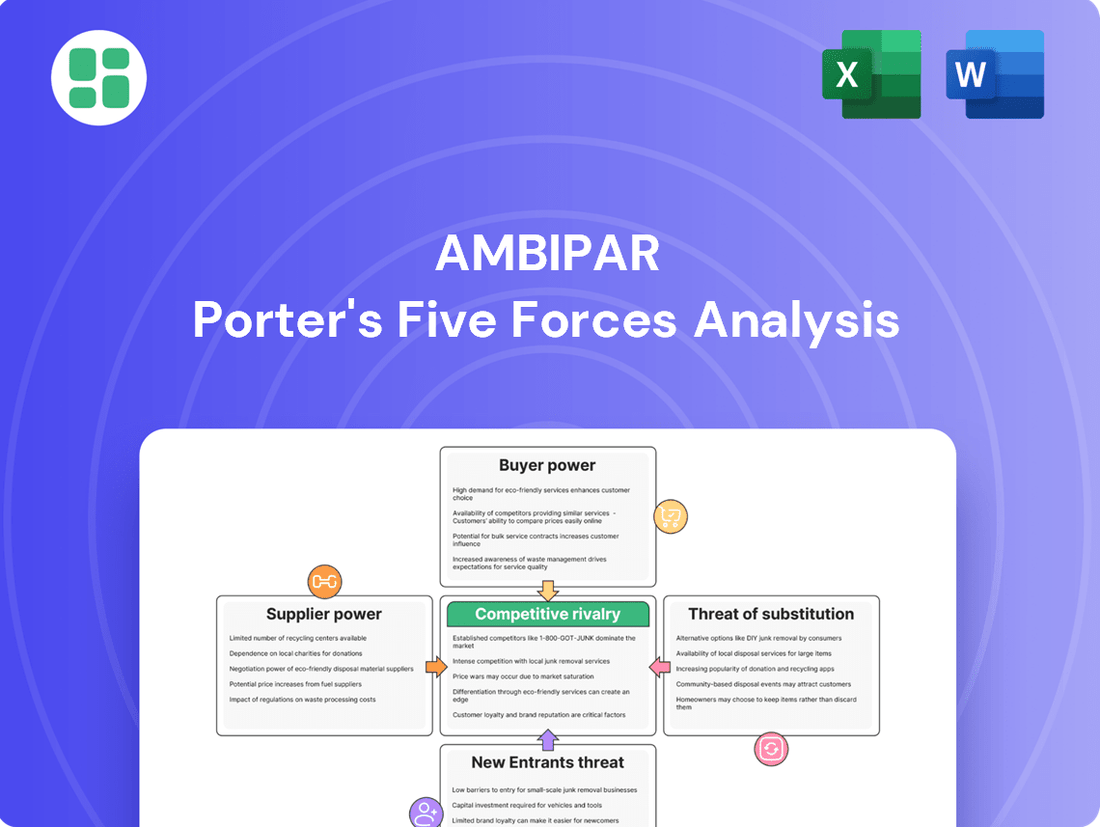
Ambipar Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ambipar Bundle
Ambipar's competitive landscape is shaped by several key forces, including the bargaining power of its buyers and the intensity of rivalry within the environmental services sector. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for assessing the company's strategic positioning and future profitability.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Ambipar’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Ambipar's reliance on a concentrated supplier base for critical inputs like specialized environmental equipment and advanced chemical agents significantly influences supplier bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the global market for certain high-performance spill containment materials saw consolidation, with a few key manufacturers dominating production. This limited supplier pool means Ambipar may face increased costs or restricted access to these essential resources, impacting its operational efficiency and profitability.
Ambipar's reliance on specialized inputs significantly shapes supplier bargaining power. For instance, the availability and cost of unique waste treatment chemicals or advanced environmental technologies directly impact Ambipar's service delivery and pricing. If these critical components are sourced from a limited number of providers or possess proprietary characteristics, suppliers gain leverage.
Ambipar faces significant switching costs when changing environmental service providers. These costs can include the expense of re-training personnel on new equipment and recalibrating existing systems to accommodate different chemical formulations or waste disposal protocols. For example, transitioning to a new hazardous waste disposal partner might necessitate extensive compliance training and new certifications for Ambipar's operational teams, making a switch a complex and costly undertaking.
The complexity of re-certifying processes and adapting to new regulatory compliance standards associated with different suppliers further elevates these switching costs. If Ambipar were to change its primary supplier for specialized industrial cleaning chemicals, it would likely need to invest in new safety data sheets, update internal handling procedures, and potentially undergo new site audits, all of which contribute to a stronger bargaining position for the existing supplier.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by Ambipar's suppliers is a significant consideration. If suppliers, such as those providing waste treatment chemicals or specialized equipment, possess the technical expertise and capital, they could potentially enter Ambipar's core business of environmental management services. This would directly transform them into competitors, leveraging their existing supply chain relationships to offer similar solutions.
The likelihood of this occurring depends on the suppliers' existing capabilities and their strategic incentives. For instance, if a supplier already has a robust R&D department focused on sustainable solutions or sees a substantial market opportunity in direct service provision, their inclination to integrate forward increases. In 2023, the global environmental services market was valued at over $1 trillion, indicating a strong incentive for players in adjacent industries to explore this lucrative sector.
- Supplier Capabilities: Assess if key suppliers have the technical know-how and operational infrastructure to deliver environmental management services.
- Market Incentives: Evaluate if the profitability and growth potential of Ambipar's market offer sufficient motivation for suppliers to become direct competitors.
- Competitive Landscape: Consider if existing competitors are also facing similar forward integration threats from their own supply chains.
Uniqueness of Supplier Offerings
The uniqueness of supplier offerings significantly impacts Ambipar's bargaining power. If suppliers provide highly specialized or proprietary technologies and services that Ambipar cannot easily substitute, their leverage increases. This is particularly relevant in niche environmental services where specialized equipment or patented treatment processes are involved.
For instance, if a key supplier holds patents for advanced waste treatment technology that Ambipar requires for specific client contracts, Ambipar's ability to negotiate favorable terms is diminished. The more unique and indispensable a supplier's contribution, the weaker Ambipar's position becomes in price and contract negotiations.
- Supplier Differentiation: Assess the degree to which Ambipar's suppliers offer unique products or services not readily available from competitors.
- Proprietary Technology: Identify if suppliers possess patented technologies or exclusive processes that are critical to Ambipar's operations or service delivery.
- Reliance on Specific Suppliers: Determine the extent to which Ambipar is dependent on a limited number of suppliers for essential inputs or specialized capabilities.
Ambipar's bargaining power with suppliers is influenced by the concentration of its supplier base and the uniqueness of the inputs it requires. A limited number of providers for specialized environmental equipment or advanced chemical agents can grant suppliers significant leverage. For example, in 2024, the market for certain high-performance spill containment materials experienced consolidation, with a few key manufacturers dominating production, potentially increasing costs for Ambipar.
The switching costs for Ambipar are also a crucial factor. Re-training staff on new equipment or recalibrating systems for different chemical formulations represents a substantial investment. This complexity, coupled with the need to re-certify processes and adapt to new regulatory standards when changing suppliers, strengthens the position of existing providers.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into environmental management services also plays a role. If suppliers have the necessary technical expertise and capital, they could become direct competitors, leveraging their existing supply chains. The global environmental services market, exceeding $1 trillion in 2023, presents a strong incentive for such moves.
| Factor | Impact on Ambipar | Example/Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier bargaining power | Consolidation in spill containment materials market |
| Switching Costs | Strengthens existing supplier position | Training, recalibration, and re-certification expenses |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for new competitors | $1 trillion+ global environmental services market (2023) |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces shaping Ambipar's industry, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic visualization of Ambipar's market landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ambipar's customer concentration is a key factor in its bargaining power. If a substantial portion of Ambipar's revenue comes from a few large industrial clients, government contracts, or major municipalities, these customers gain significant leverage. This leverage allows them to negotiate for lower prices, more favorable payment terms, or customized service agreements, thereby impacting Ambipar's profitability and pricing flexibility.
Customer switching costs for Ambipar are influenced by the complexity of environmental regulations and the integration of their services into a client's existing operations. For instance, a company relying on Ambipar for hazardous waste disposal must navigate new permitting processes and potentially re-engineer their waste management workflows if they switch providers, creating a significant barrier.
These switching costs can include the time and expense associated with vendor selection, contract negotiation, and the physical or procedural changes required to adopt a new service. For example, if Ambipar provides specialized spill response equipment that is proprietary or requires extensive training, a customer’s reluctance to incur these upfront costs can lock them in.
In 2024, businesses are increasingly focused on supply chain reliability and compliance. A disruption in environmental services can lead to severe penalties and operational shutdowns. This inherent risk makes clients hesitant to switch from established providers like Ambipar, especially if they have a proven track record, thereby increasing customer switching costs and reducing their bargaining power.
Ambipar's customers exhibit varying degrees of price sensitivity. For routine waste management or basic environmental monitoring, where services can be perceived as more commoditized, customers may actively shop for the lowest price. For instance, in 2024, many industrial sectors faced inflationary pressures, potentially leading them to scrutinize operational costs more closely, including environmental service providers.
However, for specialized services like complex emergency response or advanced environmental remediation, price sensitivity tends to be lower. In these critical situations, reliability, expertise, and speed of execution often outweigh minor price differences. Ambipar's ability to offer unique, high-value solutions can mitigate customer pressure for lower prices in these segments.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by Ambipar's customers is a key factor influencing their bargaining power. If clients, particularly large industrial or commercial entities, possess the financial resources and technical expertise, they might consider developing their own waste management or emergency response capabilities. This would reduce their dependence on external providers like Ambipar, thereby increasing their leverage in negotiations.
For instance, a major chemical manufacturer might evaluate the cost-effectiveness of establishing an in-house hazardous waste treatment facility versus continuing to outsource these services to Ambipar. If the internal investment proves to be a more economical long-term solution, this directly impacts Ambipar's customer retention and pricing power. In 2024, many industries are focusing on supply chain resilience and cost control, making such evaluations more probable.
- Customer Integration Potential: Large corporations with significant operational scale and a need for specialized waste handling or emergency preparedness are the most likely candidates to consider backward integration.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Customers will weigh the capital expenditure and ongoing operational costs of in-house services against Ambipar's pricing and service quality.
- Impact on Ambipar: Successful backward integration by key clients can lead to reduced revenue streams and increased pressure on Ambipar to maintain competitive pricing and service levels.
- Industry Trends: Growing emphasis on sustainability and regulatory compliance in waste management might incentivize some larger players to gain more direct control over these processes.
Availability of Substitute Services for Customers
The bargaining power of customers for Ambipar is significantly influenced by the availability of substitute services. In the environmental management sector, customers can often find alternative solutions, which increases their leverage.
This ease of finding comparable services from other companies directly translates to a greater ability for customers to negotiate better terms and pricing with Ambipar. For instance, if a municipality needs waste management services, they can solicit bids from multiple providers, driving down costs.
- Customer Substitutability: The environmental services market is competitive, with numerous players offering similar solutions for waste disposal, recycling, and remediation.
- Price Sensitivity: Many clients, particularly in public sectors or large industrial firms, are highly sensitive to pricing, making them actively seek out the most cost-effective options.
- Switching Costs: While some environmental services might involve initial setup or contractual obligations, the overall switching costs for customers are often moderate, further empowering them to explore alternatives.
Ambipar's customers possess considerable bargaining power, driven by factors like customer concentration, moderate switching costs, and price sensitivity in commoditized service areas. For example, in 2024, industrial clients facing economic pressures actively sought cost efficiencies, intensifying negotiations for routine waste management services.
The threat of backward integration, while present for large clients, is often mitigated by the specialized nature and regulatory complexities of environmental services. However, the availability of numerous competitors offering similar solutions means customers can readily compare offerings, thereby increasing their leverage to negotiate favorable terms and pricing.
| Factor | Impact on Ambipar | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High concentration increases leverage for key clients. | Dependence on a few large contracts can amplify this. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate to high for specialized, integrated services. | Regulatory hurdles and operational integration make switching costly for some. |
| Price Sensitivity | High for commoditized services, low for critical/specialized ones. | Inflationary pressures in 2024 heightened price scrutiny for routine services. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Low for most, but possible for very large, resource-rich clients. | Focus on supply chain control in 2024 may spur some internal evaluations. |
| Availability of Substitutes | High across many service segments. | Competitive bidding is common, empowering customers to seek alternatives. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Ambipar Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Ambipar Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally researched and formatted analysis you will receive instantly upon purchase, providing immediate strategic insights.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The environmental management and emergency response sectors are characterized by a fragmented competitive landscape. While specific market share data for all players is proprietary, industry analysis indicates a significant number of smaller, regional operators alongside larger, national and international entities. This diffusion of market power suggests that no single competitor dominates, leading to a more dynamic and potentially price-sensitive market.
The environmental management industry is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing regulatory pressures and a global focus on sustainability. This expansion creates opportunities for new entrants and existing players alike, potentially moderating the intensity of competitive rivalry.
For instance, the global environmental consulting market was valued at approximately USD 38.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly. This upward trend suggests that companies can expand their market share by capitalizing on the increasing demand for environmental services, rather than solely engaging in aggressive competition for existing business.
Ambipar's competitive rivalry is significantly influenced by the differentiation of its environmental, emergency response, and waste management services. The company distinguishes itself through specialized technological solutions and deep expertise in niche areas, which can lessen direct price competition. For instance, Ambipar's advanced spill containment technologies and tailored emergency response plans offer unique value propositions not easily replicated by all competitors.
This differentiation strategy is crucial in an industry where some services, like basic waste collection, can be more commoditized. The company's focus on integrated solutions, combining emergency response with subsequent waste treatment and remediation, further sets it apart. In 2024, Ambipar reported a strong performance in its Environmental division, highlighting the market's demand for specialized, integrated environmental solutions, which supports its differentiation efforts.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers in the environmental management sector, like those Ambipar operates within, can be substantial. These include the significant investment in specialized equipment and infrastructure necessary for waste treatment, recycling, and hazardous material handling. Companies are also often bound by long-term contracts with municipalities and industrial clients, making early termination costly and complex. Furthermore, the social responsibility associated with environmental services can create reputational costs for premature exit, discouraging companies from leaving even in less profitable periods.
These high exit barriers mean that companies, even those facing declining profitability, may continue to operate and compete aggressively. This can intensify rivalry, as firms are reluctant to divest assets or cease operations due to the difficulty and expense involved. For instance, the specialized nature of Ambipar's fleet, including vacuum trucks and specialized containment units, represents assets that are not easily redeployed to other industries, thus increasing the cost of exiting the market.
- Specialized Assets: Environmental management firms possess highly specific and often immobile assets like treatment plants and specialized vehicles, which have limited resale value outside the industry.
- Long-Term Contracts: Many companies operate under multi-year agreements for waste collection, disposal, and remediation services, creating significant financial penalties for early termination.
- Social and Reputational Costs: Exiting the environmental services market can lead to negative public perception and damage a company's brand, especially if it involves ceasing essential services.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Divesting or closing down environmental operations often involves complex regulatory approvals and compliance requirements, adding to the exit cost and time.
Cost Structure and Fixed Costs
The environmental management sector, including companies like Ambipar, is characterized by a significant cost structure heavily influenced by high fixed costs. These include substantial investments in specialized equipment for waste treatment and disposal, maintaining extensive infrastructure, and meeting stringent regulatory compliance requirements. For instance, the capital expenditure for advanced hazardous waste processing facilities can easily run into tens of millions of dollars.
This prevalence of high fixed costs often fuels intense price competition among industry players. Companies are driven to maximize their operational capacity to spread these fixed costs over a larger volume of services, which can lead to aggressive pricing strategies to secure market share and ensure profitability. This dynamic puts pressure on margins for all participants.
- High Capital Investment: Specialized equipment for services like industrial cleaning, waste transportation, and hazardous material handling represents a major fixed cost.
- Regulatory Burden: Ongoing costs associated with permits, environmental monitoring, and adherence to evolving regulations are substantial fixed expenses.
- Capacity Utilization Drive: The need to cover high fixed costs incentivizes companies to operate at or near full capacity, often leading to price wars.
- Infrastructure Maintenance: Maintaining facilities, vehicles, and specialized treatment plants incurs continuous fixed operational expenditures.
Competitive rivalry within the environmental services sector, where Ambipar operates, is moderately intense. While the market is fragmented with many players, differentiation through specialized services and integrated solutions helps mitigate direct price wars. The growing demand for sustainability services, as evidenced by the global environmental consulting market reaching approximately USD 38.5 billion in 2023, allows companies to grow without solely relying on aggressive competition for existing business.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Customers facing environmental challenges can explore alternatives to Ambipar's services. For instance, many companies are increasingly investing in robust internal waste reduction programs, aiming to minimize the need for external waste management solutions. In 2023, global corporate spending on sustainability initiatives, including waste management, saw a significant uptick, with many businesses prioritizing in-house solutions to control costs and enhance operational efficiency.
Another substitute involves companies developing their own emergency response capabilities. This can reduce reliance on external providers like Ambipar, especially for routine or predictable environmental incidents. Some large industrial players have dedicated internal teams and specialized equipment, allowing them to manage a portion of their environmental response needs internally.
Furthermore, the adoption of fundamentally different technologies presents a threat. Innovations in areas like advanced material recycling or on-site waste treatment technologies can offer customers a way to address environmental issues without engaging specialized service providers. For example, the market for circular economy solutions is projected to grow substantially, offering alternatives to traditional disposal methods.
The cost-effectiveness and efficiency of substitute environmental solutions directly impact Ambipar. If alternatives, such as in-house waste management or less specialized cleaning services, offer comparable or superior performance at a reduced cost, this poses a significant threat. For instance, if a competitor can achieve a 15% lower operational cost for industrial cleaning through automation, it directly pressures Ambipar's pricing strategy and perceived value.
Customers' willingness to switch to substitute solutions for Ambipar's environmental services is influenced by several factors. The ease with which a customer can adopt an alternative, such as using in-house waste management instead of Ambipar's specialized services, plays a significant role. Regulatory acceptance of these alternatives is also crucial; if a substitute doesn't meet environmental compliance standards, customers are less likely to consider it.
Perceived risk associated with substitutes further impacts customer propensity. For instance, if a less experienced provider offers a cheaper waste disposal service but carries a higher risk of environmental incidents, customers are often hesitant to switch from a trusted provider like Ambipar. In 2024, businesses are increasingly prioritizing compliance and reputation, making them less inclined to opt for unproven or risky alternatives, even if they appear cheaper initially.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements pose a significant threat of substitution for Ambipar's services. Innovations in areas like advanced waste-to-energy conversion or AI-driven pollution monitoring could offer more efficient and cost-effective alternatives to traditional environmental management solutions. For instance, breakthroughs in biodegradable materials might reduce reliance on conventional waste disposal methods that Ambipar currently handles.
The increasing sophistication of digital platforms for environmental compliance and reporting could also serve as a substitute. Companies might leverage these platforms to manage their environmental footprint more autonomously, thereby reducing the need for external service providers. In 2024, the global market for environmental technology and services continued to expand, with a notable surge in investment in green tech solutions, indicating a fertile ground for emerging substitute offerings.
- Emerging Waste Treatment Technologies: Innovations such as plasma gasification or advanced anaerobic digestion offer alternatives to landfilling and incineration, potentially impacting Ambipar's waste management segment.
- Digital Environmental Monitoring: IoT sensors and AI analytics provide real-time data and predictive capabilities for environmental compliance, potentially reducing the need for manual inspections and reporting services.
- Sustainable Material Innovations: Development of fully compostable or recyclable packaging and products could decrease the volume of traditional waste requiring disposal.
- Decentralized Solutions: Smaller, localized treatment facilities or on-site recycling units could emerge as substitutes for centralized waste management services.
Regulatory Changes Promoting Alternatives
Evolving environmental regulations present a significant threat of substitution for Ambipar's services. For example, new policies in Brazil, a key market for Ambipar, are increasingly emphasizing circular economy principles and waste-to-energy solutions. This could lead businesses to adopt these alternative methods, reducing their reliance on traditional waste management and environmental services that Ambipar provides.
The push for specific waste reduction methods, such as advanced recycling technologies or on-site treatment, directly substitutes for services like waste collection and disposal. In 2024, several European nations have intensified their focus on Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes, which place more onus on manufacturers to manage product end-of-life, potentially diverting business from third-party environmental service providers.
- Regulatory Push for Circular Economy: Governments are enacting policies that favor waste reduction and reuse, directly impacting demand for traditional waste management.
- Rise of On-Site Treatment Technologies: Advancements in technology allow companies to treat waste internally, lessening the need for external environmental service providers.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Schemes: These policies shift the burden of waste management to producers, potentially decreasing the market for services like those offered by Ambipar.
The threat of substitutes for Ambipar's environmental services is significant, driven by technological advancements and evolving customer preferences. Companies are increasingly exploring in-house waste reduction programs and developing their own emergency response capabilities, directly reducing reliance on external providers.
Innovations in areas like advanced material recycling and on-site waste treatment offer customers alternative ways to manage environmental challenges. For instance, the global market for circular economy solutions is projected for substantial growth, presenting a direct challenge to traditional disposal methods.
Cost-effectiveness is a key driver; if substitutes offer comparable performance at a lower price point, it pressures Ambipar's pricing. For example, if automated industrial cleaning solutions can achieve 15% lower operational costs, it impacts Ambipar's perceived value.
The ease of adoption and regulatory acceptance of alternatives also play a crucial role. In 2024, businesses prioritize compliance and reputation, making them cautious of unproven substitutes, even if they appear cheaper initially.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the environmental management and emergency response sectors demands substantial upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in specialized equipment like hazardous waste treatment units, spill containment systems, and advanced monitoring technology. For instance, acquiring a fleet of specialized response vehicles and establishing state-of-the-art treatment facilities can easily run into tens of millions of dollars.
Furthermore, stringent regulatory compliance adds another layer of financial burden. Obtaining permits, licenses, and certifications, often across multiple jurisdictions, requires significant investment in legal, technical, and administrative resources. Ambipar, for example, operates in a highly regulated environment, necessitating continuous expenditure to maintain compliance and safety standards, which acts as a formidable barrier for potential new entrants.
The environmental services sector, particularly for companies like Ambipar, faces significant regulatory and licensing hurdles. Obtaining the necessary permits and certifications to handle hazardous materials, manage waste, and ensure environmental compliance is a complex and time-consuming process. These stringent requirements act as a substantial barrier to entry, deterring many potential new competitors who may lack the expertise or capital to navigate such a demanding landscape.
Newcomers to the environmental services sector, like Ambipar, often struggle to secure reliable access to established distribution channels and customer bases. Existing players benefit from long-standing relationships with industrial clients, municipalities, and government entities, which are difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly or at a comparable scale.
Economies of Scale and Experience
Existing players in the environmental services sector, like Ambipar, often benefit significantly from economies of scale. This allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger volume of services, leading to lower per-unit costs. For instance, investing in specialized equipment for waste management or emergency response can be more cost-effective when utilized across numerous projects and clients. Ambipar's extensive network and operational footprint in 2024 likely contribute to these scale advantages, making it harder for newcomers to match their cost efficiency without substantial upfront investment.
Accumulated experience also acts as a formidable barrier. Years of operation mean established companies possess deep knowledge of regulatory landscapes, operational best practices, and client needs. This experience translates into greater efficiency and fewer costly mistakes. Ambipar’s long-standing presence and track record in managing complex environmental challenges provide a competitive edge that new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly. This accumulated expertise is particularly valuable in specialized areas such as hazardous waste treatment or industrial cleaning.
- Economies of Scale: Ambipar leverages its size for cost advantages in purchasing, operations, and R&D, making it difficult for new entrants to compete on price.
- Experience Curve: Decades of operational experience translate into greater efficiency, risk mitigation, and a deeper understanding of client needs, creating a knowledge barrier.
- Capital Intensity: The environmental services industry often requires significant capital investment in specialized equipment and infrastructure, which new entrants may find prohibitive.
- Regulatory Expertise: Established firms like Ambipar have navigated complex environmental regulations for years, a learning curve that is steep and costly for newcomers.
Brand Loyalty and Differentiation
Ambipar, like many in the environmental services sector, benefits from established brand recognition. Customers often seek out providers with a proven track record, especially when dealing with critical environmental compliance and waste management. This ingrained trust makes it challenging for newcomers to penetrate the market. For instance, in 2024, companies with long-standing reputations often secure contracts based on past performance and established relationships, a significant hurdle for any new entrant aiming to compete on reliability.
The degree of brand loyalty in the environmental services industry is substantial. Clients, particularly large corporations, prioritize stability and expertise when selecting partners for waste disposal, recycling, and remediation. A new entrant would need to invest heavily in marketing and demonstrate superior service or cost-effectiveness to sway established customer preferences. This loyalty is often built over years, making direct competition on this front a long-term strategy for new players.
Differentiation is key for new entrants, but incumbents like Ambipar have already carved out niches and built strong identities. Whether through specialized services, advanced technological capabilities, or a commitment to sustainability, established players have a head start in defining their value proposition. New companies must clearly articulate what makes them different and better to attract customers away from trusted, known entities.
- Brand Recognition: Incumbent companies in the environmental services sector often possess high brand recognition due to years of operation and successful project delivery.
- Customer Loyalty: Clients, especially in regulated industries, tend to exhibit strong loyalty to established service providers due to perceived reliability and expertise.
- Differentiation Challenge: New entrants face the significant challenge of differentiating their offerings from those of established players who have already built strong market positions.
- Barriers to Entry: The established trust and loyalty enjoyed by companies like Ambipar create a substantial barrier to entry for new competitors seeking to gain market share.
The threat of new entrants in the environmental management and emergency response sectors, where Ambipar operates, is generally considered moderate. Significant capital investment is required for specialized equipment and infrastructure, with costs easily reaching tens of millions of dollars for a comprehensive fleet and advanced facilities. For example, acquiring advanced hazardous waste treatment units and spill containment systems represents a substantial financial barrier.
Stringent regulatory requirements and the need for specialized permits and licenses further complicate market entry. Navigating these complex compliance landscapes demands considerable investment in legal, technical, and administrative resources, a hurdle that can deter many potential competitors. Ambipar's own operational history underscores the ongoing expenditure necessary to maintain high safety and compliance standards, a continuous cost for established players and a steep learning curve for newcomers.
Established players like Ambipar benefit from significant economies of scale, allowing them to spread fixed costs over a larger service volume and achieve lower per-unit costs. In 2024, Ambipar's extensive network and operational footprint likely contribute to these cost efficiencies, making it difficult for new entrants to match their pricing without substantial upfront investment. Furthermore, accumulated experience in navigating regulatory environments and operational best practices creates a knowledge barrier that new companies struggle to overcome quickly.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | High upfront investment in specialized equipment and infrastructure. | Significant financial hurdle, requiring substantial capital. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing, permits, and compliance requirements. | Demands expertise and resources to navigate, increasing entry costs. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large-scale operations. | New entrants struggle to compete on price without comparable scale. |
| Experience Curve | Deep knowledge of operations, regulations, and client needs. | New entrants lack the efficiency and risk mitigation of experienced firms. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Ambipar is built upon a robust foundation of data, including their publicly available annual reports, investor presentations, and financial statements. We also incorporate insights from industry-specific market research reports and news articles to capture the dynamic competitive landscape.