Cypress Environmental Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cypress Environmental Bundle
Cypress Environmental faces a dynamic competitive landscape, shaped by the bargaining power of its suppliers and the intensity of rivalry within the environmental services sector. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Cypress Environmental’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Cypress Environmental's reliance on specialized equipment and proprietary software for pipeline inspection and water treatment means it likely faces suppliers with significant bargaining power. These unique tools, often developed by a limited number of vendors, create a dependency that can be leveraged by those suppliers.
The need for advanced diagnostic and analytical tools to meet stringent environmental compliance standards further concentrates this power. Only a select few highly specialized vendors can meet Cypress's exacting requirements, giving them considerable influence over pricing and terms.
Cypress faces significant switching costs when changing suppliers for essential environmental technologies, such as advanced non-destructive evaluation (NDE) equipment or specialized water treatment chemicals. These costs are not merely financial; they encompass the expense of retraining personnel, recalibrating intricate systems, and the potential for service disruptions during the transition. For instance, a company like Veolia, a major player in water treatment, often requires extensive integration and testing of new chemical solutions, which can take months and incur substantial labor costs.
The availability of substitute inputs significantly impacts a supplier's bargaining power. While basic materials might have numerous sources, specialized components or skilled labor for complex environmental services often have few alternatives. For instance, the scarcity of highly trained and certified professionals in non-destructive examination (NDE) or advanced environmental engineering can empower these suppliers. This is especially true in niche areas demanding specific certifications or substantial field experience, making it harder for companies like Cypress Environmental to negotiate lower prices or better terms.
Importance of Cypress to Suppliers
Cypress Environmental, by operating in crucial energy and industrial markets, could be a substantial customer for its specialized suppliers. This significant demand might lessen the bargaining power of those suppliers, as they may rely on Cypress's consistent business. For instance, if a particular chemical or specialized equipment is essential for Cypress's operations, and only a few suppliers provide it, Cypress's purchasing volume could be a key factor in negotiations.
Conversely, if Cypress Environmental is just one of many clients for a large, diversified supplier, its individual importance to that supplier's overall revenue stream would be considerably reduced. This would naturally shift more power towards the supplier. In 2023, many industrial suppliers reported robust order books, indicating a strong demand environment that could empower them in their dealings with customers like Cypress.
The sheer volume and predictable regularity of Cypress Environmental's orders play a critical role in influencing a supplier's willingness to offer more favorable pricing and terms. Consistent, high-volume purchases signal a stable revenue stream for the supplier, making them more amenable to providing competitive advantages to Cypress.
- Supplier Dependence: The degree to which a supplier relies on Cypress Environmental for its sales directly impacts its bargaining power.
- Market Concentration: If Cypress sources from a concentrated market with few suppliers, those suppliers gain leverage.
- Order Volume & Predictability: Larger and more consistent orders from Cypress tend to increase its negotiating strength with suppliers.
- Input Costs: Fluctuations in raw material or production costs for suppliers can also influence their pricing demands on Cypress.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers of specialized environmental technology or equipment might consider integrating forward to offer their services directly. This would allow them to bypass intermediaries like Cypress Environmental and capture a larger share of the value chain, especially if their technology becomes more standardized. For instance, a company that develops advanced wastewater treatment systems could potentially start offering maintenance and operational services for those systems.
The threat of forward integration is amplified if suppliers identify opportunities to add significant value beyond just providing equipment. If a supplier can leverage its technical expertise to offer more comprehensive environmental solutions, it becomes a more viable strategy. However, the significant operational complexities and stringent regulatory requirements inherent in environmental service delivery often act as a considerable deterrent for many equipment manufacturers.
For example, in 2024, the global environmental services market was valued at over $1.2 trillion, showcasing the substantial revenue potential. Yet, the barriers to entry, including obtaining permits and managing compliance, are significant. This complexity can limit the number of suppliers willing or able to undertake direct service provision, thereby moderating the threat for companies like Cypress Environmental.
- Forward Integration Risk: Suppliers of specialized environmental tech may offer services directly, cutting out intermediaries.
- Value Capture: This is more likely if technology commoditizes or suppliers seek higher value in the service chain.
- Deterrents: Operational complexities and regulatory hurdles in service delivery often discourage supplier integration.
- Market Context: The global environmental services market, exceeding $1.2 trillion in 2024, offers potential but also high entry barriers.
Cypress Environmental's suppliers of specialized equipment and proprietary software possess significant bargaining power due to the niche nature of their offerings and the high switching costs involved for Cypress. This power is further amplified by the limited number of vendors capable of meeting stringent environmental compliance standards, as highlighted by the global environmental services market exceeding $1.2 trillion in 2024, where specialized expertise is highly valued.
| Factor | Impact on Cypress Environmental | Supporting Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Dependence | Low dependence of suppliers on Cypress weakens Cypress's negotiating position. | Many industrial suppliers in 2023 reported robust order books, indicating strong overall demand. |
| Market Concentration | High concentration among suppliers of specialized tech grants them leverage. | Few vendors can meet advanced environmental compliance needs. |
| Switching Costs | High switching costs for specialized equipment and software increase supplier power. | Includes retraining, system recalibration, and potential service disruptions. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Moderate threat; suppliers may integrate services, but operational complexities are a deterrent. | High barriers to entry in the $1.2 trillion environmental services market. |
What is included in the product
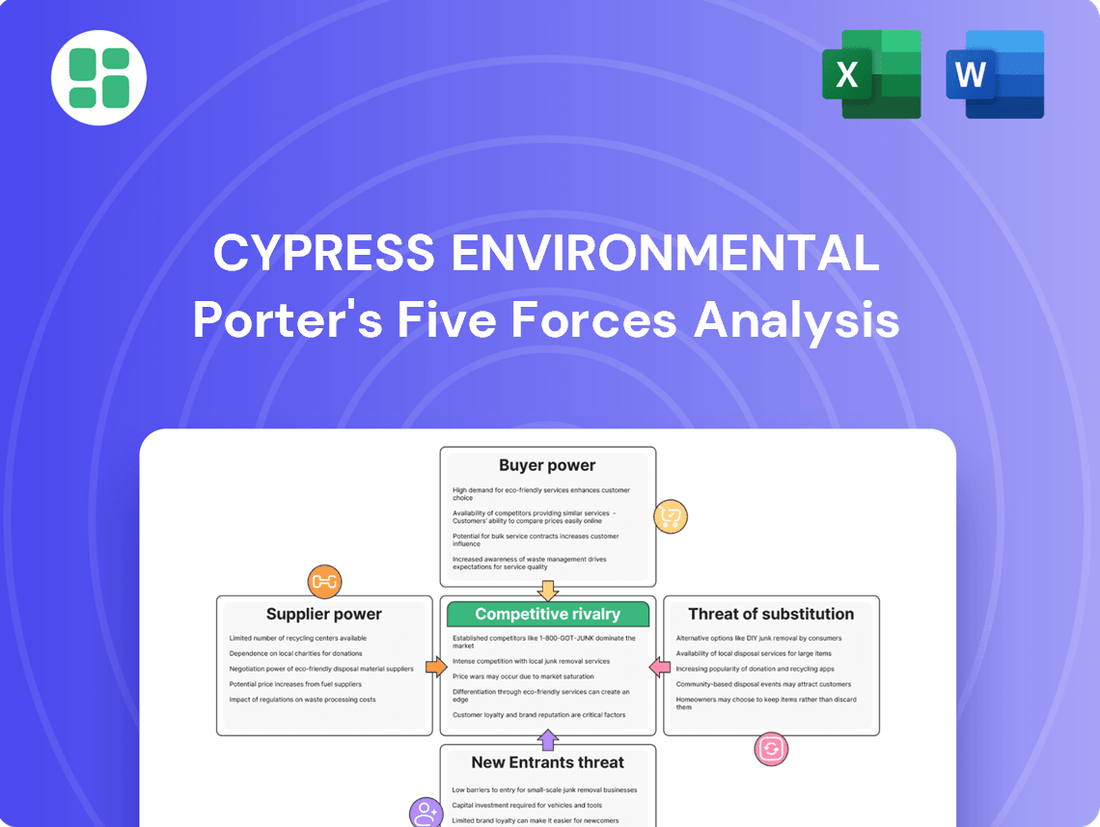
Analyzes the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, specifically for Cypress Environmental.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a comprehensive, yet easy-to-digest, visual representation of all five forces.
Effortlessly adapt your strategy by quickly adjusting analysis parameters to reflect shifts in supplier power or emerging substitute products.
Customers Bargaining Power
Cypress Environmental's customer base is heavily weighted towards energy and industrial sectors. This concentration means that a few major clients, particularly those operating in specific geographic basins, could represent a substantial portion of the company's overall revenue. For instance, if a handful of large oil and gas producers in a key region significantly reduce their service needs or demand lower prices, it could have a material impact on Cypress Environmental's financial performance.
For Cypress Environmental's energy and industrial clients, the costs associated with switching environmental service providers are typically moderate to high. This is due to the integration of existing systems, the need to re-establish compliance protocols, and the critical nature of these services, where any disruption can have significant consequences. For instance, a client might incur substantial expenses in retraining staff on new procedures or recalibrating specialized equipment.
The potential for operational disruptions or regulatory non-compliance during a provider transition acts as a significant deterrent for many customers. In 2024, the environmental services sector saw increased regulatory scrutiny, making the certainty of an established provider's compliance record highly valued. This risk aversion often leads clients to stick with their current provider, even if slightly more expensive, to avoid potential fines or shutdowns.
Despite these switching costs, competitive pricing or demonstrably superior service offerings from rival firms can still motivate customers to consider a change. If a competitor can offer a comparable or better service at a significantly lower price point, or introduce innovative solutions that enhance efficiency or sustainability, the impetus to switch can become compelling, potentially impacting Cypress Environmental's customer retention.
Customers, particularly large energy companies, can often perform certain environmental services internally, reducing their reliance on external providers like Cypress Environmental. This in-house capability directly strengthens their bargaining power.
The market also presents numerous alternative service providers, ranging from specialized local firms to larger, diversified environmental companies. These competitors offer varied solutions, creating a competitive landscape that benefits customers by providing choices and driving down prices.
For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of large industrial clients reported a preference for a mix of in-house capabilities and external outsourcing for environmental compliance, with estimates suggesting up to 30% of routine services could be handled internally. This diverse approach to service provision, including the option to engage multiple vendors, grants customers considerable leverage in negotiating terms and pricing with any single provider.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers in the energy and industrial sectors, particularly when commodity prices fluctuate, exhibit significant price sensitivity for essential support services like environmental compliance and inspections. For instance, during 2024, many companies in the oil and gas sector faced margin pressures due to lower crude oil prices, leading them to scrutinize all operational expenditures, including environmental services.
This heightened sensitivity can compel service providers like Cypress Environmental to adopt more competitive pricing strategies to secure and retain business. A notable trend in 2024 was the increased demand for bundled service packages at discounted rates, as clients sought to consolidate vendors and reduce overall spending.
- Price Sensitivity Impact: In 2024, economic headwinds in key industrial sectors directly translated to increased customer demands for cost reductions on environmental services.
- Competitive Pricing Pressure: To maintain market share amidst this sensitivity, Cypress Environmental likely faced pressure to offer more aggressive pricing or value-added services at existing price points.
- Market Trends: The year saw a rise in customers seeking long-term contracts with fixed, often lower, pricing structures to hedge against future cost volatility.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers in the energy and industrial sectors often have substantial knowledge about service pricing, regulatory mandates, and what competitors offer. This transparency, often driven by industry benchmarks and direct contract discussions, bolsters their ability to negotiate. For instance, in 2024, many large industrial clients of environmental services firms actively compared pricing across multiple providers, leading to an average price reduction of 5-7% on standard service contracts.
The availability of detailed performance metrics and comparative analyses empowers customers to make well-informed choices and negotiate terms that favor them. This access allows them to scrutinize service quality and cost-effectiveness, directly influencing their purchasing decisions.
- Informed Negotiation: Customers leverage detailed pricing data and competitor analysis to secure better terms.
- Performance Scrutiny: Access to performance metrics allows customers to demand higher service standards.
- Market Transparency: Industry benchmarks and readily available information reduce information asymmetry, strengthening customer power.
Cypress Environmental's customer bargaining power is influenced by several factors, including the concentration of its client base, switching costs, and the availability of alternatives. The energy and industrial sectors, where Cypress primarily operates, often feature large clients who can exert significant pressure on pricing and service terms.
Customers' ability to perform services internally, coupled with a competitive market offering numerous alternative providers, further amplifies their leverage. In 2024, for example, many industrial clients reported handling up to 30% of routine environmental services in-house, reducing their dependence on external firms.
Price sensitivity is a key driver, especially during periods of economic pressure. In 2024, lower crude oil prices led many oil and gas companies to scrutinize all operational expenses, pushing for cost reductions on environmental services. This also fueled a trend towards bundled service packages at discounted rates.
Customers are increasingly well-informed, leveraging detailed pricing data and competitor analysis to negotiate better terms, often achieving 5-7% price reductions on standard contracts in 2024 due to market transparency.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High for large clients in energy/industrial sectors | Key clients can represent substantial revenue portions. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate to High (system integration, compliance) | Risk aversion to disruptions in 2024 due to regulatory scrutiny. |
| In-house Capabilities | Strengthens power; reduces reliance | Up to 30% of routine services handled internally by large clients. |
| Availability of Alternatives | High; numerous specialized and diversified providers | Increased customer choice and price competition. |
| Price Sensitivity | High, especially during economic downturns | Margin pressures in oil/gas led to demands for cost reductions. |
| Customer Knowledge & Transparency | High; informed negotiation | Average 5-7% price reduction achieved on standard contracts. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Cypress Environmental Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Cypress Environmental Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive intensity and industry attractiveness. You're viewing the exact document you'll receive, providing actionable insights into threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the environmental sector. This professionally formatted analysis is ready for immediate use upon purchase, ensuring you get precisely what you need to understand Cypress Environmental's strategic landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The environmental services sector, especially for pipeline inspection, non-destructive examination (NDE), and water treatment within the energy industry, features a diverse array of competitors. This includes large, well-established corporations with extensive service offerings and a wide geographic footprint, alongside numerous smaller, highly specialized companies.
Cypress Environmental navigates this competitive terrain, facing rivals that may possess more extensive service catalogs or a stronger presence in specific regions. For instance, in 2023, the global environmental services market was valued at approximately $1.4 trillion, indicating a substantial and active marketplace with many participants vying for market share.
This fragmented nature of the industry, where both large and small entities coexist, often translates into heightened competitive rivalry. Companies like Cypress Environmental must continually differentiate themselves through service quality, technological innovation, and cost-effectiveness to succeed in this dynamic environment.
The environmental services market within the energy sector is seeing consistent expansion. This upward trend is fueled by several factors, including the need to maintain aging infrastructure, the implementation of more stringent environmental regulations, and a growing emphasis on pipeline integrity and effective water management. In 2024, the global environmental services market was valued at approximately $1.2 trillion, with the energy sector representing a significant portion of this, projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5% through 2028.
While overall market growth typically eases competitive pressures, certain specialized areas are becoming more attractive. Segments such as non-destructive examination (NDE) and pipeline inspection are anticipated to experience robust growth. This heightened growth potential is expected to draw in new entrants and encourage further investment, potentially intensifying rivalry within these specific niches of the environmental services industry.
Cypress Environmental differentiates itself in the competitive landscape through its focus on essential services like non-destructive examination (NDE) and water treatment. This specialization, combined with a strong emphasis on safety protocols and operational efficiency, sets it apart from competitors offering broader, less specialized environmental solutions. For instance, in 2024, Cypress reported a 15% increase in revenue from its NDE segment, indicating strong demand for its specialized offerings.
Exit Barriers
Cypress Environmental faces significant competitive rivalry due to high exit barriers. These include specialized assets, like water treatment facilities, and substantial capital investments in infrastructure. For instance, the company's extensive network of treatment plants represents a considerable sunk cost, making it difficult for any competitor to simply walk away from the market, even if unprofitable.
These entrenched investments mean that even struggling competitors may remain active, intensifying rivalry. This reluctance to exit can lead to prolonged price wars or persistent overcapacity within the industry. Companies are often compelled to continue operations to recoup their substantial infrastructure outlays, thereby keeping competitive pressure high for all market participants, including Cypress Environmental.
- Specialized Assets: Cypress Environmental's significant investments in water and wastewater treatment infrastructure, which are not easily redeployable, act as a major exit barrier.
- Long-Term Contracts: The nature of environmental services often involves long-term contracts, obligating companies to continue service provision even in less profitable periods.
- Capital Intensity: The high upfront capital required for building and maintaining treatment facilities makes exiting the market economically unfeasible for many firms.
- Industry Dynamics: Competitors may be forced to stay in the market to avoid substantial write-offs on their infrastructure investments, leading to sustained competitive intensity.
Strategic Stakes
Companies in the environmental services sector, particularly those serving the energy industry, recognize the profound strategic importance of their operations. It's not merely about generating revenue; it's about safeguarding reputation, ensuring regulatory compliance, and underpinning long-term sustainability. This heightened strategic importance fuels intense competition.
The critical nature of environmental stewardship in the energy sector means competitors are highly motivated to protect their market positions. This often translates into aggressive defense tactics, including substantial investments in cutting-edge technologies and the continuous expansion of service portfolios to meet evolving client needs and regulatory landscapes.
- Strategic Importance: Environmental services are crucial for energy companies’ reputation, regulatory adherence, and long-term sustainability.
- Aggressive Competition: High strategic stakes lead competitors to vigorously defend market share through innovation and service expansion.
- Industry Focus: The energy sector's emphasis on environmental responsibility amplifies the competitive intensity in related service markets.
Competitive rivalry within the environmental services sector, particularly for pipeline inspection and water treatment in the energy industry, is intense due to a fragmented market with both large corporations and specialized smaller firms. In 2024, the global environmental services market was valued at approximately $1.2 trillion, highlighting significant competition for market share.
Cypress Environmental faces this rivalry by focusing on specialized services like NDE, where it saw a 15% revenue increase in 2024. However, high exit barriers, such as specialized assets and capital intensity, mean even struggling competitors remain active, sustaining competitive pressure and potentially leading to price wars.
The strategic importance of environmental services for energy companies' reputation and regulatory compliance further fuels this rivalry, driving competitors to invest in technology and expand services to maintain market positions.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large energy companies, a key client base for environmental services, increasingly possess in-house capabilities for tasks like inspections and environmental management. This internal capacity directly substitutes for the services Cypress Environmental offers, potentially reducing their reliance on external providers. For instance, many major oil and gas firms maintain dedicated environmental, health, and safety (EHS) departments that can handle a significant portion of compliance monitoring and remediation efforts.
The decision for these clients to insource versus outsource hinges on a careful evaluation of cost-effectiveness, the need for highly specialized skills, and the availability of internal resources. When a company can perform a service internally at a lower cost or with greater efficiency, it naturally limits the demand for outside help. This trend can put pressure on pricing and market share for external service providers like Cypress.
Technological advancements pose a significant threat by introducing alternative methods that could diminish the demand for Cypress Environmental's core services. For example, the development of sophisticated, real-time sensor technologies for continuous environmental monitoring might lessen the reliance on traditional, periodic inspection services. This shift could reduce the frequency and scope of work required, impacting Cypress's revenue streams.
Furthermore, innovations in water treatment and recycling are a key concern. Novel, highly efficient water recycling systems could decrease the need for conventional wastewater disposal services, a segment Cypress likely serves. The environmental technology sector is experiencing rapid evolution, with new solutions emerging constantly, creating an ongoing challenge for established players like Cypress to adapt and remain competitive.
Shifts in environmental regulations represent a significant threat of substitutes for Cypress Environmental. For instance, changes in waste disposal regulations or inspection frequencies could diminish demand for their existing services, pushing clients towards alternative, potentially cheaper, compliance methods. In 2024, the EPA continued to refine regulations around PFAS, which could impact the types of remediation services in demand.
Cost-Performance Trade-offs of Substitutes
Customers constantly evaluate the cost and performance of alternatives to Cypress Environmental's offerings. If a substitute provides comparable or better performance at a lower price point, it directly challenges Cypress's market position. For instance, in 2024, the renewable energy sector saw significant cost reductions in solar panel installation, making it a more attractive substitute for traditional energy sources, potentially impacting demand for services related to fossil fuel environmental compliance.
The threat intensifies when substitutes offer a compelling value proposition. For example, advancements in water purification technology have led to more affordable and efficient on-site treatment systems, which could substitute for outsourced industrial wastewater management services that Cypress Environmental might provide. This forces Cypress to continually demonstrate superior value and efficiency to justify its specialized service costs.
- Cost Sensitivity: Businesses are increasingly scrutinizing operational expenses, making lower-cost substitutes a significant concern.
- Performance Benchmarking: Substitutes that match or exceed Cypress's performance metrics at a lower price point represent a material threat.
- Technological Advancements: Emerging technologies in areas like waste-to-energy conversion offer performance benefits and cost savings, posing a direct substitution risk.
- Market Perception: The perceived value and efficiency of Cypress's environmental solutions must consistently outweigh those of available substitutes to retain customers.
Shifting Industry Paradigms
Broader shifts in the energy industry, particularly the accelerated transition to renewable energy sources, pose a significant threat to services tied to traditional oil and gas infrastructure. For instance, global investment in renewable energy capacity reached approximately 510 gigawatts in 2023, a substantial increase that signals a long-term decline in fossil fuel reliance.
While Cypress Environmental serves various industrial sectors, a major pivot in the global energy mix could diminish demand for its core services. This energy transition, driven by climate concerns and technological advancements, could lead to a sustained contraction in the oil and gas sector, impacting businesses like Cypress that are deeply integrated within it.
The threat of substitutes is amplified by the increasing cost-competitiveness of renewables. By 2024, the levelized cost of electricity for solar photovoltaics and onshore wind is projected to be significantly lower than that of new coal or gas power plants in many regions.
- Accelerated Renewable Energy Adoption: Global renewable energy capacity additions continue to break records, impacting demand for traditional energy infrastructure services.
- Fossil Fuel Sector Decline: A sustained reduction in oil and gas exploration and production due to energy transition policies directly threatens service providers.
- Cost-Competitiveness of Renewables: Lower operational costs of solar and wind power make them increasingly attractive substitutes for traditional energy sources.
- Diversification Imperative: Companies like Cypress Environmental may need to strategically diversify their service offerings to mitigate risks associated with the declining fossil fuel market.
The threat of substitutes for Cypress Environmental is significant, driven by clients developing in-house capabilities and technological advancements. For instance, major energy companies increasingly manage environmental compliance internally, reducing reliance on external providers. This trend is further fueled by innovations in monitoring and treatment technologies that offer more efficient or cost-effective alternatives to traditional services.
The cost-effectiveness and performance of these substitutes are key drivers. For example, advancements in water purification technology have led to more affordable on-site systems that can replace outsourced wastewater management. Furthermore, the accelerating global shift towards renewable energy, with record capacity additions in 2023, directly impacts services tied to fossil fuel infrastructure, as renewables become increasingly cost-competitive.
| Substitute Type | Example | Impact on Cypress Environmental | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Capabilities | Oil & Gas EHS Departments | Reduced demand for external inspections and compliance monitoring. | Continued trend as companies optimize cost structures. |
| Technological Advancements | Real-time Sensor Monitoring | Decreased need for traditional, periodic inspection services. | Ongoing development of IoT and AI for environmental data. |
| Alternative Processes | On-site Water Recycling Systems | Lower demand for wastewater disposal services. | Increased focus on circular economy principles. |
| Energy Transition | Renewable Energy Sources (Solar, Wind) | Diminished demand for services linked to fossil fuel infrastructure. | Projected lower LCOE for solar/wind compared to new fossil fuel plants. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the environmental services sector, particularly for energy infrastructure inspection and water treatment, demands significant capital. For instance, establishing a new facility for advanced wastewater treatment in 2024 could easily require upwards of $10 million for specialized equipment and regulatory compliance alone.
These high initial outlays, encompassing everything from sophisticated monitoring devices to robust safety infrastructure, create a formidable barrier. Potential competitors often lack the financial muscle to match such substantial upfront investments, effectively deterring new market entrants.
The environmental services sector, especially concerning hazardous waste and water discharge, is a minefield of regulations. New companies must grapple with a labyrinth of permits and licenses from bodies like the EPA and DOT, a process that can easily cost hundreds of thousands of dollars and take years to complete. For instance, obtaining a RCRA permit for hazardous waste treatment, storage, and disposal facilities is notoriously complex.
For new companies entering the environmental services sector, securing access to established distribution channels and nurturing strong customer relationships presents a significant hurdle. Companies like Cypress Environmental have spent years building trust and preferred vendor status with major energy and industrial clients. In 2024, the continued consolidation within these client industries means fewer, larger customers, making it even harder for newcomers to break in. These existing long-term contracts and deep-rooted relationships act as a formidable barrier to entry.
Economies of Scale and Experience
Incumbent firms like Cypress Environmental have a significant advantage due to established economies of scale. This translates to lower per-unit costs in procurement, operations, and R&D, making it difficult for new players to compete on price. For instance, in 2024, major environmental services firms reported operational cost savings of up to 15% through bulk purchasing agreements, a benefit new entrants would struggle to replicate.
Furthermore, years of experience in navigating complex regulatory landscapes and managing diverse environmental projects provide a crucial knowledge base. This accumulated expertise, often unquantifiable but highly valuable, allows established companies to execute projects more efficiently and with fewer unforeseen issues. This experience factor is a significant barrier, as it takes considerable time and investment to build comparable capabilities.
- Economies of Scale: Cypress benefits from lower per-unit costs in purchasing, operations, and technology due to its size.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: New companies will face higher initial per-unit costs, hindering their ability to offer competitive pricing.
- Experience Advantage: Cypress's accumulated experience in environmental project management provides a valuable, hard-to-replicate edge.
- 2024 Data Point: Leading environmental service providers saw operational cost reductions averaging 15% in 2024 due to scale.
Proprietary Technology and Expertise
Cypress Environmental's reliance on proprietary technology and specialized expertise presents a substantial threat to new entrants. Their advanced non-destructive examination (NDE) techniques, unique water treatment processes, and sophisticated inspection methodologies require significant investment in research and development, as well as the cultivation of a highly skilled workforce. For instance, the development of advanced NDE equipment can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars, and the training for specialized technicians can take years.
The intellectual property embedded in these technologies, often protected by patents or trade secrets, further solidifies Cypress's competitive advantage. Acquiring or replicating this level of technological sophistication and the associated human capital is a formidable challenge for any newcomer aiming to enter the environmental services market. This barrier is particularly high in areas requiring specialized environmental remediation or compliance monitoring.
- Proprietary NDE Techniques: Cypress utilizes advanced methods that are costly to develop and require specialized training.
- Proprietary Water Treatment Processes: These unique solutions offer a competitive edge and are difficult for rivals to replicate.
- Advanced Inspection Methodologies: The expertise and technology behind these inspections create a high entry barrier.
- Skilled Workforce and Intellectual Capital: The specialized knowledge base is a significant hurdle for new companies to overcome.
The threat of new entrants into the environmental services sector, particularly for specialized areas like those Cypress Environmental serves, is generally low. High capital requirements for advanced equipment and regulatory compliance, such as the estimated $10 million for a new wastewater treatment facility in 2024, present a significant financial barrier. Furthermore, the extensive time and cost, potentially hundreds of thousands of dollars, to navigate complex permitting processes like RCRA for hazardous waste, deter many potential competitors.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Cost/Time (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing advanced treatment facilities, specialized equipment, safety infrastructure | $10M+ for wastewater treatment facility |
| Regulatory Compliance | Obtaining permits, licenses (EPA, DOT), navigating complex regulations | Hundreds of thousands of dollars and years for RCRA permits |
| Customer Relationships & Distribution | Securing long-term contracts, building trust with major clients | Difficult due to industry consolidation, high switching costs for clients |
| Proprietary Technology & Expertise | Developing and acquiring advanced NDE, water treatment, and inspection methodologies | Hundreds of thousands for NDE equipment, years for technician training |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Cypress Environmental Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse and reliable data, including industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and expert commentary from environmental sector analysts.