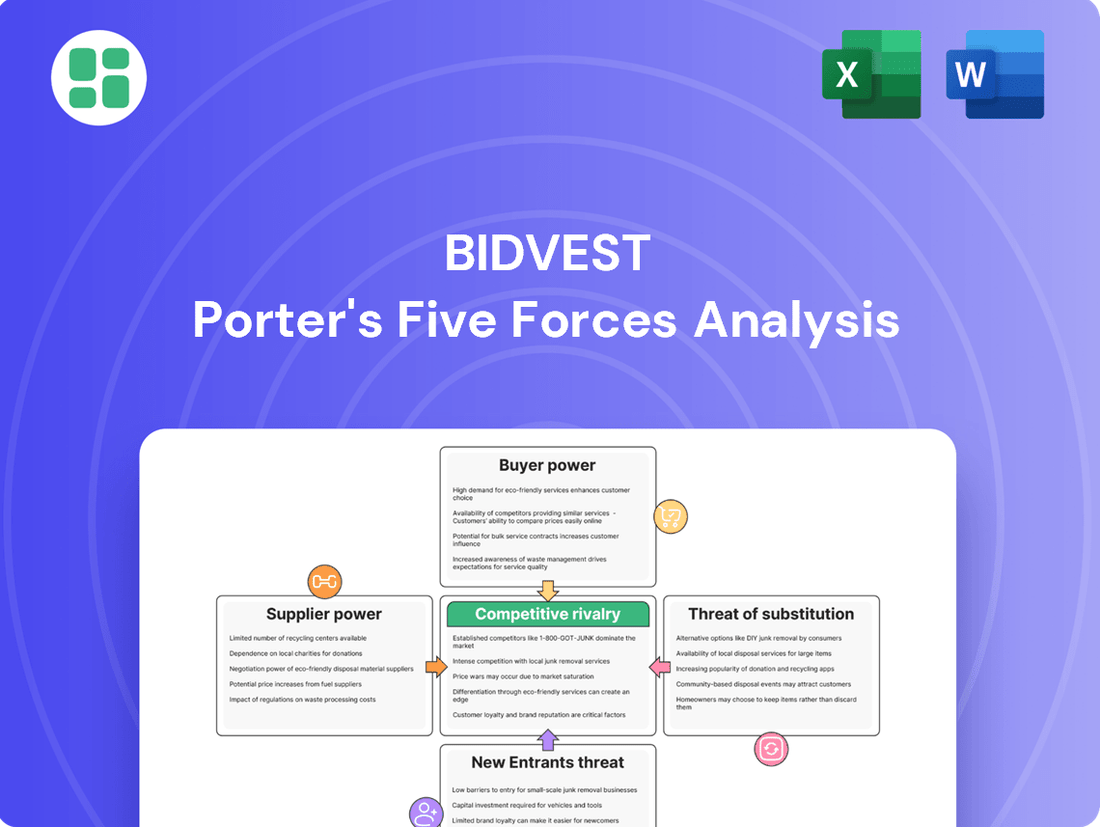
Bidvest Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bidvest Bundle
Bidvest's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the bargaining power of its suppliers to the intensity of rivalry within its diverse sectors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating its complex market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Bidvest’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Bidvest's diverse operations mean its supplier base is often fragmented, reducing supplier power in many areas. However, for specialized inputs, like advanced logistics technology or particular financial software solutions, a few highly specialized suppliers can wield significant influence due to limited alternatives. For instance, in 2024, the global market for specialized supply chain software saw a concentration where the top three providers held an estimated 60% market share, indicating potential leverage for these entities when supplying to Bidvest's logistics divisions.
The criticality of inputs for Bidvest varies significantly across its diverse business segments. For core services like hygiene solutions and freight transport, the reliability and consistent quality of supplied goods and services are absolutely paramount. For instance, a disruption in the supply of cleaning chemicals or fuel for its logistics operations could directly halt service delivery.
Disruptions or quality issues stemming from key suppliers can have a substantial ripple effect, significantly impacting Bidvest's overall operational efficiency and its ability to deliver services to its own extensive customer base. This dependence naturally enhances the bargaining power of these crucial suppliers, as Bidvest has a strong incentive to maintain good relationships and secure consistent supply.
In 2023, Bidvest's revenue from its Services division, which heavily relies on consistent input supply, was R74.6 billion. This substantial figure underscores the financial implications of any supplier-related operational disruptions.
Switching costs for Bidvest's suppliers vary significantly. For basic consumables like stationery, the ease of changing suppliers means minimal switching costs, giving suppliers less leverage.
However, when Bidvest engages with suppliers for more specialized services, such as integrated facility management or complex logistics solutions, the cost and effort to switch can be considerable. These costs can include retraining staff, integrating new systems, and the potential for operational disruptions, thereby increasing the bargaining power of those particular suppliers.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers for Bidvest is generally low across its diverse business segments. However, a significant risk emerges if a supplier in a niche area, possessing proprietary technology or a strong brand, decides to directly enter Bidvest's service or distribution channels. This could diminish Bidvest's control and profitability in that specific market.
For instance, imagine a specialized food ingredient supplier to Bidvest's catering division. If this supplier develops a unique, highly sought-after product and perceives a lucrative opportunity in offering ready-to-serve meals directly to Bidvest's clients, forward integration becomes a tangible threat. Such a move would bypass Bidvest's existing infrastructure and potentially capture a larger share of the value chain.
This scenario is amplified when the supplier's unique capabilities reduce Bidvest's bargaining power. If Bidvest heavily relies on a supplier for a critical component or service that is difficult to replicate or source elsewhere, the supplier is in a stronger position to consider such a strategic move. For example, in 2024, companies in the advanced materials sector that supply specialized components to manufacturing firms have been observed exploring direct-to-consumer models, leveraging their technological edge.
The potential impact of supplier forward integration can be significant, leading to:
- Increased competition within Bidvest's existing markets.
- Erosion of Bidvest's market share and profitability in affected segments.
- Potential loss of key customer relationships if the supplier offers superior integrated solutions.
Bidvest's Ability to Backward Integrate
Bidvest's considerable size and diversified operations offer some potential for backward integration, especially in segments where achieving economies of scale or securing essential inputs is feasible. For instance, its significant procurement volumes across various divisions could justify investments in upstream activities.
However, Bidvest's strategic emphasis on an asset-light service model in many of its core businesses means that complete backward integration isn't always the most practical or financially sound approach. This is particularly true when considering the capital intensity and operational complexity involved in such moves.
Instead of extensive backward integration, Bidvest actively manages supplier relationships and expands its supply base through initiatives like its Bidvest Supplier Diversity Programme. This program aims to foster growth and resilience within its supplier network, ensuring competitive sourcing without the need for direct ownership of upstream assets.
- Bidvest's Diversified Operations: The group operates across numerous sectors, including food services, freight, financial services, and industrial products, providing a broad base for potential integration.
- Asset-Light Strategy: Many Bidvest divisions focus on services, minimizing the need for heavy investment in manufacturing or raw material production.
- Supplier Diversity Programme: This initiative is key to Bidvest's strategy for managing supplier power by broadening and strengthening its supplier relationships.
Bidvest's bargaining power with suppliers is influenced by the criticality and uniqueness of the inputs it requires. While its scale offers some leverage, reliance on specialized inputs or suppliers with proprietary technology can shift power. For example, in 2024, the concentration in the specialized supply chain software market, where the top three providers held an estimated 60% market share, highlights potential supplier leverage for Bidvest's logistics operations.
Switching costs also play a crucial role. For commodity items, Bidvest can easily switch suppliers, limiting their power. However, for integrated solutions or specialized services, the significant costs and operational disruptions associated with changing suppliers amplify the power of those particular suppliers. Bidvest's R74.6 billion revenue in its Services division in 2023 underscores the financial impact of securing reliable inputs.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers exists in niche areas, particularly if they possess unique technology or brand strength. This could allow them to bypass Bidvest and directly serve its customers. While Bidvest's asset-light strategy limits its own backward integration, its Supplier Diversity Programme aims to build a robust and competitive supplier base, thereby managing overall supplier power.
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects Bidvest's competitive environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its markets.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Bidvest's diverse global reach across numerous commercial and consumer sectors generally limits the bargaining power of individual customers. However, significant exceptions arise with large-scale commercial contracts, like major facilities management deals or substantial freight volumes, where key clients can wield considerable influence due to the significant revenue they contribute to Bidvest.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Bidvest, particularly impacting its consumer-facing segments. For instance, in 2024, Bidvest's interim results highlighted challenges stemming from 'price sensitive customers' and a general 'declining consumer spend', directly affecting revenue streams in areas like food services and retail.
While individual consumers and smaller businesses often exhibit high price sensitivity, Bidvest's larger corporate clients tend to weigh price against other critical factors. These clients frequently prioritize the value of integrated solutions, consistent reliability, and specialized services that enhance their own operational efficiency, rather than solely focusing on the lowest possible cost.
Customers often have a wide array of substitute products and services available, impacting their bargaining power. For instance, businesses might consider handling tasks like cleaning, logistics, or even IT support in-house rather than outsourcing them. Similarly, for office supplies, customers can choose from numerous retailers, and for travel needs, a multitude of agencies and online platforms exist.
Bidvest actively addresses this by offering a comprehensive basket of services and products, aiming to increase customer value. They also highlight an unparalleled bundle of security services and technology innovation as a differentiator. For example, in 2024, Bidvest’s integrated facilities management offerings, which combine multiple services, are designed to reduce the need for customers to source these solutions from separate providers, thereby strengthening customer loyalty and reducing the perceived availability of viable substitutes.
Customer's Ability to Backward Integrate
Large corporate clients, particularly those with significant needs in areas like facilities management or logistics, might explore backward integration. For instance, a major retail chain could consider bringing its in-house cleaning or security services under its direct control if the sheer scale of operations makes it economically viable and offers a path to greater operational oversight.
However, the substantial capital outlay and the need for specialized expertise in managing these diverse service functions often present significant barriers. The complexity involved in setting up and running these operations efficiently can dilute focus from core business activities.
In 2024, the trend for many large enterprises remains focused on core competencies, making outsourcing to specialists like Bidvest a more attractive proposition. Bidvest’s ability to achieve economies of scale across numerous clients allows it to offer services at a cost and efficiency level that is difficult for individual companies to replicate internally.
- High Capital Investment: Setting up internal facilities management or logistics departments requires significant upfront spending on equipment, technology, and human resources.
- Operational Complexity: Managing diverse service operations demands specialized knowledge and management bandwidth, potentially distracting from a company's primary business.
- Economies of Scale: Specialist providers like Bidvest leverage their scale across multiple clients, achieving cost efficiencies that are hard for individual companies to match.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Many businesses find it more strategic to outsource non-core functions to concentrate resources on their primary revenue-generating activities.
Information Availability to Customers
Customers in many of Bidvest's operating sectors, especially within the business-to-business (B2B) landscape, now possess a wealth of information. This includes detailed insights into pricing structures, the specifics of service packages offered, and the performance metrics of competing businesses. For instance, in the South African food services sector, where Bidvest is a major player, online platforms and industry reports provide extensive comparative data, making it easier for corporate clients to assess value.
This heightened information availability directly translates to increased bargaining power for customers. They can more readily identify alternatives and negotiate terms that favor them, putting pressure on Bidvest to consistently deliver superior value and differentiate its offerings. For example, a large hotel group can easily compare catering quotes and service levels from multiple suppliers, forcing Bidvest to offer competitive pricing and enhanced service quality to retain their business.
Bidvest's response to this dynamic environment involves a continuous drive for innovation and a clear demonstration of its unique value proposition. The company must actively showcase how its services, efficiency, or product quality surpass those of competitors.
- Increased Information Access: Customers can easily compare pricing, service features, and competitor performance across various Bidvest markets.
- Enhanced Customer Bargaining Power: This transparency empowers customers to negotiate better terms and demand greater value.
- Competitive Pressure: Bidvest faces pressure to innovate and highlight its superior value proposition to maintain market share and profitability.
Bidvest's diverse operations mean customer bargaining power varies significantly. While large clients can negotiate favorable terms due to volume, many smaller customers have limited leverage. Bidvest's 2024 interim results noted that price-sensitive customers impacted revenue, particularly in consumer-facing segments, highlighting this dynamic.
Full Version Awaits
Bidvest Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Bidvest Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You can be confident that this professionally formatted analysis is ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Bidvest navigates markets teeming with a wide array of competitors, encompassing both multinational corporations and niche local enterprises across its diverse business segments. This broad spectrum of rivals, particularly evident in sectors such as facilities management and freight and distribution, significantly fuels competitive intensity.
Bidvest operates in diverse sectors, and the industry growth rate significantly influences competitive rivalry. While some of Bidvest's markets might be seeing steady expansion, others, like the new vehicle sector and certain renewable energy product segments, have encountered challenges, described as 'headwinds' or 'stagnant markets.' This uneven growth landscape naturally intensifies the battle for market share among existing players.
Bidvest strives to stand out by offering a wide array of products and services, coupled with integrated solutions and a commitment to innovation. This broad approach aims to cater to diverse customer needs, setting them apart from more specialized competitors.
While Bidvest emphasizes innovation and technology deployment across its operations, some of its product segments are highly commoditized. In these areas, differentiation becomes more difficult, often resulting in competition driven primarily by price.
For instance, in the food services sector, where Bidvest is a major player, the ability to innovate on core product offerings can be limited, leading to intense price wars. However, Bidvest's strategy of providing bundled services, such as catering combined with cleaning or maintenance, offers a more unique value proposition.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can keep companies operating even when profits are slim. For Bidvest, this could manifest in specialized infrastructure within its facilities management divisions or significant fixed assets tied to its freight operations. These investments make it costly and difficult to simply walk away from a struggling segment.
While Bidvest's broad diversification offers some flexibility to shift resources internally, exiting certain markets is not always straightforward. Major divestitures, such as the 2023 sale of its stake in Bidvest Bank for R4.7 billion, illustrate the complexity involved in managing such transitions, requiring strategic planning and market execution.
The presence of high exit barriers influences competitive dynamics by limiting the number of firms that can easily leave an industry. This can lead to prolonged periods of intense competition, even in mature or declining markets, as companies are reluctant to incur significant losses associated with exiting.
- High fixed asset intensity in sectors like freight and specialized infrastructure in facilities management creates significant exit barriers for Bidvest.
- The company's diverse portfolio allows for internal resource reallocation, mitigating some exit challenges.
- Major divestitures, such as the R4.7 billion sale of Bidvest Bank in 2023, highlight the strategic and financial considerations involved in exiting specific markets.
- These barriers can compel companies to remain in less profitable markets, potentially prolonging competitive pressures.
Strategic Commitments of Competitors
Competitors within Bidvest's diverse operating sectors frequently demonstrate robust strategic commitments. These often manifest as aggressive pricing tactics, substantial marketing investments, and a proactive approach to mergers and acquisitions. For instance, in the food services sector, major rivals have been observed to engage in price wars to gain market share, impacting overall profitability.
This intense competitive landscape compels Bidvest to maintain a steadfast focus on strategic acquisitions and operational efficiency as key drivers for its future growth trajectory. In 2024, Bidvest continued its acquisitive strategy, with notable transactions aimed at consolidating its position in key markets. The company's commitment to operational efficiency is reflected in its ongoing efforts to streamline supply chains and leverage technology for cost reduction.
- Aggressive Pricing: Competitors often use lower prices to attract customers, forcing Bidvest to balance market share with profitability.
- Marketing Investments: Significant spending on advertising and promotions by rivals requires Bidvest to invest similarly to maintain brand visibility.
- Acquisition Strategies: Competitors actively acquire smaller players or complementary businesses, necessitating Bidvest's strategic M&A activity to keep pace.
- Operational Efficiency Focus: Bidvest's drive for efficiency is a direct response to the cost pressures created by competitors' strategic moves.
Bidvest faces intense rivalry from a broad spectrum of competitors, ranging from large multinational corporations to specialized local firms across its various business segments. This competition is particularly fierce in areas like facilities management and freight, where market share battles are common. The uneven growth rates across Bidvest's diverse markets, with some experiencing headwinds in 2024, further intensify the struggle for dominance among existing players.
While Bidvest differentiates through integrated solutions and innovation, some of its markets are highly commoditized, leading to price-driven competition. High exit barriers, such as specialized infrastructure in freight and facilities management, mean competitors may remain in less profitable segments, prolonging competitive pressures. Bidvest's strategic response includes ongoing acquisitions, like those in 2024, and a strong focus on operational efficiency to counter aggressive rival strategies such as price wars and significant marketing investments.
| Competitive Factor | Impact on Bidvest | Bidvest's Response/Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Broad Competitor Landscape | Intense rivalry across diverse segments (e.g., facilities management, freight). | Diversification, integrated solutions, innovation. |
| Uneven Market Growth | Increased competition in stagnant or challenging markets. | Strategic resource allocation, focus on efficient segments. |
| Commoditization | Price-based competition in certain product segments. | Bundled services, value-added offerings to differentiate. |
| High Exit Barriers | Prolonged competition in less profitable markets. | Strategic divestitures (e.g., Bidvest Bank sale in 2023 for R4.7 billion), focus on core strengths. |
| Competitor Strategies (Pricing, M&A, Marketing) | Pressure on margins and market share. | Acquisitive growth (continued in 2024), operational efficiency drives, maintaining brand visibility. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Bidvest's facilities management services hinges on whether alternatives offer a better value proposition. For example, if a client can perform cleaning or security in-house for less money or with greater control, these internal operations become a viable substitute.
In 2024, many businesses are scrutinizing operational costs. If the price-performance ratio of outsourced facilities management, like Bidvest's, is perceived as less favorable than in-house solutions or competitor offerings, the threat of substitution increases significantly.
Many of Bidvest's diverse offerings, like basic office supplies or standard logistics services, face a significant threat from readily available substitutes. For instance, businesses can easily switch between different suppliers for stationery or choose alternative courier companies for less critical deliveries.
However, the threat diminishes considerably when Bidvest provides highly integrated solutions or specialized services tailored to specific client needs. In these niche areas, finding a comparable substitute that matches Bidvest's bundled offerings or technical expertise becomes much more challenging.
For example, Bidvest's integrated facilities management services, combining cleaning, security, and maintenance, present a stronger barrier to substitutes than a standalone security service. This integration reduces the ease with which a client can find a single, equally comprehensive alternative.
Customers are increasingly willing to switch to alternatives if they offer significant convenience or cost savings, and the perceived quality difference isn't too great. For instance, in 2024, the rise of direct booking platforms for travel, bypassing traditional travel agents, highlights this trend. Similarly, online marketplaces for office supplies have made it easier for businesses to find cheaper alternatives to established suppliers.
Technological Advancements Enabling Substitutes
Rapid technological progress, especially in areas like automation and digital platforms, is a significant driver for new substitutes. These advancements can offer more efficient alternatives to existing services, directly impacting industries like those Bidvest operates in. For instance, the rise of AI-powered customer service platforms could substitute traditional call center operations.
Bidvest's strategic focus on innovation and technology, including significant investments in enterprise mobility and voice technology, is a direct response to this threat. By proactively developing and deploying advanced solutions, Bidvest aims to stay ahead of potential substitutes and maintain its competitive edge. This forward-thinking approach is crucial in a rapidly evolving market landscape.
- Technological Disruption: Automation and AI are creating new, more efficient service models.
- Bidvest's Response: Investments in innovation, enterprise mobility, and voice technology aim to counter substitute threats.
- Market Impact: The availability of advanced substitutes can pressure pricing and market share for traditional offerings.
Regulatory or Policy Changes Favoring Substitutes
Changes in government regulations or policy shifts can significantly alter the competitive landscape by making substitute products or services more attractive. For instance, if a government introduces new tax breaks or subsidies for companies adopting in-house waste management solutions, this could directly reduce demand for Bidvest's environmental services. Similarly, alterations in import or export tariffs impacting the movement of goods could make alternative logistics providers or different sourcing strategies more appealing for Bidvest's clients, thereby strengthening the threat of substitutes in its freight divisions.
These regulatory shifts can create a more favorable environment for alternatives, potentially leading to a decline in market share for incumbent players like Bidvest. For example, a hypothetical 2024 policy incentivizing local sourcing of raw materials could reduce the need for international freight services, a core offering for Bidvest. Such a move would bolster the competitive position of domestic suppliers and logistics providers, presenting a clear substitute threat.
Consider the potential impact of environmental regulations. If new mandates in 2024 push businesses towards more localized and self-sufficient waste processing, it could directly challenge Bidvest's established environmental services. This could be driven by policies that favor circular economy principles or penalize traditional waste disposal methods, making in-house solutions a more cost-effective or compliant option for clients.
- Regulatory Incentives for In-House Waste Management: Policies offering tax credits or grants for businesses implementing on-site waste reduction and processing could divert clients from Bidvest's environmental services.
- Import/Export Regulation Changes: Shifts in trade policies, such as increased tariffs on imported goods or stricter customs procedures, might encourage clients to seek local suppliers or alternative shipping methods, impacting Bidvest's freight business.
- Environmental Compliance Shifts: New environmental standards or stricter enforcement could make self-managed environmental solutions more appealing than outsourcing to firms like Bidvest, especially if compliance costs for outsourcing rise.
- Support for Localized Supply Chains: Government initiatives promoting domestic production and consumption could reduce the reliance on international logistics, thereby weakening the competitive position of global freight forwarders.
The threat of substitutes for Bidvest's diverse services is significant, particularly for commoditized offerings like basic stationery or standard logistics. In 2024, businesses are highly cost-conscious, making readily available, lower-cost alternatives a constant concern. For instance, online marketplaces offer a vast array of office supplies, providing easy substitutes for traditional suppliers.
However, Bidvest mitigates this threat by offering integrated, specialized solutions that are harder to replicate. Their bundled facilities management services, combining multiple functions, create a higher barrier to substitution than single-service offerings. This strategic focus on value-added services is key to maintaining market share against potential alternatives.
Technological advancements are continuously introducing new substitutes, such as AI-powered customer service platforms potentially replacing traditional call centers. Bidvest's proactive investment in areas like enterprise mobility and voice technology, totaling millions in R&D, aims to stay ahead of these disruptive forces and solidify its competitive advantage.
Regulatory shifts can also bolster substitute threats. For example, government incentives for in-house waste management in 2024 could reduce demand for Bidvest's environmental services. Similarly, changes in trade policies impacting freight could favor local logistics providers, presenting a direct substitute challenge.
Entrants Threaten
Many of Bidvest's core operations, including freight logistics, expansive facilities management, and automotive distribution, demand substantial initial capital outlays. These investments cover essential infrastructure, specialized equipment, and significant inventory levels, creating a formidable barrier for potential new competitors seeking to enter these markets.
Bidvest's vast scale provides a formidable barrier to new entrants. Its global presence and diversified operations, spanning food services, freight, and industrial products, allow it to achieve significant economies of scale. For instance, in 2024, Bidvest's procurement volume across its various divisions likely granted it substantial bargaining power with suppliers, a feat difficult for a new, smaller competitor to replicate.
The ability to leverage economies of scope further strengthens Bidvest's position. By offering a wide array of integrated services, it can cross-sell and bundle offerings, creating value for customers that a specialized new entrant cannot easily match. This integrated approach, coupled with operational efficiencies honed over years, makes competing on cost incredibly challenging for newcomers.
For companies like Bidvest, particularly in sectors dealing with physical goods, securing access to effective distribution channels is a significant hurdle for potential new entrants. Building out the necessary logistics, warehousing, and retail partnerships takes substantial capital and time. For instance, establishing a nationwide delivery network for office supplies can cost millions in infrastructure and fleet management alone.
Bidvest's existing, well-developed distribution networks act as a formidable barrier. Their established relationships with suppliers and customers across various commercial and consumer markets mean new competitors struggle to gain the same reach and efficiency. In 2024, Bidvest's extensive logistics infrastructure, which includes over 100 distribution centers across its various divisions, significantly limits the ability of newcomers to compete on delivery speed and cost.
Brand Loyalty and Reputation
Bidvest has cultivated a robust brand and reputation, a significant barrier for new competitors. For instance, in 2024, Bidvest's continued investment in service excellence and customer relationships, a strategy that has historically yielded strong market positioning, makes it difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
New entrants must overcome the considerable hurdle of establishing trust and brand loyalty comparable to Bidvest's established presence. This requires substantial marketing investment and a proven track record, which are not easily replicated in the short term.
- Established Trust: Bidvest's long-standing commitment to reliability, evidenced by its consistent performance metrics, fosters deep customer loyalty.
- Reputational Capital: Years of delivering diverse, high-quality services have built a strong reputation that new entrants struggle to match quickly.
- Customer Inertia: Existing customers are often reluctant to switch from a trusted provider like Bidvest, even when presented with potentially lower-cost alternatives.
- Brand Differentiation: Bidvest's brand is associated with a wide range of dependable services, creating a complex challenge for new entrants aiming to differentiate themselves effectively.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policy and regulations are a significant deterrent to new entrants for companies like Bidvest, particularly in its diversified portfolio. For instance, in the financial services sector, from which Bidvest has been divesting, stringent capital requirements and extensive compliance mandates, such as those under the Basel III framework, create substantial barriers. These regulations are designed to ensure financial stability but also significantly increase the upfront investment and ongoing operational costs for any new player attempting to enter the market.
Similarly, in the freight and logistics sector, new entrants face a complex web of regulations governing transportation, safety, and environmental standards. In South Africa, for example, the National Road Traffic Act and various environmental protection laws necessitate significant investment in compliant vehicles and operational procedures. These compliance costs can easily run into millions of Rand, making it challenging for smaller, less capitalized firms to compete effectively with established players who have already absorbed these costs.
Bidvest's presence in facilities management also encounters regulatory hurdles. Sectors like healthcare and food services within facilities management often require specific licenses and adherence to strict health and safety standards. For example, obtaining certifications for hygiene and waste management in food service facilities can be a time-consuming and costly process, requiring specialized training and equipment. These regulatory complexities effectively limit the pool of potential new entrants, thereby strengthening Bidvest's position in these markets.
- Financial Services: High capital adequacy ratios and extensive regulatory compliance (e.g., Basel III) increase entry costs.
- Freight & Logistics: Compliance with national road traffic acts and environmental regulations demands significant investment in compliant fleets and operations.
- Facilities Management: Sector-specific licenses and adherence to health, safety, and hygiene standards (e.g., in healthcare or food services) are critical entry barriers.
The threat of new entrants for Bidvest is generally moderate to low due to significant capital requirements, established economies of scale, and strong brand loyalty. For instance, Bidvest's diversified operations, encompassing everything from food services to industrial supplies, necessitate substantial upfront investment in infrastructure, inventory, and distribution networks, making it difficult for smaller, new players to match its operational capacity and cost efficiencies. In 2024, the company's extensive logistics network, comprising over 100 distribution centers, further solidifies this barrier by enabling efficient and cost-effective delivery across its various business segments.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Bidvest is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Bidvest's annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific market research from reputable firms like IBISWorld and Euromonitor. This blend ensures a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.