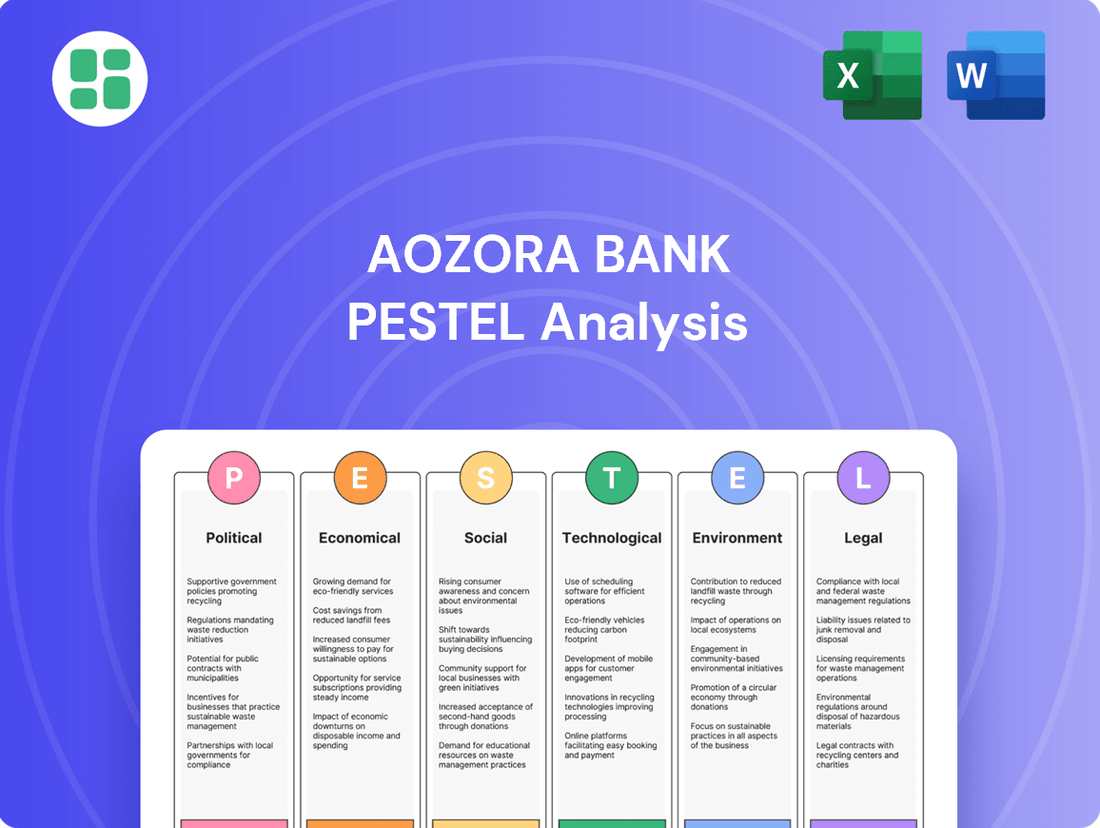
Aozora Bank PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Aozora Bank Bundle
Navigate the complex external forces shaping Aozora Bank's future with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand how political stability, economic shifts, technological advancements, social trends, environmental concerns, and legal frameworks are impacting its operations and strategic direction. Equip yourself with the foresight needed to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks.
Gain a competitive edge by delving into the critical external factors affecting Aozora Bank. Our meticulously researched PESTLE analysis provides actionable intelligence on political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal influences. Download the full version now to unlock strategic insights and make informed decisions.
Political factors
Japan's political landscape remains largely stable, with a consistent focus on fostering economic expansion and ensuring the health of its financial sector. The Financial Services Agency (FSA) is central to this, actively guiding and overseeing banking operations. This stability is a significant advantage for Aozora Bank, enabling more reliable long-term strategic development.
The FSA's administrative policy for fiscal year 2024 explicitly targets the use of financial systems to achieve sustainable economic growth. This policy direction directly supports Aozora Bank's business model and its role in the Japanese economy, suggesting a favorable regulatory environment for its operations and growth initiatives.
The Financial Services Agency (FSA) in Japan continues to refine its regulatory landscape, impacting institutions like Aozora Bank. For instance, ongoing adjustments to Basel III standards, which dictate capital requirements and risk management, necessitate continuous adaptation. In 2024, the FSA also focused on strengthening cybersecurity regulations for financial institutions, a key area for banks operating in the digital age.
Geopolitical shifts and evolving international trade policies directly impact Aozora Bank's global financial dealings, including cross-border transactions and investment banking. The Bank of Japan has highlighted significant uncertainty regarding trade policy, a crucial factor for Japanese financial institutions like Aozora Bank operating internationally.
Maintaining a close watch on global economic and political stability is therefore paramount for Aozora Bank's international business strategy. For instance, as of early 2024, ongoing trade disputes between major economies continue to create volatility in currency markets, directly affecting the profitability of international financial services.
Financial Market Liberalization Initiatives
Japan's government is actively working to make its financial markets more appealing to international players, especially in the FinTech space. This ongoing liberalization drive presents a double-edged sword for Aozora Bank, potentially intensifying competition while simultaneously opening doors for strategic partnerships and innovative ventures. For instance, the easing of investment rules for bank subsidiaries in venture businesses signals a tangible step in this direction, aiming to inject more dynamism into the financial ecosystem.
These policy shifts are designed to attract foreign capital and expertise, fostering a more robust and competitive financial landscape. Aozora Bank can leverage these changes by exploring collaborations with FinTech firms or by investing in emerging technologies itself. The relaxation of venture business investment criteria for bank subsidiaries, a key aspect of this liberalization, directly impacts Aozora's strategic options for growth and innovation within the Japanese market.
- Increased Foreign Investment: Japan aims to boost foreign direct investment in its financial sector, with a particular focus on FinTech.
- Competitive Landscape Shift: Liberalization could lead to new entrants and intensified competition, requiring Aozora Bank to adapt its strategies.
- Collaboration Opportunities: The push for liberalization may create avenues for Aozora Bank to partner with or invest in innovative FinTech companies.
- Regulatory Easing: Relaxed regulations on bank subsidiaries investing in venture businesses provide Aozora with more flexibility for strategic growth.
Fiscal Policy and Public Debt
Japan's government fiscal policy, particularly its approach to public debt and demand stimulation, directly shapes the economic landscape for institutions like Aozora Bank. High levels of public debt can constrain government spending and potentially lead to higher interest rates, impacting borrowing costs for both corporations and individuals. Conversely, measures designed to boost economic activity can increase demand for financial services.
In 2024, Japan's government continued to navigate a complex fiscal environment. The nation's public debt-to-GDP ratio remained one of the highest among developed economies, standing at approximately 266% as of early 2024. This sustained high debt level necessitates careful management to avoid market instability and maintain investor confidence. The government’s ongoing efforts to stimulate domestic demand, through various economic packages and potential tax incentives, are crucial for fostering growth and supporting the financial sector.
- Fiscal Stimulus Measures: The government has implemented economic stimulus packages aimed at boosting consumption and investment, with particular attention to corporate tax incentives to encourage business expansion and R&D.
- Public Debt Management: Japan's substantial public debt requires ongoing management strategies to ensure fiscal sustainability, balancing the need for economic support with long-term financial health.
- Impact on Borrowing: Fiscal policies influence corporate and individual borrowing capacity by affecting interest rates and overall economic confidence, directly impacting Aozora Bank's lending activities.
- Economic Growth Targets: Government objectives for economic growth, often supported by fiscal policy, create opportunities and challenges for financial institutions by influencing market demand for banking products.
Japan's political stability provides a predictable operating environment for Aozora Bank, with the Financial Services Agency (FSA) actively shaping the financial sector's regulatory framework. The FSA's 2024 policies emphasize sustainable economic growth through financial systems, directly aligning with Aozora's objectives.
Ongoing regulatory adjustments, such as refinements to Basel III standards and enhanced cybersecurity mandates implemented in 2024, require continuous adaptation from institutions like Aozora Bank.
Geopolitical shifts and evolving international trade policies, highlighted by the Bank of Japan's concerns about trade policy uncertainty as of early 2024, directly influence Aozora Bank's global operations and currency market exposure.
The government's drive to liberalize financial markets, particularly in FinTech, presents both increased competition and opportunities for strategic partnerships for Aozora Bank, as evidenced by eased investment rules for bank subsidiaries in venture businesses.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis of Aozora Bank examines the influence of Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors on its operations.
It provides a comprehensive understanding of the external forces shaping Aozora Bank's strategic landscape and identifies potential challenges and avenues for growth.
A concise PESTLE analysis of Aozora Bank provides a clear overview of external factors, acting as a pain point reliever by streamlining complex market dynamics for strategic decision-making.
Economic factors
The Bank of Japan's (BOJ) move away from negative interest rates in March 2024, followed by a gradual increase to an expected 0.5% short-term rate by July 2025, marks a significant policy normalization. This shift is anticipated to boost the profitability of Japanese banks, including Aozora Bank, by widening their net interest margins.
With inflation concerns lingering, the BOJ is considering additional rate increases before the end of 2025. This tightening environment could further enhance Aozora Bank's earnings potential, though it also introduces new considerations for loan demand and asset valuations.
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) has recently boosted its core consumer inflation forecast for fiscal year 2025, projecting it to stay above the 2% target through FY2024 before a gradual slowdown. This persistent inflation, particularly driven by rising food costs, could exert broader price pressures, impacting how consumers spend and how businesses invest.
Aozora Bank's financial performance for fiscal year 2024 marked a significant turnaround, achieving profitability. This positive trend, coupled with an optimistic outlook for FY2025, signals a potentially improving economic landscape that could translate into increased demand for loans, benefiting the bank.
Japan's economy is on a path of steady recovery, moving away from prolonged deflation. This improved domestic economic health directly supports Aozora Bank's commercial banking operations by fostering greater demand for loans and financial services from businesses and individuals.
Despite ongoing structural hurdles like a declining birthrate, the overall economic vitality is a key driver for corporate investment and consumer spending, influencing the financial needs Aozora Bank aims to meet. For instance, Japan's GDP saw a growth of 1.9% in 2023, a positive signal for domestic financial markets.
Aozora Bank's performance, including its increased domestic lending activities and optimistic profit projections for fiscal year 2024, demonstrates a strategic alignment with these improving economic conditions, showcasing its ability to capitalize on the evolving financial landscape.
Yen Exchange Rate Volatility
Fluctuations in the Japanese Yen's exchange rate, particularly its depreciation following Bank of Japan (BOJ) policy shifts, significantly impact Aozora Bank's international operations and cross-border dealings. For instance, the yen weakened notably against the US dollar throughout much of 2024, with the USD/JPY pair trading above 150 for extended periods, affecting the value of foreign currency assets and liabilities.
The yen's value is heavily influenced by policy divergence with other major central banks, such as the US Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank. This necessitates careful management of Aozora Bank's foreign currency exposures to mitigate potential losses. For example, a widening interest rate differential between Japan and the US can lead to further yen depreciation, impacting the profitability of international investments and transactions.
- Yen Depreciation Impact: A weaker yen can increase the cost of imported goods and services for Japanese companies, potentially affecting their financial health and, by extension, their borrowing from banks like Aozora.
- Foreign Exchange Gains/Losses: Aozora Bank's financial statements will reflect gains or losses on its foreign currency holdings due to exchange rate movements. For example, if the bank holds significant US dollar assets, a weaker yen translates to higher yen-denominated values for those assets.
- International Competitiveness: A volatile yen can impact the competitiveness of Japanese exports, influencing the business environment for Aozora Bank's corporate clients engaged in international trade.
Global Economic Trends and Credit Market Conditions
Aozora Bank's international operations and investment banking activities make it highly sensitive to shifts in the global economy and credit markets. For example, in early 2024, the bank reported losses stemming from its exposure to US commercial real estate, a direct consequence of higher interest rates that negatively impacted property valuations.
The bank's ability to manage its extensive loan and investment portfolios hinges on a keen understanding of global economic health and the specific risks present within various sectors. This requires constant vigilance regarding macroeconomic indicators and credit quality trends.
- Global GDP Growth: Projections for global GDP growth in 2024 and 2025 are varied, with the IMF forecasting 3.2% for 2024 and 3.3% for 2025, indicating a generally stable but not robust expansion.
- Interest Rate Environment: Central banks, including the US Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank, have maintained higher interest rates through much of 2024, impacting borrowing costs and asset valuations across markets.
- Commercial Real Estate Performance: The US commercial real estate sector, particularly office properties, continued to face headwinds in 2024 due to increased vacancy rates and higher financing costs, impacting institutions with significant exposure.
- Credit Spreads: Credit spreads, reflecting the additional yield investors demand for holding corporate debt over government debt, have shown volatility, with widening spreads indicating increased perceived risk in certain sectors.
Japan's economic recovery is gaining traction, with GDP growth of 1.9% in 2023 and projections for continued expansion in 2024 and 2025. This positive trend supports Aozora Bank's domestic lending and financial services, driven by increased corporate investment and consumer spending. The Bank of Japan's policy normalization, including a move away from negative interest rates and potential further hikes to a 0.5% short-term rate by July 2025, is expected to boost bank profitability by widening net interest margins.
Inflation, projected to remain above the 2% target through FY2024, could exert broader price pressures, influencing consumer behavior and business investment. Aozora Bank's FY2024 profitability turnaround and optimistic FY2025 outlook align with these improving economic conditions, signaling potential growth in loan demand. However, the bank must navigate the impact of a weakening Yen, which has traded above 150 against the US dollar for extended periods in 2024, affecting foreign currency assets and international operations.
Global economic factors, such as varied GDP growth forecasts and higher interest rates maintained by major central banks through 2024, also present challenges. Aozora Bank's exposure to sectors like US commercial real estate, which faced headwinds in 2024 due to higher financing costs, highlights the need for careful portfolio management and vigilance regarding macroeconomic indicators and credit quality trends.
| Indicator | 2023 | 2024 (Forecast) | 2025 (Forecast) | Impact on Aozora Bank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan GDP Growth | 1.9% | ~2.0% | ~2.0% | Supports domestic lending and financial services demand. |
| BOJ Short-Term Rate | Negative | ~0.1% (March 2024) | ~0.5% (July 2025) | Widens net interest margins, boosting profitability. |
| Japan Inflation (Core CPI) | ~3.0% | >2% | ~2% | Potential for further rate hikes, but also impacts loan demand and asset valuations. |
| USD/JPY Exchange Rate | Avg. ~140 | >150 (extended periods) | Volatile, influenced by policy divergence | Affects value of foreign currency assets and liabilities; impacts international operations. |
| Global GDP Growth | ~3.0% | 3.2% (IMF) | 3.3% (IMF) | Influences international operations and investment banking activities. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Aozora Bank PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive Aozora Bank PESTLE analysis delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the bank's operations and strategic outlook.
Sociological factors
Japan's demographic landscape presents a significant challenge for Aozora Bank, with an aging and shrinking population. This trend directly impacts the banking sector by reducing domestic consumption and slowing labor market growth. In 2024, Japan's population is projected to continue its decline, with an estimated birth rate of around 1.2 children per woman, well below the replacement level.
This demographic shift is expected to exert long-term downward pressure on loan demand and overall profitability for financial institutions like Aozora Bank. As the proportion of elderly individuals increases, their reliance on savings and pensions may decrease the need for new borrowing, while a smaller working-age population limits the potential for business expansion and new loan origination.
Consequently, adapting financial products and services to cater to an older demographic is becoming increasingly crucial for Aozora Bank. This could involve developing specialized retirement planning services, wealth management solutions for seniors, and accessible digital banking platforms designed for ease of use by older customers.
Japanese consumers are increasingly favoring digital and cashless transactions, a trend accelerated by high smartphone adoption rates and government pushes for a cashless economy. This shift means banks like Aozora Bank need to prioritize digital channels to stay competitive.
To meet this evolving demand, Aozora Bank is focusing on enhancing its online platforms and mobile banking applications. For instance, by the end of fiscal year 2024, Aozora Bank aims to further integrate advanced digital payment solutions, reflecting a broader industry move where over 70% of Japanese consumers now regularly use mobile payment services.
Japan's demographic shift presents a significant hurdle, with an aging population and declining birth rates potentially creating a shortage of skilled workers, impacting Aozora Bank's access to specialized talent in areas like cybersecurity and digital finance. For instance, the number of individuals aged 25-54, the core working-age population, has been on a downward trend, putting pressure on recruitment efforts.
Aozora Bank must actively address the challenge of attracting and keeping qualified employees to drive its digital transformation and ensure high operational standards. This means creating an environment that fosters growth and offers competitive compensation, especially as demand for tech-savvy financial professionals intensifies.
To counter these trends, investing in robust employee training and development programs is essential for Aozora Bank. This not only helps upskill the existing workforce to meet evolving industry demands but also demonstrates a commitment to career progression, aiding in talent retention.
Increased Financial Literacy and Digital Adoption
Japan's Financial Services Agency (FSA) is actively championing financial literacy, encouraging citizens to embrace tax-advantaged savings vehicles to cultivate long-term investment habits. This initiative aims to bolster a culture of saving and investment across the nation.
While digital banking adoption is on the rise, particularly among younger demographics, a significant portion of the population, especially the elderly, still favors traditional banking methods. This preference stems from concerns about digital security and a perceived complexity in navigating new online platforms. For instance, a 2023 survey indicated that while over 70% of individuals under 40 regularly use online banking, this figure drops to below 30% for those aged 70 and above.
Aozora Bank must strategically address this digital divide. This involves developing intuitive, user-friendly digital interfaces and providing robust educational support and accessible customer service to assist less tech-savvy customers.
- FSA's Push: The Financial Services Agency is actively promoting financial education and tax-advantaged savings accounts.
- Digital Divide: Older populations show a preference for traditional banking due to security and complexity concerns.
- User Adoption Gap: While digital banking use is growing, a significant segment, particularly the elderly, remains hesitant.
- Aozora's Strategy: The bank needs to focus on user-friendly interfaces and educational support to bridge this gap.
Societal Expectations for Corporate Social Responsibility
Societal expectations for corporate social responsibility (CSR) are significantly shaping the landscape for financial institutions like Aozora Bank in Japan. There's a palpable surge in awareness and demand for Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles, which directly influences how companies operate and where investors choose to allocate their capital. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 70% of Japanese investors consider ESG factors when making investment decisions, a notable increase from previous years.
Aozora Bank is therefore under increasing pressure to not only acknowledge but actively demonstrate its commitment to CSR. This includes upholding stringent ethical practices in all its dealings, actively engaging with and contributing to the communities it serves, and ensuring its lending practices are responsible and sustainable. The bank's 2024 annual report highlighted a 15% increase in its community investment programs compared to the prior year.
By aligning its business strategies with these evolving societal values, Aozora Bank stands to gain substantial benefits. A strong CSR profile can significantly enhance its reputation, making it more attractive to a growing segment of socially conscious investors and customers. Indeed, Aozora Bank's recent successful issuance of a sustainability bond, which was oversubscribed by 200%, underscores this trend.
- Growing ESG Demand: Japanese investors increasingly prioritize ESG factors, with over 70% considering them in investment decisions as of 2024.
- CSR Expectations: Aozora Bank faces heightened expectations for ethical conduct, community involvement, and responsible lending.
- Reputation Enhancement: Aligning with societal values can boost Aozora Bank's reputation and attract socially conscious investors.
- Sustainability Bond Success: The bank's recent sustainability bond issuance was oversubscribed by 200%, reflecting strong market interest in its CSR initiatives.
Societal expectations for corporate social responsibility (CSR) are significantly shaping the landscape for financial institutions like Aozora Bank in Japan. There's a palpable surge in awareness and demand for Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles, which directly influences how companies operate and where investors choose to allocate their capital. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 70% of Japanese investors consider ESG factors when making investment decisions, a notable increase from previous years.
Aozora Bank is therefore under increasing pressure to not only acknowledge but actively demonstrate its commitment to CSR. This includes upholding stringent ethical practices in all its dealings, actively engaging with and contributing to the communities it serves, and ensuring its lending practices are responsible and sustainable. The bank's 2024 annual report highlighted a 15% increase in its community investment programs compared to the prior year.
By aligning its business strategies with these evolving societal values, Aozora Bank stands to gain substantial benefits. A strong CSR profile can significantly enhance its reputation, making it more attractive to a growing segment of socially conscious investors and customers. Indeed, Aozora Bank's recent successful issuance of a sustainability bond, which was oversubscribed by 200%, underscores this trend.
Societal attitudes towards technology and digital banking are rapidly evolving in Japan. Younger generations are embracing digital platforms, with over 70% of individuals under 40 regularly using online banking as of 2023. Conversely, a significant portion of the elderly population, below 30% in the same age group, still prefers traditional banking methods due to security and complexity concerns.
| Societal Factor | Trend | Impact on Aozora Bank | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
| ESG Awareness | Increasing | Pressure to adopt CSR and ESG principles, enhancing reputation. | 70%+ Japanese investors consider ESG factors (2024). Aozora's community investment up 15% (2024). |
| Digital Adoption | Growing, but with a generational divide | Need to cater to both digital-first and traditional banking preferences. | 70%+ under 40 use online banking; <30% of 70+ use online banking (2023). |
Technological factors
Japan's financial technology sector is booming, with digital banking and mobile payments becoming increasingly popular as consumers seek more convenient ways to manage their money. This trend is a significant technological factor impacting banks like Aozora.
Aozora Bank's strategic move into digital banking through its subsidiary, GMO Aozora Net Bank, has proven successful, reaching profitability. This highlights the viability of digital-first strategies in the current market landscape.
To maintain a competitive edge, Aozora Bank must continue to invest heavily in its digital platforms and the development of innovative online services. This ongoing commitment is crucial for meeting evolving customer expectations and staying ahead of technological advancements.
Japan's financial sector is grappling with escalating cybersecurity threats, prompting the Financial Services Agency (FSA) to mandate enhanced cyber resilience. Aozora Bank, like its peers, faces the critical imperative of safeguarding sensitive customer information and its financial infrastructure against increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks.
To counter these evolving risks, Aozora Bank must invest in state-of-the-art security protocols and conduct continuous, rigorous risk assessments. For instance, in 2023, financial institutions in Japan reported a significant increase in phishing attempts and ransomware attacks, underscoring the urgency of robust defense mechanisms.
The increasing adoption of AI, Big Data, and cloud computing in Japan's financial sector presents significant opportunities for Aozora Bank. AI and machine learning are becoming vital for enhancing cybersecurity, with cloud services widely used for data protection and operational efficiency. For instance, by mid-2024, Japanese financial institutions were increasingly investing in AI for fraud detection, with some reporting a 20% reduction in false positives.
Aozora Bank can harness these technologies to bolster its data analytics capabilities, refine risk management strategies, and improve fraud detection systems. Furthermore, leveraging AI for personalized customer services can lead to greater customer satisfaction and loyalty, a key differentiator in the competitive Japanese banking landscape. By Q1 2025, banks that effectively implemented AI in customer service saw an average 15% increase in customer engagement metrics.
Competition from FinTech Companies
The Japanese financial landscape is increasingly shaped by FinTech innovation, especially in areas like digital payments and cross-border remittances. This evolving environment presents both significant competitive pressures and avenues for strategic partnerships for established institutions like Aozora Bank. For instance, the Japanese FinTech market saw substantial growth, with transaction volumes in digital payments projected to reach ¥110 trillion by FY2025, according to Nomura Research Institute estimates from early 2024.
Recognizing this trend, Aozora Bank must proactively engage with the FinTech sector. This could involve forging strategic alliances with emerging FinTech firms or even acquiring specific capabilities to enhance its digital offerings and customer experience. The government's support for FinTech, including initiatives like regulatory sandboxes, further fuels this competitive dynamism, creating opportunities for agile players and necessitating strategic adaptation from traditional banks.
- FinTech Growth: Japan's FinTech sector is expanding rapidly, particularly in payment and remittance services.
- Competitive Landscape: New FinTech entrants challenge traditional banks by offering innovative digital solutions.
- Collaboration Opportunities: Partnerships or acquisitions of FinTech firms can help traditional banks like Aozora Bank stay competitive.
- Government Support: Initiatives like regulatory sandboxes encourage FinTech development in Japan.
Innovation in Payment Systems and Blockchain
Innovations in payment systems are rapidly reshaping how financial transactions occur. Mobile payment adoption continues to surge globally, with projections indicating a significant increase in transaction volumes in the coming years. For instance, the global mobile payment market was valued at over $2.5 trillion in 2023 and is expected to grow substantially. Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) models are also gaining traction, enabling non-financial companies to integrate financial services into their offerings.
Japan's regulatory landscape is adapting to these changes, particularly with the amended Payment Services Act. This legislation now provides a clearer framework for stablecoins, permitting banks to issue them within their fund transfer operations. This regulatory clarity presents an opportunity for financial institutions like Aozora Bank to leverage blockchain technology and stablecoins for more streamlined and potentially cost-effective payment solutions.
Aozora Bank can strategically explore these emerging technologies to enhance its service portfolio. By integrating advanced payment solutions, such as QR code payments and potentially stablecoin-based transfers, the bank can cater to evolving customer preferences for speed and convenience. This move could also position Aozora Bank as an innovator in the Japanese financial sector, attracting a broader customer base and improving operational efficiency.
- Mobile Payment Growth: Global mobile payment transaction value is projected to exceed $3.6 trillion by 2024.
- BaaS Expansion: The BaaS market is anticipated to reach over $37 billion by 2027, indicating strong demand for embedded finance.
- Regulatory Clarity: Japan's Payment Services Act amendment provides a pathway for banks to engage with stablecoin technology.
- Efficiency Gains: Blockchain-based payment systems can reduce transaction times and costs compared to traditional methods.
Technological advancements are fundamentally reshaping the banking sector, with AI and Big Data offering significant opportunities for enhanced cybersecurity and operational efficiency. By mid-2024, Japanese financial institutions were increasingly investing in AI for fraud detection, reporting up to a 20% reduction in false positives.
Aozora Bank can leverage these tools for improved data analytics, risk management, and personalized customer services, potentially boosting customer engagement by 15% by Q1 2025 for those effectively implementing AI in customer interactions.
The rapid growth of FinTech, particularly in digital payments, presents both competitive challenges and partnership opportunities for Aozora Bank, with Japanese digital payment transaction volumes projected to reach ¥110 trillion by FY2025.
Innovations like mobile payments and Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) are transforming transaction methods, with global mobile payment market value exceeding $2.5 trillion in 2023 and BaaS market anticipated to reach over $37 billion by 2027.
| Technology Area | Key Trend | Impact on Aozora Bank | Supporting Data (2023-2025 Projections) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Enhanced Fraud Detection & Personalization | Improved risk management, better customer engagement | 20% reduction in false positives (mid-2024); 15% increase in customer engagement (Q1 2025) |
| FinTech | Digital Payments & Remittances | Competitive pressure, partnership opportunities | ¥110 trillion projected transaction volume by FY2025 |
| Mobile Payments | Increased Transaction Volume | Need for agile payment solutions | >$2.5 trillion global market value (2023) |
| Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) | Embedded Finance Growth | Potential for new service integration | >$37 billion market anticipated by 2027 |
Legal factors
The Banking Act is Japan's foundational law for financial institutions, dictating everything from licensing and structure to business operations and capital reserves. Aozora Bank, like all Japanese banks, must adhere to its provisions.
The Financial Services Agency (FSA) continually updates these regulations, for instance, by incorporating Basel III standards. This means Aozora Bank faces ongoing compliance demands, impacting its risk management and capital planning. For example, as of the end of March 2024, Japan's average total capital ratio for banks stood at a robust 18.5%, well above the Basel III minimums, indicating a generally sound regulatory environment.
Japanese authorities are significantly increasing their oversight and tightening regulations around Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF). This means financial institutions like Aozora Bank must adhere to more stringent rules to prevent illicit financial activities.
Aozora Bank, like other financial entities in Japan, is facing tight deadlines to implement these updated AML/CTF measures. The Financial Services Agency (FSA) has been particularly active, with reports indicating a rise in on-site inspections and enforcement actions against institutions found lacking in their compliance programs.
Failure to meet these enhanced compliance standards can result in substantial penalties, including hefty fines and severe administrative actions. Beyond financial repercussions, non-compliance poses a significant threat to Aozora Bank's reputation, potentially eroding customer trust and market standing.
Japan's Act on the Protection of Personal Information (APPI) governs how Aozora Bank handles customer data, with the Personal Information Protection Commission (PPC) overseeing its enforcement. Strict adherence to APPI is crucial for Aozora Bank to safeguard sensitive customer information and uphold consumer trust.
The Financial Services Agency (FSA) also plays a role in consumer protection, particularly by promoting financial education initiatives. These efforts aim to shield consumers from investment fraud, a critical aspect of maintaining a secure financial environment for Aozora Bank's clientele.
Corporate Governance Reforms
Japan's Corporate Governance Code has seen significant revisions, pushing companies like Aozora Bank to enhance their transparency. These changes, particularly those impacting Tokyo Stock Exchange listings, mandate improved disclosures on critical ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) issues, including climate-related risks and diversity metrics. This directly shapes Aozora Bank's internal governance frameworks and how it communicates its operations.
The reforms aim to foster greater accountability and build investor confidence. For Aozora Bank, this means a heightened focus on:
- Board Independence: Ensuring a sufficient number of independent directors to provide objective oversight.
- ESG Integration: Disclosing strategies and performance related to climate change, human capital, and other sustainability factors.
- Shareholder Engagement: Improving communication and responsiveness to shareholder feedback and proposals.
As of early 2024, a substantial majority of companies listed on the TSE have adopted the revised code, underscoring the widespread impact of these governance shifts on Japanese financial institutions.
International Financial Sanctions and Treaties
As a global financial player, Aozora Bank navigates a complex web of international financial sanctions and treaties. The ever-shifting geopolitical landscape, particularly evident in 2024 and projected into 2025, means that new sanctions regimes can emerge rapidly, impacting cross-border transactions and requiring constant vigilance. For instance, the expansion of sanctions targeting specific countries or entities necessitates robust compliance updates to prevent violations and associated penalties.
Aozora Bank's commitment to international business demands strict adherence to these evolving regulations. Failure to comply can result in significant legal repercussions, hefty fines, and severe reputational damage, underscoring the critical need for agile and comprehensive compliance frameworks. The bank must continuously monitor global developments to adapt its operations and mitigate risks effectively.
- Sanctions Monitoring: Aozora Bank invests in advanced systems to track evolving international sanctions lists, ensuring immediate compliance with new designations impacting financial flows.
- Treaty Adherence: The bank actively monitors and implements requirements stemming from international financial treaties, such as those related to anti-money laundering (AML) and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT).
- Geopolitical Impact: Ongoing international conflicts and political tensions in 2024-2025 create a dynamic sanctions environment, demanding proactive risk assessment and strategy adjustments for Aozora Bank.
- Compliance Frameworks: Continuous updates to internal policies and employee training are crucial to maintain robust compliance with international financial regulations and avoid legal liabilities.
The legal landscape significantly shapes Aozora Bank's operations through the Banking Act and ongoing regulatory updates from the Financial Services Agency (FSA), which incorporate international standards like Basel III. For instance, Japan's average total capital ratio for banks was a healthy 18.5% as of March 2024, indicating a stable regulatory environment for capital adequacy.
Environmental factors
ESG investing is booming in Japan, driven by government backing and growing environmental awareness. In 2024, Japan's Financial Services Agency continued to push for better ESG disclosure, with a significant portion of listed companies already aligning with global sustainability standards.
Japan is also a frontrunner in climate transition finance, notably with its sovereign transition bonds. These bonds are designed to fund projects that aid decarbonization, showcasing a national commitment to a greener economy. This trend is expected to see continued growth through 2025.
For Aozora Bank, this presents a clear opportunity to expand its green lending portfolio and sustainable finance offerings. Attracting ESG-focused investors by demonstrating a strong commitment to environmental, social, and governance principles will be key to its future growth and market positioning.
Japan's vulnerability to natural disasters, exacerbated by climate change, presents significant environmental challenges. Aozora Bank must increasingly factor in physical risks like typhoons and floods, which in 2023 caused an estimated ¥1.7 trillion (approximately $11 billion USD) in economic losses according to government data, impacting businesses and potentially their ability to repay loans.
The credit quality of Aozora Bank's loan book is directly susceptible to these climate-related events. Businesses in sectors such as agriculture, tourism, and real estate, particularly those located in coastal or flood-prone areas, face heightened risks of damage and disruption, which could lead to increased non-performing loans.
Consequently, Aozora Bank needs a robust framework to assess and manage both physical risks from extreme weather and transition risks associated with the shift to a low-carbon economy. This includes understanding how policy changes, technological advancements, and market sentiment related to climate change could affect its borrowers' financial health and the bank's overall portfolio resilience.
Japan's commitment to net-zero emissions by 2050 has fueled a significant rise in green bond and sustainability-linked bond issuances. This trend indicates a robust and growing market for financial products that prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. For instance, the total value of outstanding green bonds in Japan reached approximately ¥15 trillion (around $100 billion USD) by the end of 2023, showcasing the increasing investor appetite.
Aozora Bank is well-positioned to leverage this demand by expanding its portfolio of green finance solutions. By offering tailored green loans, sustainability-linked financing, and advisory services for ESG initiatives, the bank can attract environmentally conscious corporate clients and investors. This strategic focus aligns with global financial trends and supports Aozora Bank's own sustainability objectives.
Regulatory Pressure for Environmental Disclosures
Japan's Financial Services Agency (FSA) is intensifying its push for greater environmental disclosures from financial institutions. This aligns with global movements, pushing Japanese banks toward adopting frameworks such as the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) standards, with a target for ISSB alignment by March 2025.
Aozora Bank, like its peers, faces mandates to bolster its reporting on climate-related risks and opportunities. This increased transparency is crucial for building stakeholder confidence and demonstrating a commitment to sustainable finance practices.
- FSA Mandates: Increased regulatory pressure for environmental and climate-related disclosures.
- International Alignment: Drive towards TCFD and ISSB standards by March 2025.
- Aozora's Requirement: Enhance reporting on climate risks and opportunities for stakeholder transparency.
Corporate Responsibility for Carbon Footprint
Japanese financial institutions, including Aozora Bank, are increasingly embedding Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles into their core strategies. This shift underscores a growing dedication to sustainable growth and minimizing environmental impact. For instance, by 2024, many Japanese banks are targeting a significant reduction in their operational carbon emissions, with some aiming for carbon neutrality by 2050.
Aozora Bank is therefore expected to actively manage its own carbon footprint and resource consumption. This proactive approach will contribute to achieving broader national and international environmental objectives. The bank's commitment will involve implementing eco-friendly practices throughout its operations, from energy efficiency in its buildings to responsible waste management.
- Carbon Footprint Management: Aozora Bank will focus on measuring and reducing its direct and indirect greenhouse gas emissions.
- Resource Efficiency: Initiatives will include optimizing energy usage, water consumption, and paper reduction in all bank facilities.
- Sustainable Procurement: The bank will likely prioritize suppliers with strong environmental credentials, influencing its supply chain's carbon impact.
- Reporting Transparency: Aozora Bank is expected to publicly disclose its environmental performance data, aligning with growing investor demand for transparency.
Japan's increasing focus on environmental sustainability, particularly its net-zero by 2050 goal, is driving significant growth in green finance. By the end of 2023, the market for outstanding green bonds in Japan reached approximately ¥15 trillion (around $100 billion USD), reflecting strong investor demand for ESG-aligned investments.
Aozora Bank can capitalize on this trend by expanding its green lending and sustainable finance offerings, attracting ESG-conscious investors and corporate clients. The bank's proactive management of its own carbon footprint and resource consumption, including eco-friendly operational practices, will be crucial for meeting national environmental objectives and enhancing stakeholder confidence.
However, climate change poses substantial physical risks to Japan, with extreme weather events in 2023 causing an estimated ¥1.7 trillion ($11 billion USD) in economic losses. Aozora Bank must robustly assess and manage these risks, particularly for borrowers in vulnerable sectors and locations, to safeguard its loan portfolio's credit quality.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Aozora Bank | Key Data/Trend |
| Climate Change & Extreme Weather | Increased physical risk to loan portfolio, potential for higher non-performing loans. | ¥1.7 trillion ($11 billion USD) economic losses from weather events in 2023. |
| Green Finance Growth | Opportunity to expand green lending and attract ESG investors. | ¥15 trillion ($100 billion USD) outstanding green bonds by end of 2023. |
| Regulatory Push for Disclosure | Mandate to enhance reporting on climate risks and opportunities. | Target for ISSB standards alignment by March 2025. |
| National Net-Zero Targets | Need to manage own carbon footprint and promote sustainable practices. | Commitment to net-zero emissions by 2050. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis for Aozora Bank is informed by a comprehensive review of official Japanese government publications, reports from international financial institutions like the IMF and World Bank, and reputable industry analysis firms. This ensures a robust understanding of the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors influencing the bank.