Compass Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Compass Bundle
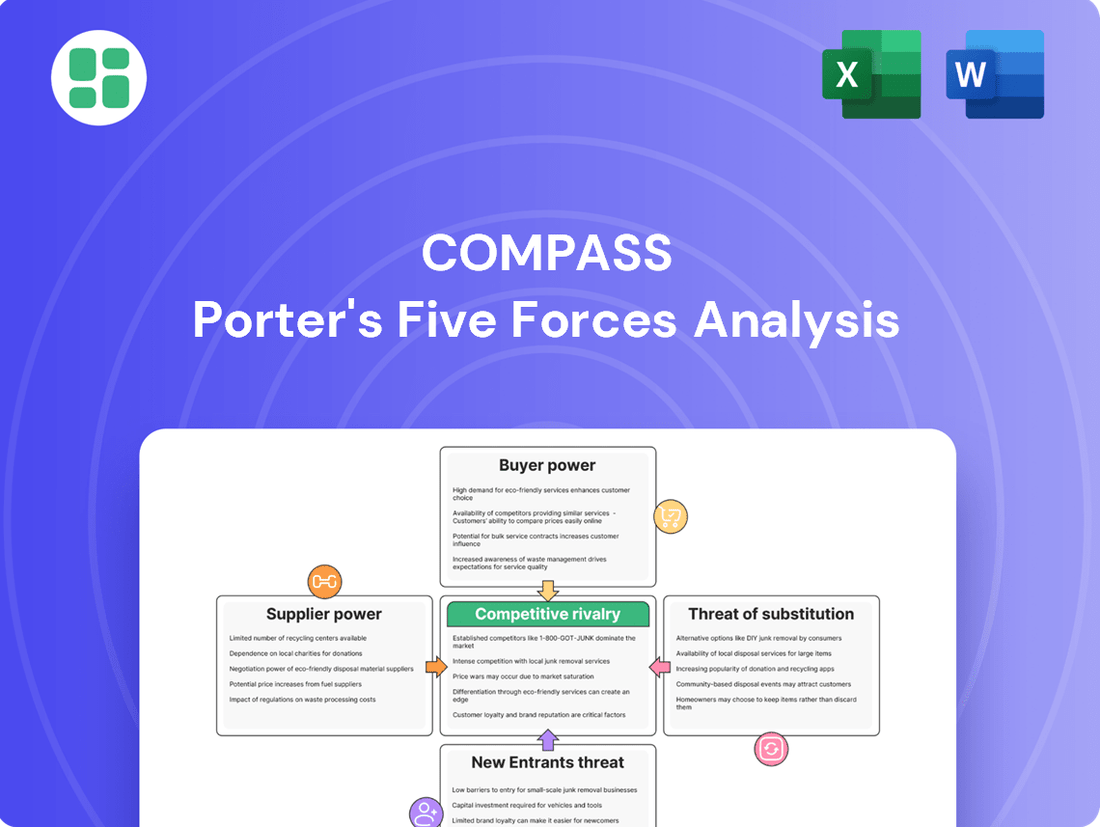
Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals how intensely Compass operates within its industry, examining threats from new entrants, the power of buyers and suppliers, and the availability of substitutes. Understanding these pressures is crucial for any business aiming to thrive.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Compass’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Compass's reliance on its proprietary technology platform positions key infrastructure, software, and data analytics suppliers with considerable bargaining power. If these suppliers provide unique or deeply integrated solutions, Compass faces high switching costs, amplifying supplier leverage. For instance, a significant portion of Compass's operational efficiency in 2024 was tied to specialized cloud infrastructure providers, whose pricing power could impact Compass's cost structure.
Real estate data providers hold significant bargaining power over Compass. Access to comprehensive and accurate market trends, property listings, and demographic information is fundamental to Compass's business model and its agents' success.
Suppliers offering exclusive or superior datasets, especially those that fuel AI-driven insights, can leverage this importance to negotiate favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, the demand for granular, real-time property data for predictive analytics continued to rise, increasing the leverage of key data aggregators.
While Compass possesses internal marketing capabilities, it may still engage external providers for specialized advertising, lead generation, or advanced digital marketing strategies. The leverage these marketing and advertising service providers hold hinges on their capacity to deliver high-quality leads or access unique marketing channels crucial for agent success and client acquisition.
The bargaining power of these suppliers is generally diminished by a fragmented market for marketing and advertising services. For instance, the digital advertising market in 2024 features numerous agencies and platforms, preventing any single provider from dictating terms to a large entity like Compass.
Talent (Real Estate Agents)
While real estate agents are Compass's primary clients, they also function as a critical supply of talent and market access. The company's success hinges on its capacity to draw in and keep high-performing agents, who are invaluable assets. This reliance means that a robust demand for top-tier agents can significantly amplify their individual bargaining power against brokerages like Compass.
The bargaining power of talent, specifically real estate agents, is a key consideration for Compass. These agents are not just customers; they are the lifeblood of the brokerage, bringing in business and representing the brand in local markets. Compass's ability to offer a compelling platform, cutting-edge technology, and supportive services directly influences its ability to attract and retain these crucial individuals.
- Agent Retention and Productivity: Compass reported that in Q1 2024, its agent retention rate remained strong, reflecting the value proposition offered to its agents. The company aims to empower agents with tools that boost their productivity, thereby increasing their overall value and leverage.
- Market Demand for Top Agents: In competitive real estate markets, the demand for highly productive and reputable agents often outstrips supply. This scarcity inherently strengthens the bargaining position of these sought-after professionals when negotiating terms with brokerages.
- Compensation and Commission Structures: The ability of agents to command higher commission splits or better support services is directly tied to their individual performance and the overall demand for their services in the market.
- Platform Value Proposition: Compass's investment in technology and agent support services is designed to mitigate the bargaining power of agents by providing a superior environment that reduces their incentive to seek alternative brokerages.
Office Space and Infrastructure Providers
Compass, as a brokerage firm with a physical footprint, relies heavily on securing office spaces and associated infrastructure. The cost and availability of these essential resources are directly influenced by the bargaining power of landlords and facility management providers.
The bargaining power of these suppliers is largely dictated by the prevailing conditions in the commercial real estate market within Compass's operating regions. In robust urban centers, where demand for prime office locations is consistently high, suppliers often wield moderate to significant leverage.
For instance, in Q1 2024, major metropolitan areas like New York City saw average office rents remain elevated, with some prime submarkets experiencing vacancy rates below 10%. This tight market dynamic grants landlords considerable power in lease negotiations.
- Supplier Dependence: Compass's need for physical office spaces in strategic locations makes it dependent on a limited number of landlords in desirable markets.
- Market Conditions: The bargaining power of office space providers fluctuates with commercial real estate vacancy rates and rental price trends in specific geographic areas.
- Competitive Landscape: In competitive urban markets, where multiple brokerages vie for premium office space, the power of suppliers to dictate terms can be substantial.
Suppliers of proprietary technology, specialized data, and essential infrastructure hold significant sway over Compass due to high switching costs and integration dependencies. For example, in early 2024, the reliance on specific cloud providers for data analytics meant Compass faced potential cost increases if these suppliers raised prices.
The bargaining power of real estate data providers is substantial, as accurate market trends and property information are critical for Compass's operations and agent success. Suppliers offering unique, AI-ready datasets, particularly those enabling predictive analytics, gained leverage in 2024, as demand for such granular insights intensified.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factor | 2024 Impact Example |
|---|---|---|
| Proprietary Tech/Cloud Providers | High switching costs, deep integration | Potential for price increases on specialized infrastructure |
| Real Estate Data Providers | Criticality of data for business model, AI-readiness | Increased leverage for providers of granular, real-time property data |
| Marketing/Advertising Services | Fragmented market limits individual provider power | Compass can leverage competition among numerous agencies |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Compass, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Pinpoint exactly where competitive pressures are biting with a visual breakdown of each force, making it easy to identify and address your biggest strategic challenges.
Customers Bargaining Power
Real estate agents hold significant bargaining power because they can easily switch brokerages or even operate independently, seeking the best commission splits, technology, and support. In 2024, the competitive landscape for agent recruitment means brokerages must offer attractive terms to retain talent.
Factors like the percentage of commission an agent keeps, access to advanced CRM systems, robust marketing tools, and the brokerage's brand recognition directly influence how much leverage agents have. If Compass, for instance, doesn't meet these agent expectations, they can readily move to a competitor.
Homebuyers and sellers, while not direct customers of Compass, wield considerable influence over the agents who are. Their increasing access to online resources allows for easier comparison of services and commission rates, putting pressure on agents and, by extension, Compass.
The National Association of Realtors (NAR) settlement, effective August 2024, is a significant factor here. This agreement allows buyers to directly negotiate agent commissions, a shift that fundamentally alters the power dynamic. For instance, if a buyer secures a lower commission rate, it directly impacts the compensation structure for the agent, who is a Compass affiliate.
This increased leverage for buyers and sellers means they can more readily shop around for agents offering the best value. In 2023, the average real estate commission in the US was around 5.5%, but with the new settlement, this figure is expected to see downward pressure as buyers gain more negotiating power, potentially impacting Compass's agent recruitment and retention strategies.
The increasing digital fluency of consumers significantly amplifies their bargaining power. These digitally savvy individuals now anticipate slick online interfaces and tailored services, placing higher demands on the technological capabilities of businesses they engage with. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of consumers across various sectors, estimated to be over 70%, reported preferring to interact with companies online for purchases and service inquiries.
This heightened expectation for digital experiences indirectly empowers consumers. It compels service providers, such as real estate brokerages, to invest heavily in technology to meet these demands. Agents, in turn, are more likely to align with brokerages that offer superior digital platforms, thereby increasing the collective leverage of these tech-forward consumers over the traditional brokerage structure.
Commission Structure and Transparency
Recent shifts in the real estate industry, notably the National Association of Realtors (NAR) settlement, have significantly boosted customer bargaining power by increasing commission transparency. This newfound clarity empowers buyers and sellers to negotiate more aggressively on agent fees, directly impacting brokerages. For instance, the settlement aims to curb the practice of listing brokers sharing commissions with buyer brokers, potentially altering transaction economics and forcing brokerages to adapt their fee structures.
This enhanced transparency allows consumers to more readily compare services and pricing, demanding greater value and competitive rates from real estate agents. Consequently, brokerages like Compass face increased pressure to justify their commission structures and demonstrate superior service offerings to retain clients. The expectation is a move towards more individualized commission agreements rather than the traditional fixed percentage.
Key impacts include:
- Increased Negotiation Leverage: Buyers and sellers can now more easily question and negotiate commission rates.
- Demand for Value: Consumers are likely to seek agents who offer demonstrably higher value for their fees.
- Pressure on Brokerage Fees: Brokerages may need to offer more flexible or lower commission structures to remain competitive.
- Shift in Commission Practices: The traditional co-brokerage commission model is being re-evaluated, potentially leading to direct negotiation between buyers and their agents.
Availability of Alternative Brokerage Models
The availability of diverse brokerage models significantly enhances customer bargaining power. Agents and their clients can easily opt for discount brokerages, flat-fee services, or even direct For Sale By Owner (FSBO) platforms, bypassing traditional or tech-forward options like Compass. This proliferation of alternatives means customers can readily switch if Compass's services are not perceived as competitive or value-driven.
In 2024, the real estate brokerage landscape continued to see a rise in alternative models. For instance, many discount brokerages maintained market share by offering significantly lower commission rates, often around 1% to 3% compared to the traditional 5% to 6% split. Flat-fee services also gained traction, providing a predictable cost structure for sellers, which directly challenges the percentage-based fees common among many established brokerages.
- Diverse Options: Customers have access to discount brokers, flat-fee services, and FSBO platforms.
- Increased Leverage: The variety of alternatives empowers customers to negotiate better terms or switch providers.
- Competitive Pressure: Compass faces pressure to remain competitive as customers can easily find lower-cost or alternative solutions.
- Market Dynamics: The ongoing growth of alternative models in 2024 underscores their impact on customer expectations and bargaining power.
The bargaining power of customers in the real estate sector has significantly increased, largely due to enhanced transparency and a wider array of service options. The NAR settlement effective August 2024, allowing buyers to directly negotiate agent commissions, is a pivotal development. This empowers consumers to seek better value, potentially driving down average commission rates from the 2023 US average of 5.5%.
The digital fluency of consumers also amplifies their leverage. By 2024, over 70% of consumers preferred online interactions, demanding slick digital interfaces. This pushes brokerages to invest in technology, giving agents more choice and indirectly increasing consumer influence on service providers. The proliferation of discount brokerages and flat-fee services in 2024 further provides consumers with readily available, lower-cost alternatives, intensifying competitive pressure on traditional models.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| NAR Settlement (Aug 2024) | Increased negotiation leverage for buyers on commissions | Direct negotiation of buyer agent commissions now permitted. |
| Digital Fluency | Higher consumer expectations for online services | >70% of consumers prefer online interactions for purchases/inquiries. |
| Alternative Brokerage Models | Greater choice and ability to bypass traditional services | Discount brokerages offer rates of 1-3%; flat-fee services gain traction. |
| Commission Transparency | Enables easier comparison of services and pricing | Potential downward pressure on the 5.5% average US commission (2023). |
Full Version Awaits
Compass Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. The comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis within this file meticulously examines the competitive landscape, detailing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The real estate brokerage sector is characterized by intense competition due to its fragmented nature. Thousands of traditional, independent, and increasingly tech-focused companies actively compete for both real estate agents and market share.
This crowded landscape, populated by national powerhouses and local specialists alike, fuels fierce rivalry. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. saw over 1.5 million actively licensed real estate agents, highlighting the sheer volume of individuals and firms vying for transactions.
Each firm strives to capture a portion of the market, leading to aggressive strategies in agent recruitment and client acquisition, further intensifying the competitive pressures within the industry.
Compass faces intense rivalry from proptech firms leveraging cutting-edge AI, VR, and data analytics, forcing constant innovation to stay ahead. Traditional brokerages are also pouring resources into technology, intensifying the competitive landscape.
For instance, Zillow Group, a major competitor, reported a revenue of $1.8 billion in 2023, demonstrating significant investment in its technology platforms. This technological arms race means companies like Compass must continuously enhance their digital offerings to attract and retain clients in the rapidly evolving real estate market.
The real estate market sees intense competition for top talent, with brokerages vying to attract and keep high-performing agents. This battleground is fought through competitive commission structures, advanced technology platforms, robust marketing assistance, and comprehensive benefits. Companies that can offer the most appealing packages will gain a significant edge.
Compass has demonstrated a strong focus on this area, achieving an impressive agent retention rate of 97.5% in the second quarter of 2025. This high retention is a testament to their ability to provide the resources and environment agents need to succeed, directly impacting their market share and operational efficiency.
Market Share Dynamics and Acquisitions
Competitive rivalry in the real estate sector is marked by continuous shifts in market share, with key players like Compass strategically acquiring competitors to bolster their presence and agent networks. This aggressive M&A strategy underscores a highly competitive environment where firms are consolidating to achieve greater economies of scale and broader geographic coverage.
Compass, for instance, has been a significant player in this consolidation trend. In 2023, the company continued its efforts to integrate acquired brokerages, aiming to leverage these moves for increased market share and operational efficiencies. This drive for expansion is a direct response to the intense competition, as companies vie for dominance.
- Market Share Volatility: The real estate market experiences frequent fluctuations in market share as companies grow organically and through acquisitions.
- Acquisition as a Growth Strategy: Firms like Compass utilize acquisitions to rapidly expand their agent base and geographical reach, a common tactic in this competitive landscape.
- Consolidation Drivers: The pursuit of economies of scale and enhanced market power fuels the ongoing consolidation trend within the industry.
Commission Compression and Regulatory Changes
Competitive rivalry is intensifying due to commission compression and evolving regulatory landscapes. Recent significant legal settlements, such as those impacting major brokerages, have driven greater transparency in commission structures, directly leading to downward pressure on agent fees. This squeeze on traditional revenue streams forces companies like Compass to differentiate their value proposition beyond just commission rates, intensifying competition on service quality and technological innovation.
The pressure on commissions is a significant factor in the brokerage industry. For instance, in 2024, several large real estate firms faced substantial settlements related to commission practices, which are expected to continue influencing fee structures across the market. This environment necessitates a strategic shift, pushing firms to invest more heavily in technology and superior customer service to justify their fees and attract both agents and clients.
- Commission Compression: Downward pressure on agent fees due to transparency and legal settlements.
- Regulatory Impact: Increased scrutiny on commission structures is forcing industry-wide adjustments.
- Differentiation Imperative: Companies must compete on service quality and technology, not just commission.
- Heightened Rivalry: Competition is increasing as firms seek to capture market share through enhanced offerings.
The real estate brokerage sector is intensely competitive, with a vast number of firms vying for agents and market share. This rivalry is amplified by technological advancements and a constant drive for talent acquisition.
Companies are investing heavily in innovative platforms, as seen with Zillow Group's reported 2023 revenue of $1.8 billion, reflecting significant tech investment. This arms race necessitates continuous digital enhancement for market relevance.
The battle for top agents is fierce, with competitive compensation, technology, and support being key differentiators. Compass's impressive 97.5% agent retention rate in Q2 2025 highlights the success of providing a supportive environment.
Consolidation through acquisitions is a prevalent strategy, with firms like Compass acquiring competitors to expand reach and agent networks, aiming for economies of scale and broader market presence.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (USD Billions) | Key Competitive Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Zillow Group | 1.8 | Technology Platform Investment |
| Compass | N/A (Publicly Traded) | Agent Retention & Support |
| National Brokerages | Varies | Market Share & Geographic Reach |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For-sale-by-owner (FSBO) platforms represent a significant substitute threat to traditional real estate brokerages. These online marketplaces empower homeowners to list and market their properties directly, bypassing agents and their associated commission fees. This direct approach appeals to a segment of sellers prioritizing cost savings over the full-service support of a professional agent.
The rise of discount brokerages and flat-fee services presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional, full-service firms. These alternative models, often charging as little as $0 per trade, directly compete by offering a lower-cost entry point for investors. For instance, by the end of 2023, many major discount brokers had eliminated commissions on stock and ETF trades, a trend that continued into 2024, making them highly attractive to cost-conscious individuals.
This shift forces established brokerages, like Compass, to re-evaluate their fee structures and clearly articulate the added value of their comprehensive services. The accessibility and affordability of these substitutes challenge the traditional commission-based revenue streams, compelling a focus on advisory, research, and personalized support to differentiate. As of early 2024, the market share of discount and robo-advisors continues to grow, indicating a sustained preference for these more economical options among a segment of the investing public.
Online real estate platforms like Zillow and Redfin offer a significant threat of substitutes for traditional real estate agents. These platforms provide vast property listings, detailed market data, and virtual tours, allowing buyers to conduct extensive research independently. In 2024, Zillow reported over 200 million monthly users, demonstrating the widespread adoption of these digital tools for property discovery.
These digital marketplaces empower consumers by enabling direct communication with sellers or listing agents, often bypassing the need for an intermediary. This direct access reduces the perceived value of traditional agent services for certain aspects of the transaction. For instance, many buyers now initiate their property search and even schedule viewings directly through these online portals.
AI-Powered Real Estate Tools
AI-powered real estate tools are emerging as a significant threat of substitutes for traditional real estate agents. These advanced platforms can automate tasks like property valuation, lead qualification, and even initial client communication, directly impacting the demand for certain agent services. For instance, in 2024, the adoption of AI in real estate is projected to streamline transaction processes, potentially reducing the time agents spend on administrative duties by up to 30%.
While not a complete replacement, these AI solutions offer a more cost-effective and efficient alternative for specific aspects of the real estate transaction. This can lead to a reduction in the overall need for human intervention in certain areas, thereby increasing the threat of substitutes. Consider the growing market for automated property management software, which saw a 15% year-over-year growth in 2023, indicating a clear shift towards technology-driven solutions.
- AI Valuation Tools: Platforms offering automated comparative market analyses (CMAs) can provide quick property valuations, challenging the traditional role of agents in this area.
- Virtual Assistants: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are increasingly handling initial client inquiries and appointment scheduling, reducing the need for agents' early-stage engagement.
- Online Listing Platforms: Enhanced search and filtering capabilities on major real estate portals allow buyers to conduct more independent property searches, potentially bypassing agents for initial discovery.
- Proptech Solutions: The broader proptech sector is developing integrated solutions for various real estate needs, from financing to legal documentation, offering alternatives to agent-facilitated services.
Fractional Ownership and Blockchain
Emerging fractional ownership models, often powered by blockchain, are changing how people interact with real estate. These platforms allow multiple investors to own a piece of a property, making real estate investment more accessible. For instance, platforms like Arrived and Landa enable investments starting from as little as $100 in single-family homes, offering an alternative to traditional, high-barrier-to-entry real estate purchases.
While these aren't direct substitutes for buying or selling a primary residence, they present alternative avenues for capital deployment within the real estate sector. This can potentially shift investment flows away from conventional property transactions, impacting demand for full ownership. By 2024, the global real estate tokenization market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, highlighting the growing significance of these alternative investment structures.
- Fractional Ownership Accessibility: Platforms allow investment in real estate starting from low amounts, democratizing access.
- Blockchain Facilitation: Distributed ledger technology enhances transparency and efficiency in fractional ownership transactions.
- Market Impact: These models offer alternative investment channels, potentially diverting capital from traditional real estate purchases.
- Market Growth: The real estate tokenization market is experiencing significant growth, indicating increasing investor interest in fractionalized assets.
The threat of substitutes in real estate is amplified by online platforms and discount services that offer lower-cost alternatives to traditional brokerages. These substitutes appeal to consumers seeking to reduce fees and streamline transactions, forcing established players to emphasize value-added services. The increasing adoption of technology, including AI and fractional ownership models, further diversifies these alternatives.
For-sale-by-owner (FSBO) platforms and discount brokerages directly challenge traditional real estate agents by offering lower commission structures or enabling direct property sales. These alternatives, like flat-fee services, gained significant traction by 2024, with many brokers eliminating trading commissions. This trend pressures firms like Compass to highlight their unique value propositions beyond basic transaction facilitation.
Online real estate portals such as Zillow and Redfin provide buyers with extensive data and search capabilities, reducing reliance on agents for initial property discovery. With over 200 million monthly users in 2024, Zillow exemplifies how digital tools empower consumers. AI-powered tools are also automating tasks like property valuation, potentially reducing agent involvement in specific service areas.
| Substitute Type | Key Features | Impact on Traditional Brokerages | 2024 Market Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| FSBO Platforms | Direct seller-to-buyer listing, reduced commission | Undermines agent commission revenue | Growing user base on platforms like Zillow |
| Discount Brokerages | Low or zero commission fees on trades | Attracts cost-sensitive investors | Elimination of trading commissions by major players |
| Online Portals (Zillow, Redfin) | Extensive listings, market data, virtual tours | Reduces agent's role in initial property search | 200M+ monthly users for Zillow |
| AI Valuation Tools | Automated property valuations (CMAs) | Challenges agent's valuation expertise | Projected 30% reduction in agent admin time |
| Fractional Ownership | Low-barrier real estate investment | Diverts capital from traditional purchases | Projected hundreds of billions in tokenization market |
Entrants Threaten
The significant capital needed to launch a national, tech-focused real estate brokerage like Compass acts as a formidable barrier. Consider that in 2023, venture capital funding for proptech companies reached $12.1 billion globally, highlighting the substantial investment required to compete. This financial hurdle deters many aspiring disruptors.
Compass benefits from strong brand recognition, a significant barrier for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, Compass reported a brand value of approximately $2.5 billion, underscoring its established market presence. This, coupled with an extensive network of over 25,000 agents nationwide, creates a formidable challenge for any new entrant aiming to gain traction and build similar levels of trust and reach.
Compass's proprietary technology platform and the vast amounts of data it has accumulated act as significant barriers to entry. Building an equivalent integrated system, especially one incorporating advanced features like AI and sophisticated data analytics, demands substantial investment in research and development and a high level of specialized expertise.
For instance, in 2024, the average R&D spending for major technology firms in the fintech sector reached billions of dollars, underscoring the capital intensity required to innovate. New entrants would face immense challenges in replicating Compass's established technological infrastructure and data moats, making it difficult to compete effectively on a similar technological footing.
Regulatory and Licensing Hurdles
The real estate sector presents substantial regulatory and licensing challenges for potential new entrants. Obtaining the necessary licenses to operate as a brokerage or even as individual agents requires significant time, effort, and adherence to strict educational and examination standards, which vary considerably by state. For instance, in 2024, states like California and New York maintain rigorous pre-licensing education requirements, often exceeding 100 hours, coupled with ongoing continuing education mandates.
These regulatory complexities extend beyond individual licensing to encompass the legal frameworks governing property transactions, contract law, disclosure requirements, and fair housing regulations. New firms must invest heavily in understanding and complying with these intricate legal structures, which can include state-specific zoning laws, environmental regulations, and landlord-tenant acts. The cost associated with legal counsel and compliance management acts as a significant deterrent, effectively raising the barrier to entry.
- Licensing Requirements: Varying educational hours and examination pass rates across states create an initial hurdle.
- Legal Frameworks: Complex transaction laws and disclosure obligations demand specialized legal expertise.
- Compliance Costs: Ongoing investment in legal reviews, training, and adherence to evolving regulations adds to operational expenses.
- State-Specific Regulations: Navigating diverse state-level rules for agency, advertising, and consumer protection requires dedicated resources.
Intense Competition and Market Saturation
The real estate brokerage sector is already a crowded space, with many regions experiencing significant market saturation. New companies entering this arena must contend with a substantial number of existing firms, many of which possess well-established client networks and substantial financial resources. This makes it challenging for newcomers to gain traction and acquire a meaningful share of the market.
For instance, in 2024, the United States saw over 2 million active real estate agents, a figure that underscores the intense competition. Established brokerages often benefit from brand recognition and long-standing relationships with buyers, sellers, and other industry professionals, creating high barriers to entry for any new entrant aiming to disrupt the status quo.
- High Number of Existing Brokerages: The sheer volume of established real estate firms presents a significant hurdle.
- Established Client Relationships: Incumbents leverage deep-rooted connections with clients, making it difficult for new entrants to attract business.
- Brand Recognition and Trust: Well-known brokerages benefit from existing trust and familiarity among consumers.
- Capital Requirements: Significant investment is often needed to build a brand, technology, and agent network to compete effectively.
The threat of new entrants for a company like Compass is generally moderate due to several significant barriers. These include the substantial capital required for operations and technology development, strong existing brand recognition, and the complexity of regulatory and licensing requirements across different states. The highly competitive landscape, with millions of existing real estate agents and established brokerages, further complicates market entry.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Supporting Data (2024 unless noted) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for technology, marketing, and agent recruitment. | Deters firms without significant funding. | Proptech funding reached $12.1 billion globally in 2023. |
| Brand Recognition | Established trust and market presence. | Makes it difficult for new brands to gain traction. | Compass brand value estimated at $2.5 billion. |
| Technology & Data | Proprietary platforms and accumulated data. | Requires substantial R&D to replicate. | Fintech R&D spending in billions for major firms. |
| Regulatory & Licensing | Complex state-specific licensing and transaction laws. | Demands significant time, cost, and legal expertise. | California and New York require 100+ hours of pre-licensing education. |
| Market Saturation | Large number of existing brokerages and agents. | Intensifies competition for market share. | Over 2 million active real estate agents in the US. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, financial statements of key players, and publicly available regulatory filings. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive pressures.