Brinker International Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Brinker International Bundle
Brinker International operates in a dynamic restaurant industry shaped by intense rivalry, significant buyer power, and the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Brinker International’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The casual dining sector, where Brinker International operates, frequently encounters a situation with a restricted number of major suppliers for critical components such as meat and poultry. This limited supplier base can grant these entities considerable influence over pricing and contractual conditions.
For instance, a handful of dominant corporations command a significant share of the U.S. meat and poultry market. This market concentration can directly affect Brinker's capacity to secure advantageous pricing for its essential food inputs.
In 2024, the U.S. Department of Agriculture reported that the top four beef processors controlled approximately 80% of the market. Similarly, the poultry sector shows high concentration. This situation means Brinker International must employ robust procurement strategies and cultivate a wide array of supplier relationships to mitigate the risk of escalating ingredient costs.
Brinker International's reliance on consistent, high-quality food and beverage supplies is critical for maintaining its brand reputation and customer experience across Chili's and Maggiano's. Suppliers of key ingredients, especially those with unique sourcing or specialized production, can exert significant bargaining power.
Disruptions in the supply chain, whether from severe weather, disease outbreaks, or broader global events, can directly impact ingredient availability and pricing. For instance, food price inflation has been a persistent challenge since 2019, directly affecting Brinker's cost of goods sold and necessitating careful supplier management.
Switching primary food and beverage suppliers for Brinker International presents substantial costs. These include negotiating new contracts, reconfiguring logistics, implementing rigorous quality control measures, and potentially adapting menu items to suit new ingredient profiles. These investments can make it challenging and expensive for Brinker to change its supplier base.
While Brinker benefits from sourcing over 80% of its ingredients domestically, mitigating some global price fluctuations, the process of onboarding new suppliers still demands significant operational adjustments. This transition period carries inherent risks to maintaining the consistent product quality that customers expect across its brands like Chili's and Maggiano's Little Italy.
The existence of these switching costs inherently strengthens the bargaining power of Brinker's current suppliers. Because it is costly and disruptive for Brinker to switch, its existing suppliers can leverage this situation to negotiate more favorable terms, potentially impacting Brinker's cost of goods sold and overall profitability.
Supplier's Ability to Forward Integrate
The threat of suppliers forward integrating into the restaurant business, like operating casual dining chains, is generally low for Brinker International. Major food producers or distributors usually focus on supplying ingredients rather than running restaurant operations.
However, there's a possibility for specialized or niche suppliers to explore direct-to-consumer models or strategic alliances that bypass established restaurant chains. This scenario would likely impact smaller, independent eateries more significantly than a large, multinational corporation like Brinker.
- Low Threat: Large food conglomerates are unlikely to directly compete by opening casual dining restaurants.
- Niche Supplier Risk: Specialized suppliers might explore direct-to-consumer sales, potentially impacting Brinker's ingredient sourcing if they shift focus.
- Scale Disadvantage: Forward integration by suppliers is less feasible against Brinker's established scale and brand recognition.
Labor Market Dynamics
The restaurant industry, including Brinker International, relies heavily on labor, making it a significant cost center. In 2024, many regions continued to experience labor shortages, particularly for entry-level positions, which inherently boosts the bargaining power of available workers. This scarcity forces employers to offer more attractive compensation and benefits to secure and retain staff.
Brinker International, operating numerous casual dining brands like Chili's and Maggiano's, manages a substantial workforce. Consequently, the company feels the impact of rising payroll taxes, escalating workers' compensation costs, and the ongoing necessity to provide competitive wages and benefits. These factors directly pressure profitability by increasing overall operating expenses.
- Labor Shortages: Persistent shortages in 2024 across the US food service sector, exacerbated by demographic shifts and evolving worker expectations, grant employees greater leverage in wage and benefit negotiations.
- Wage Inflation: Minimum wage increases and competitive pressures in 2024 pushed average hourly wages higher for restaurant staff, impacting Brinker's labor costs. For instance, the average hourly wage for food preparation and serving workers saw an upward trend throughout the year.
- Employee Retention Costs: To combat high turnover, Brinker, like its peers, likely invested more in training, benefits, and potentially signing bonuses in 2024, adding to the cost of its workforce.
- Impact on Profitability: Increased labor expenses directly reduce operating margins if not offset by price increases or efficiency gains, a key challenge for Brinker in the 2024 economic climate.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Brinker International is considerable, particularly for essential food items. The concentration within the meat and poultry sectors, where the top four beef processors controlled approximately 80% of the market in 2024, means fewer suppliers can dictate terms. This reliance, coupled with the significant costs and operational adjustments involved in switching suppliers, strengthens their position.
The high switching costs for Brinker International, encompassing contract renegotiations, logistics, and quality control, create a barrier to changing suppliers. This inertia benefits existing suppliers, allowing them to potentially negotiate more favorable terms and impact Brinker's cost of goods sold.
While the threat of suppliers forward integrating into restaurant operations is generally low, specialized suppliers might explore direct-to-consumer models. This shift could indirectly affect Brinker's ingredient sourcing by potentially reducing the availability or increasing the cost of niche ingredients.
The bargaining power of labor, a critical component for Brinker International, remains high due to ongoing labor shortages in the food service industry throughout 2024. This scarcity compels companies like Brinker to offer more competitive wages and benefits to attract and retain staff, directly increasing operating expenses.
What is included in the product
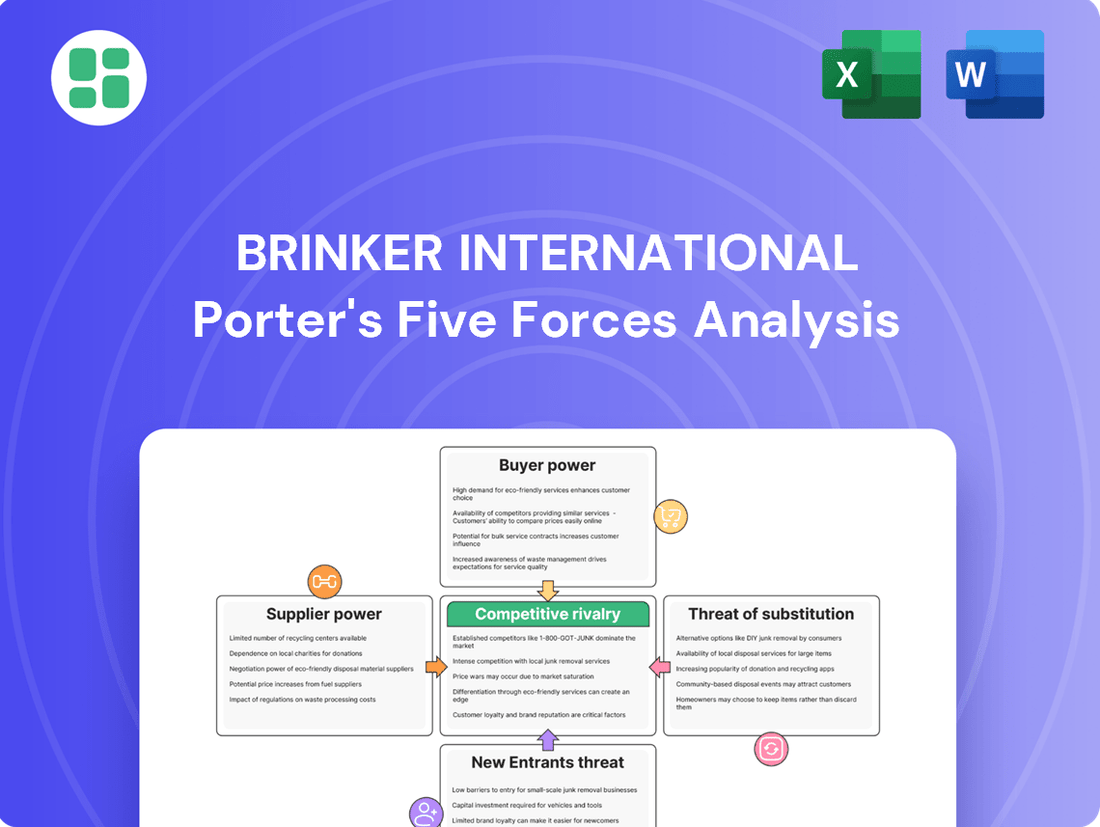
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Brinker International, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the casual dining industry.
Easily identify and address competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in the casual dining sector are quite sensitive to price, particularly with the ongoing economic pressures and the general trend of increasing menu costs. For instance, in 2024, many consumers reported cutting back on discretionary spending, including dining out, due to inflation impacting household budgets.
The sheer abundance of dining choices significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. With many casual dining competitors, fast-casual establishments, and even prepared meals from grocery stores readily available, consumers can easily shift their patronage. This ease of switching means Brinker International must carefully manage its pricing to remain competitive and retain its customer base.
Customers today have unprecedented access to information thanks to the internet and social media. They can easily compare menus, prices, and read reviews for restaurants like Brinker International's brands, such as Chili's and Maggiano's Little Italy. This readily available data significantly reduces information asymmetry, empowering diners to make more informed choices based on value and experience.
Customer switching costs in the casual dining sector, like those Brinker International operates within, are typically quite low. Diners can easily opt for a competitor’s restaurant for their next meal without incurring substantial financial outlays or experiencing significant inconvenience.
This low barrier to switching places a premium on Brinker's ability to consistently deliver a superior value proposition and a memorable dining experience. For instance, in 2024, the casual dining segment faced intense competition, with companies like Darden Restaurants, a major competitor, reporting strong performance driven by customer loyalty programs and menu innovation, highlighting the importance of customer retention strategies.
Customer Loyalty and Brand Recognition
While customers can easily switch between casual dining options, Brinker International leverages strong brand recognition, especially for its Chili's brand, to retain patrons. Loyalty programs are a key strategy to encourage repeat business and build a more committed customer base, thereby slightly reducing individual customer bargaining power. For instance, Chili's has historically seen a substantial portion of its revenue generated by repeat customers, indicating the effectiveness of these loyalty initiatives in fostering a degree of stickiness in a highly competitive market.
The effectiveness of Brinker's loyalty programs in mitigating customer bargaining power is further evidenced by consumer behavior trends. Research consistently shows that a significant percentage of diners prefer familiar establishments, especially when the dining experience meets their expectations. This preference means that even with low switching costs, a consistently positive brand experience and well-designed loyalty rewards can significantly reduce a customer's inclination to explore alternatives, thereby dampening their individual leverage.
- Brand Loyalty: Chili's, a flagship brand of Brinker International, benefits from established brand recognition, which encourages repeat patronage.
- Loyalty Programs: Brinker actively uses loyalty programs to incentivize repeat visits and build customer retention.
- Consumer Behavior: A notable segment of consumers exhibits loyalty to familiar dining brands, which can lessen individual customer bargaining power.
- Market Impact: These factors collectively help Brinker manage customer power by fostering a base of repeat diners who are less sensitive to price or competitor offerings.
Volume of Purchases by Individual Customers
Individual customer purchases at casual dining restaurants like those operated by Brinker International are generally small. This means that no single customer wields significant individual bargaining power over the company. For instance, a typical check size at a casual dining establishment is far from the volume needed to influence pricing or terms.
However, the sheer number of customers is what truly matters. Brinker's business model thrives on a high volume of individual transactions. While one customer might not have much sway, the collective sentiment and spending habits of millions of diners, especially when influenced by broader economic conditions or emerging dining trends, can indeed represent substantial bargaining power.
For example, if a significant portion of Brinker's customer base starts to feel the pinch of inflation, they might collectively reduce their spending frequency or opt for less expensive menu items. This shift in consumer behavior, driven by economic factors affecting many individuals, can indirectly pressure Brinker to adjust its pricing or offerings to maintain sales volume.
- Low Individual Purchase Volume: Most customers at casual dining chains like Brinker International make relatively small purchases, limiting the bargaining power of any single patron.
- Collective Customer Power: The aggregated demand from a large customer base is significant, and shifts in consumer sentiment or economic conditions can collectively influence Brinker's market position.
- Focus on Transaction Volume: Brinker's strategy is built on attracting a multitude of individual customers rather than relying on large orders from a few powerful buyers.
- Sensitivity to Economic Trends: The spending habits of a broad customer base are susceptible to macroeconomic factors, which can indirectly impact Brinker's pricing and menu strategies.
The bargaining power of customers in the casual dining sector, where Brinker International operates, is notably high. This stems from several factors, including price sensitivity, a wide array of dining alternatives, and easy access to information. In 2024, consumers continued to be cautious with discretionary spending due to persistent inflation, making them more inclined to seek value and compare options. For instance, many consumers reported prioritizing value-driven meals, leading casual dining establishments to focus on promotions and affordable offerings.
Brinker International, through brands like Chili's and Maggiano's Little Italy, faces a competitive landscape where customers can easily switch to other casual dining chains, fast-casual restaurants, or even home-prepared meals. This low switching cost means Brinker must continually offer compelling value and a positive dining experience to retain its customer base. For example, in 2024, competitors like Darden Restaurants emphasized customer loyalty programs and menu innovation to maintain market share, underscoring the importance of customer retention strategies in this environment.
While individual customer purchases are small, limiting their direct leverage, the collective power of a large customer base can significantly influence Brinker's strategies. Shifts in aggregate consumer sentiment or spending habits, often driven by economic conditions, can pressure the company to adjust pricing or menu selections. For example, a broad economic downturn could lead many customers to reduce dining frequency or opt for less expensive items, indirectly impacting Brinker's sales volume and strategic decisions.
| Factor | Impact on Brinker International | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | Customers are highly responsive to price changes, pressuring Brinker on menu pricing. | Inflationary pressures in 2024 increased consumer focus on value and affordability. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Numerous dining options (competitors, fast-casual, home cooking) increase customer choice and leverage. | The casual dining market remained crowded in 2024, intensifying competition for customer spending. |
| Information Accessibility | Online reviews and price comparisons empower customers to make informed decisions. | Social media and review sites continued to be primary sources for restaurant discovery and evaluation in 2024. |
| Low Switching Costs | Customers can easily change restaurants without significant financial or effort barriers. | This necessitates strong customer retention strategies, such as loyalty programs and consistent quality. |
| Brand Loyalty & Loyalty Programs | Brinker leverages brands like Chili's and loyalty programs to foster repeat business and reduce individual customer power. | Loyalty programs were critical in 2024 for driving repeat visits amidst intense competition. |
Same Document Delivered
Brinker International Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Brinker International Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the casual dining industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or missing information.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The casual dining sector is intensely competitive, featuring a multitude of established chains, independent eateries, and the growing fast-casual segment all vying for consumer attention and spending. Brinker International, operating brands like Chili's and Maggiano's, faces this crowded marketplace daily, making differentiation a critical survival strategy.
The U.S. restaurant industry is anticipated to see growth, but the casual dining sector's expansion is moderate when stacked against fast-casual or quick-service segments. For instance, Technomic projected the U.S. restaurant industry to grow by 3.7% in 2024, with casual dining’s share of that growth being more subdued.
This slower growth in a market that's already quite full means companies like Brinker International face heightened competition. Instead of easily gaining customers from a rapidly expanding market, they must actively compete for existing customers, making market share a crucial battleground.
Competitive rivalry in the casual dining sector is intense, with rivals constantly innovating menus and offering value promotions to capture market share. Brinker International, through brands like Chili's, actively participates in this by focusing on core menu items and introducing attractive deals, such as the 'Big Smasher' burger, to draw in diners amidst a crowded marketplace.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The restaurant sector, including players like Brinker International, faces significant competitive rivalry driven by high fixed costs. These costs, encompassing prime real estate leases, kitchen equipment, and a substantial workforce, create substantial hurdles for businesses looking to exit the market. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to open a full-service restaurant can range from $275,000 to over $2 million, a considerable investment that is difficult to recoup.
These elevated exit barriers mean that even restaurants experiencing financial difficulties may persist, rather than closing down. This prolonged operation by underperformers intensifies the competitive landscape, as they continue to vie for market share. This dynamic can hinder market consolidation, keeping the number of active competitors high and pressure on pricing and margins.
- High Fixed Costs: Real estate, equipment, and labor expenses are substantial in the restaurant industry.
- Exit Barriers: The significant investment makes it difficult for struggling businesses to leave the market.
- Sustained Rivalry: Underperforming competitors remain active, intensifying competition.
- Market Consolidation Hindered: High exit barriers prevent efficient market consolidation.
Strategic Initiatives and Advertising Intensity
Brinker International, along with its rivals, engages in substantial spending on marketing, advertising, and digital outreach to attract and retain customers. This heightened advertising intensity is a direct response to fierce competition within the casual dining sector.
The ongoing 'value war' among competitors, characterized by aggressive pricing and promotional activities, necessitates continuous investment in visibility and customer engagement. Furthermore, the critical importance of digital ordering capabilities means companies are heavily investing in technology to streamline the customer experience and capture market share.
- Advertising Spend: In fiscal year 2023, Brinker International reported marketing and advertising expenses of $335.5 million, representing approximately 5.3% of total revenue, underscoring the significant investment in competitive positioning.
- Digital Investment: Competitors are also prioritizing digital platforms, with many investing heavily in app development and online ordering systems, aiming to capture a larger share of the off-premise dining market which saw significant growth in recent years.
- Value Perception: The focus on value promotions, such as limited-time offers and loyalty programs, is a key tactic to differentiate brands and drive traffic amidst intense rivalry.
The competitive rivalry within the casual dining sector is exceptionally high, driven by numerous established chains and emerging fast-casual options. Brinker International, with brands like Chili's, faces constant pressure to innovate and offer compelling value propositions to attract and retain customers. This intense competition is further fueled by significant marketing and advertising expenditures by all players, aiming to capture a larger share of a moderately growing market.
The high fixed costs associated with restaurant operations, including real estate and labor, create substantial exit barriers. This means even struggling competitors tend to remain in the market, prolonging the rivalry and intensifying pressure on pricing and margins. Consequently, companies like Brinker must continually invest in digital capabilities and value-driven promotions to stand out.
| Factor | Impact on Brinker International | Key Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Intensity of Rivalry | High | Numerous competitors, moderate market growth, significant advertising spend. |
| Competitive Tactics | Menu innovation, value promotions, digital investment | Chili's Big Smasher burger, extensive marketing campaigns. |
| Exit Barriers | High | Significant investment in opening restaurants (e.g., $275k - $2M+ in 2024). |
| Marketing Spend Example | Substantial | Brinker's FY23 marketing and advertising expenses were $335.5 million (approx. 5.3% of revenue). |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Home-cooked meals, frequently chosen for health and cost savings, represent a substantial substitute for restaurant dining. In 2024, the average household continued to allocate a significant portion of its food budget to groceries for home preparation, reflecting this ongoing trend.
Grocery stores have also bolstered their prepared meal sections, offering convenient and budget-friendly options that directly vie for consumer spending. These offerings provide a quick alternative for individuals and families seeking to avoid the time commitment of cooking from scratch but still wanting a meal solution outside of a full-service restaurant.
The rise of fast-casual restaurants, which blend higher quality ingredients with the speed and convenience of quick-service models, presents a significant threat to casual dining chains like Brinker International. These establishments often attract customers seeking a better dining experience without the time commitment or cost of traditional sit-down restaurants.
Quick-service restaurants (QSRs) also continue to pose a competitive threat, particularly to value-conscious consumers. In 2024, the QSR segment remained robust, with many brands focusing on aggressive pricing strategies and convenient digital ordering options, directly siphoning off potential customers from casual dining.
Meal kit delivery services pose a significant threat to Brinker International by offering a convenient alternative for consumers who prefer to cook at home. These services, which saw substantial growth, particularly during the pandemic, provide pre-portioned ingredients and recipes, directly competing with casual dining options like those offered by Brinker.
The appeal of meal kits lies in their ability to deliver a fresh, home-cooked meal experience with reduced effort compared to traditional grocery shopping and meal preparation. For instance, the meal kit market was valued at over $15 billion globally in 2023 and is projected to continue its upward trajectory, indicating a strong and growing consumer preference for this substitute.
Other Entertainment and Leisure Options
Consumers have a wide array of choices for how they spend their discretionary income, and these options extend far beyond just dining at restaurants. Activities like attending live music events, going to the cinema, or engaging in other recreational pursuits directly compete with Brinker International's offerings for consumer dollars. In 2024, the global entertainment and leisure market was projected to reach trillions of dollars, demonstrating the significant scale of these substitute options.
This broad competitive landscape means Brinker International faces pressure not just from other casual dining chains, but from any activity that captures a consumer's leisure time and budget. For instance, a significant portion of consumer spending in 2024 was directed towards experiences, including travel and personal hobbies, further fragmenting the market.
- Broad Entertainment Choices: Consumers can allocate discretionary spending to movies, concerts, sporting events, and travel, all of which substitute for dining out.
- Leisure Time Competition: Brinker competes for consumer attention and dollars against a vast range of leisure activities, not just other food service providers.
- Market Size of Substitutes: The global entertainment and leisure market's substantial size in 2024 highlights the significant competitive threat from alternative spending categories.
Evolving Consumer Preferences
Shifts in consumer preferences present a significant threat of substitutes for Brinker International. For instance, the growing demand for plant-based options, which saw the global plant-based food market valued at approximately $30 billion in 2023 and projected to grow significantly, means consumers might opt for restaurants specializing in vegan or vegetarian fare over traditional casual dining. Similarly, a move towards more health-conscious eating, with a rising interest in personalized nutrition and functional foods, could steer customers away from Brinker's offerings towards establishments focusing on fresh, locally sourced ingredients or specific dietary needs.
Brinker must proactively adapt its menus and operational strategies to mitigate this threat. By incorporating more diverse and appealing plant-based dishes and highlighting healthier ingredient choices, Brinker can reduce the likelihood of customers seeking substitutes. For example, during 2023, many restaurant chains reported increased sales from their plant-based menu items, indicating a clear market trend that Brinker needs to address to maintain customer loyalty and market share.
- Growing demand for plant-based diets: The market for plant-based foods continues to expand, offering consumers alternatives to traditional meat-centric menus.
- Health and wellness trends: Consumers are increasingly seeking healthier meal options, pushing them towards restaurants that prioritize fresh, nutritious ingredients.
- Desire for unique dining experiences: Niche restaurants offering specialized cuisines or innovative dining concepts can attract customers looking for something beyond standard casual dining.
- Impact on Brinker's offerings: Failure to adapt menus to these evolving preferences could lead to a loss of market share as consumers seek out more suitable dining alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for Brinker International is multifaceted, encompassing everything from home cooking to alternative leisure activities. Consumers' increasing preference for convenience and health-conscious options means that grocery stores offering prepared meals and meal kit delivery services directly compete with casual dining. In 2024, the continued strength of the quick-service restaurant sector, with its focus on value and digital accessibility, also siphons off potential customers. Furthermore, the broad entertainment and leisure market, valued in the trillions globally in 2024, represents a significant draw on discretionary spending that could otherwise go towards dining out.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Impact on Brinker |
|---|---|---|
| Home-cooked Meals | Cost savings, perceived health benefits | Reduces frequency of restaurant visits |
| Grocery Prepared Foods | Convenience, affordability | Offers quick meal solutions outside of restaurants |
| Meal Kit Delivery | Convenience, fresh ingredients, home experience | Directly competes with casual dining for meal occasions |
| Fast-Casual Restaurants | Quality ingredients, speed, convenience | Attracts customers seeking better value than QSRs but faster than casual dining |
| Quick-Service Restaurants (QSRs) | Aggressive pricing, digital ordering, speed | Appeals to value-conscious and time-pressed consumers |
| Entertainment & Leisure Activities | Discretionary spending on experiences (movies, events, travel) | Competes for consumer time and budget allocation |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a casual dining restaurant chain, akin to Brinker International's brands like Chili's and Maggiano's, demands significant upfront capital. This includes expenses for prime real estate acquisition or leasing, construction and renovation, purchasing kitchen and dining equipment, and covering initial operating expenses like inventory and staffing.
While opening a single restaurant might seem manageable, the true barrier for new entrants lies in replicating Brinker's multi-unit scale. For instance, Brinker International operated over 1,300 restaurants globally as of fiscal year 2024, a scale that requires a substantial financial commitment far beyond what a small startup can typically muster, thus limiting the threat of new entrants.
Established brands like Brinker International, owner of Chili's and Maggiano's, enjoy significant brand recognition and deeply ingrained customer loyalty. This makes it tough for newcomers to quickly gain a foothold in the competitive casual dining sector. For instance, Brinker's brands have cultivated decades of customer relationships, a valuable asset that new entrants cannot easily replicate.
New restaurants entering the market must commit substantial resources to marketing and advertising campaigns to build awareness and trust. They need to convince consumers to switch from familiar favorites to an unproven option, often requiring extensive promotions and a compelling value proposition. The cost of acquiring customers in this environment can be a significant barrier.
Established restaurant giants like Brinker International benefit from deeply entrenched relationships with suppliers and distributors. These long-standing partnerships, often built over decades, grant them preferential pricing and ensure reliable access to key ingredients and resources. For instance, in 2024, major restaurant chains typically secure bulk purchasing agreements that offer significant cost advantages over smaller, newer operations.
New entrants into the casual dining sector may struggle to establish similar supply chain efficiencies. They might face higher procurement costs for ingredients or encounter difficulties in securing consistent and timely deliveries from distributors. This can directly impact their ability to maintain competitive pricing or ensure product quality, a critical factor for customer retention.
Regulatory Hurdles and Operational Complexity
The restaurant industry, including major players like Brinker International, faces significant barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory requirements. New businesses must navigate a complex web of health codes, food safety standards, and labor laws, which can impose substantial initial costs and ongoing compliance burdens. For instance, in 2024, the average startup cost for a new full-service restaurant in the U.S. could range from $275,000 to over $750,000, with a significant portion allocated to licensing and compliance.
Beyond regulatory hurdles, the operational complexity of managing a multi-unit restaurant chain presents a formidable challenge for potential new entrants. Successfully replicating consistent quality in food, service, and brand experience across numerous locations requires sophisticated supply chain management, robust training programs, and effective quality control systems. This operational intensity can deter new companies from scaling rapidly, thereby protecting established brands like Brinker International.
Consider these specific challenges for new entrants:
- Navigating diverse state and local health and safety regulations, which can vary significantly and require specialized legal and consulting expertise.
- Implementing and maintaining consistent training programs for staff across multiple sites to ensure brand standards are met, a process that demands substantial investment in human resources and operational infrastructure.
- Establishing efficient and reliable supply chains capable of supporting numerous locations while maintaining cost-effectiveness and product quality, a feat that often requires significant upfront capital and established relationships.
Economies of Scale
Brinker International, as a major player in the casual dining sector, benefits significantly from economies of scale. This advantage is evident in its purchasing power for ingredients, marketing reach, and operational efficiencies across its numerous locations, including brands like Chili's and Maggiano's Little Italy. For example, in fiscal year 2024, Brinker reported total revenue of $4.07 billion, underscoring its substantial operational footprint.
New entrants into the restaurant industry face a considerable hurdle in matching these cost advantages. Without the volume of Brinker, smaller competitors may find it difficult to negotiate favorable terms with suppliers or invest in broad-reaching marketing campaigns. This disparity in cost structure can make it challenging for new businesses to compete on price and achieve comparable profit margins, thereby acting as a deterrent to entry.
- Economies of Scale in Purchasing: Brinker's large volume allows for bulk discounts on food, beverages, and supplies, lowering per-unit costs.
- Marketing Efficiencies: A national marketing budget can be spread across many locations, reducing the cost per customer acquisition compared to a single new restaurant.
- Operational Leverage: Centralized functions like supply chain management and technology development provide cost savings that smaller entities cannot easily replicate.
- Competitive Pricing: These scale advantages enable Brinker to maintain competitive pricing, making it harder for smaller, higher-cost entrants to attract price-sensitive customers.
The threat of new entrants for Brinker International remains relatively low due to significant capital requirements, established brand loyalty, and operational complexities. New ventures must overcome substantial financial barriers, including real estate, equipment, and initial operating costs, often exceeding $750,000 for a full-service restaurant in 2024. Furthermore, replicating Brinker's scale, with over 1,300 global locations in fiscal year 2024, demands resources far beyond typical startups.
New entrants face challenges in building brand recognition and customer trust against established players like Chili's and Maggiano's, which have cultivated decades of loyalty. Marketing costs to acquire customers are high, as new businesses must convince consumers to switch from familiar favorites. Additionally, securing favorable supplier pricing and efficient supply chains, which Brinker leverages through bulk purchasing agreements in 2024, presents a significant cost disadvantage for smaller competitors.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High costs for real estate, equipment, and initial operations. | Deters new entrants lacking substantial funding. |
| Brand Loyalty & Recognition | Established brands have deep customer relationships. | Difficult for newcomers to attract customers away from trusted names. |
| Economies of Scale | Brinker's size offers cost advantages in purchasing and marketing. | New entrants struggle to match pricing and marketing reach. |
| Supply Chain Efficiency | Established relationships provide preferential pricing and reliable access. | New entrants face higher procurement costs and potential delivery issues. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating health codes, safety standards, and labor laws. | Adds significant initial costs and ongoing compliance burdens. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Brinker International Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Brinker's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld and Technomic. We also incorporate macroeconomic data and news from reputable financial publications to provide a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.