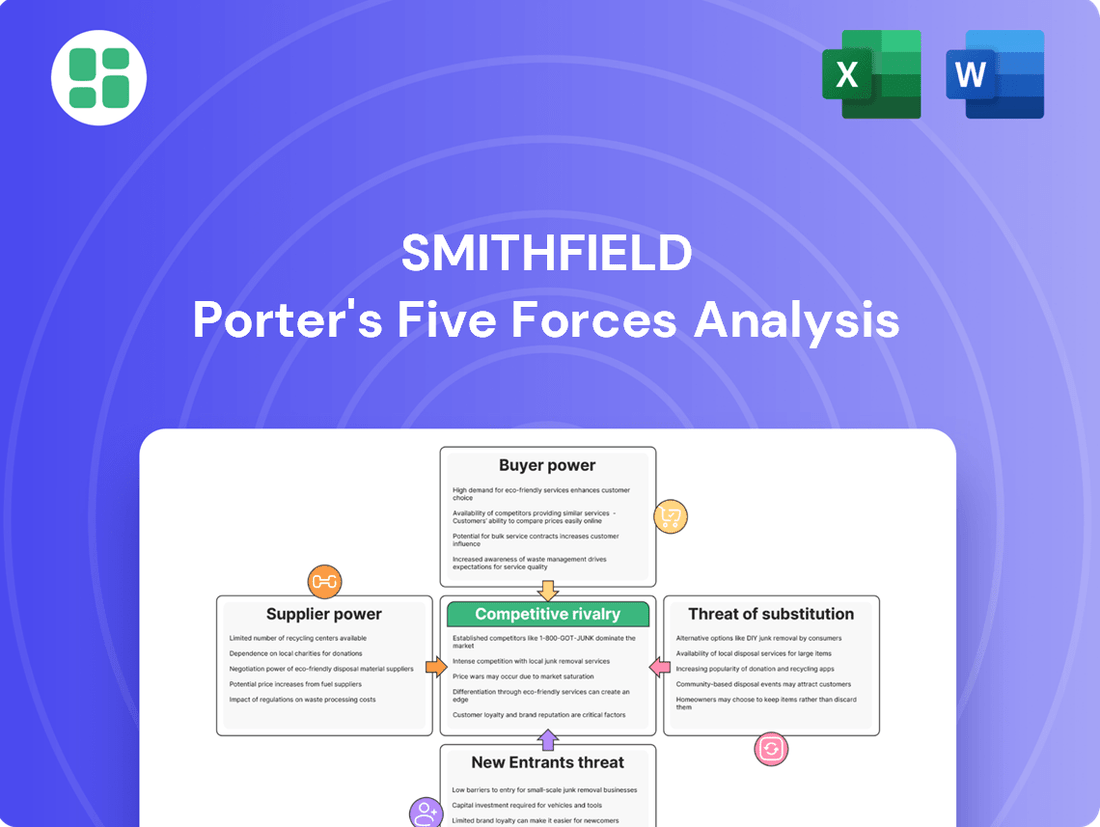
Smithfield Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Smithfield Bundle
Smithfield's position in the pork industry is significantly shaped by the intense rivalry among existing players and the substantial bargaining power of its buyers. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the competitive landscape.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the real forces shaping Smithfield’s industry—from supplier influence to the threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration is a key factor in the bargaining power of suppliers for Smithfield Foods. As the world's largest pork processor, Smithfield depends on a broad base of hog producers, encompassing both its own operations and independent farmers.
While Smithfield has been decreasing its internal hog production, opting to source more from independent suppliers, the overall concentration within hog production can still impact supplier leverage. This strategic move is partly to mitigate risks associated with fluctuating commodity markets and input costs, such as animal feed, which represented about 60% of the cost of goods sold in its Hog Production segment from 2024 through Q1 2025.
Smithfield Foods has cultivated deep-rooted relationships with many contract farmers, with some of these partnerships spanning over two decades. This longevity suggests a degree of supplier loyalty and established operational integration.
The process of switching suppliers or making significant changes to its supply chain presents Smithfield with considerable logistical hurdles. These changes could lead to temporary production disruptions and necessitate the time-consuming effort of building new supplier relationships, indicating moderate switching costs for the company.
In 2023, Smithfield's hog production costs, a key indicator of supplier leverage, saw fluctuations. While specific figures for switching costs are proprietary, the company's strategic moves, such as divesting sow farms and creating new supply entities, highlight an active management of these supplier dependencies and associated costs.
The threat of individual hog farmers integrating forward into meat processing and distribution for Smithfield is quite low. This is primarily because establishing and running a large-scale processing plant requires substantial capital, advanced technology, and specialized operational knowledge, which most individual farmers lack. For example, building a modern pork processing facility can cost tens to hundreds of millions of dollars, a prohibitive expense for typical agricultural operations.
However, larger agricultural entities, such as well-established cooperatives or vertically integrated farming businesses, could theoretically present a greater forward integration threat. These groups might possess the financial capacity and operational experience to invest in processing capabilities. While not a widespread current trend affecting Smithfield, their potential to do so remains a consideration, especially if market dynamics shift significantly.
Uniqueness of Supplier Inputs
While hogs are generally considered a commodity, the uniqueness of supplier inputs for a company like Smithfield can significantly influence its bargaining power. Even within a standardized market, the quality, health status, and consistent availability of hogs from particular farms can be paramount for efficient and profitable processing operations. This is especially true as Smithfield emphasizes animal welfare and biosecurity protocols, as detailed in its sustainability reporting, indicating a preference for suppliers who meet these specific, valued standards.
This focus on supplier practices introduces a level of differentiation that moves beyond the simple commodity nature of hogs. Smithfield's commitment to these standards means that not all suppliers are interchangeable, thereby granting a degree of leverage to those who consistently meet or exceed these expectations. For instance, farms with robust disease prevention programs or superior genetic traits might command a premium or secure more favorable terms due to their unique contributions to Smithfield's overall product quality and operational stability.
- Supplier Differentiation: While hogs are a commodity, Smithfield values specific supplier attributes like health and consistent supply, which adds uniqueness.
- Sustainability Impact: Smithfield's emphasis on animal care and biosecurity, as noted in its sustainability reports, highlights the importance of certain supplier practices.
- Beyond Commodity: These valued supplier practices move beyond basic commodity status, giving some suppliers more leverage.
Supplier's Importance to Smithfield's Business
Suppliers, especially hog producers, are fundamental to Smithfield Foods' operations as a major pork processor. The company's strategic shift towards external sourcing, reducing its in-house hog production, directly increases the leverage of these external suppliers. However, Smithfield's substantial market presence and its capacity to engage with numerous large-scale hog producers serve as a counterbalance, preventing any single supplier from wielding excessive power.
- Hog Production Reliance: Smithfield’s business model is heavily dependent on a consistent and quality supply of live hogs.
- External Sourcing Strategy: A move to procure a larger percentage of hogs externally enhances supplier importance.
- Mitigating Factors: Smithfield's scale and diversified supplier base limit the bargaining power of individual suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Smithfield Foods is moderate, influenced by several factors. While Smithfield relies heavily on hog producers, its significant market share and ability to source from numerous large producers limit the power of any single supplier. The company's strategic shift to external sourcing, however, elevates the importance of these external hog producers.
The cost of animal feed, a primary input for hog production, represented approximately 60% of the cost of goods sold in Smithfield's Hog Production segment during the period from 2024 through Q1 2025, underscoring the importance of managing these supplier costs effectively.
While Smithfield cultivates long-term relationships, the logistical challenges and costs associated with switching suppliers suggest moderate switching costs for the company. The threat of individual hog farmers integrating forward into processing is low due to the high capital and expertise required, though larger cooperatives could pose a theoretical challenge.
Smithfield's emphasis on specific supplier attributes like animal health and consistent availability, beyond the basic commodity nature of hogs, can grant leverage to those suppliers who meet these valued standards, particularly concerning biosecurity and sustainability protocols.
| Factor | Smithfield's Position | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power |
| Supplier Concentration | Diverse base of hog producers, though some consolidation exists. | Moderate; limits individual supplier power but concentration in certain regions can increase it. |
| Input Costs (Feed) | Feed represents ~60% of Hog Production COGS (2024-Q1 2025). | High; makes feed suppliers influential, impacting overall hog production costs. |
| Switching Costs | Logistical hurdles and relationship building. | Moderate; switching suppliers is disruptive but manageable. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Low for individual farmers; potential for larger cooperatives. | Low; prohibitive costs for most farmers to enter processing. |
| Supplier Differentiation | Value placed on health, consistency, and sustainability practices. | Moderate; suppliers meeting specific criteria gain some leverage. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Smithfield's position in the pork and processed meats industry.
Instantly visualize the competitive landscape for Smithfield, identifying key threats and opportunities to inform strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer concentration at Smithfield Foods is a key factor influencing its bargaining power. While the company serves a broad range of customers, including grocery chains, restaurants, and export markets, a significant portion of its revenue is tied to a few major players.
Walmart, for instance, has been a consistent and substantial customer, representing just over 11% of Smithfield's sales in recent years. Although no other single customer exceeds 10% of sales, this reliance on Walmart highlights a concentration that can empower this large retailer in price negotiations and other terms.
Customers possess significant power when they have numerous alternatives to a company's products. For Smithfield, this means consumers can easily switch to beef, chicken, or even a growing array of plant-based protein options. This ability to substitute directly impacts Smithfield's pricing power and market share.
The rise of plant-based meat alternatives presents a substantial threat, with the market anticipated to reach $15.12 billion by 2033. While this indicates a strong substitute option for consumers, it's worth noting Smithfield's own strategic entry into this space with its Pure Farmland brand, aiming to mitigate some of this customer power by offering its own alternative products.
Consumer spending habits, particularly a cautious approach to spending, can significantly impact how sensitive customers are to price changes for packaged meats. This means Smithfield must be very deliberate in its pricing strategies, aiming to strike a balance between volume and profitability.
This heightened price sensitivity can compel Smithfield to increase promotional spending to attract and retain customers, potentially squeezing profit margins. For instance, during economic downturns, consumers often trade down to less expensive brands or private labels, directly affecting sales of premium or branded packaged meats.
Customer Information Availability
Customers, from major retailers to individual buyers, now possess unprecedented access to information. This includes details on product origins, environmental commitments, and competitive pricing, significantly boosting their ability to negotiate.
This heightened transparency empowers consumers to make more informed choices, directly impacting their willingness to pay and their demands on suppliers like Smithfield. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 65% of consumers consider sustainability when making purchasing decisions, a factor that directly translates to increased customer bargaining power.
- Increased Information Access: Buyers can easily compare prices, quality, and ethical sourcing across numerous suppliers.
- Informed Purchasing Decisions: Transparency allows customers to identify the best value and hold suppliers accountable for their claims.
- Price Sensitivity: With readily available pricing data, customers are less likely to accept higher prices without justification.
- Demand for Transparency: Growing consumer awareness drives demand for clear information on product lifecycle and corporate responsibility.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by major retail customers into meat processing for companies like Smithfield is typically low. This is because meat processing is a complex, capital-intensive industry with significant regulatory hurdles, making it a difficult undertaking for retailers.
However, a more prevalent concern is the rise of private label brands by large retailers. These private labels can directly challenge Smithfield's branded offerings.
- Retailer Private Label Growth: In 2024, private label brands continued to gain market share across the grocery sector, often offering consumers a more affordable alternative to national brands. For instance, NielsenIQ data indicated that private label sales growth outpaced national brands in many food categories throughout the year.
- Pricing Pressure: The increased presence of private label meat products allows retailers to exert greater pricing pressure on suppliers like Smithfield, potentially impacting margins.
- Shelf Space Competition: Retailers control shelf space, and a strong private label offering can reduce the prominence and visibility of Smithfield's own brands, limiting consumer choice and sales opportunities.
Smithfield's customers, particularly large retailers, wield considerable bargaining power due to their significant purchasing volume and the availability of numerous alternatives. This power is amplified by increasing consumer demand for transparency and value, forcing Smithfield to carefully manage pricing and promotions.
The growing prevalence of retailer private label brands, which gained market share in 2024 according to NielsenIQ, directly challenges Smithfield's branded products and intensifies pricing pressure. While backward integration by retailers into meat processing remains unlikely due to industry complexity, the expansion of private labels significantly impacts Smithfield's competitive landscape and profit margins.
| Factor | Impact on Smithfield | Supporting Data (2024 Estimates/Trends) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Increases bargaining power of key buyers. | Walmart represented over 11% of Smithfield's sales. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Limits pricing power. | Consumers can easily switch to chicken, beef, or plant-based alternatives. |
| Price Sensitivity | Drives promotional spending and can reduce margins. | Consumers may trade down to private labels during economic uncertainty. |
| Information Access & Transparency | Empowers customers to negotiate better terms. | 65% of consumers consider sustainability in purchasing decisions (2024 survey). |
| Private Label Growth | Creates direct competition and pricing pressure. | Private label sales growth outpaced national brands in many food categories in 2024. |
Same Document Delivered
Smithfield Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Smithfield Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive instantly upon purchase, ensuring you get the full, professionally formatted report without any alterations. This detailed analysis is ready for immediate use, providing valuable insights into Smithfield's strategic landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Smithfield Foods faces intense competition in the packaged foods and meats sector. Key rivals such as Tyson Foods, Hormel Foods, and Pilgrim's Pride are significant players, each vying for market share.
While Smithfield holds the distinction of being the largest pork producer in the U.S., commanding a 23% market share, and ranks as the second-largest provider of packaged meats with a 20% market share, this demonstrates a strong presence rather than outright dominance.
The pig farming industry is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 4.9% between 2025 and 2032. This moderate expansion suggests a generally stable market. However, for established players like Smithfield, a slower growth rate in mature markets can lead to increased competition as companies vie for existing market share.
Smithfield Foods is actively differentiating its pork products, especially within its higher-margin packaged meats. Brands like Smithfield, Eckrich, and Nathan's Famous are central to this strategy, aiming to lessen reliance on volatile commodity pork prices and boost profitability via value-added offerings.
Exit Barriers
The meat processing industry faces substantial exit barriers, primarily due to the significant investment in fixed assets like processing plants and specialized farming infrastructure. These high capital requirements mean that exiting the market is not a simple decision, as companies often cannot easily recoup their investments.
This difficulty in exiting the industry can intensify competitive rivalry. Companies are often compelled to continue operations even during challenging market conditions, as the cost of shutting down and liquidating assets is prohibitive. For instance, Smithfield Foods and Tyson Foods both undertook plant closures in 2023, highlighting the complexity and expense involved in such decisions, and demonstrating how these factors can keep companies engaged in the market longer than they might otherwise prefer.
- High Capital Investment: Meat processing requires substantial investment in specialized facilities and equipment.
- Specialized Infrastructure: The need for specific infrastructure, from farms to processing lines, makes assets difficult to repurpose.
- Costly Closures: Shutting down operations involves significant costs related to severance, asset disposal, and environmental remediation.
- Sustained Rivalry: High exit barriers encourage companies to remain competitive even in downturns, prolonging market rivalry.
Diversity of Competitors
Smithfield faces a highly competitive environment due to the wide array of players in the market. Competitors range from massive, diversified food conglomerates like Tyson Foods and Hormel Foods, which possess significant scale and broad product lines, to niche, specialized producers focusing on specific protein segments or value-added products.
This diversity in competitors means a variety of strategic approaches are employed. Some focus on cost leadership through efficient operations and bulk purchasing, while others differentiate through product quality, branding, or unique market channels. For instance, Tyson Foods reported over $52 billion in revenue for fiscal year 2023, showcasing its immense scale, whereas smaller, specialized companies might operate with much leaner structures and targeted marketing efforts.
- Tyson Foods: A major competitor with a vast portfolio across poultry, beef, pork, and prepared foods.
- Hormel Foods: Known for brands like Spam and Jennie-O, demonstrating strength in specific protein categories and value-added products.
- Smaller Producers: Often focus on organic, antibiotic-free, or locally sourced products, carving out distinct market niches.
The varied strategies, cost structures, and product offerings among these competitors intensify the rivalry for Smithfield, demanding constant adaptation and strategic positioning to maintain market share and profitability.
Competitive rivalry within the meat processing industry is fierce, with Smithfield Foods facing formidable opponents like Tyson Foods and Hormel Foods. These major players, along with numerous smaller producers, constantly vie for market share through diverse strategies, from cost leadership to product differentiation.
The pig farming sector's projected 4.9% CAGR from 2025 to 2032 indicates a stable but not explosive growth environment, intensifying the battle for existing customers. Smithfield's significant market positions, such as being the largest U.S. pork producer with a 23% share, highlight the competitive landscape where even substantial shares do not guarantee dominance.
High exit barriers, stemming from massive investments in specialized processing plants and farming infrastructure, keep companies engaged in the market, even during downturns. This means rivals are less likely to leave, ensuring sustained pressure on Smithfield to innovate and maintain efficiency.
| Competitor | Key Strengths | 2023 Revenue (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Tyson Foods | Diversified protein portfolio, extensive distribution | $52.0 billion |
| Hormel Foods | Strong brand recognition, focus on value-added products | $12.1 billion |
| Pilgrim's Pride | Significant poultry producer, cost-efficient operations | $17.1 billion |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The market for meat and protein presents a significant threat of substitutes for pork. Consumers have a wide array of readily available alternatives, such as beef, chicken, turkey, lamb, and plant-based protein options. These substitutes are easily accessible in virtually all grocery stores and foodservice establishments, offering consumers flexibility in their purchasing decisions.
The abundance of these direct and indirect substitutes means that if pork prices were to increase substantially, or if consumer preferences were to shift away from pork, consumers could readily switch to other protein sources. For instance, in 2024, the average retail price of boneless pork chops saw fluctuations, and while specific comparative data against all substitutes is complex, the general trend shows that consumers often adjust their protein choices based on price and availability. The sheer volume of beef and chicken sold globally, with chicken often being a more budget-friendly option, underscores the competitive pressure from substitutes.
Plant-based meat alternatives are increasingly challenging traditional meat products by offering a better price-performance ratio, especially for consumers prioritizing health, sustainability, or ethics. The market for these alternatives is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating continued growth, making them a significant substitution threat.
Consumer trends show a growing interest in plant-based diets and flexitarianism, meaning more people are looking to cut back on meat. This shift directly impacts Smithfield's pork products, making consumers more likely to choose alternatives.
In 2024, the global plant-based meat market was valued at over $20 billion and is projected to grow significantly. This increasing market size indicates a substantial and growing threat from substitutes for traditional meat producers like Smithfield.
The availability and improving quality of plant-based and other protein alternatives, such as cultivated meat, further intensify this threat. As these substitutes become more appealing and accessible, consumer propensity to switch away from pork products rises.
Relative Price of Substitutes
The relative price of substitutes significantly impacts Smithfield Foods. Fluctuations in the prices of alternative protein sources like chicken and beef directly influence consumer purchasing decisions. For instance, if pork prices rise sharply compared to chicken, consumers will likely shift their demand, affecting Smithfield's sales volumes.
In 2024, the average retail price for pork loins saw some volatility, influenced by factors like feed costs and global supply. Meanwhile, chicken prices remained relatively stable for much of the year, presenting a more attractive option for budget-conscious consumers. This price differential can directly erode Smithfield's market share if not managed effectively through competitive pricing strategies.
- Pork Price Trends: Observing year-over-year changes in pork prices provides insight into consumer sensitivity.
- Chicken and Beef Price Benchmarks: Monitoring the pricing of key substitutes offers a clear view of competitive pressures.
- Consumer Switching Behavior: A significant price gap between pork and alternatives can lead to a noticeable shift in demand away from Smithfield products.
- Impact on Sales Volume: Direct correlation exists between the relative pricing of substitutes and Smithfield's overall sales performance.
Innovation in Substitute Products
The threat of substitutes is amplified by continuous innovation in the plant-based meat sector. Companies such as Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods are at the forefront, developing increasingly convincing and desirable alternatives to traditional meat products. This ongoing advancement means consumers have more appealing choices outside of conventional pork and beef.
Smithfield Foods itself acknowledges this dynamic by introducing its Pure Farmland plant-based product line. This strategic move highlights how established players are responding to the evolving market, where substitutes are not only present but actively improving in quality and consumer acceptance. By offering its own plant-based options, Smithfield is directly engaging with this competitive pressure.
- Plant-Based Meat Market Growth: The global plant-based meat market was valued at approximately $6.43 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $32.77 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 31.0% during the forecast period (2023-2028).
- Key Innovators: Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods have significantly invested in R&D, improving taste, texture, and nutritional profiles of their products.
- Smithfield's Response: The launch of Pure Farmland in 2019 marked Smithfield's direct entry into the plant-based category, offering a range of products like burgers, sausages, and grounds.
- Consumer Acceptance: Surveys indicate a growing segment of consumers, including flexitarians, are actively seeking and incorporating plant-based options into their diets, driven by health, environmental, and ethical concerns.
The threat of substitutes for pork remains substantial, driven by the wide availability and increasing appeal of alternatives like chicken, beef, and plant-based proteins. Consumers can easily switch between these options based on price, taste, and evolving dietary preferences.
In 2024, the competitive pricing of chicken, often more affordable than pork, continued to draw consumers. Furthermore, the plant-based meat market, valued at over $20 billion globally in 2024, is rapidly expanding, with innovators like Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods enhancing product quality and consumer acceptance, directly challenging traditional meat products.
| Protein Source | 2024 Average Retail Price (Illustrative) | Key Substitute Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Pork (e.g., Boneless Chops) | $5.50/lb | Price volatility, consumer perception |
| Chicken (e.g., Boneless Breast) | $4.00/lb | Price stability, widespread availability |
| Beef (e.g., Ground Beef) | $5.00/lb | Consumer preference, dietary trends |
| Plant-Based Burgers | $6.00/lb (approx.) | Health, sustainability, ethical concerns, innovation |
Entrants Threaten
The meat processing and hog production sectors demand significant upfront investment. Establishing modern farms, efficient processing facilities, and robust cold storage and distribution systems can easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, building a new, large-scale hog finishing facility in 2024 could cost upwards of $10 million, with processing plants representing an even larger capital outlay.
Established players like Smithfield Foods leverage substantial economies of scale in hog production, processing, and distribution. This means they can produce and sell their products at a lower cost per unit compared to smaller or newer competitors. For instance, in 2023, Smithfield Foods reported net sales of $17.3 billion, a testament to its massive operational footprint.
New entrants face a significant hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. Achieving comparable scale would necessitate immense initial capital investment, making it difficult for them to compete on price. Without this scale, new companies would likely have higher per-unit costs, putting them at a distinct disadvantage from the outset.
For new companies entering the pork industry, securing shelf space in major grocery chains and access to foodservice distributors presents a significant hurdle. Smithfield Foods, for instance, has cultivated decades-long relationships with these critical partners, creating a formidable barrier. As of early 2024, the top five grocery retailers in the U.S. control over 60% of the grocery market, making their partnerships essential for any new entrant's success.
Brand Loyalty and Differentiation
Smithfield Foods benefits from strong brand loyalty and differentiation, making it harder for new companies to enter. Established brands like Smithfield, Eckrich, and Armour have built significant consumer trust over years of consistent quality and marketing. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. packaged meat market continued to see consumers prioritize trusted brands, especially during economic fluctuations.
New entrants face substantial hurdles in replicating Smithfield's brand equity. The cost of building comparable brand recognition and consumer preference in a saturated market is immense, requiring extensive advertising campaigns and product development. In 2023, the average marketing spend for a new CPG brand launch often exceeded $1 million, a significant barrier for smaller competitors aiming to challenge established players like Smithfield.
- Brand Recognition: Smithfield's portfolio of well-known brands commands significant consumer trust.
- Marketing Investment: New entrants require substantial capital for marketing to build brand awareness.
- Market Saturation: The packaged meat industry is crowded, intensifying competition for new players.
- Consumer Loyalty: Existing brand loyalty creates a high barrier to entry for unproven competitors.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policy and regulation significantly impact the threat of new entrants in the pork industry. Stringent rules surrounding food safety, animal welfare, and environmental protection, for instance, create substantial compliance costs and operational complexities. For example, in 2024, the USDA's Food Safety and Inspection Service continued to enforce rigorous standards for meat processing plants, requiring significant investment in technology and personnel for new facilities to meet these benchmarks. These regulatory hurdles act as a considerable barrier, making it more challenging and expensive for new players to enter the market compared to established companies that have already invested in compliant infrastructure and processes.
The pork sector faces a landscape shaped by evolving regulations. New entrants must navigate a complex web of federal, state, and local laws covering everything from waste management to antibiotic use. For instance, ongoing discussions around stricter environmental regulations for hog farms, potentially including enhanced manure management systems, could require millions in upfront capital for new operations. This regulatory environment, which can change with policy shifts, demands continuous adaptation and investment, thereby raising the barrier to entry.
- Compliance Costs: New entrants must factor in significant expenses for meeting food safety, animal welfare, and environmental standards.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating a multi-layered system of federal, state, and local regulations presents a steep learning curve and operational challenge.
- Investment in Infrastructure: Meeting standards often requires substantial investment in specialized facilities and technologies, a hurdle for startups.
- Policy Uncertainty: Evolving regulations can introduce risk and necessitate further capital outlays for ongoing compliance.
The threat of new entrants in the pork processing and hog production industry is considerably low. High capital requirements, estimated to be tens to hundreds of millions of dollars for modern facilities, act as a significant initial barrier. For example, a new large-scale hog finishing facility could cost over $10 million in 2024, with processing plants representing a much larger investment.
Established players benefit from substantial economies of scale, allowing for lower per-unit costs that new entrants struggle to match. Smithfield Foods' 2023 net sales of $17.3 billion highlight its massive operational footprint. Furthermore, strong brand loyalty and established relationships with major retailers and distributors, where the top five U.S. grocers control over 60% of the market as of early 2024, create formidable competitive advantages.
The industry also faces significant regulatory hurdles and compliance costs related to food safety, animal welfare, and environmental standards. In 2024, the USDA's stringent enforcement of meat processing regulations necessitates substantial investment in technology and personnel for new facilities. Evolving environmental regulations, such as enhanced manure management systems, could demand millions in upfront capital for new hog operations.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Cost/Impact (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building modern hog farms and processing plants. | $10M+ for finishing facilities; significantly higher for processing plants. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower production costs due to large-scale operations. | Established players like Smithfield Foods (2023 net sales $17.3B) achieve significant cost advantages. |
| Distribution & Shelf Space Access | Securing access to major grocery chains and foodservice distributors. | Top 5 U.S. grocers control >60% of market; established relationships are crucial. |
| Brand Loyalty & Marketing | Building consumer trust and brand recognition. | New CPG brand launches often exceed $1M in marketing spend; established brands have years of equity. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting food safety, animal welfare, and environmental standards. | USDA enforcement requires investment; potential new environmental regs could add millions in capital costs. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Smithfield leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and consumer trend databases to assess competitive pressures.