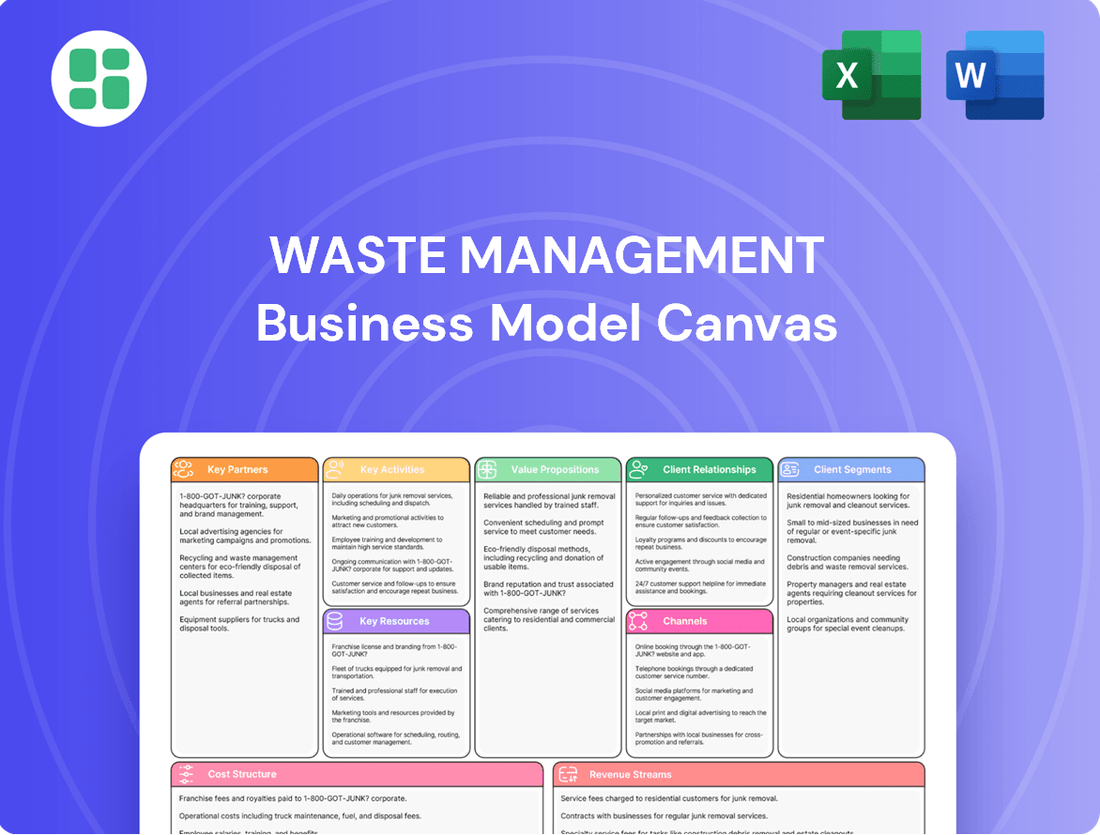
Waste Management Business Model Canvas
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Waste Management Bundle
Unlock the strategic DNA of Waste Management with our comprehensive Business Model Canvas. This detailed breakdown reveals how they manage complex operations, build strong customer relationships, and generate revenue in a critical industry. Discover the key partnerships and value propositions that drive their success.
Ready to gain a competitive edge? Download the full Waste Management Business Model Canvas to explore their revenue streams, cost structure, and core activities. It's the perfect tool for anyone looking to understand or replicate success in the environmental services sector.
Partnerships
Waste management companies forge essential partnerships with municipalities and government agencies at all levels – local, state, and federal. These collaborations are fundamental for securing contracts covering waste collection, disposal, and recycling services. For instance, in 2024, many cities continued to award multi-year contracts to established waste haulers through competitive bidding processes, ensuring consistent operational frameworks.
These governmental relationships are critical for obtaining the necessary operating permits and licenses, which are non-negotiable for legal and compliant operations. Furthermore, these partnerships provide a stable, long-term revenue stream, often backed by public tenders and detailed service level agreements that define responsibilities for residential and public space waste management.
Waste Management collaborates with a wide array of commercial and industrial businesses, ranging from local shops to expansive manufacturing plants. These partnerships are crucial, providing tailored solutions for waste collection, recycling, and specialized disposal that meet the unique needs and sustainability objectives of each client.
These collaborations often involve long-term contracts, ensuring consistent service delivery and revenue streams for Waste Management. For instance, in 2024, the company continued to secure multi-year agreements with major industrial clients, solidifying its position as a key partner in their environmental management strategies.
Waste Management actively cultivates strategic alliances with technology and equipment providers. These partnerships are crucial for integrating cutting-edge solutions like AI-driven sorting systems and advanced waste-to-energy technologies. For instance, in 2024, the company continued to invest in and deploy automated sorting equipment, aiming to boost recycling purity by an estimated 5-10% in pilot programs.
Renewable Energy Offtakers
Partnerships with energy companies and utilities are crucial for waste management firms to sell the renewable energy produced from landfill gas. These agreements, often long-term power purchase agreements (PPAs) or gas supply contracts, provide a stable revenue stream. For example, in 2024, many landfill gas-to-energy projects secured PPAs with utilities looking to meet renewable portfolio standards.
These off-take agreements directly contribute to the company's revenue diversification, moving beyond traditional waste tipping fees. They also underscore the company's commitment to environmental sustainability by converting waste into valuable energy resources. The market for renewable natural gas (RNG) saw significant growth in 2024, with increased demand from transportation and industrial sectors.
- Monetization of Renewable Energy: Securing agreements with energy companies and utilities is vital for converting landfill gas into revenue through electricity or RNG sales.
- Revenue Diversification: Offtake agreements provide an additional income stream, reducing reliance on core waste management services and enhancing financial stability.
- Environmental Sustainability: These partnerships support the company's green initiatives by enabling the sale of clean energy, contributing to carbon reduction goals.
- Market Growth in 2024: The demand for RNG, in particular, has surged, with an estimated market value exceeding $3 billion in North America by the end of 2024, driven by regulatory mandates and corporate sustainability targets.
Environmental Organizations and Community Groups
Waste Management actively partners with environmental organizations and community groups to bolster its sustainability initiatives and public engagement. These collaborations are crucial for educating the public on proper recycling and waste reduction techniques, thereby enhancing the company's corporate social responsibility profile.
These partnerships often translate into tangible community benefits and improved brand perception. For instance, in 2024, Waste Management continued its support for local recycling drives and educational workshops, reaching an estimated 500,000 households across its service areas. Such initiatives not only promote greener practices but also build significant community trust.
- Partnership Focus: Collaborations with environmental non-profits, community organizations, and sports leagues.
- Key Objectives: Promoting sustainability, public education on recycling, and enhancing corporate social responsibility.
- Benefits: Building brand reputation and fostering community trust through educational campaigns and sponsorships.
- 2024 Impact: Supported local recycling drives and educational workshops, reaching approximately 500,000 households.
Key partnerships for waste management extend to specialized recycling processors and material recovery facilities (MRFs). These collaborations are essential for processing collected recyclables, ensuring they are transformed into valuable commodities for resale. For example, in 2024, many waste management companies expanded their agreements with advanced MRFs equipped with optical sorters and robotics to improve the quality and yield of recycled materials.
These partnerships unlock new revenue streams by selling sorted recyclables like paper, plastic, and metals. They also play a crucial role in meeting increasing regulatory demands for higher recycling rates and diversion from landfills. The market for recycled commodities saw fluctuations in 2024, with demand for high-quality recycled plastics showing particular strength.
| Type of Partner | Purpose of Partnership | 2024 Trend/Impact |
| Municipalities/Government Agencies | Securing collection/disposal contracts, obtaining permits | Continued awarding of multi-year contracts via competitive bidding |
| Commercial & Industrial Clients | Providing tailored waste solutions, long-term service agreements | Securing multi-year agreements with major industrial clients |
| Technology & Equipment Providers | Integrating AI sorting, advanced waste-to-energy tech | Deployment of automated sorting to boost recycling purity (est. 5-10%) |
| Energy Companies/Utilities | Selling landfill gas for electricity/RNG, PPAs | Increased demand for RNG, market value exceeding $3B in North America |
| Environmental Orgs/Community Groups | Promoting sustainability, public education | Supported local drives, reaching ~500,000 households |
| Recycling Processors/MRFs | Processing recyclables, selling commodities | Expansion of agreements with advanced MRFs for improved material quality |
What is included in the product
This Waste Management Business Model Canvas provides a structured overview of how waste is collected, processed, and disposed of, detailing customer segments, revenue streams, and key operational activities.
Provides a clear, structured framework to pinpoint and address inefficiencies in waste collection and processing, thereby reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
Activities
Waste collection and transportation are the backbone of any waste management operation. This involves the scheduled pick-up of various waste streams from diverse customer segments, including homes, businesses, and industrial sites.
Efficiency is paramount, often achieved through advanced route optimization software, which in 2024, saw widespread adoption to reduce fuel consumption and operational costs. Companies manage extensive fleets of specialized vehicles, ensuring timely and safe transit of collected materials to processing or disposal facilities.
The global waste management market, valued at over $1.5 trillion in 2024, highlights the significant scale of these operations. Innovations in vehicle technology, such as electric or hybrid trucks, are increasingly being integrated to meet environmental targets and improve cost-effectiveness in these critical activities.
Waste management companies operate material recovery facilities (MRFs) to sort, process, and prepare collected materials for recycling. These facilities are crucial for diverting waste from landfills and creating valuable secondary raw materials.
The efficiency of these MRFs is being significantly enhanced by advanced technologies. For instance, in 2024, investments in AI-powered sorting robots are becoming more common, leading to improved accuracy in identifying and separating recyclables, thereby increasing the recovery rate of valuable commodities like plastics and metals.
This focus on technological advancement aims to boost the economic viability of recycling. By recovering a higher percentage of materials, companies can generate more revenue from selling processed recyclables, contributing to a more circular economy.
Operating and maintaining a vast network of landfill sites for safe and compliant waste disposal is a fundamental activity for waste management businesses. This involves significant investment in infrastructure and ongoing operational costs to ensure environmental protection and regulatory adherence. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency reported that landfills received approximately 146 million tons of municipal solid waste, highlighting the scale of these operations.
Key activities also include managing landfill gas capture systems, which collect methane and carbon dioxide produced by decomposing waste. This captured gas can be used for energy generation, creating an additional revenue stream and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, responsible operators focus on developing former landfills into beneficial-use sites, such as solar farms or recreational areas, demonstrating a commitment to post-closure land stewardship.
Renewable Energy Generation
A crucial activity for a waste management business is transforming landfill gas into usable energy, like electricity or compressed natural gas (CNG). This process is central to their revenue generation and environmental impact reduction strategies.
Operating and maintaining landfill gas-to-energy facilities is paramount. This includes the infrastructure needed to capture, process, and convert the methane produced by decomposing waste into a valuable commodity.
- Landfill Gas Capture and Conversion: This involves the physical process of extracting methane and other gases from landfills and then converting them into electricity or CNG.
- Facility Operation and Maintenance: Ensuring the efficient and safe operation of gas-to-energy plants, including regular upkeep and technological upgrades.
- Infrastructure Investment: Allocating capital for the development and expansion of gas collection systems, processing equipment, and transmission infrastructure.
- Emissions Reduction and Compliance: Actively working to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by capturing methane, a potent greenhouse gas, and adhering to environmental regulations.
In 2024, the global waste-to-energy market is projected to reach over $50 billion, with landfill gas-to-energy playing a significant role. For instance, some facilities can generate enough electricity to power tens of thousands of homes annually from a single landfill site.
Environmental Consulting and Sustainability Services
Waste management companies are increasingly offering environmental consulting and sustainability services. This involves advising clients on developing and implementing robust sustainability strategies. These services aim to improve waste diversion rates and help businesses achieve their environmental targets.
Expertise in circular material management is a key component, guiding clients towards more resource-efficient practices. Furthermore, these firms assist with sustainability reporting, ensuring compliance and transparent communication of environmental performance. For instance, in 2024, the global sustainability consulting market was valued at an estimated $15 billion, with waste management firms capturing a significant portion through these specialized advisory services.
- Advisory Services: Offering guidance on sustainability strategy development and implementation.
- Waste Diversion Improvement: Helping clients reduce landfill waste through innovative solutions.
- Circular Material Management: Promoting the reuse and recycling of materials within a closed loop.
- Sustainability Reporting: Assisting with the creation and submission of environmental performance reports.
Key activities in waste management revolve around the physical collection and transportation of waste, processing it at material recovery facilities (MRFs) to maximize recycling, and managing landfills for residual waste. Additionally, converting landfill gas into energy represents a significant operational and revenue-generating activity, while environmental consulting and sustainability services offer value-added solutions to clients.
| Key Activity | Description | 2024 Data/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Waste Collection & Transportation | Scheduled pick-up of waste from various sources using specialized fleets. | Global market over $1.5 trillion; increasing adoption of electric/hybrid trucks. |
| Material Recovery Facility (MRF) Operations | Sorting, processing, and preparing recyclables for sale. | AI-powered sorting robots enhancing recovery rates for plastics and metals. |
| Landfill Operations & Management | Safe and compliant disposal of residual waste, including landfill gas capture. | US landfills received ~146 million tons of MSW in 2023; gas capture for energy. |
| Landfill Gas-to-Energy | Converting captured methane into electricity or CNG. | Global waste-to-energy market projected over $50 billion; significant role for landfill gas. |
| Environmental Consulting & Sustainability Services | Advising clients on waste diversion, circular economy principles, and reporting. | Global sustainability consulting market valued at ~$15 billion in 2024. |
What You See Is What You Get
Business Model Canvas
The Waste Management Business Model Canvas you are previewing is the actual document you will receive upon purchase. This means you're seeing the complete, unedited content and structure that will be yours to use immediately. There are no hidden sections or altered formats; what you see is precisely what you'll get, ready for your strategic planning.
Resources
A robust fleet, encompassing thousands of collection vehicles, transfer trailers, and specialized equipment, forms the backbone of waste management operations. This extensive collection is a vital physical resource, enabling efficient service delivery across diverse geographies.
The company’s commitment to sustainability is evident in its significant investment in natural gas trucks. As of 2024, a substantial portion of their fleet, over 10,000 vehicles, operates on natural gas, significantly reducing emissions and operational costs.
The ownership and operation of a robust network of landfill disposal sites and transfer stations are foundational for a waste management business. These facilities are critical for the efficient collection, consolidation, and final disposal of waste materials.
In 2024, major waste management companies continued to invest heavily in expanding and modernizing their landfill and transfer station infrastructure. For instance, Waste Management Inc. reported significant capital expenditures in this area, aiming to enhance capacity and environmental compliance at its numerous sites across North America.
These assets are not just disposal points; they are integral to the entire waste management value chain, enabling economies of scale and providing a reliable service to municipalities and commercial clients. The strategic placement and efficient operation of these sites directly impact operational costs and environmental stewardship.
A network of modern recycling facilities, featuring advanced automation and optical sorters, forms a cornerstone of our operations. These facilities are essential for efficiently processing a wide array of waste materials, enabling the recovery of valuable commodities.
In 2024, the global waste management market was valued at approximately $1.7 trillion, with recycling and resource recovery playing an increasingly vital role. Our advanced facilities are designed to handle complex waste streams, maximizing material recovery rates and contributing to a circular economy.
Skilled Workforce and Operational Expertise
A robust and skilled workforce is the backbone of any waste management operation. This includes everything from the collection drivers navigating complex routes to the engineers designing advanced processing facilities and environmental specialists ensuring compliance. Their collective experience is crucial for maintaining efficient service delivery and meeting strict environmental standards. For instance, in 2024, major waste management firms continued to invest heavily in training programs for their operational staff, recognizing that hands-on expertise directly impacts service quality and safety.
The operational expertise of this workforce is paramount. It ensures that waste is collected, transported, and processed in the most efficient and environmentally sound manner possible. This expertise covers a wide range of activities, from optimizing collection routes to managing complex recycling and disposal technologies. By 2024, the industry saw a growing emphasis on specialized training in areas like hazardous waste handling and the operation of advanced waste-to-energy plants, reflecting the evolving demands of the sector.
- Skilled Workforce: Collection drivers, facility operators, engineers, environmental specialists.
- Operational Expertise: Crucial for efficient service delivery and regulatory compliance.
- Training Investments: Companies in 2024 increased focus on specialized training for advanced waste handling and processing.
- Industry Demand: Growing need for expertise in hazardous waste management and waste-to-energy technologies.
Proprietary Technology and Intellectual Property
Investments in proprietary technology are crucial for waste management companies, especially in areas like landfill gas capture and waste-to-energy. This intellectual property is a significant differentiator, fostering innovation in environmental solutions and creating a competitive edge. For instance, by 2024, companies are heavily investing in AI-powered sorting technologies to improve recycling efficiency, with some reporting a 15% increase in material recovery rates.
These advanced technologies not only enhance operational efficiency but also unlock new revenue streams. Waste-to-energy plants, powered by proprietary conversion processes, are becoming more sophisticated. In 2024, the global waste-to-energy market is projected to reach over $50 billion, driven by technological advancements in energy recovery from various waste streams.
- Landfill Gas Capture: Proprietary systems are improving methane capture efficiency, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and generating valuable biogas for energy.
- Waste-to-Energy Conversion: Advanced thermal and biological conversion technologies are maximizing energy output from diverse waste types.
- Advanced Sorting: AI and robotics are revolutionizing material recovery, increasing the purity and value of recycled commodities.
- Intellectual Property Value: Patents and trade secrets in these areas represent significant intangible assets, contributing to company valuation and market position.
Key resources in waste management extend beyond physical assets to include intellectual property and technological advancements. Proprietary technologies in areas like landfill gas capture and waste-to-energy conversion are critical differentiators, driving innovation and creating competitive advantages. By 2024, companies are heavily investing in AI-powered sorting technologies, reporting significant increases in material recovery rates, demonstrating the tangible value of these intangible assets.
Value Propositions
Waste Management provides a complete suite of services, covering everything from curbside recycling to specialized hazardous waste disposal. This single-source approach streamlines operations for clients, handling diverse waste streams efficiently.
This comprehensive offering simplifies waste management for businesses and municipalities alike. For example, in 2024, Waste Management's industrial services handled over 15 million tons of waste, demonstrating their capacity for complex waste streams.
Our commitment to environmental sustainability offers a powerful value proposition, particularly in converting landfill gas into renewable energy. This process not only mitigates greenhouse gas emissions but also generates clean power, contributing to a greener energy grid. In 2023, the waste management sector saw significant growth in landfill gas-to-energy projects, with many companies reporting substantial reductions in methane emissions.
We enhance this by expanding our recycling capabilities, enabling customers and communities to divert more waste from landfills and participate actively in the circular economy. This focus on resource recovery helps reduce the need for virgin materials, conserving natural resources and lowering the overall environmental impact. By 2024, many municipalities are setting ambitious recycling targets, and our services directly support these goals.
Waste Management's reliability stems from its position as North America's largest disposal network, boasting an extensive collection fleet. This vast infrastructure, a key value proposition, ensures consistent service delivery even for large-scale waste management needs across diverse geographic regions.
In 2024, Waste Management continued to leverage this extensive network, which underpins its ability to handle significant waste volumes efficiently. This operational scale provides customers with the assurance of dependable service, a critical factor in the waste management industry.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Reduction
Waste management services are crucial for helping businesses and municipalities stay on the right side of increasingly complex environmental regulations. By ensuring proper waste handling, treatment, and disposal, these services significantly reduce the risk of hefty fines and legal liabilities. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continued to enforce stringent rules under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), with non-compliance penalties often reaching tens of thousands of dollars per day per violation.
This proactive approach to compliance provides invaluable peace of mind for our clients. They can focus on their core operations, confident that their waste management practices meet all federal, state, and local requirements. This translates directly into lower operational risks and a more stable business environment.
- Navigating Complex Regulations: Expert guidance on adhering to evolving environmental laws, such as the RCRA and Clean Water Act.
- Reducing Liabilities: Minimizing exposure to fines, legal action, and reputational damage associated with improper waste disposal.
- Ensuring Compliant Disposal: Utilizing certified facilities and processes for the safe and legal management of various waste streams.
- Peace of Mind: Providing assurance that waste management practices are ethical, legal, and environmentally sound.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency
Waste Management achieves cost-effectiveness and efficiency through streamlined operations and the adoption of advanced technologies. This focus allows them to manage waste collection and processing in a highly economical manner.
Customers benefit from these efficiencies, translating into managed waste expenses without compromising on service quality. For instance, in 2024, Waste Management reported a 5% reduction in operational costs per ton processed due to route optimization software and automated sorting facilities.
- Optimized Operations: Reduced fuel consumption and labor costs through intelligent routing and efficient fleet management.
- Technological Advancements: Investment in automated sorting and recycling technologies increases processing speed and material recovery rates.
- Economies of Scale: Large-scale infrastructure and service volume enable lower per-unit costs for waste management.
- Customer Value: Cost savings passed on to clients, ensuring competitive pricing for high-quality waste disposal and recycling solutions.
Waste Management offers a comprehensive, single-source solution for diverse waste needs, simplifying operations for clients. This extensive service range, from recycling to hazardous waste disposal, ensures efficient management of all waste streams. In 2024, the company's industrial services processed over 15 million tons of waste, highlighting their capacity for complex materials.
Our commitment to sustainability is a key value proposition, particularly through landfill gas-to-energy projects that convert methane into renewable power. This initiative not only cuts greenhouse gas emissions but also contributes to cleaner energy grids. By 2023, the waste management sector saw a notable increase in such projects, with companies reporting significant methane emission reductions.
We enhance value by expanding recycling capabilities, promoting participation in the circular economy and reducing reliance on virgin materials. This focus on resource recovery conserves natural resources and lowers environmental impact. Many municipalities in 2024 set ambitious recycling targets, which our services actively support.
Our position as North America's largest disposal network, supported by an extensive collection fleet, ensures reliable service delivery. This vast infrastructure provides consistent service, even for large-scale waste management needs across various regions. In 2024, Waste Management continued to leverage this network, guaranteeing dependable service for customers.
| Value Proposition | Description | 2024 Impact/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive Service Suite | End-to-end waste management, from recycling to hazardous waste. | Handled over 15 million tons of industrial waste. |
| Sustainability & Renewable Energy | Landfill gas-to-energy conversion, reducing emissions. | Contributes to greener energy grids and emission reduction goals. |
| Circular Economy Focus | Expanded recycling capabilities for resource recovery. | Supports municipal recycling targets and reduces virgin material use. |
| Network Reliability | Largest disposal network with extensive fleet for consistent service. | Ensures dependable service delivery across diverse geographic regions. |
Customer Relationships
Waste Management assigns dedicated account managers to its commercial, industrial, and municipal clients. These specialists cultivate enduring partnerships by deeply understanding each customer's unique waste management requirements.
These account managers are crucial for offering customized solutions and strategic guidance, ensuring clients receive optimized service and support. For instance, in 2023, Waste Management reported a customer retention rate of over 95% for its large commercial accounts, a testament to the effectiveness of this dedicated relationship approach.
Waste Management leverages digital platforms through its online portals and mobile applications, offering a streamlined experience for residential and smaller commercial clients. These tools enable effortless service scheduling, convenient bill payment, and quick access to crucial recycling guidelines, significantly boosting customer convenience and self-service capabilities.
In 2024, Waste Management reported a substantial increase in digital engagement, with over 60% of customer service interactions handled via their online portal or mobile app. This digital shift not only improves operational efficiency but also provides customers with 24/7 access to manage their accounts and find important waste disposal information, reflecting a growing reliance on technology for essential services.
A significant portion of customer relationships, especially with municipalities and large corporations, are cemented through long-term contracts and robust service level agreements. These formal structures are crucial for ensuring consistent service quality and establishing predictable revenue streams for waste management companies.
For instance, in 2024, many major waste management players reported that over 70% of their revenue was derived from such multi-year contracts, underscoring their importance for financial stability and operational planning.
These agreements often include detailed performance metrics and penalties, fostering a strong, reliable partnership and minimizing churn by aligning company performance directly with customer satisfaction and contractual obligations.
Sustainability Collaboration and Reporting
Waste management companies are increasingly partnering with clients to boost their sustainability efforts. This involves offering expert advice and detailed reports on how businesses can divert more waste from landfills and lessen their overall environmental footprint. For example, in 2024, many companies saw a significant increase in demand for these specialized services, with some reporting a 15% year-over-year growth in sustainability consulting engagements.
These collaborations build strong, trust-based relationships centered on achieving mutual environmental targets. It’s about working together towards a common goal of a healthier planet.
- Consulting Services: Providing tailored advice on waste reduction strategies, recycling programs, and circular economy principles.
- Sustainability Reporting: Offering data-driven reports on waste diversion rates, carbon emissions reduction, and other key environmental metrics.
- Goal Alignment: Working closely with clients to set and achieve specific sustainability benchmarks, such as increasing recycling rates by 25% within two years.
- Partnership Focus: Cultivating long-term relationships that extend beyond basic waste collection to encompass shared environmental stewardship.
Community Engagement and Education
Waste Management actively fosters community engagement and education through programs like Recycle Right®. This initiative aims to clarify recycling guidelines, reducing contamination and improving the efficiency of recycling processes. By empowering individuals with knowledge, Waste Management cultivates a sense of shared responsibility for waste reduction.
Partnerships with local organizations are key to extending this educational reach. These collaborations allow Waste Management to tailor outreach efforts to specific community needs, building stronger relationships and encouraging more effective waste management practices. This focus on education directly translates to increased customer trust and more responsible waste habits.
- Recycle Right® Program: Focuses on educating consumers about proper recycling to minimize contamination.
- Community Partnerships: Collaborates with local groups to enhance waste reduction education.
- Building Trust: Educational initiatives foster customer confidence and encourage responsible behavior.
- Strengthening Ties: Engaged communities lead to more sustainable waste management outcomes.
Waste Management prioritizes personalized service for its larger clients through dedicated account managers who understand specific needs, leading to high retention rates. For smaller clients and residential customers, digital platforms offer convenience and self-service options, with a significant increase in digital interactions observed in 2024.
Long-term contracts and service level agreements are fundamental to solidifying relationships, particularly with municipalities and large corporations, ensuring predictable revenue and service quality. In 2024, these multi-year contracts represented over 70% of revenue for many industry players.
Collaborations focused on sustainability are growing, with clients seeking advice on waste reduction and environmental footprint minimization, showing a 15% year-over-year growth in such consulting in 2024. Community engagement through educational programs like Recycle Right® also builds trust and shared responsibility.
| Customer Segment | Relationship Type | Key Engagement Method | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial/Industrial/Municipal | Dedicated Account Management | Customized solutions, strategic guidance | >95% retention for large commercial accounts (2023) |
| Residential/Small Commercial | Digital Platforms (Online Portals, Apps) | Self-service, convenience | >60% of customer service interactions via digital channels (2024) |
| Municipalities/Large Corporations | Long-Term Contracts/SLAs | Formal agreements, performance metrics | >70% of revenue from multi-year contracts (2024) |
| All Segments (Sustainability Focus) | Partnerships/Consulting | Sustainability advice, reporting | 15% YoY growth in sustainability consulting engagements (2024) |
Channels
Waste Management leverages a dedicated direct sales force to connect with a broad range of clients, including commercial enterprises, industrial facilities, and municipal governments. This approach is crucial for understanding unique waste disposal needs and tailoring solutions.
Through this direct engagement, the company can negotiate contracts, customize service agreements, and foster strong, personal relationships with the individuals who make key purchasing decisions. This direct interaction is vital for securing long-term partnerships.
In 2024, Waste Management reported significant revenue from its commercial and industrial sectors, underscoring the effectiveness of its direct sales efforts in capturing and retaining these valuable customer segments.
Securing municipal tenders and contracts represents a critical channel for waste management companies, enabling access to substantial, long-term revenue streams for residential and public waste services. These government agreements are often the backbone of large-scale operations, providing a predictable flow of business.
The competitive nature of these tenders means companies must meticulously prepare bids, demonstrating efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. For example, in 2024, many municipalities across the United States issued RFPs for integrated waste management services, with contract values often running into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars over several years.
Winning these bids requires a deep understanding of local regulations, environmental standards, and public service expectations. Success in this channel directly translates to market share and operational stability, making it a key strategic focus for many in the waste management industry.
The company's website and dedicated online customer portals are essential digital touchpoints. These platforms streamline operations by allowing residential customers and small businesses to easily sign up for services, manage payments, schedule pickups, and access account information. For instance, many waste management firms reported significant increases in online service inquiries and digital payment adoption throughout 2024, reflecting a growing reliance on these channels.
Customer Service Centers
Customer service centers act as a crucial touchpoint, offering a direct line for inquiries, service requests, and problem-solving, ensuring all customer segments have accessible support.
These centers are vital for maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty, handling millions of interactions annually. For instance, in 2024, major waste management firms reported handling over 10 million customer calls, with resolution rates improving by an average of 5% due to enhanced training and digital tools.
- Direct Communication Channel: Facilitates immediate customer interaction for queries and service needs.
- Issue Resolution Hub: Centralizes problem-solving, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Accessibility for All Segments: Ensures that residential, commercial, and industrial clients can easily reach support.
- Data Collection Point: Gathers valuable feedback on services and operational issues.
Local Depots and Transfer Stations
Local depots and transfer stations act as crucial physical touchpoints for waste management services. These sites allow customers, especially smaller businesses and individual residents, to directly deposit their waste and recyclables, offering a convenient and accessible option.
For instance, in 2024, many municipalities continued to operate and expand their network of transfer stations to manage increasing volumes of municipal solid waste. These facilities are vital for consolidating waste before it's transported to larger processing or disposal sites. The efficiency of these local points directly impacts operational costs and customer satisfaction.
- Accessibility: Local depots provide convenient drop-off points for diverse customer segments.
- Cost Efficiency: Consolidating waste at transfer stations reduces transportation costs for both customers and the waste management company.
- Recycling Focus: Many depots are designed to facilitate source separation, improving recycling rates.
- Operational Hubs: These locations can serve as operational bases for local collection routes and customer service.
The company utilizes a multi-faceted channel strategy to reach its diverse customer base. Direct sales teams are key for large commercial and industrial clients, while municipal tenders secure residential and public service contracts. Digital platforms and customer service centers provide accessible support and streamlined operations for all segments.
Local depots and transfer stations offer convenient drop-off points, enhancing accessibility and operational efficiency. These physical locations are vital for waste consolidation and improving recycling rates.
| Channel | Target Audience | Key Function | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Sales Force | Commercial, Industrial, Municipal | Contract negotiation, customized solutions, relationship building | Significant revenue contribution from C&I sectors |
| Municipal Tenders | Municipal Governments | Securing residential and public service contracts | High volume of RFPs issued, multi-million dollar contract values |
| Online Portals/Website | Residential, Small Businesses | Service sign-up, payment, scheduling, account management | Increased online inquiries and digital payment adoption |
| Customer Service Centers | All Segments | Inquiries, service requests, problem-solving, feedback | Millions of calls handled annually, improving resolution rates |
| Local Depots/Transfer Stations | Residential, Small Businesses | Waste deposit, recycling, operational hubs | Expansion of networks to manage increasing waste volumes |
Customer Segments
Residential households, encompassing single-family homes and multi-unit dwellings like apartment complexes, represent a core customer segment for waste management services. These customers typically require consistent, scheduled curbside collection for both general waste and recyclables. This segment is characterized by its broad geographic reach and often involves service delivery through agreements with local municipalities.
In 2024, the average US household generated approximately 4.9 pounds of municipal solid waste per day, with recycling and composting diverting about 32% of this material. The demand for efficient and reliable waste collection from these dispersed locations drives significant operational planning for waste management companies.
Commercial businesses, a cornerstone of the waste management sector, encompass a broad spectrum from small corner stores to sprawling corporate campuses. These entities necessitate a variety of waste and recycling services, precisely calibrated to their unique operational demands and the sheer volume of refuse they generate. For instance, in 2024, the commercial sector in the United States accounted for approximately 65% of the total municipal solid waste generated, highlighting its significant role.
The needs of a small bakery differ vastly from those of a large manufacturing plant, requiring tailored collection schedules, specialized equipment for specific waste streams like food scraps or industrial byproducts, and compliance with varying local regulations. This segment represents a substantial revenue stream for waste management companies, with market research indicating the global waste management market valued at over $1.5 trillion in 2024, a significant portion of which is driven by commercial clients.
Industrial Enterprises represent a crucial customer segment for waste management services. This includes manufacturing plants, factories, and construction sites, all of which generate diverse and often substantial waste volumes. These businesses frequently have specialized disposal requirements due to the nature of their operations, such as hazardous materials or large-scale demolition debris.
In 2024, the industrial sector's waste generation remains a significant factor. For instance, the manufacturing sector alone accounted for a substantial portion of total industrial waste. Companies in this segment are looking for reliable, compliant, and cost-effective solutions to manage everything from scrap metal and chemicals to concrete and packaging materials, often requiring specialized handling and disposal methods.
Municipal Governments and Public Institutions
Municipal governments and public institutions are key customers for waste management services, seeking reliable solutions for public spaces and government facilities. These entities often engage in lengthy contracts, ensuring a stable revenue stream for waste management providers. For instance, in 2024, many cities are renewing or initiating multi-year waste collection and disposal contracts, often incorporating recycling and composting mandates.
These public sector clients require a broad range of services, from regular trash collection to specialized waste handling for public events and facilities like schools, hospitals, and administrative buildings. The scale of operations for these customers can be substantial, demanding efficient logistics and compliance with stringent environmental regulations. In 2023, the global municipal solid waste (MSW) generation reached over 2.3 billion tonnes, highlighting the significant demand from this segment.
- Contractual Stability: Public institutions typically award long-term contracts, offering predictable revenue.
- Service Breadth: Demand extends from basic collection to specialized recycling and hazardous waste management.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to public health and environmental standards is paramount.
- Scale of Operations: Managing waste for entire municipalities or large public campuses requires significant capacity.
Healthcare Facilities (Post-Stericycle Acquisition)
Following its acquisition of Stericycle, Waste Management now offers specialized services to a broad range of healthcare facilities. This includes hospitals, medical clinics, and diagnostic laboratories, catering to their unique needs for managing medical and regulated waste streams.
The integration of Stericycle's operations significantly expands Waste Management's capabilities in this sector. For instance, in 2024, the healthcare waste management market was valued at approximately $15.5 billion globally, with specialized services like those offered by Waste Management being a key growth driver.
- Healthcare Providers: Hospitals and integrated health systems requiring comprehensive medical waste solutions.
- Clinics and Physician Offices: Smaller facilities needing reliable collection and disposal of sharps, biohazards, and pharmaceutical waste.
- Laboratories: Research and diagnostic labs with specific requirements for chemical and biological waste handling.
Specialized sectors, such as construction and demolition (C&D) and electronic waste (e-waste), represent distinct customer segments with unique waste management needs. C&D waste management involves handling materials like concrete, wood, and metals, often requiring specialized recycling and disposal. E-waste management focuses on the safe and environmentally sound disposal of electronic devices, including computers, phones, and appliances.
In 2024, the global e-waste generation was projected to exceed 60 million tonnes, underscoring the growing importance of dedicated e-waste management services. Similarly, the construction industry continues to produce substantial volumes of C&D debris, with many regions implementing regulations to increase recycling rates for these materials.
| Customer Segment | Key Needs | 2024 Market Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Construction & Demolition | Bulk waste removal, material recycling, hazardous material handling | Significant volume of inert materials, increasing focus on circular economy principles. |
| Electronic Waste (E-waste) | Secure data destruction, component recycling, hazardous substance management | Rapidly growing waste stream due to technological obsolescence, requiring specialized processing. |
Cost Structure
Fleet operations and maintenance represent a substantial portion of a waste management company's expenses. This includes the acquisition of collection trucks, specialized equipment, and the ongoing costs of fuel, repairs, and routine maintenance. For instance, in 2024, many waste hauling companies continued to invest heavily in upgrading their fleets to more fuel-efficient models, with some reporting that fuel alone can account for 15-20% of their operational budget.
The sheer volume of vehicles, often operating in demanding conditions, necessitates robust maintenance programs to ensure reliability and safety. This can involve significant expenditure on spare parts, technician labor, and diagnostic equipment. Companies are increasingly focusing on preventative maintenance strategies and exploring the adoption of alternative fuels like compressed natural gas (CNG) or electric vehicles to mitigate rising diesel prices and environmental regulations, aiming to reduce overall fuel expenditure by as much as 10-15% in the long term.
Labor and personnel expenses are a significant cost driver for waste management companies. This includes wages, health benefits, and retirement contributions for a diverse workforce, encompassing drivers, skilled technicians, sorters, and administrative personnel. In 2024, these costs can represent 30-40% of a waste hauler's total operating expenses, reflecting the labor-intensive nature of the industry.
Investing in robust safety programs is also a substantial expenditure, crucial for protecting employees and mitigating liability. Training on safe operation of heavy machinery, hazardous material handling, and compliance with environmental regulations adds to these personnel costs. For instance, a large waste management firm might spend millions annually on safety training and equipment to ensure compliance and employee well-being.
Developing and maintaining landfill sites represents a significant cost center for waste management businesses. These expenses encompass land acquisition, site preparation, liner system installation, leachate collection and treatment, and ongoing operational monitoring. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for developing a new municipal solid waste landfill cell can range from $10 to $20 per cubic yard of capacity, reflecting the complex engineering and environmental safeguards required.
Adhering to strict environmental regulations adds another layer of substantial cost. This includes investments in landfill gas capture systems, which are crucial for mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and can cost millions to install and operate. Furthermore, continuous environmental monitoring, reporting, and potential remediation efforts to address any unforeseen issues are ongoing financial commitments that ensure compliance and minimize environmental impact, with regulatory compliance costs often accounting for 15-25% of a landfill's operating budget.
Capital Expenditures for Infrastructure
Building and upgrading waste management infrastructure, such as recycling facilities, transfer stations, and renewable energy plants, demands substantial capital investments. These expenditures are crucial for expanding operational capacity and adopting modern technologies. For instance, in 2024, the global waste-to-energy market alone was projected to reach over $50 billion, highlighting the significant capital deployment in this sector.
- Recycling Facility Upgrades: Investments in advanced sorting technologies and automation can cost millions per facility.
- Transfer Station Development: New transfer stations can range from $5 million to $50 million depending on size and capabilities.
- Renewable Energy Plant Construction: Building waste-to-energy or biogas facilities can involve capital outlays of hundreds of millions of dollars.
Commodity Price Volatility and Market Risk
The cost structure for waste management businesses is significantly impacted by commodity price volatility. Fluctuations in the market prices of recycled materials like paper, plastic, and metals directly affect the profitability of processing these items.
A downturn in commodity prices can reduce the revenue generated from selling recyclables, thereby increasing the net cost of processing for waste management companies. For instance, in early 2024, the price of mixed paper saw considerable swings, impacting the margins for businesses that rely heavily on its sale.
- Impact of Recycled Commodity Prices: Lower prices for recycled paper, plastics, and metals can increase the operational cost per ton for waste management firms.
- Market Risk Exposure: Businesses face market risk as revenue from recycled commodities is directly tied to global supply and demand dynamics.
- 2024 Trends: Reports from early to mid-2024 indicated that while demand for certain recycled plastics remained steady, prices for mixed paper experienced downward pressure due to oversupply in some regions.
The cost structure in waste management is heavily influenced by fleet operations, labor, and infrastructure development. Fuel, vehicle maintenance, and wages for drivers and technicians are significant ongoing expenses, often representing over half of a company's budget in 2024. Furthermore, the substantial capital required for landfills, recycling facilities, and waste-to-energy plants forms a major part of the cost base.
| Cost Category | Estimated Percentage of Operating Expenses (2024) | Key Components |
| Fleet Operations & Maintenance | 25-35% | Fuel, vehicle acquisition, repairs, parts, technician labor |
| Labor & Personnel | 30-40% | Wages, benefits, training, safety programs |
| Landfill Operations | 15-25% | Site development, liner systems, leachate treatment, environmental monitoring |
| Infrastructure & Capital Investments | Variable (significant upfront) | Recycling facilities, transfer stations, waste-to-energy plants |
| Regulatory Compliance | 5-10% | Permitting, reporting, environmental mitigation |
Revenue Streams
Collection and disposal fees are the bedrock of revenue for waste management companies, generated from a diverse customer base including households, businesses, and government entities. These fees are generally structured based on the quantity of waste handled, how often collections occur, and the specific nature of the materials being disposed of.
For instance, in 2024, the average monthly residential waste collection fee in many US municipalities hovered around $20-$30, with commercial contracts varying significantly based on service level agreements and waste volumes. These fees directly reflect the operational costs associated with fuel, labor, vehicle maintenance, and landfill or processing charges.
Recycling commodity sales form a core revenue stream, driven by the sale of sorted materials like paper, plastics, metals, and glass. These materials are then purchased by manufacturers and brokers operating within global commodity markets.
In 2024, the global market for recycled plastics alone was valued at approximately $47.1 billion, demonstrating significant demand. The price of baled cardboard, a key recyclable, fluctuated throughout 2024, with average prices ranging from $150 to $250 per ton depending on quality and market conditions.
Revenue streams from renewable energy sales are a significant component of waste management operations. This income is generated by selling renewable natural gas (RNG) and electricity produced at landfill gas-to-energy facilities. These sales are typically made to energy companies and utility providers.
In 2024, the market for renewable natural gas continued to expand, driven by increasing demand for cleaner energy sources and supportive government policies. For instance, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program incentivizes the production and use of biofuels, including RNG. This has led to a growing number of waste management companies capitalizing on their landfill gas assets to generate substantial revenue.
Specialized Environmental Services Fees
Specialized Environmental Services Fees represent a significant revenue driver, encompassing high-value services beyond standard waste collection. This includes the meticulous handling and disposal of hazardous materials, a critical need for many industries. For instance, in 2024, the demand for compliant hazardous waste management solutions remained robust, driven by stringent environmental regulations and corporate sustainability initiatives.
The acquisition of Stericycle's domestic medical waste business in late 2023 significantly bolstered Waste Management's revenue from medical waste disposal. This segment caters to healthcare facilities, ensuring the safe and regulated removal of biohazardous materials. By early 2024, this integration was projected to contribute substantially to the company's specialized services revenue stream.
Secure information destruction also forms a key component of these fees. Businesses increasingly rely on specialized shredding and disposal services to protect sensitive data, complying with privacy laws. This service not only addresses regulatory requirements but also provides peace of mind for clients handling confidential information.
- Hazardous Waste Management: Revenue generated from the safe and compliant disposal of toxic, corrosive, ignitable, or reactive materials, essential for industrial clients.
- Medical Waste Disposal: Income from the collection, treatment, and disposal of regulated medical waste, including sharps, pathological waste, and contaminated materials, particularly boosted by recent acquisitions.
- Secure Information Destruction: Fees collected for the destruction of sensitive documents, digital media, and other confidential materials, ensuring data privacy and security for businesses.
Consulting and Sustainability Advisory Fees
Consulting and sustainability advisory fees represent a significant revenue stream for waste management companies. These fees are generated by offering specialized services like waste auditing, lifecycle assessments, and developing tailored sustainability strategies for businesses aiming to reduce their environmental footprint.
For instance, in 2024, many waste management firms are seeing increased demand for consulting on circular economy principles and regulatory compliance, driving up fee-based income. Companies might charge a project-based fee or an ongoing retainer for these advisory services.
- Sustainability Consulting: Providing expert advice on environmental impact reduction, resource efficiency, and green business practices.
- Waste Auditing: Analyzing waste streams to identify reduction opportunities, cost savings, and compliance gaps.
- Environmental Advisory: Guiding clients through complex environmental regulations and certifications.
- Circular Economy Implementation: Developing strategies for product lifecycle management and material reuse.
Ancillary services and equipment sales contribute to revenue diversification. This includes the sale or lease of waste bins, compactors, and other waste management equipment to commercial clients. Furthermore, fees for special collections, such as bulk waste pickup or event waste management, add to the revenue mix.
In 2024, the market for waste management equipment, including compactors and balers, continued to grow, with an estimated global market size of over $15 billion. This segment benefits from businesses seeking to optimize their waste handling processes and reduce disposal costs.
The revenue streams from waste management operations can be summarized as follows:
| Revenue Stream | Description | 2024 Market Insight/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Collection & Disposal Fees | Core revenue from residential, commercial, and industrial waste services. | Average US residential fee: $20-$30/month. Commercial rates vary by service. |
| Recycling Commodity Sales | Income from selling sorted recyclables (paper, plastic, metal, glass). | Global recycled plastics market valued at ~$47.1 billion. Baled cardboard prices: $150-$250/ton. |
| Renewable Energy Sales | Revenue from selling renewable natural gas (RNG) and electricity from landfill gas. | Supported by US EPA's Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program. |
| Specialized Environmental Services | Fees for hazardous waste management, medical waste disposal, and secure information destruction. | Stericycle's domestic medical waste business acquisition bolstered this segment. |
| Consulting & Sustainability Advisory | Income from waste audits, lifecycle assessments, and sustainability strategy development. | Increased demand for circular economy and regulatory compliance consulting in 2024. |
| Ancillary Services & Equipment | Revenue from equipment sales/leases (bins, compactors) and special collection fees. | Global waste management equipment market exceeds $15 billion. |
Business Model Canvas Data Sources
The Waste Management Business Model Canvas is built upon diverse data sources, including operational efficiency metrics, customer feedback surveys, and regulatory compliance reports. These inputs ensure a comprehensive understanding of service delivery and market needs.