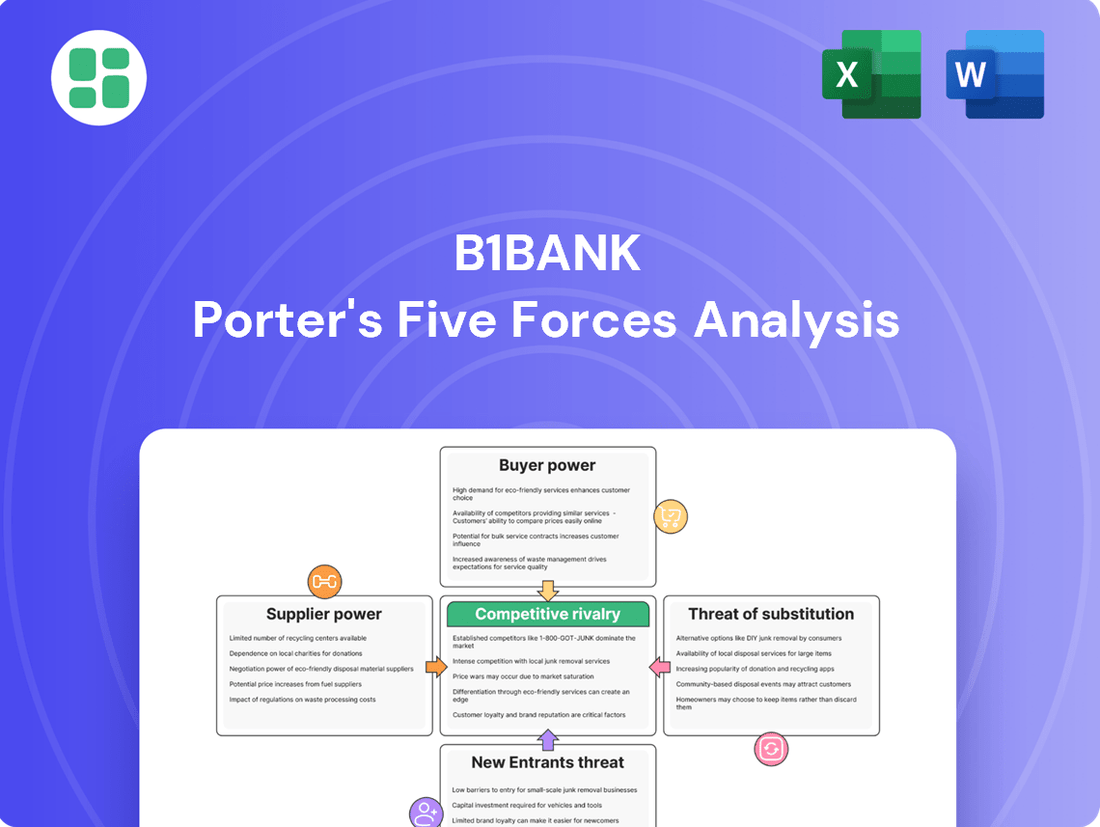
b1BANK Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
b1BANK Bundle
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for b1BANK reveals the intense competitive landscape, highlighting significant threats from new entrants and the considerable bargaining power of buyers. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating b1BANK's market effectively.
The complete report goes beyond this snapshot, offering a deep dive into supplier power, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry, providing a comprehensive strategic outlook for b1BANK. Unlock the full analysis to gain actionable insights and drive smarter decision-making for b1BANK.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers in the core banking software sector is considerable for b1BANK due to market concentration. A handful of dominant providers, including Temenos, Mambu, FIS, and Oracle, control a significant portion of this essential technology landscape. This limited competition allows these specialized software firms to exert substantial leverage when negotiating terms with banks.
The global core banking systems market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating a substantial increase in demand for these critical services. This upward trend in demand further strengthens the position of the few key software suppliers, as banks increasingly rely on their platforms to maintain and modernize operations.
The bargaining power of suppliers is significantly amplified when switching costs for essential technology systems are high. For financial institutions, migrating from one core banking system to another is a monumental task, often taking years and costing millions, with substantial risks tied to data integrity and operational continuity. b1BANK's own core conversion planned for Q2 2025 underscores this reality, demonstrating the deep integration and financial commitment required to change such foundational technology.
Banks' reliance on specialized human capital, particularly in tech and risk management, means that a scarcity of top talent can significantly empower these skilled individuals as suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the demand for cybersecurity experts in the financial sector outstripped supply, leading to salary increases of up to 15% in some regions, directly impacting a bank's labor costs.
Regulatory Compliance Vendors
Regulatory compliance vendors hold significant bargaining power over b1BANK due to the escalating complexity of financial regulations. Banks increasingly rely on specialized RegTech solutions and expert consultants to navigate these intricate requirements, making them dependent on these third-party providers.
The global RegTech market was valued at approximately $11.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong demand and reliance on these services. This growing market underscores the essential nature of compliance vendors.
- High Switching Costs: Implementing and integrating new compliance systems can be costly and time-consuming for banks, creating a barrier to switching vendors.
- Specialized Expertise: Regulatory compliance vendors possess niche knowledge and technology that are difficult for banks to replicate in-house.
- Limited Vendor Pool: For certain highly specialized compliance needs, the number of qualified vendors may be limited, further concentrating power.
Payment Network Providers
Payment network providers, such as Mastercard, wield considerable bargaining power over banks like b1BANK. This is because these networks offer the essential infrastructure for processing transactions, a critical function for any financial institution. b1BANK's recognition as a 2024 Mastercard Innovation Award winner highlights its reliance on and integration with such networks.
The dependency of banks on these payment systems means that network providers can influence terms and fees. Their control over the technology and standards for payment processing gives them leverage.
- Network Dominance: A few major payment networks process the vast majority of global transactions, concentrating power.
- Interoperability Requirements: Banks must adhere to network standards, limiting their ability to switch providers easily.
- Innovation Dependence: Banks often rely on network providers for advancements in payment technology, further solidifying the providers' position.
The bargaining power of suppliers for b1BANK is significant, particularly with core banking software providers and regulatory compliance vendors. High switching costs for these critical systems, coupled with a limited pool of specialized vendors, mean these suppliers hold considerable leverage. For instance, the global RegTech market's growth to an estimated $11.2 billion in 2023 highlights the essential nature of these services and the dependence banks have on them.
| Supplier Type | Market Concentration | Switching Costs | Impact on b1BANK |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Banking Software | High (few dominant providers) | Very High (years, millions, operational risk) | Significant leverage in negotiations |
| Regulatory Compliance (RegTech) | Moderate to High (specialized niche) | High (integration, expertise) | Dependence on vendors for compliance |
| Payment Networks (e.g., Mastercard) | High (few dominant networks) | High (interoperability, standards) | Influence on transaction fees and terms |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting b1BANK, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking sector.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry power dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
b1BANK's target customers, including small and medium-sized businesses, entrepreneurs, and professionals, are increasingly digitally savvy. This heightened customer sophistication means they expect intuitive and efficient online banking services, readily available through various digital channels.
The growing comfort with digital platforms translates into higher expectations for self-service options. As of early 2024, data suggests that over 70% of SMBs in developed economies prefer digital channels for routine banking transactions, a significant increase from previous years.
Consequently, b1BANK's ability to provide robust and user-friendly digital self-service offerings directly impacts customer satisfaction and their bargaining power. Banks that excel in this area can foster loyalty, while those lagging may face increased pressure on pricing and service terms.
Customers of b1BANK, like those in Louisiana and Texas, have a wide array of banking choices. Beyond traditional institutions, they can turn to numerous regional and national banks, as well as community banks and credit unions. This extensive competition means customers can easily shop around for the best deals.
In 2024, the banking sector continued to see robust competition. For instance, the number of FDIC-insured commercial banks in the U.S. remained substantial, providing consumers with many alternatives. This availability empowers customers to demand better terms and pricing, as they can readily switch to a competitor offering more favorable conditions.
Middle market companies and small businesses are increasingly exploring non-traditional lenders for their financing needs. A recent survey indicated that a significant portion, around 40% of these businesses, plan to seek funding from alternative sources. This trend directly impacts b1BANK's commercial lending customers, providing them with viable options should traditional bank credit policies become less accommodating.
Price Sensitivity for Deposits and Loans
Customers’ sensitivity to deposit rates and loan costs significantly impacts banks like b1BANK, especially in shifting interest rate landscapes. This price sensitivity fuels a competitive environment for attracting and retaining deposits, often referred to as a 'war for deposits'. When customers push back against lower returns on their savings, even when market conditions dictate, their bargaining power grows, potentially squeezing banks' net interest margins.
In 2024, the Federal Reserve maintained interest rates at elevated levels throughout much of the year, prompting depositors to seek higher yields. This led to increased competition among banks for funding. For instance, some regional banks reported significant increases in their cost of deposits as they offered more competitive rates to retain customer balances.
- Deposit Rate Competition: Customers actively compare and switch banks for even minor increases in deposit yields, forcing banks to offer more attractive rates.
- Loan Cost Sensitivity: Borrowers, both individuals and businesses, are highly attuned to loan interest rates, seeking the most favorable terms.
- Impact on Net Interest Margin (NIM): Increased deposit costs and potentially lower loan origination volumes due to higher borrowing costs can compress a bank's NIM.
- Customer Retention Challenges: Banks face the challenge of retaining customers who are willing to move their funds for better returns, increasing customer acquisition costs.
Low Switching Costs for Basic Services
For basic banking services like checking and savings accounts, customers can often switch banks with minimal friction. This is particularly true as digital onboarding becomes more prevalent, allowing new customers to open accounts online in a matter of minutes. For instance, in 2024, many neobanks and traditional banks alike reported significant increases in digital account openings, highlighting the ease of switching for consumers.
This low barrier to entry for basic banking products means customers have the leverage to shop around for the best rates on deposits or the most favorable terms on simple loans. They can easily compare offerings from different institutions, putting pressure on banks to remain competitive. This dynamic is a key aspect of the bargaining power of customers in the banking sector.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers can move basic accounts with ease, often completing the process online within minutes.
- Digital Onboarding: The rise of digital platforms has significantly reduced the time and effort required to switch banks.
- Competitive Landscape: Many banks offer similar basic services, encouraging customers to seek better terms elsewhere.
- Customer Leverage: The ability to switch easily empowers customers to demand better rates and services from their financial institutions.
Customers’ ability to switch financial providers easily significantly amplifies their bargaining power. This ease is particularly evident with basic banking products like checking and savings accounts, where digital onboarding in 2024 allowed for account opening in mere minutes. For instance, many neobanks and traditional banks reported substantial growth in digital account openings, underscoring the minimal friction involved in changing institutions.
The increasing availability of digital channels and streamlined processes means customers can readily compare offerings and move their funds for better rates or terms. This low barrier to switching empowers customers to demand more competitive pricing and services, directly impacting b1BANK's ability to retain its customer base without offering superior value.
| Metric | 2023 (Estimate) | 2024 (Projection) | Impact on Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Account Opening Time (Minutes) | 5-10 | 2-5 | Increased |
| Customer Switching Rate (Basic Accounts) | 15-20% | 18-23% | Increased |
| Availability of Online Comparison Tools | High | Very High | Increased |
Preview Before You Purchase
b1BANK Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces analysis for b1BANK, offering a thorough examination of competitive pressures within the banking sector. The document you see here is precisely the same comprehensive analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, ensuring you get the full, professionally formatted report without any placeholders or alterations.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The banking landscape in Louisiana and Texas is densely populated with regional and community banks, intensifying competition for b1BANK. This fragmented market means b1BANK faces numerous local rivals, each vying for customer deposits and loans.
b1BANK's strategic acquisition of Progressive Bancorp in late 2023, valued at approximately $133 million, directly addresses this competitive pressure by bolstering its presence in North Louisiana. This move signifies a proactive approach to consolidation and market share expansion in a crowded field.
Large national banks like JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, Wells Fargo, and Citibank command substantial market share and possess vast branch and ATM networks, presenting a formidable competitive challenge even to regional players like b1BANK. These giants often attract business owners due to their perceived stability and comprehensive service offerings, potentially siphoning away valuable deposits from smaller institutions.
Fintech companies and non-bank lenders are intensifying their competition, directly challenging traditional banks like b1BANK for market share. These agile players are leveraging innovative digital platforms and niche financial services to attract customers, putting pressure on established institutions. For instance, the global fintech market size was projected to reach over $332 billion in 2024, a testament to its growing influence.
Embedded finance and open banking continue to be significant forces, presenting both challenges and opportunities for b1BANK. These trends allow non-traditional providers to integrate financial services into everyday platforms, potentially disintermediating banks. In 2023, the value of embedded finance transactions globally was estimated to be around $7.2 trillion, highlighting the scale of this shift.
Economic Uncertainty and Margin Pressure
Economic uncertainty and fluctuating interest rates are significantly impacting the banking sector, leading to considerable pressure on net interest margins. In 2024, many banks experienced this squeeze as deposit costs rose while loan demand remained somewhat subdued in certain segments, forcing them to compete more aggressively for market share.
This financial pressure intensifies competitive rivalry within the industry. Banks are increasingly looking for ways to differentiate themselves and attract customers, whether through enhanced digital offerings, specialized loan products, or more competitive pricing, all while navigating a potentially slower economic growth environment.
- Margin Squeeze: Rising deposit costs and interest rate volatility compressed net interest margins for many banks in 2024.
- Intensified Competition: Banks are fighting harder for customers and loan growth in a challenging economic climate.
- Focus on Efficiency: Cost control and operational efficiency become critical as revenue growth becomes more difficult.
Focus on Digital Transformation and Innovation
Competitive rivalry in the banking sector is intensely fueled by digital transformation. Banks are pouring resources into technology to boost operational efficiency and elevate the customer experience. For instance, in 2024, the global banking sector's IT spending was projected to reach $220 billion, highlighting this critical investment area.
b1BANK's strategic focus on its own technological advancements, including core conversion projects, directly mirrors this industry-wide imperative. Staying competitive necessitates continuous modernization and a commitment to innovation. This digital push is not just about keeping pace; it's about differentiating services and attracting a digitally-savvy customer base.
- Digital Investment: Banks globally are increasing their IT budgets, with significant portions allocated to digital transformation initiatives.
- Customer Experience: Technology is a key driver in enhancing user interfaces, mobile banking capabilities, and personalized financial services.
- Core Modernization: Projects like b1BANK's core conversion are essential for agility, enabling faster product development and integration of new technologies.
- Competitive Necessity: Failure to innovate digitally can lead to market share erosion as more agile, tech-forward competitors emerge.
Competitive rivalry within the banking sector remains a significant force, intensified by a fragmented market and the rise of non-traditional players. b1BANK faces pressure from both established national institutions and agile fintech companies, necessitating strategic investments in technology and customer experience to maintain its market position.
The drive for digital transformation is a key battleground, with banks globally increasing IT spending. For instance, global banking IT spending was projected to reach $220 billion in 2024, underscoring the critical need for modernization. This investment aims to enhance operational efficiency and attract a digitally-savvy customer base.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on b1BANK |
|---|---|---|
| Regional & Community Banks | Numerous local rivals, fragmented market | Intensified competition for deposits and loans |
| Large National Banks | Vast networks, comprehensive services, perceived stability | Attract business owners, potential deposit erosion |
| Fintech & Non-Bank Lenders | Innovative digital platforms, niche services | Direct challenge for market share, disintermediation risk |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The proliferation of fintech and digital payment platforms presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional banking services. Companies like Stripe, which processed over $1 trillion in payment volume in 2023, and PayPal, with its 427 million active accounts, offer seamless alternatives for businesses and consumers alike. These platforms often provide lower transaction fees and faster settlement times than many traditional banking channels, directly challenging banks' revenue streams in payment processing.
Alternative lending platforms present a significant threat to traditional banks like b1BANK. Businesses are increasingly turning to online lenders, peer-to-peer platforms, and other non-bank financial institutions for capital, bypassing conventional banking channels. This shift is often driven by dissatisfaction with traditional bank credit policies, which can be perceived as rigid or slow.
In 2024, data suggests a growing reliance on these alternatives. For instance, the small business lending market saw substantial growth in non-bank originations. Many businesses report exploring these options due to faster approval times and more flexible underwriting criteria compared to traditional banks, indicating a clear substitute for bank loans.
Credit unions present a notable threat due to their member-owned structure, which often translates to more favorable terms for businesses and individuals. For instance, in 2024, the average credit union loan rate for small businesses was approximately 1.5% lower than the national average for commercial banks, making them an attractive alternative for cost-conscious clients.
Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFIs) also pose a competitive threat, particularly by catering to underserved markets with tailored financial products and services. These institutions are crucial for economic development in specific geographic areas, offering specialized support that traditional banks might not prioritize, thus capturing a segment of the market.
Internal Corporate Finance Solutions
For larger corporations with substantial resources, the threat of substitutes for traditional banking services in treasury management and short-term financing is significant. These businesses can leverage internal expertise and technology to handle functions like cash flow optimization and even provide intercompany loans, thereby reducing their dependence on external banking partners. The global treasury management market itself is expanding, projected to reach approximately $3.7 billion by 2026, underscoring the drive for more sophisticated in-house capabilities.
This internal capability acts as a direct substitute, particularly for routine treasury operations. For instance, a company might implement advanced ERP systems with integrated treasury modules, allowing for real-time cash visibility and automated payment processing. This reduces the need for external banks to provide these fundamental services.
- Internal treasury management systems can replicate many basic banking functions.
- The growing treasury management market suggests increased investment in in-house solutions.
- Large corporations can finance short-term needs through internal capital or intercompany lending.
- Technological advancements enable greater self-sufficiency in financial operations.
Investment Management Firms and Brokerages
Customers looking for wealth management and investment services at b1BANK face a significant threat from substitutes. Independent investment firms and brokerages offer a wide range of alternatives, often specializing in niche markets or providing highly personalized advice. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. wealth management industry saw continued growth, with independent advisors managing trillions of dollars in assets.
These substitutes can attract clients by offering competitive fee structures, access to a broader universe of investment products, or more advanced digital platforms. Many of these firms, unlike traditional banks, focus solely on investment services, allowing them to dedicate more resources to client-specific strategies. The ease with which clients can transfer their assets to these specialized providers underscores the competitive pressure on b1BANK's affiliate, Smith Shellnut Wilson, LLC.
The threat is amplified by the increasing accessibility of robo-advisors and online brokerage platforms. These digital solutions, which have seen substantial user base expansion in recent years, offer low-cost investment management and can be particularly appealing to younger or more digitally-savvy investors. By mid-2024, assets managed by robo-advisors were projected to exceed $2 trillion globally, highlighting their growing market share.
- Broad Market Reach: Independent firms and brokerages cater to diverse client needs, from high-net-worth individuals to retail investors.
- Specialized Expertise: Many substitutes offer deep expertise in specific asset classes or investment strategies not always available through a bank's affiliate.
- Technological Advancement: Digital platforms and robo-advisors provide convenient, often lower-cost alternatives for investment management.
- Client Mobility: The relatively low cost and ease of transferring investment accounts make it simple for customers to switch providers if they find better value or service elsewhere.
The threat of substitutes for traditional banking services is multifaceted, encompassing fintech innovations, alternative lending, credit unions, CDFIs, and in-house corporate capabilities. These substitutes often offer greater flexibility, lower costs, or specialized services that can draw customers away from incumbent banks.
Fintech platforms like Stripe and PayPal are rapidly gaining market share in payment processing, with Stripe alone handling over $1 trillion in payments in 2023. Alternative lenders and credit unions are also making inroads, with credit unions offering lower loan rates for small businesses, averaging 1.5% less than commercial banks in 2024.
| Substitute Type | Key Offering | 2023/2024 Data Point | Impact on Banks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech Payment Platforms | Seamless digital payments | Stripe processed over $1 trillion in payment volume (2023) | Reduced transaction fee revenue |
| Alternative Lending | Faster, flexible business loans | Growth in non-bank originations for small businesses (2024) | Loss of loan origination business |
| Credit Unions | Member-centric financial services | Average small business loan rate ~1.5% lower than banks (2024) | Attracts cost-sensitive borrowers |
| Robo-Advisors | Low-cost investment management | Global AUM projected to exceed $2 trillion (mid-2024) | Competition for wealth management clients |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants for b1BANK is significantly mitigated by high regulatory barriers and substantial capital requirements. Establishing a new bank in the U.S. involves a rigorous approval process from federal and state bodies like the FDIC and Federal Reserve, demanding significant upfront investment and compliance expertise. Despite some initiatives to streamline chartering, the pace of new bank formation has remained slow, with an average of only 10 new charters granted annually between 2010 and 2023.
The banking industry, particularly for institutions like b1BANK, is heavily reliant on established reputation and customer trust. Building this takes years, if not decades, and substantial capital investment. For instance, a 2023 survey indicated that while trust in large national banks remained relatively stable, smaller or newer institutions experienced a noticeable dip in consumer confidence, highlighting the advantage incumbents hold.
New entrants would find it incredibly difficult to immediately replicate the level of trust and brand recognition that b1BANK has cultivated. This barrier means that potential competitors cannot simply enter the market with a similar product offering; they must also overcome the significant hurdle of convincing customers to switch from a trusted, well-known provider.
New banks entering the financial sector face a significant hurdle in building a robust deposit base. Existing institutions, like established players in the US market, often leverage long-standing customer relationships and brand trust to retain and attract deposits. For instance, in early 2024, the average interest rate on savings accounts at major banks remained competitive, making it challenging for new entrants to offer significantly more attractive rates without impacting profitability.
Without a substantial deposit foundation, new entrants are compelled to rely on more expensive wholesale funding markets. This reliance can significantly increase their cost of capital, putting them at a disadvantage compared to incumbent banks with access to cheaper, stable deposit funding. In 2023, the cost of wholesale funding for smaller, newer financial institutions saw an upward trend as market liquidity tightened.
Scalability and Technology Investment
New entrants face a significant hurdle in matching the technological prowess of established banks. The cost of acquiring and implementing modern core banking software and robust digital infrastructure is substantial, estimated to run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars for comprehensive upgrades. This high capital requirement acts as a considerable barrier, especially when incumbents are consistently investing in their own digital transformation initiatives, making it difficult for newcomers to achieve parity quickly.
The ongoing digital transformation within the banking sector means that existing players are not static. They are continuously upgrading their systems, enhancing customer experience through mobile apps, and leveraging data analytics. For a new entrant, not only is the initial technology investment massive, but there's also the ongoing need to keep pace with these rapid advancements, further increasing the financial burden and risk.
- High Capital Outlay: Core banking software and digital infrastructure upgrades can cost banks upwards of $100 million, a prohibitive cost for many potential new entrants.
- Continuous Investment: Established banks regularly reinvest in technology, with many allocating 10-15% of their revenue to IT spending, creating an ever-moving target for newcomers.
- Economies of Scale: Larger, incumbent banks benefit from economies of scale in technology adoption and maintenance, which new entrants struggle to replicate initially.
Incumbent Advantage in Customer Relationships
b1BANK's deep-rooted connections with small and medium-sized businesses, entrepreneurs, and professionals, particularly within Louisiana and Texas, present a significant barrier to new entrants. These localized relationships are cultivated through personalized service and community engagement, fostering strong customer loyalty.
Dislodging these established loyalties requires new competitors to offer substantial incentives or highly differentiated services, a costly and time-consuming endeavor. For instance, in 2023, community banks like b1BANK often saw higher customer retention rates compared to larger national institutions due to their localized focus.
- Established Trust: b1BANK's long-standing presence in Louisiana and Texas has built a foundation of trust, making customers hesitant to switch.
- Personalized Service: The bank's focus on understanding the unique needs of its target demographic fosters strong, enduring relationships.
- Market Penetration Costs: New entrants would face significant marketing and operational costs to build comparable local brand recognition and customer bases.
- Customer Inertia: Many small business owners and professionals are less likely to switch banking partners unless there is a compelling, immediate benefit.
The threat of new entrants for b1BANK is low due to high regulatory hurdles and substantial capital needs, with new bank charters averaging only around 10 annually between 2010 and 2023. Building customer trust and brand recognition, which takes years, is another significant barrier, as evidenced by a 2023 survey showing consumer confidence dips for newer institutions compared to established ones. Furthermore, acquiring a substantial deposit base is challenging for newcomers, as incumbents like b1BANK leverage existing relationships and competitive savings rates, as seen in early 2024, making it difficult to attract funds without impacting profitability.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Supporting Data/Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Requirements | Rigorous approval processes from FDIC, Federal Reserve, and state bodies. | High compliance costs and lengthy setup times. | Average of 10 new bank charters granted annually (2010-2023). |
| Capital Investment | Significant upfront capital needed for operations and technology. | Prohibitive cost for many potential entrants. | Core banking software and digital infrastructure upgrades can exceed $100 million. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Established banks benefit from years of customer loyalty and proven track records. | Difficulty in attracting customers away from trusted incumbents. | 2023 surveys indicate consumer confidence lags for newer financial institutions. |
| Economies of Scale (Technology) | Incumbents leverage scale for technology adoption and maintenance. | New entrants struggle to match technological parity and cost-efficiency. | Established banks allocate 10-15% of revenue to IT spending. |
| Customer Relationships | Deep, localized relationships cultivated through personalized service. | High costs and time required to replicate established market penetration. | Community banks like b1BANK often show higher customer retention due to localized focus. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our b1BANK Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and regulatory filings from banking authorities. This comprehensive data allows for a robust assessment of industry rivalry, supplier and buyer power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.