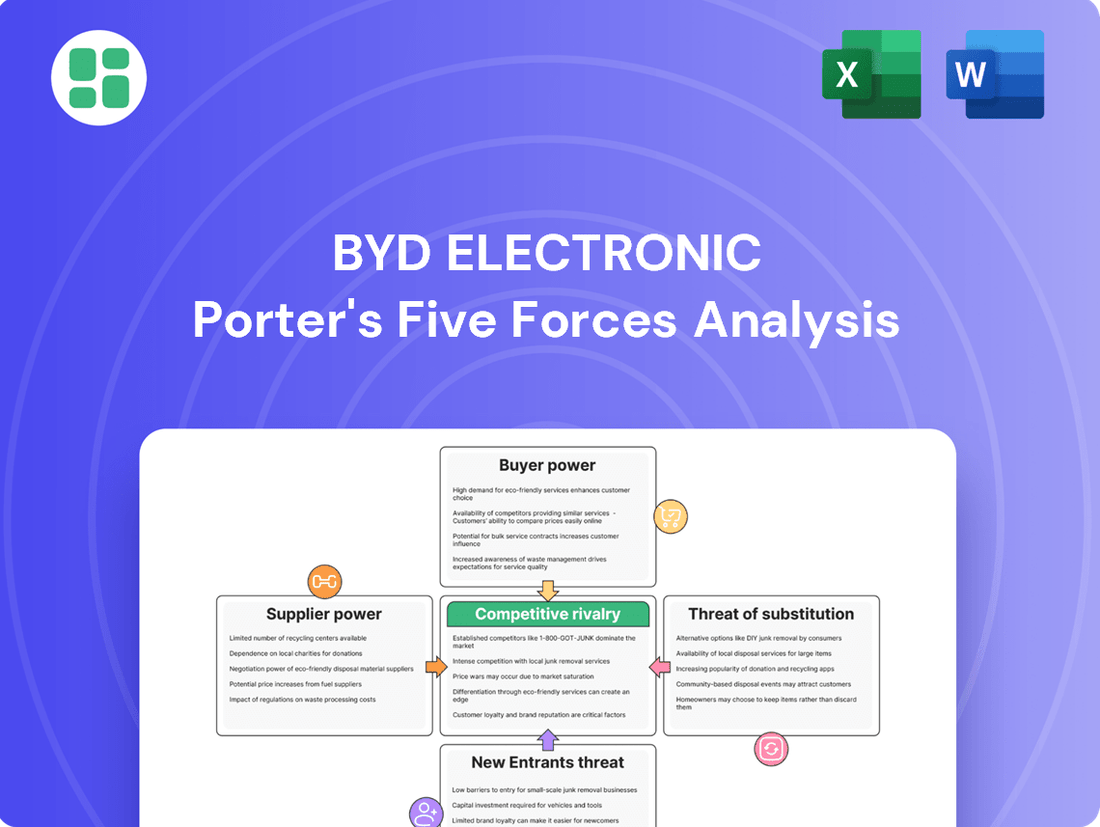
BYD Electronic Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
BYD Electronic Bundle
BYD Electronic faces a dynamic landscape shaped by intense rivalry and the constant threat of new entrants in the competitive electronics manufacturing sector. Understanding the power of its suppliers and the growing influence of buyers is crucial for strategic advantage.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping BYD Electronic’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers for critical components, such as advanced semiconductors and specialized display technologies, directly influences their leverage over BYD Electronic. When the pool of providers for these unique offerings is small, their bargaining power escalates, potentially driving up costs and creating supply chain risks for BYD Electronic.
BYD Electronic's strategic decision to pursue vertical integration, producing a significant portion of its components internally, serves as a crucial countermeasure against this supplier power. This integration aims to reduce reliance on external suppliers for key inputs, thereby strengthening BYD Electronic's negotiating position and enhancing supply chain resilience.
The criticality of certain components to BYD Electronic's final products, such as proprietary chips for intelligent systems or advanced camera modules for smartphones, grants those suppliers increased leverage. For instance, if a specific advanced semiconductor is essential for BYD's electric vehicle control units and only a few manufacturers can produce it to the required specifications, those suppliers hold significant bargaining power. This reliance on specialized, high-value inputs can dictate terms and pricing.
A high reliance on a single source for essential, high-value components directly amplifies supplier power. If BYD Electronic depends heavily on one supplier for a unique battery management system component, that supplier can command higher prices or dictate more favorable payment terms. This concentration of sourcing for critical parts creates a vulnerability that suppliers can exploit.
BYD Electronic's strategic approach of vertical integration actively works to mitigate this supplier power. By developing in-house capabilities for key components, such as their own battery technology or semiconductor design, BYD reduces its dependence on external suppliers. This strategy, exemplified by their significant investments in battery production, aims to secure supply chains and gain greater control over costs and innovation, thereby diminishing supplier leverage.
The costs BYD Electronic faces when switching from one supplier to another are a significant factor in supplier bargaining power. These costs can include re-tooling manufacturing lines, redesigning products to accommodate new components, or the lengthy process of re-qualifying parts to meet quality and performance standards. For instance, if a key electronic component requires extensive testing and validation before integration, the expense and time involved can deter BYD Electronic from seeking alternative suppliers.
High switching costs effectively lock BYD Electronic into relationships with its current suppliers, granting those suppliers greater leverage. This leverage allows suppliers to potentially negotiate more favorable terms, such as higher prices or less flexible delivery schedules, knowing that BYD Electronic will incur substantial penalties for switching. This dynamic is particularly relevant in the fast-paced electronics industry where component reliability and compatibility are paramount.
BYD Electronic actively works to mitigate these high switching costs by prioritizing the standardization of components across its product lines. By using common parts from multiple approved suppliers, the company aims to reduce the impact of re-tooling and re-qualification should a supplier change become necessary. This strategy enhances BYD Electronic's flexibility and reduces its dependence on any single supplier, thereby diminishing supplier bargaining power.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward and competing directly with BYD Electronic significantly amplifies their bargaining power. This is especially true for suppliers of advanced, technology-driven components who could bypass BYD Electronic and offer their integrated solutions directly to the end-users. For instance, a supplier of advanced display technology could potentially move into producing complete display modules for smartphones, thereby directly challenging BYD Electronic’s position in that market segment.
BYD Electronic's robust in-house manufacturing and assembly capabilities serve as a crucial countermeasure against this threat. By controlling a significant portion of its production chain, BYD Electronic can reduce its reliance on external suppliers for critical components and integrated solutions. In 2024, BYD Electronic's vertical integration strategy, particularly in areas like battery technology and electric vehicle manufacturing, demonstrated its commitment to controlling key value chain elements, thereby mitigating supplier power.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers possessing the capability and motivation to enter BYD Electronic's market as direct competitors bolster their bargaining leverage.
- Technology Component Suppliers: This risk is heightened with suppliers of specialized, technology-intensive components who might offer end-to-end solutions to BYD Electronic's clientele.
- BYD Electronic's Defense: BYD Electronic's substantial manufacturing prowess acts as a deterrent, allowing it to absorb or replicate supplier capabilities internally.
Supplier's Share of BYD Electronic's Purchases
The bargaining power of suppliers for BYD Electronic is influenced by how much of a single supplier's business BYD Electronic represents. If BYD Electronic is a crucial client for a supplier, that supplier might have less leverage. Conversely, if a supplier's sales are not heavily reliant on BYD Electronic, their power increases.
BYD Electronic's significant purchasing volume generally grants it considerable leverage over its suppliers. For instance, in 2024, BYD Electronic's substantial orders for components like semiconductors and battery materials likely allowed them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms. This scale is a key factor in mitigating supplier power.
- Supplier Dependence: The extent to which a supplier depends on BYD Electronic for its revenue directly impacts its bargaining power. A supplier with a diversified customer base will likely have more power.
- BYD Electronic's Purchasing Scale: As a major player in the electric vehicle and electronics manufacturing sectors, BYD Electronic's large-scale procurement activities typically provide it with significant negotiation leverage.
- Component Criticality: The importance of a specific component to BYD Electronic's production process also plays a role. If a component is unique or difficult to source elsewhere, the supplier of that component may wield greater power.
- Supplier Concentration: The number of available suppliers for critical components affects bargaining power. A market with few suppliers for a key input generally favors those suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for BYD Electronic is significantly shaped by the concentration of suppliers for critical components. When few suppliers can provide essential items like advanced semiconductors or specialized display technologies, their leverage increases, potentially raising costs for BYD Electronic.
BYD Electronic's vertical integration strategy, particularly its substantial investments in battery production and internal component manufacturing, serves as a key defense against supplier power. This approach reduces reliance on external sources, strengthening BYD's negotiating position and enhancing supply chain stability.
The switching costs associated with changing suppliers, including re-tooling and re-qualification, can lock BYD Electronic into existing relationships, granting suppliers greater leverage to dictate terms. BYD Electronic mitigates this by standardizing components across its product lines, increasing flexibility and reducing dependence.
The threat of suppliers engaging in forward integration, potentially becoming direct competitors, also amplifies their bargaining power, especially for technology-driven components. BYD Electronic's extensive in-house manufacturing capabilities help counter this by enabling internal absorption or replication of supplier functions.
| Factor | Impact on BYD Electronic | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High for specialized components, increasing supplier leverage. | Vertical integration, diversifying supplier base where possible. |
| Switching Costs | Significant for critical components, limiting flexibility. | Component standardization across product lines. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Elevated for technology suppliers, posing competitive risk. | Robust in-house manufacturing and R&D capabilities. |
| BYD's Purchasing Scale | Large volume provides significant negotiation leverage. | Leveraging scale for favorable pricing and terms. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to BYD Electronic's position in the electronics manufacturing and automotive sectors.
Streamline competitive analysis by instantly visualizing BYD Electronic Porter's Five Forces, identifying key pressures and opportunities for strategic advantage.
Customers Bargaining Power
BYD Electronic's customer base includes major smart device brands and automotive manufacturers, many of whom are powerful Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). This concentration of large, high-volume buyers gives them considerable leverage.
These significant customers can effectively negotiate for lower prices and more favorable contract terms, directly impacting BYD Electronic's profitability. For instance, BYD Electronic's reported revenue growth in 2024 was significantly boosted by increased market share with key international clients, underscoring the substantial influence these large customers wield.
The bargaining power of BYD Electronic's customers is significantly influenced by how easy or difficult it is for them to switch to other manufacturers or component suppliers. If customers can easily find alternatives, perhaps due to standardized components or a plentiful supply of similar Electronic Manufacturing Services (EMS) providers, they gain more leverage to negotiate prices or terms. For instance, if a customer relies on a component that many suppliers can produce, BYD Electronic faces greater pressure.
BYD Electronic actively works to increase customer stickiness by offering comprehensive solutions and leveraging its vertical integration. This strategy aims to make it more difficult and costly for customers to move their business elsewhere. By controlling more of the supply chain and providing a wider array of services, BYD Electronic can create dependencies that raise switching costs. For example, a customer deeply integrated into BYD Electronic's supply chain for multiple components might face substantial disruption and expense if they tried to find a new partner for all those needs.
Customers in the fiercely competitive consumer electronics and automotive industries are highly attuned to pricing. This inherent price sensitivity compels BYD Electronic to adopt and maintain competitive pricing, which in turn constrains its capacity to boost profit margins.
The electric vehicle (EV) market, for example, has witnessed aggressive price reduction tactics. These strategies can directly impact component suppliers like BYD Electronic, creating downward pressure on their pricing and profitability.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers can significantly enhance their bargaining power if they possess the capability to produce components or manage manufacturing processes in-house. While this is less frequent in the highly specialized electronics sector, major Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) might explore bringing in production of critical components internally for strategic reasons.
BYD Electronic's robust vertical integration and deep manufacturing expertise present a substantial hurdle for customers attempting full backward integration. For instance, BYD's comprehensive supply chain, from battery production to vehicle assembly, demonstrates a level of control that makes replication difficult for most clients. In 2023, BYD reported revenue of RMB 602.34 billion (approximately $85 billion USD), showcasing the scale and complexity of its operations which are hard for customers to match.
- Customer Capability: The ability of BYD Electronic's customers to manufacture components or manage production internally directly increases their bargaining leverage.
- Strategic Component Production: Large OEMs may consider in-house production for key strategic components, although this is less common in complex electronics manufacturing.
- BYD's Advantage: BYD's extensive vertical integration and specialized knowledge make it challenging for customers to achieve complete backward integration.
- Market Scale: BYD's significant market presence and operational scale, evidenced by its substantial revenue figures, create a high barrier to entry for potential customer integration efforts.
Customer Access to Information
Customers armed with detailed knowledge about product expenses, supply chain intricacies, and available alternative providers are in a stronger position to negotiate favorable terms. This increased transparency within the electronics manufacturing services (EMS) sector allows buyers to push for better pricing, directly impacting BYD Electronic's profit margins.
For instance, in 2024, BYD Electronic reported a significant revenue increase, demonstrating its capacity to navigate such customer-driven price pressures. The company's ability to maintain profitability suggests effective cost management and strong supplier relationships, mitigating the impact of informed customer demands.
- Informed Customers Drive Negotiations: Buyers with access to cost data and supplier comparisons can negotiate more aggressively.
- Transparency Pressures Margins: Openness in the EMS market empowers customers to seek better deals, potentially squeezing BYD Electronic's profitability.
- BYD Electronic's 2024 Resilience: The company's strong financial performance in 2024 indicates it can effectively manage these customer-driven pressures.
- Strategic Cost Management: BYD Electronic's profitability suggests successful strategies in controlling operational expenses and supply chain costs.
BYD Electronic's customers, particularly large OEMs in the smart device and automotive sectors, wield significant bargaining power due to their high volume purchases and the availability of alternative suppliers. This leverage allows them to negotiate for lower prices and more favorable terms, directly affecting BYD's profitability. For example, BYD Electronic's revenue growth in 2024 was partly driven by securing business with major international clients, highlighting the impact of these powerful buyers.
The ease with which customers can switch to competitors, especially for standardized components, further amplifies their negotiating strength. BYD Electronic counters this by enhancing customer loyalty through integrated solutions and vertical integration, thereby increasing switching costs. The company's substantial revenue in 2023, reaching approximately $85 billion USD, underscores the scale of operations that customers would need to replicate to achieve backward integration, a difficult feat.
| Customer Leverage Factor | Impact on BYD Electronic | Supporting Data/Example |
| High Volume Purchases | Negotiating Power for Lower Prices | Major smart device and automotive OEMs |
| Availability of Alternatives | Increased Negotiation Strength | Standardized components, numerous EMS providers |
| Customer Stickiness Initiatives | Mitigation of Switching Costs | Vertical integration, comprehensive solutions |
| Backward Integration Threat | Potential for In-house Production | Less common in complex electronics, but possible for strategic components |
| Market Scale & Revenue | Barrier to Customer Integration | 2023 Revenue: ~$85 billion USD |
What You See Is What You Get
BYD Electronic Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for BYD Electronic, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. You are viewing the exact, professionally formatted document that will be delivered instantly upon purchase, ensuring no surprises and immediate usability for your business strategy. This analysis provides an in-depth examination of industry rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitute products, all presented in the final version you will receive.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The electronics manufacturing services (EMS) and intelligent systems sectors are booming, driven by demand from AI data centers and the automotive industry. This robust growth, with the global EMS market projected to expand by 6.6% from 2024 to 2029, generally softens competitive pressures by offering ample opportunities. However, it also intensifies the race among companies to secure dominant positions within these rapidly expanding markets.
BYD Electronic faces intense competition from a broad spectrum of global and regional Electronic Manufacturing Services (EMS) providers. Key rivals such as Foxconn, Luxshare Precision, and Goertek boast significant scale and established relationships with major tech brands, creating a crowded marketplace for securing lucrative contracts.
The competitive landscape is further complicated by the sheer diversity of these players. Competitors range from massive, diversified conglomerates to more specialized niche manufacturers, each with unique strengths in terms of technology, geographic reach, and cost structures. This heterogeneity means BYD Electronic must constantly adapt its strategies to counter rivals of varying sizes and capabilities.
In 2024, the EMS market is projected to reach over $700 billion globally, underscoring the immense scale of competition. BYD Electronic's ability to innovate and maintain operational efficiency is critical for navigating this fragmented and dynamic environment, where market share is fiercely contested.
While BYD Electronic excels in vertical integration and offering complete solutions, the Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) sector often sees standardized components and processes, making strong product differentiation a hurdle. This can lead to intense competition, especially when customers face low switching costs, making it easier for rivals to attract clients with minor price or service advantages.
BYD Electronic counters this by focusing on advanced module integration and fostering strategic partnerships, which serve as key differentiators. For instance, in 2023, BYD Electronic reported revenue growth of 22.5% year-on-year, reaching approximately RMB 177.8 billion, demonstrating its ability to capture market share despite competitive pressures.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers in the electronics manufacturing sector, where BYD Electronic operates, are notably high. These barriers, such as specialized machinery and significant capital investments in production lines, make it difficult and costly for companies to leave the market even when facing losses. For instance, the semiconductor manufacturing industry, a key area for electronics, requires billions in investment for a single fabrication plant. This situation can trap underperforming firms, leading to prolonged intense competition as they strive to recover their sunk costs.
The persistence of these struggling competitors fuels aggressive rivalry, often manifesting as price wars. Companies may slash prices to maintain market share and cover their substantial fixed costs, eroding profitability for all players. The electronics manufacturing sector is characterized by high fixed costs related to research and development, tooling, and sophisticated assembly equipment. BYD Electronic, like its peers, must navigate this landscape where the inability to exit easily intensifies the fight for survival and market dominance.
- High Capital Investment: Setting up advanced electronics manufacturing facilities, including clean rooms and specialized assembly lines, can cost hundreds of millions to billions of dollars.
- Specialized Assets: Many assets, like precision robotics and testing equipment, are highly specific to electronics production and have limited resale value outside the industry.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to suppliers and customers through long-term agreements can bind companies to operations even when unprofitable.
- Workforce Skills: The presence of a highly skilled and specialized workforce in areas like semiconductor fabrication represents another barrier, as retraining or redeploying such talent is challenging.
Strategic Stakes and Aggressiveness of Competitors
Competitors in BYD Electronic's diverse markets, from established automotive giants to agile new entrants in the EV and electronics sectors, are locked in a fierce battle for market dominance. This rivalry is characterized by aggressive strategies aimed at capturing market share and achieving technological superiority.
Companies are channeling significant capital into research and development, advanced automation, and artificial intelligence to secure a competitive advantage. For instance, the global automotive industry, where BYD Electronic is a major player, saw R&D spending reach approximately $200 billion in 2024, a testament to this intense innovation drive.
- BYD Electronic's key competitors in the EV market include Tesla, Volkswagen, and General Motors.
- In the electronics manufacturing services (EMS) sector, rivals like Foxconn and Pegatron are known for their aggressive expansion and technological adoption.
- The rapid advancements in AI integration across industries are forcing all players to invest heavily, with global AI spending projected to exceed $2 trillion by 2030.
- This relentless pursuit of growth, particularly in high-demand areas like electric vehicles and AI-powered solutions, directly fuels the intensity of competition BYD Electronic faces.
BYD Electronic operates in highly competitive sectors, facing rivals with substantial scale and established market positions, particularly in electronics manufacturing services and automotive components. The sheer volume of players, from large conglomerates to niche specialists, means BYD Electronic must constantly adapt its strategies to maintain its edge.
The intense rivalry is driven by significant R&D investments and a race for technological superiority, especially with the booming demand from AI data centers and the automotive industry. For example, global automotive R&D spending reached approximately $200 billion in 2024, highlighting the aggressive innovation efforts across the sector.
While BYD Electronic benefits from vertical integration, the standardized nature of many electronic components can make differentiation challenging, leading to price-sensitive competition. This environment necessitates continuous innovation and operational efficiency to capture market share, as evidenced by BYD Electronic's 22.5% revenue growth in 2023.
High exit barriers, such as substantial capital investments in specialized machinery, mean that even struggling competitors remain in the market, intensifying price wars and the fight for dominance. This dynamic is particularly evident in the electronics manufacturing sector, which requires billions in investment for advanced facilities.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Customers might bypass large Electronic Manufacturing Services (EMS) providers like BYD Electronic by opting for increased in-house production or by engaging smaller, specialized niche manufacturers. This shift could be driven by a desire for greater control or unique capabilities not offered by large-scale providers.
While full in-house manufacturing of highly complex electronics remains capital-intensive, a growing trend towards modularized production or strategic alliances with smaller, agile manufacturing partners presents a viable alternative. For instance, companies seeking rapid prototyping or specific component expertise might find these smaller players more responsive than a large EMS provider.
The increasing sophistication of software and cloud-based solutions presents a significant threat of substitution for BYD Electronic. For intelligent products and automotive systems, these advancements can diminish the reliance on specific, advanced hardware components that BYD Electronic typically supplies. This trend suggests a potential shift where physical parts are replaced by virtual or software-defined functionalities, impacting demand for traditional hardware.
The automotive sector, in particular, is witnessing substantial growth in AI-driven systems, largely powered by advanced software. This software-centric development could lead to a scenario where the core intelligence and functionality are delivered through code and algorithms rather than dedicated hardware modules, thereby substituting hardware offerings. For instance, by 2024, the global automotive software market was projected to reach over $60 billion, highlighting the increasing value placed on software capabilities.
Rapid advancements in material science and new manufacturing technologies present a significant threat of substitutes for BYD Electronic. For instance, breakthroughs in areas like advanced composites or novel semiconductor materials could lead to entirely new ways of building electronic components, potentially bypassing BYD Electronic's current product lines and manufacturing expertise. This means that a new material or process could emerge that performs the same function as BYD Electronic's current offerings but is cheaper or more efficient.
Innovations such as additive manufacturing (3D printing) are also on the horizon, offering the potential for on-demand, customized component production that could disrupt traditional supply chains. BYD Electronic, recognizing this, actively invests in research and development. In 2023, BYD Group, which includes its electronics segment, allocated approximately 10.4 billion RMB (around $1.4 billion USD) to R&D, a substantial increase from previous years, demonstrating a commitment to staying at the forefront of technological change and mitigating this substitution threat.
Shift in Consumer Preferences
A significant shift in consumer preferences towards simpler, less intelligent, or more repairable devices could reduce demand for the complex, high-tech components and integrated solutions that BYD Electronic specializes in. While current trends, such as the continued growth in the global smartphone market which saw shipments increase by approximately 3.5% in 2023 according to IDC, still favor smart devices, unexpected shifts could pose a substitution threat. For instance, a surge in demand for feature phones or basic communication devices, perhaps driven by privacy concerns or a desire for digital detox, would directly impact the market for BYD Electronic's advanced offerings.
BYD Electronic's diversified portfolio, spanning areas like automotive electronics and new energy, helps mitigate this specific risk. However, within its core electronics manufacturing segment, a substantial move away from highly integrated smart products could see consumers opting for alternative solutions or even simpler, less technologically dependent devices. This could manifest as a growing market for refurbished or easily repairable electronics, which would bypass the need for the sophisticated components BYD Electronic produces.
- Consumer Preference Shift: A move towards simpler, less intelligent, or more repairable electronics presents a threat.
- Market Impact: Reduced demand for complex, high-tech components and integrated solutions BYD Electronic offers.
- Potential Drivers: Privacy concerns or a desire for digital detox could fuel demand for simpler devices.
- Mitigation: BYD Electronic's diversified portfolio provides some resilience against this specific threat.
Economic Downturn and Cost-Cutting
During economic downturns, consumers and businesses tend to cut costs, which can lead them to seek out less expensive, more basic alternatives to premium products. This presents a significant threat of substitution for BYD Electronic, as customers might opt for lower-cost components or devices instead of BYD's potentially higher-priced offerings. For instance, the European EMS market saw negative growth in 2024, indicating a general trend towards reduced spending on electronics manufacturing services, which could translate to customers exploring cheaper substitute solutions.
This shift impacts BYD Electronic by potentially reducing demand for its higher-margin products and forcing a reconsideration of its product mix and pricing strategies to remain competitive. Companies facing economic pressure might delay upgrades or choose refurbished equipment, directly substituting new purchases from BYD.
- Economic Downturn Impact: Reduced consumer and business spending leads to a preference for cheaper alternatives.
- Substitution Threat: Customers may switch from premium BYD products to more basic or lower-cost substitutes.
- Market Evidence: The European EMS market's negative growth in 2024 highlights a broader trend of cost-cutting and potential substitution.
- BYD's Challenge: Pressure on revenue from premium segments necessitates strategic adjustments in product and pricing.
The threat of substitutes for BYD Electronic is multifaceted, encompassing shifts in technology, consumer preferences, and economic conditions. For instance, advancements in software-defined functionalities could reduce the need for specific hardware components, as seen in the automotive sector where the global software market was projected to exceed $60 billion by 2024. Similarly, new materials or additive manufacturing techniques might offer alternative production methods that bypass traditional EMS providers.
Consumer demand can also shift, with a potential move towards simpler, more repairable devices posing a risk to BYD Electronic's focus on complex, high-tech products. While the smartphone market showed resilience with a 3.5% shipment increase in 2023, unexpected changes in consumer behavior, such as a preference for digital detox, could favor less technologically dependent alternatives. Economic downturns further exacerbate this threat, as cost-conscious customers may opt for cheaper components or refurbished goods, a trend reflected in the European EMS market's negative growth in 2024.
| Substitution Threat Area | Specific Example/Trend | Potential Impact on BYD Electronic | Relevant Data Point (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technological Advancements | Software-defined features replacing hardware | Reduced demand for specific hardware components | Global automotive software market projected >$60 billion by 2024 |
| Manufacturing Innovations | Additive manufacturing (3D printing) | Disruption of traditional supply chains, alternative production methods | BYD Group R&D investment: ~10.4 billion RMB (~$1.4 billion USD) in 2023 |
| Consumer Preference Shifts | Demand for simpler, repairable electronics | Lower demand for complex, high-tech integrated solutions | Global smartphone shipments increased ~3.5% in 2023 |
| Economic Conditions | Cost-cutting during downturns | Shift to lower-cost components or refurbished alternatives | European EMS market experienced negative growth in 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the electronics manufacturing services (EMS) and intelligent device component sectors demands significant capital. Companies need to invest heavily in state-of-the-art machinery, cutting-edge research and development, and robust supply chain networks. For example, setting up a modern semiconductor fabrication plant can cost billions of dollars, a prohibitive sum for most new entrants.
This substantial financial hurdle acts as a strong deterrent, protecting established players like BYD Electronic. The sheer scale of investment required means that only well-funded organizations can realistically consider entering these competitive markets. This capital intensity significantly limits the threat of new entrants, allowing existing firms to maintain their market positions.
Existing players like BYD Electronic leverage substantial economies of scale in manufacturing, procurement, and research and development. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit production costs, a significant barrier for newcomers. For instance, BYD Electronic's extensive production capacity, reportedly over 100 million units annually for certain components in 2024, enables them to negotiate better raw material prices and spread R&D expenses across a larger output.
New entrants would find it challenging to match these cost efficiencies without achieving comparable production volumes and accumulating years of operational experience. The steep learning curve associated with optimizing complex manufacturing processes further disadvantages those just entering the market. BYD Electronic's vertical integration, controlling many aspects of its supply chain, also contributes to its cost advantage and makes it harder for new competitors to replicate its operational model.
BYD Electronic's formidable technological prowess, underscored by its extensive patent portfolio and a deeply entrenched vertically integrated supply chain, presents a significant hurdle for potential new entrants. The company's control over critical components, such as advanced batteries and specialized semiconductors essential for automotive intelligent systems, means that rivals must undertake substantial time and capital investment to replicate this technological foundation. For instance, BYD's significant R&D spending, which reached approximately 10.3 billion RMB in 2023, directly fuels this proprietary advantage, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to compete on a level playing field.
Access to Distribution Channels and Customer Relationships
New entrants face a formidable barrier in establishing robust distribution channels and securing long-term contracts with major global customers, a critical aspect for companies like BYD Electronic. These established relationships, often built over years, create a significant competitive moat, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to gain comparable market access and visibility.
BYD Electronic's strong partnerships, for instance, with key players in the consumer electronics sector, solidify its differentiated market position. In 2023, BYD Electronic continued to leverage its extensive supply chain network, which is crucial for delivering high-volume, quality products demanded by global brands.
- Distribution Channel Barriers: New entrants struggle to replicate BYD Electronic's established network of distributors and retailers, vital for reaching a broad customer base.
- Customer Relationship Moat: Long-standing relationships with major clients, such as those in the smartphone and automotive sectors, provide BYD Electronic with preferential access and volume commitments, which are hard for new players to secure.
- Reputational Advantage: BYD Electronic's proven track record of reliability and quality enhances its ability to attract and retain high-value customers, a reputation that new entrants must painstakingly build.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policies and regulations present a significant threat to new entrants in the electronics sector. Stringent environmental standards, such as those implemented by the European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive, can require substantial investment in compliance and product redesign, making it harder for newcomers to enter the market. Similarly, varying trade policies and tariffs across different regions, like the U.S.-China trade tensions impacting component sourcing, add layers of complexity and cost that can deter new players.
These regulatory hurdles and evolving environmental standards can significantly increase the upfront capital and operational costs for new companies. For instance, the push towards circular economy principles and extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes in markets like Germany necessitates robust recycling and waste management infrastructure, a considerable undertaking for nascent businesses. BYD, as a global player, actively navigates these diverse regulatory landscapes, factoring them into its strategic decisions for new plant locations and supply chain management.
- Regulatory Hurdles: New entrants face compliance costs associated with diverse international standards, from product safety certifications to data privacy laws.
- Environmental Standards: Increasingly strict regulations on materials, energy efficiency, and end-of-life product management raise the barrier to entry.
- Trade Policies: Tariffs, import/export restrictions, and geopolitical considerations can disrupt supply chains and increase costs for new companies, particularly those reliant on global sourcing.
- Government Support for Local Industries: Policies favoring domestic manufacturers can create an uneven playing field, making it challenging for foreign or smaller new entrants to compete.
The threat of new entrants into the electronics manufacturing services (EMS) and intelligent device component sectors is significantly dampened by substantial capital requirements. Establishing state-of-the-art facilities, including semiconductor fabrication plants, can cost billions, a prohibitive barrier for most. For example, the ongoing global demand for advanced chip manufacturing capacity means new entrants face immense upfront investment to even begin competing with established players.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our BYD Electronic Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of publicly available data, including BYD's annual reports, investor presentations, and filings with regulatory bodies like the Shenzhen Stock Exchange. We also incorporate insights from reputable industry research firms and automotive market intelligence reports.