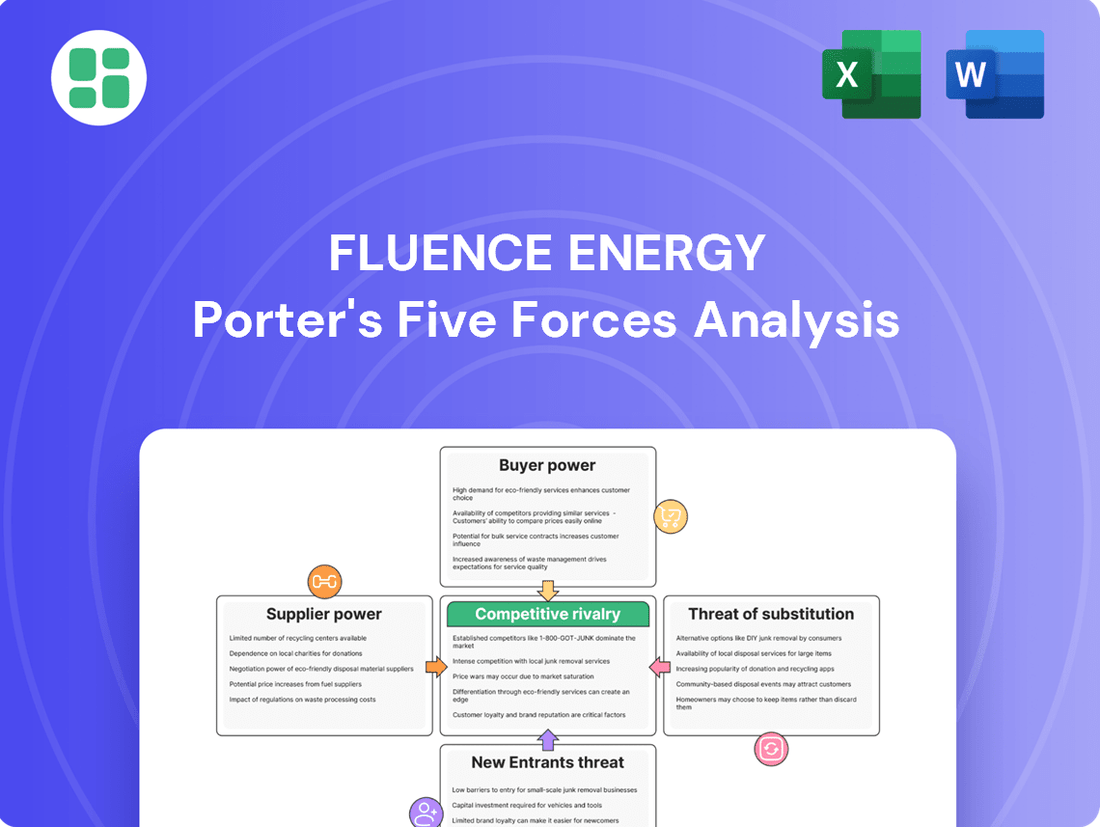
Fluence Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Fluence Energy Bundle
Fluence Energy operates in a dynamic energy storage market, facing significant pressures from both established players and emerging technologies. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, buyer power, and the threat of substitutes is crucial for navigating this evolving landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Fluence Energy’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Fluence Energy's reliance on battery cell manufacturers, a sector often dominated by a few global leaders, significantly shapes supplier bargaining power. This concentration, particularly for advanced chemistries like lithium-ion and LFP, allows these suppliers to exert considerable influence over pricing and availability.
The market for battery cells, especially for large-scale energy storage solutions, is characterized by a limited number of dominant suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the top five battery cell manufacturers accounted for over 70% of the global market share, underscoring the concentrated nature of this supply chain.
Geopolitical tensions and trade policies, such as tariffs on imports from China, further bolster supplier leverage. These factors can directly increase procurement costs and complicate supply chain strategies for companies like Fluence Energy operating in regions such as North America, potentially impacting project economics.
Fluence Energy's reliance on critical raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel for its battery storage systems places significant bargaining power in the hands of suppliers. The upstream supply chain for these essential components is concentrated in specific geographic regions. For instance, Australia and Chile are major lithium producers, while the Democratic Republic of Congo accounts for a substantial portion of global cobalt supply.
This geographical concentration means that suppliers in these areas hold considerable leverage. Furthermore, the burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) market also competes for these same minerals. For example, in 2024, the demand for EVs continued to surge, putting upward pressure on lithium prices. This increased demand from another major sector directly impacts the availability and cost of these materials for energy storage solutions like those offered by Fluence.
Fluence Energy's reliance on specialized component and technology providers, beyond basic battery cells, significantly shapes supplier bargaining power. This includes critical elements like inverters, sophisticated power electronics, and the advanced software underpinning its Fluence IQ platform.
Suppliers of these highly specialized technologies often hold unique expertise and proprietary intellectual property. This can create a limited pool of viable alternatives for Fluence, granting these suppliers considerable leverage in negotiations.
The dependency on such niche providers directly impacts Fluence's cost structure and the speed at which it can innovate and bring new solutions to market. For instance, in 2023, the global energy storage system market saw significant growth, with demand for advanced power electronics and software solutions increasing, potentially strengthening the hand of key suppliers in this segment.
Logistics and Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Fluence Energy's global footprint means that logistics and shipping providers hold significant sway over its supply chain efficiency and costs. Disruptions, whether from geopolitical events or natural disasters, can cause considerable delays and inflate transportation expenses for essential components and finished energy storage systems. For instance, the Suez Canal blockage in March 2021, though not directly related to Fluence, highlighted the fragility of global shipping routes, impacting countless industries and demonstrating how easily supply chains can be disrupted, potentially increasing the bargaining power of logistics firms.
These vulnerabilities can directly impact Fluence's ability to meet project timelines and budget constraints. The cost of shipping large-scale battery systems, often transported by sea, is a substantial part of overall project expenses. As of early 2024, global shipping rates, while having eased from pandemic peaks, remain sensitive to fuel prices and geopolitical stability, giving carriers more leverage.
- Logistics costs are a significant factor in Fluence's project economics.
- Geopolitical instability and natural disasters can disrupt shipping, increasing costs and lead times.
- The bargaining power of logistics suppliers can be amplified by supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Delays in component or finished product delivery directly affect Fluence's ability to execute projects on time and within budget.
Potential for Supplier Vertical Integration
A significant factor impacting Fluence Energy's bargaining power of suppliers is the growing trend of vertical integration within the battery industry. This means battery manufacturers or even raw material producers are increasingly acquiring or partnering with companies further down the supply chain, like battery cell producers or energy storage system integrators. For instance, in 2024, several major battery manufacturers announced plans or completed acquisitions to gain more control over their supply chains, aiming to secure critical materials and manage costs more effectively.
This consolidation can shift the balance of power towards these integrated suppliers. By controlling more stages of production, they can potentially reduce the number of independent suppliers available to companies like Fluence Energy. This concentration of market control can lead to greater influence over pricing and terms, potentially increasing costs for Fluence Energy.
The potential for supplier vertical integration directly impacts Fluence Energy's ability to negotiate favorable terms:
- Reduced Supplier Options: As suppliers integrate, the pool of independent, competitive suppliers may shrink.
- Increased Cost Control for Suppliers: Integrated suppliers can better manage their own costs, giving them more leverage in pricing negotiations.
- Potential for Higher Input Prices: Consolidation can lead to less price competition among suppliers, potentially driving up the cost of battery components and systems for Fluence Energy.
- Supply Chain Security Concerns: While integration aims for security, it can also create dependencies on a smaller number of powerful entities.
Fluence Energy faces considerable supplier bargaining power due to the concentrated nature of battery cell manufacturing. In 2024, the top five global battery cell manufacturers held over 70% of the market share, giving them significant leverage in pricing and supply availability. This concentration is further amplified by Fluence's reliance on critical raw materials like lithium and cobalt, where production is geographically concentrated, and demand from the booming EV sector intensifies competition for these resources.
The bargaining power of suppliers is also influenced by the increasing vertical integration within the battery industry. By 2024, several major battery producers were actively acquiring or partnering with companies across the supply chain, aiming to control raw materials and production. This consolidation reduces the number of independent suppliers available to companies like Fluence, potentially leading to higher input prices and less favorable negotiation terms.
Furthermore, specialized component providers, such as those supplying advanced inverters and power electronics, possess unique intellectual property and expertise. This limited pool of alternatives grants these niche suppliers substantial bargaining power, impacting Fluence's cost structure and innovation timelines. Global logistics providers also exert influence, with shipping rates in early 2024 remaining sensitive to fuel prices and geopolitical stability, directly affecting Fluence's project economics and delivery schedules.
| Factor | Impact on Fluence Energy | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Cell Manufacturing Concentration | High supplier leverage on pricing and availability | Top 5 manufacturers held >70% global market share |
| Raw Material Supply Chain Concentration | Increased costs and supply volatility due to limited sources and competing demand | High demand from EV sector driving up lithium prices |
| Vertical Integration by Suppliers | Reduced supplier options, potential for higher input prices | Major battery manufacturers pursuing supply chain consolidation |
| Specialized Component Providers | Leverage due to unique IP and limited alternatives | Growing demand for advanced power electronics and software |
| Logistics and Shipping | Impact on project economics and delivery timelines | Shipping rates sensitive to fuel prices and geopolitical stability |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive intensity surrounding Fluence Energy by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors in the energy storage market.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures and strategic positioning with a dynamic, interactive model.
Empower data-driven strategy by easily adjusting variables to simulate market shifts and competitive responses.
Customers Bargaining Power
Fluence Energy's customer base is dominated by large utilities, independent power producers, and developers who are involved in massive energy storage projects, often in the multi-megawatt to gigawatt range. These are not small buyers; they are sophisticated entities that know the market well.
These major players typically participate in rigorous competitive bidding processes. Their substantial purchasing volumes give them considerable sway. For instance, securing a single large contract can represent a significant portion of a company's annual revenue, amplifying the buyer's leverage.
The recent experience of delays in Fluence signing large customer contracts directly illustrates this customer bargaining power. When buyers have the ability to delay or walk away from deals due to their size and the availability of alternatives, it puts pressure on suppliers like Fluence to offer more favorable terms.
The grid-scale battery energy storage market is highly competitive, with many system integrators worldwide offering similar solutions. Companies like Tesla, Sungrow, Wärtsilä, and Powin provide comparable battery energy storage systems (BESS), giving customers ample options.
This abundance of choice significantly boosts customer bargaining power. Buyers can leverage the availability of multiple providers to negotiate more favorable pricing, contract terms, and service level agreements, which can put pressure on integrators' profit margins.
Large energy storage projects often require highly customized solutions, giving customers significant leverage. However, Fluence is seeing increased standardization in battery containers and system designs, which makes it easier for customers to compare offerings and potentially negotiate harder on price.
Customers also typically seek long-term service and maintenance agreements. While these provide Fluence with predictable recurring revenue, they also create an ongoing opportunity for customers to negotiate terms based on operational performance and support needs, further influencing Fluence's bargaining power.
Cost Sensitivity and Economic Viability
Customers are keenly focused on the total upfront cost of energy storage systems, as this directly influences their project's financial feasibility and payback period. For instance, the Levelized Cost of Storage (LCOS) is a critical metric for utility-scale projects, and Fluence's ability to offer competitive LCOS figures is paramount.
While battery costs have decreased substantially, with lithium-ion battery pack prices falling by over 90% from 2010 to 2023, Fluence's customers remain sensitive to any price increases stemming from import duties or supply chain disruptions. These fluctuations can significantly impact project economics, forcing customers to seek cost mitigation strategies.
- Customer Cost Sensitivity: Buyers scrutinize the total installed cost of energy storage, directly impacting their ROI.
- Battery Price Trends: Despite a significant decline in battery prices, tariffs and supply chain issues can cause cost volatility.
- Cost Absorption Pressure: Customers will push for Fluence to absorb cost increases or find more economical alternatives.
Evolving Regulatory Landscape and Incentives
The bargaining power of customers in the energy storage sector is significantly influenced by the evolving regulatory landscape and available incentives. Government policies, such as the US Investment Tax Credit (ITC), directly encourage customer investment in energy storage solutions by reducing upfront costs. For instance, the ITC has been a major driver for renewable energy and storage project deployment, making it more attractive for businesses and individuals to adopt these technologies.
However, the dynamic nature of these regulations can also empower customers. Uncertainty or potential changes in tax incentives, renewable energy mandates, or grid interconnection rules can lead customers to delay investment decisions or demand more favorable terms to offset policy-related risks. This can increase their leverage, as Fluence Energy and other providers must adapt to shifting customer priorities driven by legislative developments.
- Government policies like the US ITC directly impact customer investment decisions by lowering the cost of energy storage.
- Tax incentives, such as the ITC, have historically boosted adoption rates for renewable energy and storage.
- Regulatory uncertainty can give customers more bargaining power as they seek to mitigate risks associated with policy changes.
- Mandates for renewable energy integration create demand but can also be leveraged by customers negotiating terms.
Fluence Energy's customers, primarily large utilities and developers, wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial purchasing volumes and the availability of numerous competitors. These sophisticated buyers participate in competitive bidding, where securing large contracts is crucial for suppliers, allowing them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms. The market's competitiveness, with players like Tesla and Wärtsilä offering similar solutions, further amplifies this leverage. Recent contract delays for Fluence underscore how buyers can pressure suppliers by delaying or walking away from deals, especially when alternatives are readily available.
Customers are highly sensitive to the total cost of ownership, particularly the Levelized Cost of Storage (LCOS), which directly impacts project economics. Despite a significant drop in battery prices, falling over 90% from 2010 to 2023, customers remain vigilant against price increases due to tariffs or supply chain issues, pushing Fluence to absorb these costs or find cheaper alternatives.
| Customer Factor | Impact on Fluence | Example/Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Purchasing Volume | High leverage due to large project sizes | Fluence's Q1 2024 results showed a backlog of $2.9 billion, indicating large individual contracts are key. |
| Competitive Landscape | Pressure to offer competitive pricing and terms | The energy storage market is projected to grow significantly, with numerous global players vying for market share. |
| Cost Sensitivity | Demand for cost optimization and favorable LCOS | Fluence must balance innovation with cost-effectiveness to meet customer demands for competitive project economics. |
Full Version Awaits
Fluence Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Fluence Energy Porter's Five Forces analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the energy storage sector. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. The document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to download after payment, providing a complete and actionable understanding of Fluence Energy's strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The grid-scale battery energy storage market is incredibly competitive, with major global companies like Tesla, Sungrow, Wärtsilä, and Powin all vying for dominance alongside Fluence Energy. This fierce rivalry is a constant factor in the rapidly growing, yet highly contested, sector.
Fluence Energy itself has acknowledged these competitive pressures, which have contributed to their recently revised financial guidance. This indicates that market share gains and pricing strategies are critical battlegrounds for all players in this space.
The energy storage sector is experiencing a fierce competitive rivalry, largely driven by rapid technological advancements. Companies like Fluence are pushing boundaries in battery chemistry, aiming for higher energy density and longer lifespans. For instance, Fluence's recent product developments often highlight improvements in system efficiency, directly impacting the cost-effectiveness of their solutions for customers.
This relentless innovation means that staying ahead requires significant and continuous investment in research and development. Fluence, for example, actively pursues new software solutions for optimizing energy storage systems and enhancing grid integration capabilities. The market demands constant upgrades and new product introductions, making R&D a critical determinant of competitive success.
The energy storage market is becoming increasingly competitive, with new players and expanding manufacturing capacity for batteries. This surge in supply is directly translating into significant pricing pressure across the sector. For instance, the average price of lithium-ion battery packs for electric vehicles, a key component in many storage solutions, saw a notable decrease in 2023, continuing a trend that puts pressure on all participants in the value chain.
This intense competition often forces companies like Fluence Energy into aggressive bidding wars for new projects. While winning contracts is crucial for market share, these low-margin bids can severely impact profitability. Integrators must carefully navigate the delicate balance between offering competitive pricing to secure deals and ensuring their operations remain financially sustainable, especially when factoring in fluctuating supply chain costs and potential tariffs on imported components.
Shifting Regional Market Dynamics
While global players exist, regional market leadership in energy storage is highly dynamic. Local policies, access to raw materials, and competitor strategies significantly influence this. For example, Chinese energy storage integrators are increasingly targeting markets in Europe and the Middle East, driven by intense domestic competition and overcapacity. This regional shift intensifies the competitive landscape for companies like Fluence Energy.
This regional variability introduces a complex layer to competitive rivalry. Companies must navigate diverse regulatory environments and adapt to localized supply chain strengths. The aggressive international expansion of Chinese firms, for instance, directly challenges established players in new territories.
- Regional Dominance Fluctuation: Market leadership can change quickly based on local factors, not just global scale.
- Chinese Expansion Impact: Chinese integrators are actively entering European and Middle Eastern markets, fueled by domestic oversupply and competition.
- Strategic Adaptation: Companies like Fluence Energy must continuously adapt their strategies to address these shifting regional competitive dynamics.
Importance of Project Backlog and Delivery Track Record
Securing a robust project backlog and showcasing a strong delivery track record are paramount in the energy storage sector. Companies are evaluated not just on their initial proposals but on their proven capacity to execute large, intricate projects successfully. Fluence's substantial backlog, exceeding $3.2 billion as of their Q2 2024 earnings report, highlights its competitive position. However, the industry's emphasis remains squarely on the timely and efficient deployment of these projects, which directly impacts future revenue and market share.
The competitive rivalry in energy storage is intensified by the need for demonstrable project execution. Clients prioritize partners who can reliably bring complex systems online, on time and within budget. This focus means that while a large backlog is a positive indicator, the actual delivery performance is a more critical determinant of ongoing success and future contract awards. Companies that consistently meet or exceed delivery expectations build trust and a reputation that directly counters competitors relying solely on lower initial bids.
- Project Backlog as a Competitive Differentiator: Fluence's significant project backlog, reported at over $3.2 billion in Q2 2024, serves as a key indicator of its market strength and competitive standing.
- Delivery Track Record's Crucial Role: Beyond initial bids, the ability to reliably execute and deliver large-scale, complex energy storage projects is a critical factor that influences customer choice and future business.
- Industry Focus on Deployment Efficiency: The energy storage market places a high premium on timely and efficient project deployment, making proven execution capabilities a paramount concern for clients and a driver of competitive advantage.
- Reputation Built on Successful Execution: Consistent and successful project delivery builds trust and a strong market reputation, which is essential for securing new contracts and maintaining a competitive edge against rivals.
The competitive landscape for Fluence Energy is defined by intense rivalry from established global players like Tesla and Sungrow, as well as emerging regional competitors. This dynamic market is characterized by rapid technological advancements, leading to constant pressure on pricing and innovation. For instance, the average price of lithium-ion battery packs, a core component, saw a significant decrease in 2023, impacting margins for all participants.
Companies are forced into aggressive bidding to secure projects, often leading to lower profitability. Fluence's substantial project backlog, exceeding $3.2 billion as of Q2 2024, underscores its competitive positioning, but successful project execution remains paramount for sustained success. The increasing presence of Chinese integrators in European and Middle Eastern markets further intensifies this global competition.
| Competitor | Key Market Presence | Recent Developments |
|---|---|---|
| Tesla | Global (US, Europe, Asia) | Continued expansion of Megapack production, focus on grid services. |
| Sungrow | Global (Asia, Europe, Americas) | Strong market share in utility-scale storage, expanding product portfolio. |
| Wärtsilä | Global (Europe, Americas, Asia) | Focus on integrated energy solutions and software platforms. |
| Powin | North America, Asia | Rapid growth in North American market, emphasis on modular solutions. |
| Chinese Integrators (e.g., BYD, CATL) | China, expanding globally | Aggressive pricing, growing capacity, targeting international markets. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While lithium-ion batteries currently lead grid-scale energy storage, especially for shorter durations, a significant shift is underway with the emergence of long-duration energy storage (LDES) technologies. These emerging alternatives, including flow batteries, compressed air energy storage (CAES), thermal storage, and hydrogen solutions, are rapidly improving their viability.
These LDES technologies offer the crucial advantage of longer discharge durations, making them increasingly competitive substitutes for lithium-ion in applications requiring extended power supply. For instance, by 2024, the global LDES market is projected to see substantial growth, with some estimates suggesting a market size reaching tens of billions of dollars as these technologies mature and become more cost-effective.
Traditional grid infrastructure, particularly natural gas peaker plants, continues to represent a significant substitute for battery energy storage systems. These plants are designed to quickly ramp up and meet demand during peak hours, a function that Fluence's storage solutions also aim to fulfill. While the global push for decarbonization is a strong tailwind for renewables and storage, the established presence and operational capabilities of these conventional assets mean they haven't been entirely displaced yet.
Despite the growing appeal of cleaner energy solutions, the installed capacity of natural gas peaker plants remains substantial. For instance, in the United States, natural gas generation accounted for approximately 40% of total electricity generation in 2023, with peaker plants playing a crucial role in grid reliability during periods of high demand. This existing infrastructure, though carbon-intensive, offers a proven and often lower upfront cost alternative for meeting immediate peak load needs, thereby posing a threat to the widespread adoption of battery storage.
Furthermore, advancements in grid transmission and distribution infrastructure can also diminish the immediate necessity for new battery storage deployments. By improving the efficiency and capacity of the existing grid, utilities can better manage load fluctuations and integrate intermittent renewable sources without relying as heavily on dedicated storage solutions. Investments in grid modernization, such as smart grid technologies and enhanced transmission lines, can therefore act as a substitute threat by reducing the perceived urgency for battery storage to address grid stability and peak demand challenges.
Demand-side management (DSM) strategies, which aim to reduce or shift energy consumption, present a significant threat by potentially lessening the need for Fluence's energy storage solutions. For instance, smart grid technologies and dynamic pricing can incentivize consumers to use less power during peak hours, directly impacting the demand for storage that balances these peaks. In 2023, the global DSM market was valued at approximately $27.5 billion, demonstrating a substantial existing adoption of these alternative approaches.
Energy efficiency improvements across all sectors also serve as a potent substitute. By making buildings, appliances, and industrial processes consume less energy, the overall demand for new energy supply and, consequently, the need for energy storage capacity is diminished. The International Energy Agency reported in 2024 that energy efficiency measures saved the equivalent of the European Union's total energy consumption in 2023, highlighting the scale of this threat.
Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems with Integrated Management
The rise of hybrid renewable energy systems, blending solar or wind with sophisticated management, presents a substitution threat. These systems optimize generation and consumption, potentially lessening the demand for standalone battery storage solutions.
While these hybrids often incorporate batteries, their core value lies in integrated management, which can reduce the required scale of dedicated storage capacity. For instance, by intelligently dispatching renewable generation, the reliance on stored energy can be minimized.
- Hybridization as Substitution: Integrated renewable generation and management systems offer an alternative to relying solely on battery storage for grid services.
- Optimization Focus: The emphasis shifts from pure storage to optimizing the entire energy flow, potentially reducing the need for large, standalone battery installations.
- Market Trends: In 2023, the global hybrid renewable energy market saw significant growth, with projects increasingly incorporating advanced energy management software to maximize asset utilization.
Alternative Battery Chemistries Beyond Lithium-Ion
The threat of substitutes for Fluence Energy, particularly concerning its core battery storage solutions, is amplified by the rapid development of alternative energy storage technologies. Beyond different storage mediums like thermal or mechanical systems, the emergence of new battery chemistries presents a significant challenge.
Sodium-ion batteries, for instance, are gaining traction as a viable substitute for lithium-ion. These alternatives often boast lower material costs, which is a critical factor in grid-scale deployments. For example, by mid-2024, the cost of sodium-ion battery cells was projected to be around 30-50% lower than comparable lithium-ion cells, making them an attractive option for cost-sensitive projects.
These emerging chemistries offer different performance profiles, such as varying energy densities and charge/discharge rates, which could cater to specific grid applications where lithium-ion might not be the optimal or most economical choice. This diversification of options for customers means Fluence must continuously innovate and demonstrate the superior value proposition of its lithium-ion based systems or adapt its offerings.
- Emerging Battery Chemistries: Sodium-ion batteries are a key substitute, offering potential cost advantages over lithium-ion.
- Cost Competitiveness: Projections in mid-2024 indicated sodium-ion cells could be 30-50% cheaper than lithium-ion.
- Performance Differentiation: Alternative chemistries may offer unique characteristics suitable for specific grid-scale applications.
- Market Disruption Potential: New battery technologies can provide customers with diverse and potentially more economical choices, impacting market share.
The threat of substitutes for Fluence Energy's battery storage solutions is multifaceted, encompassing both alternative storage technologies and demand-reduction strategies. Emerging long-duration energy storage (LDES) technologies, such as flow batteries and compressed air energy storage, are becoming increasingly viable, offering longer discharge durations that compete with lithium-ion for extended power needs.
Traditional grid infrastructure, like natural gas peaker plants, remains a significant substitute, providing rapid response to peak demand at often lower upfront costs. In 2023, natural gas accounted for about 40% of U.S. electricity generation, highlighting its continued role. Demand-side management strategies and energy efficiency improvements also reduce the overall need for new energy storage capacity.
Furthermore, advancements in grid transmission and distribution, alongside the rise of hybrid renewable energy systems that integrate generation and management, can diminish the reliance on standalone battery storage. The market for sodium-ion batteries is also growing, with mid-2024 projections suggesting cell costs could be 30-50% lower than lithium-ion, presenting a significant cost-competitive substitute.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the grid-scale energy storage sector, where Fluence operates, necessitates immense upfront capital. This includes significant investment in research and development, building advanced manufacturing capabilities for system integration, and securing funding for the deployment of large-scale projects. For instance, as of early 2024, projects can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars.
These substantial financial prerequisites act as a strong deterrent, significantly limiting the pool of potential new entrants. Only companies with considerable financial backing can realistically consider competing with established players like Fluence, effectively raising the barrier to entry.
The significant technological hurdles in developing and deploying grid-scale battery energy storage systems present a substantial barrier to new entrants. Fluence, for instance, leverages deep expertise in battery chemistry, power electronics, and advanced energy management software, exemplified by its Fluence IQ platform. Acquiring or replicating this specialized knowledge and intellectual property, built over years of research and development, is a formidable challenge for any newcomer aiming to compete in this sophisticated market.
The energy sector, including Fluence Energy's market, is a minefield of regulations. New companies must navigate a complex web of permits and standards, which can vary significantly by location. For instance, securing grid interconnection agreements, a crucial step for energy storage projects, can take anywhere from months to over a year depending on the utility and region, adding substantial time and cost to market entry.
Need for Established Customer Relationships and Track Record
Utilities and large developers, Fluence’s core clientele, heavily weigh a vendor’s proven history of successful project execution and existing relationships. Newcomers face a steep climb in cultivating this essential trust and winning initial substantial contracts without a demonstrable past performance.
This inherent bias towards established entities acts as a substantial hurdle for new market entrants aiming to gain a foothold.
- Customer Loyalty and Switching Costs: Established players often benefit from strong customer loyalty, making it difficult for new entrants to lure away clients.
- Reputation and Brand Recognition: Fluence, having delivered significant projects, benefits from strong brand recognition and a reputation for reliability, which new entrants lack.
- Access to Capital: Securing the substantial capital required for large-scale energy storage projects is more challenging for new, unproven companies compared to established firms.
Challenges in Supply Chain Access and Integration
New entrants face significant hurdles in establishing robust and cost-effective supply chains for essential components like battery cells. Established companies often benefit from established supplier relationships, which can translate into preferential pricing and guaranteed availability.
Securing competitive access to these critical materials is particularly challenging in a market susceptible to disruptions and geopolitical factors. For instance, the global battery supply chain, heavily reliant on materials like lithium and cobalt, has seen price volatility. In 2023, lithium carbonate prices experienced significant fluctuations, impacting the cost of battery production for all players.
- Supply Chain Dominance: Incumbents leverage existing supplier contracts and volume discounts.
- Material Scarcity: Access to key battery materials like lithium and cobalt can be limited and subject to price swings.
- Geopolitical Risk: Global supply chains for energy storage components are vulnerable to trade policies and regional instability.
The threat of new entrants into the grid-scale energy storage market, where Fluence operates, is moderate. While the sector presents lucrative opportunities, significant barriers exist. These include the substantial capital required for projects, advanced technological expertise, regulatory complexities, and the need for established customer trust.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Fluence Energy Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of verified data, drawing from company annual reports, industry-specific market research, regulatory filings, and reputable financial news outlets to capture a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.