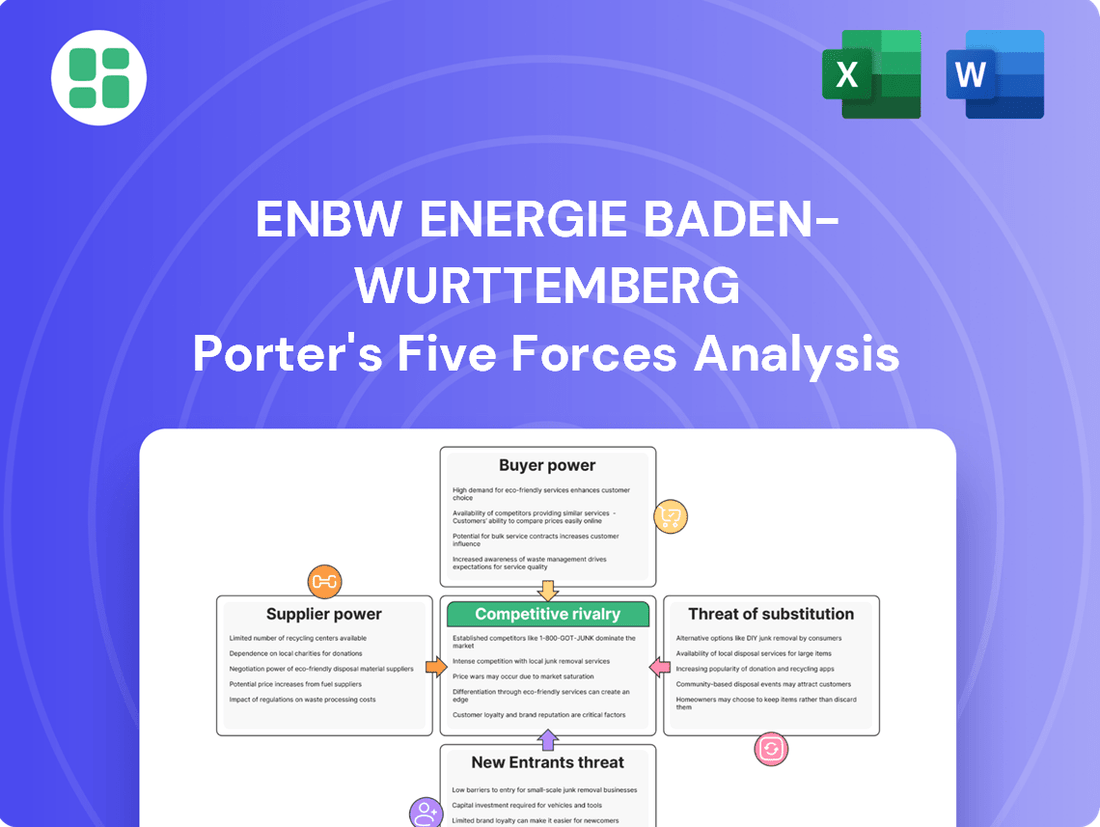
EnBW Energie Baden-Wurttemberg Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
EnBW Energie Baden-Wurttemberg Bundle
EnBW Energie Baden-Württemberg navigates a complex energy landscape, facing significant threats from new entrants and the intense rivalry among existing players. Understanding the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers is crucial for its strategic positioning. The threat of substitutes, particularly from renewable energy sources, also demands constant adaptation.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping EnBW Energie Baden-Württemberg’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for essential fossil fuels like natural gas and coal is a considerable factor for EnBW, given the global market dynamics and geopolitical events that can impact pricing and availability. Even as EnBW strategically shifts towards renewable energy, its ongoing reliance on these traditional energy sources means that a concentrated group of major producers can significantly influence supply agreements and costs.
EnBW's significant investment in renewable energy, especially offshore wind and solar, places it in a position of reliance on a select group of highly specialized manufacturers for critical components like wind turbines and advanced solar panels. These suppliers often possess unique, proprietary technology, granting them substantial leverage, particularly for major undertakings such as the He Dreiht offshore wind farm project.
The German energy transition, a massive undertaking, is driving a significant demand for skilled labor. EnBW itself plans to hire 10,000 skilled workers by 2026, highlighting the intense competition for talent. This scarcity of specialized engineers, technicians, and project managers directly translates to increased bargaining power for the available workforce.
This heightened demand means that skilled individuals can command higher wages and better benefits, potentially increasing EnBW's operational costs. Furthermore, recruitment challenges may arise as companies vie for the same limited pool of qualified professionals, impacting project timelines and execution.
Grid Technology and Infrastructure Providers
EnBW's significant investments in grid modernization, such as the SuedLink project, highlight the bargaining power of specialized suppliers. These providers offer critical high-voltage transmission equipment, smart grid technologies, and digital solutions essential for EnBW's infrastructure expansion. In 2023, EnBW announced plans to invest approximately €5 billion in grid expansion and modernization by 2027, underscoring its reliance on these suppliers.
The limited number of suppliers for such complex technologies, coupled with their specialized expertise, allows them to exert considerable influence. This can translate into higher pricing and potential impacts on project schedules, directly affecting EnBW's operational efficiency and expansion timelines.
- Specialized Equipment: Suppliers of high-voltage transformers and advanced grid control systems often operate in niche markets with few competitors.
- Technological Dependency: EnBW's adoption of smart grid solutions relies on suppliers with proprietary digital platforms and integration capabilities.
- Project Scale: The sheer scale of projects like SuedLink, which involves thousands of kilometers of new power lines, creates concentrated demand that suppliers can leverage.
Regulatory and Consulting Services
The German energy sector's stringent regulatory environment and the ongoing energy transition necessitate specialized legal, environmental, and strategic consulting. These services are crucial for EnBW to navigate complex compliance requirements, secure project approvals, and conduct thorough market analysis. The highly specialized knowledge possessed by these consulting firms grants them significant bargaining power.
For instance, in 2024, the German government continued to implement ambitious renewable energy targets, requiring extensive legal interpretation and environmental impact assessments for new infrastructure projects. Consulting firms with proven expertise in these niche areas, such as navigating the Federal Immission Control Act (Bundes-Immissionsschutzgesetz) or securing permits for offshore wind farms, can command premium fees.
- Specialized Expertise: Consulting firms possess unique knowledge in energy law, environmental regulations, and market dynamics, which are difficult for EnBW to replicate internally.
- Regulatory Complexity: The intricate and evolving regulatory landscape in Germany, particularly concerning the Energiewende, increases reliance on external expert advice.
- Project Dependency: Approval for major energy projects, including renewable energy installations and grid upgrades, often hinges on successful navigation of regulatory processes guided by consultants.
- Market Analysis Needs: Understanding the competitive landscape and future market trends requires specialized analytical skills that external consultants provide.
The bargaining power of suppliers for EnBW is significant, particularly for specialized components and services. This leverage stems from the limited number of qualified providers, the proprietary nature of their technology, and the critical role these suppliers play in large-scale energy projects. EnBW's reliance on these specialized firms for everything from wind turbine parts to expert legal consultation means these suppliers can command higher prices and influence project timelines.
| Supplier Category | Key Components/Services | EnBW's Reliance | Supplier Bargaining Power Factors | Example/Data Point (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Equipment Manufacturers | Wind turbines, solar panels, inverters | Crucial for offshore wind (e.g., He Dreiht) and solar projects | Proprietary technology, high R&D costs, few global players | In 2024, major offshore wind turbine orders continued to see price increases due to high demand and supply chain pressures. |
| Grid Infrastructure Suppliers | High-voltage transformers, smart grid technology, digital solutions | Essential for grid modernization (e.g., SuedLink) | Specialized engineering, complex manufacturing, limited competition | EnBW's planned €5 billion investment in grid expansion by 2027 highlights sustained demand for these specialized suppliers. |
| Skilled Labor & Consulting | Specialized engineers, technicians, legal/environmental consultants | Needed for energy transition projects and regulatory compliance | Scarcity of talent, complex regulatory environment, niche expertise | By 2026, EnBW aims to hire 10,000 skilled workers, indicating intense competition for talent in 2024. |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for EnBW Energie Baden-Württemberg assesses the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes within the German energy market.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing EnBW's Porter's Five Forces, providing a strategic roadmap to navigate industry pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Residential customers in Germany are indeed price-sensitive, a key factor influencing EnBW's market position. In 2023, the average household electricity price in Germany stood at approximately 40.12 cents per kilowatt-hour, a figure that significantly impacts consumer decisions when choosing an energy provider.
While customer inertia exists, the liberalized German energy market allows for relatively easy switching between providers. This ease of switching amplifies the pressure on EnBW to maintain competitive pricing structures to retain and attract its residential customer base.
However, EnBW can leverage bundled services, such as combining electricity, gas, and water offerings, to foster customer loyalty and create a degree of stickiness, mitigating some of the direct price competition.
EnBW's large industrial and commercial clients wield considerable negotiating power due to their substantial energy needs. These clients often secure customized contracts and demand competitive pricing, a trend amplified by the increasing demand for green energy solutions. For instance, in 2024, major industrial consumers are actively exploring direct power purchase agreements (PPAs) from renewable sources or investing in on-site generation, directly challenging traditional utility supply models and EnBW's pricing power.
The increasing demand for green energy solutions significantly bolsters the bargaining power of EnBW's customers. Consumers and businesses alike are actively seeking sustainable and climate-neutral energy options. This trend means customers can more readily switch to providers offering greener alternatives, pushing EnBW to invest more heavily in renewable energy projects and energy-efficient services to retain their business.
Impact of Decentralized Generation
The increasing adoption of decentralized energy generation, such as rooftop solar and battery storage, significantly bolsters customer bargaining power against traditional utilities like EnBW. Customers can now generate their own power, directly reducing their reliance on grid electricity. For instance, in Germany, solar photovoltaic (PV) capacity has seen substantial growth, with installations reaching approximately 8.9 gigawatts (GW) in 2023 alone, contributing to a cumulative installed capacity of over 80 GW by the end of that year. This shift offers consumers more choices and the ability to negotiate better terms or switch providers more readily.
This trend directly impacts EnBW by potentially lowering overall demand for their grid-supplied power. As more customers invest in self-generation and storage solutions, their need for traditional utility services diminishes. This increased customer autonomy translates into a stronger position for customers when dealing with energy providers.
- Reduced Dependence: Customers can meet a larger portion of their energy needs through self-generated power, lessening their dependence on EnBW.
- Increased Options: The proliferation of distributed energy resources provides customers with alternative energy supply options beyond the traditional utility model.
- Negotiating Leverage: With the ability to generate their own power or purchase from alternative sources, customers gain stronger leverage in price and service negotiations with EnBW.
- Market Disruption: Decentralization challenges the established utility business model, forcing providers to adapt and potentially offer more competitive services to retain customers.
Regulatory Consumer Protection
The German regulatory framework actively protects consumers, a key factor influencing their bargaining power. Provisions within this framework, such as those simplifying the process for customers to switch energy suppliers, directly empower them. For instance, in 2023, the German Federal Network Agency reported a significant number of supplier changes, indicating the effectiveness of these consumer-friendly regulations in fostering a competitive market where customers can more readily seek better deals.
These regulations indirectly enhance customer bargaining power by establishing a baseline of fair market practices and ensuring supply security. This regulatory environment fosters trust and reduces perceived risks for consumers, making them more confident in exercising their choice and negotiating power. The emphasis on consumer safeguards means that energy providers, like EnBW, must compete not only on price but also on service quality and transparency to retain their customer base.
- Facilitated Supplier Switching: Regulations streamline the process for consumers to change energy providers, increasing competitive pressure on existing suppliers.
- Supply Security Guarantees: Provisions ensuring continuous energy supply reduce customer risk, making them more willing to explore alternative providers.
- Promoting Fair Market Practices: Regulatory oversight aims to prevent unfair pricing or contract terms, bolstering customer confidence and their ability to negotiate.
Customers possess significant bargaining power due to the liberalized German energy market, which allows for easy switching between providers. This ease of switching, coupled with a growing demand for green energy solutions, pushes EnBW to offer competitive pricing and sustainable options. For example, in 2024, many industrial clients are actively pursuing direct power purchase agreements (PPAs) for renewable energy, directly impacting EnBW's pricing leverage.
The increasing adoption of decentralized energy generation, like rooftop solar, further empowers customers. By generating their own power, customers reduce reliance on traditional utilities. Germany's installed solar PV capacity exceeded 80 GW by the end of 2023, with an additional 8.9 GW installed in 2023 alone, illustrating this trend and enhancing customer negotiation power.
Furthermore, German regulations actively protect consumers by simplifying the process of switching energy suppliers. This regulatory environment, as evidenced by numerous supplier changes reported in 2023, ensures that providers like EnBW must compete on price, service quality, and transparency to retain their customer base.
| Factor | Impact on EnBW | Customer Action | Data Point (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Liberalization | Increased competition | Switching providers for better rates | Easy switching process facilitated by regulations |
| Green Energy Demand | Pressure to invest in renewables | Seeking providers with sustainable offerings | Growing demand for green energy solutions |
| Decentralized Generation | Reduced reliance on grid supply | Investing in solar and storage for self-sufficiency | Over 80 GW cumulative solar PV capacity in Germany by end of 2023 |
| Regulatory Protection | Need for competitive pricing and service | Exercising choice and negotiating power | Significant number of supplier changes reported in 2023 |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
EnBW Energie Baden-Wurttemberg Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis of EnBW Energie Baden-Württemberg, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the energy sector. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, providing actionable insights without any placeholders or surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The German energy sector is a battleground for several major integrated utilities. EnBW faces stiff competition from giants like RWE, E.ON, Uniper, and Vattenfall. These companies don't just dabble; they operate across the entire energy spectrum, from producing power to managing the grids and offering services to end-users.
The liberalized retail energy market in Germany, EnBW's primary operating ground, is intensely competitive. Numerous regional and municipal utilities, alongside newer, agile players, actively compete for residential and commercial customers. This dynamic environment necessitates a strong focus on competitive pricing, customer retention, and the development of innovative service packages to capture and maintain market share.
The rapid shift towards renewable energy sources and decentralized power generation is significantly heating up competition within the energy sector. Companies are now fiercely vying for lucrative investment opportunities in areas such as wind and solar farm development, crucial grid upgrades, and emerging energy services like electric vehicle charging infrastructure and hydrogen production. This dynamic environment demands constant innovation and strategic positioning.
EnBW is actively addressing this intensified rivalry by making substantial commitments. The company plans to invest a considerable €50 billion by 2030, a clear strategy to solidify its standing and capitalize on the evolving energy market. This investment is geared towards securing a strong presence in renewable energy, grid modernization, and the burgeoning fields of e-mobility and hydrogen, demonstrating a proactive approach to future energy demands.
Regulatory Framework and Policy Influence
The German energy sector is a prime example of how regulatory shifts can dramatically impact competitive dynamics. EnBW, like its peers, navigates a landscape shaped by ambitious renewable energy targets, such as the goal to have 80% of gross electricity consumption covered by renewables by 2030, and the ongoing coal phase-out. These policies directly influence investment decisions and the profitability of different energy sources. In 2023, Germany's renewable energy sources accounted for approximately 55% of gross electricity consumption, a significant increase driven by policy support.
Policy advocacy is a crucial competitive tool for energy companies. EnBW actively participates in dialogues with policymakers to shape regulations that foster investment in areas like grid modernization and renewable energy expansion. For instance, the German government's focus on accelerating grid expansion, with significant investment planned, creates both opportunities and challenges for established players and new entrants alike. This proactive engagement helps ensure a more predictable and supportive environment for EnBW's strategic initiatives.
- Renewable Energy Targets: Germany aims for 80% renewable electricity by 2030.
- Coal Phase-Out: A key policy impacting the energy mix.
- Grid Expansion Investment: Significant government funding allocated to grid infrastructure.
- Policy Advocacy: EnBW's engagement to influence regulatory frameworks.
Technological Innovation and Digitalization
Competitive rivalry in the energy sector, particularly for companies like EnBW, is significantly intensified by the relentless pace of technological innovation and digitalization. The imperative to develop and implement advanced solutions in areas such as smart grids, sophisticated energy storage systems, and user-friendly digital customer platforms fuels this rivalry. Companies are compelled to make substantial investments in these cutting-edge technologies to maintain their market position and offer differentiated, efficient services.
The drive for innovation extends to emerging fields like electromobility, where companies are vying to provide integrated charging infrastructure and energy management solutions. This necessitates continuous research and development, pushing firms to stay ahead of technological curves. For instance, in 2024, global investment in clean energy technologies, a significant portion of which is driven by digitalization and innovation, reached record highs, underscoring the competitive pressure to adopt these advancements.
- Smart Grid Development: Companies are investing heavily in upgrading grid infrastructure to enable better monitoring, control, and integration of renewable energy sources.
- Energy Storage Solutions: Innovation in battery technology and other storage methods is crucial for grid stability and the efficient use of intermittent renewables.
- Digital Customer Engagement: Developing intuitive apps and platforms for energy management, billing, and customer service is a key differentiator.
- Electromobility Infrastructure: Expanding charging networks and offering integrated energy solutions for electric vehicles is a growing competitive battleground.
Competitive rivalry in the German energy sector is fierce, with EnBW facing strong opposition from established players like RWE and E.ON, as well as numerous municipal and agile providers in the liberalized retail market. This intense competition spans the entire energy value chain, from generation to customer services.
The ongoing energy transition, with its emphasis on renewables and decentralized power, further fuels this rivalry. Companies are aggressively pursuing investments in wind, solar, grid modernization, and emerging areas like e-mobility and hydrogen. This necessitates continuous innovation and strategic positioning to capture market share and secure future growth opportunities.
Germany's ambitious renewable energy targets, aiming for 80% of gross electricity consumption from renewables by 2030, alongside policies like the coal phase-out, significantly shape the competitive landscape. EnBW's planned €50 billion investment by 2030 underscores its commitment to navigating and capitalizing on these evolving market dynamics and policy-driven shifts.
Technological advancements, particularly in smart grids, energy storage, and digital customer platforms, are critical differentiators. Companies are investing heavily to enhance efficiency and offer value-added services, with global clean energy technology investments reaching record highs in 2024, highlighting the pressure to innovate and stay competitive.
| Key Competitors | Market Presence | Strategic Focus |
| RWE | Integrated (Generation, Grids, Retail) | Renewable expansion, decarbonization |
| E.ON | Integrated (Grids, Customer Solutions) | Grid modernization, energy efficiency, e-mobility |
| Uniper | Generation, Energy Trading | Gas supply, transition to low-carbon energy |
| Vattenfall | Integrated (Generation, Grids, Retail) | Fossil-free energy, offshore wind |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitute for conventional energy consumption is energy efficiency, driven by improved insulation, smart home technologies, and more efficient appliances. These measures directly reduce the overall demand for electricity and gas from utilities, posing a significant long-term threat to traditional revenue streams.
In 2024, the adoption of energy-efficient technologies continues to accelerate. For instance, the global smart home market, a key driver of demand reduction, was projected to reach over $150 billion by the end of 2024. This trend directly impacts the volume of energy that utilities like EnBW need to supply, potentially eroding market share and revenue.
The rise of distributed generation, particularly rooftop solar PV and battery storage, presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional utility services. By 2024, the decreasing costs of solar panels and energy storage systems are making self-consumption increasingly attractive for both households and businesses. For instance, the International Energy Agency reported that renewable energy sources, including solar, accounted for a substantial portion of new power capacity additions globally in recent years, indicating a growing trend towards decentralized energy production.
For heating and cooling, substitutes like heat pumps, district heating networks, and biomass systems are increasingly available, lessening reliance on traditional energy sources. For instance, Germany's federal government has been actively promoting heat pump adoption, with subsidies aiming to accelerate their market penetration. This policy-driven shift directly impacts the competitive landscape by offering viable alternatives to conventional heating methods.
Emerging Energy Storage Technologies
The threat of substitutes for EnBW is intensifying with advancements in energy storage technologies. These innovations allow consumers and businesses to store electricity, whether from renewable sources or during off-peak hours, thereby decreasing their reliance on continuous grid supply. This shift can directly substitute services traditionally provided by utilities, especially during peak demand periods.
For instance, the global energy storage market, excluding pumped hydro, was valued at approximately $150 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly.
- Falling Battery Costs: Lithium-ion battery prices have seen a substantial decline, making energy storage solutions more economically viable for a broader range of applications.
- Grid-Scale Storage Deployment: Major projects are coming online, demonstrating the capability of storage to provide grid services and reduce reliance on traditional generation.
- Decentralized Energy Systems: The rise of microgrids and behind-the-meter storage empowers end-users to manage their energy consumption more autonomously.
- Emergence of Alternative Storage: Beyond batteries, technologies like compressed air energy storage and green hydrogen are maturing, offering diverse substitution pathways.
Behavioral Changes and Reduced Consumption
Societal shifts are increasingly pushing consumers towards more mindful energy usage. This is fueled by growing environmental consciousness and the impact of rising energy prices. For instance, in Germany, average household electricity consumption per capita saw a slight decrease in 2023 compared to previous years, reflecting these behavioral changes.
These evolving attitudes can be viewed as a form of diffuse substitution for traditional energy sales. When individuals and businesses actively seek to lower their energy consumption through efficiency measures or lifestyle adjustments, they are essentially reducing the demand for energy products and services offered by companies like EnBW.
- Reduced Demand: Behavioral changes directly lower the volume of energy consumers need, impacting sales.
- Efficiency Gains: Investments in energy-efficient appliances and home insulation by consumers act as substitutes for higher energy consumption.
- Cost Sensitivity: Higher energy bills in 2023 and projected increases for 2024 are accelerating the adoption of energy-saving behaviors.
- Environmental Awareness: A growing segment of the population prioritizes reducing their carbon footprint, leading to conscious energy reduction.
The threat of substitutes for EnBW is significant, driven by energy efficiency, distributed generation, and alternative heating solutions. These substitutes directly reduce demand for traditional energy supply. For instance, the global smart home market was projected to exceed $150 billion in 2024, indicating a strong trend towards energy reduction.
Furthermore, the decreasing costs of solar PV and battery storage empower consumers to generate and store their own energy, effectively substituting grid-supplied electricity. The energy storage market, excluding pumped hydro, was valued around $150 billion in 2023, highlighting the growing viability of these alternatives.
| Substitute Category | Key Drivers | 2024 Impact |
| Energy Efficiency | Smart home tech, insulation | Reduced overall energy demand |
| Distributed Generation | Rooftop solar, battery storage | Decreased reliance on grid supply |
| Alternative Heating | Heat pumps, district heating | Lower demand for gas/electricity heating |
Entrants Threaten
The energy sector, especially for building and maintaining large-scale generation and transmission infrastructure, demands incredibly high capital outlays. This substantial financial requirement acts as a significant deterrent for any potential new companies looking to enter the market.
For instance, EnBW itself has outlined an ambitious investment plan of €50 billion by 2030. This figure underscores the immense capital necessary to establish and operate effectively within this industry, creating a formidable barrier to entry for newcomers.
The German energy market presents a formidable barrier to entry due to its extensive regulatory framework. Navigating complex licensing procedures, obtaining necessary environmental permits, and adhering to stringent compliance requirements demand significant expertise and resources, effectively favoring established entities like EnBW.
In 2024, the energy sector in Germany continued to grapple with evolving regulations, particularly concerning renewable energy integration and grid stability. These ongoing regulatory shifts mean that any newcomer must invest heavily in legal and compliance teams, a cost that established players have already absorbed.
Established grid infrastructure presents a significant barrier for new entrants. Companies like EnBW possess extensive, owned electricity and gas distribution networks, crucial for reaching customers. Gaining access to these vital infrastructures on fair and affordable terms is a major hurdle, hindering competition in the distribution and retail energy sectors.
Brand Loyalty and Customer Relationships
Established utilities like EnBW benefit from deeply ingrained brand loyalty and trust, particularly with long-term residential and industrial customers. This makes it challenging for newcomers to attract and retain a significant customer base. For instance, in 2023, EnBW reported a strong customer retention rate, underscoring the difficulty new entrants face in disrupting these established relationships.
Building comparable brand recognition and fostering customer loyalty demands considerable investment in marketing and a sustained period of operation. New entrants often struggle to match the perceived reliability and service quality that incumbent utilities have cultivated over decades. The energy sector's inherent need for consistent supply and established infrastructure further solidifies the advantage of existing players.
- Brand Loyalty: EnBW's established brand equity acts as a significant barrier.
- Customer Relationships: Long-standing ties with residential and industrial clients are difficult to replicate.
- Marketing Investment: New entrants require substantial resources to build brand awareness and trust.
- Time Horizon: Acquiring a comparable customer base takes considerable time and effort.
Technological Expertise and Integration Complexity
Operating an integrated energy business like EnBW, which encompasses generation, trading, grids, and customer solutions, requires substantial technological expertise. This spans from managing traditional power plants to deploying advanced renewable energy sources and sophisticated smart grid technologies. For instance, EnBW's significant investments in offshore wind, such as the recent progress on the Gotteskoog wind farm, highlight the need for specialized engineering and project management skills.
New entrants often find it challenging to acquire and integrate this broad spectrum of technological know-how. The complexity of integrating diverse energy systems, from generation to distribution and customer interface, creates a significant barrier. This integration complexity means that even with capital, replicating the operational efficiency and technological depth of established players like EnBW is a considerable hurdle.
- Technological Depth: EnBW's portfolio includes nuclear, coal, gas, hydro, solar, and wind power, demanding expertise across all these generation types.
- Grid Integration: Managing and modernizing energy grids to accommodate distributed renewable sources requires advanced IT and engineering capabilities, a core competency for established utilities.
- Customer Solutions: Developing and managing smart home technologies, e-mobility charging infrastructure, and digital energy services necessitates significant software development and data analytics expertise.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex energy regulations across multiple markets adds another layer of difficulty for potential new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for EnBW Energie Baden-Württemberg is generally low, primarily due to the substantial capital requirements and regulatory complexities inherent in the energy sector. Building and maintaining energy infrastructure, from generation plants to distribution grids, demands billions in investment, a significant barrier for any new player. For example, EnBW's own €50 billion investment plan through 2030 illustrates the scale of capital needed.
The German energy market's intricate regulatory landscape, including licensing and environmental permits, further deters new entrants. Established players like EnBW have already navigated these hurdles, possessing the necessary expertise and compliance infrastructure. In 2024, ongoing regulatory shifts related to renewable energy integration continue to add layers of complexity, requiring significant legal and compliance resources that newcomers must build from scratch.
Existing grid infrastructure, owned and operated by companies like EnBW, represents another formidable barrier. New entrants face significant challenges in securing access to these vital networks on favorable terms, hindering their ability to reach customers. Furthermore, EnBW benefits from strong brand loyalty and established customer relationships, built over decades, making it difficult for new companies to attract and retain a substantial customer base, as evidenced by EnBW's strong customer retention rates in 2023.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for generation and distribution infrastructure. | Significant deterrent due to massive upfront costs. |
| Regulatory Environment | Complex licensing, permits, and compliance in the German energy market. | Favors established players with existing expertise and resources. |
| Infrastructure Access | Established companies own extensive grid networks. | Difficult for new entrants to secure fair and affordable access. |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Decades of trust and established customer ties. | Challenging for newcomers to acquire customers and build comparable brand equity. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for EnBW Energie Baden-Württemberg leverages data from company annual reports, energy industry regulatory filings, and specialized market research reports to comprehensively assess competitive dynamics.
We integrate information from financial statements, energy sector trade publications, and government energy policy documents to provide a thorough evaluation of EnBW's competitive landscape.