Digital China Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Digital China Holdings Bundle
Digital China Holdings operates within a dynamic tech landscape where understanding competitive pressures is paramount. Our analysis reveals how buyer power, supplier influence, and the threat of new entrants are actively shaping its market position.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Digital China Holdings’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Digital China Holdings' reliance on a concentrated group of key IT component and software suppliers significantly impacts its bargaining power. When a few dominant vendors control essential hardware, like advanced semiconductors, or proprietary software, Digital China faces limited alternatives, increasing supplier leverage. This concentration is especially pronounced for cutting-edge technologies, where specialized knowledge and production capabilities are scarce.
Switching suppliers for Digital China Holdings can be a costly endeavor. These costs often include the expense of re-certifying new vendors, the technical hurdles of integrating unfamiliar technologies, and the risk of disrupting established supply chains. For instance, in 2024, many companies found that the integration of new cloud solutions alone could cost upwards of 15-20% of the initial software investment, a significant barrier to switching.
Suppliers providing highly unique or essential IT products and intellectual property, like cutting-edge AI models or specialized cloud infrastructure, wield significant bargaining power. Digital China's strategic focus on Big Data and AI means it depends on suppliers leading these advancements, thereby amplifying their influence.
Supplier's Ability to Forward Integrate
The ability of suppliers to forward integrate significantly impacts Digital China's bargaining power. If major IT product or software suppliers choose to offer their solutions and services directly to end-customers, they could effectively bypass intermediaries like Digital China. This move would naturally enhance their leverage in the market.
While this strategy is less prevalent for pure hardware manufacturers, it's a notable and expanding trend among cloud and software vendors. These companies are increasingly building and controlling their own service ecosystems, which allows them to engage directly with the end-user. For instance, many major cloud providers, by 2024, were offering integrated hardware, software, and managed services, directly competing with traditional distribution models.
- Supplier Integration Threat: Major IT suppliers can bypass distributors by offering direct-to-customer solutions.
- Cloud & Software Trend: This bypass is particularly evident with cloud and software vendors building their own service ecosystems.
- Market Impact: Such integration can diminish the role and bargaining power of distributors like Digital China.
- 2024 Data: By 2024, many leading cloud providers had already established comprehensive direct-to-customer service models.
Importance of Digital China to Suppliers
Digital China's significant footprint within China's expansive IT landscape positions it as a vital conduit for numerous IT hardware and software vendors, both international and domestic. This extensive distribution network, a key asset for Digital China, can diminish the bargaining power of its suppliers. For instance, in 2023, Digital China reported revenues of approximately RMB 120 billion, underscoring its substantial market influence.
The potential loss of Digital China as a major client could severely curtail a supplier's market penetration and sales volume within China.
- Digital China's market share in IT distribution in China is substantial, making it a critical partner for suppliers.
- Its extensive reach can dictate terms, thereby potentially lowering supplier power.
- In 2024, the IT distribution market in China continued to be dominated by a few key players, including Digital China, solidifying its leverage.
Digital China's substantial market presence in China's IT distribution sector, with revenues around RMB 120 billion in 2023, significantly counterbalances supplier power. This scale makes Digital China a critical channel for vendors, limiting their ability to dictate terms and potentially reducing their leverage. The concentration of the Chinese IT distribution market in 2024 further solidified the position of major players like Digital China.
| Factor | Impact on Digital China | Supporting Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier bargaining power | Reliance on few vendors for advanced semiconductors and proprietary software. |
| Switching Costs | Increases supplier bargaining power | Integration costs for new tech (e.g., cloud) can reach 15-20% of investment (2024 estimate). |
| Supplier Uniqueness/IP | Increases supplier bargaining power | Dependence on leading Big Data and AI suppliers. |
| Supplier Forward Integration | Increases supplier bargaining power | Cloud providers increasingly offer direct-to-customer integrated services (observed by 2024). |
| Digital China's Market Share | Decreases supplier bargaining power | RMB 120 billion revenue in 2023; vital conduit for vendors in China. |
| Digital China's Distribution Network | Decreases supplier bargaining power | Extensive reach can influence terms; market dominated by few key players in 2024. |
What is included in the product
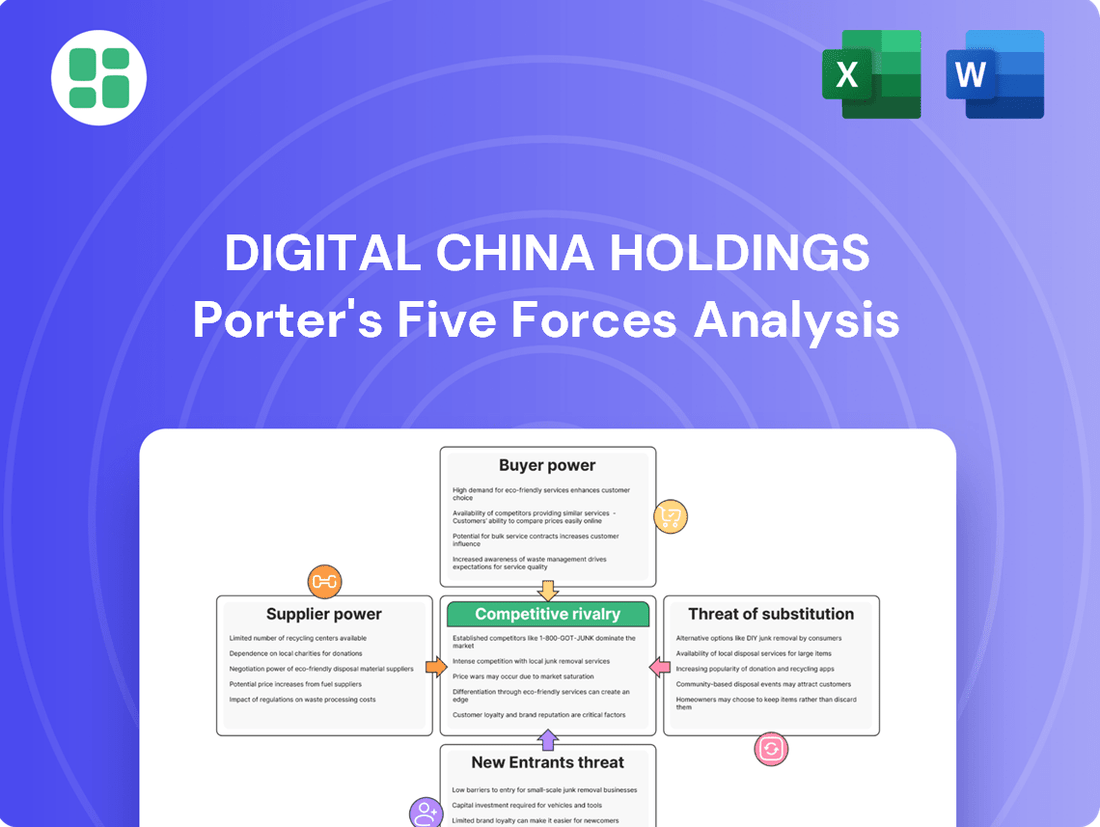
A Porter's Five Forces analysis for Digital China Holdings reveals the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and ultimately shapes the company's strategic positioning.
Instantly assess Digital China Holdings' competitive landscape with a visual, easy-to-understand breakdown of Porter's Five Forces, simplifying complex market dynamics for strategic clarity.
Customers Bargaining Power
Digital China Holdings' customer base is broad, spanning numerous industries and government entities, which typically dilutes individual customer bargaining power. This wide reach means no single customer usually represents an overwhelmingly large portion of revenue.
However, significant exceptions arise with major enterprise clients and government bodies undertaking large-scale IT infrastructure projects or digital transformation initiatives. These substantial, strategically vital purchases grant these key customers considerable leverage in negotiations, influencing pricing and terms.
For instance, in 2023, Digital China reported revenue of approximately RMB 100 billion, with its government and enterprise segments forming the backbone of its business. While specific customer concentration data isn't publicly detailed, the sheer scale of these large deals underscores the potential for concentrated customer power.
For IT services like system integration and intricate cloud solutions, switching providers can be a significant undertaking for customers. These costs often include the complex process of data migration, the necessity of re-training staff on new systems, and the potential for disruptive operational interruptions during the transition. This financial and operational burden effectively limits how easily customers can move away from Digital China Holdings.
Customers in China are increasingly empowered by a widening array of IT solutions and service providers. This includes a robust domestic market of integrators, direct access to global cloud platforms, and the growing capability for in-house IT development.
The IT services landscape in China is notably fragmented. In 2023, the top four IT service providers collectively captured only a modest market share, highlighting the abundance of alternative options available to customers. This fragmentation directly translates to enhanced bargaining power for buyers, as they can readily switch or negotiate with numerous players.
Customer Price Sensitivity
In China's competitive IT sector, particularly in product distribution, customers often exhibit significant price sensitivity. This means they are keenly aware of pricing and actively compare options to find the best value.
Digital China's financial performance in 2024, which saw a reported revenue decline amid intense competition, underscores this customer behavior. It indicates that buyers are prioritizing cost-effective solutions, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers in China's IT market frequently compare prices, seeking the most economical options.
- Revenue Impact: Digital China's revenue dip in 2024 suggests customers are leveraging price competition.
- Increased Leverage: This sensitivity empowers customers, giving them greater influence over pricing and terms.
Customers' Ability to Backward Integrate
Customers' ability to backward integrate poses a significant threat to Digital China Holdings. Large enterprises or government entities, particularly those with substantial IT needs, might choose to develop their own in-house capabilities. This could involve building proprietary software or establishing internal system integration teams, thereby lessening their dependence on external service providers like Digital China.
While this move requires considerable investment, it becomes a viable and attractive option for strategic IT projects. For instance, a major financial institution in 2024 might invest heavily in custom AI-driven analytics platforms to gain a competitive edge, bypassing traditional IT vendors. This capability directly enhances their bargaining power, as they can credibly threaten to bring services in-house if terms are not favorable.
The potential for backward integration is amplified when customers possess specialized knowledge or can acquire it relatively easily. Consider the trend in cloud computing; many companies are building internal cloud infrastructure or leveraging multi-cloud strategies, reducing reliance on single vendors. This strategic shift grants them greater control and leverage in negotiations with IT service providers.
Digital China must therefore offer compelling value propositions that go beyond basic service provision, focusing on innovation, cost-efficiency, and specialized expertise that is difficult for customers to replicate internally. The ability of customers to perform these functions themselves is a key factor influencing pricing and contract terms.
Digital China Holdings faces considerable customer bargaining power due to the fragmented nature of China's IT services market, where numerous providers compete. Customers, especially large enterprises and government bodies, can readily switch or negotiate with various players, a situation exacerbated by their increasing price sensitivity. For instance, Digital China's reported revenue decline in 2024 highlights how buyers prioritize cost-effectiveness, amplifying their leverage.
The significant costs associated with switching IT providers, including data migration and retraining, do offer some protection for Digital China. However, the growing trend of customers developing in-house IT capabilities, driven by specialized knowledge and the accessibility of cloud technologies, presents a direct challenge. This potential for backward integration empowers customers to negotiate more favorable terms, as they can credibly threaten to bring services in-house.
| Factor | Impact on Digital China Holdings | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Market Fragmentation | Increases customer choice and bargaining power. | Top 4 IT service providers held modest market share in 2023. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers prioritize cost, giving them leverage. | Digital China's revenue decline in 2024 linked to intense price competition. |
| Switching Costs | Limits customer ability to switch, providing some vendor power. | High costs for data migration, retraining, and operational disruption. |
| Backward Integration Potential | Customers developing in-house capabilities reduces reliance on vendors. | Growing adoption of multi-cloud strategies and custom AI platforms by enterprises. |
Same Document Delivered
Digital China Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview provides a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Digital China Holdings, detailing the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. This analysis is crucial for understanding the strategic positioning and potential challenges faced by Digital China Holdings in the evolving digital economy.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The competitive landscape for Digital China Holdings within China's IT services sector is characterized by significant fragmentation and a broad array of players. This means there isn't one dominant company, but rather a multitude of smaller and medium-sized enterprises vying for market share.
This intense rivalry stems from the sheer volume and diversity of competitors, ranging from established domestic IT service providers and system integrators to newer, agile cloud service specialists. For instance, in 2023, the Chinese IT services market saw hundreds of companies actively competing, with no single entity holding more than a 7% market share, underscoring the fragmented nature of the industry.
The IT services and digital transformation markets in China are showing strong growth, with projected Compound Annual Growth Rates (CAGRs) of 9.3% and 14.20% respectively from 2024 through 2030. This expansion offers a degree of relief from intense rivalry by presenting more opportunities for all players.
However, the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence and big data analytics are creating new arenas for competition. Companies are vying for dominance in these emerging fields, intensifying the rivalry as they seek to leverage these transformative technologies.
Digital China Holdings is actively differentiating itself by focusing on 'Big Data + A.I.' and 'AI for Process.' This strategic move is vital in an IT product landscape where many offerings can become mere commodities, often leading to price-based competition.
By delivering unique, integrated digital solutions and specialized AI capabilities, Digital China aims to carve out a distinct market position. For instance, in 2023, the company reported a significant increase in its cloud and big data services revenue, indicating growing customer demand for these advanced solutions.
This differentiation strategy directly combats intense rivalry by offering value beyond basic IT functionalities. The ability to provide sophisticated AI-driven insights and process automation allows them to command premium pricing and foster customer loyalty, thereby reducing the pressure of competing solely on cost.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
Digital China Holdings operates within an industry characterized by substantial upfront investments. The IT solutions and services sector demands significant capital for robust infrastructure, ongoing research and development, and the cultivation of highly skilled technical talent. For instance, establishing advanced data centers or developing proprietary software platforms requires millions in initial outlay, creating a high barrier to entry.
These substantial fixed costs, coupled with other significant exit barriers, intensify competitive rivalry. Specialized assets, like custom-built server farms or unique intellectual property, are difficult to redeploy or sell, effectively trapping companies in the market. Furthermore, long-term customer contracts can bind firms to ongoing service obligations, discouraging premature withdrawal even when profitability wanes. This situation often leads to aggressive competition as companies strive to maintain market share and cover their fixed expenses.
The pressure to remain competitive is particularly acute for companies like Digital China Holdings. In 2024, the global IT services market was valued at approximately $1.3 trillion, with intense competition driving down margins for many players. Companies are forced to compete fiercely on price and service quality to retain clients and justify their substantial fixed investments.
- High Infrastructure and R&D Costs: The IT sector necessitates significant investment in data centers, cloud computing resources, and continuous innovation in software and hardware.
- Specialized Assets and Long-Term Contracts: Unique technological equipment and binding service agreements make exiting the market costly and complex.
- Intensified Price Competition: High fixed costs compel companies to operate at high capacity, often leading to aggressive pricing strategies to secure business.
- Market Dynamics in 2024: The global IT services market, valued around $1.3 trillion in 2024, reflects a highly competitive landscape where firms must battle to maintain market share and cover their operational expenditures.
Strategic Stakes and Aggressiveness of Competitors
The Chinese government's strong push for the Digital China initiative, with a particular focus on artificial intelligence (AI), creates exceptionally high strategic stakes for all IT companies operating within the country. This government emphasis translates into significant opportunities for those who can align with national priorities.
Consequently, competitors are expected to exhibit considerable aggressiveness in their pursuit of market share and lucrative government contracts. This aggressive stance will likely manifest through substantial investments in research and development, strategic partnerships, and aggressive marketing campaigns to capture a dominant position.
- High Strategic Stakes: The Digital China initiative and government AI focus mean substantial rewards for leading IT firms, driving intense competition.
- Aggressive Market Pursuit: Companies are investing heavily in new technologies and forming partnerships to gain an edge and secure government business.
- Government Contracts as a Driver: The availability of significant government contracts in areas like AI and digital infrastructure fuels competitive intensity.
- Market Share Focus: Firms are prioritizing market share acquisition, understanding that early dominance can lead to long-term advantages in this rapidly growing sector.
The competitive rivalry for Digital China Holdings is fierce, driven by a fragmented market and high barriers to entry. Companies invest heavily in R&D and infrastructure, with significant fixed costs forcing aggressive pricing to maintain market share. The government's Digital China initiative, particularly in AI, amplifies these stakes, encouraging substantial investments and strategic partnerships.
| Key Factor | Impact on Rivalry | Example/Data Point |
| Market Fragmentation | Intensifies competition as many players vie for share. | No single player held over 7% market share in China's IT services in 2023. |
| High Fixed Costs | Pressures companies to compete aggressively on price and volume. | Global IT services market valued at $1.3 trillion in 2024, with high operational expenditures. |
| Government Initiatives (Digital China, AI) | Elevates strategic importance and drives aggressive investment. | Companies are investing heavily in AI R&D to align with national priorities. |
| Differentiation Strategy | Mitigates price-based competition by offering unique value. | Digital China's focus on 'Big Data + A.I.' and 'AI for Process' aims to command premium pricing. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing availability of generic IT products and open-source solutions presents a significant threat of substitutes for Digital China Holdings. Customers, particularly in the basic IT distribution segments, can readily choose less specialized, lower-cost hardware and software alternatives. For instance, the global open-source software market was projected to reach over $135 billion in 2024, demonstrating a robust and expanding alternative to proprietary systems.
Customers, particularly large enterprises, increasingly bypass traditional IT service integrators by engaging directly with major cloud providers like Alibaba Cloud and Huawei Cloud. This trend is fueled by the growing capabilities and accessibility of cloud and edge computing solutions, which offer viable alternatives to services previously provided by companies like Digital China Holdings.
The threat of substitutes for Digital China Holdings' services, particularly in the realm of IT development and management, can be significant. Larger enterprises with substantial in-house capabilities might opt to build and manage their IT infrastructure and software solutions internally. This approach directly bypasses the need for external providers, effectively acting as a substitute.
This internal development is particularly viable when organizations can leverage existing expertise and resources, thereby reducing their dependence on third-party vendors. For instance, a major financial institution in 2024 might allocate a considerable portion of its IT budget towards internal projects, aiming for greater control and customization of its digital backbone.
Emergence of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
The rise of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) presents a significant threat by enabling businesses to access IT functionalities as services rather than purchasing and integrating traditional software. This shift diminishes the need for direct software ownership, allowing companies to subscribe to essential IT capabilities. For instance, in 2024, the global SaaS market was projected to reach over $326 billion, highlighting its widespread adoption and the increasing reliance on service-based IT solutions.
This trend directly impacts companies like Digital China Holdings by offering readily available, often more cost-effective alternatives to proprietary or custom-built solutions. Businesses can now leverage cloud-based platforms for a wide range of needs, from customer relationship management to data analytics, without substantial upfront investment in hardware or software licenses. This accessibility lowers the barrier to entry for competitors and can commoditize certain IT functions that were previously a core offering.
- Reduced reliance on traditional software: Businesses can now subscribe to IT functionalities as services, bypassing the need for direct software procurement and integration.
- Cost-effectiveness and scalability: SaaS and PaaS models often offer more flexible and scalable pricing, making them attractive alternatives to on-premise solutions.
- Market penetration of cloud services: The global SaaS market's continued growth, with projections indicating further expansion in the coming years, underscores the increasing threat from service-based IT offerings.
Advancements in AI and Automation Tools
The rapid evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional IT services. Routine tasks like system maintenance, customer support, and even aspects of software coding are increasingly being automated, potentially reducing the demand for human-led IT services. For instance, by 2024, it's estimated that AI will automate up to 30% of IT help desk tasks, a notable increase from previous years.
Digital China Holdings recognizes this trend and has integrated an 'AI for Process' strategy. This approach aims to leverage AI to enhance efficiency and offer new, AI-powered services, thereby mitigating the direct substitution threat by transforming its service offerings. This strategic pivot is crucial as the market shifts towards more intelligent and automated solutions.
The impact of AI on the IT services sector is substantial. Companies that fail to adapt risk losing market share to more agile, AI-driven competitors. Digital China's proactive stance suggests an effort to stay ahead of this curve.
- AI in IT Services: Automation is increasingly handling routine IT tasks.
- Market Shift: Demand is growing for AI-enhanced IT solutions.
- Digital China's Strategy: 'AI for Process' aims to capitalize on AI advancements.
- Impact by 2024: Up to 30% of IT help desk tasks could be automated.
The threat of substitutes for Digital China Holdings is substantial, driven by the increasing availability of open-source software and generic IT products, which offer lower-cost alternatives to proprietary solutions. Furthermore, the direct engagement of large enterprises with major cloud providers like Alibaba Cloud and Huawei Cloud bypasses traditional IT service integrators, fueled by accessible cloud and edge computing capabilities.
The rise of SaaS and PaaS models allows businesses to subscribe to IT functionalities, diminishing the need for direct software ownership and impacting companies like Digital China Holdings by offering cost-effective alternatives. For instance, the global SaaS market was projected to exceed $326 billion in 2024, underscoring the widespread adoption of service-based IT solutions.
AI and automation also present a significant substitution threat, as routine IT tasks are increasingly handled by machines, potentially reducing demand for human-led services. By 2024, AI was estimated to automate up to 30% of IT help desk tasks, prompting Digital China to adopt an 'AI for Process' strategy to mitigate this risk.
| Substitute Type | Description | Market Indicator (2024 Projection) |
| Open-Source Software | Lower-cost alternatives to proprietary systems. | Global market projected over $135 billion. |
| Cloud Providers (Direct Engagement) | Enterprises bypass integrators for direct cloud services. | Growing capabilities of Alibaba Cloud, Huawei Cloud. |
| SaaS/PaaS | IT functionalities accessed as services. | Global SaaS market projected over $326 billion. |
| AI & Automation | Automating routine IT tasks. | Up to 30% of IT help desk tasks potentially automated. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering China's IT product distribution and complex IT solutions sector demands significant upfront investment. Companies need capital for inventory management, robust infrastructure, research and development, and attracting a highly skilled technical workforce. For instance, establishing a nationwide distribution network for IT products can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars.
Digital China, as a major player, leverages considerable economies of scale. This allows them to negotiate better prices with suppliers and operate more efficiently, making it difficult for smaller, newer companies to compete on cost. In 2023, Digital China Holdings reported revenue of approximately RMB 20.3 billion, demonstrating their substantial operational footprint.
New entrants to Digital China's market would struggle to replicate its extensive distribution channels and supply networks. Digital China has cultivated deep, long-standing relationships with key IT product manufacturers and software vendors, a significant barrier for any newcomer seeking to establish a comparable presence.
Gaining the trust of both suppliers and customers in this established ecosystem presents a formidable hurdle. For instance, in 2024, Digital China's robust partner ecosystem included over 10,000 IT solution providers, a testament to its entrenched market position.
Digital China Holdings, a prominent entity and a fixture on the Fortune China 500 list, benefits from significant brand recognition and deeply entrenched customer loyalty. This makes it challenging for newcomers to gain traction in the market.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in replicating Digital China's established reputation and the trust it has cultivated over years of operation. Overcoming this requires substantial investment in marketing campaigns and dedicated efforts to build new relationships.
Regulatory Barriers and Government Policies
While China's negative list for market access has been shortened, certain sectors still retain regulatory requirements or require specific licenses, acting as a significant hurdle for new entrants. For instance, the digital advertising sector, a key area for companies like Digital China Holdings, often necessitates compliance with evolving advertising laws and platform-specific approvals.
Navigating China's intricate regulatory landscape, particularly concerning data privacy and cybersecurity, presents substantial challenges. New entrants must contend with laws like the Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL), which came into full effect in November 2021, demanding robust data handling protocols and potentially significant investment in compliance infrastructure. The Cybersecurity Review Measures, updated in 2021, also impose strict requirements on critical information infrastructure operators and data processing activities.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Specific licenses or permits are often required for operating in sensitive digital sectors, increasing the cost and time to market for new players.
- Data Compliance Costs: Adhering to China's stringent data privacy and cybersecurity laws, such as PIPL, necessitates considerable investment in technology and legal expertise.
- Evolving Legal Framework: The dynamic nature of Chinese regulations requires continuous adaptation and monitoring, posing an ongoing threat to less established companies.
Technological Expertise and Talent Acquisition
The IT services and solutions market, particularly in rapidly evolving fields like artificial intelligence, big data, and cloud computing, requires a deep well of specialized technological expertise. New companies entering this space must contend with fierce competition for highly skilled talent, a critical factor for innovation and service delivery.
Furthermore, matching the capabilities of established players necessitates substantial investment in research and development. For instance, in 2024, the global IT services market was projected to reach over $1.3 trillion, with significant growth driven by these advanced technologies, highlighting the high barrier to entry due to R&D costs and talent acquisition needs.
- Talent Competition: High demand for AI, big data, and cloud specialists creates intense competition for skilled professionals.
- R&D Investment: New entrants must allocate significant capital to R&D to develop competitive technologies and services.
- Market Size & Growth: The massive and growing IT services market, exceeding $1.3 trillion in 2024, underscores the financial commitment required to gain traction.
The threat of new entrants into Digital China's market is moderate, primarily due to substantial capital requirements for infrastructure and talent, alongside established economies of scale that favor incumbents. Digital China's significant revenue of approximately RMB 20.3 billion in 2023 and its extensive network of over 10,000 IT solution providers in 2024 act as significant deterrents.
Regulatory hurdles and the need for compliance with data privacy laws like PIPL add complexity and cost for newcomers. Furthermore, intense competition for specialized IT talent and the high investment needed for R&D in areas like AI and cloud computing create a challenging entry environment.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | Significant investment needed for inventory, infrastructure, and R&D. | High barrier due to upfront costs. |
| Economies of Scale | Digital China's size allows for better pricing and operational efficiency. | Difficult to compete on cost. |
| Distribution Networks | Established relationships with suppliers and vendors. | Challenging to replicate reach and access. |
| Brand Recognition & Trust | Years of operation have built strong customer loyalty. | Requires substantial marketing and trust-building efforts. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to data privacy (PIPL) and cybersecurity laws. | Increases costs and time to market. |
| Talent & R&D | Competition for skilled professionals and investment in innovation. | Demands significant resources for competitiveness. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Digital China Holdings is built upon a foundation of robust data, including the company's annual reports, investor presentations, and public filings. We supplement this with insights from reputable industry research reports and market intelligence platforms to capture the competitive landscape.