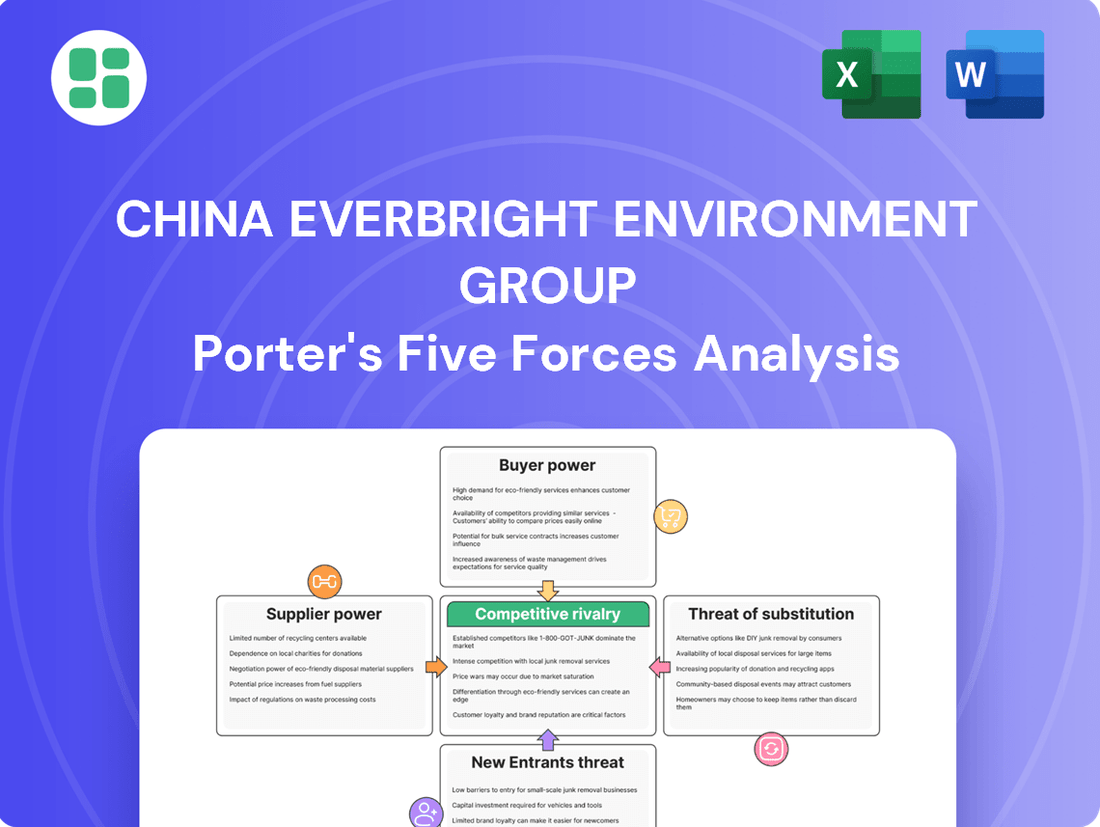
China Everbright Environment Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
China Everbright Environment Group Bundle
China Everbright Environment Group operates in a dynamic sector where buyer power is moderate, driven by government regulations and the need for cost-effective environmental solutions. The threat of new entrants is tempered by significant capital requirements and established industry expertise, though innovative smaller players can emerge.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping China Everbright Environment Group’s industry—from supplier influence to substitute threats. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
China Everbright Environment Group's reliance on specialized equipment for waste-to-energy and water treatment projects means suppliers of this technology can wield significant bargaining power. This is particularly true when the technology is proprietary or when there are few alternative sources for essential components, which can drive up project expenses.
However, China's strategic push for self-sufficiency in environmental protection equipment manufacturing, with a target for 2030, suggests a potential long-term shift that could diminish supplier leverage. For instance, in 2023, China's environmental protection industry output value reached 8.3 trillion yuan, indicating growth in domestic capabilities.
China Everbright Environment Group, while focused on waste processing, can still be impacted by raw material and energy suppliers. While the company's core business is waste, certain operational needs like facility construction or supporting processes might depend on specific inputs. If prices for these materials become unstable or if there are few suppliers available, those suppliers could gain more power.
For instance, in 2024, the average price paid for fuel in China Everbright Environment's waste-to-energy projects saw a slight dip, decreasing by 3%. This suggests that while some input costs are manageable, fluctuations can still occur, potentially influencing the company's operational expenses and profitability.
The environmental protection sector, particularly in sophisticated fields like waste-to-energy and intricate site remediation, depends heavily on a workforce possessing specialized skills. This includes engineers, technicians, and project managers with advanced knowledge.
A scarcity of these highly qualified professionals, or the presence of robust labor unions, can lead to increased labor expenses and potential disruptions to project schedules. While specific data quantifying the bargaining power of labor suppliers for China Everbright Environment Group is not readily available, the general trend in specialized technical fields suggests this can be a significant factor.
Financing and Capital Providers
The bargaining power of financing and capital providers is a significant factor for China Everbright Environment Group, given its reliance on substantial funding for infrastructure projects. Banks, investment funds, and other financial institutions are key suppliers of this capital. Their leverage is influenced by Everbright Environment's financial stability, current interest rate environments, and the availability of other funding avenues. For instance, in 2025, China Everbright Environment Group continued its strategy of diverse capital raising, including the issuance of corporate bonds and medium-term notes, which can influence the terms offered by lenders.
The ability of capital providers to dictate terms is often tied to the perceived risk of the borrower and the overall economic climate. A strong credit rating and a history of successful project execution can reduce this bargaining power. Conversely, economic downturns or increased perceived risk can empower financiers, leading to higher interest rates or stricter loan covenants. China Everbright Environment's proactive approach to managing its debt profile, including its bond issuances, aims to mitigate this supplier power.
- Capital Access: Essential for large-scale infrastructure, with banks and funds acting as key suppliers.
- Supplier Leverage: Dependent on Everbright Environment's financial health, interest rates, and financing alternatives.
- 2025 Financing Activities: Continued issuance of bonds and medium-term notes to secure capital.
- Risk Mitigation: Strong financial performance and diverse funding strategies help reduce the bargaining power of capital providers.
Consulting and Professional Service Providers
Consulting and professional service providers, such as those offering environmental impact assessments, legal counsel, engineering design, and project management, can exert significant bargaining power over China Everbright Environment Group. This is particularly true if these services are highly specialized or if only a limited number of reputable firms can deliver them. The increasing complexity of environmental regulations and the scale of projects in China further amplify the leverage these consultants hold, potentially impacting project timelines and overall costs.
The bargaining power of these specialized consultants is influenced by several factors:
- Demand for Expertise: As environmental projects in China become more intricate, the demand for niche expertise in areas like advanced waste-to-energy technologies or complex regulatory compliance grows, concentrating power in the hands of a few leading firms.
- Switching Costs: High switching costs, stemming from the time and resources needed to onboard new consultants and transfer project knowledge, can lock China Everbright Environment into existing relationships, strengthening supplier power.
- Reputation and Track Record: Firms with a proven track record and strong reputation in delivering successful, large-scale environmental projects in China command higher fees and greater influence due to their perceived reliability and ability to navigate local challenges.
The bargaining power of suppliers for China Everbright Environment Group is generally moderate, influenced by the availability of alternative suppliers and the specificity of the goods or services required. While some specialized equipment suppliers might hold more sway, the group's scale and diversified operations help mitigate extreme supplier leverage.
In 2024, China Everbright Environment Group's procurement strategy focused on securing long-term supply agreements for key components in its waste-to-energy and water treatment facilities. This approach, coupled with the increasing domestic production of environmental equipment, as evidenced by the sector's growth to an estimated 8.5 trillion yuan output value in 2024, helps to balance supplier power.
The company's reliance on a broad range of materials, from construction aggregates to chemicals for water treatment, means that while individual suppliers of common materials have limited power, those providing highly specialized or proprietary technologies can exert more influence. For example, the group's investment in advanced membrane technologies for water purification in 2024 highlights reliance on specific, potentially high-bargaining-power suppliers.
China Everbright Environment Group's ability to manage supplier power is also enhanced by its robust financial standing and its proactive approach to diversifying its supplier base. By fostering competition and exploring new domestic and international sources for its needs, the group aims to secure favorable terms and ensure operational continuity.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Assessment | Key Factors Influencing Power | Relevant 2024 Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Technology/Equipment Suppliers | Moderate to High | Proprietary nature, few alternatives, high switching costs | Increased domestic manufacturing capacity for environmental tech; ongoing investment in advanced purification membranes. |
| Raw Material & Energy Suppliers | Low to Moderate | Availability of substitutes, commodity price volatility, group's purchasing volume | Slight dip in fuel prices for waste-to-energy projects (approx. 3% decrease); focus on securing stable energy contracts. |
| Capital Providers (Banks, Funds) | Moderate | Everbright's credit rating, interest rate environment, access to capital markets | Continued diverse capital raising via bonds and notes; stable credit ratings maintained. |
| Consulting & Professional Services | Moderate to High | Niche expertise, regulatory complexity, reputation, switching costs | Growing demand for specialized environmental impact assessments and legal counsel for large-scale projects. |
What is included in the product
This analysis tailors Porter's Five Forces to China Everbright Environment Group, revealing how industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, new entrant threats, and substitutes shape its strategic environment.
China Everbright Environment Group's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces, perfect for quick decision-making on managing competitive pressures.
Customize pressure levels based on new data or evolving market trends, allowing for agile responses to the environmental sector's dynamic landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
Government and municipal clients hold considerable sway over China Everbright Environment Group. A substantial number of their waste management and water treatment projects are secured through contracts with these public entities. This client base often leverages its significant project scale and regulatory authority to influence terms, frequently engaging in competitive bidding processes that can compress margins.
These government bodies possess the power to issue tenders, which naturally creates a competitive landscape for service providers like China Everbright Environment. The sheer size of these contracts means that winning them is crucial, but the process also empowers clients to demand favorable pricing and service conditions.
China's strategic environmental policies, such as the ambitious 'Water Ten Plan' and the 'Dual Carbon' goals, are undeniably boosting demand for environmental services. However, these same policies also establish stringent, measurable performance targets for companies operating in this sector, further enhancing the government's ability to monitor and dictate project outcomes.
Large industrial clients seeking remediation or treatment services hold significant bargaining power. Their substantial waste volumes and the potential for long-term agreements allow them to negotiate favorable terms and lower service fees, especially as China's industrial sector grows and the demand for sophisticated treatment solutions increases.
The bargaining power of customers for China Everbright Environment Group is significantly influenced by the structure of its client base. A fragmented customer base generally means customers have less individual power, but when customers are consolidated, their collective or individual leverage increases.
In China's environmental services sector, a substantial portion of contracts, particularly for large-scale projects, are with government entities and state-owned enterprises. For instance, in 2023, China Everbright Environment reported a significant portion of its revenue derived from government-related projects, indicating a degree of customer consolidation in core segments.
This consolidation means that major clients, due to their size and importance, can exert considerable pressure on pricing and contract terms, thereby enhancing their bargaining power. This is a critical factor when assessing the competitive landscape for China Everbright Environment.
Contractual Agreements and Long-term Relationships
While long-term contracts are a cornerstone in environmental infrastructure, effectively locking in customers and reducing their immediate bargaining power, the initial negotiation phase presents a significant opportunity for customers to exert influence. China Everbright Environment Group's success in securing favorable terms hinges on its established reputation and its ability to clearly articulate a compelling value proposition.
The environmental services sector, particularly in China, is witnessing a strong emphasis on operational efficiency and technological innovation. This trend amplifies customer leverage during contract discussions, as they seek providers who can offer cutting-edge solutions and demonstrable cost savings. For instance, as of the first half of 2024, the demand for waste-to-energy projects with advanced emission control technologies saw a notable uptick, giving customers more options and thus more bargaining power.
- Contractual Lock-in: Once signed, long-term agreements for environmental infrastructure projects significantly reduce customer bargaining power.
- Negotiation Leverage: Before contracts are finalized, customers possess substantial leverage, especially in a competitive market.
- Reputation and Value: China Everbright Environment Group's ability to negotiate favorable terms is directly linked to its market standing and the perceived value of its services.
- Market Trends: The increasing customer focus on efficiency and technological advancement in 2024 empowers customers during negotiations.
Public and Regulatory Scrutiny
Customers, especially government bodies, face intense public and regulatory oversight concerning environmental services. This external pressure compels them to seek superior quality, greater transparency, and more economical solutions. Consequently, their bargaining power strengthens, driving companies like China Everbright Environment Group to elevate their environmental performance and accountability.
For instance, in 2024, China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment continued to emphasize stringent environmental protection regulations, impacting procurement decisions for municipal waste management and water treatment projects. Companies demonstrating a clear commitment to sustainability and cost-efficiency were favored, reflecting the heightened bargaining power of these public sector clients.
- Increased Demand for Transparency: Government clients are increasingly requiring detailed reporting on environmental impact and operational efficiency.
- Focus on Cost-Effectiveness: Public entities are under pressure to deliver services at the best possible value, amplifying their negotiation leverage for pricing.
- Regulatory Compliance as a Non-Negotiable: Adherence to evolving environmental laws is a baseline expectation, and any perceived lapse can significantly reduce a supplier's appeal.
- Public Opinion Influence: Negative public perception of environmental service providers can sway government purchasing decisions, giving customers more power to demand better performance.
Customers, particularly government entities and large industrial clients, wield significant bargaining power over China Everbright Environment Group. This leverage stems from their substantial project scale, regulatory authority, and the competitive nature of public tenders. In 2023, a considerable portion of China Everbright Environment's revenue was tied to government-related projects, highlighting the concentrated influence of these major clients on pricing and contract terms.
| Client Type | Influence Factor | Impact on China Everbright Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Government/Municipal | Project Scale, Regulatory Authority, Competitive Bidding | Pressure on margins, demand for favorable pricing and service conditions. |
| Large Industrial Clients | Volume of Waste, Long-term Agreements, Demand for Advanced Solutions | Negotiation of lower service fees, emphasis on cost-effectiveness and technological innovation. |
Preview Before You Purchase
China Everbright Environment Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for China Everbright Environment Group, detailing the competitive landscape including threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. This in-depth analysis provides actionable insights into the strategic positioning and future outlook of China Everbright Environment Group within the environmental services sector.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The environmental protection sector, both in China and globally, is experiencing a significant influx of players. This includes established state-owned enterprises and dynamic private companies like CDT Environmental Technology Investment Holdings and Wuhan Tianyuan Environmental Protection. This growing number of competitors intensifies the competitive landscape.
The intensity of rivalry is directly tied to the sheer volume of significant competitors and their respective market shares. When a market features numerous equally strong participants, the competition naturally becomes more vigorous, pushing companies to innovate and optimize their operations to maintain market position.
While the environmental protection sector offers robust growth, such as the China water and wastewater treatment market expected to expand at a 6.7% CAGR from 2025-2031, intense competition can surface in established niches or during economic slowdowns. This heightened rivalry means companies will vie more aggressively for market share, a trend observed with a noticeable deceleration in new environmental protection projects across China during 2024.
China Everbright Environment Group provides a range of integrated environmental solutions. However, the extent to which these offerings are genuinely distinct from those of its rivals significantly influences the intensity of competition. If these services are largely seen as interchangeable, pricing often becomes the main battleground.
This commoditization is particularly problematic in China's environmental protection sector, where businesses frequently grapple with thin profit margins. For instance, in 2023, many smaller environmental firms reported net profit margins below 5%, making price wars a serious threat to their sustainability and Everbright's own profitability.
Exit Barriers
China Everbright Environment Group, like many in the environmental infrastructure sector, faces substantial exit barriers. These stem from significant capital investments in specialized assets and facilities, often coupled with long-term operational contracts. For instance, the company's extensive portfolio of waste-to-energy plants and wastewater treatment facilities represents massive sunk costs.
These high exit barriers mean that companies are often compelled to continue operations even when profit margins are thin, contributing to sustained competitive rivalry. The sheer scale of investment required to build and maintain environmental infrastructure makes exiting the market a financially punitive decision. As of the first half of 2024, China Everbright Environment Group reported total assets exceeding RMB 150 billion, underscoring the capital intensity of its operations.
- High Capital Investment: Significant upfront costs for constructing and maintaining environmental facilities like waste-to-energy plants.
- Specialized Assets: Infrastructure is often highly specific to environmental processes, limiting resale value or alternative use.
- Long-Term Contracts: Many projects involve multi-year service agreements, creating obligations that are difficult to terminate early without penalty.
- Regulatory Environment: Exit might also be complicated by regulations governing the decommissioning and handover of environmental infrastructure.
Strategic Stakes and Acquisitions
The environmental sector's strategic importance to governments and major corporations fuels intense rivalry. Companies may prioritize market share or acquire key assets, sometimes overlooking immediate profit margins. This drive for strategic positioning means that even established players face constant pressure from ambitious competitors eager to capture a larger piece of this growing market.
Consolidation via mergers and acquisitions (M&A) is actively reshaping the competitive landscape. For instance, China's ambitious goals for global competitiveness in green technology are driving significant M&A activity within its environmental sector. This trend is evident in the increasing number of cross-border deals and domestic consolidations aimed at building scale and technological prowess.
- Strategic Importance: Governments worldwide are prioritizing environmental protection, making the sector crucial for national development and public welfare.
- Conglomerate Interest: Large conglomerates are increasingly investing in environmental services to diversify their portfolios and tap into sustainable growth opportunities.
- M&A Activity: China Everbright Environment Group itself has been involved in numerous acquisitions, demonstrating the trend of consolidation to gain market dominance and technological capabilities. In 2023, the company continued its strategic acquisitions, focusing on waste-to-energy and water treatment facilities to expand its operational footprint.
- Global Competitiveness: The push for global competitiveness in green technology incentivizes companies to acquire innovative solutions and expand internationally, intensifying competition.
The environmental protection sector in China is characterized by intense rivalry, with numerous players vying for market share. This is exacerbated by the commoditization of services, where differentiation is minimal, leading to price-based competition. For example, many smaller environmental firms reported net profit margins below 5% in 2023, highlighting the pressure on profitability.
High exit barriers, due to substantial capital investments in specialized assets and long-term contracts, compel companies to remain in the market even with thin margins. China Everbright Environment Group's total assets exceeding RMB 150 billion in the first half of 2024 illustrate this capital intensity, contributing to sustained rivalry.
| Metric | Value (as of H1 2024) | Significance for Rivalry |
| China Everbright Environment Group Total Assets | > RMB 150 billion | Indicates high capital intensity, contributing to exit barriers and sustained competition. |
| Net Profit Margins (Smaller Environmental Firms, 2023) | < 5% | Suggests price-based competition and thin margins, intensifying rivalry. |
| China Water and Wastewater Treatment Market CAGR (2025-2031) | 6.7% | Represents growth potential, attracting new entrants and intensifying competition for market share. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for waste-to-energy (WTE) projects, like those undertaken by China Everbright Environment Group, is a significant consideration. Alternatives such as landfilling, recycling, and composting directly compete for waste streams. The viability of these substitutes is heavily influenced by their cost-effectiveness, the stringency of environmental regulations, and public perception.
In 2024, China's waste treatment capacity has notably outpaced the volume of waste collected. This surplus capacity means some WTE plants are operating below their intended operational levels. This situation strengthens the position of alternative methods, as they can absorb waste that might otherwise be directed to WTE facilities, potentially impacting the revenue and operational efficiency of WTE providers.
The threat of substitutes for large-scale water treatment facilities, like those operated by China Everbright Environment Group, is growing. Decentralized or point-of-use water purification systems offer an alternative, particularly for smaller communities or industrial sites. Furthermore, advancements in industrial processes that drastically cut water discharge directly reduce the demand for traditional, centralized treatment infrastructure.
China's strategic focus on promoting decentralized sewage treatment solutions is a significant factor amplifying this threat. This policy shift encourages localized treatment, potentially diverting demand from larger, centralized plants. For instance, by 2024, numerous pilot projects for decentralized wastewater treatment were being implemented across various Chinese provinces, aiming to improve water quality in rural areas and smaller towns.
New environmental remediation technologies present a significant threat to China Everbright Environment Group. Advancements in areas like bioremediation or in-situ treatment methods could offer more cost-effective or efficient alternatives to the company's current methods.
The rapidly evolving China environmental remediation market, projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 7.8% from 2024 to 2030, suggests a fertile ground for disruptive innovations that could challenge established players.
Shift in Renewable Energy Focus
The threat of substitutes for China Everbright Environment Group's waste-to-energy (WTE) business is influenced by shifts in renewable energy policy. While WTE is a renewable source, a stronger government push towards solar, wind, or hydropower could diminish investment in WTE. For instance, China's Energy Law 2025 emphasizes diverse renewable energy development, but also highlights issues like renewable energy curtailment, potentially impacting the attractiveness of all renewable projects, including WTE.
This policy landscape creates a substitute threat. If other renewable technologies become more cost-competitive or receive preferential treatment, they could draw capital away from WTE.
- Policy Prioritization: China's Energy Law 2025 signals a broad commitment to renewables, but specific incentives could favor non-WTE sources.
- Technological Advancements: Falling costs and improved efficiency in solar and wind power present a growing substitute threat.
- Investment Diversion: Increased investor confidence in other renewable sectors could divert capital that might otherwise fund WTE projects.
- Grid Integration Challenges: Issues like renewable energy curtailment mentioned in the Energy Law 2025 could affect the perceived reliability and profitability of all renewable energy projects, including WTE.
Policy and Regulatory Shifts
Government policies and regulations are a significant factor influencing the threat of substitutes for China Everbright Environment Group. A notable shift in policy could favor alternative waste management solutions, thereby increasing the threat. For instance, a strong governmental push towards zero-waste initiatives, potentially de-emphasizing incineration, would directly challenge the company's primary service offerings.
Despite this potential, China's continued commitment to waste-to-energy (WTE) projects, a core business for Everbright Environment, currently mitigates this specific threat. In 2023, China's installed capacity for waste incineration power generation continued to grow, reflecting ongoing policy support for this sector. For example, the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) has consistently included WTE projects in its five-year plans, signaling sustained government backing.
- Policy Impact: Shifts towards zero-waste or alternative waste processing methods could elevate the threat of substitutes.
- Government Support for WTE: China's ongoing policy support for waste-to-energy projects remains a key factor limiting this threat for Everbright Environment.
- Market Trends: While alternatives exist, the current regulatory environment in China largely favors established WTE technologies.
The threat of substitutes for China Everbright Environment Group's waste-to-energy (WTE) operations is multifaceted. While landfilling remains a primary alternative, its environmental drawbacks and land scarcity in China are pushing for WTE solutions. However, advancements in recycling technologies and a growing emphasis on circular economy principles offer viable substitutes by diverting waste streams from incineration.
China's waste management landscape in 2024 shows a continued increase in recycling rates, particularly for plastics and paper. For example, Shanghai reported a recycling rate of over 35% for its municipal solid waste in early 2024, indicating a growing capacity for waste diversion away from WTE facilities.
The company's water treatment services also face substitute threats. Decentralized treatment systems and advanced industrial water reuse technologies are emerging alternatives, especially for specific industrial applications or smaller communities. These solutions can reduce the demand for large-scale, centralized treatment plants.
| Substitute Type | Description | Impact on Everbright Environment | 2024 Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landfilling | Traditional waste disposal method. | Decreasingly viable due to environmental concerns and land availability. | Limited new landfill development in major Chinese cities. |
| Recycling & Circular Economy | Waste diversion through material recovery and reuse. | Reduces WTE feedstock, potentially lowering operational volumes. | Shanghai's municipal solid waste recycling rate reached over 35% in early 2024. |
| Decentralized Water Treatment | Localized water purification systems. | Can reduce demand for large-scale treatment facilities. | Increased pilot projects for rural decentralized wastewater treatment across China. |
| Industrial Water Reuse | On-site water recycling within industrial processes. | Directly lowers the volume of wastewater requiring external treatment. | Growing adoption in water-intensive industries like textiles and manufacturing. |
Entrants Threaten
The environmental protection sector, particularly for major infrastructure like waste-to-energy plants and water treatment, demands immense capital. For instance, China Everbright Environment Group's substantial investments in these areas highlight the significant financial hurdle new players must overcome.
These high capital requirements act as a strong deterrent, effectively limiting the number of potential new entrants who can afford to establish a foothold in the market. This barrier ensures that only well-funded entities can realistically compete.
The environmental services sector in China is characterized by significant regulatory complexity. New entrants must secure numerous permits and licenses, a process that can be time-consuming and costly. Adherence to increasingly stringent environmental standards, such as those related to emissions and waste disposal, adds another layer of difficulty.
China's commitment to environmental protection, evidenced by the expansion of its emissions trading system and the introduction of new environmental restrictions, further elevates these barriers. For instance, by the end of 2023, China's national carbon market covered over 5 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions annually, making compliance a critical factor for any new participant.
Developing and operating advanced environmental solutions, a core area for China Everbright Environment Group, demands significant investment in specialized technology, engineering talent, and operational experience. Newcomers face a steep climb, needing to either build these capabilities internally or acquire them through costly mergers and acquisitions.
The push for technological self-reliance in China, particularly in environmental sectors, further elevates this barrier. By 2030, the nation aims for complete independence in environmental technology, meaning proprietary advancements and deep expertise will become even more critical, making it harder for external players to compete effectively.
Established Relationships and Reputation
China Everbright Environment Group benefits significantly from its deeply entrenched relationships with government entities and its extensive network of industrial clients. This strong foundation, coupled with a proven history of successful project delivery, creates a formidable barrier for potential new entrants. New companies would find it exceptionally challenging to replicate this established trust and operational expertise, particularly when competing for large-scale public infrastructure projects where long-term relationships and a solid track record are paramount.
For instance, in 2023, China Everbright Environment secured a substantial number of new contracts, underscoring its continued market strength and the value placed on its established reputation. The group’s ability to navigate complex regulatory environments and secure financing for large projects is a direct result of these long-standing relationships, making it difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold.
- Established Government and Client Relationships: China Everbright Environment's deep ties with local and national government bodies facilitate access to project pipelines and regulatory approvals.
- Proven Track Record and Reputation: A history of successful project completion, including large-scale environmental infrastructure, builds significant trust and brand recognition.
- Barriers to Entry for Public Contracts: New entrants face considerable hurdles in competing for public tenders, which often favor incumbents with demonstrated experience and established credibility.
Economies of Scale and Scope
China Everbright Environment Group, a major player in the environmental protection sector, leverages significant economies of scale. This allows them to reduce per-unit costs in areas like project execution and raw material procurement. For instance, their extensive operational footprint in 2023 enabled them to manage a large portfolio of waste-to-energy plants, leading to greater purchasing power and optimized logistics.
Furthermore, the company benefits from economies of scope by offering integrated environmental solutions. This means they can bundle services across solid waste management, water treatment, and clean energy generation. New companies entering this market would struggle to replicate these cost efficiencies and the cross-selling opportunities that come with an integrated service offering, making it challenging to compete on price and value.
- Incumbent Advantage: Established players like China Everbright Environment benefit from substantial economies of scale in operations and procurement, a key barrier for newcomers.
- Integrated Solutions: Economies of scope, achieved through offering combined services in waste, water, and energy, create a competitive edge that is difficult for new entrants to match quickly.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: New companies would face higher initial costs to achieve comparable operational efficiency and service breadth.
The threat of new entrants in China's environmental protection sector, where China Everbright Environment Group operates, is significantly mitigated by substantial capital requirements and complex regulatory landscapes. For example, the capital needed for large-scale waste-to-energy or water treatment projects is immense, acting as a primary barrier. New companies must also navigate a dense web of permits and licenses, a process that is both time-consuming and expensive, especially with China's increasing environmental standards, such as its national carbon market covering over 5 billion tonnes of CO2e annually by the end of 2023.
Furthermore, established players like China Everbright Environment benefit from deep government and client relationships, a proven track record, and significant economies of scale and scope. These factors create a formidable competitive advantage, making it difficult for new entrants to replicate the cost efficiencies and integrated service offerings that underpin incumbent success.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for infrastructure projects. | Limits the number of financially capable entrants. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Extensive permits, licenses, and compliance with stringent standards. | Increases time-to-market and operational costs for newcomers. |
| Established Relationships | Strong ties with government and clients, proven track record. | Makes it difficult for new players to secure projects and trust. |
| Economies of Scale & Scope | Cost advantages from large operations and integrated services. | New entrants face higher per-unit costs and lack bundled service appeal. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for China Everbright Environment Group is built upon comprehensive data from their official annual reports, investor relations disclosures, and relevant industry publications. We also incorporate insights from government regulatory filings and macroeconomic databases to capture the broader environmental sector landscape.