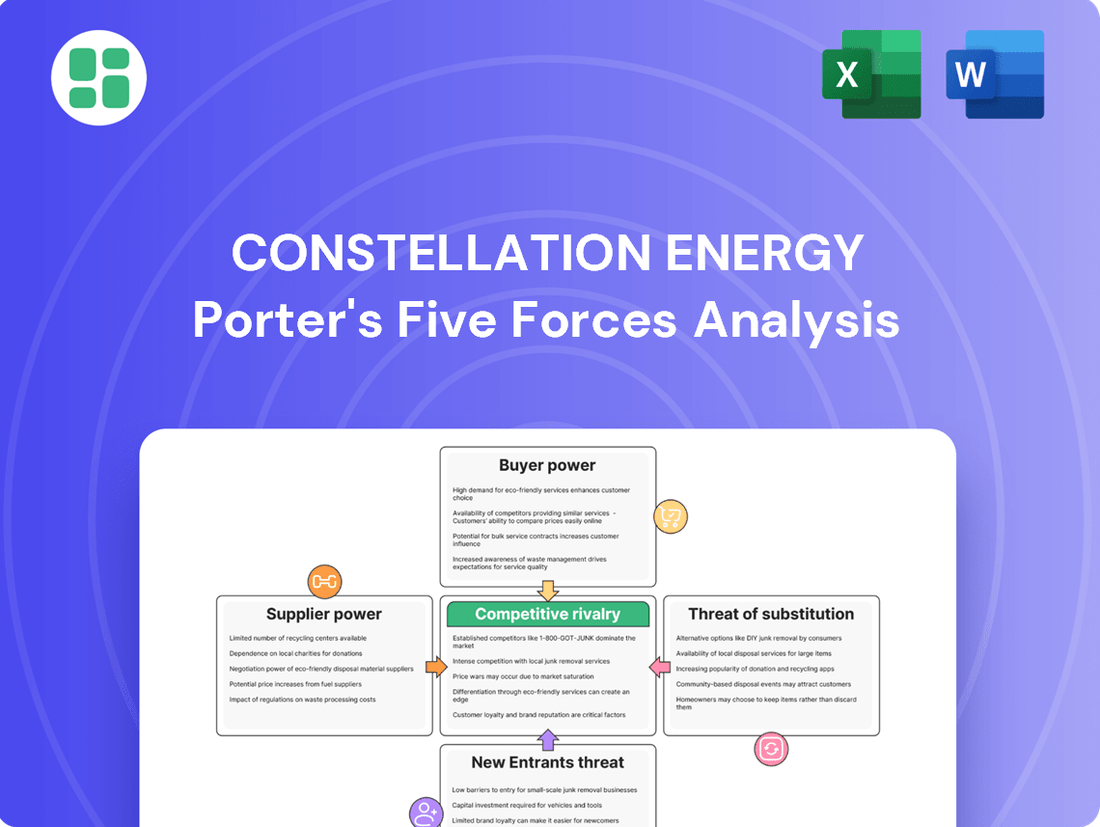
Constellation Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Constellation Energy Bundle
Constellation Energy navigates a complex energy landscape, facing significant bargaining power from its large industrial customers and intense rivalry within the utility sector. Understanding these pressures is crucial for any stakeholder.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Constellation Energy’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Constellation Energy's reliance on highly specialized suppliers for crucial elements like nuclear fuel and advanced renewable energy technology significantly impacts its bargaining power. The limited number of qualified providers in these niche sectors, particularly for nuclear components, grants these suppliers considerable leverage.
High switching costs and the unique, often proprietary, nature of their offerings further strengthen the suppliers' position. For instance, the specialized nature of enriched uranium fuel, with few global producers, means Constellation faces limited options and higher prices, a dynamic evident in the global nuclear fuel market which saw prices for some uranium products fluctuate significantly in 2024 based on supply chain concerns and geopolitical events.
Suppliers of specialized nuclear-grade materials and services, along with intricate components for massive wind and solar installations, hold significant bargaining power. This leverage stems from the unique nature of their offerings and the substantial costs involved in switching. For Constellation Energy, moving to a different supplier for these critical inputs would necessitate costly re-qualification processes and extensive regulatory approvals, making such transitions impractical and expensive.
The stringent regulatory and safety standards in the nuclear and large-scale renewable energy sectors significantly limit the number of qualified suppliers. For instance, suppliers for nuclear components must adhere to rigorous quality assurance programs and obtain specific certifications, a process that can take years and substantial investment. This scarcity of compliant suppliers naturally increases their leverage.
In 2024, companies like Constellation Energy, heavily involved in nuclear power, rely on a specialized supply chain. Suppliers who can meet these demanding requirements, such as those certified by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) for safety-critical parts, possess considerable bargaining power. Their ability to navigate complex compliance landscapes makes them indispensable, allowing them to command higher prices and favorable contract terms.
Limited Forward Integration Threat
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into energy generation for Constellation Energy is considerably low. This is primarily due to the massive capital requirements, complex regulatory landscapes, and the sheer operational expertise needed to run power plants. For instance, building a new utility-scale solar farm can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, and a nuclear plant runs into the billions. These barriers make it economically unfeasible for most suppliers to directly compete with established energy generators like Constellation.
This limited forward integration capability by suppliers directly dampens their bargaining power. Suppliers of fuel, equipment, or technology are therefore less likely to leverage their position by entering Constellation's core business. In 2024, the average cost to build a new natural gas power plant in the US was estimated to be between $1,000 to $2,000 per kilowatt, a significant deterrent for potential entrants.
- High Capital Outlay: Building power generation facilities requires billions in upfront investment, a significant barrier for suppliers.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating environmental permits, grid interconnection, and operational licenses is a substantial hurdle.
- Operational Expertise: Managing complex energy infrastructure demands specialized knowledge and skilled personnel.
- Limited Profitability: Entering a mature market with established players offers uncertain returns on such massive investments.
Impact of Global Supply Chain Dynamics
Geopolitical developments and global supply chain disruptions, particularly evident in 2022 and 2023, have significantly impacted the availability and cost of critical raw materials and components for energy infrastructure. This volatility grants suppliers of specialized equipment and rare earth minerals greater leverage in negotiating pricing and delivery terms with companies like Constellation Energy.
For instance, the ongoing global semiconductor shortage, which continued to affect various industries through 2024, can delay the production of advanced control systems and smart grid technologies essential for modern energy facilities. This scarcity directly translates to increased supplier bargaining power, potentially leading to higher upfront costs for new projects and maintenance.
- Increased Material Costs: The price of key materials like copper and lithium, crucial for grid modernization and battery storage, saw significant fluctuations in 2024 due to supply constraints and heightened demand, strengthening supplier pricing power.
- Extended Lead Times: Disruptions in manufacturing hubs and shipping logistics have led to longer lead times for specialized components, forcing energy companies to accept supplier-preferred delivery schedules and potentially pay premiums for faster service.
- Limited Supplier Options: For highly specialized or proprietary equipment, the limited number of qualified manufacturers means suppliers can dictate terms more aggressively, especially when demand outstrips supply.
Constellation Energy faces significant supplier bargaining power, particularly from providers of specialized nuclear fuel and advanced renewable energy components. The limited number of qualified suppliers in these niche sectors, coupled with high switching costs and proprietary technologies, grants these suppliers considerable leverage.
Suppliers of critical inputs like enriched uranium and specialized parts for large-scale wind turbines possess strong bargaining power due to the specialized nature of their products and the significant costs associated with changing providers. For example, the global nuclear fuel market experienced price volatility in 2024 due to supply chain vulnerabilities, directly impacting Constellation's procurement costs.
The stringent regulatory and safety requirements in the nuclear and renewable energy sectors further restrict the supplier pool. Suppliers meeting these rigorous standards, such as those certified by the NRC for nuclear components, are indispensable and can command premium pricing. In 2024, the need for NRC-certified parts meant Constellation had to work with a select group of suppliers who could navigate complex compliance landscapes.
The bargaining power of suppliers is amplified by global supply chain disruptions and geopolitical events, as seen with semiconductor shortages impacting smart grid technologies through 2024. This scarcity increases supplier leverage, leading to higher costs and extended lead times for essential components.
| Factor | Impact on Constellation Energy | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Specialized Nuclear Fuel Suppliers | High Bargaining Power | Price volatility due to supply chain concerns and geopolitical events. |
| Advanced Renewable Component Suppliers | Moderate to High Bargaining Power | Limited number of manufacturers for proprietary technologies. |
| Switching Costs | High | Costly re-qualification and regulatory approvals for new suppliers. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Restricts Supplier Pool | NRC certification for nuclear parts creates scarcity and supplier leverage. |
| Global Supply Chain Disruptions | Increased Supplier Leverage | Semiconductor shortages and material cost fluctuations (e.g., copper, lithium) impacted lead times and pricing in 2024. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects Constellation Energy's competitive environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the energy sector.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive pressures, allowing for proactive strategy adjustments to mitigate threats and capitalize on opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Constellation Energy's diverse customer base, spanning wholesale utilities, industrial and commercial clients, government bodies, and residential consumers, generally limits the bargaining power of any single customer segment. This wide reach means that the company isn't overly reliant on any one group, which is a strength. For instance, in 2023, Constellation reported that its retail electricity segment served millions of residential and business customers across various regions, showcasing this broad market penetration.
Residential and smaller commercial customers often exhibit significant price sensitivity, particularly in deregulated retail electricity markets where multiple suppliers compete. This sensitivity can lead to downward pressure on prices as customers evaluate and switch providers based on cost, even with minor switching fees. For instance, in competitive markets, a small percentage difference in electricity rates can drive customer decisions, influencing Constellation Energy's pricing strategies for these segments.
Large industrial and commercial clients, especially those with massive energy needs such as data centers, wield considerable bargaining power. These entities often secure long-term power purchase agreements (PPAs), actively seeking competitive pricing that compels Constellation Energy to present attractive terms.
In 2023, Constellation Energy reported that a significant portion of its revenue was derived from its commercial and industrial customer base, highlighting the importance of retaining these key accounts. The ability of these large customers to switch suppliers or invest in on-site generation, though costly, creates a constant pressure for Constellation to maintain competitive pricing and service levels, directly impacting its profit margins.
Wholesale Market Dynamics
In the wholesale energy market, Constellation Energy faces powerful customers in the form of large utilities and grid operators. These entities are highly knowledgeable buyers, possessing significant market insight and robust procurement strategies. Their capacity to switch between various energy suppliers or even develop their own generation assets directly curtails Constellation's ability to dictate prices.
The bargaining power of customers in the wholesale market is substantial, influencing Constellation Energy's pricing flexibility and market share. For instance, in 2024, the increasing trend of utilities investing in distributed generation and energy storage solutions, often driven by state-level renewable portfolio standards and grid modernization initiatives, provides them with greater leverage. This allows them to negotiate more aggressively or reduce their reliance on traditional wholesale power purchases.
- Sophisticated Buyers: Large utilities and grid operators possess deep market understanding and advanced procurement capabilities.
- Alternative Options: Customers can choose from multiple power generators or invest in their own generation capacity.
- Impact on Pricing: This customer power limits Constellation's ability to set premium prices for its energy products and services.
- Market Trends: The growing trend of utility-led distributed generation and storage investments in 2024 further amplifies customer bargaining power.
Availability of Alternative Energy Solutions
The increasing availability of alternative energy solutions significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. Customers can increasingly opt for rooftop solar installations or implement robust energy efficiency programs, thereby diminishing their dependence on traditional utility providers like Constellation Energy. This shift empowers them to negotiate more favorable terms or even switch providers if current offerings are not competitive.
For instance, in 2024, the U.S. solar market continued its strong growth trajectory. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), residential solar installations saw a substantial increase, with projections indicating continued expansion through 2025. This growing accessibility to self-generation directly translates to a greater ability for consumers to exert pressure on energy suppliers.
- Increased Customer Options: Rooftop solar and energy efficiency measures offer viable alternatives to grid power.
- Reduced Reliance on Utilities: Customers can lower their consumption from traditional providers.
- Enhanced Negotiation Leverage: Alternative solutions give customers more power to demand better pricing and service.
- Market Trend: Residential solar installations have shown consistent growth, empowering more consumers with choices.
Constellation Energy's diverse customer base generally limits the bargaining power of any single segment, as the company isn't overly reliant on any one group. However, large industrial and commercial clients, along with wholesale utilities, possess significant leverage due to their substantial energy needs and ability to explore alternatives like on-site generation. Residential customers, while numerous, can exert price sensitivity in competitive retail markets, pressuring Constellation to offer attractive rates.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Level | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Residential & Small Commercial | Moderate to High (Price Sensitive) | Price sensitivity, availability of competing suppliers, switching costs. |
| Large Industrial & Commercial | High | Volume of consumption, long-term contracts, potential for self-generation, negotiation expertise. |
| Wholesale Utilities & Grid Operators | High | Sophisticated procurement, multiple supplier options, investment in distributed generation, market knowledge. |
Same Document Delivered
Constellation Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Constellation Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the energy sector. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately upon purchase, ensuring transparency and immediate utility for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The energy generation sector is defined by substantial fixed costs, especially for nuclear and large-scale renewable power plants. This necessitates fierce competition to ensure these expensive assets operate at maximum capacity, driving down per-unit costs. For instance, the capital expenditure for a new nuclear plant can easily run into billions of dollars, creating a high barrier to entry and a strong incentive for existing players to maintain high utilization rates.
Industry consolidation is a significant trend, with companies like Constellation Energy actively acquiring other power generators. In 2023, Constellation completed its acquisition of a significant portion of its generation fleet from NRG Energy for $700 million, demonstrating a strategic move to expand its footprint and operational scale. Such mergers and acquisitions can dramatically alter the competitive dynamics, potentially leading to fewer, larger players in the market.
Constellation Energy faces intense rivalry from other major utilities and independent power producers, many of whom also boast diverse generation capabilities, including substantial natural gas and renewable energy sources. This competitive landscape means companies are constantly vying for market position and customer loyalty.
In the first quarter of 2025, Constellation Energy commanded an estimated market share of approximately 6.74% within the broader utilities sector. This figure highlights its significant presence but also underscores the substantial portion of the market held by its competitors.
Electricity demand is on the rise, fueled by data center expansion and the broader trend of electrification. For instance, the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) projected a 1.3% annual increase in total U.S. electricity consumption from 2023 to 2050. This growing market presents significant opportunities for energy providers.
However, this demand growth is met with an increasingly competitive landscape. The rapid build-out of solar and wind power, coupled with the cost-effectiveness of natural gas, means companies like Constellation Energy face intense competition for new projects and market share. In 2023, renewable energy sources accounted for approximately 23% of U.S. electricity generation, a figure that continues to climb.
Regulatory and Policy Landscape
The competitive landscape for Constellation Energy is significantly shaped by the evolving regulatory and policy environment at both state and federal levels. Policies promoting clean energy, such as the Inflation Reduction Act's nuclear production tax credit, directly impact the cost-competitiveness of nuclear power, a core offering for Constellation. For instance, the IRA's credit, which began in 2024 and extends through 2032, provides up to $15 per megawatt-hour for nuclear power, a substantial incentive that can alter investment decisions and operational strategies for energy producers.
These policy shifts can create pronounced competitive advantages or disadvantages. For example, states with mandates for renewable energy or carbon reduction goals may favor Constellation's clean energy portfolio, while regions with less stringent environmental regulations or those actively phasing out nuclear power could present greater challenges. The market structure itself, often dictated by regulatory bodies, determines how Constellation interacts with competitors and customers, influencing pricing power and market access.
- Impact of IRA: The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022, effective from 2024, offers a production tax credit of up to $15/MWh for nuclear power, bolstering the financial viability of existing and new nuclear facilities.
- State-Level Policies: State-specific renewable portfolio standards (RPS) and clean energy mandates directly influence demand for Constellation's nuclear and renewable energy generation.
- Market Deregulation/Reregulation: Changes in wholesale electricity market rules and regulations can significantly alter competitive dynamics, affecting pricing and Constellation's ability to secure long-term contracts.
- Carbon Pricing Mechanisms: The adoption of carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems in various jurisdictions would further enhance the competitive advantage of Constellation's zero-emission nuclear fleet.
Focus on Carbon-Free and Reliability
Constellation Energy's competitive rivalry is significantly shaped by its focus on carbon-free and reliable energy. As the nation's largest producer of carbon-free energy, with a substantial portion derived from nuclear power, the company holds a distinct advantage.
This strong position allows Constellation to effectively attract and retain customers, particularly those with ambitious decarbonization targets. For instance, major technology firms are increasingly seeking energy partners who can guarantee a clean and consistent power supply to meet their sustainability mandates.
- Largest Carbon-Free Producer: Constellation is the largest producer of carbon-free electricity in the United States.
- Nuclear Power Dominance: A significant portion of their carbon-free output comes from nuclear generation, ensuring baseload reliability.
- Decarbonization Appeal: This focus directly appeals to corporations aiming to reduce their carbon footprint.
- 2023 Performance: In 2023, Constellation reported adjusted EBITDA of $4.6 billion, reflecting strong operational performance and market demand for their clean energy solutions.
Constellation Energy faces a highly competitive environment driven by the substantial capital required for power generation assets and the ongoing trend of industry consolidation. Companies actively acquire peers to gain scale, as seen in Constellation's 2023 acquisition of NRG Energy's generation fleet for $700 million. This dynamic intensifies rivalry among large utilities and independent power producers, all vying for market share and customer loyalty in a growing but contested market.
The increasing demand for electricity, particularly from data centers and electrification efforts, is met by a diverse and competitive supply. The rapid expansion of solar and wind power, alongside the cost-effectiveness of natural gas, presents a challenging landscape for established players like Constellation. In 2023, renewables made up about 23% of U.S. electricity generation, a share that continues to grow, directly impacting competition.
Regulatory and policy shifts, such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), significantly influence competitive dynamics. The IRA's nuclear production tax credit, effective from 2024, offers up to $15 per megawatt-hour, enhancing the competitiveness of nuclear power, a core asset for Constellation. This creates a more favorable environment for companies with clean energy portfolios in regions with supportive policies.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Competitive Factor | Constellation's Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| Major Utilities | Duke Energy, Southern Company | Scale, diverse generation mix, customer base | Largest carbon-free producer, strong nuclear fleet |
| Independent Power Producers (IPPs) | Vistra Corp., NextEra Energy | Renewable energy development, operational efficiency | Significant renewable portfolio, nuclear reliability |
| Emerging Renewable Developers | Various smaller solar/wind companies | Agility, focus on specific technologies | Leveraging existing infrastructure and regulatory support |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing adoption of distributed generation, particularly rooftop solar coupled with battery storage, poses a significant threat of substitution for traditional utility providers like Constellation Energy. As of early 2024, the cost of solar panels has fallen by over 90% in the last decade, making it a more accessible option for consumers looking to generate their own power.
This trend allows both residential and commercial customers to decrease their dependence on grid electricity, directly impacting the demand for power supplied by larger energy companies. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. saw a record 37% year-over-year growth in new solar installations, signaling a clear shift towards self-generation.
Improvements in energy efficiency technologies, like smart thermostats and better insulation, directly reduce the need for purchased electricity. For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy reported that by 2023, advancements in building envelopes alone could cut residential energy consumption by up to 30%.
Demand-side management programs, which incentivize customers to reduce usage during peak hours, also act as a substitute for traditional power generation. In 2024, many utilities reported significant participation in these programs, with some seeing a reduction in peak demand by as much as 10-15% in participating areas.
Large industrial clients, especially those with substantial energy needs, are increasingly exploring on-site power generation as a viable alternative to traditional utility providers. These clients are motivated by a desire for greater control over their energy expenditures and a more reliable supply chain, particularly in light of fluctuating market prices.
Natural gas combined heat and power (CHP) systems are a significant driver of this trend, offering both electricity and thermal energy from a single fuel source. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy highlighted the growing adoption of CHP technologies across various industrial sectors, noting their efficiency gains and cost-saving potential for large consumers.
Fuel Switching by Industrial Consumers
Industrial consumers, particularly those with flexible energy needs, can switch between electricity and direct fuel sources like natural gas based on cost and availability. This capability acts as a significant threat of substitutes for electricity providers like Constellation Energy. For instance, in 2024, a substantial portion of industrial energy consumption across sectors like manufacturing and chemicals retained the potential for fuel switching, impacting overall electricity demand.
While not a perfect substitute in every application, the ability of industrial users to opt for natural gas or other fuels directly can erode Constellation's customer base and reduce the volume of electricity sold. This dynamic is particularly pronounced in energy-intensive industries where fuel costs represent a significant operational expense. The ongoing volatility in natural gas prices throughout 2024 directly influenced these switching decisions, creating a tangible threat to Constellation's market share.
- Fuel Switching Capability: Industrial processes can often utilize natural gas or other fuels directly, bypassing electricity for certain operations.
- Demand Reduction: This switching capability directly reduces the overall demand for electricity, impacting revenue for providers like Constellation Energy.
- Price Sensitivity: The economic viability of fuel switching is heavily influenced by the relative prices of electricity versus alternative fuels, such as natural gas.
- Market Impact: In 2024, fluctuations in natural gas prices demonstrated the real-world impact of this threat, as some industrial consumers adjusted their energy sourcing strategies.
Emerging Energy Technologies
Emerging energy technologies represent a significant long-term threat of substitution for Constellation Energy. Future advancements in areas like advanced geothermal systems, small modular nuclear reactors (SMRs) developed by competitors, or even breakthroughs in fusion energy could offer fundamentally different and potentially more cost-effective or environmentally benign generation methods. For instance, by 2024, the global investment in clean energy technologies, including advanced renewables and next-generation nuclear, has seen substantial growth, indicating a dynamic landscape where new solutions are constantly being developed.
These evolving technologies challenge the established energy infrastructure and business models. If these substitutes become commercially viable and widely adopted, they could reduce demand for Constellation's existing generation assets, particularly those reliant on traditional fuel sources. The potential for lower operational costs or superior environmental performance from these substitutes could lead customers to switch, impacting Constellation's market share and profitability.
Consider the following potential substitute threats:
- Advanced Geothermal: Technologies that can access deeper, hotter geothermal resources more efficiently could unlock vast amounts of baseload power with minimal environmental impact.
- Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): Beyond Constellation's own SMR initiatives, other developers are progressing with designs that promise enhanced safety, scalability, and potentially lower upfront costs for nuclear power generation.
- Fusion Energy: While still in developmental stages, a successful commercial fusion power plant would represent a paradigm shift, offering a virtually limitless and clean energy source.
- Next-Generation Battery Storage: Significant improvements in battery energy density, lifespan, and cost reductions could make intermittent renewable sources more reliable and competitive, reducing the need for traditional baseload power.
The threat of substitutes for Constellation Energy is multifaceted, stemming from distributed generation, energy efficiency, and industrial fuel switching. Rooftop solar coupled with battery storage, for example, allows consumers to reduce reliance on grid power. By early 2024, solar panel costs had dropped over 90% in a decade, making self-generation more accessible. In 2023, U.S. solar installations grew by a record 37% year-over-year.
Energy efficiency measures also play a role. Smart thermostats and improved building insulation can significantly cut electricity demand. The U.S. Department of Energy noted by 2023 that building envelope advancements alone could reduce residential energy consumption by up to 30%. Furthermore, demand-side management programs, incentivizing reduced usage during peak times, saw significant participation in 2024, with some areas reducing peak demand by 10-15%.
Large industrial clients are increasingly exploring on-site generation, often using natural gas combined heat and power (CHP) systems, to gain control over costs and ensure supply reliability. The U.S. Department of Energy highlighted growing CHP adoption in 2024 for its efficiency and cost savings. Industrial consumers with flexible needs can also switch between electricity and direct fuel sources like natural gas based on price, a capability that directly impacts electricity demand for providers like Constellation. Fluctuations in natural gas prices throughout 2024 underscored this threat, influencing industrial energy sourcing strategies.
| Substitute Type | Key Driver | Impact on Constellation | 2023/2024 Data Point |
| Distributed Generation (Solar + Storage) | Decreasing costs, consumer desire for independence | Reduced demand for grid electricity | 37% YoY growth in U.S. solar installations (2023) |
| Energy Efficiency | Technological advancements, cost savings | Lower overall electricity consumption | Up to 30% potential reduction in residential use via building envelope tech (by 2023) |
| Industrial Fuel Switching | Cost arbitrage, supply chain control | Erosion of industrial customer base, reduced electricity sales volume | 10-15% peak demand reduction in some areas via demand-side management (2024) |
Entrants Threaten
The electricity generation and supply industry, particularly for large-scale nuclear and utility-scale renewable projects, demands colossal capital outlays. For instance, building a new nuclear power plant can easily cost tens of billions of dollars, creating a formidable hurdle for potential newcomers.
Constellation Energy, as a major player, leverages significant economies of scale through its extensive existing infrastructure. This allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger output, resulting in lower per-unit production costs compared to smaller, less established entities.
New entrants into the energy sector, especially those considering nuclear power like Constellation Energy, encounter a formidable barrier in the form of extensive regulatory and licensing requirements. These processes are not only complex but also exceptionally lengthy, demanding significant time and resources to navigate. For instance, obtaining approval for a new nuclear power plant can take many years, involving meticulous reviews by agencies such as the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) in the United States.
The need to comply with a myriad of state and federal environmental, safety, and operational regulations further amplifies this challenge. These regulations cover everything from plant design and construction to waste disposal and decommissioning, creating a high hurdle for any new player. In 2024, the ongoing scrutiny and evolving standards for energy infrastructure ensure that this regulatory burden remains a substantial deterrent to new entrants seeking to compete with established companies like Constellation.
Gaining access to established electricity transmission and distribution infrastructure presents a formidable barrier for potential new entrants in the energy sector. This existing network is often aging and experiencing congestion, necessitating substantial capital outlays and intricate coordination for any new interconnections. Such complexities inherently benefit incumbent firms that already possess established grid access and relationships.
Brand Loyalty and Established Customer Relationships
Constellation Energy benefits significantly from its deeply entrenched customer relationships, particularly with its extensive base of wholesale and large commercial clients secured through long-term contracts. This established network creates a substantial barrier for any new player attempting to enter the market.
Building the necessary trust and brand recognition in the highly regulated and capital-intensive energy sector is a lengthy and costly endeavor for new entrants. For instance, in 2024, the capital expenditure required to establish a new, competitive energy generation and distribution network is estimated to be in the billions of dollars, a significant hurdle.
- Established Customer Base: Constellation Energy serves millions of residential and business customers, many under multi-year agreements.
- Brand Recognition: Decades of operation have solidified Constellation's brand as a reliable energy provider.
- Switching Costs: For many commercial clients, the process and potential disruption of switching energy providers are significant deterrents.
- Regulatory Hurdles: New entrants face extensive regulatory approvals and compliance requirements, adding to the time and cost of market entry.
Specialized Expertise and Workforce
Operating a complex energy fleet, particularly nuclear facilities, demands a highly specialized and skilled workforce. This technical expertise is not easily acquired, posing a significant barrier for potential new entrants. For instance, the U.S. nuclear industry faced a shortage of qualified personnel, with the average age of nuclear engineers increasing, highlighting the long lead times for training and development.
New companies entering the energy sector would need to invest heavily in recruiting and training personnel with specific knowledge in areas like nuclear reactor operation, advanced grid management, and renewable energy integration. The scarcity and high cost of such talent make it a substantial hurdle. In 2024, the demand for specialized energy sector roles, such as grid modernization engineers and cybersecurity experts for power infrastructure, continued to outpace supply, driving up compensation and recruitment challenges.
- Specialized Skills Gap: The energy industry, especially nuclear, requires highly specific technical skills that take years to develop.
- High Training Costs: New entrants must absorb significant costs for workforce training and certification.
- Talent Scarcity: A limited pool of experienced professionals in critical energy fields makes recruitment difficult and expensive.
- Long Development Cycles: Building a competent workforce from scratch can take a decade or more, delaying market entry and operational readiness.
The threat of new entrants for Constellation Energy is significantly low due to immense capital requirements, stringent regulatory frameworks, and the need for specialized expertise. For example, the U.S. Energy Information Administration reported in 2024 that the average cost to build a new utility-scale solar farm can range from $1 million to $2 million per megawatt, and nuclear projects are exponentially higher, making entry prohibitively expensive for most.
Furthermore, the established customer base and brand loyalty cultivated by Constellation, coupled with high switching costs for commercial clients, present a substantial deterrent. Navigating the complex web of state and federal regulations, including those overseen by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), demands considerable time and financial investment, further limiting the appeal for new market participants.
The difficulty in accessing existing transmission infrastructure and the scarcity of specialized talent, particularly in nuclear operations, also act as significant barriers. These factors collectively ensure that new entrants face a steep uphill battle to compete effectively with established players like Constellation Energy.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Constellation Energy Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including SEC filings, investor relations reports, and industry-specific market research from firms like S&P Global Market Intelligence. This comprehensive approach ensures a deep understanding of the competitive landscape.