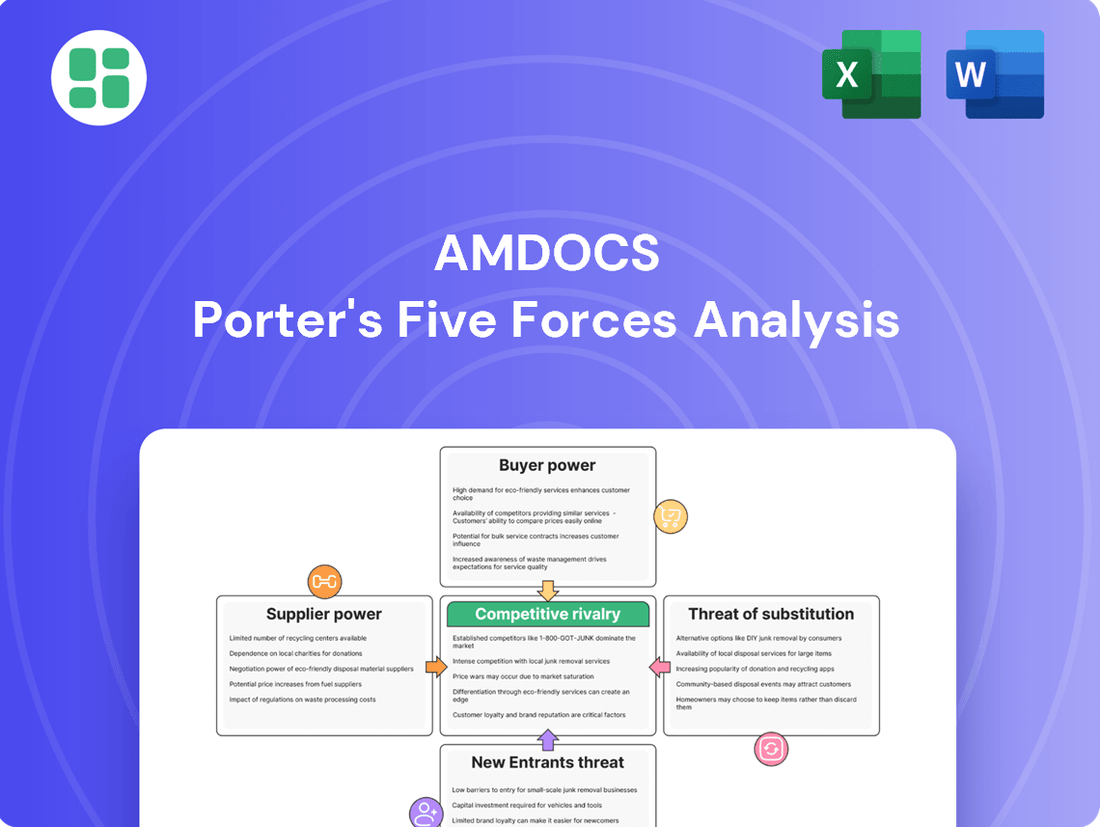
Amdocs Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Amdocs Bundle
Amdocs operates in a dynamic telecom software market, facing moderate to high competitive rivalry and significant buyer power from large service providers. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The threat of substitutes and new entrants presents ongoing challenges, requiring Amdocs to innovate constantly. Supplier power, while present, is generally less impactful than other forces.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Amdocs’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Amdocs' reliance on highly specialized software components and database technologies means that suppliers of these critical elements, especially those with proprietary offerings, can wield considerable bargaining power. This is particularly true if Amdocs faces high switching costs or if there are very few alternative vendors for essential technologies that underpin their billing or network automation solutions. For instance, a significant portion of Amdocs' revenue is tied to its billing and charging systems, which often integrate with complex, specialized databases and middleware.
Amdocs' reliance on a highly skilled talent pool, particularly in areas like software engineering, AI/ML, and telecom domain expertise, significantly influences supplier bargaining power. The scarcity of these specialized skills, especially with the accelerated adoption of technologies like generative AI, can empower these human capital suppliers. This increased leverage translates into higher labor costs and intensified recruitment difficulties for Amdocs.
Amdocs' reliance on foundational software platforms and specific intellectual property, often governed by licensing agreements, grants significant bargaining power to its suppliers. This dependency is particularly acute for technologies integrated into Amdocs' core product and service offerings, influencing cost structures and product roadmaps.
Vendor Lock-in for Niche Solutions
For highly specialized or niche solutions that Amdocs integrates, certain suppliers possess unique capabilities, leading to a degree of vendor lock-in. Replacing these suppliers can be complex, time-consuming, and disruptive to Amdocs' product development and client delivery. This is particularly relevant in areas like advanced AI-driven analytics or specialized network function virtualization (NFV) components where Amdocs relies on specific proprietary technologies.
Amdocs' reliance on these niche suppliers can elevate their bargaining power. This is because the cost and effort associated with switching to an alternative vendor for these critical, specialized functions can be substantial. For instance, if a core AI engine for network optimization is supplied by a single vendor, Amdocs faces significant integration challenges and potential delays if that vendor increases prices or faces operational issues.
- Vendor Lock-in: Amdocs' dependence on specialized suppliers for unique capabilities creates a risk of vendor lock-in, making it difficult and costly to switch providers.
- Complexity of Replacement: Replacing niche solution suppliers often involves significant time, resources, and potential disruption to Amdocs' existing product roadmap and service delivery.
- Impact on Product Delivery: This dependence can hinder Amdocs' agility in adapting to market changes or integrating new technologies if key suppliers are not flexible or raise costs.
Global Supply Chain Dynamics
The bargaining power of suppliers for Amdocs is significantly influenced by global supply chain dynamics. Geopolitical shifts, such as trade tensions or regional conflicts, can concentrate manufacturing or raw material sourcing in fewer locations, thereby increasing supplier leverage. For instance, the semiconductor industry, a critical component for many technology providers, has seen significant consolidation and regional reliance, impacting pricing and availability for downstream customers.
Recent years have highlighted the fragility of global supply chains, with events like the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent logistical bottlenecks leading to widespread disruptions. These disruptions can empower suppliers by creating scarcity and driving up costs for essential components and services Amdocs relies on. The company’s extensive managed services business, which often involves long-term commitments and integration of various technologies, makes it particularly sensitive to fluctuations in the cost and availability of these inputs.
- Regional Concentration: A significant portion of critical component manufacturing, like advanced semiconductors, remains concentrated in East Asia, giving suppliers in these regions considerable pricing power.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The average lead time for key electronic components saw increases of up to 50% in 2023 compared to pre-pandemic levels, directly impacting Amdocs' procurement costs.
- Geopolitical Instability: Ongoing trade disputes and political tensions can further limit sourcing options and exacerbate supplier bargaining power.
- Specialized Services: For highly specialized software development or niche hardware components, a limited number of qualified suppliers can command higher prices.
Amdocs' reliance on specialized software, proprietary technologies, and a skilled workforce grants significant bargaining power to its suppliers. This is amplified by vendor lock-in risks and the complexity of switching providers for critical components. Geopolitical factors and recent supply chain disruptions further empower suppliers, leading to increased costs and potential procurement challenges for Amdocs.
| Factor | Impact on Amdocs | Supporting Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Software & IP | High supplier bargaining power due to unique capabilities and integration complexity. | Amdocs' billing and charging systems often rely on proprietary databases, increasing dependence. |
| Skilled Talent Pool | Suppliers of specialized talent (AI/ML engineers, telecom experts) can command higher wages. | The demand for AI/ML talent saw wage increases of 15-20% in 2023 for specialized roles. |
| Global Supply Chain Dynamics | Concentration in manufacturing and geopolitical tensions increase supplier leverage. | Semiconductor supply chain disruptions in 2023 led to average component lead time increases of up to 50%. |
| Vendor Lock-in | High switching costs for niche solutions limit Amdocs' negotiation flexibility. | Replacing a core AI engine for network optimization can involve months of integration and significant expense. |
What is included in the product
Amdocs' Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intense competitive landscape, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes impacting its market position.
Amdocs' Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, actionable framework to identify and mitigate competitive threats, transforming complex market dynamics into manageable strategic insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
Amdocs' customer base is dominated by large, consolidated telecommunications, media, and entertainment companies worldwide. These major clients, including giants like AT&T and BT, wield considerable bargaining power. Their ability to negotiate favorable terms stems from the sheer volume of their business and the critical reliance Amdocs has on these substantial contracts, which often represent a significant portion of Amdocs' overall revenue.
Amdocs' customers, often large telecommunications operators, face substantial hurdles when considering a switch from Amdocs' established platforms. The deep integration of Amdocs' software, covering critical functions like billing, customer relationship management (CRM), and network automation, means that changing providers isn't a simple swap. This embedded nature creates very high switching costs.
The complexity and risk associated with migrating from a system that underpins a carrier's core operations are immense. This includes data migration, system reconfigurations, and extensive testing, all of which translate into significant financial outlay and potential for operational disruption. For instance, a major telecom provider might spend millions and require months of planning and execution to transition its billing system, a process that severely limits their immediate bargaining power once an Amdocs solution is in place.
Amdocs' ability to deeply customize its solutions and integrate them into client operations creates long-term engagements. This strategic alignment, often solidified through multi-year contracts, builds a strong reliance between Amdocs and its customers, effectively mitigating some of the customer's inherent bargaining power. For instance, Amdocs' revenue from managed services, which typically involves these long-term, integrated relationships, represented a significant portion of its overall business, demonstrating the value of this customer lock-in.
Customer Demand for Integrated Solutions
Customers increasingly desire integrated, end-to-end solutions that simplify their operations and improve customer experiences. This includes everything from billing processes to digital transformation initiatives and network automation. Amdocs' capability to provide these comprehensive suites, such as their amAIz platform and AI & Data Platform, lessens a customer's motivation to source individual components from different providers.
This integrated offering slightly reduces the bargaining power of customers who might otherwise leverage the ability to negotiate terms for separate services. By offering a unified solution, Amdocs can capture more value and command stronger pricing power.
- Customer demand for integrated solutions: Businesses are actively seeking unified platforms for billing, digital transformation, and network automation to streamline operations.
- Amdocs' integrated offerings: Platforms like amAIz and Amdocs' AI & Data Platform provide comprehensive, end-to-end capabilities.
- Reduced customer leverage: The availability of integrated solutions diminishes a customer's ability to negotiate favorable terms on individual components by sourcing from multiple vendors.
- Impact on bargaining power: By offering a complete package, Amdocs can strengthen its position against customers who might otherwise seek to fragment their technology stack.
Customer In-House Development Capabilities
Large customers, particularly major telecommunications operators, might possess substantial in-house IT development teams. This capability presents a potential threat, as these clients could theoretically develop their own software solutions instead of procuring them from external vendors like Amdocs. While building proprietary systems is often a complex and expensive undertaking, the mere existence of this internal option can significantly enhance a customer's bargaining power during negotiations.
For instance, a large operator considering an Amdocs contract might leverage its internal development capacity as a negotiating tactic. This doesn't necessarily mean they will build the solution themselves, but the perceived alternative can lead to more favorable terms, such as lower pricing or enhanced service level agreements. This latent threat, even if rarely acted upon, is a crucial factor in understanding customer leverage.
- Customer In-House Development Capabilities: Large clients may have internal IT teams capable of developing software, reducing reliance on external providers.
- Negotiating Leverage: This internal capacity provides customers with a stronger position during contract discussions with vendors like Amdocs.
- Latent Threat: While often not fully realized due to cost and complexity, the potential for in-house development acts as a significant bargaining chip.
- Impact on Vendor Strategy: Vendors must consider these customer capabilities when pricing, structuring contracts, and demonstrating value.
The bargaining power of Amdocs' customers is significant, primarily due to the concentrated nature of the telecommunications industry. Major clients like AT&T and Deutsche Telekom represent substantial revenue streams, giving them leverage in negotiations. These large operators often have sophisticated internal IT departments, capable of developing some software solutions themselves, which serves as a credible threat during contract discussions.
| Customer Type | Bargaining Power Factor | Example Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Large Telecom Operators | High Volume Purchases | Negotiate lower prices and favorable contract terms. |
| In-house IT Capabilities | Can threaten to develop solutions internally, increasing negotiation leverage. | |
| High Switching Costs (for Amdocs) | Once Amdocs' systems are deeply integrated, customers have less immediate power to switch, but the initial negotiation is key. |
What You See Is What You Get
Amdocs Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Amdocs Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape within the telecommunications software and services industry. You are viewing the exact document you will receive, fully formatted and ready for immediate download and use upon purchase, ensuring no surprises or placeholder content.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The communications software and services market is a crowded arena, featuring formidable global competitors. Amdocs finds itself in direct competition with giants like Oracle and Salesforce, as well as major IT service providers such as Accenture, and specialized telecom vendors like Huawei. This intense rivalry means Amdocs is constantly vying for significant contracts and market share against players with substantial resources and established client relationships.
Competitive rivalry in the telecommunications software sector, where Amdocs operates, is intense and fueled by companies striving to stand out through technological innovation and deep specialization. Amdocs itself is a prime example, focusing on areas like 5G monetization and cloud-native solutions to meet the evolving needs of service providers.
The market sees companies differentiating not just on technology but also on specialized vertical expertise, such as Amdocs' emphasis on cloud and AI innovations. This allows them to offer integrated solutions that address complex industry challenges, driving a dynamic competitive landscape.
Amdocs operates in a market where customers, particularly large telecommunications companies, are highly sensitive to price due to the substantial investment required for software and services. This sensitivity is amplified by the common practice of contractual bidding for major projects, where price becomes a critical differentiator.
Competitors actively engage in aggressive pricing strategies and offer flexible engagement models, alongside compelling service level agreements, to win new contracts and secure renewals. For instance, in 2024, the global telecom software market saw intense competition, with companies like Amdocs, Oracle, and IBM vying for market share, often through competitive pricing tenders for large-scale digital transformation projects.
Market Share Dynamics in Digital Transformation
The telecom industry's push towards digital transformation, including cloud adoption and AI, intensifies competition. Companies like Amdocs are vying to be the go-to partner for service providers navigating these changes, especially in the 5G landscape. This rivalry is evident as firms invest heavily in R&D and strategic partnerships to secure market share in these evolving areas.
Amdocs, for instance, is focused on accelerating service providers' cloud migration, aiming to differentiate itself in the 5G era. This strategic imperative means Amdocs is in direct competition with other software and services providers who are also targeting the lucrative digital transformation market within telecommunications.
- Intensified Rivalry: The digital transformation wave, encompassing cloud migration and AI, is a key battleground for telecom software and service providers.
- Amdocs' Focus: Amdocs aims to be a preferred partner for service providers, particularly in accelerating cloud migration and capitalizing on 5G opportunities.
- Market Share Capture: Competitors are actively seeking to capture new business by offering advanced solutions that enable digital transformation.
- Strategic Investments: Companies are making significant investments in R&D and partnerships to gain a competitive edge in this dynamic market.
Regional and Niche Competitors
Beyond the major global competitors, Amdocs also faces pressure from smaller, nimble regional players and niche specialists. These companies often focus on specific segments, such as network orchestration or digital billing solutions.
These specialized firms can offer highly customized solutions and competitive pricing for particular functionalities, directly challenging larger incumbents like Amdocs in those specific areas. For instance, in 2024, several European telecom operators have reported exploring partnerships with smaller, specialized vendors for specific cloud-native network functions, seeking faster deployment and cost efficiencies.
- Niche Specialization: Smaller competitors thrive by concentrating on specific technologies or services, offering depth of expertise that larger, more diversified companies may not match.
- Agility and Pricing: Their leaner structures allow for quicker adaptation to market changes and often enable more aggressive pricing strategies for their specialized offerings.
- Tailored Solutions: These players can provide highly customized solutions that precisely meet the unique requirements of certain market segments or individual clients.
The competitive rivalry within the communications software and services sector is fierce, driven by a mix of global giants, IT service providers, and specialized vendors. Amdocs competes directly with companies like Oracle, Salesforce, Accenture, and Huawei, all vying for substantial contracts and market share. This intense competition necessitates constant innovation and strategic differentiation, as seen in Amdocs' focus on 5G monetization and cloud-native solutions.
Price sensitivity among large telecommunications clients is a significant factor, especially in contractual bidding for major projects. Competitors often engage in aggressive pricing and flexible engagement models, including robust service level agreements, to win business. For example, in 2024, the global telecom software market experienced heightened competition, with firms like Amdocs, Oracle, and IBM actively participating in competitive tenders for digital transformation initiatives.
The ongoing digital transformation in the telecom industry, including cloud adoption and AI integration, further fuels this rivalry. Companies are investing heavily in research and development and forging strategic partnerships to secure positions in these evolving areas. Amdocs' strategy to accelerate service providers' cloud migration highlights this competitive drive for market leadership in the 5G era.
Furthermore, Amdocs also contends with smaller, agile regional players and niche specialists who excel in specific segments like network orchestration or digital billing. These firms often provide highly tailored solutions and competitive pricing, posing a direct challenge to larger incumbents in their specialized domains. In 2024, reports indicated that some European telecom operators were exploring collaborations with these smaller vendors for specific cloud-native network functions to achieve faster deployments and cost efficiencies.
| Competitor Type | Key Players | Differentiation Strategy | Market Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Giants | Oracle, Salesforce | Broad product portfolios, established client relationships | Significant market share, high resource capabilities |
| IT Service Providers | Accenture | End-to-end solutions, integration expertise | Strong presence in large-scale digital transformation projects |
| Specialized Telecom Vendors | Huawei | Deep industry focus, specific technology solutions | Targeted competition in key telecom infrastructure areas |
| Niche Specialists | Various regional/segment-specific firms | Agility, tailored solutions, competitive pricing | Challenging incumbents in specific functionalities |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large communication service providers, with their substantial IT departments, can choose to build or tailor their own billing, CRM, and network management solutions. This internal development, though often resource-intensive, presents a direct alternative for operators with unique or proprietary needs.
For instance, in 2024, many major telecom companies continued to invest heavily in their internal digital transformation initiatives, with some allocating billions to in-house software development to gain greater control and customization over their core operational systems.
The rise of mature open-source software presents a significant substitute threat to Amdocs' traditional offerings. These alternatives, covering IT infrastructure and application layers relevant to telecom, are gaining traction. For instance, the global open-source software market was valued at approximately $22.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a growing appetite for these solutions.
Open-source options can be particularly appealing due to their lower initial costs and enhanced flexibility. This makes them an attractive substitute, especially for non-mission-critical systems within telecommunications operations. Companies are increasingly leveraging open-source for cloud-native development and infrastructure management, areas where Amdocs has historically provided proprietary solutions.
While Amdocs excels in specialized telecom solutions, generic enterprise software platforms from companies like Salesforce or SAP present a potential threat. These platforms can offer basic Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) functionalities that might overlap with some Amdocs offerings.
However, these generic solutions often fall short in providing the deep, industry-specific functionalities, stringent compliance requirements, and intricate monetization capabilities crucial for the telecommunications sector, which are Amdocs' core strengths.
Cloud-Native Microservices and APIs
The increasing adoption of cloud-native architectures and microservices presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional, integrated software providers. Operators can now assemble custom solutions by integrating specialized, best-of-breed components through APIs. This modularity directly challenges the need for monolithic, end-to-end platforms, allowing for the substitution of individual functionalities rather than an entire suite.
This trend empowers telecommunications companies to build more agile and tailored systems. For instance, by 2024, the global cloud computing market is projected to reach over $1 trillion, indicating a strong industry-wide shift towards flexible, cloud-based solutions. This growth fuels the development and availability of specialized microservices that can perform specific functions, such as customer management or billing, more efficiently and cost-effectively than a single, large platform.
- Modular Integration: APIs enable seamless integration of diverse microservices, allowing operators to pick and choose functionalities.
- Reduced Vendor Lock-in: This approach lessens dependence on a single vendor for all software needs, increasing flexibility.
- Cost Efficiency: Operators can potentially reduce costs by using specialized, often more competitively priced, microservices for specific tasks.
- Innovation Acceleration: The ability to quickly swap or add new microservices allows for faster adoption of new technologies and features.
Managed Services from Other IT Providers
Other major IT services and consulting firms present a significant threat of substitutes. These companies often provide comprehensive managed services that can overlap with Amdocs' core offerings. For instance, they might bundle software solutions with extensive service delivery, presenting a compelling alternative to Amdocs' more product-focused approach.
These competitors can leverage their broad IT expertise and existing client relationships to offer integrated solutions. For example, Accenture, a major player in IT consulting and services, reported revenues of approximately $64.1 billion for its fiscal year ending August 31, 2023, demonstrating the scale and reach of potential substitutes.
- Broad IT Service Offerings: Competitors like IBM, Capgemini, and TCS offer a wide array of IT services, including cloud management, cybersecurity, and application development, which can be bundled to substitute Amdocs' specialized offerings.
- Technology Agnosticism: These firms are often less tied to specific software vendors, allowing them to integrate solutions from various providers, potentially offering more flexible or cost-effective alternatives.
- Scale and Resources: Larger IT conglomerates possess substantial resources for research and development, sales, and service delivery, enabling them to compete effectively across different market segments.
- Bundled Solutions: The ability to package software with extensive implementation, maintenance, and support services creates a strong substitute for customers seeking end-to-end solutions rather than just software products.
The threat of substitutes for Amdocs stems from various sources, including in-house development by large communication service providers and the growing adoption of open-source software. These alternatives offer flexibility and cost advantages, challenging Amdocs' proprietary solutions.
Modular integration of best-of-breed microservices, facilitated by cloud-native architectures, also presents a significant substitute threat. This approach allows operators to build custom solutions, reducing reliance on monolithic platforms.
Furthermore, major IT services and consulting firms offer comprehensive managed services that can act as substitutes by bundling software with extensive delivery capabilities.
The global IT services market, valued at over $1.3 trillion in 2023, highlights the scale of these potential substitutes, many of which are increasingly offering cloud-native and modular solutions.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Amdocs | Example Data/Trend (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Development | Customization, Control, Proprietary Needs | Reduces demand for off-the-shelf solutions | Major telcos continued significant investment in internal digital transformation in 2024. |
| Open-Source Software | Lower Cost, Flexibility, Community Support | Offers cost-effective alternatives for certain functionalities | Global open-source market reached ~$22.7 billion in 2023, with strong growth projected. |
| Modular/Cloud-Native Solutions | API Integration, Best-of-Breed, Agility | Challenges monolithic platform dominance | Cloud computing market projected to exceed $1 trillion in 2024, fueling microservice adoption. |
| IT Services/Consulting Firms | Bundled Services, End-to-End Solutions, Existing Relationships | Provides integrated alternatives to software-only offerings | Accenture's FY2023 revenue was ~$64.1 billion, showcasing the scale of these service providers. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the telecom software and services market, particularly in areas like cloud-native platforms and AI-driven solutions, demands immense capital. For instance, developing and maintaining the sophisticated, scalable software Amdocs offers, alongside robust R&D for emerging technologies, necessitates billions in investment. This financial hurdle significantly limits the number of new players capable of competing effectively.
The telecommunications industry is a minefield of regulations, demanding intricate knowledge of billing systems, network infrastructure, and legal compliance. For any newcomer, the steep learning curve to master these specialized areas, alongside navigating the labyrinthine regulatory frameworks, presents a formidable barrier.
Amdocs benefits immensely from decades of cultivating deep, trust-based relationships with major communication service providers. These long-standing partnerships are not easily replicated, making it difficult for new entrants to gain a foothold.
The inherent risk aversion of customers concerning critical operational systems means they are unlikely to switch from proven, reliable partners like Amdocs. A new entrant would face a significant hurdle in convincing these established players to migrate away from systems they trust and have relied upon for years, a testament to Amdocs' proven track record.
Economies of Scale and Scope
The threat of new entrants in the software and services sector for telecommunications, media, and entertainment is significantly mitigated by the substantial economies of scale and scope enjoyed by established players like Amdocs. These incumbents have optimized their operations across a broad spectrum of offerings, from software development to customer support, leading to lower per-unit costs.
Newcomers would struggle to match these cost efficiencies and the breadth of a comprehensive portfolio. For instance, Amdocs' extensive R&D investments and global service delivery infrastructure allow them to spread fixed costs over a much larger revenue base. In 2023, Amdocs reported revenue of $4.7 billion, indicative of the scale required to compete effectively.
- Economies of Scale: Amdocs leverages its size to reduce costs in software development, deployment, and ongoing support, making it difficult for smaller, newer companies to compete on price.
- Economies of Scope: The ability to offer a wide range of integrated solutions across different service areas (e.g., billing, customer management, network services) provides a competitive advantage that new entrants would find hard to replicate quickly.
- High Initial Investment: Entering this market requires substantial upfront capital for technology development, sales, and establishing a global support network, posing a significant barrier for potential new competitors.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Technology
Amdocs’ substantial investment in intellectual property, including a vast patent portfolio and proprietary software developed over decades, presents a formidable barrier to new entrants. For instance, Amdocs' commitment to R&D, which saw significant investment in 2023, fuels the continuous innovation of platforms like amAIz. This technological moat requires newcomers to either undertake costly and time-consuming IP development or secure expensive licenses, thereby deterring market entry.
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by Amdocs' established intellectual property and proprietary technology. Developing comparable software and securing necessary patents can cost new companies hundreds of millions of dollars, a prohibitive expense for many. For example, in 2024, the average cost to patent a complex software system can range from $5,000 to $15,000 in the US, not including the extensive development costs.
- Significant IP Portfolio: Amdocs holds a large number of patents and proprietary software assets.
- High Development Costs: New entrants face substantial costs to replicate Amdocs' technology.
- Licensing Barriers: Acquiring licenses for existing Amdocs technology is often prohibitively expensive.
- R&D Investment: Amdocs' ongoing investment in research and development, exceeding $1 billion annually in recent years, continually strengthens its technological advantage.
The threat of new entrants into the telecom software and services market is considerably low due to the immense capital required for research, development, and infrastructure. Amdocs' substantial revenue, reaching $4.7 billion in 2023, underscores the scale of operations necessary to compete. This high barrier to entry, coupled with significant upfront investment in technology and global support networks, deters many potential new players.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Amdocs' Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Extremely High | Significant financial resources for R&D and infrastructure |
| Intellectual Property | Costly to replicate | Extensive patent portfolio and proprietary software |
| Customer Relationships | Difficult to establish | Long-standing, trust-based partnerships with major CSPs |
| Regulatory Complexity | Steep learning curve | Deep understanding of industry-specific regulations |
| Economies of Scale & Scope | Challenging to achieve | Lower per-unit costs and broad integrated solutions |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Amdocs Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, integrating information from Amdocs' own investor relations disclosures, annual reports, and SEC filings with industry-specific market research reports and analyst forecasts.