Autobio Diagnostics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Autobio Diagnostics Bundle
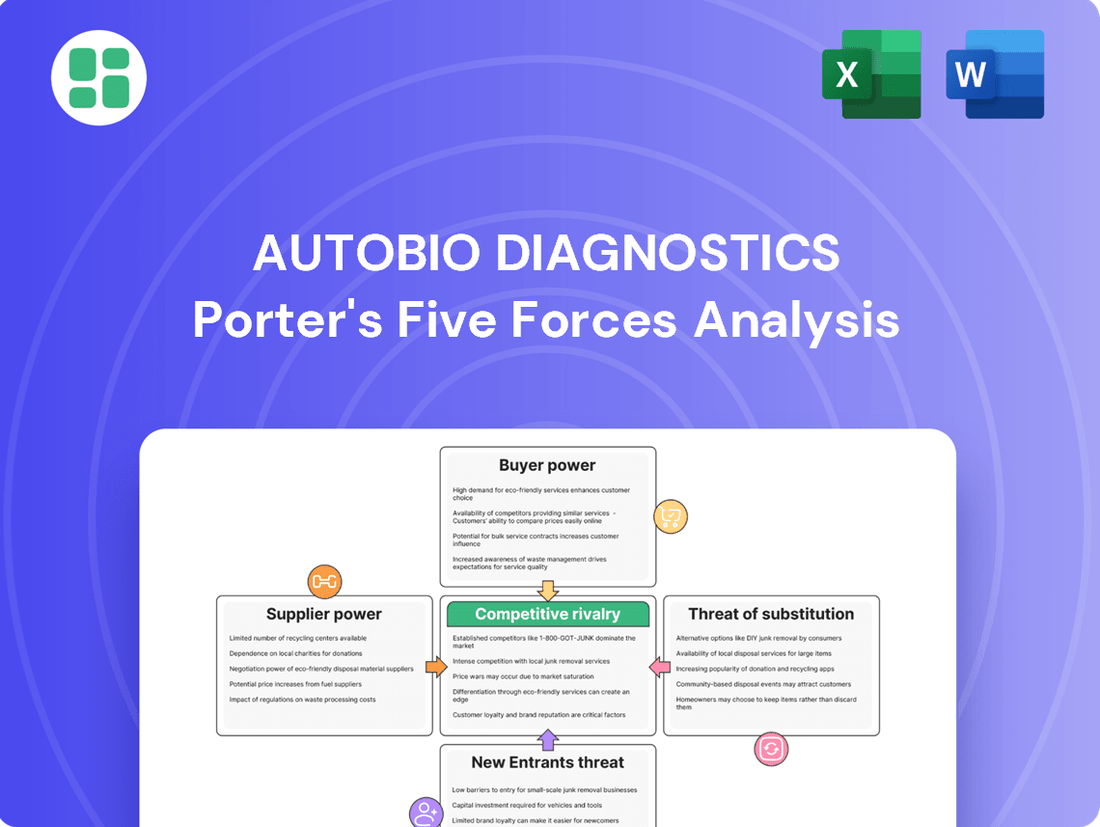
Autobio Diagnostics operates within a dynamic market, and understanding the forces shaping its competitive landscape is crucial. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats posed by new entrants and substitutes.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Autobio Diagnostics’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Autobio Diagnostics relies on a diverse range of suppliers for critical components like antibodies, enzymes, and specialized chemicals. A concentrated supplier market, where a few dominant players control the supply of essential raw materials, significantly amplifies their bargaining power. For instance, if only two or three companies globally produce a specific high-purity enzyme crucial for Autobio's diagnostic kits, those suppliers can dictate terms and pricing, potentially impacting Autobio's cost of goods sold.
Autobio Diagnostics faces moderate bargaining power from its suppliers due to the switching costs involved in changing diagnostic reagent and equipment providers. These costs can include the need for requalification of new products, recalibration of existing instruments, and potential disruptions to laboratory workflows, all of which can be time-consuming and expensive.
For instance, if Autobio needs to switch a key supplier for its immunoassay reagents, the process might require extensive validation studies to ensure the new reagents perform comparably to the old ones. This validation process can take several months and incur significant labor costs, effectively raising the barrier to switching and granting suppliers more leverage.
While specific figures for Autobio's switching costs are proprietary, industry benchmarks suggest that the initial investment in validating a new diagnostic reagent can range from tens of thousands to over a hundred thousand dollars, depending on the complexity and regulatory requirements. This financial and operational hurdle empowers suppliers who can demonstrate consistent quality and reliable delivery.
Autobio Diagnostics' suppliers hold significant bargaining power when their offerings are highly unique or differentiated. For instance, if key diagnostic reagents rely on proprietary technologies or patented chemical compounds not readily available from other sources, Autobio is more dependent on these specific suppliers.
In 2024, the market for advanced diagnostic reagents saw continued consolidation, with a few key players dominating the supply of novel assay components. This limited the pool of alternative suppliers for Autobio, particularly for specialized immunoassay kits or advanced molecular diagnostic probes, thereby increasing supplier leverage.
When suppliers provide specialized services, such as custom assay development or unique quality control protocols that are critical to Autobio's product performance, their bargaining power is amplified. The absence of readily available substitutes for these specialized services means Autobio has fewer options to switch, giving suppliers more sway in pricing and terms.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into the In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) manufacturing space poses a significant challenge to Autobio Diagnostics. If key suppliers, particularly those holding critical intellectual property or possessing advanced manufacturing capabilities, decide to produce their own diagnostic kits or platforms, they would directly compete with Autobio. This move would not only disrupt Autobio's supply chain but also empower suppliers with greater leverage in pricing and contract negotiations, as they could dictate terms or even withdraw supply to favor their own integrated operations.
Consider the scenario where a supplier of specialized reagents or assay components, which are vital for Autobio's product performance, decides to leverage their expertise and patents to enter the IVD market themselves. For instance, if a supplier of advanced nanoparticle technology, crucial for certain diagnostic assays, were to develop their own IVD products using this technology, they could potentially undercut Autobio or prioritize their internal product lines. This forward integration by suppliers is a real concern in the highly innovative IVD sector, where proprietary technology is a key differentiator.
- Supplier Capabilities: Assess if key suppliers possess the manufacturing infrastructure, technical expertise, and R&D capabilities to enter IVD production.
- Intellectual Property: Evaluate the extent to which suppliers hold patents or proprietary knowledge that could be leveraged for their own IVD product development.
- Market Incentives: Analyze the potential profitability and market share suppliers could gain by bypassing Autobio and selling directly to end-users or distributors.
- Industry Trends: Observe if there are any prevailing trends in the broader diagnostics supply chain that indicate a move towards vertical integration by component manufacturers.
Importance of Autobio Diagnostics to Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers for Autobio Diagnostics hinges on Autobio's significance as a customer. If Autobio represents a substantial revenue stream for its suppliers, their leverage in price negotiations or terms is reduced because they depend on Autobio's continued business. For instance, if Autobio accounts for over 10% of a key reagent supplier's annual sales, that supplier will likely be more accommodating.
Conversely, if Autobio is a minor client for its suppliers, the suppliers hold more power. This is particularly true for specialized components or raw materials where Autobio may have fewer alternative sourcing options. In such scenarios, suppliers can dictate terms, potentially increasing prices or limiting supply, which directly impacts Autobio's cost structure and operational continuity.
- Customer Significance: Autobio's purchase volume relative to a supplier's total sales dictates the power balance.
- Supplier Dependence: High dependence of suppliers on Autobio's orders weakens supplier bargaining power.
- Market Concentration: If few suppliers offer critical components, their power over Autobio increases.
- Switching Costs: High costs for Autobio to switch suppliers amplify supplier bargaining power.
Autobio Diagnostics faces a moderate to high bargaining power from its suppliers, particularly for specialized reagents and proprietary components. The concentration of key suppliers in the diagnostic reagent market, coupled with significant switching costs for Autobio, grants these suppliers considerable leverage. In 2024, industry trends indicated continued consolidation among reagent providers, further limiting Autobio's alternative sourcing options and increasing supplier influence over pricing and terms.
The bargaining power of Autobio's suppliers is influenced by several factors, including the uniqueness of their offerings, the switching costs incurred by Autobio, and Autobio's significance as a customer. Suppliers with patented technologies or highly specialized manufacturing capabilities can command higher prices and more favorable terms. Conversely, Autobio's ability to influence supplier behavior increases if it represents a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Autobio's Position |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Market Concentration | High | Limited alternative suppliers for critical components |
| Switching Costs | Moderate to High | Significant costs associated with requalification and workflow disruption |
| Product Differentiation | High | Reliance on proprietary reagents and patented technologies |
| Autobio's Customer Significance | Variable | Depends on Autobio's purchase volume relative to supplier's total sales |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects Autobio Diagnostics' competitive environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the diagnostics market.
Instantly grasp the competitive landscape with a visually intuitive five forces summary, enabling swift strategic adjustments to mitigate market pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Autobio Diagnostics' customer base is largely concentrated among clinical laboratories. If a few major laboratory chains or large hospital networks represent a disproportionately large share of Autobio's revenue, these entities wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial purchase volumes.
For instance, in 2023, while specific customer concentration data for Autobio Diagnostics isn't publicly detailed, the broader in-vitro diagnostics market often sees key accounts contributing 10-20% of a supplier's total sales. A more fragmented customer base, with many smaller labs, would inherently dilute this individual customer leverage.
Switching from Autobio Diagnostics' products to a competitor can involve significant costs for customers. These can include the expense and time required for retraining laboratory staff on new equipment and software, as well as the critical process of revalidating instruments to ensure accuracy and compliance with regulatory standards. For instance, a hospital laboratory might face costs upwards of $50,000 to $100,000 per instrument for revalidation and retraining when changing diagnostic platforms.
High switching costs effectively reduce the bargaining power of customers. When it's costly and time-consuming to switch, customers are less likely to pressure Autobio for lower prices or better terms, as the effort involved in changing providers outweighs the potential benefits. This inertia benefits Autobio by retaining its customer base, even if competitors offer slightly more attractive pricing.
Conversely, if switching costs were low, customers would have greater leverage. They could more easily demand concessions, such as discounts or enhanced service agreements, by threatening to move to a competitor. The current landscape for diagnostic equipment, often characterized by integrated systems and specialized training, generally presents moderate to high switching costs for Autobio's clientele.
Customers of Autobio Diagnostics likely possess a moderate to high level of information regarding product alternatives and pricing, especially given the increasing availability of online resources and comparative reviews in the healthcare technology sector. This awareness can significantly impact pricing negotiations.
The price sensitivity of Autobio's customers, which include hospitals, clinics, and research institutions, can vary. Larger, centralized procurement departments may exhibit higher price sensitivity due to bulk purchasing power and budget constraints, potentially exerting more pressure on Autobio's pricing strategies.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers, such as large clinical laboratory networks or hospital groups, poses a significant challenge to Autobio Diagnostics. These entities might develop their own diagnostic tests or reagents, thereby cutting out external suppliers. This capability directly increases customer bargaining power.
The economic viability and technical feasibility of customers producing their own diagnostic solutions are key determinants of this threat. If it becomes cost-effective and technically straightforward for major labs to manufacture reagents in-house, Autobio's pricing power and market share could be negatively impacted. For instance, advancements in automated lab equipment and reagent synthesis technologies could lower the barrier to entry for such in-house production.
- Customer Integration Potential: Large hospital systems and independent diagnostic labs possess the capital and technical expertise to explore in-house reagent development.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: The decision to integrate backward hinges on whether the cost savings and control gained outweigh the investment in R&D, manufacturing, and quality assurance.
- Technological Enablers: Innovations in reagent formulation and automated production lines can reduce the complexity and cost of in-house manufacturing for customers.
- Market Dynamics: A highly competitive reagent market with slim margins can incentivize larger customers to seek cost efficiencies through vertical integration.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
The availability of substitute in-vitro diagnostic (IVD) products significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. If Autobio Diagnostics' customers, such as hospitals and clinical laboratories, can easily find alternative diagnostic solutions from competitors that offer comparable or superior performance, or even better cost-effectiveness, they gain leverage. This situation forces Autobio to be more competitive on pricing and product features to retain its market share.
For instance, the IVD market is dynamic, with numerous players offering a wide array of diagnostic tests and platforms. In 2024, the global IVD market was valued at approximately $90 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5-7% through 2030, indicating robust competition and a constant influx of new technologies and products. This competitive landscape means customers have a plethora of choices.
- High Availability of Substitutes: The IVD market is characterized by a broad range of competitors offering similar diagnostic tests for various diseases and conditions.
- Performance Parity: Many competitors can match or exceed the performance metrics of Autobio's products, reducing customer switching costs.
- Value Proposition: Customers can often find alternative solutions that offer a better overall value, considering price, accuracy, turnaround time, and support services.
- Technological Advancements: Rapid advancements in diagnostic technologies mean new and improved alternatives are frequently introduced, further empowering customers.
Autobio Diagnostics faces significant customer bargaining power, particularly from large clinical laboratories and hospital networks that represent substantial purchase volumes. These key accounts can leverage their buying power to negotiate better pricing and terms. For example, in the broader IVD market, major accounts can often account for 10-20% of a supplier's sales, giving them considerable influence.
Switching costs for customers are a key factor mitigating this power. Retraining staff and revalidating instruments can cost tens of thousands of dollars per instrument, making customers hesitant to switch providers. This inertia helps Autobio retain its client base, even when competitors offer slightly lower prices.
Customers are increasingly informed about alternatives and pricing, especially with readily available online resources. Price sensitivity varies, with larger procurement departments often exhibiting higher sensitivity due to budget constraints, which can translate into increased pressure on Autobio's pricing strategies.
The threat of backward integration, where customers develop their own diagnostic solutions, also increases their bargaining power. Advancements in automation and reagent synthesis technologies can lower the barriers for large labs to produce reagents in-house, potentially impacting Autobio's market share and pricing power.
| Factor | Impact on Autobio | Customer Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High reliance on few large labs | Moderate to High |
| Switching Costs | Significant investment in retraining/revalidation | Low to Moderate |
| Information Availability | Customers well-informed on alternatives | Moderate |
| Price Sensitivity | Varies by customer size and procurement structure | Moderate |
| Backward Integration Threat | Potential for customers to produce own reagents | Moderate to High |
What You See Is What You Get
Autobio Diagnostics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Autobio Diagnostics, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the in-vitro diagnostics market. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, providing actionable insights without any hidden alterations or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The in vitro diagnostics (IVD) market is a competitive landscape. Autobio Diagnostics faces significant rivalry from a substantial number of global players across immunoassay, microbiology, biochemistry, and molecular diagnostics. For instance, in 2024, the global IVD market was valued at approximately $100 billion, with key players like Roche Diagnostics, Abbott Laboratories, Siemens Healthineers, and Danaher Corporation holding substantial market shares.
While these large corporations dominate, the market also features a multitude of smaller, specialized companies. These firms often focus on niche areas or innovative technologies, adding another layer of competition. This dynamic means Autobio must contend with both broad-spectrum competitors and highly focused specialists, driving continuous innovation and price pressure.
The in-vitro diagnostics (IVD) market is indeed experiencing strong growth, projected to reach approximately $100 billion globally by 2024. This expansion, fueled by increasing demand for early disease detection and personalized medicine, creates an attractive landscape for competitors.
However, this very growth, coupled with rapid technological innovation and a crowded marketplace, intensifies competitive rivalry. Companies are constantly vying for market share, pushing for new product development and market penetration.
While a high growth rate can sometimes temper rivalry, in the IVD sector, the pace of innovation and the broad appeal of the market mean that even with expansion, companies must aggressively compete to capture and maintain their position.
Autobio Diagnostics differentiates its products through continuous innovation, particularly in areas like chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) systems and reagents. This focus on advanced technology and performance aims to set its offerings apart in a crowded in-vitro diagnostics (IVD) market. For instance, in 2023, Autobio continued to expand its CLIA menu, adding new assays that address unmet clinical needs.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers in the in-vitro diagnostics (IVD) market can significantly prolong competitive rivalry. High asset specificity, where specialized equipment and facilities are difficult to repurpose, acts as a major deterrent to exiting. For instance, companies heavily invested in specific immunoassay platforms or molecular diagnostic machinery face substantial losses if they attempt to divest these assets.
Emotional and strategic attachments also play a role; founders or long-term management may have deep commitments to their existing product lines or market positions. Furthermore, regulatory obligations, such as maintaining product registrations and quality certifications, create ongoing costs and complexities that discourage a swift exit, even if a segment is underperforming.
These factors contribute to a situation where competitors may continue to operate and compete aggressively, even in mature or declining IVD market segments. This sustained rivalry can suppress profitability for all players involved.
- High Asset Specificity: IVD companies often invest in highly specialized manufacturing equipment and R&D facilities tailored to specific diagnostic technologies, making them difficult to sell or redeploy.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Maintaining product approvals and compliance with bodies like the FDA or EMA requires ongoing investment and effort, discouraging companies from simply ceasing operations.
- Strategic Commitments: Established market presence and brand loyalty in certain IVD areas can create a reluctance to abandon these positions, even when facing intense competition.
- Potential for Prolonged Rivalry: In 2024, the IVD market, particularly in areas like infectious disease testing post-pandemic, still sees players maintaining operations due to these barriers, leading to price pressures and slower growth in some sub-segments.
Strategic Stakes
The in-vitro diagnostics (IVD) market holds immense strategic importance for major global healthcare players. For large multinational corporations, defending and expanding their share within the IVD sector is often a cornerstone of their overall healthcare business strategy. This criticality fuels aggressive competitive tactics as companies vie for dominance.
The IVD market’s strategic value is underscored by its consistent growth. For instance, the global IVD market was valued at approximately $90 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $130 billion by 2029, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6.5%. This robust expansion makes it a highly attractive segment for investment and a battleground for market share.
- Market Share Defense: Companies like Roche Diagnostics, Abbott Laboratories, and Siemens Healthineers invest heavily in R&D and marketing to protect their existing market positions in key diagnostic areas.
- Portfolio Synergy: IVD revenues often complement sales of pharmaceuticals and other medical devices, creating a synergistic effect that enhances the value of a company's broader healthcare offerings.
- Technological Advancement: The rapid pace of innovation in areas like molecular diagnostics and liquid biopsy intensifies competition, as early movers gain significant advantages.
Autobio Diagnostics operates in a fiercely competitive in-vitro diagnostics (IVD) market. The presence of numerous global players, including giants like Roche Diagnostics and Abbott Laboratories, alongside specialized niche companies, intensifies rivalry. This dynamic, driven by rapid technological advancements and a growing market, forces companies to continuously innovate and maintain competitive pricing.
The sheer number of competitors, coupled with high exit barriers such as specialized assets and regulatory requirements, ensures that rivalry remains a persistent challenge. Even with market growth, companies must aggressively compete for share, leading to price pressures and a constant need for differentiation.
In 2024, the global IVD market, valued around $100 billion, showcases this intense competition. Autobio's strategy of focusing on areas like chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) systems and expanding its assay menu is a direct response to this challenging environment.
The strategic importance of the IVD sector for major healthcare corporations further fuels this rivalry. Companies invest heavily to protect their market share and leverage portfolio synergies, making it imperative for players like Autobio to maintain a strong competitive edge through innovation and product development.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The price-performance trade-off of substitutes presents a significant threat to Autobio Diagnostics. While not direct in-vitro diagnostic (IVD) products, alternative diagnostic methods can fulfill similar patient needs. For instance, medical imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans, though often more expensive upfront, offer comprehensive anatomical insights that certain IVD tests might not provide. In 2024, the global medical imaging market was valued at approximately $100 billion, indicating substantial investment and patient reliance on these modalities.
Emerging AI-driven diagnostic tools also represent a growing substitute threat. These technologies, by analyzing vast datasets and identifying patterns invisible to the human eye, can potentially offer faster and more accurate diagnoses for certain conditions, sometimes at a lower long-term cost than traditional lab-based testing. The investment in AI in healthcare diagnostics saw a significant surge in 2024, with venture capital funding reaching record highs, signaling rapid innovation and adoption.
The threat of substitutes for Autobio Diagnostics' products is significant, primarily from alternative diagnostic methods and technologies. The increasing availability and accessibility of these substitutes directly impact Autobio's market position. For instance, the global point-of-care diagnostics market was valued at approximately USD 30 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong shift towards more immediate and accessible testing solutions that can bypass traditional laboratory settings.
Furthermore, the proliferation of home-based diagnostic kits, covering areas like infectious diseases and chronic condition monitoring, presents a direct substitute for many of Autobio's laboratory-based offerings. This trend is fueled by technological advancements and a consumer desire for convenience and self-management of health. The accessibility of these kits through online platforms and pharmacies means that patients can often bypass clinical laboratories altogether for certain diagnostic needs.
The willingness of clinical labs and hospitals to switch to alternative diagnostic methods is a key factor. For Autobio Diagnostics, this means considering how easily new technologies can be integrated into existing workflows and whether they have received necessary regulatory approvals, like FDA clearance in the US.
Perceived clinical utility also plays a significant role. If substitute technologies offer comparable or superior diagnostic accuracy, faster turnaround times, or lower costs without compromising patient care, adoption rates will increase. For instance, advancements in point-of-care testing (POCT) present a potential substitute threat to traditional laboratory-based diagnostics, offering quicker results directly at the patient's bedside.
In 2024, the global POCT market was valued at approximately USD 35 billion and is projected to grow, indicating a strong customer interest in more accessible and immediate diagnostic solutions, which could impact Autobio's market share if its offerings are not competitive in this evolving landscape.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
The pace of technological advancement in substitute fields is a significant concern for Autobio Diagnostics. Rapid innovation in areas like non-invasive diagnostics and advanced imaging techniques constantly presents new alternatives that could potentially bypass the need for Autobio's current product offerings. For instance, the increasing sophistication of wearable health trackers and AI-powered symptom checkers could offer consumers preliminary diagnostic insights, reducing reliance on traditional laboratory tests.
This evolving landscape means that the threat of substitution isn't static; it's a dynamic force driven by ongoing research and development. As these technologies mature and become more accessible, they could erode Autobio's market share. Consider the growth in the telehealth sector, which often integrates with these emerging diagnostic tools, further amplifying the substitution threat by providing a convenient delivery mechanism for alternative health assessments.
The potential for these substitutes to offer comparable or even superior convenience and cost-effectiveness is a key driver of this threat.
- Advancements in Non-Invasive Diagnostics: Technologies like liquid biopsies and advanced genetic sequencing are becoming more precise and accessible, offering alternatives to traditional blood tests.
- Growth in AI-Powered Health Monitoring: Wearable devices and smartphone apps are increasingly capable of detecting health anomalies, potentially reducing the need for early-stage diagnostic lab work.
- Telehealth Integration: The rise of telehealth platforms often incorporates these new diagnostic methods, creating a more seamless and convenient substitute pathway for patients.
- Imaging Technology Improvements: Enhanced MRI, CT scan, and ultrasound technologies provide more detailed insights, sometimes negating the need for certain laboratory analyses.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Environment for Substitutes
The regulatory landscape significantly influences the viability of substitute diagnostic methods. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance process for new diagnostic tests can be lengthy and costly, potentially delaying market entry for innovative substitutes. In 2024, the FDA continued to streamline pathways for certain in vitro diagnostics, but the burden remains substantial for novel technologies.
Reimbursement policies set by payers like Medicare and private insurers are equally critical. Favorable reimbursement rates can significantly boost the adoption of substitute diagnostic tools by making them economically attractive to healthcare providers and patients. Conversely, restrictive or low reimbursement can stifle market penetration, even for superior diagnostic alternatives.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Stringent approval processes, like those managed by the FDA, can slow the introduction of substitute diagnostic technologies.
- Reimbursement Impact: Payment policies from Medicare and private insurers directly affect the economic feasibility and uptake of alternative diagnostic methods.
- Market Penetration: Favorable regulatory pathways and reimbursement support accelerate the adoption of new diagnostic substitutes, while unfavorable conditions hinder it.
The threat of substitutes for Autobio Diagnostics is substantial, stemming from alternative diagnostic approaches and emerging technologies. These substitutes can fulfill similar patient needs, often with greater convenience or different cost structures. For instance, medical imaging continues to offer comprehensive anatomical insights, with the global medical imaging market valued at approximately $100 billion in 2024.
AI-driven diagnostics and point-of-care testing (POCT) are also significant substitutes, offering faster results and increased accessibility. The global POCT market was valued at around $35 billion in 2024, highlighting a strong demand for immediate diagnostic solutions. Furthermore, home-based diagnostic kits are increasingly bypassing traditional lab settings, driven by consumer demand for self-management and convenience.
The ease with which clinical labs and hospitals can adopt these substitutes, coupled with their perceived clinical utility and cost-effectiveness, directly impacts Autobio's market position. Rapid advancements in non-invasive diagnostics and wearable health monitoring further amplify this threat, presenting dynamic alternatives that could erode market share.
| Substitute Category | Key Technologies | 2024 Market Value (Approx.) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Imaging | MRI, CT Scans, Ultrasound | $100 billion | Comprehensive anatomical insights |
| AI-Driven Diagnostics | Pattern Recognition, Data Analysis | Significant VC investment surge | Speed, accuracy, potential cost savings |
| Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) | Rapid tests, Biosensors | $35 billion | Convenience, immediate results |
| Home-Based Diagnostics | Infectious disease kits, Chronic monitoring | Growing market segment | Consumer convenience, self-management |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the in-vitro diagnostics (IVD) market demands a substantial financial commitment. Developing novel diagnostic tests and platforms requires significant investment in research and development, often running into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars for cutting-edge technologies. For instance, establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities compliant with stringent regulatory standards like FDA and CE marking can easily cost upwards of $50 million.
Furthermore, the need for sophisticated laboratory equipment, automated testing systems, and specialized software adds another layer of considerable capital expenditure. Companies like Roche Diagnostics and Abbott Laboratories, leaders in the IVD space, have invested billions over the years to build and maintain their extensive product portfolios and global manufacturing footprints. This high barrier to entry, driven by the sheer scale of financial resources needed for R&D, production, and regulatory compliance, effectively deters many potential new competitors.
The in-vitro diagnostics (IVD) industry faces significant barriers to entry due to rigorous regulatory frameworks. Navigating approvals like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for medical devices or obtaining CE marking and adhering to the In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) in Europe demands substantial investment in time and resources.
These complex compliance processes, including extensive clinical validation and quality management systems, naturally favor established companies with proven track records and dedicated regulatory affairs departments. For instance, the cost of bringing a new IVD to market can easily run into millions of dollars, a significant deterrent for smaller, less capitalized entrants.
New companies entering the in-vitro diagnostics (IVD) market face significant hurdles in securing access to critical distribution channels. Established players, including Autobio Diagnostics, have spent years building strong relationships with clinical laboratories, hospitals, and other healthcare providers, creating robust supply chains that are difficult for newcomers to replicate. For instance, in 2024, the global IVD market, valued at over $100 billion, is heavily influenced by these entrenched distribution networks, where brand loyalty and proven reliability are paramount.
Gaining shelf space or preferred supplier status within these established networks is a substantial barrier. New entrants often struggle to demonstrate the same level of consistent quality, regulatory compliance, and logistical efficiency that existing companies offer. This difficulty in accessing and navigating these channels means that even innovative diagnostic solutions may struggle to reach their target customers, impacting market penetration and revenue generation for potential new competitors.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Autobio Diagnostics faces a significant threat from new entrants due to the substantial cost advantages enjoyed by established players. These incumbents benefit from economies of scale in areas like manufacturing, where higher production volumes lead to lower per-unit costs. For instance, in 2024, major diagnostic equipment manufacturers often operate plants with capacities exceeding 100,000 units annually, allowing them to spread fixed costs over a larger output. This scale also extends to research and development (R&D) and marketing efforts, where larger companies can invest more heavily, building brand recognition and customer loyalty that new entrants struggle to match.
The experience curve further solidifies the position of existing firms. As companies produce more over time, they learn to optimize processes, reduce waste, and improve efficiency, leading to lower costs. This accumulated knowledge, often referred to as learning-by-doing, can be a formidable barrier. New entrants must invest heavily to reach a similar level of operational efficiency, often taking years to overcome this initial cost disadvantage.
- Economies of Scale: Established players in the diagnostics market, like Roche Diagnostics and Abbott Laboratories, leverage massive production volumes to drive down per-unit costs for reagents and equipment.
- R&D Investment: In 2024, leading diagnostic companies allocated billions to R&D, creating a high bar for new entrants needing to match innovation and product development cycles.
- Marketing and Distribution: Incumbents possess established sales forces and distribution networks, built over decades, which new entrants must replicate at considerable expense.
- Experience Curve Benefits: Years of operational refinement allow established firms to achieve higher yields and lower manufacturing overheads compared to nascent competitors.
Proprietary Product Differences and Brand Identity
Autobio Diagnostics, like many established players in the in-vitro diagnostics (IVD) sector, benefits from a significant moat created by proprietary product differences and a strong brand identity. The company has invested heavily in research and development, leading to patented technologies that offer unique diagnostic capabilities. For instance, their advanced immunoassay platforms and specific biomarker detection kits are protected by patents, making it difficult for newcomers to replicate their performance or offer equivalent solutions without infringing on intellectual property. This technological differentiation is a key barrier.
Existing players, including Autobio Diagnostics, have cultivated strong brand recognition and customer loyalty over years of reliable performance and service. In the IVD market, trust and consistency are paramount, as diagnostic accuracy directly impacts patient care and treatment decisions. Autobio's established reputation for quality and accuracy means that healthcare providers are often hesitant to switch to unproven new entrants, even if they offer lower prices. This loyalty, built on a track record of performance, presents a substantial hurdle for new companies seeking market acceptance.
The challenge for new entrants is amplified by the need to not only match but also surpass the performance and reliability of established brands like Autobio Diagnostics. This requires substantial upfront investment in R&D, manufacturing, and regulatory approvals, alongside a significant marketing effort to build brand awareness and trust. For example, the IVD market in 2024 is characterized by intense competition, with companies like Roche Diagnostics and Abbott Laboratories holding significant market share, further solidifying the advantages of established players with differentiated offerings.
- Patented Technologies: Autobio Diagnostics holds patents on key immunoassay and molecular diagnostic technologies, creating unique product features that are difficult to replicate.
- Brand Recognition and Loyalty: Years of consistent performance and quality have fostered strong brand loyalty among healthcare providers, making them reluctant to adopt solutions from new, unproven entrants.
- Differentiation Hurdle: New companies must invest heavily to differentiate their products and build trust, facing the challenge of overcoming the established reputations and technological advantages of firms like Autobio.
- Market Acceptance: The IVD sector's emphasis on accuracy and reliability means that new entrants face a rigorous vetting process, with established players like Autobio having a significant head start in gaining market acceptance.
The threat of new entrants for Autobio Diagnostics is moderate. While the in-vitro diagnostics (IVD) market requires substantial capital for R&D and regulatory compliance, new companies can still emerge, especially with advancements in technology and niche market focus.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Autobio Diagnostics Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from annual reports, industry-specific market research, and regulatory filings to capture the competitive landscape accurately.
We leverage a comprehensive mix of primary and secondary data, including financial statements, analyst reports, and government databases, to meticulously evaluate supplier power, buyer bargaining, and the threat of new entrants.