Cantaloupe Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cantaloupe Bundle
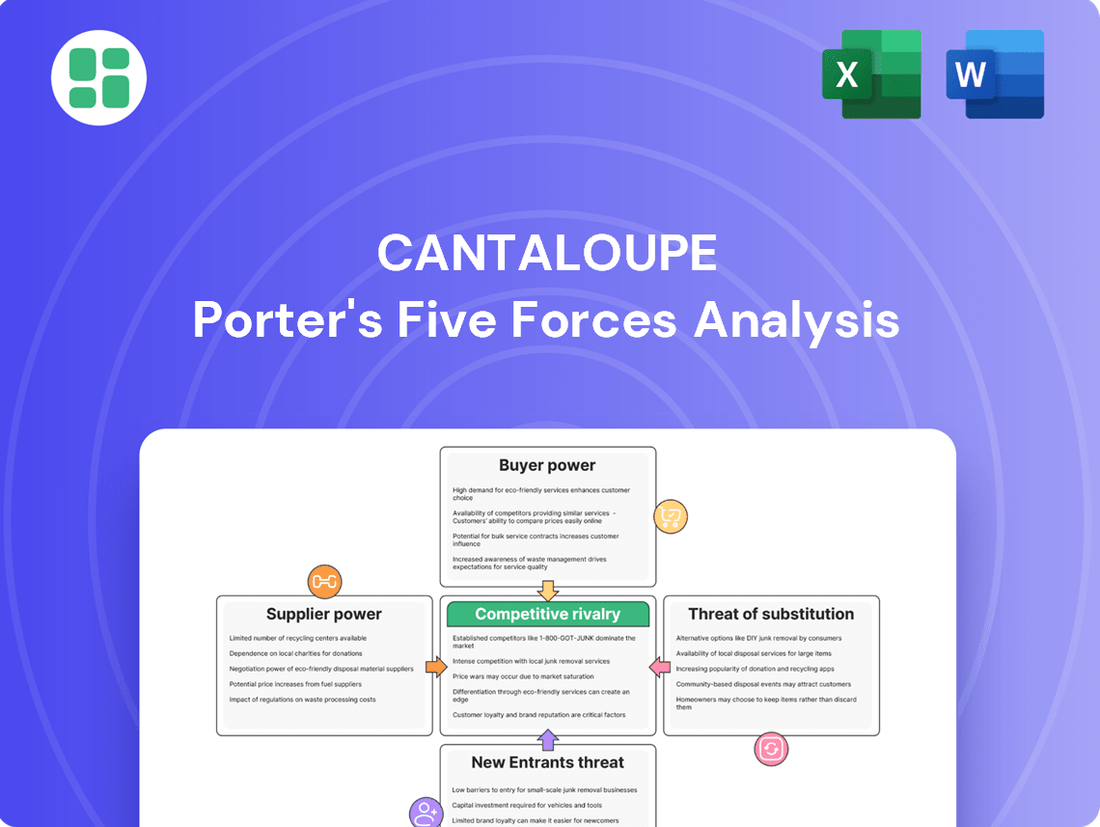
Cantaloupe's Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals a moderately competitive landscape, with significant buyer power and a moderate threat from substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Cantaloupe’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Cantaloupe Inc. depends on a select group of suppliers for critical, specialized hardware, including payment readers and telemetry devices. This reliance on a limited pool of providers for these integrated solutions gives these suppliers a degree of bargaining power. For instance, if Cantaloupe faces significant costs to switch its existing system architecture or recertify new hardware, these switching costs further bolster supplier leverage.
Cantaloupe's reliance on major payment networks like Visa and Mastercard, along with payment processors, significantly impacts its bargaining power. These entities are fundamental to Cantaloupe's ability to process transactions, a core component of its business model.
While Cantaloupe's transaction volume provides some leverage, the critical nature of these payment services means the networks largely dictate terms, including transaction fees and operational compliance. For instance, Visa and Mastercard consistently adjust interchange fees, which directly affect the cost structure for companies like Cantaloupe.
Cantaloupe relies on software and cloud services, a sector with varying supplier power. While general cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure offer ample choice, increasing competition, specialized software for vending management or data analytics might have fewer providers. This concentration could give those niche suppliers more leverage, impacting Cantaloupe's costs and service availability.
Hardware Component Manufacturers
Cantaloupe's reliance on hardware component manufacturers for its physical devices, such as cashless readers and kiosks, means these suppliers can wield significant bargaining power. When raw material prices for components like semiconductors or display panels increase, or if supply chains face disruptions, these costs can be passed on to Cantaloupe, impacting its profitability. For example, the global semiconductor shortage experienced in 2021-2023 significantly drove up component costs across many industries, including those supplying hardware for payment systems.
However, the extent of this power is often mitigated by the availability of alternative suppliers for standard components. If Cantaloupe can source essential parts from multiple manufacturers, it reduces the leverage any single supplier holds. This diversification strategy is crucial for maintaining cost control and supply chain resilience. In 2024, many technology companies continued to focus on diversifying their supplier base to counter geopolitical risks and potential disruptions.
- Component Cost Sensitivity: Cantaloupe's margins can be directly affected by the price of components like microchips and displays.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Disruptions, such as those seen in 2021-2023 due to global events, can increase supplier leverage.
- Mitigating Factor: Access to multiple suppliers for standard parts can significantly reduce the bargaining power of individual manufacturers.
Intellectual Property and Licensing
Suppliers who possess critical intellectual property (IP) or patents, particularly in areas like payment processing security or the Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity essential for Cantaloupe's vending machine operations, can wield considerable bargaining power. Cantaloupe might find itself needing to license these proprietary technologies, directly impacting its operational costs and flexibility. This reliance on licensed IP can lead to significant fees and restrictive usage rights, making it difficult and expensive to switch to alternative solutions or develop comparable in-house capabilities.
For instance, in 2024, companies specializing in secure payment gateway technology often command premium licensing fees due to the increasing demand for PCI compliance and fraud prevention. The average annual licensing cost for advanced payment security software can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on the features and scale of deployment. This financial burden directly affects Cantaloupe's profitability and its ability to negotiate favorable terms, as the unique nature of the IP limits its alternatives.
- Intellectual Property Dominance: Suppliers holding patents for secure payment processing or IoT communication protocols create a dependency for Cantaloupe.
- Licensing Costs: The need to license critical IP can result in substantial ongoing fees, impacting Cantaloupe's cost structure.
- Limited Alternatives: The specialized nature of such IP makes it challenging for Cantaloupe to find or develop in-house substitutes, strengthening supplier leverage.
- Negotiating Disadvantage: Cantaloupe may face unfavorable terms and conditions when negotiating licensing agreements due to the essential nature of the technology.
Cantaloupe's reliance on specialized hardware suppliers, particularly for payment readers and telemetry devices, grants these providers significant bargaining power. The high costs associated with switching existing systems or recertifying new hardware further solidify this leverage, making it difficult and expensive for Cantaloupe to change suppliers.
The critical nature of payment networks like Visa and Mastercard, along with payment processors, means these entities largely dictate terms, including transaction fees. While Cantaloupe's transaction volume offers some leverage, the essential role of these services allows networks to influence costs. For example, interchange fee adjustments by Visa and Mastercard directly impact Cantaloupe's operating expenses.
Suppliers holding crucial intellectual property, such as patents for secure payment processing or IoT connectivity, also possess considerable bargaining power. Cantaloupe may need to license these proprietary technologies, leading to substantial fees and restrictive usage rights, making it challenging to find or develop alternatives.
| Supplier Type | Impact on Cantaloupe | Example of Leverage | Mitigating Factors |
| Specialized Hardware (Payment Readers, Telemetry) | High bargaining power due to reliance and switching costs. | Supplier dictates terms for critical components. | Availability of alternative suppliers for standard parts. |
| Payment Networks (Visa, Mastercard) | Significant influence through transaction fees and compliance. | Ability to adjust interchange fees impacting Cantaloupe's costs. | Cantaloupe's transaction volume provides some negotiation leverage. |
| Intellectual Property Holders (Payment Security, IoT) | Can command premium licensing fees for essential technologies. | Need for licensing restricts flexibility and increases costs. | Development of in-house capabilities or open-source alternatives. |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Cantaloupe's competitive environment dissects the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry rivalry, supplier power, buyer bargaining, new entrants, and substitutes.
Customers Bargaining Power
Cantaloupe serves a vast and diverse customer base, encompassing everything from small, independent vending machine operators to large, sophisticated micro-market chains. This wide distribution means that no single client commands a substantial percentage of Cantaloupe's overall revenue.
In 2023, Cantaloupe's revenue reached $192.7 million, with its customer base comprising thousands of operators across North America. This fragmentation inherently limits the bargaining power of any individual customer, as their business, while important, is not critical to Cantaloupe's financial stability.
Customers who fully embrace Cantaloupe's integrated platform, encompassing hardware, software, and payment processing, encounter moderate switching costs. This integration creates a sticky ecosystem that discourages easy departure.
The process of moving existing vending machines, retraining employees on a new software interface, and reconfiguring payment terminals represents a significant investment of both time and money for businesses. For instance, a large vending operator might have hundreds or even thousands of machines to update.
These integration hurdles effectively diminish the bargaining power of customers. Once a business is deeply embedded within Cantaloupe's system, the effort and expense required to switch to a competitor become substantial deterrents, solidifying Cantaloupe's position.
Many unattended retail operators, particularly smaller businesses, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This means they closely scrutinize transaction fees and subscription costs, which are crucial for Cantaloupe's revenue. For instance, in 2024, the average transaction fee for unattended retail solutions can range from 2% to 5%, making even small percentage differences impactful for operators with high transaction volumes.
This heightened sensitivity to pricing puts collective pressure on Cantaloupe. Operators are likely to seek out competitors offering more favorable fee structures or value-added services at a lower overall cost. This dynamic forces Cantaloupe to remain competitive and consistently demonstrate the value proposition of its offerings to retain its customer base.
Availability of Alternative Solutions
The bargaining power of Cantaloupe's customers is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative solutions. Customers, particularly larger operators, can explore other payment processing providers, standalone vending management software (VMS), or even simpler, less integrated systems. This variety of options, even if not perfectly matching Cantaloupe's integrated offering, grants customers leverage. For instance, the global vending machine market, valued at approximately USD 11.5 billion in 2023 and projected to grow, presents numerous players offering competing services.
The presence of these alternatives means that customers aren't locked into a single provider. They can shop around for better pricing, features, or service levels. This competitive landscape empowers them to negotiate terms or switch if they feel Cantaloupe's pricing or offerings are not aligned with their needs. In 2024, the market for VMS is also expanding, with new entrants and established software companies enhancing their capabilities, further diversifying customer choices.
- Diverse Payment Processing Options: Customers can choose from various payment gateways and processors, some of which may offer more competitive rates or specialized features.
- Standalone VMS Solutions: Many companies offer dedicated vending management software that handles inventory, sales, and route optimization, providing an alternative to integrated Cantaloupe solutions.
- Simpler, Cost-Effective Alternatives: For smaller operators, basic inventory tracking or manual sales reconciliation methods might suffice, representing a lower-cost, albeit less sophisticated, alternative.
- Negotiating Power: The existence of these alternatives allows customers to negotiate pricing and service agreements with Cantaloupe, as they can credibly threaten to switch to a competitor.
Industry Consolidation and Large Customers
While the unattended retail market can appear fragmented, the potential for consolidation among larger operators is a key factor. As these operators grow, their increased purchasing volume grants them greater leverage. This means they can negotiate for more favorable terms and pricing from suppliers like Cantaloupe.
Large enterprise clients, such as Premier Foodservice, already demonstrate this amplified bargaining power. These significant customers often require highly customized solutions or demand better pricing structures, putting pressure on suppliers to adapt their offerings and terms to secure and retain their business.
- Industry Consolidation: Potential for larger unattended retail operators to gain significant market share through mergers and acquisitions.
- Increased Purchasing Volume: Consolidated operators can negotiate better terms due to buying power.
- Enterprise Client Demands: Large clients like Premier Foodservice can influence supplier offerings and pricing.
- Negotiating Power: Greater volume and strategic importance of large clients enhance their ability to dictate terms.
Cantaloupe's customer base is highly fragmented, meaning no single client holds significant sway. For instance, in 2023, the company served thousands of operators, preventing any one from dictating terms. While customers using integrated platforms face moderate switching costs, the availability of alternative payment processors and standalone vending management software in 2024 provides leverage.
Price sensitivity among operators, especially smaller ones, intensifies this pressure, as even minor fee differences matter. For example, 2024 transaction fees typically range from 2% to 5%. Furthermore, industry consolidation could amplify the bargaining power of larger operators, enabling them to negotiate better terms due to increased purchasing volumes.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Fragmentation | Lowers bargaining power | Thousands of operators served in 2023; no single client dominates revenue. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate; lowers bargaining power | Integrated hardware, software, and payment processing create sticky ecosystems. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Increases bargaining power | Diverse payment gateways, standalone VMS, and simpler solutions available in 2024. |
| Price Sensitivity | Increases bargaining power | Operators scrutinize fees; 2024 transaction fees range from 2% to 5%. |
| Industry Consolidation | Increases bargaining power for larger operators | Potential for larger operators to gain leverage through increased purchasing volume. |
Full Version Awaits
Cantaloupe Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Cantaloupe Porter's Five Forces Analysis will equip you with a deep understanding of the competitive landscape, enabling strategic decision-making. You're previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The unattended retail technology market is buzzing with a wide array of players, including specialized payment processors, vending management software providers, and even established hardware manufacturers making a digital leap. This broad spectrum means companies like Nayax and Square, known for their fintech solutions, are now competing directly with traditional vending giants such as Crane Co. This dynamic mix of specialized and broad-market competitors significantly fuels the intensity of rivalry.
The unattended retail sector, including markets like self-checkout and smart vending, is booming. In 2024, this growth is fueled by consumer demand for convenience and the widespread adoption of cashless transactions. This rapid expansion naturally draws in new entrants and spurs existing companies to innovate aggressively, creating a highly competitive landscape.
Companies are investing heavily in technology to capture market share. For instance, advancements in AI for inventory management and contactless payment systems are becoming standard. This innovation race means businesses must constantly upgrade their offerings to stay relevant, as seen with the increasing deployment of smart fridges and automated retail kiosks across various locations.
Cantaloupe stands out by offering a comprehensive, integrated platform that includes payment processing, remote device monitoring, and inventory management. This end-to-end solution aims to simplify operations for its clients.
Competitors often try to differentiate by focusing on niche markets with specialized features, adopting aggressive pricing strategies, or tailoring solutions for specific industries like vending or micro-markets. For instance, some competitors may offer advanced analytics or unique payment integrations not found in broader platforms.
Given this landscape, Cantaloupe's ability to innovate and continuously improve its existing features, while potentially exploring new functionalities, is paramount. Staying ahead requires ongoing investment in research and development to maintain its competitive edge in a dynamic market.
Market Share and Customer Acquisition
Cantaloupe demonstrates a substantial market presence with over 32,000 active customers and 1.3 million active devices as of early 2024. This scale provides a strong foundation, but the competitive landscape is dynamic.
Rival companies are aggressively pursuing market share, often employing strategies like competitive pricing and strategic alliances to onboard new clients. This creates a challenging environment for Cantaloupe to not only acquire new customers but also to retain its existing base.
- Market Share: Cantaloupe serves over 32,000 active customers.
- Device Footprint: The company manages 1.3 million active devices.
- Competitive Tactics: Rivals are using aggressive pricing and partnerships to gain customers.
- Customer Retention Focus: Intense competition necessitates a strong focus on retaining existing clients.
Global and Regional Competition
Cantaloupe faces a dynamic competitive landscape, with its strong presence in the U.S., U.K., EU, Australia, and Mexico. However, the intensity of rivalry differs significantly across these regions.
Localized competitors with deep market penetration or global players possessing robust regional networks can significantly amplify competitive pressure in specific territories. For instance, in the U.S., Cantaloupe contends with established players like Nayax and Ingenico, while in Europe, regional specialists often hold sway. This necessitates a flexible strategic approach to navigate these varied competitive environments effectively.
- U.S. Market: Cantaloupe competes with companies like Nayax, which reported a 30% revenue growth in 2023, and Ingenico, a major player in payment terminals.
- European Market: Regional competitors, often with specialized payment solutions for specific industries, present a challenge. For example, smaller European fintech firms are increasingly offering integrated payment and vending solutions.
- Asia-Pacific: While Cantaloupe has a presence, local payment gateway providers and vending machine operators in countries like Japan and South Korea offer strong competition.
The competitive rivalry in the unattended retail technology market is intense, driven by a growing number of specialized and broad-market players. Companies like Nayax, which saw a 30% revenue increase in 2023, and established entities such as Crane Co. are actively competing with Cantaloupe. This dynamic is further amplified by aggressive pricing strategies and the formation of strategic alliances by rivals seeking to capture market share and onboard new clients.
Innovation is a key battleground, with companies investing heavily in technologies like AI for inventory management and advanced contactless payment systems. This constant push for technological superiority means businesses must continually upgrade their offerings to remain competitive, as seen with the increasing adoption of smart vending solutions. Cantaloupe's substantial customer base of over 32,000 and 1.3 million devices as of early 2024 highlights its position, but the need for continuous improvement and feature enhancement is critical to maintain its edge.
Regional variations in competition are also significant, with localized competitors and global networks creating distinct challenges in markets like the U.S. and Europe. For example, in the U.S., Cantaloupe faces competition from Nayax and Ingenico, while Europe sees strong performance from regional specialists and emerging fintech firms offering integrated solutions.
| Competitor Example | Key Offering | 2023 Performance Indicator |
| Nayax | Fintech solutions, payment processing | 30% revenue growth |
| Crane Co. | Vending hardware, payment solutions | Established market presence |
| Ingenico | Payment terminals | Major player in payment hardware |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitute for Cantaloupe's digital payment and management solutions remains the persistent use of manual systems and cash transactions. Many smaller operators still rely on traditional methods like manual inventory tracking and cash-only sales, presenting a lower-cost, albeit less efficient, alternative. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of the convenience services market, particularly smaller, independent operators, continued to utilize cash as a primary payment method, representing a direct substitute for digital payment adoption.
Generic payment processors pose a significant threat by offering basic transaction capabilities that bypass specialized vending solutions. While potentially cheaper per transaction, these options lack the integrated inventory tracking and operational analytics that Cantaloupe provides, potentially leading to higher overall costs through inefficiency. For instance, a generic processor might charge 2.5% per transaction, whereas integrated solutions like Cantaloupe, while potentially having a slightly higher base fee, offer value through reduced stockouts and optimized routes, which can save operators more in the long run.
The threat of substitutes for Cantaloupe's comprehensive telemetry and inventory solutions comes from simpler, less integrated tools. Operators might opt for basic telemetry devices or manual inventory tracking methods instead of a full end-to-end platform. These alternatives provide rudimentary data on sales and stock levels, serving as a viable substitute for those who don't prioritize advanced data analytics or operational optimization.
While these basic tools lack the depth of insights offered by Cantaloupe, their lower cost and simpler implementation make them attractive to certain segments of the market. For instance, a small vending operator with a limited number of machines might find manual tracking sufficient. This is especially true if their primary concern is basic sales reconciliation rather than sophisticated demand forecasting or route optimization, which Cantaloupe's platform excels at.
Direct Consumer Payment Apps
Direct consumer payment apps, like standalone mobile wallets not directly integrated with a vending machine's operational backend, pose a partial threat by potentially bypassing Cantaloupe's payment processing. While these apps could facilitate a transaction, they do not offer the integrated management and data insights that Cantaloupe provides to vending operators, thus limiting their substitutive power for the overall service. For instance, while mobile payment adoption is widespread, with estimates suggesting over 70% of smartphone users in developed markets utilize mobile payment options by 2024, the specific integration with vending machine software remains key.
This means that while a consumer might use a generic payment app, the operator misses out on the benefits of a connected system.
- Partial Substitution: Direct consumer payment apps can replace the payment function but not the broader operational management benefits.
- Limited Value for Operators: These alternative payment methods don't provide the same level of efficiency or data for vending machine operators.
- Market Penetration: Widespread adoption of mobile payments globally, exceeding 70% in many developed economies by 2024, highlights consumer preference for convenience.
In-house Developed Solutions
Large enterprise operators, particularly those with significant scale, may consider developing their own proprietary software for managing unattended retail operations and payment processing. This represents a substantial investment in terms of cost and complexity.
For very large players, this in-house development can be a strategic alternative to relying on third-party solutions, offering greater control and potentially avoiding ongoing licensing or transaction fees. For instance, a major convenience store chain with thousands of locations might find the upfront investment justifiable to eliminate recurring software costs.
While the initial outlay for developing a robust in-house system can be considerable, potentially running into millions of dollars for a comprehensive platform, the long-term savings and customization benefits can make it a compelling substitute. This approach allows for tailored features that precisely match the operator's unique business processes and future growth strategies.
The threat of substitutes from in-house developed solutions is amplified for operators who possess strong internal IT capabilities and a clear vision for their technology roadmap. These entities are better positioned to undertake such a complex project and realize its potential benefits.
The threat of substitutes for Cantaloupe's offerings stems from simpler, less integrated solutions and even manual processes. While not as feature-rich, these alternatives are often more cost-effective for smaller operators. For instance, in 2024, many smaller vending machine operators continued to rely on manual inventory tracking and cash transactions, representing a direct substitute for digital payment and management systems.
Generic payment processors also pose a threat by offering basic transaction capabilities without the integrated analytics Cantaloupe provides. While potentially cheaper per transaction, these lack the efficiency gains of a full platform. For example, a generic processor might charge 2.5% per transaction, whereas integrated solutions offer value through reduced stockouts and optimized routes.
The market also sees simpler telemetry and inventory tools as substitutes for Cantaloupe's comprehensive solutions. These basic alternatives offer rudimentary data, appealing to operators prioritizing lower costs over advanced analytics. A small operator with few machines might find manual tracking sufficient if their focus is basic sales reconciliation rather than sophisticated demand forecasting.
| Substitute Type | Key Feature | Operator Benefit | Cantaloupe's Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Systems/Cash | Low initial cost, simplicity | Reduced upfront investment | Efficiency, data analytics, reduced errors |
| Generic Payment Processors | Basic transaction processing | Potentially lower per-transaction fees | Integrated inventory, route optimization, detailed analytics |
| Basic Telemetry/Manual Tracking | Rudimentary data collection | Lower cost, easier implementation | Advanced insights, predictive analytics, operational efficiency |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the unattended retail technology market, like the one Cantaloupe operates in, demands significant upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in developing reliable hardware, building robust software infrastructure, and securing necessary payment gateway certifications. For instance, the cost of developing and manufacturing smart vending machines or micro-markets can easily run into millions of dollars.
Furthermore, establishing a widespread sales and support network to compete effectively requires substantial financial backing. This high initial investment acts as a formidable barrier, deterring many potential new entrants from even attempting to challenge established players like Cantaloupe.
The significant technological hurdles in developing integrated platforms for vending operations act as a substantial barrier to entry. Creating a seamless system that combines IoT for remote monitoring, fintech for secure payments, robust cloud infrastructure, and advanced cybersecurity demands specialized knowledge across multiple disciplines.
Aspiring competitors face immense difficulty in replicating the sophisticated technological stack already established by incumbent players. For instance, a new entrant would need to invest heavily in R&D to match the capabilities of companies like Cantaloupe, which already offers comprehensive solutions like its Seed™ platform, known for its advanced telemetry and payment processing.
This high degree of technical expertise required means that new entrants are unlikely to quickly develop a competitive product. The ongoing evolution of technology, particularly in areas like AI-driven inventory management and predictive maintenance, further raises the bar, requiring continuous investment and skilled personnel, making it a challenging landscape for newcomers.
Cantaloupe benefits significantly from its extensive installed base of active customers and devices, which is a key factor in creating strong network effects. This means that as more users and devices join the Cantaloupe ecosystem, the platform becomes more valuable for everyone, attracting more services and generating richer data. For instance, in 2023, Cantaloupe reported a substantial increase in its active cashless payment devices, underscoring the scale of its network.
New companies entering the market find it incredibly difficult to overcome this established advantage. They must not only replicate Cantaloupe's existing infrastructure but also invest heavily in building trust and convincing customers to switch from a familiar and reliable system. This often involves a lengthy and expensive process of customer acquisition and relationship building, making it a significant barrier to entry.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance
The payment processing industry faces significant regulatory hurdles that act as a substantial barrier to entry. New companies must meticulously adhere to stringent compliance standards, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and various data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA. For instance, achieving PCI DSS Level 1 compliance, the highest level, can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars annually for robust security measures and ongoing audits.
Navigating these complex legal and security requirements demands considerable investment in compliance infrastructure and expertise. This includes developing secure systems, implementing rigorous data protection protocols, and undergoing regular, costly assessments. The sheer complexity and financial commitment required to meet these obligations deter many potential new entrants, thereby protecting existing players.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: PCI DSS compliance alone can cost businesses between $5,000 to over $500,000 annually depending on size and complexity.
- Data Privacy Laws: Adherence to GDPR and CCPA necessitates significant investment in data governance and security, with potential fines for non-compliance reaching millions.
- Security Infrastructure Investment: New entrants must build and maintain secure payment gateways and data storage, requiring substantial upfront capital expenditure.
Brand Recognition and Market Penetration
Cantaloupe has cultivated significant brand recognition and a robust presence within the unattended retail sector. This established reputation makes it challenging for new companies to gain traction.
New entrants face the daunting task of substantial investment in marketing and sales to achieve even minimal visibility. They must overcome the ingrained brand loyalty that existing players, like Cantaloupe, have fostered over time.
Furthermore, the established distribution networks of companies such as Cantaloupe present a considerable barrier. Replicating this reach requires significant capital and time, often proving prohibitive for newcomers.
- Brand Loyalty: Consumers are often loyal to familiar unattended retail solutions, making it hard for new brands to break through.
- Marketing Investment: New entrants need to spend heavily on advertising and promotion to build awareness against established brands.
- Distribution Access: Securing prime locations and efficient logistics is crucial, and existing players already have these channels.
- Market Penetration Costs: Gaining market share requires overcoming established players' advantages, demanding significant upfront capital.
The threat of new entrants into the unattended retail technology market, where Cantaloupe operates, is moderate to low. Significant capital is required for hardware, software, and payment gateway certifications, with costs potentially running into millions for smart vending machines. For example, developing and manufacturing advanced unattended retail hardware demands substantial upfront investment.
The technological complexity of integrated platforms, including IoT, fintech, and cybersecurity, presents a high barrier. New companies struggle to match the R&D investment of established players like Cantaloupe, which leverages its advanced Seed™ platform.
Cantaloupe's extensive installed base and strong network effects, evidenced by its substantial increase in active cashless payment devices in 2023, make it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. Building trust and convincing customers to switch requires considerable time and financial resources.
Stringent regulatory compliance, such as PCI DSS Level 1 certification, incurs significant costs, potentially hundreds of thousands of dollars annually. Adherence to data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA further adds to the financial and operational burden for new entrants.
Established brand recognition and loyalty, coupled with the high costs of marketing and securing distribution channels, further deter new competitors. Overcoming these entrenched advantages necessitates significant upfront capital and strategic effort.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Cost/Impact |
| Capital Requirements | Developing and manufacturing advanced unattended retail hardware and software. | Millions of dollars for initial setup and production. |
| Technological Expertise | Creating integrated platforms with IoT, fintech, and cybersecurity. | High R&D investment to match incumbent capabilities. |
| Network Effects | Building a large installed base and customer network. | Significant customer acquisition costs and time to build trust. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adhering to PCI DSS, GDPR, CCPA, and other security standards. | $5,000 to over $500,000 annually for PCI DSS compliance; millions in potential fines for data privacy breaches. |
| Brand Recognition & Distribution | Establishing brand loyalty and securing distribution channels. | Substantial marketing investment and time to build market presence. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Cantaloupe Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from agricultural market reports, USDA statistics, and industry trade publications to assess competitive intensity and market dynamics.