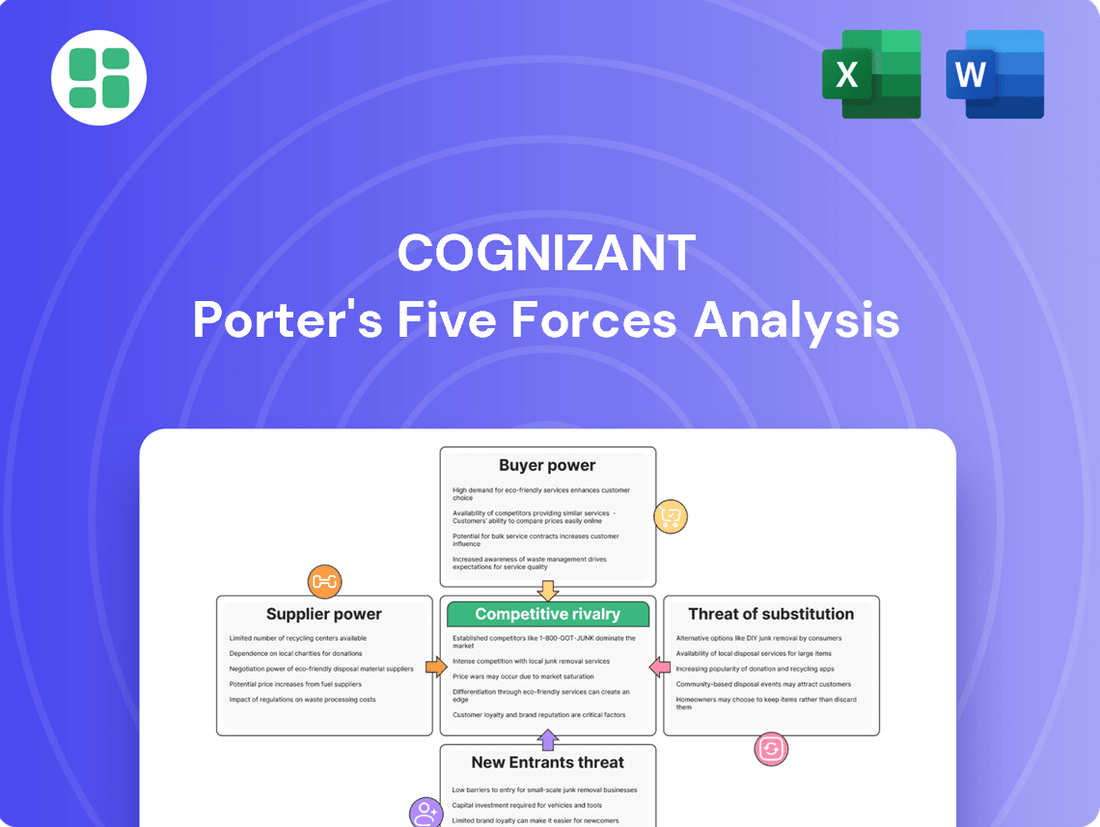
Cognizant Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cognizant Bundle
Understanding Cognizant's competitive landscape requires a deep dive into the five forces that shape its industry. From the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers to the threat of new entrants and substitutes, each element plays a crucial role in defining its market position.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis unlocks a comprehensive understanding of these dynamics, revealing the intensity of competition and Cognizant's strategic responses. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Cognizant's reliance on a specialized talent pool, particularly in high-demand fields like artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and cybersecurity, significantly influences supplier power. The scarcity of these highly skilled IT professionals and consultants means that these individuals, in essence, become suppliers of critical human capital.
The global shortage of specialized tech talent directly translates into increased bargaining power for these professionals. This can manifest as demands for higher salaries, more attractive benefits packages, and greater flexibility, all of which can impact Cognizant's operational costs and its capacity to fulfill client projects effectively.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for cloud computing experts outstripped supply, leading to average salary increases of 15-20% for these roles in many markets. Similarly, cybersecurity professionals saw their compensation rise due to the escalating threat landscape, putting pressure on companies like Cognizant to retain and attract top talent.
Major technology platform providers like Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud hold significant bargaining power over IT services firms such as Cognizant. Cognizant's reliance on these cloud infrastructures for delivering digital transformation projects means these vendors can influence pricing through licensing and service fees. For instance, in 2023, the global cloud computing market was valued at over $500 billion, with these three providers dominating a substantial share, giving them considerable leverage.
Niche consulting firms and specialized subcontractors can wield significant bargaining power over larger entities like Cognizant, particularly when they possess unique, in-demand expertise. Their ability to command higher rates stems from the difficulty in finding comparable skills elsewhere, especially for highly bespoke or cutting-edge technological solutions. This is evident in the IT services sector where demand for AI, cybersecurity, and specialized cloud migration skills consistently outstrips supply, allowing smaller, focused players to negotiate favorable terms.
Data and Analytics Tool Providers
The bargaining power of data and analytics tool providers for Cognizant is a significant factor. Companies relying on advanced platforms for business intelligence and data integration, like Cognizant, often depend on specialized software and data sources. The proprietary nature of these tools can limit alternatives, potentially increasing costs for Cognizant. For instance, if a key analytics platform used by Cognizant experiences a price hike, it directly impacts their cost structure and the value proposition offered to clients.
The essentiality of these tools for delivering cutting-edge insights means Cognizant has limited room to negotiate without potentially compromising service quality. In 2024, the market for AI-driven analytics platforms saw substantial investment, with companies like Snowflake and Databricks reporting significant revenue growth, indicating strong demand and pricing power for leading providers. This trend suggests that suppliers of these critical technologies hold considerable leverage.
- High Switching Costs: Implementing and integrating new data analytics platforms can be complex and expensive, creating high switching costs for Cognizant.
- Supplier Concentration: A few dominant players often control advanced analytics and AI tools, concentrating bargaining power among a limited number of suppliers.
- Proprietary Technology: The unique and advanced nature of many data analytics solutions means few direct substitutes are available.
- Industry Dependence: Cognizant's ability to offer competitive insights is directly tied to the capabilities of its data and analytics tool providers.
Infrastructure and Connectivity Providers
The bargaining power of infrastructure and connectivity providers for Cognizant is moderate. While there are numerous telecom and data center providers globally, the specialized nature of high-speed, reliable, and secure connectivity required for IT services means that switching costs can be significant. In 2024, global IT infrastructure spending was projected to reach over $1.3 trillion, indicating a substantial market but also highlighting the critical role these suppliers play.
- Dependence on Reliable Networks: Cognizant's ability to deliver services across geographies hinges on robust network infrastructure from companies like AT&T, Verizon, or regional equivalents.
- Data Center Services: The availability and cost of data center space and services from providers such as Equinix or Digital Realty directly impact Cognizant's operational costs and scalability.
- Switching Costs: Migrating complex IT operations and data between different infrastructure providers can be time-consuming and expensive, limiting Cognizant's ability to easily shift suppliers.
- Supplier Consolidation: In certain regions, a degree of consolidation among major telecommunication and data center providers can increase their leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Cognizant is influenced by the specialized nature of IT talent and technology platforms. Scarcity of highly skilled professionals in areas like AI and cloud computing grants these individuals significant leverage, driving up compensation demands. Furthermore, major cloud infrastructure providers such as AWS and Azure hold considerable sway due to Cognizant's reliance on their services for project delivery.
Niche consulting firms with unique expertise can also command higher rates, as finding comparable skills is challenging. The essentiality of advanced data analytics and AI tools for providing competitive insights further amplifies the power of their providers. High switching costs associated with integrating these platforms, coupled with supplier concentration and proprietary technology, solidify their strong negotiating position.
| Supplier Type | Key Providers | Impact on Cognizant | 2024 Data Point/Trend |
| Specialized IT Talent | Individual Professionals | Increased salary and benefit costs | 15-20% salary increase for cloud experts |
| Cloud Infrastructure | AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud | Pricing leverage on services and licensing | Global cloud market > $500 billion (2023) |
| Niche Consulting/Subcontractors | Specialized Firms | Higher rates for unique expertise | High demand for AI, Cybersecurity skills |
| Data & Analytics Platforms | Snowflake, Databricks | Potential price hikes, limited alternatives | Strong revenue growth for leading providers |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Cognizant, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a clear, actionable framework for understanding industry dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Cognizant's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by client concentration. A few major clients can wield considerable power, demanding lower prices or more favorable terms due to the substantial revenue they represent. For instance, in 2023, Cognizant's top ten clients accounted for approximately 26% of its total revenue, highlighting the leverage these large customers possess.
Switching costs for Cognizant's customers can significantly influence their bargaining power. If it's difficult and expensive for a client to move their IT services to a competitor, they are less likely to switch, giving Cognizant more leverage. These costs can include the expense of migrating data, retraining staff on new systems, and the effort involved in integrating a new provider's services with existing infrastructure.
For instance, a large enterprise relying on Cognizant for complex cloud migration and custom software development likely faces substantial switching costs. These can encompass not just direct financial outlays but also the disruption to business operations during the transition period. In 2023, the IT services market saw continued demand for specialized skills, meaning retraining costs for a client's internal teams could be considerable if they were to switch providers.
Customer price sensitivity for IT services like those offered by Cognizant is a significant factor. In 2024, many businesses continued to face budget pressures, making them more inclined to negotiate pricing or seek out providers offering more competitive rates. This is particularly true in a market with numerous alternative IT service providers, where the perceived value of a specific vendor's offering directly impacts a customer's willingness to pay a premium.
Customer Knowledge and Information Asymmetry
Cognizant's clients are increasingly sophisticated, possessing a strong understanding of IT services and industry pricing benchmarks. This heightened customer knowledge significantly reduces information asymmetry, empowering clients to negotiate more favorable terms. For instance, many large enterprises now have robust internal IT departments and experienced procurement teams that can effectively evaluate service proposals and identify areas for cost optimization.
Well-informed clients can leverage their expertise to challenge Cognizant's pricing structures and demand greater transparency in service delivery. This pressure is amplified when clients have access to comparative data on IT service costs and performance metrics from other vendors. As of early 2024, the global IT services market continues to see a trend towards greater client-side expertise, with many organizations investing heavily in digital transformation and upskilling their internal teams.
- Informed Clients Drive Price Pressure: Clients with deep IT knowledge can more effectively negotiate pricing, pushing for competitive rates based on industry standards.
- Reduced Information Asymmetry: As clients gain more insight into service costs and value, the gap in information between them and Cognizant narrows, shifting bargaining power.
- Impact on Service Quality Demands: Enhanced client understanding also leads to higher expectations regarding the quality and efficiency of IT services delivered.
- Benchmarking and Vendor Comparisons: Clients actively benchmark Cognizant’s offerings against competitors, using this data to strengthen their negotiating position.
Threat of Customer In-Sourcing
The threat of customer in-sourcing poses a significant challenge to Cognizant. Clients may choose to build or expand their internal IT capabilities, diminishing their need for external partners like Cognizant. This shift is often driven by a desire for greater strategic control and cost savings.
Factors such as the increasing availability of skilled IT talent globally and the perceived cost-effectiveness of managing IT functions in-house can amplify this threat. For instance, companies looking to reduce reliance on third-party vendors might invest in developing their own cybersecurity or cloud management teams.
- Increased In-sourcing Potential: As technology becomes more commoditized, clients might find it more feasible and cost-effective to bring IT functions in-house.
- Talent Availability: The global IT talent pool's growth, particularly in areas like cloud computing and data analytics, makes in-sourcing a more viable option for many businesses.
- Strategic Control: Companies seeking tighter control over their IT infrastructure, data security, and innovation pipelines may opt for in-sourcing to align IT directly with business objectives.
- Cost Optimization: For certain routine or high-volume IT tasks, clients may calculate that in-sourcing offers long-term cost advantages over outsourcing contracts.
Cognizant's customers possess considerable bargaining power, particularly due to client concentration, where a few major clients can demand better terms. In 2023, Cognizant's top ten clients represented about 26% of its revenue, underscoring the leverage these large accounts hold.
Switching costs for clients are a key factor influencing their power; high costs make clients less likely to move to competitors, thus strengthening Cognizant's position. These costs can include data migration, retraining, and integration efforts.
Price sensitivity is also a major driver, especially as businesses in 2024 faced budget constraints, leading them to seek more competitive pricing. This is amplified in a market with many IT service providers, where perceived value directly impacts willingness to pay a premium.
Sophisticated clients, armed with industry knowledge and benchmarks, can effectively negotiate pricing and demand greater transparency. This trend is evident as many enterprises bolster their internal IT expertise, as seen in the ongoing digital transformation initiatives in early 2024.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Trend (as of 2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Client Concentration | High (for large clients) | Top 10 clients accounted for ~26% of revenue in 2023. |
| Switching Costs | Lowers customer power | Complex IT projects (e.g., cloud migration) incur significant migration and retraining expenses. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Budget pressures in 2024 increased client focus on cost-effectiveness. |
| Customer Knowledge | Increases customer power | Growing internal IT expertise and benchmarking capabilities among clients. |
Full Version Awaits
Cognizant Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Cognizant Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape within the IT services industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and insightful analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises and full readiness for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Cognizant operates in a highly competitive landscape populated by a significant number of large, global IT service providers. Companies like Accenture, Tata Consultancy Services (TCS), Infosys, and Wipro are major players with comparable capabilities, directly vying for market share and client contracts. This sheer volume of substantial rivals intensifies the competition.
Beyond these giants, the market also includes a multitude of smaller, specialized niche players. These firms often focus on specific technologies or industries, offering tailored solutions that can challenge larger competitors. The presence of both broad-spectrum global firms and focused niche providers creates a dynamic and aggressive competitive environment for Cognizant.
The IT and professional services industry's growth rate significantly influences competitive rivalry. In segments experiencing slower growth, such as certain mature IT outsourcing areas, competition intensifies as companies vie for market share from a limited pool of opportunities. This dynamic forces businesses like Cognizant to differentiate more aggressively on price or specialized services.
Conversely, rapid expansion in areas like cloud computing, AI, and digital transformation can temper direct competition. For instance, the global IT services market was projected to reach over $1.3 trillion in 2024, indicating substantial growth potential that can absorb multiple players. This robust growth allows companies to expand without necessarily taking share directly from rivals, though intense competition for talent and innovation remains.
Cognizant's competitive rivalry is significantly influenced by the differentiation of its services. While many IT services can be commoditized, Cognizant strives to distinguish itself through specialized industry expertise, particularly in areas like healthcare and financial services, and by developing proprietary methodologies for digital transformation and cloud migration. This focus on unique capabilities helps to mitigate direct price-based competition.
However, the IT services landscape remains intensely competitive. In 2024, the global IT services market is projected to reach over $1.3 trillion, with a substantial portion still subject to commoditization, especially for more basic or standardized offerings. When services are perceived as similar across providers, rivalry intensifies, often leading to price wars and reduced profit margins for companies like Cognizant.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
Cognizant, like other major IT service providers, faces significant exit barriers in the market. These can include substantial investments in physical infrastructure, such as data centers and office spaces, which are difficult to divest without significant loss. Furthermore, long-term contracts with clients often tie companies into service delivery for extended periods, making a swift exit impractical and financially burdensome.
The specialized nature of employee skills within the IT services sector also contributes to high exit barriers. Companies invest heavily in training and developing a workforce with expertise in areas like cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity. Disbanding or reallocating these highly skilled personnel can be challenging and costly, potentially leading to reputational damage if service commitments are not met during an exit process.
- High Capital Investment: IT firms often have significant fixed assets, including specialized software licenses and hardware, that depreciate rapidly and are hard to recover upon exit.
- Long-Term Client Commitments: Many IT service contracts span several years, creating obligations that prevent immediate withdrawal from the market. For instance, in 2024, major IT service providers continue to manage multi-year digital transformation projects for large enterprises.
- Specialized Workforce: The need for highly skilled and niche talent in areas like AI and cloud migration means companies have invested substantially in human capital, making it difficult to shed these resources quickly without incurring substantial severance costs and potential legal liabilities.
- Reputational Costs: Abruptly exiting projects or the market can severely damage a company's reputation, impacting its ability to engage in future business ventures or attract talent.
Intensity of Competition for Talent
The intense competition for skilled IT professionals significantly heightens rivalry among service providers like Cognizant. This constant battle for top talent drives up labor costs, forcing companies to invest heavily in recruitment, training, and retention programs. For instance, in 2024, the global IT talent shortage remained a critical issue, with reports indicating that companies were spending an average of 20% more on IT salaries compared to the previous year to secure qualified individuals.
This talent scarcity means that service providers are not only competing for client contracts but also for the very human capital required to deliver those services. Companies must differentiate themselves through attractive compensation, career development opportunities, and a strong company culture to win the war for talent. This directly impacts pricing strategies and the ability to scale operations efficiently, as the availability of skilled personnel becomes a key bottleneck.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: In 2024, median IT recruitment costs for specialized roles often exceeded $5,000, reflecting the difficulty in finding qualified candidates.
- Retention Challenges: High demand led to increased employee turnover, with voluntary attrition rates in the IT sector averaging 15-20% annually in many regions.
- Wage Inflation: The need to attract and retain talent resulted in significant wage inflation for IT roles, with some specialized skills seeing salary increases of up to 30% year-over-year.
- Impact on Service Delivery: Limited availability of key skills can delay project timelines and impact the quality of service delivery, directly affecting competitive positioning.
Competitive rivalry within the IT services sector is intense, driven by numerous global players and specialized niche firms. Cognizant competes directly with giants like Accenture, TCS, and Infosys, all offering similar capabilities. This crowded market, where differentiation is key, means companies must constantly innovate and leverage unique strengths, such as Cognizant's industry-specific expertise in healthcare and financial services, to stand out. The global IT services market, projected to exceed $1.3 trillion in 2024, offers growth but also fuels aggressive competition for market share and talent.
| Competitor | Market Cap (Approx. USD Billion, Mid-2024) | Key Service Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Accenture | 190+ | Digital Transformation, Cloud, Strategy, Operations |
| Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) | 170+ | IT Services, Consulting, Business Solutions |
| Infosys | 70+ | Digital Services, Cloud, AI, Consulting |
| Wipro | 40+ | IT Consulting, Digital Transformation, Cloud |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitute for external IT services, like those offered by Cognizant, is the strengthening or development of in-house IT departments. Companies are increasingly finding it feasible to bring IT functions back internally due to advancements in readily available software, cloud computing platforms, and the ability to acquire skilled IT talent.
This shift is driven by the growing accessibility of sophisticated IT tools and the potential for cost savings and greater control. For instance, the rise of low-code/no-code platforms allows business users to develop applications with minimal IT intervention, directly reducing the need for external development services. Furthermore, the cloud computing model, with its pay-as-you-go pricing, makes it more economical for many businesses to manage their own infrastructure and software needs rather than outsourcing.
In 2024, many enterprises are re-evaluating their outsourcing strategies, with a significant portion indicating a desire to insource critical IT functions. This trend is supported by the increasing availability of specialized IT talent in the global market, making it easier for companies to build robust internal teams capable of handling complex projects that were once exclusively the domain of external providers.
The rise of automation and AI tools presents a significant threat of substitution for IT service providers like Cognizant. These technologies can increasingly handle routine IT tasks, data analysis, and even certain client interactions, potentially lowering the cost and increasing the efficiency of service delivery compared to traditional human-led models.
For example, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can automate repetitive, rule-based tasks, and AI-powered platforms are becoming more sophisticated in areas like software testing and basic customer support, directly impacting the demand for certain service lines.
In 2024, the global market for AI in IT operations was projected to reach tens of billions of dollars, indicating a substantial and growing investment in these substitute technologies by businesses seeking operational efficiencies.
The rise of sophisticated open-source software and readily available Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms presents a significant threat of substitutes for companies like Cognizant. These alternatives offer comparable functionalities, often at a fraction of the cost of custom development or traditional IT services. For instance, the global open-source software market was valued at approximately $22.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong preference for cost-effective solutions.
These off-the-shelf solutions, with their lower upfront investment and quicker deployment cycles, directly challenge the demand for the bespoke development and managed services that form a core part of Cognizant's business. As businesses increasingly adopt these accessible platforms, they may reduce their reliance on external consulting firms for building and maintaining complex systems, thereby impacting revenue streams.
Freelance Platforms and Gig Economy
The proliferation of freelance platforms and the expanding gig economy presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional IT service providers like Cognizant. These platforms directly connect businesses with a vast pool of individual freelancers and small, specialized teams, offering a more agile and often cost-effective alternative for specific project needs.
This trend allows companies to bypass the overhead associated with larger, long-term engagements, accessing niche skills on demand. For instance, platforms like Upwork and Fiverr saw substantial growth, with Upwork reporting over $3.5 billion in gross service volume in 2023, indicating a strong preference for flexible, project-based talent acquisition.
- Increased Accessibility to Niche Skills: Businesses can readily find specialized talent for short-term projects, reducing the need for full-time hires or lengthy outsourcing contracts.
- Cost Efficiency: Freelancers often operate with lower overheads, translating to competitive pricing for project-based work compared to established service firms.
- Agility and Speed: The gig economy enables rapid team formation and project initiation, offering a faster turnaround for specific deliverables.
- Market Growth: The global freelance platform market size was valued at approximately $1.5 trillion in 2023 and is projected to continue its upward trajectory, underscoring the shift in how businesses procure talent.
Specialized Boutique Consultancies
Specialized boutique consultancies pose a significant threat of substitutes for larger, more generalized firms like Cognizant. These smaller firms often possess deep expertise in rapidly evolving, niche areas such as artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, or specific cloud platforms. For instance, a boutique firm focused solely on quantum computing implementation might offer more targeted and cutting-edge solutions than a large consultancy with a broader, less specialized practice in that area.
These boutiques can be particularly attractive to clients seeking highly tailored solutions or rapid adaptation to new technologies. Their perceived agility and focused knowledge allow them to address specific pain points more effectively. In 2024, the demand for specialized digital transformation expertise continued to surge, with many companies prioritizing deep technical skills over generalist advice, thus increasing the appeal of these niche players.
The threat is amplified by the ability of these boutiques to offer competitive pricing for their specialized services, often leveraging leaner operational models. Clients may find that engaging a boutique for a specific project yields better results and a higher return on investment compared to a broader engagement with a larger firm. This dynamic means that even if Cognizant offers a comprehensive suite of services, clients with very specific needs might opt for a specialized substitute.
- Niche Expertise: Boutiques excel in specific technologies (e.g., AI, blockchain) or industries.
- Tailored Solutions: They offer customized approaches, contrasting with broader service packages.
- Agility & Speed: Smaller firms can often pivot and deliver results more quickly.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Specialized services can sometimes be more affordably priced for targeted needs.
The threat of substitutes for IT service providers like Cognizant is multifaceted, stemming from the rise of in-house capabilities, automation, readily available software, and specialized boutique firms. Companies are increasingly insourcing IT functions, leveraging advancements in cloud computing and the availability of skilled talent. For example, in 2024, many enterprises re-evaluated outsourcing, with a significant portion indicating a desire to bring critical IT functions back internally due to the growing accessibility of specialized IT talent.
Automation and AI tools further substitute traditional IT services by handling routine tasks and data analysis more efficiently. The global market for AI in IT operations was projected to reach tens of billions of dollars in 2024, highlighting significant investment in these technologies. Additionally, the growth of open-source software and SaaS platforms offers cost-effective alternatives, with the open-source market valued at approximately $22.7 billion in 2023.
The gig economy, facilitated by platforms like Upwork (which reported over $3.5 billion in gross service volume in 2023), provides agile and cost-efficient access to specialized skills, bypassing traditional outsourcing models. Similarly, boutique consultancies focusing on niche areas like AI or cybersecurity offer tailored, cutting-edge solutions that can be more attractive than the broader services of larger firms, particularly as demand for specialized digital transformation expertise surged in 2024.
| Substitute Category | Key Drivers | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| In-house IT Departments | Advancements in cloud, talent availability | Many enterprises re-evaluating outsourcing for insourcing in 2024 |
| Automation & AI Tools | Efficiency in routine tasks, data analysis | Global AI in IT operations market projected in tens of billions in 2024 |
| Open-Source & SaaS | Cost-effectiveness, faster deployment | Open-source software market valued at ~$22.7 billion in 2023 |
| Gig Economy/Freelance Platforms | Agility, niche skills, cost efficiency | Upwork reported over $3.5 billion in gross service volume in 2023 |
| Specialized Boutique Consultancies | Deep niche expertise, tailored solutions | Surging demand for specialized digital transformation expertise in 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
Starting a global professional services firm like Cognizant demands immense capital. We're talking about significant investments in state-of-the-art infrastructure, cutting-edge technology, and building a substantial, skilled workforce. These upfront costs alone can easily run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars.
Existing players, like Cognizant, benefit from considerable economies of scale. They've already made those massive investments and can spread their fixed costs across a much larger revenue base. This allows them to offer services at a lower per-unit cost than a newcomer could, creating a substantial hurdle for anyone looking to enter the market.
Established brand recognition and deep client relationships act as significant barriers to entry in the IT services sector. Cognizant's long history has fostered trust and a proven track record, making it difficult for newcomers to compete for substantial contracts. In 2023, Cognizant reported revenue of $18.1 billion, a testament to its established market position and client loyalty.
New entrants face considerable hurdles in securing the highly specialized talent essential for competing in the IT services sector. Established firms like Cognizant have cultivated deep pools of experienced professionals and robust training programs, making it difficult for newcomers to attract and retain top-tier employees. For instance, in 2023, the IT services industry continued to grapple with a talent shortage, with demand for cloud, AI, and cybersecurity skills outstripping supply, a dynamic that favors incumbents with established recruitment channels and employee development initiatives.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
Navigating the complex web of regulations and compliance requirements presents a significant barrier for new entrants, particularly in sectors like financial services and healthcare. The need to adhere to stringent data privacy laws, such as GDPR and CCPA, along with industry-specific mandates, demands substantial investment in technology and expertise, making market entry costly and time-consuming.
For instance, in 2024, the financial services industry continues to grapple with evolving anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations, requiring new firms to implement robust compliance frameworks from inception. Similarly, healthcare providers face increasing scrutiny over patient data security under HIPAA, necessitating significant upfront expenditure on secure systems and ongoing training.
- Data Privacy Compliance Costs: New entrants may face millions in upfront costs for data security infrastructure and legal counsel to ensure compliance with global privacy regulations.
- Industry-Specific Certifications: Obtaining necessary certifications, like PCI DSS for payment processing or FDA approvals for medical devices, can take years and incur substantial fees.
- Geographic Regulatory Divergence: Operating across multiple jurisdictions requires understanding and adhering to a patchwork of differing regulations, escalating compliance complexity and costs.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Methodologies
Cognizant's extensive portfolio of intellectual property, including proprietary frameworks and unique methodologies honed over decades, acts as a significant barrier to new entrants. These intangible assets, developed through substantial investment in research and development, enable more efficient and effective service delivery, making it challenging for newcomers to match Cognizant's established capabilities and client trust. For instance, in 2024, Cognizant continued to invest heavily in AI and digital transformation IP, aiming to further differentiate its service offerings and solidify its competitive moat.
New entrants often struggle to replicate the depth and breadth of services that established players like Cognizant offer, largely due to the latter's accumulated knowledge and proprietary tools. The cost and time required to develop comparable intellectual property are substantial, creating a high hurdle for aspiring competitors. This is particularly true in specialized areas like cloud migration or cybersecurity, where established firms possess unique, battle-tested methodologies.
- Proprietary Methodologies: Cognizant’s unique frameworks for digital transformation and IT modernization are difficult and expensive for new companies to replicate.
- Intellectual Property Investment: In 2024, Cognizant’s ongoing investment in R&D for AI and data analytics further strengthens its IP portfolio, creating a competitive advantage.
- Service Delivery Efficiency: Established firms leverage their IP to achieve greater efficiency and quality, posing a significant challenge for new entrants aiming to compete on service excellence.
The threat of new entrants in the IT services sector, where Cognizant operates, is generally low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital required for establishing a global professional services firm, including significant investments in infrastructure and talent. For example, building a strong presence in 2024 necessitates advanced technology platforms and a large, skilled workforce, creating a high initial cost barrier.
Economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents like Cognizant, which has already made massive investments, allow them to offer services at lower per-unit costs. Cognizant's 2023 revenue of $18.1 billion highlights its scale, making it difficult for new players to match pricing. Furthermore, established brand recognition and deep client relationships are crucial, as evidenced by Cognizant's long-standing trust and proven track record in securing major contracts.
The IT services industry in 2024 continues to face a talent shortage, particularly in high-demand areas like AI and cloud computing. Established firms such as Cognizant possess robust recruitment channels and employee development programs, giving them a distinct advantage in attracting and retaining top talent over newcomers. Navigating complex regulations and compliance, especially concerning data privacy like GDPR and CCPA, also demands significant investment, further deterring new market entrants.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example Data/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment in infrastructure, technology, and talent. | Hundreds of millions to billions of dollars for global operations. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to spreading fixed costs over larger revenue. | Cognizant's 2023 revenue of $18.1 billion demonstrates significant scale advantage. |
| Brand Recognition & Client Relationships | Established trust and proven track record are hard to replicate. | Difficulty for new entrants to secure large contracts against incumbents. |
| Talent Acquisition & Retention | Competition for specialized skills like AI and cloud computing. | Industry-wide talent shortages in 2024 favor firms with established recruitment. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Costs associated with adhering to data privacy and industry-specific laws. | Millions in upfront costs for security infrastructure and legal counsel. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive mix of data, including publicly available financial statements, market research reports from leading firms, and industry-specific trade publications to provide a robust understanding of competitive dynamics.