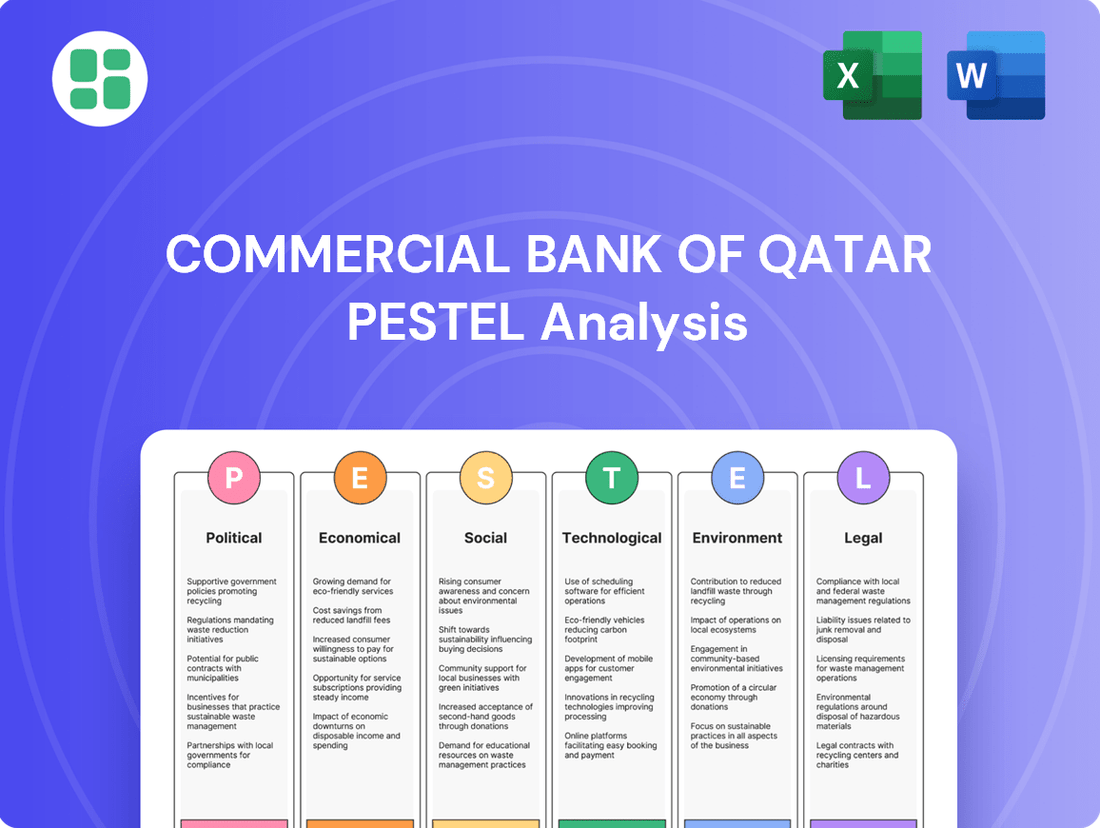
Commercial Bank of Qatar PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Commercial Bank of Qatar Bundle
Uncover the critical political, economic, and technological factors shaping Commercial Bank of Qatar's strategic landscape. Our comprehensive PESTLE analysis provides actionable intelligence, empowering you to anticipate market shifts and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Download the full report to gain a decisive advantage.
Political factors
Qatar's consistently stable political environment acts as a bedrock for its banking sector, bolstering investor trust and enabling strategic, long-term decision-making. This stability is crucial for financial institutions like Commercial Bank of Qatar.
The Qatari government actively supports its banking sector, demonstrating a commitment to financial stability and mitigating risks such as external debt outflows. This sovereign backing is a significant advantage, enhancing the resilience of banks like Commercial Bank of Qatar.
For instance, during periods of global economic uncertainty, the Qatari government's interventions have often been key in maintaining liquidity and confidence within the domestic banking system, a trend observed through to early 2025.
The Qatar National Vision 2030 and the Third National Development Strategy (NDS3), launched in 2024, are pivotal political drivers shaping Qatar's economic landscape. These strategies prioritize economic diversification away from hydrocarbons and emphasize sustainable development, directly influencing the banking sector's operational focus and growth opportunities. For instance, NDS3 aims to increase the non-oil GDP contribution to 60% by 2030, a target that necessitates robust financial sector support for emerging industries.
Commercial Bank of Qatar actively integrates its strategic pillars, such as accelerating digital transformation and embedding sustainability into its core operations, with these national blueprints. This strategic alignment ensures the bank's initiatives, including expanding digital banking services and financing green projects, are not only compliant but also synergistic with the nation's long-term developmental trajectory, fostering a favorable environment for its growth and contribution to the Qatari economy.
Geopolitical tensions in the Middle East continue to be a notable factor, yet Qatar's economic outlook remains robust, which is a positive sign for its banking sector. This stability provides a solid foundation for institutions like Commercial Bank of Qatar.
While heightened regional tensions could theoretically lead to capital outflows, the Qatari government's unwavering support for its domestic banks serves as a crucial buffer against such risks. This backing is a significant mitigating factor for the banking industry.
As a major financial institution, Commercial Bank of Qatar is positioned to benefit from this supportive environment. However, the bank must maintain a keen awareness of evolving regional dynamics to effectively navigate any potential challenges.
Economic Diversification Policies
Qatar's commitment to economic diversification, as outlined in its National Vision 2030 and further emphasized in the National Development Strategy 3 (NDS3), is significantly reshaping the financial landscape. This strategic pivot away from heavy reliance on hydrocarbons presents Commercial Bank of Qatar (CBQ) and other financial institutions with substantial opportunities to finance growth in non-oil sectors. For instance, the tourism sector, a key focus area, saw significant investment in infrastructure and hospitality leading up to the 2022 FIFA World Cup, and continued development plans are in place. Banks are increasingly supporting projects in logistics, manufacturing, technology, and healthcare, aligning with government objectives to build a more robust and resilient economy. This diversification drive is crucial for sustainable long-term growth.
The government's strategy actively encourages a private sector-led growth model, which directly translates into higher demand for a broader range of financial services from banks like CBQ. This includes corporate lending for expansion, trade finance for import/export activities in new industries, and investment banking services for public-private partnerships (PPPs) and capital raising. NDS3 specifically targets increased private sector contribution to GDP, fostering an environment where financial institutions play a pivotal role in facilitating this transition. The expansion of services into these emerging industries is a direct response to these policy directives, positioning CBQ to capitalize on new revenue streams.
- Economic Diversification: Qatar aims to reduce its dependence on oil and gas, with NDS3 setting targets for non-oil sector growth.
- New Lending Opportunities: Banks are supporting sectors like tourism, logistics, manufacturing, and technology, creating new avenues for credit and investment.
- Private Sector Focus: Government policies under NDS3 prioritize private sector-led growth, boosting demand for diverse financial services.
- Public-Private Partnerships: CBQ is positioned to finance and facilitate PPPs as part of the nation's development strategy.
Regulatory Oversight by QCB
The Qatar Central Bank (QCB) is the primary guardian of Qatar's financial ecosystem, implementing policies that foster stability and growth. Its regulatory framework, encompassing capital adequacy ratios, liquidity management, and comprehensive risk assessment protocols, directly shapes the operational landscape for institutions like Commercial Bank of Qatar.
These QCB directives are not merely guidelines; they are mandates that Commercial Bank of Qatar must adhere to. For instance, QCB's Basel III implementation requires banks to maintain specific capital buffers. As of the latest available data, the QCB mandates a minimum Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) of 13%, a figure Commercial Bank of Qatar consistently meets, demonstrating its financial robustness under regulatory scrutiny.
The QCB's oversight extends to ensuring sound corporate governance and consumer protection within the banking sector. This stringent supervision bolsters the confidence of both domestic and international investors in Qatari financial institutions. Commercial Bank of Qatar’s adherence to these regulations, such as its reported CAR of 18.5% as of Q1 2024, underscores its commitment to operational integrity and strengthens its market position.
- QCB Mandates: Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) minimum of 13% per Basel III.
- Commercial Bank of Qatar Performance: Reported CAR of 18.5% in Q1 2024.
- Regulatory Impact: Enhances operational integrity and investor confidence.
- QCB's Role: Ensures monetary and financial stability through robust oversight.
The Qatari government's commitment to economic diversification, particularly through the National Development Strategy 3 (NDS3) launched in 2024, is a significant political driver. This strategy actively encourages private sector growth and aims to increase the non-oil GDP contribution, creating new lending opportunities for banks like Commercial Bank of Qatar in sectors such as technology, manufacturing, and tourism.
Government policies under NDS3 prioritize private sector-led growth, increasing demand for diverse financial services from institutions like Commercial Bank of Qatar, including corporate lending and trade finance. The focus on public-private partnerships also presents opportunities for the bank to facilitate national development projects.
The Qatar Central Bank (QCB) plays a crucial regulatory role, ensuring financial stability through mandates like capital adequacy ratios. Commercial Bank of Qatar's reported Capital Adequacy Ratio of 18.5% in Q1 2024, exceeding the QCB's 13% minimum, demonstrates its adherence to these regulations and strengthens investor confidence.
| Political Factor | Impact on Commercial Bank of Qatar | Supporting Data/Initiative |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Diversification Strategy (NDS3) | Creates new lending opportunities in non-oil sectors. | NDS3 aims to increase non-oil GDP contribution; focus on technology, manufacturing, tourism. |
| Private Sector Growth Emphasis | Boosts demand for diverse financial services. | NDS3 prioritizes private sector contribution to GDP; supports corporate lending and trade finance. |
| Qatar Central Bank (QCB) Regulation | Ensures financial stability and operational integrity. | Mandates minimum CAR of 13%; Commercial Bank of Qatar reported 18.5% CAR in Q1 2024. |
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the external macro-environmental factors impacting the Commercial Bank of Qatar, covering Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal dimensions.
It offers actionable insights for stakeholders to navigate the dynamic landscape and identify strategic opportunities and potential threats.
A PESTLE analysis for Commercial Bank of Qatar offers a structured approach to identifying and mitigating external challenges, thereby relieving the pain of navigating complex market dynamics.
This analysis serves as a vital tool for proactive strategic planning, enabling the bank to anticipate and adapt to political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental shifts, thus easing the burden of unforeseen disruptions.
Economic factors
Qatar's real GDP growth is anticipated to average approximately 2% for 2024-2025, with expectations of an acceleration driven by the significant North Field Expansion project. This economic expansion directly correlates with the banking sector's profitability and the demand for credit, impacting institutions like Commercial Bank of Qatar (CBQ).
While elevated hydrocarbon prices have historically been a strong driver for Qatar's economy, a potential moderation in these prices could influence the liquidity levels within the banking sector. CBQ's financial health is therefore intrinsically linked to these prevailing macroeconomic conditions and the broader trajectory of national economic growth.
The interest rate environment presents a key challenge for Commercial Bank of Qatar. With the Qatari riyal pegged to the US dollar, the bank will likely see its profitability moderate as global interest rates, influenced by US Federal Reserve decisions, begin to decline. For example, if the Fed implements rate cuts in late 2024 or early 2025, Qatar's rates will follow suit.
While a lower interest rate environment can squeeze net interest margins, it also offers potential benefits. Reduced borrowing costs could alleviate financial strain on various sectors of the Qatari economy, potentially lowering the cost of risk for the bank. This shift necessitates a strategic review of Commercial Bank of Qatar's lending and deposit-taking strategies to maintain competitiveness and profitability.
Domestic credit growth in Qatar is projected to moderate. This slowdown is largely attributed to the winding down of significant infrastructure development, coupled with a more measured pace of non-hydrocarbon economic expansion. For instance, the Qatar Central Bank reported that total domestic credit extended by banks grew by approximately 6.5% year-on-year by the end of Q3 2024, a deceleration from previous periods.
Qatari banks, including Commercial Bank of Qatar (CBQ), carry substantial exposure to the real estate sector, a segment known for its cyclical nature. This sector represents a considerable share of the overall domestic credit portfolio, making bank asset quality susceptible to market fluctuations. As of mid-2024, real estate loans constituted roughly 25% of the total loan book for major Qatari banks.
Managing this real estate exposure is a key challenge for CBQ and its peers. However, ongoing government initiatives aimed at economic diversification, alongside potential interest rate adjustments by the Qatar Central Bank, could provide support for stabilizing asset quality within the real estate portfolio. These factors are critical in mitigating potential risks associated with the sector's inherent volatility.
Inflation and Consumer Spending
Inflation rates and consumer spending are critical indicators for the banking sector. For instance, Qatar's inflation rate saw a significant increase in 2022, reaching 5.0% according to the Qatar Central Bank (QCB). However, proactive monetary policies implemented by the QCB have been effective in moderating these pressures, aiming for price stability. This controlled inflation environment is beneficial for commercial banks as it supports predictable consumer spending patterns.
The management of inflation directly impacts consumer purchasing power and confidence, which in turn affects demand for banking products like loans and savings accounts. As inflation moderates, consumers are more likely to engage in spending and investment activities, creating opportunities for banks. Commercial Bank of Qatar (CBQ) needs to closely monitor these trends to tailor its retail offerings and marketing strategies effectively, ensuring they align with the evolving economic conditions and consumer sentiment.
- Inflation Moderation: Qatar's inflation rate, which peaked in 2022, has been brought under control through QCB's monetary policies, fostering a more stable economic climate for banking.
- Consumer Spending Influence: Stable inflation supports consumer purchasing power, directly impacting the demand for retail banking products and services.
- Strategic Banking Response: CBQ must adapt its product development and marketing to reflect current consumer confidence and spending capacity, driven by inflation management.
Foreign Funding and Liquidity
Qatar's banking sector, including Commercial Bank of Qatar (CBQ), traditionally relies heavily on foreign funding. This reliance, while historically supported by strong government backing, presents a degree of vulnerability. For instance, as of late 2024, international interbank lending rates, a key indicator of foreign funding costs, have shown a moderate increase, reflecting global monetary policy tightening.
However, the landscape is shifting. With the substantial completion of major infrastructure projects that previously absorbed significant capital, Qatar's demand for external funding is gradually decreasing. This trend suggests a growing expectation for domestic sources to increasingly underpin credit expansion within the economy. Data from the Qatar Central Bank indicates a slight rise in the loan-to-deposit ratio for the system as a whole in Q3 2024, hinting at this evolving dynamic.
CBQ's liquidity management must therefore adapt to these changing funding dynamics. Strategies need to proactively incorporate a greater emphasis on nurturing and leveraging local deposit bases to meet future credit growth requirements. This proactive approach will be crucial for maintaining robust liquidity profiles amidst a potentially less accessible or more costly foreign funding environment.
- Reliance on Foreign Funding: Historically, Qatari banks have depended on international markets for liquidity, a factor that can be sensitive to global financial conditions.
- Infrastructure Project Impact: The winding down of large-scale infrastructure spending reduces the immediate need for substantial foreign capital injections into the banking system.
- Shift to Local Funding: There's an increasing expectation that domestic deposits will play a more significant role in funding future credit growth, requiring banks to enhance their retail and corporate deposit-gathering capabilities.
- CBQ's Liquidity Strategy: Commercial Bank of Qatar must refine its liquidity management to align with this transition, prioritizing stable domestic funding sources.
Qatar's economic growth, projected to average around 2% for 2024-2025, is primarily driven by the North Field Expansion, influencing credit demand and bank profitability. While high hydrocarbon prices have bolstered liquidity, any moderation could impact banks like Commercial Bank of Qatar (CBQ).
The interest rate environment poses a challenge, with a pegged riyal meaning Qatar's rates will likely follow US Federal Reserve decisions. Declining rates, anticipated for late 2024 or 2025, could squeeze net interest margins but also reduce borrowing costs for the economy, potentially lowering risk for CBQ.
Domestic credit growth is moderating, with real estate loans making up about 25% of major Qatari banks' books as of mid-2024. This exposure to a cyclical sector requires careful management, though government diversification efforts and potential rate adjustments may offer support.
Inflation has been managed effectively by the Qatar Central Bank, with rates moderating from a 2022 peak of 5.0%. This stability supports consumer spending and demand for banking products, necessitating that CBQ tailor its offerings to current economic conditions and consumer confidence.
Preview Before You Purchase
Commercial Bank of Qatar PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of the Commercial Bank of Qatar delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting its operations. You'll gain valuable insights into the strategic landscape the bank navigates.
Sociological factors
Qatar's population is notably young, with a significant portion under 30, and a substantial expatriate workforce, estimated to be around 88% of the total population as of early 2024. This demographic profile fuels a high demand for digital banking solutions and a wide array of financial products, from retail banking to wealth management, tailored to both local and international needs. The Commercial Bank of Qatar can leverage this by expanding its digital platforms and offering specialized services that cater to the unique financial behaviors and aspirations of this diverse and tech-oriented populace.
Rapid urbanization, particularly in and around Doha, presents a clear opportunity for Commercial Bank of Qatar to refine its branch network strategy. As more people concentrate in urban centers, the need for convenient, accessible banking touchpoints, including digital kiosks and mobile banking services, intensifies. The bank's ability to adapt its physical and digital presence to meet the evolving needs of these concentrated populations will be crucial for maintaining market share and customer engagement in these dynamic urban environments.
Qatar boasts a remarkably high internet penetration rate, exceeding 99% as of early 2024, which fuels a significant demand for sophisticated digital banking services. This widespread connectivity means consumers are increasingly comfortable and expectant of seamless online and mobile financial interactions, pushing banks to innovate rapidly.
Consumer behavior in Qatar strongly favors digital payment solutions, with mobile payments and contactless technology seeing substantial uptake. This trend directly influences how Commercial Bank of Qatar (CBQ) must structure its service delivery, prioritizing user-friendly digital platforms and innovative payment options to meet these evolving preferences.
In response to these shifts, CBQ has made substantial investments in its digital transformation initiatives, aiming to enhance its online and mobile banking capabilities. These strategic investments are designed to align with and capitalize on the growing digital literacy and changing consumer expectations within the Qatari market, ensuring the bank remains competitive.
Commercial Bank of Qatar can leverage Qatar's drive for financial inclusion to grow its customer base. This means making banking easier for more people. In 2023, Qatar's financial inclusion rate stood at 97%, indicating a strong foundation for expansion.
By offering simple, accessible financial products, Commercial Bank can tap into previously underserved segments of the population. This aligns with Qatar National Vision 2030's aim to foster a diversified and inclusive economy, potentially opening up new revenue streams for the bank.
Workforce and Talent Development
The availability of skilled talent, especially in data science and digital innovation, is paramount for Commercial Bank of Qatar's growth. The bank actively invests in developing its internal talent pool and fostering high-performing teams to drive its strategic goals, including digital transformation initiatives. For instance, as of early 2024, Commercial Bank of Qatar has continued its focus on digital upskilling programs, aiming to equip its employees with the necessary competencies for the evolving financial landscape.
Nationalization policies in Qatar significantly shape the bank's recruitment and training strategies. These efforts aim to increase the proportion of Qatari nationals in the workforce, requiring tailored development programs and career progression pathways. This focus on localization supports Qatar's Vision 2030 by building a robust domestic talent base within the financial sector.
- Talent Availability: Critical need for data scientists and digital innovators in Qatar's financial sector.
- Internal Development: Commercial Bank of Qatar prioritizes cultivating internal talent for strategic objectives.
- Nationalization Impact: Qatari workforce nationalization influences recruitment and training approaches for the bank.
- Digital Upskilling: Ongoing investment in programs to enhance employee digital competencies.
Cultural Values and Islamic Finance
Qatar's strong adherence to Islamic values significantly shapes its financial landscape, with a notable demand for Sharia-compliant products. This cultural preference presents a clear opportunity for financial institutions like Commercial Bank of Qatar (CBQ) to cater to a substantial segment of the population by offering or integrating Islamic finance solutions.
The growth in Islamic finance is evident, with projections indicating continued expansion. For instance, the global Islamic finance market was valued at over USD 3.6 trillion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 5.9 trillion by 2028, demonstrating robust growth. CBQ's strategic approach must acknowledge and potentially leverage these deeply ingrained cultural values to effectively serve its customer base and capture market share.
- Market Demand: A significant portion of Qatar's population prefers Sharia-compliant financial services, driving demand for Islamic banking products.
- Growth Potential: The expanding global and regional Islamic finance sector offers considerable growth opportunities for banks that can adapt their offerings.
- Competitive Advantage: Integrating or offering Islamic finance solutions can provide CBQ with a competitive edge by appealing to a culturally specific customer segment.
- Regulatory Alignment: Understanding and aligning with the principles of Islamic finance is crucial for regulatory compliance and market acceptance.
Qatar's young and diverse population, with a high expatriate percentage (around 88% in early 2024), drives demand for digital banking and varied financial products. Urbanization, especially in Doha, necessitates adaptable branch strategies and enhanced digital touchpoints.
High internet penetration (over 99% in early 2024) fuels demand for sophisticated digital banking, with consumer behavior strongly favoring digital payments and contactless technology. Commercial Bank of Qatar is investing in digital transformation to meet these expectations.
Financial inclusion is high in Qatar (97% in 2023), offering opportunities for Commercial Bank of Qatar to expand its customer base with accessible products, aligning with national development goals.
The strong preference for Sharia-compliant services presents a significant opportunity for Commercial Bank of Qatar, given the global Islamic finance market's substantial growth, projected to reach USD 5.9 trillion by 2028 from USD 3.6 trillion in 2023.
| Sociological Factor | Description | Impact on Commercial Bank of Qatar | Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | Young population, high expatriate workforce | Demand for digital banking, diverse financial products | Expatriates ~88% of population (early 2024) |
| Urbanization | Concentration of population in urban centers | Need for convenient digital and physical banking access | Rapid growth in Doha |
| Digital Literacy & Adoption | High internet penetration, preference for digital payments | Drives demand for advanced online/mobile services | Internet penetration >99% (early 2024) |
| Cultural Values | Preference for Sharia-compliant financial products | Opportunity for Islamic finance offerings | Global Islamic finance market USD 3.6T (2023) |
| Financial Inclusion | High level of financial inclusion | Potential for customer base expansion | Financial inclusion rate 97% (2023) |
Technological factors
Commercial Bank of Qatar (CBQ) has made digital transformation a cornerstone of its strategy, pouring substantial investment into technology to elevate customer experience and streamline operations. This commitment is evident in their focus on digital innovations, including the CBQ Mobile App, which facilitates smoother services and paperless transactions. These advancements directly address the growing consumer demand for convenient and efficient digital banking solutions, a trend that is rapidly reshaping the financial landscape.
The fintech ecosystem in Qatar is experiencing significant growth, driven by initiatives like the Qatar Fintech Hub and the Qatar Central Bank's (QCB) fintech strategy. This environment fosters innovation, pushing traditional banks like Commercial Bank of Qatar (CBQ) to adapt and collaborate with emerging fintech players.
Fintech firms are introducing disruptive solutions, including digital wallets, streamlined online payment systems, and AI-driven financial advisory services. These advancements present both competitive pressures and opportunities for partnerships, compelling CBQ to integrate these technologies to enhance its service offerings.
CBQ's engagement with this dynamic fintech landscape is crucial for maintaining its competitive edge. By embracing fintech innovation, the bank aims to deliver advanced financial services that meet the evolving demands of its customer base.
The surge in digital banking necessitates advanced cybersecurity and stringent data privacy. Commercial Bank of Qatar, like its peers, must prioritize safeguarding customer information against evolving cyber threats to maintain trust. In 2024, the global financial sector saw a significant increase in sophisticated cyberattacks, underscoring the critical need for robust defenses.
Investing in state-of-the-art security protocols is crucial for preventing fraud and ensuring compliance with regulations such as Qatar's Personal Data Privacy Protection Law. Commercial Bank of Qatar actively employs continuous screening and data protection measures to mitigate these risks, reflecting a commitment to secure digital operations.
AI and Automation in Banking
The banking sector in Qatar, including Commercial Bank of Qatar (CBQ), is heavily influenced by advancements in AI and automation. These technologies are crucial for boosting operational efficiency, improving risk assessment capabilities, and strengthening fraud detection mechanisms. CBQ's strategic focus on these areas is evident through its substantial investments in technology infrastructure and data architecture, enabling the deployment of AI-driven models.
These investments allow CBQ to refine its operations and enhance customer engagement through more precise targeting. The bank’s commitment to innovation in AI has been acknowledged, highlighting its proactive approach to adopting cutting-edge solutions. For instance, by early 2024, many leading Qatari banks were exploring or implementing AI for personalized financial advice and automated customer service, aiming to reduce operational costs by an estimated 15-20% in routine tasks.
Key technological impacts include:
- Enhanced Customer Experience: AI-powered chatbots and personalized recommendations improve customer interactions and service delivery.
- Improved Risk Management: Machine learning algorithms offer more accurate credit scoring and fraud detection, minimizing financial losses.
- Operational Efficiency: Automation of back-office processes, such as data entry and transaction processing, leads to cost savings and faster turnaround times.
- Data Analytics: Advanced analytics enable deeper insights into customer behavior and market trends, informing strategic decisions.
Open Banking and APIs
Qatar's commitment to open banking is evident in the Qatar Central Bank's (QCB) ongoing development of a comprehensive framework. Major financial institutions, such as Qatar National Bank (QNB), have already introduced open API services, signaling a significant shift in the financial landscape.
This technological evolution enables secure data exchange and streamlined payment integrations between banks and third-party developers. Such advancements are crucial for driving innovation and intensifying competition within the financial sector, ultimately benefiting consumers through enhanced services.
Commercial Bank of Qatar has a clear opportunity to capitalize on these open banking initiatives. By embracing these technologies, the bank can introduce novel financial products, elevate its customer service offerings, and contribute to greater financial inclusion across Qatar.
- Open Banking Framework: The QCB is actively developing an open banking framework, expected to be fully operational by late 2024, providing regulatory clarity for API integration.
- API Adoption: QNB reported a 30% increase in API usage for customer-facing applications in the first half of 2024, demonstrating growing adoption.
- Innovation Potential: Open banking is projected to create new revenue streams for banks, with estimates suggesting a potential 5-10% increase in digital service revenue by 2026 through partnerships.
- Customer Experience: Banks leveraging open APIs can offer personalized financial management tools, potentially increasing customer engagement by up to 20%.
Technological advancements are fundamentally reshaping Qatar's banking sector, with Commercial Bank of Qatar (CBQ) actively investing in digital transformation. The bank's focus on mobile apps and paperless transactions addresses the increasing consumer demand for digital convenience.
The burgeoning fintech scene in Qatar, supported by initiatives like the Qatar Fintech Hub, is pushing banks like CBQ to innovate and partner with new players. This dynamic environment fosters the adoption of solutions like digital wallets and AI-driven financial advice.
Cybersecurity remains paramount, with CBQ prioritizing data protection against rising global cyber threats. By early 2024, financial institutions were increasingly adopting AI for personalized services and operational efficiency, aiming for significant cost reductions.
Qatar's move towards open banking, with a framework expected by late 2024, will enable secure data sharing and new service integrations. CBQ has a clear opportunity to leverage these developments for new products and enhanced customer experiences.
| Area | 2024/2025 Focus | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Transformation | Mobile App Enhancement, Paperless Transactions | Improved Customer Experience, Operational Efficiency |
| Fintech Integration | Partnerships, AI-driven Advice | Disruptive Solutions, Competitive Edge |
| Cybersecurity | Data Privacy, Fraud Prevention | Customer Trust, Regulatory Compliance |
| Open Banking | API Development, Data Exchange | Innovation, Financial Inclusion |
Legal factors
Commercial Bank of Qatar operates under the stringent regulatory framework established by the Qatar Central Bank (QCB), a key factor ensuring the nation's financial stability. These QCB regulations mandate specific capital adequacy ratios and liquidity requirements, benchmarks that Commercial Bank of Qatar consistently surpasses. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, the bank reported a Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) of 18.5%, well above the Basel III minimum of 10.5% and the QCB's stipulated higher requirements.
Commercial Bank of Qatar must adhere to Qatar's stringent Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorism Financing (CFT) laws, notably Law No. 20 of 2019, which mandates rigorous Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures. These regulations require financial institutions to conduct comprehensive customer due diligence, monitor transactions continuously, and report any suspicious activities to the authorities. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties, underscoring the critical need for robust AML/KYC frameworks within the bank's operations.
Qatar's Personal Data Privacy Protection Law, enacted to align with global standards, mandates stringent controls over how financial institutions handle customer information. Commercial Bank of Qatar, like its peers, must invest in robust cybersecurity measures and transparent data handling policies to comply. Failure to adhere can result in significant penalties and reputational damage, especially as digital transactions surged by an estimated 25% in Qatar during 2024, increasing the attack surface.
Corporate Governance Standards
Adherence to robust corporate governance standards is paramount for Commercial Bank of Qatar, influencing its transparent reporting, board oversight, and ethical operations. The bank's commitment is evident in its annual corporate governance report and the incorporation of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) metrics into executive remuneration packages, a trend increasingly adopted by leading financial institutions globally.
Strong governance practices are crucial for bolstering investor confidence and ensuring the responsible stewardship of the bank's assets and operations. For instance, the bank's 2023 Corporate Governance Report highlighted a board independence rate of 80%, exceeding typical benchmarks and signaling a commitment to objective decision-making.
- Transparent Reporting: Ensuring all financial and operational information is readily accessible and clearly communicated to stakeholders.
- Board Oversight: Maintaining an independent and effective board of directors responsible for strategic direction and risk management.
- Ethical Conduct: Upholding the highest standards of integrity and compliance in all business dealings.
- ESG Integration: Linking executive compensation to the achievement of environmental, social, and governance targets, as seen in the bank's 2024 remuneration policies.
Digital Banking Regulations (e-KYC, Digital-only banks)
Qatar Central Bank (QCB) is actively modernizing its financial sector through new digital banking regulations. This includes introducing e-KYC (electronic Know Your Customer) rules and a framework specifically for digital-only banks, signaling a significant shift towards a more digitized financial ecosystem. These measures are designed to streamline customer onboarding while maintaining robust security protocols.
The new e-KYC regulations mandate strict controls for electronic customer verification, encouraging the adoption of advanced technologies. This includes the use of biometrics and multi-factor authentication to ensure secure remote onboarding processes. For instance, by late 2024, many financial institutions in the region saw a significant increase in digital onboarding, with some reporting over 60% of new accounts opened remotely.
Commercial Bank of Qatar, like other financial institutions, must continuously update its digital platforms and procedures to align with these evolving legal standards. This proactive adaptation is crucial for maintaining compliance and offering secure, efficient digital banking services to its customers. The bank’s investment in digital transformation, which saw a notable increase in its IT budget for 2024, reflects this commitment.
The QCB's framework for digital-only banks also presents opportunities for innovation and competition within the market. These regulations aim to foster a secure environment for new digital banking models, potentially leading to enhanced customer experiences and greater financial inclusion. By mid-2025, it is anticipated that several new digital banking licenses will be issued, further shaping the competitive landscape.
Commercial Bank of Qatar operates under a robust legal framework, primarily dictated by the Qatar Central Bank (QCB). This includes strict adherence to capital adequacy ratios, with the bank maintaining a CAR of 18.5% in Q1 2024, exceeding Basel III minimums. Furthermore, compliance with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorism Financing (CFT) laws, such as Law No. 20 of 2019, necessitates rigorous Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures and transaction monitoring.
The bank also navigates Qatar's Personal Data Privacy Protection Law, demanding strong cybersecurity and transparent data handling, especially as digital transactions grew by an estimated 25% in Qatar during 2024. Corporate governance is paramount, with an 80% board independence rate noted in the 2023 report, ensuring objective decision-making and ethical operations.
QCB's modernization efforts include new digital banking regulations and e-KYC rules, pushing for secure remote onboarding technologies. Commercial Bank of Qatar is adapting its digital platforms, reflected in its increased IT budget for 2024, to meet these evolving legal standards and enhance customer experience.
| Legal Factor | Key Regulations/Laws | Impact on Commercial Bank of Qatar | Relevant Data/Examples |
| Regulatory Compliance | QCB Regulations, Basel III | Mandatory capital adequacy and liquidity requirements. | CAR of 18.5% (Q1 2024), exceeding minimums. |
| AML/CFT | Law No. 20 of 2019 | Rigorous KYC, transaction monitoring, and reporting obligations. | Strict adherence to due diligence procedures. |
| Data Privacy | Personal Data Privacy Protection Law | Robust cybersecurity and transparent data handling policies required. | 25% surge in digital transactions (2024) increases compliance focus. |
| Corporate Governance | Internal policies, ESG integration | Emphasis on transparent reporting, board oversight, and ethical conduct. | 80% board independence rate (2023 report). |
| Digital Banking | QCB Digital Banking Framework, e-KYC | Adaptation to digital onboarding and new banking models. | Increased IT budget for 2024; adoption of biometrics and multi-factor authentication. |
Environmental factors
Commercial Bank of Qatar (CBQ) actively integrates its sustainability efforts with Qatar's National Environment and Climate Change Strategy (QNECCS), launched in 2021. This national blueprint guides environmental protection and climate action, directly impacting the banking sector's commitment to green finance. CBQ's alignment with QNECCS demonstrates its dedication to fostering Qatar's sustainable development goals.
Commercial Bank of Qatar's strategic focus on sustainability is clearly demonstrated in its 2024 Sustainability Report, underscoring the growing importance of ESG factors in the banking sector. The bank's integration of ESG principles throughout its operations, coupled with an impressive 'A' rating from MSCI ESG, signals a strong commitment to responsible business conduct.
Furthermore, the direct linkage of executive remuneration to ESG performance metrics in 2024 highlights a tangible commitment to achieving sustainability goals. This approach not only enhances transparency but also aligns leadership incentives with the bank's broader environmental and social objectives.
Commercial Bank of Qatar is actively promoting green finance, evidenced by its CHF 225 million Green Bond issuance in September 2024, the largest of its kind from Qatar. This move underscores a commitment to environmental sustainability and aligns with global trends in responsible investing.
The bank further supports eco-conscious endeavors through specialized products like Green Vehicle Loans and Green Mortgage Loans. These financial tools are designed to encourage the adoption of environmentally friendly transportation and housing solutions, directly contributing to a greener economy.
These initiatives reflect Commercial Bank of Qatar's strategic direction to be a key player in Qatar's transition to a low-carbon economy. By integrating green finance into its core offerings, the bank aims to foster sustainable development and meet the growing demand for environmentally responsible financial products.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
The Commercial Bank of Qatar (CBQ) is actively working to reduce its carbon footprint. They have a clear goal: to cut greenhouse gas emissions from their own operations by 25% by the year 2030, using 2021 as the baseline. This commitment shows a strong focus on environmental responsibility.
To achieve this, CBQ is implementing several practical measures. These include installing solar panels to harness renewable energy, transitioning their vehicle fleet to electric models, and making their bank facilities more energy-efficient. These initiatives are key components of their strategy to minimize their environmental impact.
CBQ's efforts in carbon footprint reduction are part of a broader trend in the financial sector towards sustainability. For instance, by 2024, many financial institutions are expected to report on their Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, with increasing pressure to address Scope 3 emissions as well. CBQ's proactive stance positions them favorably within this evolving landscape.
- Target: 25% reduction in operational greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 (vs. 2021).
- Initiatives: Solar panel installation, electric vehicle fleet conversion, energy consumption optimization.
- Industry Trend: Growing emphasis on emissions reporting and reduction across financial institutions.
Sustainable Operations
Commercial Bank of Qatar is actively integrating sustainability into its core operations, moving beyond mere financial support for green initiatives. This includes a strong push towards paperless transactions and the widespread adoption of digital payment methods, significantly reducing paper consumption.
The bank has set an ambitious target to electrify its entire vehicle fleet by 2025, a move designed to directly combat carbon emissions and promote cleaner transportation. These internal operational changes underscore a commitment to environmental responsibility, aiming to minimize waste and foster a more eco-friendly banking environment for its customers.
- Paperless Transactions: Increased adoption of digital platforms reduces reliance on paper, aligning with sustainability goals.
- Fleet Electrification: Aiming for 100% electric fleet by 2025 to lower operational carbon footprint.
- Digital Payments: Promoting digital payment methods further minimizes physical resource usage.
- Waste Reduction: Operational efficiencies contribute to overall waste minimization within the bank's activities.
Environmental factors are increasingly shaping Commercial Bank of Qatar's strategy, aligning with Qatar's National Environment and Climate Change Strategy. The bank's 2024 Sustainability Report highlights a strong ESG focus, evidenced by an MSCI ESG 'A' rating and executive pay linked to sustainability targets.
CBQ is actively promoting green finance, exemplified by its CHF 225 million Green Bond issuance in September 2024, the largest from Qatar. This supports eco-friendly products like Green Vehicle Loans and Green Mortgage Loans, contributing to a low-carbon economy.
The bank aims to cut operational greenhouse gas emissions by 25% by 2030 (from a 2021 baseline) through solar panel installation and fleet electrification, targeting 100% electric vehicles by 2025. This proactive stance on emissions reduction and digital transformation, including paperless transactions, positions CBQ favorably within the evolving sustainable finance landscape.
| Environmental Initiative | Target/Status | Date/Period | Impact |
| Operational GHG Emission Reduction | 25% by 2030 (vs. 2021) | Ongoing | Reduced carbon footprint |
| Green Bond Issuance | CHF 225 million | September 2024 | Financing for green projects |
| Fleet Electrification | 100% electric fleet | By 2025 | Lower operational emissions |
| MSCI ESG Rating | A | 2024 | Strong ESG performance |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our Commercial Bank of Qatar PESTLE Analysis is meticulously constructed using data from official Qatari government ministries, reports from the Qatar Central Bank, and analyses from leading international financial institutions like the IMF and World Bank. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental landscape impacting the bank.