The Reader's Digest Association, Inc. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
The Reader's Digest Association, Inc. Bundle
The Reader's Digest Association, Inc. faces a dynamic competitive landscape shaped by several key forces. Understanding the intensity of buyer power, the threat of substitutes, and the influence of suppliers is crucial for navigating its market. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore The Reader's Digest Association, Inc.’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The Reader's Digest Association, Inc. relies on a diverse range of content creators and journalists. While a broad talent pool exists, highly specialized or well-regarded contributors, particularly for exclusive or unique pieces, can negotiate higher compensation, thereby increasing their bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, industry reports indicated a growing demand for niche expertise in areas like investigative journalism and specialized lifestyle content, which could empower those creators.
The increasing integration of AI in content generation presents a dynamic shift. While AI tools can potentially streamline certain content creation processes and, in some cases, commoditize more routine writing tasks, the need for human oversight in ensuring quality, authenticity, and editorial integrity remains paramount. This human element, especially for Reader's Digest's trusted brand, continues to hold significant value.
The Reader's Digest Association, Inc.'s reliance on paper and printing suppliers for its print publications significantly influences its operational costs. In 2024, the global paper market continued to experience volatility, with some regions reporting a 5-10% increase in paper prices due to ongoing supply chain challenges and increased demand from packaging sectors. This dependence grants these suppliers considerable leverage, especially when faced with disruptions like those seen in recent years.
While Reader's Digest's substantial order volumes can offer some negotiation power, the broader industry trends, including the consolidation of printing companies and the increasing cost of raw materials, can still tip the scales in favor of suppliers. This dynamic means that managing these supplier relationships effectively is crucial for controlling production expenses and maintaining profit margins in the competitive publishing landscape.
Digital platform and software providers hold significant bargaining power over The Reader's Digest Association, Inc. due to their essential role in content delivery and management. Companies relying heavily on proprietary content management systems or specialized digital advertising platforms can face substantial costs if these suppliers increase licensing fees or alter service terms. For instance, a shift in a major cloud service provider's pricing structure could directly impact The Reader's Digest's operational expenses.
The concentration of key software vendors in the digital media space further amplifies their influence. If only a few providers offer critical functionalities, such as advanced analytics or unique content distribution tools, they can dictate terms more effectively. This situation is common in niche software markets where development costs are high, limiting the number of viable competitors and thus strengthening the position of existing suppliers.
Direct Mail Service Providers (e.g., Postal Services)
For The Reader's Digest Association, direct mail service providers, primarily postal services, represent a significant supplier force. Their ability to influence costs through postage rates directly impacts Reader's Digest's profitability, especially given the company's reliance on direct marketing. In 2024, the United States Postal Service (USPS) continued to implement price adjustments, with several increases impacting bulk mail rates, a key component for direct marketers.
The bargaining power of these suppliers stems from their often monopolistic or oligopolistic nature. For instance, the USPS holds a legal monopoly on delivering non-urgent mail. This lack of direct competition limits Reader's Digest's ability to negotiate lower prices or find alternative, equally widespread distribution channels for its direct mail campaigns.
- Monopolistic Advantage: Postal services often operate as government-sanctioned monopolies, limiting competitive pricing pressures.
- Price Sensitivity: Increases in postage costs directly erode profit margins for direct mail-heavy businesses like Reader's Digest.
- Service Dependency: Disruptions in postal services can halt critical marketing and sales operations.
- Limited Alternatives: While private carriers exist, they often cannot match the universal reach and cost-effectiveness of postal services for mass mailings.
Advertising Technology Providers
Advertising technology providers, crucial for The Reader's Digest Association's digital ad revenue through programmatic advertising and audience targeting, possess significant bargaining power. The complexity and effectiveness of these sophisticated tools, essential for maximizing ad revenue and personalizing content delivery, contribute to their leverage. Major ad tech platforms often operate on a limited-competition basis, further strengthening their position.
- High switching costs: Integrating new ad tech can be complex and time-consuming, making it difficult for The Reader's Digest to switch providers.
- Essential functionality: The core functions provided by these platforms are vital for modern digital advertising, giving suppliers considerable influence.
- Limited number of dominant players: The ad tech landscape is often dominated by a few key players, reducing the options available to publishers like The Reader's Digest.
- Data integration and analytics: The ability of these providers to offer advanced data integration and analytics capabilities further solidifies their value proposition.
The Reader's Digest Association, Inc. faces considerable bargaining power from its paper and printing suppliers. In 2024, global paper prices saw increases, with some regions experiencing 5-10% hikes due to supply chain issues and demand from the packaging industry. This reliance on a few large paper mills and printing firms means Reader's Digest has limited options to negotiate lower costs, especially when these suppliers face their own raw material or logistical challenges.
What is included in the product
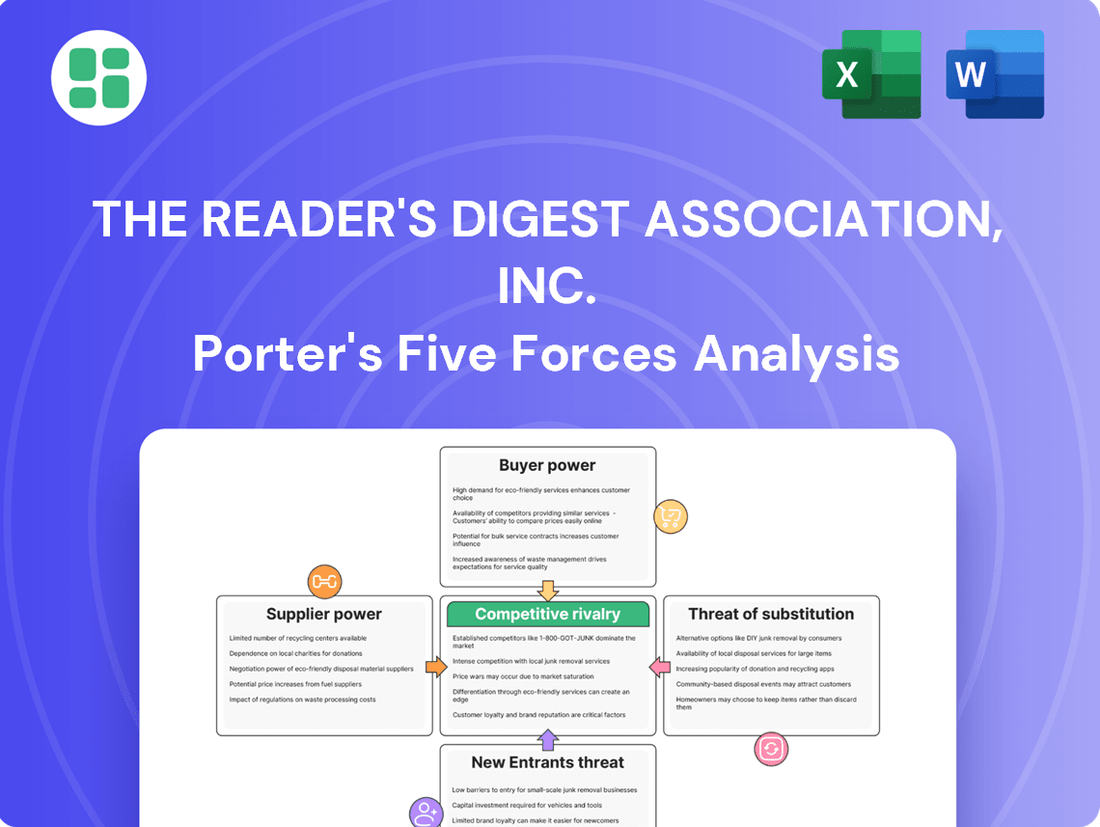
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping The Reader's Digest Association, Inc.'s market, revealing buyer power, supplier leverage, threat of substitutes, new entrants, and industry rivalry.
The Reader's Digest Association, Inc. Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces—perfect for quick decision-making and understanding competitive pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual magazine and book subscribers, by themselves, don't hold much sway. Think about it; one person canceling their Reader's Digest subscription isn't going to make a dent. This is because the financial impact of a single subscriber is quite small for a company like The Reader's Digest Association.
However, when you look at all these individual subscribers together, their collective power becomes more noticeable. If many people decide to stop subscribing, that's a different story. This becomes especially true in 2024, as consumers are facing what's often called subscription fatigue, meaning they're overloaded with monthly charges and are more likely to cut back.
The ease with which a subscriber can switch to a competitor or simply cancel altogether is a key factor. With so many digital and print content options available, from other magazines to online articles and streaming services, Reader's Digest faces a constant challenge to keep subscribers engaged and prevent them from leaving.
Direct marketing product buyers, like those engaging with The Reader's Digest Association, Inc., generally possess moderate bargaining power. This is primarily due to the sheer volume of alternative purchasing options available to them. In 2024, the continued expansion of e-commerce means consumers can easily compare prices and product features across countless retailers and direct-to-consumer brands.
The ease with which consumers can switch between different direct marketing offers, whether through catalogs, infomercials, or online ads, forces companies like Reader's Digest to remain highly competitive. In a market where switching costs are low, buyers can readily seek out better deals or more appealing products, compelling the company to consistently deliver strong value propositions and attractive pricing to retain its customer base.
Advertisers, especially major corporations, wield considerable bargaining power with The Reader's Digest Association. Their substantial ad budgets allow them to negotiate favorable rates and demand precise targeting capabilities. In 2024, the continued shift towards digital advertising means advertisers can easily compare ROI across various media, putting pressure on traditional publishers to demonstrate value.
Digital Content Consumers
Digital content consumers wield significant bargaining power due to the vast availability of free and low-cost alternatives. This ease of access to news, entertainment, and information from numerous platforms diminishes reliance on any single provider like Reader's Digest.
This dynamic forces publishers to differentiate themselves by offering unique value propositions to retain their audience. For instance, in 2024, the global digital content market continued its robust growth, with subscription services and ad-supported models competing fiercely for consumer attention.
- Abundant Free Content: Platforms like YouTube, TikTok, and various news aggregators offer vast amounts of content without direct cost to the consumer, setting a low price expectation.
- Low Switching Costs: Consumers can effortlessly shift between different content providers with minimal effort or financial penalty.
- Information Overload: The sheer volume of available content means consumers are less likely to be loyal to one source if their needs are met elsewhere.
- Price Sensitivity: In 2024, a significant portion of consumers demonstrated a preference for bundled deals or subscription tiers that offer perceived value for money, impacting pricing strategies for content providers.
Bulk Purchasers/Institutional Buyers
The Reader's Digest Association, Inc. faces significant bargaining power from bulk purchasers and institutional buyers. These entities, including libraries, educational institutions, and corporate clients, can leverage the substantial volume of their magazine, book, or content license acquisitions to negotiate more favorable pricing, volume discounts, and tailored package deals. The strategic importance and scale of these bulk transactions directly influence the negotiating leverage held by these customers.
For instance, consider the impact on subscription revenue. In 2024, the subscription model continues to be a cornerstone of media companies' revenue streams. Large institutional subscriptions, which can represent thousands of individual access points, provide a predictable revenue base but also a concentrated point of negotiation. A single large library system or corporate client canceling or renegotiating terms can have a noticeable impact on The Reader's Digest Association's top-line figures.
- Volume Discounts: Institutional buyers often demand tiered discounts based on the number of subscriptions or content licenses purchased, directly impacting per-unit profitability.
- Customized Packages: These buyers may request tailored content bundles or licensing agreements that deviate from standard offerings, requiring additional administrative and content development resources.
- Strategic Importance: The decision of a major educational consortium or a large corporate entity to adopt or reject The Reader's Digest Association's content can influence market perception and attract or deter smaller clients.
- Negotiating Leverage: The ability of these bulk purchasers to switch to alternative content providers or to delay or reduce their commitments gives them considerable power in price and term negotiations.
Individual subscribers for The Reader's Digest Association, Inc. have low bargaining power as their individual impact is minimal. However, collective action, amplified by 2024's subscription fatigue, can increase their sway. Low switching costs and abundant content alternatives further empower consumers to move away from providers if dissatisfied.
Direct marketing buyers possess moderate power due to the vast array of purchasing options available, especially with e-commerce growth in 2024. Low switching costs between different direct marketing offers compel companies like Reader's Digest to offer competitive value and pricing.
Advertisers, particularly large corporations, hold significant bargaining power due to their substantial ad budgets and ability to negotiate favorable rates. In 2024, the shift to digital advertising allows advertisers to easily compare ROI, pressuring publishers to demonstrate value effectively.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
The Reader's Digest Association, Inc. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview provides a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis of The Reader's Digest Association, Inc., detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of the company. The document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to download after payment, ensuring you receive the complete, professionally formatted analysis without any alterations or missing sections.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Reader's Digest Association, Inc. contends with intense rivalry from numerous traditional print publishers. These competitors, ranging from broad-interest magazines to specialized publications and book imprints, vie for the same audience and advertising dollars.
This competitive landscape is further shaped by the overall health of the print media industry. In 2024, the magazine publishing sector continued to navigate a challenging environment, with many legacy publications experiencing flat or declining print circulation and advertising revenues, forcing a greater reliance on digital strategies.
Key battlegrounds include securing reader subscriptions, attracting advertisers seeking to reach specific demographics, and securing prominent placement in retail distribution channels. Publishers are constantly innovating with content and formats to maintain engagement in a crowded market.
Digital-first media companies, such as online news portals and social media platforms, represent a substantial and escalating competitive threat to traditional players like The Reader's Digest Association. These digital rivals often provide free content and highly personalized user experiences, directly competing for consumer attention and advertising revenue.
The intense rivalry is further fueled by the accessibility of digital platforms, allowing new entrants to emerge rapidly. For instance, the digital advertising market continues its robust growth, with global digital ad spending projected to reach over $700 billion in 2024, a significant portion of which is siphoned from traditional media channels.
Reader's Digest Association's direct marketing segment faces intense rivalry from a broad spectrum of competitors. These include e-commerce giants, traditional catalog retailers, and numerous other direct mail businesses, all vying for consumer attention and spending.
The direct marketing landscape is dynamic and expanding, but this growth fuels fierce competition. Success hinges on sophisticated strategies emphasizing personalization and automation to connect with consumers effectively.
In 2024, the direct mail market continued to show resilience, with companies investing in data analytics to refine targeting. For instance, the U.S. Postal Service reported handling billions of pieces of mail annually, underscoring the ongoing relevance and competitive nature of direct marketing channels.
Content Platforms and Aggregators
Large content platforms and aggregators like Google News and Apple News present a significant competitive challenge. By curating and distributing content from numerous publishers, these platforms can siphon off audience attention that might otherwise go directly to Reader's Digest's owned websites and apps. This indirect competition can diminish direct traffic and engagement, impacting Reader's Digest's ability to monetize its content through subscriptions or advertising on its own properties.
These aggregators often leverage sophisticated algorithms to personalize content delivery, making them highly attractive to users seeking tailored information. For instance, Google News alone boasts hundreds of millions of users globally, creating a vast potential audience that Reader's Digest must compete to capture. In 2024, digital advertising spend on platforms like Google and Meta continued to grow, further highlighting the dominance of these aggregators in the digital media landscape.
- Indirect Competition: Platforms like Google News and Apple News aggregate content from various sources, acting as indirect rivals.
- Audience Fragmentation: Reader's Digest faces the challenge of fragmented audiences increasingly relying on aggregators for news and entertainment.
- Reduced Direct Traffic: Aggregators can divert traffic away from Reader's Digest's owned digital properties, impacting engagement and revenue.
- Monetization Impact: The shift in audience behavior affects Reader's Digest's ability to monetize content through direct advertising and subscriptions.
Niche Content Providers
Reader's Digest faces increasing competition from niche content providers, including independent creators and specialized digital publications. These focused outlets cater to very specific interests, drawing away segments of the broader audience that Reader's Digest traditionally served. For instance, the creator economy has exploded, with platforms like Substack reporting over one million paid subscribers in 2023, showcasing the demand for specialized content directly from individuals.
This fragmentation means that while Reader's Digest offers a wide array of content, it may struggle to capture the deep engagement that highly specialized platforms can achieve. The sheer volume of online content available means consumers can easily find hyper-relevant material, potentially diminishing the appeal of a more generalist approach. In 2024, the digital publishing landscape continues to be characterized by this trend towards specialization.
- Increased Competition: The rise of independent creators and specialized digital platforms intensifies rivalry for audience attention.
- Audience Fragmentation: Niche content providers attract specific interest groups, potentially reducing Reader's Digest's broad appeal.
- Creator Economy Impact: Platforms like Substack highlight the growing subscriber base for specialized, creator-driven content.
- Digital Landscape Shift: The ongoing trend in 2024 favors highly focused content over generalist offerings.
The Reader's Digest Association faces intense rivalry from both traditional print media and a growing array of digital-first competitors. This competition is amplified by the increasing fragmentation of audiences, who are increasingly turning to specialized content creators and large content aggregators for their information and entertainment needs.
In 2024, the digital advertising market continued its expansion, with global spending projected to exceed $700 billion, drawing significant revenue away from legacy print publications. This shift forces traditional players like Reader's Digest to adapt by enhancing their digital strategies and content personalization to retain audience engagement and advertising share.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Reader's Digest | 2024 Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Print Publishers | Broad and niche magazines, book imprints | Competition for subscriptions and ad revenue | Continued pressure on print circulation and ad sales |
| Digital-First Media Companies | Online news, social media platforms | Captures audience attention and digital ad spend | Global digital ad spend projected over $700 billion |
| Content Aggregators | Google News, Apple News | Diverts direct traffic, impacts monetization | Hundreds of millions of users globally |
| Niche Content Providers | Independent creators, specialized digital publications | Siphons off specific interest groups | Substack reported over 1 million paid subscribers in 2023 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat to The Reader's Digest Association comes from the abundance of free online content. Websites, blogs, social media, and user-generated platforms offer a vast ocean of information, news, and entertainment at no cost, directly challenging the value proposition of paid subscriptions and print publications.
This readily available free content erodes the perceived need for consumers to pay for curated or professionally produced material. For example, in 2024, the average time spent daily on social media globally exceeded 2.5 hours, indicating a strong preference for accessible, often free, digital content consumption.
The threat of substitutes for The Reader's Digest Association is significant, particularly from digital entertainment. Streaming services like Netflix and Spotify, along with the booming podcast and gaming industries, directly vie for consumers' limited leisure time and attention. This means less time is available for traditional reading material.
In 2024, the digital entertainment market continued its robust growth. For instance, global spending on video streaming services was projected to exceed $100 billion, demonstrating a clear consumer preference for easily accessible, on-demand content. This trend directly siphons potential readers away from print publications.
The accessibility and often lower cost of digital alternatives further amplify this threat. Many streaming services offer vast libraries for a monthly fee that can be less than the cost of a few magazines, making them an attractive substitute for entertainment and information consumption.
Social media platforms are increasingly becoming the primary source for news and content, especially for younger audiences. This shift directly challenges traditional media outlets like Reader's Digest, as consumers bypass established channels for information discovery.
In 2024, a significant portion of adults, particularly Gen Z and Millennials, reported getting their news primarily from social media. For instance, Pew Research Center data consistently shows that platforms like TikTok and Instagram are major news sources for younger demographics, impacting how publishers reach and engage their readership.
Libraries and Public Domain Content
Public libraries represent a significant threat of substitution for The Reader's Digest Association. They provide free access to a wide array of reading materials, including books and magazines, directly competing with Reader's Digest's core offerings. This free access model means consumers can obtain similar content without incurring any cost.
The proliferation of public domain content online further amplifies this threat. Classic literature and historical texts are readily available for free, offering consumers alternatives to newly published or curated content. For instance, Project Gutenberg offers over 60,000 free eBooks, many of which are literary classics that might otherwise be purchased.
In 2024, library circulation numbers continue to show strong engagement. According to the American Library Association, public libraries across the United States reported millions of physical and digital checkouts, indicating a sustained demand for library services as a cost-effective alternative to commercial publications.
- Free Access: Libraries offer books, magazines, and digital content at no cost to the user.
- Public Domain Content: Online platforms provide free access to classic literature and informational material.
- Cost Savings: Consumers can avoid purchasing publications by utilizing these free resources.
- Circulation Data: Public libraries in 2024 continued to report high circulation numbers, demonstrating their appeal as substitutes.
Alternative Direct Marketing Channels
The threat of substitutes for The Reader's Digest Association's direct marketing business is significant, particularly from alternative direct marketing channels. These substitutes offer businesses different ways to connect with consumers, often at a lower cost or with greater targeting precision than traditional mailers.
Email marketing, social media advertising, and other digital channels have become powerful alternatives. For instance, in 2024, global digital ad spending was projected to reach over $600 billion, highlighting the substantial shift towards these platforms. Telemarketing also remains a viable, albeit sometimes controversial, substitute for direct outreach.
These alternative channels can often provide more immediate feedback and analytics compared to direct mail, allowing for quicker campaign adjustments. The accessibility and reach of digital platforms mean that companies can potentially engage a broader audience more efficiently.
- Email Marketing: Offers direct communication at a fraction of the cost of physical mail, with high open and click-through rates when done effectively.
- Social Media Advertising: Provides granular targeting options based on demographics, interests, and behaviors, allowing for highly personalized campaigns.
- Telemarketing: Enables direct verbal interaction with potential customers, facilitating immediate responses and relationship building.
- Digital Advertising Channels: Includes search engine marketing (SEM), display advertising, and video ads, which offer broad reach and measurable results.
The threat of substitutes for The Reader's Digest Association is substantial, primarily from the wealth of free digital content and entertainment options available. Consumers have numerous cost-free or low-cost alternatives for information and leisure, directly impacting the demand for paid print publications and subscription services.
In 2024, the continued dominance of social media as a news source, with platforms like TikTok and Instagram being primary outlets for younger demographics, significantly diverts attention from traditional media. Furthermore, the robust growth of the digital entertainment market, with global spending on video streaming services projected to exceed $100 billion in 2024, offers compelling alternatives that consume leisure time previously allocated to reading.
Public libraries also present a strong substitute, offering free access to books, magazines, and digital resources. For instance, in 2024, public libraries across the US reported millions of checkouts, underscoring their role as a cost-effective alternative for content consumption.
Additionally, for Reader's Digest's direct marketing business, substitutes like email marketing and social media advertising offer more cost-effective and targeted outreach. Global digital ad spending was expected to surpass $600 billion in 2024, indicating a major shift towards these digital channels.
| Substitute Category | Key Examples | 2024 Relevance/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Free Digital Content | Social Media, Blogs, User-Generated Platforms | Average daily social media use exceeded 2.5 hours globally. |
| Digital Entertainment | Streaming Services, Podcasts, Gaming | Global video streaming spending projected over $100 billion. |
| Public Libraries | Books, Magazines, Digital Resources (Free Access) | Millions of checkouts reported by US public libraries. |
| Alternative Marketing Channels | Email Marketing, Social Media Ads, Telemarketing | Global digital ad spending projected over $600 billion. |
Entrants Threaten
The digital landscape has seen a dramatic reduction in the cost and complexity of creating and distributing content. Platforms like WordPress and Substack, alongside social media channels, allow anyone to become a publisher with little to no initial capital outlay.
This democratization of publishing means that individuals and small groups can now compete with established entities like The Reader's Digest Association. For instance, the creator economy, fueled by platforms like YouTube and TikTok, saw creator earnings surge. In 2024, it was estimated that over 50 million people globally identify as content creators, a testament to the low barrier to entry.
This influx of new content creators, often operating with lean overheads, poses a significant threat. They can quickly establish an audience and monetize their work through various digital channels, directly impacting market share and advertising revenue for traditional publishers.
Niche digital publishers pose a significant threat by easily targeting specific, underserved audiences with specialized content. They bypass traditional distribution and large editorial needs, allowing for rapid market penetration. For instance, in 2024, the digital publishing market continued its growth, with specialized platforms demonstrating strong engagement metrics, often outperforming broader content providers in their specific verticals.
The rapid evolution of AI-powered content generation presents a significant threat of new entrants for The Reader's Digest Association. AI tools can now produce articles, summaries, and even creative pieces with increasing sophistication, lowering the barrier to entry for new digital publications or content platforms.
These AI tools allow for the creation of vast amounts of content at a fraction of the cost and time traditionally required, potentially flooding the market with easily produced material. For instance, by mid-2024, generative AI models were demonstrating capabilities to produce human-quality text across various genres, making it feasible for new players to scale their content operations rapidly without substantial human editorial teams.
This influx of AI-generated content could dilute the value of professionally curated and edited content, forcing established players like Reader's Digest to compete on volume and speed, rather than solely on quality and brand reputation. The ability of new entrants to leverage AI for cost-effective content creation directly challenges traditional business models that rely on human expertise and established production workflows.
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) E-commerce Startups
The threat of new entrants from direct-to-consumer (D2C) e-commerce startups is significant for The Reader's Digest Association, Inc. These new players can quickly establish an online presence, utilizing social media and digital marketing to reach consumers directly. This bypasses traditional, more costly direct mail channels, lowering the barrier to entry.
New D2C e-commerce businesses can rapidly gain traction by leveraging accessible online platforms and sophisticated digital marketing strategies. For example, in 2024, the global e-commerce market continued its robust growth, with projections indicating further expansion. This digital-first approach allows startups to operate with lower overheads compared to established companies with legacy infrastructure.
The ease with which new D2C brands can launch and scale presents a direct competitive challenge. Consider the rise of subscription box services and niche online retailers, many of which have disrupted traditional retail models. In 2023, D2C brands saw continued investment, with many securing significant funding rounds to fuel their growth and market penetration.
- Low Capital Requirements: Digital storefronts and online advertising are often less capital-intensive than establishing physical retail or extensive direct mail operations.
- Agile Marketing: D2C startups excel at using social media and influencer marketing to build brand awareness and customer loyalty quickly.
- Direct Customer Relationships: These new entrants build direct relationships with customers, gathering valuable data and feedback for rapid product iteration and personalized offers.
- Market Fragmentation: The digital landscape allows for niche targeting, enabling new entrants to carve out specific market segments that might be overlooked by larger, more generalized companies.
High Barriers in Traditional Print Publishing
While digital publishing has dramatically lowered entry barriers, the traditional print publishing sector, where The Reader's Digest Association operates, still presents substantial hurdles for newcomers. Establishing a large-scale print operation demands significant capital investment. This includes acquiring and maintaining expensive printing presses, building robust physical distribution networks, and cultivating established brand recognition to gain consumer trust and market share.
The sheer cost associated with these operational necessities acts as a powerful deterrent. For instance, a modern commercial printing press can cost millions of dollars, and establishing a nationwide distribution system involves complex logistics and substantial ongoing operational expenses. In 2024, the cost of paper and ink also remained a significant factor, impacting the profitability of new entrants without established economies of scale.
These high capital requirements and the need for established infrastructure mean that new companies looking to compete directly with established players like The Reader's Digest Association in the traditional print market face a steep uphill battle. They must overcome not only the financial outlay but also the challenge of building brand loyalty and reaching a wide audience through established, often costly, channels.
Key barriers include:
- High Capital Expenditure: Significant investment needed for printing equipment and distribution infrastructure.
- Established Brand Recognition: Incumbents benefit from years of building consumer trust and awareness.
- Distribution Network Costs: Creating and maintaining physical delivery systems is expensive and complex.
- Economies of Scale: Existing players leverage scale for lower per-unit production and distribution costs.
While digital channels offer low entry barriers, the traditional print publishing domain presents substantial capital requirements for new entrants. Establishing large-scale printing operations and physical distribution networks demands significant financial investment, acting as a deterrent.
In 2024, the cost of essential materials like paper and ink remained a considerable factor, further impacting the feasibility for new players lacking established economies of scale. These high initial costs, coupled with the need to build brand recognition and access costly distribution channels, create formidable obstacles.
The threat of new entrants into the print sector is therefore moderate, primarily due to these significant capital and infrastructure demands that favor established companies like The Reader's Digest Association.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Investment in printing presses, distribution logistics, and initial inventory. | High; requires substantial upfront funding. |
| Brand Recognition | Established trust and awareness built over time. | High; new entrants struggle to gain immediate credibility. |
| Distribution Networks | Access to physical delivery systems for print publications. | High; costly and complex to replicate existing networks. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high-volume production. | High; new entrants face higher per-unit costs initially. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for The Reader's Digest Association, Inc. is built upon a foundation of diverse and reliable data sources. This includes publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Statista and IBISWorld, and relevant trade publications that track media and publishing trends.
We also incorporate insights from competitor announcements, news archives, and government regulatory filings to capture the full competitive landscape. This comprehensive approach ensures a robust understanding of the forces shaping the industry.