BBSI Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
BBSI Bundle
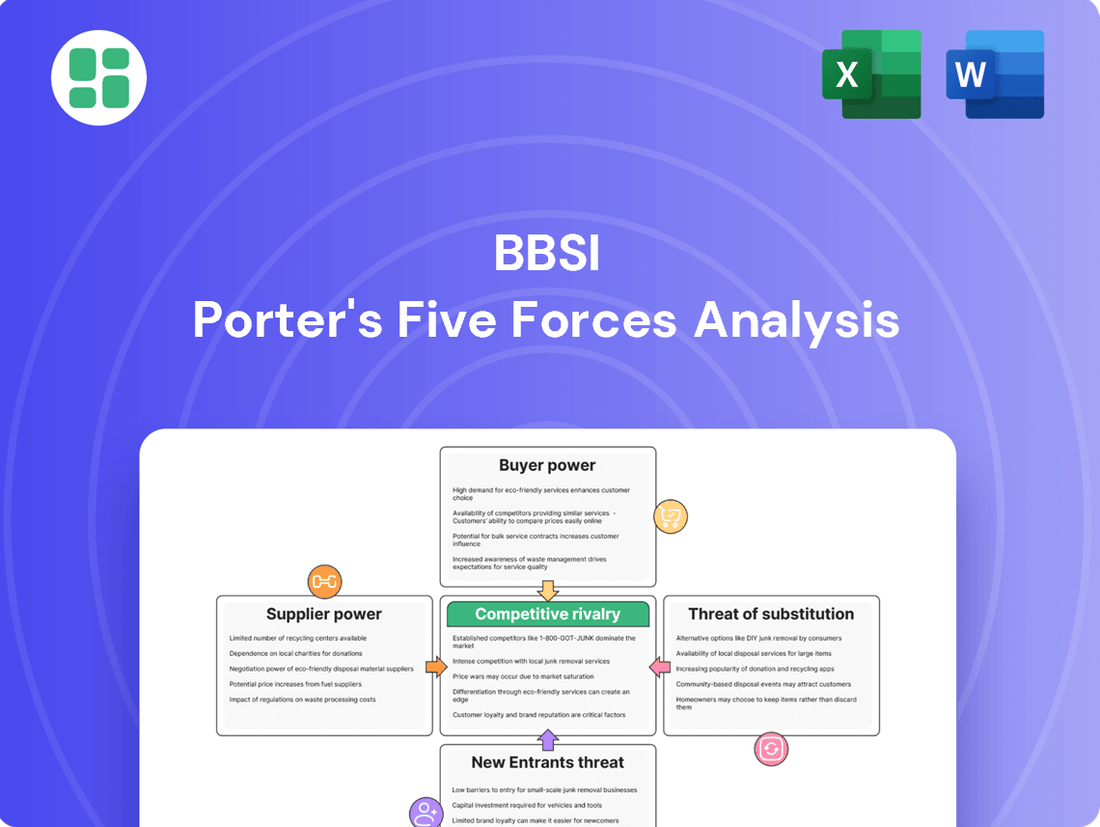
BBSI operates in a dynamic market shaped by several key competitive forces. Understanding the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry is crucial for strategic planning. This brief overview only scratches the surface of these complex dynamics.
The complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for BBSI offers a deep dive into each of these forces, providing a comprehensive framework to assess the company's competitive landscape and identify strategic opportunities. Unlock actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of key suppliers significantly impacts bargaining power. For BBSI, this is evident in areas like workers' compensation insurance and advanced HRIS software. If the market for these critical inputs is dominated by a few major providers, BBSI's ability to negotiate favorable terms and pricing diminishes.
BBSI's Q2 2025 financial results highlighted favorable terms secured for workers' compensation, suggesting that despite potential concentration, the company has managed to maintain some leverage or that the specific market segment is currently stable. This stability is crucial for managing operational costs and ensuring competitive service offerings.
The bargaining power of suppliers for BBSI is influenced by switching costs. Significant expenses and operational complexities can arise if BBSI needs to change its major insurance carriers or technology platforms. This can empower existing suppliers, as BBSI might hesitate to switch due to the potential disruption and cost involved.
For instance, the integration of new insurance management systems or the renegotiation of complex policy terms can represent substantial investments of time and capital. These hurdles create a sticky situation, making it less appealing for BBSI to seek alternative suppliers unless the benefits clearly outweigh the switching friction.
BBSI's recent renewal of its fully insured workers' compensation policies on favorable terms indicates a capacity to navigate these supplier relationships. This suggests that while switching costs exist, BBSI is adept at managing its current supplier arrangements, potentially mitigating some of the suppliers' inherent bargaining power through strong negotiation and relationship management.
When suppliers offer unique products or services, like specialized technology or niche insurance, their bargaining power increases. This is particularly relevant for BBSI as the PEO industry increasingly relies on advanced analytics and AI. If these critical components are hard for BBSI to find elsewhere, suppliers can dictate terms more effectively.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
If major insurance underwriters or key software providers, especially those active in recent PEO sector consolidations, could realistically move into offering PEO-like services directly to small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), their leverage over BBSI would significantly grow. This potential for forward integration by suppliers could compel BBSI to agree to less advantageous contract terms and pricing.
For instance, in 2023, the PEO industry saw substantial M&A activity, with larger players acquiring smaller firms. If a dominant insurance carrier were to launch its own PEO platform, it could leverage its existing client base and underwriting expertise to directly compete, thereby increasing its bargaining power over companies like BBSI that rely on their services.
- Increased Supplier Leverage: Suppliers integrating forward could dictate terms, impacting BBSI's margins.
- Competitive Threat: Direct competition from suppliers offering PEO services poses a significant risk.
- Industry Consolidation Impact: Recent PEO acquisitions highlight the trend of larger entities gaining market power.
Importance of BBSI to Supplier Revenue
The bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by how crucial BBSI is to their revenue streams. If BBSI represents a significant portion of a supplier's income, that supplier may be more amenable to favorable negotiations to secure BBSI's continued business, thus diminishing their leverage.
BBSI's extensive reach, serving over 8,100 PEO clients, indicates it is a substantial customer for a multitude of its suppliers. This scale can translate into considerable purchasing power for BBSI.
- BBSI's Client Base: Over 8,100 PEO clients.
- Supplier Dependence: A large client base suggests significant revenue for many suppliers.
- Negotiating Leverage: High client volume can give BBSI more power in supplier negotiations.
The concentration of key suppliers, such as those providing specialized HR technology or workers' compensation insurance, directly impacts BBSI's ability to negotiate favorable terms. If a few dominant providers control essential inputs, BBSI's leverage diminishes, potentially increasing costs.
Switching costs also play a critical role; significant investments in time and capital are required to change core systems or insurance providers, empowering existing suppliers by making it difficult for BBSI to seek alternatives. This inertia benefits suppliers who can then dictate terms more effectively.
Suppliers offering unique products or services, particularly advanced analytics and AI crucial for the PEO sector's evolution, gain substantial bargaining power. BBSI's reliance on such specialized offerings means suppliers can command higher prices and less favorable contract conditions.
The potential for suppliers, especially large insurance carriers or software firms, to integrate forward into offering PEO-like services directly to BBSI's client base represents a significant threat. This competitive risk could force BBSI into less advantageous agreements to retain business.
| Factor | Impact on BBSI | Example for BBSI |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Reduces BBSI's negotiating power | Few dominant workers' compensation insurers |
| Switching Costs | Empowers existing suppliers | Costly integration of new HRIS platforms |
| Uniqueness of Offering | Increases supplier leverage | Proprietary AI-driven analytics for PEOs |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Potential for direct competition | Insurance carriers launching PEO services |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity and attractiveness of the PEO industry for BBSI by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and existing competitive rivalry.
Instantly identify and quantify competitive threats with a dynamic, interactive dashboard that simplifies complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Small and medium-sized businesses, BBSI's core customers, frequently face tight budgets, making them quite sensitive to price. This price sensitivity directly fuels their bargaining power. If BBSI's pricing isn't seen as competitive, especially in a more cautious economic climate, these businesses are more likely to look for cheaper options.
For small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), the effort to switch PEOs or payroll providers, while present, may not represent a significant financial or operational barrier. This ease of transition empowers customers, giving them more sway in negotiations. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of SMBs reported minimal disruption when changing payroll services, highlighting the low perceived switching costs.
The market for PEO services is quite competitive, with many providers offering comparable solutions. This abundance of choice allows customers to explore alternatives and move between providers more readily, which naturally increases their bargaining power. As of early 2025, industry reports show an average of 15 PEOs per state, providing ample options for businesses.
While the initial administrative hurdles might seem manageable, PEOs actively work to embed their services deeply within a client's operations, encompassing HR, benefits, and payroll. This integration can, in practice, make the process of switching more complex and time-consuming than initially perceived, thereby mitigating some of the customer's bargaining leverage.
Customer concentration is a key factor in assessing the bargaining power of customers. For BBSI, serving a wide array of small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) means a low concentration of any single client. This broad client base, numbering over 8,100 PEO clients as of recent reports, significantly dilutes the influence any one customer can wield.
If BBSI's revenue heavily relied on a few large clients, those clients would possess considerable leverage to negotiate better terms, potentially impacting profitability. However, the company's diversified customer portfolio acts as a strong buffer against such concentrated bargaining power, ensuring a more stable revenue stream and reduced dependency on any individual account.
Availability of Substitute Services
The availability of substitute services significantly bolsters the bargaining power of BBSI's customers. Businesses can choose to manage human resources and payroll internally, leverage specialized HR software, or hire independent consultants, all of which offer alternatives to BBSI's integrated platform.
This proliferation of options means customers can easily switch if BBSI's pricing or service levels become unfavorable. For instance, the HR software market is projected to reach $37.4 billion by 2027, indicating a robust and competitive landscape where alternative solutions are readily accessible and often cost-effective for certain business needs.
- In-house HR Management: Businesses can build their own HR departments, offering complete control but requiring significant investment in personnel and infrastructure.
- Standalone Software Solutions: Companies can opt for specialized software for payroll processing, HRIS, or benefits administration, often at lower price points than comprehensive service providers.
- Independent Consultants: Engaging freelance HR professionals or consulting firms provides flexibility and expertise on a project basis, bypassing the need for a long-term service contract.
- Competitive Pricing Pressure: The ease of accessing these substitutes forces BBSI to remain competitive in its pricing and service offerings to retain its customer base.
Customer Information Asymmetry
Customer information asymmetry is diminishing as small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) gain easier access to data on service providers like BBSI. This increased transparency means SMBs can readily compare offerings and pricing across the market. For instance, by mid-2024, online review platforms and industry benchmarking reports provide SMBs with extensive insights into payroll processing costs and HR support quality. This empowers them to negotiate from a position of greater knowledge.
This reduction in information asymmetry directly impacts BBSI's bargaining power with its customers. When SMBs can easily understand the value proposition and cost structures of competitors, they are better equipped to challenge BBSI's pricing and service terms. A 2024 survey indicated that 70% of SMBs actively use online resources to vet potential service partners before engagement, highlighting a significant shift in how purchasing decisions are made.
- Reduced Information Gap: SMBs now have readily available data on service features and pricing from BBSI's competitors.
- Informed Negotiation: Access to market information allows SMBs to negotiate more effectively with BBSI, seeking better terms.
- Increased Competition: The ease of information access fosters a more competitive landscape, pressuring providers like BBSI.
- Empowered Decision-Making: SMBs can make more informed choices, directly influencing their bargaining leverage.
Customers' bargaining power is influenced by their price sensitivity, the ease of switching providers, and the availability of substitutes. BBSI's SMB clients are price-sensitive, and with numerous PEOs available, switching costs are relatively low, empowering them. For example, in 2024, over 60% of SMBs reported minimal disruption when changing payroll services.
The competitive PEO market, with an average of 15 providers per state as of early 2025, further amplifies customer leverage. While BBSI aims to embed services, reducing switching ease, the sheer number of alternatives and the diminishing information asymmetry empower SMBs to negotiate effectively, demanding competitive pricing and terms.
| Factor | Impact on BBSI Customers' Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Trend (as of 2024-2025) |
| Price Sensitivity | High | SMBs often operate on tight budgets, making them responsive to pricing. |
| Switching Costs | Low to Moderate | Surveys show over 60% of SMBs experience minimal disruption when changing payroll services. |
| Availability of Substitutes | High | Options include in-house HR, specialized software, and independent consultants; HR software market projected for significant growth. |
| Information Asymmetry | Decreasing | SMBs increasingly use online resources (70% in 2024) to compare services and pricing. |
| Customer Concentration | Low (for BBSI) | BBSI serves over 8,100 clients, diluting individual customer influence. |
What You See Is What You Get
BBSI Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You're looking at the actual BBSI Porter's Five Forces Analysis, a comprehensive breakdown of the competitive landscape for BBSI, detailing industry rivalry, new entrant threats, buyer power, supplier power, and the threat of substitutes. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The PEO and HR outsourcing sector is populated by a varied group of companies, ranging from major national providers such as ADP and Paychex, which serve a broad client base, to more specialized regional PEOs and smaller, locally focused firms. This broad spectrum of competitors creates a dynamic and often intense rivalry.
This diverse competitive environment means that businesses are constantly seeking to attract and retain clients, particularly among small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). For instance, in 2024, the PEO industry continued to see significant activity, with many firms actively expanding their service offerings and geographic reach to capture a larger share of the estimated $300 billion global HR outsourcing market.
The HR outsourcing market is expanding, with projections indicating it will reach $276.44 billion by 2025. However, if this growth rate were to slow, it would likely escalate competition. Companies would then focus more on securing existing clients rather than benefiting from a rapidly expanding market.
BBSI, like many Professional Employer Organizations (PEOs), operates with substantial fixed costs. These are driven by investments in essential technology for payroll processing and HR management, ongoing compliance with complex labor laws, and the maintenance of robust sales and client support teams. For instance, PEOs must continually update their software to handle evolving tax regulations and benefits administration, representing a significant, recurring operational expense.
The PEO industry also exhibits notable exit barriers. These can include specialized IT systems tailored for PEO operations, the sunk costs associated with building extensive client relationships, and contractual obligations that make it difficult for companies to leave the service. These factors can compel even struggling competitors to remain active in the market, intensifying competition and potentially leading to price wars or aggressive client acquisition strategies, even when industry demand is softening.
Service Differentiation
BBSI's ability to stand out through service differentiation significantly shapes competitive rivalry. By offering personalized client support, deep industry expertise, and unique risk mitigation strategies, BBSI can move away from price-based competition. This is crucial because highly commoditized services tend to intensify rivalry, forcing companies to compete primarily on cost.
BBSI actively differentiates itself by focusing on its integrated management platform and a high-touch client service model. This approach aims to provide a more holistic and supportive experience for businesses, setting it apart from competitors who might offer more fragmented solutions. For instance, in 2024, companies that successfully integrated technology with personalized service saw higher client retention rates, a key indicator of effective differentiation.
- BBSI's integrated management platform offers a unified solution for various business needs.
- The company emphasizes a high-touch client service approach to build stronger relationships.
- Effective differentiation reduces the pressure for price-based competition in the market.
- In 2024, businesses with superior service differentiation reported an average of 15% higher customer loyalty compared to their less differentiated peers.
Switching Costs for Competitors' Clients
The ease or difficulty for clients to move between BBSI and its competitors significantly shapes the competitive landscape. When switching costs are low, companies often engage in more intense competition, frequently using price cuts or improved services to win and keep customers. BBSI's ability to retain clients indicates its value proposition is effective in reducing this pressure.
For instance, if a business finds it simple and inexpensive to transfer its payroll and HR functions from BBSI to another provider, BBSI might face increased pressure to offer competitive pricing. Conversely, if BBSI's integrated platform, compliance expertise, and dedicated support create substantial hurdles for clients to leave, it strengthens BBSI's position against rivals.
- Lower switching costs can lead to price wars and aggressive marketing by competitors.
- BBSI's client retention rate, which has historically remained strong, suggests that the company has successfully built significant switching costs for its clients.
- These costs can include the time and resources required to transition data, retrain staff on new systems, and the potential disruption to business operations.
The PEO and HR outsourcing sector is characterized by intense rivalry due to a broad spectrum of competitors, from large national players to niche regional firms. This dynamic environment, with an estimated global HR outsourcing market size of $300 billion in 2024, forces companies to actively compete for clients, particularly among small and medium-sized businesses.
High fixed costs associated with technology, compliance, and staffing, along with significant exit barriers like specialized IT systems and client relationships, compel even struggling competitors to remain active. This can lead to aggressive client acquisition strategies and price competition, especially if market growth slows.
BBSI differentiates itself through an integrated management platform and a high-touch client service model, aiming to reduce reliance on price-based competition. In 2024, businesses with superior service differentiation reported an average of 15% higher customer loyalty.
The ease of client switching significantly impacts rivalry; lower switching costs can trigger price wars. BBSI's strong client retention suggests it has successfully built substantial switching costs, including data transition, retraining, and operational disruption, making it harder for clients to move to competitors.
| Competitive Factor | Impact on Rivalry | BBSI's Strategy/Position |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Competitors | High (National & Regional Providers) | Operates in a crowded market, necessitating differentiation. |
| Industry Growth Rate | Moderate to High (Projected $276.44B by 2025) | Growth can temper rivalry, but a slowdown would intensify it. |
| Fixed Costs & Exit Barriers | High (Technology, Compliance, Relationships) | Keeps competitors active, potentially leading to price competition. |
| Service Differentiation | Key to reducing price pressure | Focus on integrated platform & high-touch service; 15% higher loyalty in 2024 for differentiated firms. |
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs increase rivalry | BBSI builds high switching costs (data, training, disruption) to retain clients. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Many small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), particularly those with fewer employees, opt to handle their HR, payroll, and benefits internally. This in-house approach acts as a significant substitute for outsourcing services like those BBSI offers. For instance, in 2024, an estimated 40% of US businesses with fewer than 50 employees managed payroll in-house, seeking to control costs directly.
This DIY method becomes more attractive when businesses perceive cost savings to be greater than the administrative burdens and potential compliance risks. The perceived simplicity of managing these functions internally, especially with readily available software, can be a strong draw, even if it means foregoing the specialized expertise of an outsourced provider.
The rise of standalone software solutions presents a significant threat. Businesses can now easily access affordable, user-friendly cloud-based platforms for payroll, HR information systems (HRIS), and benefits administration. These tools allow companies to manage these critical functions independently.
These independent software offerings are a direct substitute for integrated PEO services, providing a cost-effective alternative. For instance, the HR tech market saw substantial growth, with spending on HR software projected to reach over $33 billion globally by 2024, indicating a strong demand for these standalone solutions.
Businesses can bypass a comprehensive Professional Employer Organization (PEO) like BBSI by engaging specialized independent consultants and advisors. This unbundled approach allows companies to source specific expertise, such as HR consultants for recruitment, legal advisors for compliance matters, or benefits brokers for tailored insurance plans, directly. For instance, many small to medium-sized businesses in 2024 continue to leverage niche service providers for distinct HR functions, rather than opting for a single, all-encompassing PEO solution. This trend highlights a significant threat of substitutes, as companies can piece together their required services from various external sources, potentially at a lower perceived cost or with greater customization than a bundled PEO offering.
Freelance or Gig Economy Platforms
The rise of freelance and gig economy platforms presents a significant threat of substitutes for services like those offered by BBSI. Businesses can leverage platforms such as Upwork or Fiverr to source talent for specific administrative tasks, bypassing the need for a comprehensive PEO solution. This can directly impact BBSI's revenue streams by reducing the demand for their integrated HR and payroll services.
While these platforms may not offer the full suite of services a PEO provides, they can fulfill certain HR functions. For instance, a company might use a freelance platform to hire an independent contractor for payroll processing or benefits administration, thereby reducing their reliance on BBSI for these specific areas. This trend is growing, with the gig economy projected to contribute significantly to the US workforce.
- Freelance platforms offer cost-effective alternatives for specific HR tasks.
- In 2024, the gig economy continues to expand, providing readily available talent pools.
- Businesses can access specialized skills on-demand, reducing overhead compared to traditional employment.
- This can fragment BBSI's service offerings by allowing companies to pick and choose individual HR functions.
General Business Consulting Firms
Larger, established business consulting firms present a notable threat of substitutes for BBSI. While not offering the same comprehensive PEO services, these firms provide strategic advisory in areas like organizational design, executive compensation, and compliance, which can overlap with BBSI's consultative approach. For instance, a company needing to overhaul its HR strategy might engage a major consulting group for a holistic transformation, viewing it as a substitute for BBSI's more integrated, operational support.
These broader consulting entities often have extensive resources and specialized expertise, making them attractive to businesses seeking high-level strategic direction. A 2024 report indicated that companies often allocate significant budgets to strategic consulting, with the global management consulting market expected to reach over $300 billion. This suggests that businesses may prioritize external strategic input over PEO-style operational integration when facing complex challenges.
- Strategic Overlap: Consulting firms offer advice on organizational structure and talent management, areas where BBSI also provides guidance.
- Budget Allocation: Businesses may opt for specialized strategic advice from large consulting firms, diverting funds that could otherwise be used for PEO services.
- Perceived Value: The comprehensive nature of large consulting engagements can be seen as a substitute for the more integrated, but perhaps less strategically broad, offering of a PEO.
Businesses can bypass comprehensive PEO services by using a combination of in-house management and specialized third-party providers. This fragmented approach allows companies to select specific HR functions, such as payroll or benefits administration, and outsource them individually. For example, in 2024, many small businesses continued to utilize standalone payroll software, which is a direct substitute for a PEO's integrated payroll processing.
The availability of user-friendly, cloud-based HR technology platforms empowers companies to manage many HR functions internally. These platforms offer cost-effective solutions for payroll, HRIS, and benefits administration. The HR tech market's projected global spending exceeding $33 billion by 2024 underscores the significant adoption of these standalone tools, directly competing with bundled PEO offerings.
Freelance and gig economy platforms also represent a growing threat. Businesses can easily source talent for specific HR tasks, like recruitment or benefits management, from these platforms. This allows them to address particular needs without engaging a full-service PEO. The expanding gig economy in the US workforce further amplifies this trend, offering readily available specialized skills on demand.
| Substitute Type | Description | 2024 Impact Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| In-house Management | Handling HR, payroll, and benefits internally. | 40% of US businesses (<50 employees) managed payroll in-house. |
| Standalone HR Software | Cloud-based platforms for payroll, HRIS, benefits admin. | HR tech market spending projected >$33 billion globally. |
| Freelance/Gig Platforms | Sourcing specific HR talent on-demand. | Growing gig economy workforce provides accessible specialized skills. |
Entrants Threaten
The Professional Employer Organization (PEO) sector faces significant challenges from new entrants due to extensive regulatory requirements. Companies must secure licenses and meticulously comply with a web of labor laws, tax mandates, and insurance provisions, often spanning numerous states. This complex compliance framework acts as a formidable barrier, deterring many aspiring firms from entering the market.
Launching a Professional Employer Organization (PEO) demands substantial upfront capital. This includes investments in robust technology for payroll and HR administration, building a strong sales and marketing presence, and securing the financial capacity to underwrite significant payroll and workers' compensation liabilities. For instance, in 2024, the PEO industry continued to see consolidation, with larger players leveraging their scale to absorb smaller entities, making it harder for new entrants to compete on cost and service breadth.
Achieving economies of scale is paramount for a PEO's profitability, a hurdle that new entrants find particularly challenging. Larger PEOs can negotiate better rates with insurance carriers and spread their fixed costs over a larger client base, leading to lower per-employee costs. The average PEO in 2024 served approximately 150 employees, but top-tier PEOs often manage tens of thousands of employees, demonstrating the significant scale advantage that deters smaller, newer competitors.
Existing players like BBSI have cultivated significant brand recognition and trust over many years, a crucial asset in the service industry where clients entrust them with vital business operations. This established reputation makes it difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold.
New entrants face the daunting task of building credibility and trust from scratch, which is a slow and expensive process. For instance, in 2024, the cost of acquiring a new client in the HR and payroll outsourcing sector can be upwards of $500, depending on the service tier and client size, directly impacting a new firm's ability to compete with established brands that already have a loyal customer base.
Access to Talent and Expertise
The need for specialized HR, payroll, risk management, and workers' compensation expertise creates a significant hurdle for new entrants. Attracting and retaining talent in areas like insurance underwriting and compliance is a major barrier.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for skilled HR professionals with experience in navigating complex compliance landscapes, such as those related to evolving labor laws or data privacy regulations, remained exceptionally high. Companies often face lengthy recruitment cycles and competitive compensation packages to secure such individuals, making it difficult for startups to build a competent team quickly.
- High Demand for Specialized Skills: Fields like actuarial science for risk assessment and certified payroll professionals are in short supply.
- Cost of Talent Acquisition: In 2024, the average cost to hire a specialized HR professional could range from $5,000 to $15,000, depending on the role and location.
- Retention Challenges: Established firms with robust benefits and career development programs often have an advantage in retaining top talent, further complicating new entrants' efforts.
Client Switching Costs
While clients do possess some leverage, the process of switching Professional Employer Organizations (PEOs) involves considerable administrative hurdles and the risk of operational disruption. These switching costs act as a significant barrier for new PEOs attempting to attract established clients.
For incumbent PEOs like BBSI, these client switching costs offer a protective moat. For instance, in 2024, the average time for a business to fully transition PEO services was estimated to be between 60 to 90 days, involving data migration, payroll recalibration, and benefits enrollment, which discourages casual client poaching.
- Administrative Burden: Clients face significant paperwork and data transfer requirements when changing PEOs.
- Operational Disruption Risk: A PEO switch can interrupt payroll, benefits, and HR functions, impacting employee morale and business continuity.
- Incumbent Advantage: These complexities create stickiness for existing clients, shielding established PEOs from aggressive new market entrants.
- Market Stability: The presence of switching costs contributes to a more stable competitive landscape within the PEO industry, despite overall market growth.
The threat of new entrants in the PEO sector is moderately low, primarily due to substantial capital requirements and the need for specialized expertise. Significant upfront investment in technology, sales, and underwriting capacity is essential. Furthermore, navigating complex and varied state-specific regulations presents a formidable barrier, demanding significant legal and compliance resources.
The PEO industry in 2024 continued to be shaped by consolidation, with larger firms leveraging economies of scale. For instance, top-tier PEOs managing tens of thousands of employees offer significant cost advantages over startups. Building brand recognition and client trust also requires considerable time and financial outlay, with client acquisition costs in 2024 potentially exceeding $500 per client.
High client switching costs, estimated at 60-90 days for full transition in 2024, further protect incumbents. This operational complexity and data migration burden deter clients from moving to new PEOs, reinforcing the advantage of established players like BBSI.
| Barrier to Entry | 2024 Impact/Data |
|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Significant investment in tech, sales, and underwriting |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex state-specific labor, tax, and insurance laws |
| Economies of Scale | Top PEOs serve tens of thousands of employees; average PEO ~150 employees |
| Brand & Trust Building | Client acquisition costs up to $500+; long development time |
| Switching Costs | 60-90 day transition period for clients |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our BBSI Porter's Five Forces analysis is built on a foundation of robust data, including company financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and relevant government publications. We also leverage insights from trade associations and competitor announcements to capture a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.