EPAM Systems Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
EPAM Systems Bundle
EPAM Systems operates in a dynamic IT services landscape, where buyer power is significant due to readily available alternatives. The threat of new entrants is moderate, balanced by high switching costs and established client relationships.
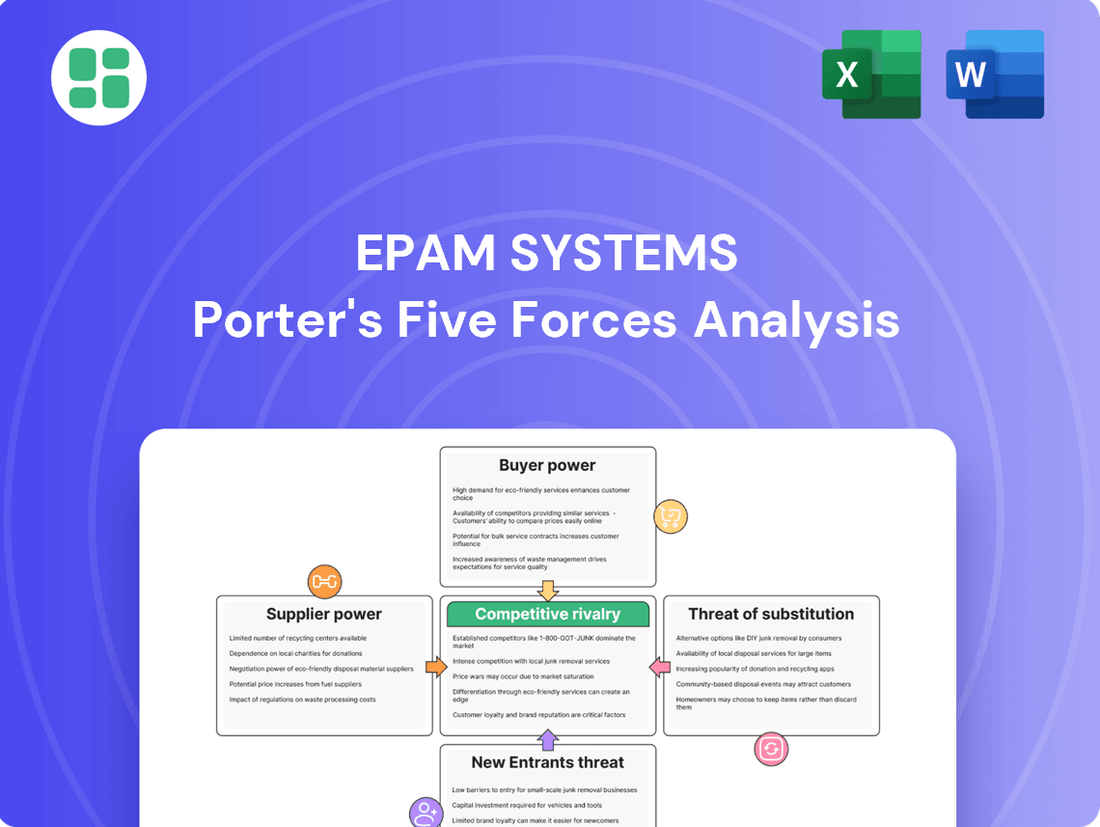
The full analysis reveals the strength and intensity of each market force affecting EPAM Systems, complete with visuals and summaries for fast, clear interpretation.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
EPAM Systems' reliance on a global pool of highly specialized IT talent, such as AI/ML engineers and cloud architects, is a key factor in supplier bargaining power. The intense demand for these niche skills means that the professionals possessing them hold considerable leverage. This scarcity directly translates into increased recruitment and retention expenses for EPAM, impacting operational costs.
EPAM Systems' reliance on specialized software and cloud infrastructure for its digital transformation services means that suppliers of these critical inputs hold significant sway. If the pool of providers for these advanced technologies is limited, these suppliers can command higher prices or more favorable terms, directly impacting EPAM's cost structure and profitability.
EPAM Systems invests heavily in its workforce, with personnel expenses representing a significant portion of its operational costs. In 2023, EPAM's total employee compensation, including salaries, benefits, and training, amounted to billions of dollars, highlighting the high cost of acquiring and retaining skilled technical professionals. This substantial financial commitment to human capital means that talented engineers and developers, as the suppliers of labor, possess considerable bargaining power.
Potential Supply Constraints in Emerging Technologies
As EPAM Systems ventures into rapidly evolving fields such as quantum computing and blockchain, the limited availability of specialized talent in these emerging technologies significantly amplifies supplier power. This scarcity means EPAM may face increased costs to secure these critical skills, potentially impacting project budgets and timelines.
The demand for expertise in areas like AI-driven cybersecurity and advanced data analytics is projected to grow substantially. For example, the global AI market was valued at approximately $200 billion in 2023 and is expected to see a compound annual growth rate of over 37% through 2030, indicating a highly competitive talent landscape.
- Talent Scarcity: Limited pools of quantum computing and blockchain engineers create leverage for suppliers.
- Premium Costs: EPAM may need to offer higher compensation or benefits to attract and retain scarce talent.
- Investment in Development: The company might need to increase investment in internal training programs to build its own talent pipeline.
- Strategic Sourcing: EPAM will likely need to develop robust strategies for identifying and engaging with specialized talent providers.
Limited Forward Integration by Suppliers
While individual IT professionals possess significant bargaining power, the global IT talent market's fragmentation and the substantial capital and organizational hurdles for these individuals to directly offer comprehensive digital transformation services limit their ability to integrate forward. This means suppliers, in this context, are less likely to directly compete with EPAM Systems by offering end-to-end solutions. For example, in 2024, the IT services market continued to see a strong demand for specialized skills, but the infrastructure required to manage large-scale projects remains a barrier for individual contractors.
However, the landscape isn't entirely static. The emergence of specialized niche firms, capable of providing highly focused but integrated services, could present a more consolidated supplier threat. These smaller, agile entities might leverage specific technological expertise to bypass some of the traditional barriers to forward integration, potentially impacting EPAM's market share in those specific segments.
The bargaining power of suppliers is thus moderated by the difficulty of individual IT professionals to achieve forward integration. While the IT talent pool is vast, the practicalities of building a full-service digital transformation offering remain a significant deterrent for most, thereby capping this specific supplier threat.
The bargaining power of suppliers for EPAM Systems is primarily driven by the scarcity of highly specialized IT talent, particularly in emerging fields like AI, cloud computing, and quantum computing. This demand allows these skilled professionals and niche firms to command premium compensation and favorable terms, directly impacting EPAM's operational costs and profitability.
EPAM's significant investment in its workforce, with personnel expenses representing a substantial portion of its costs, underscores the leverage held by its talent suppliers. For instance, in 2023, EPAM's total employee compensation was in the billions, reflecting the high value placed on skilled engineers. The global AI market's projected growth, expected to exceed 37% annually through 2030, further intensifies competition for this talent.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on EPAM | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized IT Talent (e.g., AI/ML Engineers) | High Scarcity & Demand | Increased recruitment & retention costs | Continued high demand, with AI talent commanding 20-30% higher salaries than general software engineers. |
| Software & Cloud Infrastructure Providers | Limited providers of advanced tech | Potential for higher prices, impacting cost structure | Major cloud providers (AWS, Azure, GCP) continue to dominate, allowing for price leverage on specialized services. |
| Niche Service Firms | Focused expertise, potential for integration | May challenge EPAM in specific segments | Growth in specialized boutique firms offering integrated solutions in areas like cybersecurity and data analytics. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects EPAM Systems' competitive environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Understand and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing EPAM's bargaining power of buyers and suppliers with intuitive heatmaps.
Customers Bargaining Power
EPAM Systems' customer base is notably concentrated, with its top 10 clients accounting for a substantial percentage of its overall revenue. This means that a small number of major clients wield significant bargaining power.
For instance, in 2023, EPAM's top 10 clients represented approximately 30% of its total revenue. This concentration implies that the loss of even one of these key accounts could have a material adverse effect on EPAM's financial results and operational stability.
EPAM Systems actively pursues long-term contracts, typically spanning 24 to 36 months. This strategic approach locks in a significant portion of its revenue as recurring, thereby diminishing the immediate ability of clients to negotiate terms mid-contract.
These multi-year commitments provide EPAM with substantial revenue stability and predictability, insulating it from short-term market fluctuations and reducing the bargaining leverage customers might otherwise wield. For instance, in 2023, EPAM reported that approximately 80% of its revenue was recurring, a testament to the success of its long-term contract strategy.
For large enterprises, transitioning away from a digital transformation and software engineering partner like EPAM Systems carries substantial costs, extensive timelines, and potential operational disruptions. This complexity inherently limits their ability to easily switch providers.
EPAM's deep integration of its custom-built solutions and proprietary platforms into client IT infrastructures creates significant switching barriers. These embedded systems make it costly and time-consuming for clients to migrate to a competitor, thereby reducing their bargaining power once an engagement is underway.
Criticality of Services to Client Operations
EPAM Systems' services are frequently woven into the very fabric of their clients' operations, particularly concerning critical digital transformation and modernization projects. This deep integration means that the services provided are not merely add-ons but essential components for clients to achieve their strategic goals and maintain competitive advantage.
The mission-critical nature of the complex software solutions EPAM delivers significantly curtails the bargaining power of customers. Clients understand that disrupting these core systems by switching providers could lead to substantial operational inefficiencies and financial losses, making them hesitant to exert undue pressure on pricing or terms.
- Integral to Client Operations: EPAM's offerings are often central to clients' digital innovation and business modernization efforts, making them indispensable.
- High Switching Costs: The complexity and criticality of EPAM's solutions create high switching costs for clients, reducing their leverage.
- Risk Aversion: Clients prioritize the reliability and quality of services for mission-critical applications, limiting their willingness to risk disruption by demanding lower prices.
- Client Retention: In 2023, EPAM reported that 97% of its revenue came from existing clients, highlighting the sticky nature of its services and the resulting limited customer bargaining power.
Internal Development Capabilities of Clients
While EPAM Systems excels at offering specialized external expertise, a significant trend is the growth of in-house software development capabilities within large enterprise clients. This internal capacity acts as a powerful bargaining tool for customers.
The ability for clients to develop solutions internally puts pressure on EPAM regarding pricing and the terms of service agreements. For instance, if a client can build a comparable system for a lower cost internally, they are less likely to accept higher prices from EPAM.
- Client In-House Development: Many large organizations are investing in and expanding their internal IT and software engineering teams, reducing reliance on external vendors for core development tasks.
- Cost Comparison: Clients can benchmark EPAM's service costs against their own internal development expenses, using this data to negotiate more favorable rates.
- Strategic Control: Developing in-house provides clients with greater control over their intellectual property, development timelines, and strategic direction, which can be leveraged in negotiations.
- Talent Acquisition: The increasing availability of skilled software developers globally, often at competitive rates, further empowers clients to consider in-house solutions.
EPAM's bargaining power is somewhat tempered by the growing trend of clients building their own in-house software development capabilities. This internal capacity allows clients to benchmark EPAM's pricing and negotiate more effectively, especially as global talent acquisition becomes more accessible.
The increasing sophistication of client IT departments means they can more readily assess the cost-effectiveness of EPAM's services against internal development, potentially pressuring EPAM on service agreement terms and pricing.
| Factor | Impact on EPAM's Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data (2023/2024 Estimates) |
| Client In-house Development | Increases bargaining power; clients can compare EPAM's costs to internal development. | While EPAM's 2023 revenue from existing clients was 97%, the rise in internal IT investment by large enterprises is a growing counter-force. Specific data on client in-house development growth is proprietary but widely observed in industry reports. |
| Cost Comparison | Empowers clients to negotiate better rates by leveraging internal cost benchmarks. | Clients can leverage internal development cost savings as a negotiation point, though EPAM's specialized expertise often justifies its pricing. |
| Strategic Control | Clients gain leverage by retaining greater control over IP and development timelines. | This is a qualitative factor, but clients seeking full control over critical projects may favor in-house solutions, influencing their negotiation stance with EPAM. |
Same Document Delivered
EPAM Systems Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete EPAM Systems Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of competitive forces within the IT services sector. The document you see is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, providing a professionally formatted and actionable strategic overview. No placeholders or samples are presented; this is the actual, ready-to-use analysis for your business intelligence needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
EPAM Systems operates in a fiercely competitive landscape, contending with numerous global IT service giants. Companies like Accenture, Cognizant, Infosys, Tata Consultancy Services, and IBM Global Services offer a similar breadth of digital engineering and consulting services, creating intense rivalry.
The sheer scale and established market presence of these competitors mean they possess significant resources for R&D, talent acquisition, and global reach. For instance, in 2023, Accenture reported revenues of $64.9 billion, highlighting the substantial financial muscle EPAM must contend with.
The competition for specialized talent, especially in cutting-edge fields such as artificial intelligence and cloud computing, is incredibly fierce. This intense rivalry directly impacts companies like EPAM Systems, as they must constantly strive to attract and keep the best minds.
To secure and retain these highly skilled professionals, EPAM and its competitors are compelled to offer competitive salary packages and robust benefits. This necessity has a direct effect on operational expenditures and the capacity to deliver services effectively, as talent acquisition and retention become a significant cost factor.
The IT services market experienced a noticeable slowdown in late 2024, with macroeconomic uncertainty prompting clients to scrutinize spending. This environment directly impacts competitive rivalry, as companies like EPAM face heightened pressure on pricing and project acquisition.
Clients are navigating a delicate balance between essential digital transformation initiatives and stringent cost management. This dual focus means service providers must demonstrate exceptional value to secure and retain business, intensifying the competitive landscape for EPAM and its peers.
Differentiation Through Niche Expertise and Innovation
EPAM carves out its competitive advantage by concentrating on specialized areas like intricate digital platform engineering and leveraging its strong engineering roots. This focus allows them to stand apart from competitors offering more generalized services.
The company's substantial investments in artificial intelligence (AI) and generative AI (GenAI) further solidify its differentiation strategy. These advanced capabilities enable EPAM to tackle complex client challenges, moving beyond simple cost competition.
- Niche Expertise: Deep focus on complex digital platform engineering and software development.
- Innovation Investment: Significant capital allocation towards AI and GenAI technologies.
- Competitive Edge: Differentiation achieved through specialized technical skills and advanced solutions, not just price.
Geographic and Industry Diversification
EPAM Systems operates in over 50 countries, a broad geographic reach that helps dilute the impact of intense competition within any single region. Its diversification across numerous industry verticals, including financial services, healthcare, and retail, further spreads its competitive exposure. For instance, in 2023, EPAM reported revenue from its North America segment was approximately $2.6 billion, while Europe contributed around $1.1 billion, showcasing its global footprint.
This extensive diversification means EPAM faces specialized local competitors in various markets and larger global IT service providers across multiple sectors simultaneously. While this strategy reduces reliance on any one market, it necessitates managing a complex competitive landscape. The company's ability to compete effectively across these varied environments is crucial for maintaining its market position.
- Global Reach: EPAM's presence in over 50 countries mitigates localized competitive pressures.
- Industry Breadth: Diversification across sectors like financial services, healthcare, and retail spreads competitive risk.
- Fragmented Competition: EPAM contends with both niche local players and broad-based global competitors.
- Revenue Distribution (2023): North America ($2.6B) and Europe ($1.1B) highlight significant geographic market engagement.
EPAM Systems faces intense competition from large, established IT service providers like Accenture and IBM, who boast significant financial resources and global reach. The battle for top engineering talent is particularly fierce, driving up costs for attracting and retaining skilled professionals. This competition intensifies when clients prioritize both digital transformation and cost savings, forcing EPAM to demonstrate clear value beyond price.
| Competitor | Approx. 2023 Revenue (USD Billions) | Key Service Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Accenture | 64.9 | Digital Transformation, IT Services, Consulting |
| Cognizant | 19.4 | Digital, Technology, Consulting, Operations |
| Infosys | 18.1 | Digital, Cloud, Data Analytics, Engineering |
| Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) | 28.0 | IT Services, Consulting, Business Solutions |
| IBM Global Services | 62.0 (approx. for Consulting & Software segments) | Hybrid Cloud, AI, Consulting, IT Infrastructure |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing adoption of low-code/no-code platforms poses a growing threat of substitutes for EPAM Systems. These platforms allow businesses to build applications with significantly less traditional coding, directly impacting the demand for custom software development services. For instance, the low-code market was projected to reach $45.5 billion in 2022 and was expected to grow to $187 billion by 2030, according to Gartner.
This trend empowers citizen developers within organizations, potentially reducing their reliance on external IT service providers like EPAM for certain types of application development. Companies can achieve faster deployment cycles and lower development costs, making these platforms an attractive alternative to more complex, bespoke solutions.
Many large enterprises are building out their internal software development teams, creating a significant threat of substitutes for companies like EPAM Systems. This trend is particularly noticeable in sectors like technology and financial services, where companies are investing heavily in in-house IT capabilities to gain more control and potentially reduce long-term costs. For example, a significant portion of Fortune 500 companies have been expanding their internal digital transformation teams, directly impacting the demand for external software development services.
For less complex business requirements, readily available commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) software and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms present a significant threat of substitution for EPAM Systems. These pre-built solutions, such as Salesforce for CRM or Workday for HR, often come with lower upfront costs and quicker implementation times, making them attractive alternatives for clients seeking standardized functionalities.
The market for COTS and SaaS solutions is vast and continues to grow. For instance, the global SaaS market was projected to reach over $200 billion in 2024, offering a wide array of options that can fulfill many common business needs without the need for custom development. This accessibility directly challenges EPAM's custom-engineered solutions, particularly for clients with less unique or highly standardized operational demands.
AI-Driven Automation and Generative AI Tools
The rapid evolution of AI, especially generative AI, presents a significant threat of substitution for EPAM Systems. These tools can automate many core functions within software development, quality assurance, and even client consulting, potentially diminishing the need for traditional human-led engineering services. For instance, by mid-2024, many firms reported using AI for code generation, which can accelerate development cycles but also reduce the billable hours for human developers.
While EPAM is at the forefront of integrating AI into its service offerings, the increasing accessibility and capability of these AI solutions could lower the barrier to entry for competitors or even enable clients to perform certain tasks in-house. This could shift demand away from the comprehensive, human-centric engineering and digital transformation services EPAM provides. The market is already seeing a rise in specialized AI development firms, which act as direct substitutes for certain project types.
The impact is already being felt as companies explore AI-powered solutions for efficiency gains. A 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of IT leaders were actively investigating or piloting generative AI for software development tasks. This trend suggests a potential future where a portion of EPAM's revenue streams, particularly those focused on routine coding and testing, could be challenged by more cost-effective AI alternatives.
- AI Automation Threat: Generative AI tools can automate software development, testing, and consulting, acting as a substitute for human-led engineering services.
- Market Adoption: By mid-2024, many companies were already leveraging AI for code generation, impacting traditional development workflows and billable hours.
- Competitive Landscape: The rise of specialized AI development firms and in-house AI capabilities poses a direct substitution risk to EPAM's core service offerings.
- Client Efficiency Focus: Over 60% of IT leaders in a 2024 survey were exploring AI for development efficiency, signaling a potential shift in demand for outsourced engineering.
Management Consulting Firms Offering Technology Implementation
Traditional management consulting firms are increasingly broadening their technology implementation capabilities, presenting a significant threat of substitution for EPAM Systems. These established players are leveraging their existing strategic advisory relationships to secure technology projects, offering comprehensive digital transformation services that directly compete with EPAM's core business.
This trend is particularly pronounced as businesses seek integrated solutions, making it easier for clients to turn to their trusted strategic partners for technology execution rather than engaging separate specialized firms. For instance, major consulting houses like Accenture, Deloitte, and PwC have robust technology implementation arms, often boasting billions in revenue from these services. In 2023, Accenture reported its Technology segment revenue reached $24.2 billion, highlighting the scale of this competitive force.
The ability of these consulting giants to offer end-to-end services, from strategy formulation to implementation and ongoing support, creates a powerful value proposition for clients. This can directly impact EPAM’s market share, especially in large-scale digital transformation initiatives where clients prefer a single point of accountability.
- Growing Market Share: Major consulting firms are actively expanding their technology services, aiming to capture a larger share of the digital transformation market.
- Integrated Service Offerings: These firms provide a combined strategic and implementation approach, appealing to clients seeking holistic solutions.
- Leveraging Existing Relationships: Deep-seated client trust and ongoing advisory roles allow these consultancies to seamlessly transition into technology implementation projects.
- Financial Muscle: The significant revenue generated by the technology arms of large consulting firms demonstrates their substantial capacity and competitive presence.
The threat of substitutes for EPAM Systems is multifaceted, stemming from advancements in technology and evolving client strategies. Low-code/no-code platforms, readily available COTS/SaaS solutions, the rapid rise of AI, and the expansion of traditional management consulting firms into technology implementation all present viable alternatives to EPAM's custom software development and digital transformation services. These substitutes often promise faster deployment, lower costs, or integrated solutions, directly challenging EPAM's value proposition.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Impact on EPAM | Market Data/Trend (2024) |
| Low-Code/No-Code Platforms | Faster development, citizen developers, reduced reliance on IT experts | Decreased demand for traditional custom coding | Low-code market projected to reach $187 billion by 2030 (Gartner) |
| COTS/SaaS Solutions | Pre-built functionalities, lower upfront costs, quicker implementation | Challenges custom solutions for standardized needs | Global SaaS market projected to exceed $200 billion in 2024 |
| AI Automation (Generative AI) | Code generation, automated testing, potential for in-house task execution | Reduces need for human-led development for certain tasks | Over 60% of IT leaders exploring AI for development efficiency (2024 survey) |
| Traditional Consulting Firms | Integrated strategy and technology implementation, leveraging existing client relationships | Direct competition for large digital transformation projects | Accenture's Technology segment revenue was $24.2 billion in 2023 |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the digital platform engineering and software development services market, especially at EPAM Systems' scale, demands a massive upfront investment. This includes building robust technological infrastructure and acquiring cutting-edge tools. For instance, in 2024, major tech firms are investing billions in AI development and cloud infrastructure, setting a high bar for any newcomer.
Beyond financial capital, securing and nurturing a deep bench of highly skilled engineers and developers is paramount. The competition for top talent in areas like AI, cloud computing, and cybersecurity is fierce. In 2024, the average salary for a senior software engineer in the US can exceed $150,000, highlighting the significant ongoing talent acquisition costs that act as a formidable barrier to entry for new players.
EPAM Systems boasts a robust brand reputation built on consistent engineering quality and deep, long-standing client relationships, often extending over many years. This established trust and proven track record create a significant barrier for newcomers. For instance, EPAM's commitment to client success is reflected in its high client retention rates, a testament to the value they deliver and the strong partnerships they cultivate.
EPAM Systems thrives on intricate, high-stakes digital transformation and product development. These projects require a profound understanding across numerous technologies and diverse industries, making it difficult for newcomers to quickly match EPAM's accumulated knowledge and practical experience. For instance, EPAM's deep capabilities in areas like cloud engineering, data analytics, and AI, honed over years of client engagements, represent a significant barrier to entry.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
EPAM Systems operates globally, necessitating adherence to a complex array of international regulations and compliance standards, particularly within highly regulated sectors like financial services and healthcare. New entrants would face substantial upfront costs and expertise requirements to navigate these diverse legal and operational landscapes, significantly raising the barrier to entry.
For instance, in 2024, the global regulatory technology market was projected to reach over $120 billion, highlighting the significant investment required for compliance. Companies entering EPAM's space must demonstrate proficiency in areas such as GDPR, HIPAA, and various financial sector regulations, which demand continuous monitoring and adaptation.
- Significant Investment in Compliance: New entrants must allocate substantial capital and resources to develop or acquire the necessary expertise and systems to meet global regulatory demands.
- Industry-Specific Expertise: Understanding and implementing compliance frameworks for sectors like banking, insurance, and pharmaceuticals requires specialized knowledge that is costly and time-consuming to build.
- Geographic Complexity: Operating across multiple jurisdictions means managing a constantly evolving patchwork of national and regional regulations, adding layers of difficulty and expense.
Economies of Scale and Global Delivery Model
EPAM Systems leverages significant economies of scale derived from its extensive global delivery model. This model, which includes numerous development centers across various continents, allows EPAM to achieve considerable cost efficiencies. For instance, by distributing talent and operations, they can optimize resource allocation and reduce overheads compared to more localized competitors.
New entrants face a substantial barrier to entry due to the difficulty in replicating EPAM's scale and the associated cost advantages. Establishing a comparable network of distributed talent centers and achieving similar operational efficiencies would require massive upfront investment and time. This makes it challenging for newcomers to compete on price or service delivery speed without a comparable global footprint.
- Global Presence: EPAM operates in over 50 countries, enabling optimized talent sourcing and cost management.
- Cost Efficiencies: The scale of operations allows for competitive pricing that is hard for smaller firms to match.
- Talent Pool Access: A vast, globally distributed talent pool provides flexibility and cost-effectiveness in project staffing.
- Operational Maturity: Years of experience in managing a global delivery network have refined processes, further solidifying EPAM's competitive edge.
The threat of new entrants in EPAM Systems' market is moderate. While the demand for digital engineering services is high, the significant capital required for talent acquisition, technological infrastructure, and global operations presents a substantial barrier. Established brand reputation and deep industry expertise further deter newcomers.
New players must overcome the challenge of replicating EPAM's extensive global delivery model and the associated economies of scale. This includes building a comparable network of development centers and achieving operational efficiencies, which demands massive upfront investment and time, making it difficult to compete on price or speed.
The need for specialized industry knowledge, particularly in regulated sectors, and navigating complex international compliance standards also raises the entry bar. For instance, in 2024, the global regulatory technology market's projected growth to over $120 billion underscores the significant investment required for compliance alone.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in technology, infrastructure, and talent. | Significant financial hurdle. |
| Talent Acquisition | Competition for skilled engineers, with average senior engineer salaries exceeding $150,000 in the US (2024). | High ongoing operational costs. |
| Brand Reputation & Client Relationships | Established trust and long-term client partnerships. | Difficult to displace incumbents. |
| Technical Expertise & Experience | Deep understanding of complex technologies and diverse industries. | Steep learning curve for newcomers. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to global and industry-specific regulations. | Requires substantial investment in expertise and systems. |
| Economies of Scale | Global delivery model offers cost efficiencies. | Challenging to match pricing and service delivery speed. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our EPAM Systems Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive data strategy, drawing from EPAM's official investor relations disclosures, annual reports, and SEC filings. We supplement this with data from reputable industry analysis firms like Gartner and Forrester, as well as market intelligence platforms such as Statista and IBISWorld, to provide a robust assessment of the competitive landscape.