Strategic Education Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Strategic Education Bundle
Strategic Education navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry, evolving buyer power, and the ever-present threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp the company's competitive position.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Strategic Education’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Strategic Education, Inc. (SEI) can face significant supplier bargaining power when relying on a limited number of providers for specialized online learning platforms or content management systems. For instance, if only a handful of companies offer the advanced, proprietary technology SEI needs to deliver its educational services, those suppliers gain leverage.
In 2023, SEI's technology infrastructure is crucial for its operations, and dependence on a few specialized technology providers means these suppliers can command higher prices or dictate terms, impacting SEI's costs and operational flexibility.
If Strategic Education, Inc. faces significant costs and complexities when changing technology or content providers, current suppliers hold more power. These substantial switching costs could involve data migration, extensive staff retraining, and the potential for interruptions in ongoing educational programs, making it difficult for Strategic Education to change suppliers easily.
When suppliers offer highly unique or deeply integrated solutions, their bargaining power significantly increases. For instance, if a strategic education provider relies on proprietary learning management systems or specialized content development tools that competitors cannot easily access, these suppliers gain leverage.
This differentiation creates a dependency for the education provider, making it harder to switch suppliers without incurring substantial costs or disrupting operations. In 2024, the market for specialized EdTech solutions saw significant growth, with companies offering AI-driven personalized learning platforms commanding premium pricing due to their unique capabilities.
Threat of Supplier Forward Integration
The potential for key technology or content suppliers to integrate forward presents a significant threat. If these suppliers begin offering education services directly to institutions or students, SEI could face direct competition. This shift would fundamentally alter the supplier-customer dynamic, potentially diminishing SEI's leverage.
Consider the scenario where a major learning management system provider, which currently licenses its platform to SEI, decides to develop its own curriculum and support services. This move would transform them from a crucial technology partner into a direct competitor, potentially capturing a significant portion of SEI's market share. For instance, in 2024, several EdTech platforms saw substantial investment, signaling a trend towards broader service offerings.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: Key technology and content providers could bypass SEI and offer services directly to end-users.
- Shift in Bargaining Power: Suppliers gain leverage by becoming competitors, not just vendors.
- Market Disruption: SEI could lose market share if suppliers offer more attractive, integrated solutions.
- 2024 EdTech Investment Trends: Significant capital flowed into EdTech, enabling potential expansion of services by existing suppliers.
Importance of Supplier Inputs to SEI's Core Services
Strategic Education, Inc. (SEI) relies heavily on specialized inputs for its core educational offerings, particularly in areas like advanced AI-driven personalized learning platforms and bespoke curriculum development. The degree to which SEI’s value proposition and the quality of its educational outcomes are tied to these specific supplier inputs directly influences supplier power.
If these critical inputs are indeed indispensable and difficult to replicate or substitute, then SEI’s suppliers will possess significant leverage. This leverage can translate into higher costs for SEI, potentially impacting its profitability and competitive pricing strategies. For instance, a key provider of AI-powered adaptive learning software, if unique and highly effective, could command premium pricing, forcing SEI to either absorb these costs or pass them on to students.
- Dependency on AI and Curriculum Specialists: SEI’s commitment to innovative learning experiences means a dependence on cutting-edge AI providers and expert curriculum designers.
- Impact of Indispensable Inputs: When these inputs are crucial for delivering SEI's core value, suppliers gain substantial bargaining power.
- Potential for Increased Costs: Suppliers of unique or highly specialized educational technology and content can dictate higher prices, affecting SEI's operational expenses.
- Leverage in Negotiations: The more unique and critical a supplier's offering, the stronger their position to negotiate favorable terms with SEI.
Strategic Education, Inc. (SEI) faces significant supplier bargaining power when its specialized inputs, like advanced AI learning platforms, are critical and hard to substitute. This leverage allows suppliers to command higher prices, impacting SEI's costs and profitability. In 2024, the EdTech market saw specialized AI solutions command premium pricing due to their unique capabilities, highlighting this dynamic.
| Factor | Impact on SEI | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited providers of specialized tech increase supplier leverage. | Growth in EdTech solutions means some niche providers may dominate specific segments. |
| Switching Costs | High costs to change providers limit SEI's ability to switch. | Integrating new AI platforms can involve substantial data migration and retraining costs. |
| Input Differentiation | Unique or integrated solutions give suppliers more power. | AI-driven personalized learning platforms are highly differentiated offerings. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Suppliers could become competitors, reducing SEI's market position. | Major EdTech platforms are expanding service offerings, potentially entering direct competition. |
What is included in the product
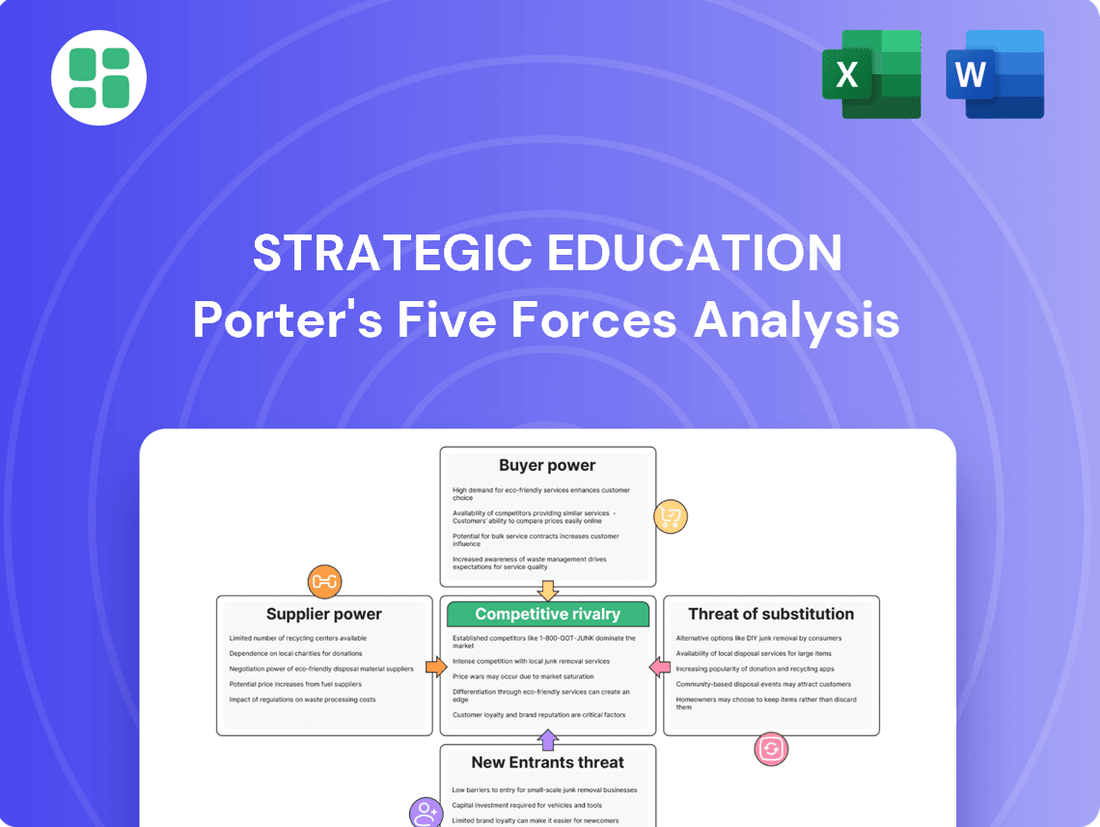
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Strategic Education, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces, turning complex market dynamics into actionable insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
Strategic Education, Inc.'s (SEI) customer concentration is a key factor in their bargaining power. If a significant portion of SEI's revenue comes from a small number of large institutions or employers, these clients gain considerable leverage. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, SEI reported total revenue of $1.37 billion. The dependency on a few major clients means they can negotiate more favorable terms, potentially impacting SEI's pricing and service offerings.
Customer switching costs are a critical factor in determining how much power buyers have over Strategic Education, Inc. (SEI). If it's easy and inexpensive for universities or employers to move to another service provider or build their own solutions, they can demand lower prices or better terms from SEI.
For instance, if SEI's platform requires significant upfront investment or complex integration with existing university systems, switching becomes difficult. This difficulty, or high switching cost, means customers have less leverage. In 2023, the education technology market saw continued investment, with companies focusing on seamless integration to retain clients, a trend likely to continue into 2024.
Universities and educational institutions are increasingly feeling the pinch of budget constraints, making them more sensitive to the prices charged for online program management (OPM) services. This financial pressure means they're pushing for more competitive pricing and better value from providers like Strategic Education, Inc. For example, in 2024, many public universities faced state funding cuts, directly impacting their operational budgets and their willingness to spend on external services.
Customer Information and Market Transparency
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by how informed they are about competing online program management (OPM) providers and their services. When customers have access to detailed information about various OPM options, their ability to negotiate better terms with Strategic Education, Inc. increases. For instance, in 2024, the OPM market continued to see a surge in providers offering diverse pricing models and service packages, making it easier for institutions to compare and contrast offerings.
Greater transparency in the education services market directly empowers customers, enabling them to more effectively evaluate and select OPM partners. This transparency allows institutions to benchmark pricing, service levels, and student outcomes across different providers. Strategic Education, Inc. faces this dynamic as potential clients can readily access data points that inform their purchasing decisions.
- Increased Market Transparency: In 2024, online resources and industry reports provided more granular data on OPM provider performance and pricing structures.
- Informed Decision-Making: Institutions can now more easily compare OPM providers based on factors like student retention rates, graduation success, and cost-effectiveness.
- Negotiating Leverage: This enhanced information flow gives customers stronger grounds to negotiate favorable contract terms and service level agreements with OPM companies like Strategic Education.
Threat of Customer Backward Integration
The capacity and willingness of universities and employers to develop and manage their online programs, technology solutions, and student support services internally represent a significant threat of backward integration for Strategic Education, Inc. If institutions can cost-effectively bring these services in-house, their reliance on Strategic Education diminishes, increasing their bargaining power.
For example, many universities are investing heavily in their own learning management systems and online course development capabilities. In 2024, the global e-learning market was projected to reach over $400 billion, with a significant portion of this growth driven by institutions building out their internal digital infrastructure.
This trend means that universities might choose to develop their own student support services, such as online tutoring or career counseling, rather than outsourcing them. This internal development reduces the need for external providers like Strategic Education, thereby strengthening the university's position.
- Internal Capability Development: Universities are increasingly building in-house expertise in online pedagogy, instructional design, and educational technology.
- Cost-Effectiveness Analysis: Institutions regularly evaluate the cost savings associated with managing services internally versus outsourcing them.
- Control Over Student Experience: Backward integration allows universities to maintain tighter control over the quality and consistency of the student experience.
- Market Trends: The growing maturity of the online education sector provides more readily available technology and expertise for institutions to leverage internally.
Customers' bargaining power over Strategic Education, Inc. (SEI) is amplified by their increasing access to market information and the growing transparency in the online program management (OPM) sector. In 2024, institutions could readily compare pricing, service offerings, and student outcomes from various providers, giving them a distinct advantage in negotiations. This heightened awareness empowers universities and employers to demand more competitive terms and better value from SEI.
The ability of customers to develop their online education capabilities in-house also significantly bolsters their bargaining power against SEI. As institutions invest in their own technology and expertise, their reliance on external OPM providers diminishes. For example, the global e-learning market's projected growth to over $400 billion in 2024 highlights the trend of institutions building internal digital infrastructure, reducing their need for outsourced solutions and strengthening their negotiating position.
| Factor | Impact on SEI's Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Trend (2023-2024) |
| Customer Concentration | High if few large clients dominate revenue. | SEI's FY2023 revenue was $1.37 billion; dependency on major clients increases their leverage. |
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs empower customers. | Market trend: Focus on seamless integration to retain clients, implying lower switching costs. |
| Price Sensitivity | Increased sensitivity due to budget constraints. | 2024: Many public universities faced state funding cuts, increasing price sensitivity. |
| Information Availability | High availability increases negotiation leverage. | 2024: Surge in providers with diverse models, easy comparison of offerings. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Stronger if institutions can develop services internally. | 2024: Institutions investing in internal digital infrastructure; e-learning market projected >$400 billion. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Strategic Education Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Strategic Education Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of industry competition and profitability. The document you see is precisely what you will receive, fully formatted and ready for immediate use upon purchase. Gain actionable insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the education sector.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Strategic Education, Inc. operates in a highly competitive online education sector. The market features a substantial number of players, ranging from established Online Program Managers (OPMs) and traditional universities rapidly expanding their digital offerings to agile new ed-tech startups.
This diverse competitive landscape means Strategic Education must contend with a wide array of strategies and business models. For instance, in 2024, the global online education market was valued at over $300 billion, indicating significant investment and a crowded field of providers vying for market share.
The intensity of rivalry is further amplified by the varying sizes and capabilities of these competitors. Some may offer specialized niche programs, while others provide comprehensive degree pathways, forcing Strategic Education to continuously innovate in its program management, technology solutions, and student support services.
The growth rate of the online education services market significantly influences competitive rivalry. A slowing growth environment, such as the observed decline in new Online Program Management (OPM) partnerships, typically escalates competition as companies vie more aggressively for existing market share. For instance, in 2023, the OPM market experienced a noticeable slowdown in partnership formations compared to previous years, forcing established providers to focus on retaining existing clients and seeking new revenue streams from smaller institutions or specialized programs.
Strategic Education, Inc.'s ability to differentiate its offerings, such as through its unique online learning platforms and career services, directly impacts competitive rivalry. In 2023, the company reported that its Capella University segment continued to focus on competency-based education, a differentiator that aims for superior student outcomes. This focus can shift competition away from pure price wars towards value-based propositions, potentially softening direct rivalry.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
Strategic Education, Inc. operates in an environment where high fixed costs for technology, curriculum, and staff necessitate aggressive competition. These substantial upfront investments, like those in developing robust online learning platforms, mean companies must strive for scale and market share to achieve profitability.
High exit barriers, such as long-term commitments to educational institutions and the specialized nature of the assets, further intensify this rivalry. Companies are essentially locked into the industry, forcing them to compete fiercely to recoup their investments and maintain operational viability.
- High Fixed Costs: Strategic Education's investments in digital infrastructure and course content represent significant fixed costs that must be amortized over a large student base.
- Exit Barriers: Long-term partnerships with universities and the specialized nature of educational technology create substantial barriers to exiting the market.
- Intensified Rivalry: These factors compel existing players to compete aggressively on price, program offerings, and student outcomes to secure and retain market share.
Strategic Stakes and Market Share Importance
The education services sector is characterized by intense competition, driven by the strategic importance of market share, a strong brand reputation, and the cultivation of long-term partnerships. Companies like Strategic Education, Inc. are deeply invested in this market, making them highly motivated to aggressively pursue institutional and employer affiliations, as well as student enrollments.
The pursuit of these affiliations and enrollments directly fuels the competitive rivalry. For instance, in 2023, Strategic Education, Inc. reported total revenue of $761.5 million, underscoring the significant financial stakes involved in capturing and retaining market share within the higher education landscape. This financial performance highlights the direct correlation between market presence and revenue generation, intensifying the drive to outmaneuver competitors.
- Strategic Importance of Market Share: Companies view market share as a key indicator of success and a driver of future growth in the education sector.
- Brand Reputation as a Differentiator: A strong brand reputation is crucial for attracting students and building trust with institutional and employer partners, directly impacting competitive positioning.
- Long-Term Partnerships are Key: Establishing and maintaining enduring relationships with institutions and employers provides a stable base of enrollments and revenue, intensifying rivalry for these valuable connections.
- Financial Stakes Drive Competition: Significant revenue figures, such as Strategic Education, Inc.'s $761.5 million in 2023, demonstrate the substantial financial incentives that fuel aggressive competition for market dominance.
The competitive rivalry within Strategic Education, Inc.'s market is fierce, characterized by a large number of players, including established OPMs, universities, and ed-tech startups. This crowded landscape, with the global online education market exceeding $300 billion in 2024, forces companies to compete aggressively on various fronts.
Factors like high fixed costs for technology and curriculum, coupled with significant exit barriers due to long-term partnerships, compel businesses to constantly innovate and vie for market share. This intense competition is further fueled by the strategic importance of market share and brand reputation, as highlighted by Strategic Education's 2023 revenue of $761.5 million, demonstrating the substantial financial stakes involved.
| Metric | Value (2023/2024 Data) | Implication for Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| Global Online Education Market Value | >$300 billion (2024) | Indicates a large, attractive market with many participants, intensifying competition. |
| Strategic Education, Inc. Revenue | $761.5 million (2023) | Shows significant financial stakes, driving aggressive pursuit of market share. |
| OPM Partnership Growth | Slowdown observed in 2023 | Forces existing players to compete more intensely for existing market share and clients. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Strategic Education, Inc.'s (SEI) offerings is significant, primarily stemming from the burgeoning landscape of alternative online learning providers. Institutions and individuals seeking online education solutions have a growing array of choices beyond traditional OPM partnerships.
Many universities are increasingly investing in developing their online programs internally, thereby reducing their reliance on external OPM providers like SEI. This trend is fueled by a desire for greater control over curriculum, student experience, and revenue streams. Furthermore, the ed-tech sector is replete with specialized companies offering modular solutions, such as advanced learning management systems (LMS) or bespoke content creation tools, which can be integrated to build custom online learning environments without a full-service OPM.
For instance, the global ed-tech market was valued at approximately $121 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially. This expansion indicates a robust ecosystem of alternative solutions that can potentially fulfill the needs previously met by OPMs. Companies like Coursera for Campus and 2U, while also operating in the OPM space, offer flexible partnership models that can be perceived as substitutes by institutions looking for specific components of online program delivery rather than a comprehensive outsourcing solution.
The rise of micro-credentials and alternative skill-based training, such as bootcamps offered by tech giants and specialized educational platforms, presents a growing threat of substitutes for traditional degree programs. These shorter, often more affordable, and highly focused programs are rapidly gaining traction, offering a quicker route to acquiring in-demand job skills. For instance, by mid-2024, the global online education market, which heavily features these alternative pathways, was projected to reach over $370 billion, demonstrating a significant shift in how individuals acquire professional competencies.
The rise of Open Educational Resources (OER) and Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional educational providers like Strategic Education, Inc. These platforms offer a vast array of free or low-cost learning materials and even complete courses, directly accessible to students and institutions alike.
While OER and MOOCs may not always grant formal degrees, they effectively address specific learning needs, providing an alternative to the comprehensive, often higher-cost, services offered by established institutions. For instance, Coursera reported over 90 million learners enrolled in its courses by the end of 2023, highlighting the massive reach and appeal of these alternative learning pathways.
Employer-Led Training and Corporate Universities
The rise of employer-led training and corporate universities presents a significant threat of substitutes for external education providers. Companies are increasingly investing in their own learning and development infrastructure to tailor programs precisely to their strategic goals and skill gaps. This trend is driven by a desire for greater control over content, delivery, and cost-effectiveness.
For instance, in 2023, companies globally were projected to spend over $350 billion on employee training and development, a figure expected to continue its upward trajectory. This substantial investment by corporations in building internal capabilities directly diminishes the reliance on external educational institutions for workforce upskilling and reskilling.
- Reduced Demand: As more companies develop robust in-house training, the pool of potential clients for external education services shrinks.
- Cost Efficiency: Building internal programs can be more cost-effective for large organizations over the long term compared to paying external providers for ongoing training needs.
- Customization: Corporate universities allow for highly specialized and proprietary training content that external providers may not be able to replicate.
- Talent Retention: Investing in employee development through internal programs can also serve as a tool for talent retention, further solidifying the in-house solution.
Cost-Effectiveness and Perceived Value of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for Strategic Education, Inc. (SEI) is significantly shaped by the cost-effectiveness and perceived value of alternative learning solutions. If universities, employers, or individuals can achieve comparable learning outcomes or career advancement through more affordable avenues, the appeal of SEI's offerings diminishes.
For instance, the rise of free or low-cost online courses and certifications from platforms like Coursera or edX, which often partner with reputable universities, presents a direct substitute. Many of these platforms offer specialized skills training that can be acquired at a fraction of the cost of a full degree program. In 2024, the global e-learning market was valued at over $370 billion, demonstrating a substantial and growing alternative to traditional educational models.
Consider these factors influencing the threat:
- Cost Comparison: The tuition fees for SEI's institutions, such as Purdue Global or Strayer University, are often higher than what it costs to complete a specialized certificate or even a degree through online platforms or community colleges. For example, a bachelor's degree from Purdue Global can cost upwards of $40,000, while a comparable online program from another provider might be under $20,000.
- Perceived Value and Outcomes: While SEI emphasizes career readiness and comprehensive support, many substitute options are increasingly recognized by employers for delivering specific, in-demand skills. The perceived return on investment for these lower-cost alternatives can be higher for individuals focused on immediate job market needs.
- Accessibility and Flexibility: The sheer accessibility and flexibility of many online substitutes, allowing learners to study at their own pace and on their own schedule, can be a significant draw, especially for working professionals. This flexibility often rivals or exceeds that offered by more traditional, even online, degree programs.
- Alternative Credentialing: The growing acceptance of micro-credentials, bootcamps, and industry-specific certifications as valid indicators of competence directly challenges the traditional degree as the sole pathway to career success. This trend allows individuals to bypass the longer and more expensive commitment of a full degree program.
The threat of substitutes for Strategic Education, Inc. (SEI) is substantial, driven by the increasing availability and acceptance of alternative learning pathways. These substitutes offer comparable or specialized learning outcomes, often at a lower cost and with greater flexibility than traditional degree programs.
For instance, the global ed-tech market's projected growth to over $370 billion by 2024 underscores the vastness of alternative solutions. These range from micro-credentials and bootcamps to employer-led training, all competing for learners seeking specific skills and career advancement.
The cost-effectiveness of these alternatives is a key differentiator. While a bachelor's degree from an SEI institution might exceed $40,000, many online certifications or skill-based programs can be completed for under $20,000, offering a compelling value proposition for cost-conscious learners.
| Substitute Type | Examples | Key Advantages | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Courses & Certifications | Coursera, edX, Udacity | Specialized skills, flexibility, lower cost | $50 - $5,000 |
| Skill-Based Bootcamps | General Assembly, Flatiron School | Intensive training, career services, rapid upskilling | $5,000 - $15,000 |
| Employer-Led Training | Internal corporate L&D programs | Customized content, direct career relevance, cost control | Varies (significant internal investment) |
| Micro-Credentials | Digital badges, professional certifications | Targeted skills, quick validation, often lower cost | $100 - $2,000 |
Entrants Threaten
While basic e-learning platforms might seem accessible, competing with Strategic Education, Inc. (STRA) demands substantial capital. New entrants need to invest heavily in sophisticated technology, high-quality curriculum design, and robust student support systems to even approach STRA's established offerings.
For instance, STRA's commitment to its online infrastructure and program development requires significant ongoing expenditure. In fiscal year 2023, the company reported total operating expenses of $1.5 billion, reflecting the substantial investment needed to maintain and enhance its educational services, a figure that new competitors would need to match or exceed.
The higher education sector presents significant barriers to entry due to its intricate and constantly changing regulatory framework. Accreditation requirements, for instance, are rigorous and time-consuming, often demanding years of preparation and substantial investment to meet standards set by bodies like the Higher Learning Commission or regional accreditors.
Government oversight, particularly for online programs, adds another layer of complexity. For example, in 2024, institutions seeking to offer distance education must comply with evolving state authorization rules and federal regulations concerning student data privacy and program quality, which can deter new players lacking specialized legal and compliance teams.
Successfully navigating these regulatory hurdles requires not only deep understanding but also considerable financial resources. Many aspiring entrants find the cost and effort associated with obtaining and maintaining compliance, including audits and reporting, to be prohibitive, thus limiting the threat of new competition.
Strategic Education, Inc. (SEI) enjoys significant advantages due to its deeply ingrained brand recognition and decades-long relationships with educational institutions and corporate clients. This established trust makes it difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
New entrants must invest heavily in building a comparable reputation and forging new partnerships, a process that is both time-consuming and financially demanding in the competitive education landscape. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, SEI reported continued strength in its student enrollment numbers, underscoring the loyalty its brand commands.
Access to Talent and Specialized Expertise
New entrants into the strategic education sector face a significant hurdle in accessing a specialized talent pool. This includes professionals like instructional designers, educational technologists, student support specialists, and marketing experts who understand the unique landscape of higher education. For instance, in 2024, the demand for skilled edtech professionals saw a notable increase, with many institutions reporting difficulties in filling these critical roles, leading to higher recruitment costs and longer hiring timelines.
The ability to recruit and retain this specialized talent acts as a substantial barrier to entry. Consider the competition for experienced faculty and administrative staff; established institutions often have strong employer brands and more competitive compensation packages, making it challenging for newcomers to attract top-tier individuals. In 2023, the average salary for instructional designers in the US education sector rose by approximately 7%, reflecting this intense competition for expertise.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: New entrants must invest heavily in recruitment agencies, advertising, and competitive salaries to attract qualified personnel.
- Retention Challenges: Retaining specialized staff can be difficult due to the high demand and the allure of established, well-funded educational organizations.
- Skill Gaps: A general shortage of professionals with combined expertise in education, technology, and business strategy can further exacerbate entry barriers.
- Onboarding and Training: New entrants also need to factor in the time and resources required for onboarding and training new employees to align with their specific educational models and operational needs.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Existing players like Strategic Education, Inc. (SEI) leverage significant economies of scale in areas such as technology infrastructure, content development, and administrative operations. This allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger student base, leading to lower per-unit costs.
New entrants face a substantial hurdle in matching SEI's scale. To compete on pricing and quality, they would need to invest heavily in similar infrastructure and content, which is a considerable barrier to entry. The experience curve effect further disadvantages newcomers, as established firms have refined their processes and offerings over time, increasing efficiency and reducing costs.
- Economies of Scale: SEI's large student enrollment (e.g., approximately 95,000 students across its brands as of recent reporting periods) allows for cost efficiencies in technology, marketing, and administrative functions.
- Experience Curve: Decades of operational experience have enabled SEI to optimize its online learning platforms, curriculum delivery, and student support services, creating a cost and quality advantage.
- Capital Investment: A new entrant would require substantial upfront capital to build comparable technology platforms and develop a comprehensive course catalog, making it difficult to compete with established players on cost.
- Brand Recognition: SEI benefits from established brand recognition, which reduces customer acquisition costs compared to a new entrant needing to build trust and awareness.
The threat of new entrants for Strategic Education, Inc. (SEI) is mitigated by substantial capital requirements and regulatory complexities. New competitors must overcome significant hurdles in technology investment, curriculum development, and compliance with evolving educational standards. For example, the cost of developing and maintaining high-quality online learning platforms and ensuring adherence to accreditation standards represents a considerable financial barrier, deterring many potential entrants in 2024.
Brand loyalty and established relationships further solidify SEI's market position, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. Building a comparable reputation and trust within the education sector requires extensive time and resources, a challenge underscored by SEI's consistent student enrollment figures reported in early 2024. The need for specialized talent, from instructional designers to educational technologists, also presents a significant barrier, with high demand and recruitment costs in 2024 making it difficult for new entities to attract and retain key personnel.
Economies of scale achieved by SEI, stemming from its large student base and optimized operational processes, create a cost advantage that new entrants struggle to match. This scale allows SEI to spread fixed costs, such as technology infrastructure and content development, over a broader student population, resulting in lower per-unit costs. The experience curve effect, where SEI has refined its offerings over decades, further enhances its efficiency and cost-effectiveness, presenting a formidable challenge for any new competitor aiming to enter the market in 2024.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants | SEI's Advantage (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Investment in technology, curriculum, and infrastructure. | High upfront costs deter new players. | SEI has established robust systems and ongoing R&D budgets. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Accreditation, state authorizations, federal compliance. | Time-consuming and costly to navigate. | SEI possesses dedicated compliance teams and a history of successful accreditation. |
| Brand Recognition & Relationships | Established trust and partnerships with institutions/corporates. | Difficult for newcomers to build comparable credibility. | SEI benefits from decades of brand building and client loyalty. |
| Talent Acquisition | Need for specialized educational and technical staff. | High recruitment costs and competition for skilled personnel. | SEI attracts talent through its established reputation and resources. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost efficiencies from large student base and operations. | New entrants cannot match SEI's per-unit cost advantage. | SEI's extensive student enrollment (approx. 95,000 in recent periods) drives significant cost efficiencies. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Strategic Education Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from educational institution annual reports, government education statistics, and industry-specific market research reports to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.