Arteria Networks Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Arteria Networks Bundle
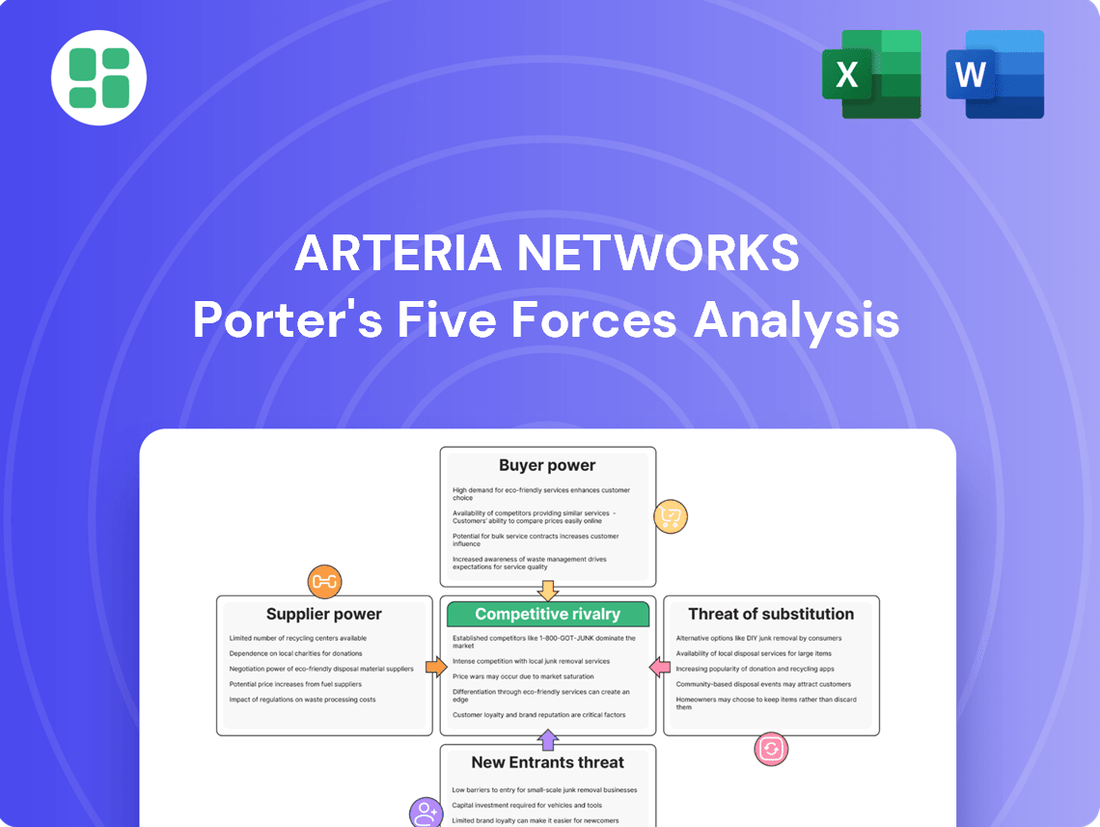
Arteria Networks operates within a dynamic landscape shaped by intense competition and evolving market demands. Understanding the underlying forces at play is crucial for navigating this environment effectively. Our analysis delves into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Arteria Networks’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The telecommunications sector, including companies like Arteria Networks, faces a significant challenge due to the limited number of specialized manufacturers for essential components like high-capacity fiber optic cables and core network equipment. This scarcity means these suppliers hold considerable sway, potentially driving up costs for Arteria, particularly for cutting-edge or proprietary technologies. For instance, in 2023, the global optical fiber cable market was dominated by a few key players, with Corning and Prysmian Group holding substantial market shares, underscoring this concentration.
Arteria Networks' dependence on these specific vendors for critical infrastructure components inherently weakens its negotiation position. This reliance can translate into less favorable pricing and terms, impacting the company's operational expenses and profitability. The limited alternatives available for procuring such specialized equipment mean that suppliers can often dictate terms, making it difficult for Arteria to secure competitive pricing or flexible contract arrangements.
Suppliers offering highly specialized technology, such as advanced fiber optic components or proprietary network management software, can wield significant bargaining power. This power is amplified when Arteria Networks incurs substantial costs and time to integrate these solutions, making switching to a different vendor a complex and expensive undertaking. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for businesses to migrate critical IT infrastructure, which includes network hardware, often ranges from tens of thousands to millions of dollars, depending on scale and complexity.
The demand for highly skilled telecommunications engineers, network architects, and data center specialists remains robust, fueled by the ongoing rollout of 5G networks and the expansion of AI-driven infrastructure. This intense demand directly translates into increased bargaining power for these professionals.
A significant shortage of these specialized talents can lead to higher labor costs and increased recruitment expenses for companies like Arteria Networks. These skilled individuals, in essence, act as critical 'suppliers' of expertise, giving them considerable leverage in the employment market.
In 2024, the average salary for a senior network engineer in the US, for example, saw an approximate 7% increase compared to the previous year, reflecting this tight labor market. This upward pressure on wages underscores the substantial bargaining power held by skilled technicians and engineers in the telecommunications sector.
Access to Real Estate and Infrastructure for Network Expansion
For Arteria Networks, which relies heavily on physical real estate and infrastructure for its network expansion, the bargaining power of property owners and utility companies is a critical factor. Access to data center locations and rights-of-way for fiber optic cables can be constrained, directly impacting expansion capabilities and costs.
The limited availability and escalating costs of suitable land, building space, and access to existing utility conduits can significantly inflate Arteria Networks' operational and expansion expenses. Securing advantageous agreements with these essential suppliers is therefore paramount to managing capital expenditure and maintaining competitive pricing.
- Limited Site Availability: In 2024, the demand for prime data center locations and strategically positioned fiber routes remained high, particularly in urban and high-growth areas, potentially increasing leasing and acquisition costs for Arteria Networks.
- Infrastructure Access Fees: Utility providers often charge substantial fees for access to existing conduits or poles, which can represent a significant portion of the upfront cost for new fiber deployments.
- Negotiating Leverage: When few alternative sites or conduit access points exist, suppliers gain considerable leverage, enabling them to dictate terms and pricing, thereby affecting Arteria Networks' profitability.
Dependence on Energy Providers for Data Center Operations
Data centers, like those operated by Arteria Networks, are incredibly reliant on a consistent and cost-effective power supply. This makes energy providers a significant factor in their operational success.
In areas where there are few power utility companies or where energy prices are volatile, these suppliers can hold substantial leverage over Arteria Networks. This is because reliable electricity is not just a convenience; it's a fundamental necessity for keeping servers running and data flowing.
The growing demand for power, particularly with the rise of AI and its computational needs, is only intensifying the bargaining power of energy suppliers. This trend directly impacts Arteria Networks' operational costs, as seen in the broader industry where data center electricity expenses are a major component of their overall budget.
- Energy Intensity: Data centers consume vast amounts of electricity, often ranking among the largest industrial energy users.
- Supplier Concentration: In certain geographic regions, the market for electricity supply might be dominated by a limited number of utility companies.
- Price Volatility: Fluctuations in energy markets, driven by factors like fuel costs and geopolitical events, can directly affect the cost of power for data centers.
- AI's Power Demand: The computational demands of artificial intelligence are projected to significantly increase data center energy consumption in the coming years, potentially giving power providers more leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Arteria Networks is substantial, primarily due to the specialized nature of telecommunications equipment and the limited number of manufacturers. This concentration allows suppliers of essential components like fiber optic cables and core network hardware to dictate terms and influence pricing, directly impacting Arteria's operational costs.
Furthermore, the high switching costs associated with integrating proprietary technologies and the scarcity of specialized talent in areas like network engineering amplify supplier leverage. Property owners and utility companies also hold significant power, especially concerning access to data center locations and rights-of-way for fiber deployment, as limited availability drives up costs and restricts Arteria's expansion options.
Energy providers represent another critical supplier group with considerable bargaining power, particularly given the high energy consumption of data centers and the increasing demand from AI infrastructure. In regions with concentrated energy markets or volatile prices, Arteria Networks faces heightened exposure to rising electricity costs, impacting overall profitability.
| Supplier Type | Key Dependencies | Impact on Arteria Networks | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Component Manufacturers | Fiber optic cables, core network equipment | Higher input costs, less favorable pricing | Dominance by few players (e.g., Corning, Prysmian) continues, with specialized tech commanding premiums. |
| Specialized Talent | Network engineers, architects | Increased labor costs, recruitment challenges | Salaries for senior network engineers saw ~7% increase in the US in 2024, reflecting high demand. |
| Real Estate/Infrastructure | Data center sites, rights-of-way | Elevated leasing/acquisition costs, expansion constraints | Demand for prime data center locations remains high, increasing costs for Arteria. |
| Energy Providers | Electricity supply | Volatile operational expenses, potential cost pass-throughs | AI's growing power demand is expected to increase data center energy consumption significantly. |
What is included in the product
Arteria Networks' Porter's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its industry, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the overall competitive rivalry.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each Porter's Five Forces element.
Customers Bargaining Power
In Japan's telecommunications landscape, residential and business customers enjoy a wide array of internet service provider choices. This includes not only established incumbent telecom operators but also a growing number of alternative fiber providers. This extensive availability empowers customers to readily compare pricing and service offerings, directly influencing Arteria Networks' pricing power.
The Japanese telecom market is a highly competitive arena, featuring several key players vying for market share. For instance, in 2023, NTT Docomo, KDDI, and SoftBank collectively held a significant portion of the mobile market, indicating a concentrated but competitive environment that extends to broadband services. This intense competition inherently grants customers a considerable degree of choice, allowing them to switch providers if they find better value elsewhere, thus increasing customer bargaining power against Arteria Networks.
For residential clients and many small to medium-sized businesses, the effort and expense involved in switching internet providers are often minimal, particularly when attractive introductory offers are available. This ease of transition significantly amplifies customer bargaining power, pressuring Arteria Networks to maintain competitive pricing and appealing service bundles to secure customer loyalty.
The telecommunications market is characterized by a wide array of tariff plans and providers, offering consumers ample choice and further bolstering their ability to negotiate or switch. For instance, in 2024, the average monthly cost for broadband services in many developed nations remained competitive, with providers frequently offering discounts to attract new subscribers, a trend that directly impacts Arteria Networks' pricing strategies.
Large enterprise clients and data center operators represent a significant customer segment for Arteria Networks, often requiring substantial volumes of connectivity and data center services. This high demand translates into strategic importance, granting these clients considerable bargaining power. For instance, in 2023, data center services revenue for companies in the telecommunications sector saw a notable increase, reflecting the growing reliance on these infrastructure providers by large businesses.
These major customers can leverage their purchasing volume to negotiate highly customized service level agreements (SLAs), secure preferential pricing structures, and demand bespoke solutions tailored to their specific operational needs. Arteria's involvement in major international submarine cable projects, such as the AUG East and JAKO cables, underscores its commitment to serving these demanding clients with high-capacity, low-latency connectivity, further solidifying the clients' influence in negotiations.
Customer Sophistication and Access to Information
Arteria Networks' financially-literate customer base, including individual investors and business strategists, possesses a high degree of market awareness. This sophistication means they are keenly aware of prevailing market prices for network services, understand emerging technological capabilities, and can readily compare Arteria's offerings against those of its competitors. Consequently, these customers are empowered to negotiate for better terms and demand greater value, putting pressure on Arteria to consistently deliver exceptional performance and reliability.
The increased transparency in the telecommunications sector, fueled by readily available data and industry analysis, further amplifies customer bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of enterprise IT decision-makers reported using third-party benchmarking reports to evaluate vendor pricing and service level agreements, with over 60% indicating this practice influenced their purchasing decisions.
- Informed Negotiation: Customers leverage detailed market intelligence to negotiate pricing and service terms.
- Value Expectation: High customer sophistication drives demand for superior performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Access to competitor data allows customers to identify and demand better value propositions.
- Influence on Pricing: Well-informed customers can exert downward pressure on prices by readily switching providers if value expectations are not met.
Demand for Value-Added Services Beyond Basic Connectivity
Customers are increasingly looking for more than just basic internet access from providers like Arteria Networks. They want integrated solutions that include things like managed IT support, robust cybersecurity, and seamless cloud services. This shift means customers have more leverage because they can choose providers who offer these bundled, value-added packages.
The demand for these advanced services directly impacts Arteria Networks, compelling them to expand their offerings and invest in new capabilities. This trend is a significant factor across the telecommunications sector, with many companies now focusing on providing managed cybersecurity and cloud consumption services to meet evolving customer needs.
- Demand for Integrated Solutions: Customers are moving beyond simple connectivity to seek comprehensive IT solutions.
- Increased Customer Leverage: The desire for bundled services empowers customers to negotiate better terms or switch providers.
- Industry Trend: Telecoms are increasingly offering managed cybersecurity and cloud services to retain and attract customers.
The bargaining power of customers in Japan's telecommunications market is substantial, driven by a highly competitive landscape and a wide array of service providers. This environment allows customers, from individual consumers to large enterprises, to readily compare offerings and switch providers, putting pressure on Arteria Networks to maintain competitive pricing and superior service quality. For instance, in 2024, the average monthly cost for broadband in many developed nations remained competitive, with frequent discounts offered to new subscribers.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Arteria Networks |
|---|---|---|
| Residential & SMBs | Low switching costs, attractive introductory offers, wide provider choice | Downward pressure on pricing, need for value-added bundles |
| Large Enterprises & Data Centers | High volume purchasing, need for customized SLAs, strategic importance | Negotiation of preferential pricing, bespoke solutions, and stringent SLAs |
| Financially-Literate Customers | High market awareness, understanding of emerging tech, competitor benchmarking | Demand for exceptional performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness |
Preview Before You Purchase
Arteria Networks Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases Arteria Networks' comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase. You can trust that this preview accurately represents the complete, ready-to-use report, providing valuable strategic insights without any hidden surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Japanese telecommunications landscape is fiercely contested, with giants like NTT Docomo, KDDI, and SoftBank holding substantial market share. These established carriers, alongside other prominent internet service providers such as Internet Initiative Japan, create an environment of intense rivalry.
Arteria Networks faces formidable competition from these incumbents due to their vast existing infrastructure, extensive customer relationships, and deep financial reserves. Their ability to engage in aggressive marketing campaigns and price competition directly impacts Arteria's market position and growth potential.
While Arteria Networks focuses on fiber-optic solutions for buildings and businesses, the fundamental high-speed internet and data center services offered by competitors often present a similar profile. This similarity can intensify competition, particularly on price, potentially squeezing profit margins for all players in the market.
The telecommunications sector, as of early 2024, continues to see providers vying for market share with comparable core connectivity offerings. For instance, major broadband providers reported average revenue per user (ARPU) figures that reflect intense competition, with many struggling to significantly increase prices without risking customer churn.
To counter this, Arteria Networks needs to highlight its unique selling propositions, such as its proprietary fiber backbone, optimized low-latency network routes, and the ability to deliver highly customized connectivity solutions. These differentiators are crucial for moving beyond commoditized service offerings and commanding premium pricing.
Competitors are aggressively investing in their 5G and fiber optic networks, offering consumers and businesses more advanced and widespread connectivity. This ongoing build-out means Arteria Networks faces a constant need to upgrade and expand its own infrastructure to keep pace. For instance, in Japan, a key market, telecom operators are accelerating 5G rollout, with major players like NTT Docomo and KDDI significantly boosting their capital expenditures in this area throughout 2024 and into early 2025. This intense competition necessitates substantial and continuous investment from Arteria to maintain its market position and service capabilities.
Market Growth Rate and Impact on Intensity of Rivalry
The telecommunications and data center sectors in Japan are exhibiting consistent expansion, fueled by escalating data usage, the ongoing deployment of 5G technology, and a growing appetite for cloud-based services. This growth environment, while generally beneficial, doesn't eliminate competitive pressures.
While market expansion can theoretically dampen rivalry by offering ample opportunities for all participants, the reality is that fierce competition for market share within specialized areas, such as premium residential fiber optic connections or tailored enterprise solutions, can still provoke aggressive strategic maneuvers from industry players.
The fiber optics market, a key segment within telecommunications, is particularly noteworthy for its strong growth trend. For example, the Japanese government has been actively promoting fiber optic network expansion, with penetration rates continuing to climb. In 2023, fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) subscriptions in Japan surpassed 30 million, indicating a dynamic and competitive landscape.
- Sustained Market Growth: Japan's telecom and data center markets are expanding due to increased data consumption and 5G adoption.
- Segmented Rivalry: Despite overall growth, intense competition exists for market share in specific niches like high-speed residential fiber.
- Fiber Optics Momentum: The fiber optics market shows a robust growth trajectory, with FTTH subscriptions exceeding 30 million in 2023.
Strategic Partnerships and Mergers & Acquisitions Among Competitors
Competitors in the telecommunications infrastructure sector are actively pursuing strategic partnerships and mergers and acquisitions (M&A) to bolster their market positions. These moves aim to broaden geographical reach, integrate cutting-edge technologies, and consolidate market share, thereby intensifying rivalry.
Arteria Networks itself has strategically partnered with AT TOKYO, enhancing its data center interconnection capabilities. Such collaborative efforts among industry players can aggregate their strengths, leading to the formation of more robust and formidable competitive entities. This dynamic necessitates Arteria's continuous evaluation and adaptation of its own strategic alliances to maintain a competitive edge.
- Increased Consolidation: M&A activity in the broader telecom infrastructure space saw significant investment in 2024, with deals focused on expanding fiber networks and 5G capabilities. For instance, a major European telecom operator completed a significant acquisition in early 2024 to bolster its fiber footprint by 20%.
- Technology Acquisition: Partnerships are often driven by the need to acquire or integrate new technologies, such as advanced networking solutions or cybersecurity platforms. Companies are investing heavily in R&D, with a notable increase in venture capital funding for innovative telecom tech startups throughout 2024.
- Enhanced Market Reach: Collaborations allow companies to tap into new markets and customer segments more efficiently than organic growth alone.
- Competitive Response: Arteria must remain agile, as these strategic realignments by rivals can quickly alter the competitive landscape, demanding proactive adjustments to its partnership and acquisition strategies.
Arteria Networks operates in a highly competitive Japanese telecommunications market, facing intense rivalry from established giants like NTT Docomo, KDDI, and SoftBank. These incumbents possess significant advantages in infrastructure, customer base, and financial resources, enabling aggressive pricing and marketing strategies that directly challenge Arteria's market position.
The similarity in core high-speed internet and data center services offered by competitors, even those outside Arteria's specific fiber-to-building focus, intensifies price-based competition, potentially impacting profit margins across the sector. As of early 2024, many broadband providers struggled to raise average revenue per user (ARPU) without risking customer loss, underscoring this competitive pressure.
Competitors are actively upgrading their 5G and fiber optic networks, necessitating continuous investment from Arteria to remain competitive. For example, Japanese telecom operators significantly increased capital expenditures on 5G rollouts throughout 2024 and into early 2025, a trend Arteria must match to maintain its service capabilities.
Strategic moves like mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships are common, as companies aim to expand their reach and integrate new technologies. This consolidation trend, with significant investment in fiber and 5G infrastructure occurring in 2024, requires Arteria to be agile and adapt its own strategic alliances to stay ahead.
| Competitor | Key Strengths | Competitive Action (2024-2025 Focus) |
|---|---|---|
| NTT Docomo | Vast infrastructure, large customer base, strong brand loyalty | Accelerated 5G network expansion, fiber optic upgrades |
| KDDI | Integrated services (mobile, broadband, finance), extensive retail presence | Increased 5G investment, strategic partnerships for IoT solutions |
| SoftBank | Aggressive pricing, strong mobile data offerings, growing enterprise services | Focus on AI integration in network services, fiber network expansion |
| Internet Initiative Japan (IIJ) | Enterprise-focused solutions, strong data center capabilities | Expanding cloud connectivity, enhancing cybersecurity offerings |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing capability of mobile broadband, especially 5G and the anticipated 6G, poses a significant threat to Arteria Networks' traditional fixed-line services. For many residential customers and some businesses, high-speed mobile internet is becoming a direct substitute for fiber optic connections. As of early 2024, 5G deployment continues to expand, offering speeds that can reach up to 10 Gbps with very low latency, making it an attractive alternative where fiber infrastructure is less developed or for users prioritizing wireless flexibility.
The ongoing global rollout and performance improvements of 5G networks directly challenge the market share of fixed broadband providers. This trend is expected to accelerate as 6G technology, currently in its research and development phases, promises even greater speeds and capabilities, further blurring the lines between mobile and fixed internet access and potentially reducing customer reliance on wired solutions.
Satellite internet, particularly from Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellations like Starlink, presents a growing threat of substitutes for traditional broadband providers. These services are becoming a viable alternative, especially in areas where deploying fiber infrastructure is prohibitively expensive due to geographical challenges. For instance, Starlink reported over 2 million subscribers globally by the end of 2023, demonstrating significant market penetration.
While older geostationary satellite internet suffered from high latency, LEO systems have drastically improved this, offering speeds up to 100 Mbps and reducing latency to levels comparable to some terrestrial services. This makes satellite internet a credible substitute for users who lack access to fiber or even reliable cable internet, directly impacting the customer base of companies like Arteria Networks in underserved regions.
While Arteria Networks primarily champions fiber optic technology, traditional cable internet and DSL remain viable substitutes for residential connectivity, especially in areas where fiber deployment is still catching up. These established technologies, despite generally offering lower speeds than fiber, often present a more budget-friendly option for consumers. For instance, as of early 2024, the average monthly cost for cable internet plans in the US can range from $60 to $80, while DSL might be even lower, making them attractive alternatives where fiber isn't readily available or perceived as too expensive.
Cloud Computing and Edge Computing as Alternatives to On-Premise Data Centers
Cloud computing, particularly public cloud services from providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, presents a substantial threat of substitution for Arteria Networks' on-premise data center solutions. Businesses are increasingly opting for the scalability and flexibility of cloud infrastructure, which can reduce their reliance on physical data centers. This shift is partly fueled by the growing demand for advanced capabilities like artificial intelligence (AI) and the need for more agile IT environments.
The global public cloud services market was projected to reach over $600 billion in 2024, indicating a strong preference for these outsourced solutions. This growth means fewer companies are investing in or expanding their own data center footprints.
- Public Cloud Adoption: Businesses can access computing power, storage, and services on demand, bypassing the need for dedicated physical infrastructure.
- Edge Computing Growth: As AI and real-time processing demands increase, edge computing offers distributed processing closer to data sources, further diminishing the need for centralized, on-premise data centers for certain workloads.
- Cost and Scalability Advantages: Cloud services often provide a more predictable cost structure and the ability to scale resources up or down rapidly, which can be more appealing than the capital expenditure and fixed capacity of traditional data centers.
- Reduced IT Overhead: Outsourcing to cloud providers shifts the burden of hardware maintenance, security, and upgrades away from internal IT departments.
Fixed Wireless Access (FWA)
Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional wired internet services, including those potentially offered by Arteria Networks. FWA leverages existing cellular infrastructure, such as 4G LTE and 5G networks, to deliver broadband internet to end-users without requiring physical cable installations. This makes it a particularly attractive alternative in areas where laying fiber optic cable is prohibitively expensive or logistically challenging.
The adoption of FWA is accelerating worldwide, driven by its cost-effectiveness and rapid deployment capabilities. For instance, in 2023, global FWA connections were projected to reach over 100 million, with significant growth expected in the coming years as 5G networks mature. This technology directly competes with wired broadband by offering comparable speeds and lower upfront infrastructure costs for providers.
- Cost-Effectiveness: FWA bypasses the high capital expenditure associated with trenching and laying fiber optic cables to individual premises.
- Rapid Deployment: Services can be rolled out much faster than wired alternatives, allowing providers to capture market share quickly, especially in underserved rural or suburban areas.
- Growing Performance: Advances in 5G technology are enabling FWA to offer speeds that are increasingly competitive with fiber, making it a viable substitute for a wider range of users.
- Market Penetration: By mid-2024, FWA was estimated to account for a notable percentage of new broadband subscriptions in several key markets, indicating its growing threat to established wired providers.
The threat of substitutes for Arteria Networks is multifaceted, encompassing advancements in mobile technology, satellite internet, and even established wired alternatives. High-speed mobile broadband, particularly 5G, offers a compelling wireless alternative, with speeds potentially reaching 10 Gbps. Satellite internet, especially from LEO constellations, is also gaining traction, with over 2 million global subscribers by the end of 2023, providing a viable option in areas lacking robust wired infrastructure. Even traditional cable and DSL remain competitive due to their lower costs, with average US cable plans costing $60-$80 monthly in early 2024.
Cloud computing represents another significant substitution threat, as businesses increasingly favor the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public cloud services over on-premise data centers. The global public cloud market was projected to exceed $600 billion in 2024, reflecting this strong trend. Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) also directly challenges wired providers, leveraging cellular networks for rapid deployment and competitive speeds, with global FWA connections estimated to surpass 100 million in 2023.
| Substitute Technology | Key Advantage | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| 5G Mobile Broadband | High Speed, Wireless Flexibility | Up to 10 Gbps potential speeds |
| LEO Satellite Internet | Remote Area Access, Improving Latency | Over 2 million global subscribers (end of 2023) |
| Cable/DSL Internet | Cost-Effectiveness | US Cable plans avg. $60-$80/month (early 2024) |
| Public Cloud Services | Scalability, Reduced IT Overhead | Global market projected >$600 billion (2024) |
| Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) | Rapid Deployment, Cost-Effective Infrastructure | Over 100 million global connections projected (2023) |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a nationwide fiber-optic network and data center infrastructure, as Arteria Networks has done, demands substantial capital. The sheer cost of laying fiber optic cables across vast distances, procuring advanced networking equipment, and constructing robust data centers presents a formidable financial barrier. For instance, the average cost to deploy fiber to the home can range from $500 to $1,500 per premise, illustrating the scale of investment required.
These significant upfront expenditures effectively deter most potential new entrants. The immense financial commitment needed to replicate Arteria Networks' existing infrastructure makes it economically unfeasible for smaller companies or startups to compete. This high capital requirement acts as a powerful deterrent, limiting the threat of new competitors entering the market.
The telecommunications sector in Japan is characterized by stringent government regulation and demanding licensing procedures. These requirements are in place to foster fair competition and protect consumers.
For any new company looking to enter the Japanese market, navigating this intricate web of regulations and obtaining the necessary licenses is a significant hurdle. This process can be both time-consuming and expensive, effectively deterring potential new competitors.
New entrants in the telecommunications sector, particularly those looking to compete with established players like Arteria Networks, face significant hurdles in securing access to essential infrastructure. This includes vital assets such as utility poles, underground conduits, and direct building access points, which are frequently controlled by incumbent operators who can limit or charge for their use. For instance, in 2024, the cost of securing rights-of-way for new fiber optic deployments can run into millions of dollars per mile, depending on the location and existing agreements.
Arteria Networks, by contrast, possesses a substantial advantage due to its proprietary optical fiber backbone and extensive network of access lines. This established infrastructure, coupled with existing rights-of-way secured over years of operation, significantly lowers the barrier to entry for Arteria itself and creates a formidable obstacle for potential new competitors. Building a comparable network from the ground up in 2024 would require immense capital investment and a lengthy development timeline, often exceeding a decade, making it economically unviable for many new entrants.
Brand Loyalty and Established Customer Relationships of Incumbents
Major incumbent telecom players, including established providers like Arteria Networks, leverage significant brand recognition and deep-seated customer loyalty. These long-standing relationships, particularly with business clients and residential building managers, create a formidable barrier for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, customer retention rates for established broadband providers often exceeded 90%, demonstrating the stickiness of existing services.
New entrants face the substantial challenge of overcoming this inertia. They would require considerable investment in marketing campaigns and compelling incentives to persuade customers to switch from trusted, familiar providers. The cost of acquiring a new customer in the telecom sector can be as high as $1,500, a significant hurdle for any new player attempting to gain market share.
- Brand Loyalty: Incumbents benefit from established trust and recognition.
- Customer Relationships: Long-term ties, especially with businesses, are hard to break.
- Switching Costs: Customers often face inconvenience or contractual obligations when changing providers.
- Marketing Investment: New entrants need substantial funds to attract customers from established players.
Technological Complexity and Need for Specialized Expertise
The intricate nature of operating and maintaining Arteria Networks' high-capacity fiber infrastructure and advanced data centers presents a substantial barrier to new entrants. This field demands a deep well of technical expertise and a highly skilled workforce, which are not easily replicated or acquired quickly.
New companies would face significant hurdles in developing or obtaining the specialized knowledge required to compete effectively. For example, the demand for talent in the data center industry in 2024 remained exceptionally high, with reports indicating a shortage of qualified network engineers and data center technicians.
- High Capital Investment: Building out a comparable fiber network and data center facilities requires immense upfront capital, often in the billions of dollars.
- Technical Know-How: Expertise in areas like optical networking, cloud architecture, and cybersecurity is crucial and takes years to cultivate.
- Skilled Labor Shortage: The global shortage of skilled IT professionals, particularly in network engineering and data center operations, makes it difficult for new players to staff their operations adequately.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the complex web of telecommunications and data privacy regulations in different jurisdictions adds another layer of difficulty for potential entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Arteria Networks is generally low due to significant barriers. Building a nationwide fiber-optic network requires immense capital, with fiber deployment costs per premise often ranging from $500 to $1,500 in 2024, making it a substantial financial hurdle. Furthermore, stringent government regulations and complex licensing procedures in the telecommunications sector add considerable time and expense for any new player. Access to essential infrastructure like utility poles and conduits, often controlled by incumbents, presents another significant challenge, with rights-of-way costs potentially reaching millions per mile in 2024.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024 Data/Estimate |
| Capital Requirements | Cost of building fiber networks and data centers | $500 - $1,500 per premise for fiber deployment |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Licensing and compliance in the telecom sector | Time-consuming and expensive navigation |
| Infrastructure Access | Securing rights-of-way and existing infrastructure | Millions of dollars per mile for rights-of-way |
| Technical Expertise | Operating and maintaining advanced networks | High demand and shortage of skilled IT professionals |
| Brand Loyalty & Switching Costs | Customer retention for incumbents | Customer retention rates often exceeding 90% |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Arteria Networks is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and regulatory filings from relevant authorities.