Accuray Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Accuray Bundle
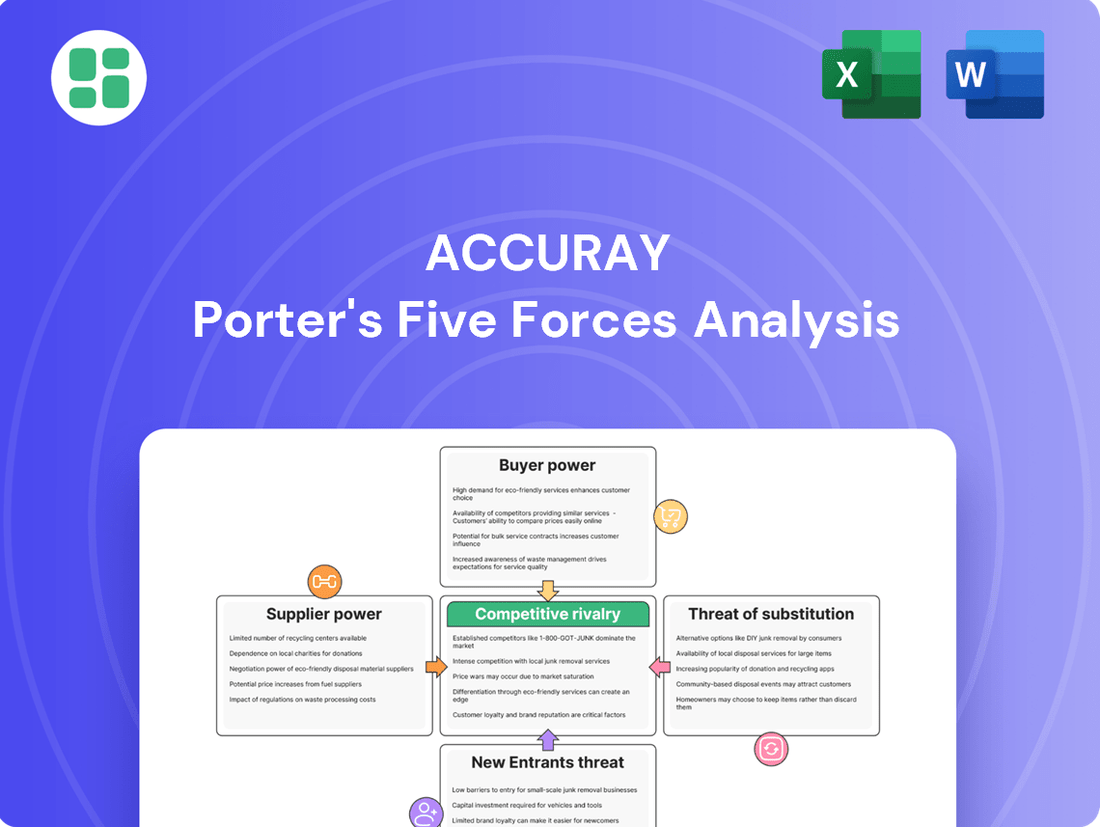
Accuray navigates a complex landscape shaped by powerful industry forces, from intense rivalry to the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for anyone looking to grasp their competitive positioning and strategic outlook.
This brief overview only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Accuray’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Accuray's reliance on a select group of suppliers for highly specialized components, like advanced imaging subsystems and precision robotic actuators, significantly bolsters supplier bargaining power. These aren't off-the-shelf parts; they're often custom-engineered to meet the exacting standards of Accuray's radiosurgery and radiation therapy systems. For instance, the development and manufacturing of a unique linear accelerator head or a high-precision robotic arm demand specialized expertise and significant capital investment from suppliers, limiting the pool of viable alternatives.
Suppliers to the medical device sector, including those serving Accuray, face rigorous regulatory mandates like FDA and ISO 13485, covering quality, safety, and performance. This regulatory landscape significantly narrows the field of qualified vendors.
The extensive compliance requirements create substantial barriers to entry and increase the expense and complexity associated with changing suppliers. Consequently, these factors bolster the negotiating leverage of established, compliant suppliers.
The medical device supply chain, including for companies like Accuray, has been navigating significant headwinds. In 2024, persistent raw material shortages and extended production lead times continued to affect the industry. For instance, the semiconductor shortage, while easing, still impacted the availability of certain electronic components crucial for Accuray's radiation therapy systems.
These ongoing disruptions grant suppliers greater leverage. When critical inputs are scarce or their cost increases, suppliers can more easily dictate terms, pricing, and delivery schedules. This situation directly impacts Accuray's ability to manage its production costs and meet customer demand efficiently, as witnessed by the increased logistics expenses reported by many medical device manufacturers throughout 2024.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Technology
Suppliers possessing proprietary intellectual property or unique manufacturing processes for critical components can significantly elevate their bargaining power. For Accuray, this could translate into substantial switching costs, as adopting alternative suppliers would necessitate considerable investment in research and development, rigorous testing, and obtaining necessary regulatory re-approvals. This technological moat effectively entrenches the influence of existing suppliers.
The reliance on specialized, patented technologies for key sub-systems, such as advanced radiation delivery mechanisms or sophisticated software for treatment planning, grants these suppliers considerable leverage. Accuray's inability to easily replicate or substitute these proprietary elements means that suppliers can dictate terms, potentially impacting pricing and supply chain stability. For instance, a supplier holding patents on a critical imaging sensor could command premium pricing, knowing Accuray has limited alternatives without extensive re-engineering.
- Proprietary Technology: Suppliers may own patents or trade secrets for essential components, limiting Accuray's substitution options.
- High Switching Costs: Integrating new suppliers requires significant R&D, testing, and regulatory hurdles, making it costly and time-consuming for Accuray.
- Supplier Leverage: Proprietary technology allows suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, potentially increasing Accuray's cost of goods sold.
- Market Dependence: Accuray's dependence on a few specialized suppliers for critical, patented technologies reinforces their bargaining power in the market.
Supplier Consolidation and Scale
Supplier consolidation in the medical device industry means fewer, larger players can dictate terms. For instance, in 2024, the global medical device contract manufacturing market saw significant M&A activity, with major players acquiring smaller specialized firms. This trend concentrates power, allowing these consolidated entities to potentially increase prices for components and services used by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) like Accuray.
These larger suppliers often provide a comprehensive suite of services, from component manufacturing and sterilization to packaging and distribution. This integration makes them highly valuable and harder for companies like Accuray to replace, thereby strengthening their bargaining position. For example, a single supplier offering end-to-end solutions can be more attractive than managing multiple vendors, giving that supplier leverage in negotiations.
- Consolidation Increases Supplier Leverage: Mergers and acquisitions in the medical device supply chain create larger, more dominant suppliers.
- Integrated Services Add Value: Suppliers offering a full spectrum of services (manufacturing, sterilization, logistics) become more critical to OEMs.
- Reduced OEM Alternatives: As suppliers consolidate, OEMs have fewer alternative sources for specialized components and services.
- Potential for Price Increases: Stronger bargaining power can translate into higher costs for OEMs.
Accuray's bargaining power with its suppliers is notably constrained by the specialized nature of its components and the stringent regulatory environment. Suppliers with proprietary technologies, such as patented imaging sensors or unique robotic actuators, hold significant sway, as switching them involves substantial R&D, testing, and regulatory re-approvals for Accuray. This reliance on unique, often patented, inputs allows these suppliers to dictate terms and pricing, impacting Accuray's cost of goods sold.
The medical device sector's regulatory demands, including FDA and ISO 13485 compliance, create high barriers to entry for new suppliers, consolidating power among existing, qualified vendors. This regulatory burden, combined with supplier consolidation through M&A activity observed in 2024, further amplifies supplier leverage. For instance, the global medical device contract manufacturing market experienced notable M&A in 2024, leading to fewer, larger suppliers capable of dictating terms and potentially increasing prices for essential components used by OEMs like Accuray.
Supply chain disruptions, such as raw material shortages and extended lead times that persisted through 2024, also empower suppliers. Scarcity of critical inputs, like specialized semiconductors, grants suppliers greater control over pricing and delivery schedules. This situation directly affects Accuray's production efficiency and cost management, as evidenced by increased logistics expenses reported across the medical device industry in 2024.
| Factor | Impact on Accuray | Supplier Leverage | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Components | High reliance on unique, custom-engineered parts | Strong | Continued demand for precision engineering |
| Proprietary Technology | Limited alternatives for patented sub-systems | Very Strong | Suppliers with unique IP can command premium pricing |
| Regulatory Compliance | High barriers to entry for new suppliers | Strong | Strict FDA/ISO standards favor established vendors |
| Supplier Consolidation | Fewer, larger suppliers dominate the market | Strong | M&A activity in 2024 concentrated market power |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Scarcity of raw materials and extended lead times | Strong | Semiconductor shortages and logistics issues persisted |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive landscape for Accuray by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the radiation oncology market.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of all five forces, enabling proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Accuray's primary customers, hospitals and cancer treatment centers, face substantial capital expenditure when acquiring radiosurgery and radiation therapy systems. For instance, CyberKnife systems, a key Accuray offering, represent a significant investment, often running into millions of dollars per unit. This high upfront cost necessitates thorough research and negotiation by these healthcare providers.
Because of the immense financial commitment involved, these customers possess considerable bargaining power. They meticulously evaluate system efficacy, long-term operational costs, and service agreements. This often translates into demands for favorable pricing, extended warranties, and flexible financing structures, all of which can influence Accuray's profitability and pricing strategies.
Healthcare systems and large purchasing groups significantly amplify customer bargaining power by consolidating demand. This aggregation allows them to negotiate more favorable terms for pricing, service agreements, and installation for medical equipment. For instance, major hospital networks can wield their substantial purchasing volume to secure concessions from medical device manufacturers like Accuray.
Healthcare providers face significant hurdles when considering a switch from established radiation therapy systems, such as Accuray's CyberKnife or TomoTherapy. The investment in a particular platform often entails substantial costs for retraining clinical staff, reconfiguring existing hospital infrastructure to accommodate new equipment, and managing potential disruptions to ongoing patient treatment schedules. These high switching costs can limit a customer's immediate leverage.
For instance, the initial capital outlay for advanced radiation therapy systems can range from millions to tens of millions of dollars, making the decision to purchase a critical one. This significant financial commitment, coupled with the operational complexities of integration and staff re-education, means that healthcare providers meticulously evaluate their options before committing to a vendor. Consequently, while switching costs reduce immediate bargaining power, they also elevate the importance of the initial purchase decision.
Demand for Value-Based Care and Outcomes
The healthcare industry's pivot towards value-based care significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Patients and providers now scrutinize not only the technological sophistication of medical equipment but also its demonstrable impact on patient recovery, cost savings, and overall efficiency.
This growing emphasis on tangible results means customers are better positioned to negotiate terms, demanding clear evidence of clinical superiority and economic advantages from Accuray's radiation therapy systems. For instance, in 2024, the global value-based healthcare market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, reflecting this fundamental shift.
- Focus on Outcomes: Healthcare purchasers prioritize solutions that prove better patient results and reduced long-term costs.
- Evidence of Efficacy: Customers demand data demonstrating clinical advantages and return on investment for new technologies.
- Cost-Effectiveness Demands: The drive for efficiency empowers buyers to seek systems offering both advanced treatment and economic benefits.
- Negotiating Leverage: This focus on value gives customers greater power to negotiate pricing and service agreements with suppliers like Accuray.
Long Sales Cycles and Public Procurement
The bargaining power of customers in the medical device industry, particularly for high-value capital equipment like those Accuray offers, is significantly influenced by long sales cycles and intricate public procurement processes. These extended decision-making pathways, often involving numerous stakeholders from clinical staff to procurement departments and finance committees, grant customers considerable leverage to scrutinize options and demand better pricing or contract terms. For instance, a typical hospital purchasing a major piece of radiotherapy equipment can take 12-24 months from initial research to final installation. This lengthy engagement allows buyers to thoroughly compare competing technologies and negotiate aggressively, directly impacting Accuray's pricing power.
Public procurement, especially within government-funded healthcare systems, adds another layer of complexity that amplifies customer bargaining power. These processes often involve competitive bidding, strict compliance requirements, and mandated price transparency. In 2024, many public health systems globally are under pressure to optimize spending, making them even more sensitive to price and value propositions. This environment necessitates that Accuray not only demonstrate technological superiority but also offer compelling financial solutions and robust service agreements to secure contracts, thereby increasing customer leverage.
The extended evaluation period inherent in these long sales cycles allows customers to:
- Thoroughly assess alternative technologies and vendors.
- Negotiate pricing, service agreements, and financing options.
- Influence product specifications based on evolving clinical needs.
- Leverage competitive bids to secure more favorable terms.
Accuray's customers, primarily hospitals and cancer treatment centers, wield significant bargaining power due to the substantial investment required for their advanced radiation therapy systems. The high upfront costs, often in the millions of dollars for systems like CyberKnife, necessitate meticulous evaluation of efficacy, operational expenses, and service contracts, leading to demands for better pricing and flexible terms.
Consolidated purchasing power from large hospital networks and group purchasing organizations further amplifies customer leverage. These entities can negotiate more favorable pricing and service agreements by aggregating demand, a trend evident in 2024 as healthcare systems sought to optimize capital expenditures.
The shift towards value-based care in healthcare also empowers customers. They increasingly demand demonstrable clinical outcomes and cost-effectiveness, pushing suppliers like Accuray to provide robust data supporting the economic and therapeutic benefits of their technologies. This focus on tangible results strengthens their negotiating position.
Long sales cycles and complex public procurement processes, often spanning 12-24 months, grant customers extended periods to scrutinize alternatives, negotiate terms, and leverage competitive bidding. In 2024, public health systems' focus on cost optimization intensified this dynamic, making price and value propositions critical for securing contracts.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point (2024) |
| High Capital Expenditure | Increases bargaining power | CyberKnife systems can cost millions, prompting detailed negotiation. |
| Consolidated Demand | Increases bargaining power | Large hospital networks leverage purchasing volume for better terms. |
| Value-Based Care | Increases bargaining power | Customers demand proven patient outcomes and cost savings. |
| Long Sales Cycles/Public Procurement | Increases bargaining power | Extended evaluation periods allow for aggressive price negotiation. |
Same Document Delivered
Accuray Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Accuray Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the radiation oncology market. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, offering actionable insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The radiation oncology and radiosurgery arena is a competitive space, largely shaped by a handful of major global entities. Companies like Varian Medical Systems, now part of Siemens Healthineers, Elekta AB, and Hitachi Ltd. are significant players, alongside Accuray itself. These established competitors bring substantial financial backing, advanced research and development infrastructure, and robust worldwide sales and service networks to the market, intensifying the rivalry.
The radiation therapy industry, where Accuray operates, is characterized by very high fixed costs. These costs stem from the immense investment required for research and development of sophisticated treatment systems, the establishment of specialized manufacturing plants, and the creation of a worldwide service and support network. For example, Accuray's CyberKnife and TomoTherapy systems represent significant technological advancements requiring ongoing R&D expenditure.
These substantial fixed costs create a strong incentive for companies to achieve high sales volumes. By maximizing the utilization of their manufacturing capacity and service infrastructure, firms can better spread these overheads, thereby lowering the per-unit cost. This drive for volume often translates into intensified price competition as players vie to capture market share and achieve greater economies of scale.
In 2023, Accuray reported total R&D expenses of $129.5 million, highlighting the continuous investment needed to maintain a competitive edge. This financial commitment underscores the capital-intensive nature of developing and manufacturing advanced medical equipment, directly contributing to the pressure to maximize sales and capacity utilization.
Competitive rivalry in the radiation oncology market is fierce, fueled by relentless innovation. Companies are constantly pushing the boundaries to differentiate their treatment systems. This often means enhancing precision, integrating artificial intelligence for smarter treatment planning, developing adaptive therapy capabilities that adjust to patient changes during treatment, and ultimately, aiming for better patient outcomes.
Accuray, for instance, strategically positions its CyberKnife and TomoTherapy platforms as offering uniquely precise treatment solutions. However, it’s crucial to recognize that rivals are not standing still; they are also rapidly advancing their technological offerings. For example, Elekta's Unity MR-Linac system provides real-time visualization during treatment, a significant differentiator.
The drive for differentiation means that companies invest heavily in research and development. Accuray's R&D spending in fiscal year 2023 was $87.2 million, a testament to this competitive landscape. This innovation race ensures that product differentiation remains a key battleground, directly impacting market share and pricing power.
Market Growth and Regional Opportunities
The global radiation oncology and radiosurgery market is set for robust expansion, fueled by increasing cancer diagnoses and the growing preference for precise treatment methods, especially in developing economies. This upward trend in market size, with projections indicating significant growth through 2025, naturally intensifies competition as companies aggressively pursue market share in these burgeoning regions.
This dynamic environment means that while opportunities are abundant, the competitive rivalry is high. Established players and new entrants alike are investing heavily in research and development and expanding their sales and distribution networks to capture a larger piece of the pie.
- Market Growth Projection: The global radiation oncology market was valued at approximately $6.5 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach over $10 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of around 9-10%.
- Emerging Market Focus: Regions like Asia-Pacific are expected to see the fastest growth, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and a rising cancer burden.
- Competitive Landscape: Key players such as Varian Medical Systems, Elekta, and Accuray are actively engaged in strategic partnerships and product innovations to maintain and expand their market positions.
- Impact of Innovation: The development of advanced technologies, including AI-powered treatment planning and adaptive radiotherapy, further fuels competition by offering differentiated solutions.
Service and Software Ecosystem Competition
Competitive rivalry in the radiation oncology sector extends significantly beyond the initial sale of hardware. Companies like Accuray are increasingly competing on the strength of their service contracts, which are crucial for ongoing maintenance and support of complex treatment machines. For instance, Accuray's service revenue represented a notable portion of its total revenue in recent periods, highlighting its importance.
Furthermore, the competition is fierce in software solutions that are integral to treatment planning and delivery. Accuray, along with competitors, offers sophisticated software that optimizes patient treatment, and this area is a key battleground for market share. The development of integrated digital health platforms, aiming to connect various aspects of patient care and data management, also fuels this rivalry, as companies strive to create comprehensive ecosystems around their core offerings to enhance customer loyalty and recurring revenue streams.
- Service Contracts: Essential for ongoing revenue and customer retention, covering maintenance, upgrades, and technical support for radiation therapy equipment.
- Software Solutions: Competition is intense in treatment planning software, AI-driven analytics, and patient management systems that enhance treatment efficacy and operational efficiency.
- Ecosystem Development: Companies are building integrated digital health platforms to create a sticky environment, linking hardware, software, and patient data, but this also invites competition from specialized healthcare IT firms.
Competitive rivalry in the radiation oncology market is intense, driven by a few dominant global players like Varian (Siemens Healthineers), Elekta, and Accuray. These companies compete fiercely on technological innovation, investing heavily in R&D to offer more precise and effective treatments. For example, Accuray's fiscal year 2023 R&D spending was $87.2 million, reflecting this commitment to staying ahead.
The high fixed costs associated with developing and manufacturing advanced radiation therapy systems, such as Accuray's CyberKnife and TomoTherapy, create pressure to maximize sales volumes. This often leads to aggressive pricing strategies and a focus on capturing market share. The global radiation oncology market, valued at approximately $6.5 billion in 2023, is projected to exceed $10 billion by 2028, further intensifying the competition as companies vie for growth.
Beyond hardware, competition extends to crucial service contracts and sophisticated software solutions for treatment planning and delivery. Companies are also building integrated digital health platforms to foster customer loyalty and recurring revenue. This multi-faceted competition, encompassing innovation, pricing, service, and software, defines the dynamic landscape.
| Company | Key Products | 2023 R&D Spend (Approx.) | Market Share (Est.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuray | CyberKnife, TomoTherapy | $87.2 million | 5-10% |
| Varian (Siemens Healthineers) | TrueBeam, Edge, Ethos | Significant (part of Siemens Healthineers) | 30-40% |
| Elekta | Versa HD, Unity MR-Linac | Significant (private company) | 20-30% |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional cancer treatments like chemotherapy, conventional surgery, and external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) represent significant substitutes for Accuray's advanced radiosurgery and stereotactic radiotherapy systems. These established modalities are broadly accessible and frequently employed as initial treatment options, contingent upon the specific cancer type and its progression. For instance, chemotherapy remains a cornerstone in treating many systemic cancers, with the global chemotherapy market valued at approximately $100 billion in 2023.
While Accuray's technologies boast superior precision and potentially reduced side effects, the widespread availability and established efficacy of traditional methods present a considerable competitive threat. Conventional surgery, for example, continues to be the primary treatment for many localized solid tumors. In 2024, the global surgical oncology market is projected to reach over $200 billion, highlighting the substantial market share occupied by these more traditional approaches.
The cost-effectiveness and familiarity of conventional treatments also contribute to their substitutability. Many healthcare systems and patients may opt for these proven, albeit less precise, methods due to established reimbursement pathways and a lower perceived barrier to entry compared to newer, specialized technologies. External beam radiation therapy, a long-standing cancer treatment, continues to be a dominant force, with significant infrastructure already in place worldwide.
The rise of advanced systemic therapies presents a substantial threat to radiation therapy. Treatments like immunotherapy, targeted drugs, and gene editing, such as CAR-T cell therapy, are becoming increasingly effective for various cancers. For instance, in 2024, the global CAR-T cell therapy market was valued at approximately $5.5 billion and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong shift towards these alternative treatment modalities.
These innovative systemic approaches can offer potent, non-radiation-based solutions that may directly compete with or even replace the role of radiation in certain oncological treatment plans. This evolving landscape means that Accuray, a leader in radiation oncology, must continually innovate to demonstrate the unique value and efficacy of its technologies against these burgeoning alternatives.
Brachytherapy, also known as internal radiation therapy, presents a significant threat of substitution for Accuray's external beam radiation systems. This method involves placing radioactive sources directly inside or near the tumor, offering an alternative treatment modality. For instance, in prostate cancer treatment, brachytherapy is a well-established option that competes directly with external beam radiation.
Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
Advances in minimally invasive surgical techniques, particularly robotic-assisted procedures, present a growing threat of substitution for radiation therapy in treating certain localized cancers. These surgical approaches allow for the precise excision of tumors, often resulting in shorter patient recovery periods compared to traditional methods, directly challenging radiation's role as a primary treatment modality.
The increasing adoption of these less invasive surgical options is a significant factor. For instance, the global robotic surgery market was valued at approximately $6.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $13.5 billion by 2028, indicating a strong market shift towards surgical solutions that can compete with or replace radiation therapy in specific oncological scenarios.
- Robotic-assisted surgery offers enhanced precision, potentially leading to better oncological outcomes and reduced side effects compared to some radiation techniques.
- Quicker recovery times associated with minimally invasive procedures can be a strong draw for patients, influencing treatment choice.
- The expanding capabilities of surgical robots are enabling them to tackle a wider range of tumor types previously considered primarily candidates for radiation.
Patient and Physician Preferences
Patient and physician preferences significantly shape the threat of substitutes for radiation therapy. The decision-making process is deeply personal, factoring in individual patient desires, the treating physician's experience, specific tumor attributes, and the anticipated side effects of various treatments. This complexity means that alternatives to radiation are continually being weighed.
The growing availability of a wide array of cancer treatment modalities, combined with a more informed and engaged patient population actively participating in shared decision-making, intensifies the evaluation of substitutes against radiation therapy. For instance, advancements in targeted therapies and immunotherapies, which offer different mechanisms of action and potential side effect profiles, present viable alternatives that patients and physicians actively consider.
- Personalized Treatment Decisions: Patient preferences, physician expertise, tumor characteristics, and side effect profiles are key drivers in selecting cancer treatments, influencing the perceived threat of substitutes to radiation therapy.
- Increasing Patient Awareness: Greater patient knowledge about diverse treatment options, including surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapies, empowers individuals to actively compare and choose alternatives to radiation.
- Shared Decision-Making: Collaborative discussions between patients and physicians, where all available treatment pathways are thoroughly evaluated, foster an environment where substitutes are constantly assessed against the benefits and drawbacks of radiation.
The threat of substitutes for Accuray's advanced radiation systems is significant, primarily stemming from established cancer treatments like chemotherapy and conventional surgery. These modalities, while less precise, are widely accessible and often the initial choice for many patients. For example, the global chemotherapy market was valued at around $100 billion in 2023, demonstrating its continued dominance.
Furthermore, innovative systemic therapies such as immunotherapy and CAR-T cell therapy are rapidly advancing, offering potent alternatives that bypass radiation altogether. The CAR-T cell therapy market alone was valued at approximately $5.5 billion in 2024, highlighting the substantial growth and adoption of these non-radiation-based treatments.
Minimally invasive surgical techniques, particularly robotic-assisted surgery, also pose a considerable threat. The global robotic surgery market reached about $6.9 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow substantially, indicating a preference for surgical solutions that can compete with or replace radiation's role in treating localized cancers.
| Treatment Modality | Market Value (Approx. 2023/2024) | Key Substitute Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | $100 Billion (2023) | Broad accessibility, established efficacy for systemic cancers |
| CAR-T Cell Therapy | $5.5 Billion (2024) | Advanced systemic therapy, non-radiation-based mechanism |
| Robotic Surgery | $6.9 Billion (2023) | Minimally invasive, enhanced precision, potentially quicker recovery |
Entrants Threaten
The high capital investment needed to enter the advanced radiosurgery and radiation therapy system market presents a significant barrier to new entrants. Developing and manufacturing these sophisticated medical devices demands substantial outlays for research, cutting-edge technology, and specialized production facilities. For instance, the development cycle for a new linear accelerator system can easily span several years and cost hundreds of millions of dollars, covering everything from initial design to regulatory approvals and clinical trials.
The medical device sector faces formidable barriers to entry due to extensive regulatory oversight. Agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European CE marking require rigorous testing and lengthy approval processes, often taking several years and substantial capital investment before a product can reach the market.
For instance, obtaining FDA clearance for a new medical device can cost millions of dollars and involve multiple stages, from pre-clinical studies to post-market surveillance. This significant financial and temporal commitment deters many potential new competitors.
Accuray's strong intellectual property, including its extensive patent portfolio for radiosurgery and radiation therapy systems, acts as a formidable barrier to new entrants. This proprietary technology makes it challenging and legally perilous for newcomers to design and market comparable products without risking patent infringement. For instance, in 2023, Accuray continued to invest heavily in R&D, further solidifying its technological lead and patent protection.
Need for Specialized Expertise and Talent
The design, development, manufacturing, and servicing of high-precision radiation therapy systems, like those offered by Accuray, require a deep bench of specialized scientific, engineering, and clinical talent. This isn't a field where generalists can easily step in; it demands individuals with advanced degrees and specific experience in areas such as medical physics, biomedical engineering, and radiation oncology. For instance, the development of Accuray's CyberKnife system involved intricate work in robotics, imaging, and precise beam delivery, all requiring highly specialized skill sets.
Attracting and retaining this caliber of talent is a significant challenge and a substantial cost for any potential new entrant. The competition for these experts is fierce, not only within the medical device industry but also from other high-tech sectors. Companies like Accuray invest heavily in recruitment and ongoing training to maintain their competitive edge, creating a barrier that's difficult for newcomers to overcome without considerable resources and established networks.
Consider the following:
- Specialized Education: Many roles require PhDs or Master's degrees in physics, engineering, or related medical fields.
- Industry Experience: Proven track records in medical device development, particularly in radiation therapy, are highly valued.
- Regulatory Knowledge: Understanding FDA and international regulatory pathways for complex medical equipment is crucial.
- Clinical Collaboration: Experience working alongside oncologists, radiation therapists, and hospital administrators is essential for product development and adoption.
Established Relationships and Brand Loyalty
Established relationships and brand loyalty present a significant barrier to new entrants in the medical technology sector, particularly for companies like Accuray, which operates in the radiation oncology market. Existing players have cultivated deep-seated connections with healthcare providers, oncologists, and medical physicists through years of collaboration and support. This loyalty is reinforced by robust brand reputations, comprehensive training programs, and seamless integration into existing clinical workflows, making it challenging for newcomers to disrupt the status quo.
For instance, in 2024, the medical device industry continued to see high customer retention rates for established brands, with many healthcare systems prioritizing continuity of care and proven performance. New entrants often face the hurdle of demonstrating equivalent or superior efficacy and reliability, alongside building trust within a highly specialized and risk-averse field.
- Long-term Partnerships: Incumbent firms have invested heavily in building trust and demonstrating value to key opinion leaders and decision-makers in healthcare institutions.
- Brand Equity: A strong brand reputation, often built over decades, signifies reliability and quality, which is paramount in life-saving medical equipment.
- Integrated Ecosystems: Established companies offer not just the primary technology but also associated software, service, and training, creating a sticky ecosystem that is difficult for new entrants to replicate.
- Switching Costs: The financial and operational costs associated with replacing existing, integrated systems can be substantial for healthcare providers, further solidifying the position of established players.
The threat of new entrants for Accuray is generally low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements for developing advanced radiosurgery and radiation therapy systems, often costing hundreds of millions for R&D and regulatory approvals, deter many potential competitors. For example, bringing a new linear accelerator to market can take years and immense investment. Furthermore, stringent regulatory hurdles from bodies like the FDA demand rigorous testing and lengthy approval processes, adding millions in costs and significant time delays, making market entry exceptionally difficult for newcomers.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Accuray is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including publicly available company financial reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings. We also integrate insights from reputable industry research firms and market intelligence platforms to capture current market dynamics and competitive landscapes.