Costs: High costs for Freund to change suppliers bolster supplier power.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly curtails supplier bargaining power for Freund. If the pharmaceutical industry, and by extension Freund, can readily source alternative raw materials or components that meet rigorous quality and regulatory requirements, suppliers lose their leverage. For instance, if a key active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) can be sourced from multiple manufacturers or if alternative excipients are easily integrated into formulations, suppliers cannot unilaterally impose higher prices or unfavorable contract terms. This competitive landscape compels suppliers to offer better value to retain business.
In 2024, the global pharmaceutical excipients market, a key area where Freund might face supplier power, was valued at approximately $10.5 billion. The presence of numerous players offering a wide array of excipients, from binders to coatings, means that Freund has considerable options. For example, companies specializing in cellulose derivatives or starches, widely used excipients, often face competition from other producers, limiting their ability to dictate terms. This broad availability of alternatives directly translates to reduced supplier leverage.
- Reduced Dependence: Freund’s ability to switch suppliers for critical components, such as specialized solvents or packaging materials, diminishes the power of any single supplier.
- Competitive Pricing: With multiple suppliers for similar inputs, Freund can negotiate more favorable pricing, as seen in the contract manufacturing sector where price competition is fierce.
- Innovation Drive: The search for substitutes can also spur innovation in Freund's own processes, as they might develop in-house capabilities or find novel materials that bypass traditional supplier constraints.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the pharmaceutical supply chain experienced disruptions, yet the underlying availability of many common chemical inputs remained robust due to a diversified global manufacturing base, which generally favors buyers like Freund.
The bargaining power of suppliers is a critical factor in Freund Corporation's operational costs and profitability. When suppliers can command higher prices or dictate terms, it directly impacts Freund's ability to compete. This power is amplified when suppliers are concentrated, inputs are differentiated, or switching costs for Freund are high.
In 2024, the pharmaceutical excipients market, a key area for Freund, was valued at around $10.5 billion. The presence of numerous suppliers for many common excipients limits individual supplier leverage. However, for highly specialized components, such as unique chemical compounds or precision-engineered parts, supplier power can be substantial, especially if only a few entities produce them.
| Factor | Impact on Freund | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases supplier power. | If 3 suppliers control 80% of a critical component, their leverage is high. |
| Input Differentiation | Unique inputs give suppliers more power. | A proprietary chemical compound for a patented drug formulation. |
| Switching Costs | High costs for Freund to switch suppliers empower suppliers. | Re-validation of a critical excipient can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Suppliers entering Freund's market increases their power. | A large excipient producer potentially developing finished pharmaceutical products. |
What is included in the product
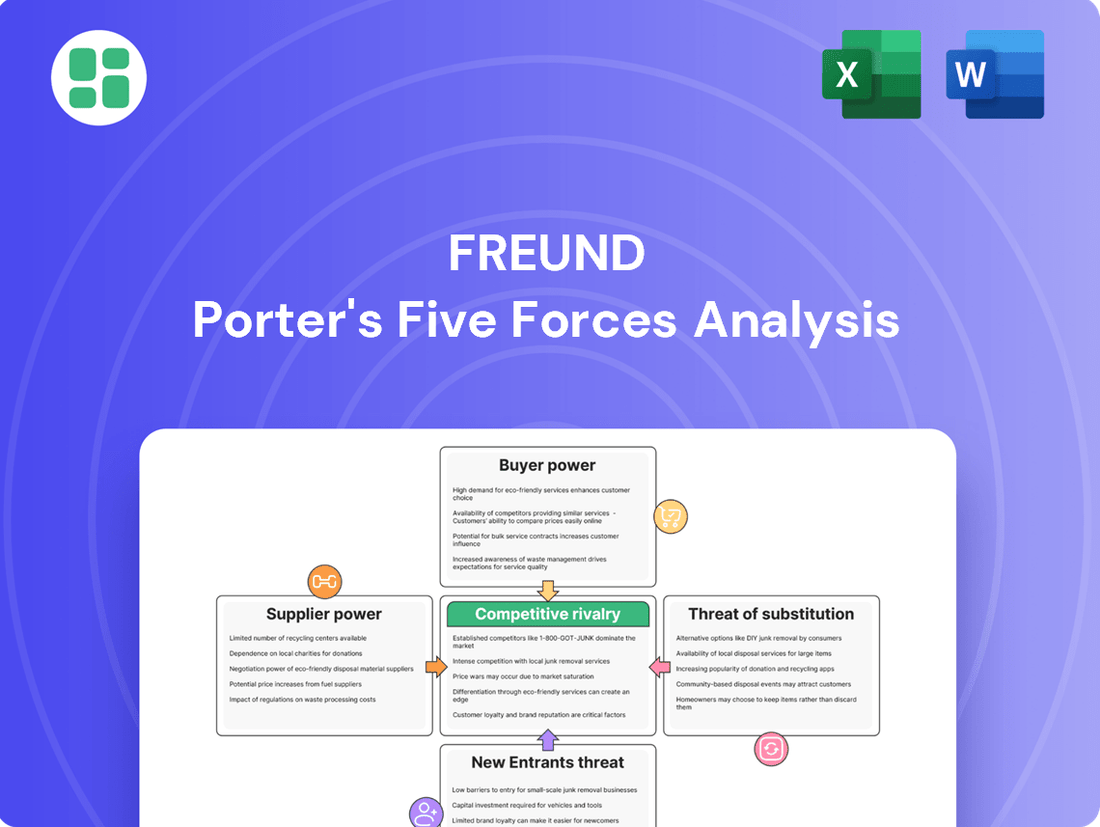
Freund's Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity and profitability potential of its operating environment by examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Understand competitive intensity at a glance with a visual representation of all five forces, simplifying complex market dynamics for confident strategic choices.
Customers Bargaining Power
Freund Corporation's customer base, predominantly pharmaceutical companies, presents varying levels of bargaining power. If Freund relies heavily on a few major clients, these large entities can exert significant pressure for price reductions or bespoke product development, impacting Freund's profitability. For instance, if the top 5 pharmaceutical clients represented over 60% of Freund's 2024 revenue, their collective bargaining power would be substantial.
Conversely, a diverse and widespread customer base, where no single client accounts for a material portion of sales, dilutes individual customer leverage. This fragmentation allows Freund to maintain more favorable pricing and terms, as the loss of any one customer would have a minimal impact on overall business performance.
Customer switching costs in the pharmaceutical industry are notably high, particularly when adopting new machinery or excipients. These costs encompass rigorous validation processes, securing necessary regulatory approvals, extensive employee training, and the potential for significant disruption to established production lines. For instance, a switch in a key excipient might necessitate re-validation of the entire drug formulation, a process that can take 12-18 months and cost millions of dollars.
Because of these substantial barriers, pharmaceutical companies are often hesitant to switch suppliers, even when presented with slightly lower prices from competitors. This reluctance significantly diminishes the bargaining power of customers. In 2024, the average cost for a pharmaceutical company to switch a critical raw material supplier was estimated to be between $500,000 and $2 million, depending on the complexity of the ingredient and the regulatory environment.
Freund's ability to offer highly differentiated or proprietary machinery and excipients significantly curtails customer bargaining power. When Freund's products boast unique features, superior performance, or distinct regulatory advantages that are difficult for competitors to match, customers face limited alternatives, thereby reducing their leverage in price negotiations.
This differentiation is particularly impactful in specialized pharmaceutical applications where specific functionalities and compliance are paramount. For instance, if Freund's new encapsulation machine, launched in early 2024, offers a 15% increase in production speed compared to the industry average, this unique selling proposition strengthens Freund's position.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers backward integrating, meaning they start producing the goods or services they currently buy, can significantly shift power. For instance, if pharmaceutical companies began manufacturing their own specialized machinery or key excipients, it would reduce their reliance on external suppliers, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
However, the feasibility of this varies greatly. While some large pharmaceutical firms might explore in-house production of certain excipients, the intricate design and manufacturing of complex pharmaceutical machinery represent a highly specialized and capital-intensive endeavor. This makes backward integration into machinery production a less common and more formidable challenge for most customers in this sector.
Consider the pharmaceutical machinery market. In 2023, the global pharmaceutical machinery market was valued at approximately $16.5 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% through 2030. This indicates a robust and complex industry, where developing the expertise and infrastructure for in-house manufacturing would be a substantial undertaking for most drug companies.
- Customer Backward Integration: Pharmaceutical companies may consider producing their own machinery or excipients.
- Excipient Production: In-house manufacturing of some excipients is more feasible for large pharma companies than machinery.
- Machinery Manufacturing Complexity: Designing and producing specialized pharmaceutical machinery is highly technical and capital-intensive.
- Market Data: The global pharmaceutical machinery market was valued at around $16.5 billion in 2023, highlighting the specialized nature of this industry.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
The price sensitivity of pharmaceutical companies is a key determinant of their bargaining power. This sensitivity is directly linked to how much Freund's products contribute to their overall production expenses and the tangible value they receive from these products. For instance, if Freund supplies critical machinery essential for maintaining product quality and adhering to stringent regulatory compliance, pharmaceutical firms are likely to exhibit lower price sensitivity. This is because the cost of such equipment is often a smaller fraction of their total operational costs, and its failure could lead to significant financial and reputational damage.
Conversely, when Freund's offerings are more akin to commoditized excipients, the situation shifts. In these scenarios, price becomes a much more dominant factor in purchasing decisions. Pharmaceutical companies, especially larger ones with significant purchasing volumes, can leverage this price focus to negotiate more favorable terms. For example, in 2024, the global market for pharmaceutical excipients was valued at approximately $9.5 billion, with intense competition among suppliers often driving down prices and increasing buyer power.
- Price Sensitivity Factors: The cost of Freund's products relative to a pharmaceutical company's total production costs.
- Value Derived: The importance of Freund's products for product quality, compliance, and operational efficiency.
- Critical Machinery: Customers are less price-sensitive for equipment that ensures product quality and regulatory adherence.
- Commoditized Excipients: Price becomes a significant factor, increasing customer bargaining power in these segments.
The bargaining power of customers is a crucial element in Porter's Five Forces analysis. For Freund Corporation, this power is influenced by factors such as customer concentration, switching costs, product differentiation, the threat of backward integration, and price sensitivity.
A concentrated customer base, where a few large pharmaceutical companies account for a significant portion of Freund's revenue, grants these clients considerable leverage. Conversely, a fragmented customer base dilutes individual customer power. High switching costs for pharmaceutical companies, stemming from regulatory hurdles and validation processes, generally reduce their inclination to change suppliers, thereby limiting their bargaining power.
Freund's ability to offer unique, high-performance machinery or proprietary excipients further weakens customer leverage. The threat of backward integration, while possible for some excipients, is less feasible for complex machinery due to high capital and technical requirements. Customer price sensitivity is lower for critical, value-adding products and higher for commoditized offerings.
| Factor | Impact on Freund's Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Example (2024 unless noted) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High concentration increases power | Top 5 clients representing >60% of 2024 revenue |
| Switching Costs | High costs decrease power | 12-18 month, $0.5M-$2M cost to switch critical excipient |
| Product Differentiation | High differentiation decreases power | 15% faster encapsulation machine (launched early 2024) |
| Backward Integration Threat | Low threat decreases power | $16.5B (2023) pharma machinery market complexity |
| Price Sensitivity | Low sensitivity for critical products, high for commoditized | $9.5B (2024) pharma excipient market competition |
Preview Before You Purchase
Freund Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're previewing the final version of our comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis. This document meticulously breaks down the competitive landscape of an industry, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. What you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis that will be available to you instantly after purchase, providing you with actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The pharmaceutical machinery and excipients sectors are populated by a blend of global giants and specialized niche players. This diversity means Freund Porter faces competition from companies of varying sizes and focuses, all seeking to capture market share.
With a significant number of competitors, particularly those possessing comparable technological expertise and market presence, the intensity of rivalry escalates. These companies actively compete for the same pool of pharmaceutical clients, driving down prices and demanding innovation.
For instance, in 2024, the global pharmaceutical excipients market was valued at approximately $9.5 billion, with numerous companies like BASF, DuPont, and Roquette competing alongside smaller, specialized suppliers. Similarly, the pharmaceutical machinery market, projected to reach over $20 billion by 2025, sees competition from giants like Bosch Packaging Technology and Syntegon, as well as specialized equipment manufacturers.
The pharmaceutical industry's growth rate is a crucial factor influencing competitive rivalry. In 2024, the global pharmaceutical market was projected to reach approximately $1.6 trillion, with an anticipated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6-7% through 2030. This robust expansion generally allows machinery and excipient suppliers to grow by meeting increased demand rather than aggressively competing for existing market share.
However, a slowing growth rate would intensify competition. If the industry's expansion decelerates, companies would likely engage in more aggressive pricing strategies and marketing efforts to capture a larger slice of a smaller pie. This dynamic can lead to price wars and increased promotional spending, squeezing profit margins for all players.
Conversely, a rapidly expanding market, like the one seen in recent years driven by advancements in biologics and personalized medicine, provides ample room for growth. Companies can expand their production capacity and sales without directly encroaching on competitors' established customer bases, thus mitigating direct rivalry.
High levels of product differentiation and a commitment to continuous innovation are key strategies to dampen intense competitive rivalry. Freund, for instance, carves out its niche through advanced coating, granulation, and powder processing systems, complemented by specialized excipients. This focus on unique technological capabilities and product attributes allows the company to stand apart in the market.
However, the effectiveness of this differentiation hinges on the ability to maintain a lead. If competitors can readily replicate or even surpass Freund's innovations, the pressure of rivalry will persist. For example, if a competitor in the pharmaceutical excipients market launches a similar advanced granulation technology in early 2024, it directly challenges Freund's market position.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers significantly influence competitive rivalry. When businesses find it difficult or costly to leave an industry, perhaps due to specialized assets like those in pharmaceutical manufacturing, they may persist even when profits dwindle. This can lead to prolonged periods of excess capacity and intensified price competition as companies fight for market share rather than exiting.
The pharmaceutical sector, for instance, often presents high exit barriers. The specialized nature of manufacturing facilities, adherence to stringent regulatory requirements, and substantial investments in research and development mean that exiting the market is not a simple decision. Companies may continue to operate, albeit at reduced profitability, rather than abandon these sunk costs.
- Specialized Assets: Pharmaceutical plants require highly specific equipment and infrastructure, making them difficult to repurpose or sell.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Exiting a regulated industry like pharmaceuticals involves complex de-licensing and compliance procedures.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to suppliers or distributors can lock companies into operations for extended periods.
- Brand Value: The significant investment in building brand reputation can be lost if a company exits, representing a substantial unrecoverable cost.
Fixed Costs and Capacity
Industries with substantial fixed costs, such as those involved in manufacturing heavy equipment or semiconductors, frequently witness heightened competitive rivalry when there's an oversupply of production capacity. For instance, in the automotive sector, high fixed costs associated with assembly lines mean manufacturers are strongly motivated to operate at or near full capacity. This drive to spread fixed costs often translates into aggressive pricing strategies to capture market share and keep production lines running, as seen with increased incentives and discounts offered by major automakers during periods of lower demand.
When capacity exceeds demand, companies face immense pressure to utilize their fixed assets. This situation incentivizes price competition as firms scramble to secure sales and cover their ongoing operational expenses. For example, the global semiconductor industry, known for its extremely high fixed costs in fabrication plants, experienced intense price competition in late 2023 and early 2024 as demand softened following a period of rapid expansion, with average selling prices for certain memory chips declining by over 20% year-over-year.
- High Fixed Costs Drive Capacity Utilization: Industries like aerospace manufacturing or petrochemicals have significant upfront investments, compelling firms to maximize output to achieve economies of scale.
- Excess Capacity Fuels Price Wars: When production capacity outstrips market demand, companies often resort to price cuts to fill order books and cover fixed expenses, leading to reduced profitability across the sector.
- Strategic Capacity Management is Crucial: Freund must meticulously manage its production capacity, aligning it with realistic market demand forecasts to mitigate the risk of being drawn into damaging price wars.
- Impact on Profitability: In 2024, sectors with excess capacity, such as certain segments of the consumer electronics manufacturing, saw profit margins squeezed as companies engaged in price-based competition to move inventory.
The pharmaceutical machinery and excipients markets are characterized by intense competition, driven by a mix of global leaders and specialized providers. This rivalry is fueled by a significant number of players vying for the same customer base, often leading to price pressures and a constant need for innovation. For instance, in 2024, the global pharmaceutical excipients market, valued at approximately $9.5 billion, saw major players like BASF and DuPont competing with numerous smaller firms.
The intensity of this rivalry is further shaped by industry growth. A robustly growing market, such as the global pharmaceutical sector projected to reach around $1.6 trillion in 2024 with a 6-7% CAGR, generally allows companies to expand without direct conflict. However, any slowdown in this growth would likely intensify competition, potentially triggering price wars as companies fight for a larger share of a slower-expanding market.
Freund's strategy of focusing on differentiated, technologically advanced products, like specialized coating and granulation systems, helps mitigate direct rivalry. However, this advantage is only sustained if competitors cannot easily replicate their innovations. The presence of high exit barriers, such as specialized assets and regulatory complexities within the pharmaceutical industry, can also prolong competitive battles by discouraging companies from leaving, even when profitability is low.
Industries with high fixed costs, like pharmaceutical manufacturing, often experience heightened rivalry when production capacity exceeds demand. Companies are then incentivized to operate at full capacity, leading to aggressive pricing to cover expenses. In 2024, sectors with excess capacity, such as certain consumer electronics manufacturing segments, saw profit margins squeezed due to price-based competition.
| Market Segment | Estimated 2024 Value | Key Competitors (Examples) | Competitive Intensity Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Excipients | ~$9.5 Billion | BASF, DuPont, Roquette | Numerous players, price sensitivity |
| Pharmaceutical Machinery | ~$20 Billion (projected by 2025) | Bosch Packaging Technology, Syntegon | Technological advancements, customer demand |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary threat of substitutes for Freund's pharmaceutical processing machinery stems from emerging alternative technologies. Continuous manufacturing, for instance, offers a compelling alternative to traditional batch processing, potentially reducing the need for Freund's established equipment lines. This shift could impact Freund's market share if they don't adapt their product offerings to align with these evolving production methodologies.
Pharmaceutical companies increasingly turn to Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) as a viable alternative to building and maintaining their own manufacturing facilities. This trend offers a substitute service for Freund's core machinery business, as CMOs already have the necessary infrastructure and specialized knowledge. The expanding CMO sector, valued at an estimated USD 140 billion in 2023 and projected to grow, directly influences the demand for new machinery as CMOs scale their operations.
For Freund's excipients business, a significant threat arises from generic or different excipients. These can be lower-cost alternatives or entirely new classes of materials that offer comparable functional benefits to pharmaceutical manufacturers.
Formulators might switch to these substitutes if they provide better performance, a more attractive price point, or a smoother regulatory approval process. For instance, in 2024, the global excipients market saw increased competition with a rise in biosimilar development, which often necessitates the use of cost-effective, readily available excipients.
Freund's specialized excipients must therefore clearly demonstrate their superior value proposition, whether through enhanced drug delivery, improved stability, or unique formulation advantages, to counter this substitution threat.
Shift to Alternative Drug Delivery Methods
A significant long-term threat to Freund Porter's business could emerge from a fundamental shift away from traditional oral solid dosage forms. If drug delivery methods evolve to favor injectables, transdermals, or other non-oral systems, the demand for Freund's core machinery, which is heavily geared towards oral solids, could substantially decrease. This would represent a direct substitution threat, impacting the company's market share and revenue streams.
Consider the growing market for biologic drugs, many of which are administered via injection or infusion, bypassing the need for oral solid dosage manufacturing equipment. For instance, the global biologics market was valued at approximately $220 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a trend that could indirectly impact Freund's reliance on traditional drug forms.
- Innovation in Drug Delivery: Advances in nanotechnology and microneedle patches offer alternative, non-oral delivery routes that bypass traditional tablet and capsule manufacturing.
- Biologics Market Growth: The expanding market for biologics, which are often injected or infused, represents a growing segment of the pharmaceutical industry that does not utilize oral solid dosage equipment. In 2024, the biologics market is expected to continue its robust growth trajectory, potentially reaching over $300 billion.
- Patient Preference Shifts: Increasing patient preference for less invasive or more convenient drug administration methods could accelerate the adoption of non-oral delivery systems.
In-house Development of Basic Tools
The threat of substitutes for specialized pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment, particularly for basic or customized tools, is generally low. Complex machinery requires significant R&D and manufacturing expertise, making in-house development impractical for most pharmaceutical firms. However, for simpler, less critical processing steps, some companies might explore in-house development or utilize highly niche local fabricators. This can represent a minor substitution risk, especially if these internal solutions offer cost advantages or unique customization not readily available off-the-shelf.
While the overall market for advanced pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment is robust, with companies like Thermo Fisher Scientific and Sartorius AG dominating, the threat of substitutes for very basic tools does exist. For instance, a pharmaceutical company might develop a simple, proprietary mixing apparatus internally rather than purchase a standard, off-the-shelf model. This is more likely to occur in R&D or early-stage production where flexibility is paramount and the capital investment for specialized machinery is prohibitive. For example, a small biotech startup in 2024 might opt to build a custom bioreactor support system from readily available components rather than invest in a high-end, multi-million dollar system for a niche application.
- Low Threat for Complex Machinery: Developing sophisticated pharmaceutical processing equipment requires specialized engineering, materials science, and regulatory compliance, making it a significant barrier for in-house development by pharmaceutical companies.
- Minor Threat for Basic Tools: For simpler, less critical processing steps or highly customized needs, pharmaceutical companies may consider in-house development or sourcing from niche local fabricators, representing a marginal substitution risk.
- Cost and Customization Drivers: Internal development of basic tools can be driven by potential cost savings or the need for highly specific functionalities not met by standard market offerings.
- Industry Example: A pharmaceutical firm might fabricate a custom jig or fixture for a specific vial handling process in-house, rather than purchasing a generic solution.
The threat of substitutes for Freund's pharmaceutical processing machinery is driven by technological advancements and evolving industry practices. Continuous manufacturing offers a more efficient alternative to traditional batch processing, potentially reducing the need for Freund's current equipment. Furthermore, the rise of Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) provides a service substitute, as these companies already possess the necessary infrastructure.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the pharmaceutical machinery and excipients sectors demands significant capital for R&D, state-of-the-art manufacturing, specialized equipment, and extensive inventory. For instance, developing and validating a single new pharmaceutical processing machine can cost millions, creating a formidable financial hurdle.
This high upfront investment acts as a powerful deterrent, effectively shielding established companies like Freund Corporation from a surge of new competitors. The sheer scale of investment needed to meet stringent regulatory and quality standards for pharmaceutical-grade products is a major barrier.
The pharmaceutical industry's stringent regulatory environment presents a significant threat of new entrants. Companies must adhere to rigorous quality, safety, and efficacy standards set by bodies like the FDA and EMA. Navigating these complex approval processes for both manufacturing and product ingredients is a costly and lengthy endeavor, often taking years and millions of dollars.
For instance, the average cost to bring a new drug to market, including R&D and regulatory approval, can exceed $2.6 billion as of recent estimates. This substantial financial and time commitment acts as a powerful deterrent, especially for smaller, less established companies looking to enter the market. Established players like Freund, with existing infrastructure and experience in compliance, are better positioned to manage these hurdles.
Established players in many industries, including those where Freund might operate, benefit significantly from economies of scale. For instance, in the automotive sector, major manufacturers can leverage massive production volumes to reduce per-unit costs for components, assembly, and even R&D. In 2024, companies with substantial market share often boast lower operating expenses per unit compared to smaller, emerging competitors. This cost advantage makes it challenging for new entrants to match pricing without substantial initial investment and achieving similar production volumes.
The experience curve further solidifies this advantage. As companies gain more experience in production and process optimization, they learn to perform tasks more efficiently, leading to lower costs over time. For example, a company that has been manufacturing semiconductors for decades will have refined its processes, reducing waste and increasing yield rates. This accumulated knowledge, often translated into lower production costs, creates a high barrier for newcomers who lack this historical learning curve.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Technology
Freund Corporation's robust portfolio of patents, proprietary designs, and accumulated technical expertise in specialized machinery and excipient formulations presents a significant barrier to new entrants. These intellectual property rights make it difficult and costly for competitors to replicate Freund's product offerings. For instance, the pharmaceutical excipient market, where Freund operates, often sees companies investing heavily in R&D to develop unique formulations, with patent protection being a key differentiator. The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office reported over 600,000 utility patents granted in 2023 alone, highlighting the competitive landscape and the value of protected innovation.
New entrants would need to either invest substantial resources in developing their own novel technologies or risk infringing on existing patents, which could lead to costly legal battles. This discourages market entry by those lacking comparable R&D capabilities or significant capital for legal defense. Companies like Freund leverage these protections to maintain their market share and pricing power, as evidenced by the premium pricing often associated with patented pharmaceutical ingredients.
- Patented Technology: Freund likely holds patents on key machinery components and unique excipient compositions.
- R&D Investment: New entrants require substantial investment to develop non-infringing alternatives or their own proprietary technology.
- Market Protection: Intellectual property rights shield Freund's existing market position from direct replication.
- Legal Risk: Potential infringers face significant legal and financial risks from patent enforcement.
Access to Distribution Channels and Customer Relationships
New entrants in the pharmaceutical sector face substantial hurdles in securing access to established distribution channels and cultivating vital customer relationships. Building these networks, which often involve intricate logistics and strong ties with pharmaceutical manufacturers, requires considerable time and investment, often spanning many years.
Gaining market entry and establishing credibility with pharmaceutical clients, who are inherently risk-averse and prioritize dependable suppliers with a track record of success, presents a significant barrier. For instance, in 2024, pharmaceutical companies continued to emphasize supply chain security, with 78% of surveyed executives citing it as a top priority, making it difficult for unproven entities to secure contracts.
Freund's existing distribution infrastructure and hard-won reputation act as formidable competitive advantages. These established relationships and market presence are not easily replicated, as evidenced by the fact that it can take an average of 3-5 years for a new pharmaceutical distributor to achieve significant market penetration in developed economies.
- Distribution Channel Access: New entrants struggle to penetrate established pharmaceutical supply chains.
- Customer Relationships: Building trust with risk-averse pharmaceutical companies is a lengthy process.
- Freund's Advantages: Existing networks and reputation provide a significant competitive edge.
- Market Entry Timeframe: Significant investment and time are required to establish credibility.
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by the substantial capital requirements in the pharmaceutical machinery and excipients sectors. Developing and validating new processing equipment can cost millions, and navigating stringent regulatory approvals for pharmaceutical-grade products is both time-consuming and expensive, often exceeding billions for drug development. These high upfront investments act as a powerful deterrent, protecting established firms like Freund Corporation.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and expert interviews to provide a comprehensive understanding of competitive dynamics.