TT Electronics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
TT Electronics Bundle
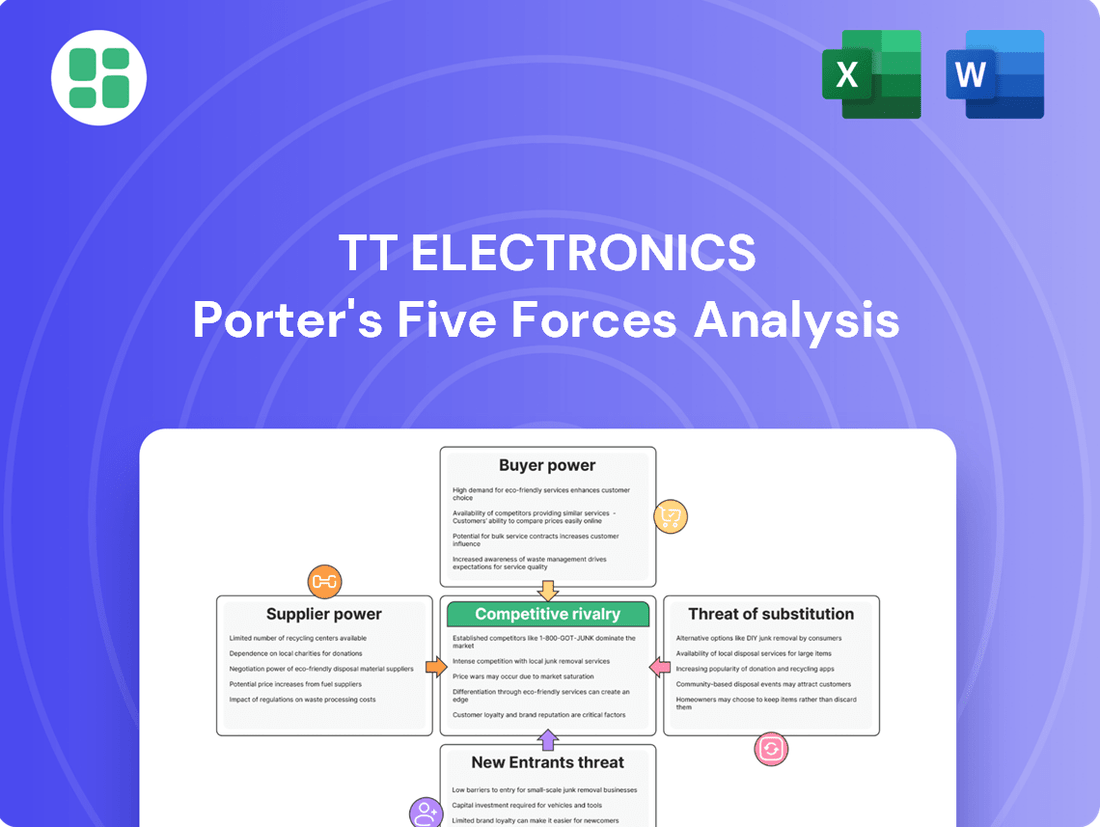
TT Electronics operates in a competitive landscape shaped by several key forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of substitutes and new entrants is crucial for strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore TT Electronics’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
TT Electronics' reliance on specialized inputs for demanding sectors like aerospace and defense means a limited supplier pool for critical components. For instance, the global market for certain high-performance semiconductors, essential for TT Electronics' advanced solutions, is dominated by a handful of manufacturers. This concentration grants these suppliers significant leverage, allowing them to influence pricing and supply availability.
Switching costs for TT Electronics can be quite significant. For instance, re-tooling manufacturing lines to accommodate a new supplier's components can incur substantial capital expenditure. In 2023, capital expenditures for TT Electronics were £38.6 million, illustrating the scale of investment in their production capabilities, which would need to be replicated for a new supplier.
Furthermore, in highly regulated sectors like aerospace or automotive, where TT Electronics operates, re-certifying components from a new supplier is a time-consuming and costly process. This often involves rigorous testing and documentation, adding to the expense and delay of switching. Such hurdles effectively lock TT Electronics into existing supplier relationships, thereby increasing supplier bargaining power.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers poses a significant challenge for TT Electronics. If suppliers decide to produce electronic components or integrated solutions themselves, they would directly enter into competition with TT Electronics, potentially disrupting established supply chains and market dynamics.
This risk is amplified when suppliers possess unique technologies or substantial manufacturing capacity. For instance, a supplier with advanced semiconductor fabrication capabilities could begin offering finished modules, directly encroaching on TT Electronics' business segments. Such a move would not only create a competitor but also potentially limit TT Electronics' access to crucial inputs, thereby increasing supplier bargaining power.
Importance of Supplier's Input to TT Electronics' Cost Structure
The proportion of TT Electronics' total costs tied to a supplier's input directly influences that supplier's bargaining power. When a supplier provides critical, high-value components that are essential for TT Electronics' product performance, the supplier gains significant leverage. This is because any price increase or supply disruption from such a supplier can substantially impact TT Electronics' profitability and its ability to offer competitive pricing.
For instance, in 2024, TT Electronics' cost of goods sold was approximately £500 million. If a significant portion of this, say 30% or £150 million, was attributable to a single supplier's specialized electronic components, that supplier would hold considerable sway. This necessitates careful management of these supplier relationships to mitigate risks and maintain cost control.
- Critical Components: Suppliers of high-performance, specialized electronic components that are difficult to substitute hold greater power.
- Cost Significance: The larger a supplier's input is as a percentage of TT Electronics' total cost of goods sold, the more leverage that supplier possesses.
- Supply Chain Dependency: If TT Electronics relies heavily on a few suppliers for essential materials or components, those suppliers' bargaining power increases.
- Impact on Pricing: Suppliers of key inputs can influence TT Electronics' final product pricing by dictating their own component costs.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly curtails the bargaining power of suppliers for TT Electronics. When TT Electronics can readily find alternative materials or components, or adopt new technologies, the leverage of any individual supplier is weakened. This flexibility allows TT Electronics to negotiate more favorable terms and maintain cost control.
In 2024, the electronics components market saw continued innovation in materials science and manufacturing processes. For instance, advancements in semiconductor fabrication and the increasing use of specialized polymers offer viable alternatives to traditional materials. This diversification of input options means TT Electronics is less reliant on any single supplier, thereby reducing their ability to dictate terms or prices.
- Reduced Supplier Leverage: The presence of substitutes directly diminishes a supplier's ability to command higher prices or impose unfavorable terms.
- Increased Sourcing Flexibility: TT Electronics can switch between suppliers or input types if one becomes too costly or unreliable.
- Technological Adoption: Embracing new technologies often introduces new material options, further fragmenting supplier power.
Suppliers of critical, specialized components for TT Electronics, particularly in sectors like aerospace and defense, wield significant bargaining power. This is due to a limited supplier base for high-performance inputs, such as advanced semiconductors, where a few manufacturers dominate the market. The substantial costs and time involved in re-certifying components, as seen in 2023's £38.6 million capital expenditure, further entrench TT Electronics with existing suppliers, amplifying their leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers is also heightened when their products represent a significant portion of TT Electronics' costs. For example, if a single supplier's components accounted for 30% of TT Electronics' estimated £500 million cost of goods sold in 2024, that supplier would possess considerable influence over pricing and supply. The threat of forward integration by these suppliers, especially those with proprietary technology, also increases their power by potentially creating direct competition.
| Factor | Impact on TT Electronics | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High | Limited manufacturers for high-performance semiconductors |
| Switching Costs | High | Re-tooling and re-certification processes |
| Cost of Goods Sold (2024 Estimate) | £500 million | Supplier input as a percentage of COGS impacts leverage |
| Capital Expenditure (2023) | £38.6 million | Indicates investment scale for production, affecting switching costs |
| Availability of Substitutes | Moderate to High | Advancements in materials science and new technologies offer alternatives |
What is included in the product
This analysis meticulously examines the five competitive forces impacting TT Electronics, offering insights into industry rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a clear, visual representation of TT Electronics' Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
TT Electronics operates in specialized sectors like industrial, medical, and aerospace, which can mean a smaller base of major clients. This concentration means a few large customers can wield significant bargaining power simply due to the sheer volume of their orders and their importance to TT Electronics' overall sales figures.
The degree to which TT Electronics' products are standardized or customized significantly influences customer bargaining power. For highly specialized, engineered solutions designed for demanding, performance-critical applications, customers face substantial switching costs and technical hurdles when considering alternative suppliers. This inherent difficulty in changing providers inherently limits their ability to negotiate aggressively.
Conversely, when TT Electronics offers more standardized or commoditized electronic components, the landscape shifts. In these segments, customers have a wider array of choices from various manufacturers. This increased availability of alternatives empowers them to exert greater pressure on TT Electronics, demanding more favorable pricing, better payment terms, or enhanced service levels.
Customer switching costs are a significant factor in the aerospace and medical sectors where TT Electronics operates. In these mission-critical industries, changing suppliers often necessitates extensive and costly re-qualification procedures for components, potentially involving months of testing and regulatory approvals. For instance, a new semiconductor supplier for an aircraft's flight control system would require a complete re-validation of its performance and reliability, a process that can easily cost hundreds of thousands of dollars and significantly delay product launches.
These high barriers to switching mean that customers have less leverage to demand lower prices or more favorable terms from TT Electronics. The investment in time, money, and the inherent risk of introducing a new, unproven component into a critical system effectively locks customers into their existing relationships, thus diminishing their bargaining power.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity for TT Electronics is a key factor in their bargaining power. If a component TT Electronics supplies is essential for a customer's product performance and reliability, even if it represents a smaller portion of the total cost, customers are likely to tolerate higher prices. This is because the risk of failure or poor performance from a cheaper, less reliable alternative outweighs the cost savings.
Conversely, in applications where the electronic component is a significant cost driver for the end product and its function is less critical, customers will exhibit much higher price sensitivity. In these scenarios, TT Electronics faces greater pressure to compete on price, potentially reducing their profit margins.
- Price Sensitivity Drivers: Criticality to end-product performance versus cost contribution.
- TT Electronics' Advantage: High criticality allows for greater pricing power.
- Market Pressure: Cost-driven applications necessitate competitive pricing.
- 2024 Data Insight: While specific TT Electronics customer price sensitivity data isn't publicly detailed, the broader electronics component market in 2024 saw continued demand for high-reliability parts in sectors like automotive and aerospace, supporting premium pricing for critical components.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Customers, especially significant players in industrial and defense sectors, possess the potential and motivation to develop their own electronic components or sub-assemblies. This capability for backward integration directly amplifies their bargaining leverage.
TT Electronics must consistently deliver compelling and value-added solutions to dissuade these customers from pursuing in-house production, thereby maintaining their reliance on TT Electronics as a supplier.
- Threat of Backward Integration: Large customers in sectors like aerospace and defense may have the technical expertise and financial resources to manufacture critical electronic components internally.
- Customer Leverage: If customers can effectively integrate backward, they can reduce their dependence on TT Electronics, leading to greater price sensitivity and demands for better terms.
- TT Electronics' Response: To counter this, TT Electronics needs to focus on innovation, cost efficiency, and superior service to remain the preferred supplier.
- Market Dynamics: For instance, in 2024, the increasing complexity of defense electronics might make backward integration more challenging for some customers, but the drive for supply chain security remains a strong motivator.
The bargaining power of TT Electronics' customers is influenced by order volume and the concentration of its client base. In specialized sectors like aerospace and medical, where TT Electronics operates, a few major clients can command significant influence due to their substantial order sizes, directly impacting TT Electronics' revenue streams and sales figures.
Switching costs play a crucial role, especially in critical industries. For highly engineered or customized components, the expense and time involved in re-qualifying new suppliers, potentially costing hundreds of thousands of dollars as seen in aerospace in 2024, severely limit customers' ability to switch, thus reducing their bargaining power.
Customer price sensitivity is heightened when TT Electronics' components are significant cost drivers for the end product. In such cases, customers exert greater pressure for lower prices, potentially impacting TT Electronics' profit margins, though this is balanced by the high-value proposition of critical components where reliability trumps cost.
The potential for customers to integrate backward and produce components in-house also grants them leverage. While the increasing complexity of defense electronics in 2024 might make this more challenging, the drive for supply chain security remains a motivator for some large clients, compelling TT Electronics to continuously offer superior value.
| Factor | Impact on TT Electronics | Customer Leverage | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High dependence on key clients | Significant for large volume buyers | Specialized sectors maintain client concentration |
| Switching Costs | High in aerospace/medical | Low ability to switch due to re-qualification | Regulatory hurdles remain high in critical industries |
| Price Sensitivity | Varies by component criticality | High for cost-significant, low-criticality parts | Demand for high-reliability parts supported premium pricing |
| Backward Integration Threat | Risk of losing business to in-house production | Potential to reduce supplier dependence | Supply chain security a key driver for integration considerations |
Same Document Delivered
TT Electronics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete TT Electronics Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of industry competition and profitability. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises and full readiness for your strategic planning. You can trust that this comprehensive analysis is precisely what you'll be able to download and utilize without delay.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The electronic components and integrated solutions market is populated by a diverse array of players, from large global corporations to highly specialized niche firms. This broad spectrum of competitors, each with varying sizes and strategic aims, fuels intense rivalry. For instance, in 2024, the global electronic components market was valued at hundreds of billions of dollars, indicating a significant number of participants vying for a piece of this substantial pie.
This competitive landscape means companies like TT Electronics face pressure not only from other large, diversified manufacturers but also from smaller, agile companies that excel in specific technological areas. This dynamic can lead to aggressive pricing strategies and a constant push for innovation as firms battle for market share and technological leadership.
The overall growth rate across TT Electronics' key markets—industrial, medical, aerospace, and defense—significantly influences competitive rivalry. When these sectors experience slower growth, the fight for existing market share intensifies, often resulting in increased price competition as companies vie for a larger portion of a less expanding market. For instance, a slowdown in industrial automation could directly impact the pricing strategies of electronic component suppliers.
Conversely, robust growth in specific areas can temper this rivalry. Sectors like healthcare technology and electrification, which are projected to see substantial expansion through 2024 and beyond, offer ample opportunities for multiple players to grow without directly cannibalizing each other's market share. This high-growth environment allows companies to focus on innovation and capacity expansion rather than solely on aggressive pricing tactics.
TT Electronics thrives on engineered electronics and cutting-edge technologies tailored for demanding applications, a strategy that directly influences competitive rivalry. The industry's intensity is amplified by how well companies differentiate their products and how quickly they innovate.
Companies that consistently introduce novel solutions, protect their inventions with patents, and clearly distinguish their products can achieve premium pricing and maintain a strong market position. This is evident in TT Electronics' commitment to research and development, with significant investments aimed at fostering this innovation pipeline.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
TT Electronics faces intensified competition due to high exit barriers for its rivals. Specialized manufacturing assets, like advanced semiconductor fabrication equipment, represent significant sunk costs that make it difficult for companies to simply shut down operations. For instance, the capital expenditure for a new wafer fabrication plant can easily run into billions of dollars, locking companies into continued production even when market demand is weak.
Long-term customer contracts also act as a powerful exit barrier. Companies committed to supplying components for extended periods, perhaps for automotive or aerospace programs, cannot easily divest themselves of these obligations. This contractual commitment can keep even financially strained competitors active, contributing to market overcapacity. In 2024, many electronics manufacturers reported extended lead times for critical components, suggesting that capacity utilization remains high, partly due to these entrenched commitments.
The electronics industry, particularly in segments like power management or sensor technology where TT Electronics operates, often involves high fixed costs associated with research and development, testing, and regulatory compliance. These substantial fixed costs compel companies to continue operating to spread them over a larger production volume, even if profitability is marginal. This dynamic can lead to aggressive pricing strategies and price wars as competitors fight to maintain market share and cover their overheads.
- Specialized Assets: High capital investment in manufacturing equipment creates significant financial hurdles for exiting competitors.
- Contractual Obligations: Long-term supply agreements lock companies into continued production, limiting their ability to withdraw.
- High Fixed Costs: Substantial R&D and operational expenses necessitate continued production to achieve economies of scale.
- Market Dynamics: These barriers can result in overcapacity and price competition, even during economic downturns.
Strategic Stakes and Acquisitions
The electronic components market is highly strategic, attracting significant interest from large, diversified conglomerates. This interest often translates into aggressive competition, particularly through mergers and acquisitions, as companies vie for market share and technological advantage. For instance, TT Electronics itself has been the subject of acquisition interest, highlighting the perceived value and strategic importance of its operations within the broader electronics landscape.
The trend of consolidation in the electronics sector means that companies are frequently looking to acquire competitors or divest non-core assets to strengthen their market position. This dynamic can significantly intensify rivalry, as players seek to secure critical technologies, expand their geographical reach, or achieve economies of scale. The ongoing M&A activity underscores the high stakes involved in this competitive arena.
- Strategic Importance: The electronic components sector is a key area for diversified conglomerates seeking to enhance their technology portfolios and market access.
- Consolidation Trend: Mergers and acquisitions are a significant driver of competitive intensity, as companies aim to gain strategic advantages.
- Acquisition Activity: TT Electronics' history of being a target for acquisition attempts, alongside its own divestments, demonstrates the active M&A environment.
- Market Reach and Technology: Companies compete fiercely to acquire essential technologies and expand their market presence through strategic deals.
The competitive rivalry within the electronic components and integrated solutions market is fierce, driven by a large number of players ranging from global giants to niche specialists. This intensity is further fueled by the strategic importance of the sector, leading to significant merger and acquisition activity as companies seek to bolster their market share and technological capabilities. For example, the global market for semiconductors, a core component of many electronic systems, was projected to reach over $600 billion in 2024, indicating a massive arena with numerous participants.
Companies like TT Electronics must constantly innovate and differentiate their offerings to stand out. This is particularly true in high-growth sectors like medical technology and electrification, which are expanding rapidly through 2024, offering opportunities for multiple players to grow without direct conflict. However, in slower-growing industrial or automotive segments, price competition can become more pronounced as firms fight for a larger slice of a less expanding pie.
High exit barriers, such as specialized manufacturing assets and long-term contracts, keep even struggling competitors in the market, contributing to potential overcapacity and price pressures. Furthermore, substantial fixed costs in R&D and compliance necessitate continuous operation to spread these expenses, reinforcing the competitive drive to maintain sales volumes. This environment demands continuous investment in innovation, as demonstrated by TT Electronics' focus on advanced technologies for demanding applications.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Technological leaps in areas like advanced materials and software-defined functionalities pose a significant threat of substitution for TT Electronics. For example, the rise of wireless power transfer could diminish demand for traditional wired connectors, a core product area for many electronics manufacturers. In 2024, global investment in research and development for new energy solutions, including wireless charging, saw a substantial increase, indicating a growing market for these alternatives.
Customers constantly weigh the price and performance of substitutes against TT Electronics' products. If a rival solution offers similar functionality for less money, or better performance at the same price point, the threat escalates. This is especially true in segments where cost is a primary driver, such as in the high-volume consumer electronics sector.
Customer willingness to switch to substitutes for TT Electronics' components hinges on several factors. Perceived risk is a major hurdle; if a substitute is seen as less reliable or untested, adoption will be slow. Ease of integration also plays a crucial role; a substitute that requires significant redesign or re-qualification will face resistance. Furthermore, the value proposition of the alternative, in terms of cost, performance, or features, must be compelling enough to offset these switching costs.
In high-stakes sectors like aerospace and defense, where TT Electronics has a strong presence, the threat of substitutes is significantly mitigated. The stringent reliability, safety, and certification requirements mean that adopting new, unproven components is an extremely high-risk proposition. For instance, the qualification process for a new electronic component in an aircraft can take years and cost millions, making companies hesitant to switch unless absolutely necessary and the substitute offers a demonstrably superior and thoroughly validated solution.
Evolution of Software-Defined Solutions
The increasing prevalence of software-defined functionality in electronic systems presents a significant threat of substitutes for TT Electronics. As more features are virtualized and managed by sophisticated software algorithms, including AI, the need for specialized hardware components could diminish. This shift towards software-centric solutions could lead to a decline in demand for certain physical components, impacting hardware-focused manufacturers.
For instance, the automotive sector is increasingly adopting software-defined architectures where features like advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are primarily driven by software rather than dedicated hardware modules. This trend means that a single, powerful processing unit running advanced algorithms can replace multiple specialized chips. In 2024, the global automotive software market was valued at approximately $35 billion, with a significant portion dedicated to these evolving functionalities, indicating a clear move away from purely hardware-dependent solutions.
- Software Virtualization: Core functionalities are being consolidated into software, reducing the reliance on bespoke hardware.
- AI and Machine Learning: Advanced algorithms are taking over tasks previously requiring specialized processing hardware.
- Market Trends: The growing automotive software market, projected to reach over $60 billion by 2030, highlights the shift towards software-defined vehicles.
- Component Demand Impact: This evolution may decrease demand for specific, single-purpose electronic components that TT Electronics produces.
Material Science Innovations
Breakthroughs in material science represent a significant threat of substitutes for TT Electronics. Innovations like advanced composites or organic electronics could yield new components with enhanced performance or reduced production costs, directly challenging TT Electronics' current offerings in sensors and power management devices. For instance, the burgeoning field of perovskite solar cells, while not a direct component substitute, demonstrates how new material classes can rapidly disrupt established technologies by offering competitive or superior energy conversion efficiencies, potentially impacting the broader electronics market TT Electronics serves.
The development of novel materials can create entirely new product categories that bypass the need for traditional electronic components. Imagine self-healing circuit boards or biodegradable conductive inks; these could offer functional equivalents to TT Electronics' products but with entirely different manufacturing processes and cost structures. The market for advanced materials is projected for substantial growth, with global advanced materials market expected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars by 2028, indicating the potential scale of disruption.
- New Material Properties: Innovations in materials science can lead to components with superior thermal conductivity, electrical resistance, or mechanical strength compared to existing TT Electronics products.
- Cost Reduction Potential: Novel manufacturing techniques for these advanced materials could significantly lower production costs, making them a more attractive alternative for customers.
- Emerging Technologies: The rise of technologies like printed electronics or flexible displays relies on new material formulations that could directly substitute for traditional PCB-based or rigid component solutions.
The threat of substitutes for TT Electronics is multifaceted, stemming from technological advancements and evolving customer preferences. Innovations in areas like wireless power transfer and software-defined functionalities can directly replace traditional wired connectors and specialized hardware components. For example, the automotive sector's increasing reliance on software-defined architectures, with a global automotive software market valued around $35 billion in 2024, highlights this shift away from hardware-centric solutions.
Customers evaluate substitutes based on price, performance, reliability, and ease of integration. If an alternative offers comparable or superior functionality at a lower cost, or with less integration effort, the threat intensifies. This is particularly true in cost-sensitive sectors like consumer electronics.
Breakthroughs in material science also pose a threat, with new materials offering enhanced properties or reduced production costs. The advanced materials market, projected to reach hundreds of billions by 2028, underscores the potential for disruption from novel components like those used in printed electronics or flexible displays.
In high-specification industries like aerospace, the threat is lower due to stringent qualification processes. However, even here, demonstrably superior and validated substitute solutions can eventually gain traction, albeit over longer adoption cycles.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the electronic components manufacturing sector, particularly for high-performance applications, demands significant upfront capital. This includes substantial investment in research and development, state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and specialized machinery. For instance, establishing a new semiconductor fabrication facility can cost billions of dollars, creating a formidable barrier.
Achieving economies of scale is another major hurdle for newcomers. Larger, established players benefit from lower per-unit production costs due to higher output volumes. This cost advantage makes it challenging for new entrants to compete on price, effectively limiting the number of viable competitors entering the market.
TT Electronics' commitment to developing innovative technologies and engineered solutions is underscored by its significant investment in proprietary designs and patents. These intellectual property assets create substantial barriers to entry, as potential competitors would face considerable costs and legal hurdles in replicating TT Electronics' advanced offerings. For instance, in 2023, the company reported significant R&D expenditure, demonstrating its ongoing efforts to maintain a technological edge.
The industrial, medical, aerospace, and defense sectors are heavily regulated. This means electronic component suppliers like TT Electronics must navigate stringent certifications and comply with international standards. For instance, achieving AS9100 certification for aerospace can take over a year and significant investment.
New companies entering these markets face substantial time and cost barriers to meet these demanding regulatory requirements. The lengthy qualification processes for components, which can extend for years, significantly delay market entry and amplify the initial investment risks for any new competitor.
Access to Distribution Channels and Supply Chains
Newcomers face significant hurdles in securing reliable global supply chains and accessing established distribution networks for specialized electronic components. These established channels are crucial for reaching customers efficiently.
Companies like TT Electronics have cultivated deep, long-term relationships with key distributors and end-users. This existing network creates a formidable barrier for new entrants attempting to gain market traction and secure consistent sales, as evidenced by the difficulty new players often experience in securing shelf space or preferred supplier status.
The threat of new entrants is therefore moderated by the substantial investment and time required to build comparable supply chain and distribution capabilities. For instance, in 2023, the global electronic components market saw continued consolidation, with established players leveraging their scale to maintain strong distribution partnerships, making it harder for smaller, newer firms to compete on access.
- Established Relationships: TT Electronics benefits from decades-long partnerships with major electronics distributors and direct customers, providing preferential access and volume.
- Supply Chain Integration: New entrants struggle to replicate the integrated and resilient global supply chains that established firms have developed, often facing higher costs and longer lead times.
- Distribution Channel Barriers: Gaining access to critical distribution channels, especially for specialized or high-volume components, requires significant negotiation power and proven reliability, which new companies typically lack.
Brand Reputation and Customer Loyalty
In performance-critical sectors, brand reputation is a significant barrier to entry. TT Electronics, for instance, has cultivated a strong reputation for reliability and quality over decades, fostering deep customer loyalty. This trust is hard-won and difficult for newcomers to replicate, especially when the consequences of product failure are substantial.
Established companies like TT Electronics have built enduring relationships with clients who prioritize proven performance. New entrants face an uphill battle in convincing these customers to switch, particularly when their brand history is less established. For example, in the aerospace sector, where TT Electronics has a strong presence, supplier qualification processes are rigorous and lengthy, often favoring incumbents with a track record of success.
- Brand Reputation: TT Electronics benefits from a long-standing reputation for quality and reliability in demanding industries.
- Customer Loyalty: Established relationships and trust make it difficult for new entrants to capture market share.
- Performance-Critical Applications: In sectors like aerospace and medical, product failure has severe consequences, reinforcing loyalty to proven suppliers.
- Barriers to Entry: The time and investment required to build comparable brand trust and customer loyalty are substantial for new competitors.
The threat of new entrants in the electronic components market, particularly for specialized applications where TT Electronics operates, is generally low. Significant capital investment for R&D and manufacturing facilities, coupled with the need for economies of scale, creates substantial financial barriers. For example, establishing a new semiconductor fabrication plant can cost billions of dollars, a figure far beyond the reach of most new entrants.
Intellectual property and proprietary designs, as demonstrated by TT Electronics' R&D investments in 2023, further deter new competition by requiring costly replication or licensing. Stringent regulatory compliance, such as AS9100 certification for aerospace, adds years and significant expense to market entry. In 2023, the global electronic components market saw continued consolidation, with established players leveraging their scale to maintain strong distribution partnerships, making it harder for smaller, newer firms to compete on access.
Established relationships with distributors and customers, built over decades, are critical. Newcomers struggle to replicate the integrated and resilient global supply chains that established firms have developed, often facing higher costs and longer lead times. Brand reputation and customer loyalty in performance-critical sectors like aerospace and medical, where TT Electronics has a strong presence, further solidify these barriers, as customers prioritize proven reliability over new offerings.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our TT Electronics Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse and credible data sources, including TT Electronics' own annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific market research reports from firms like IHS Markit and Gartner.