Payless Shoes Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Payless Shoes Bundle
Payless Shoes faced intense rivalry from established and online retailers, significantly impacting its profitability. The threat of new entrants was moderate, as establishing a physical presence required substantial capital, but online-only competitors could enter with lower overhead. Buyer power was high, with consumers easily comparing prices and switching between brands, especially with the rise of e-commerce.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Payless Shoes’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration at Payless ShoeSource was a significant factor in its bargaining power. The footwear industry, particularly for mass-market retailers, often relies on a relatively concentrated group of large manufacturers, especially those in Asia. For instance, in 2024, a substantial portion of global footwear production is concentrated in countries like Vietnam and China, with a limited number of major factories handling large volumes. This concentration means that if a few key suppliers were to experience production issues or decide to increase prices, Payless would have less flexibility in sourcing and could face higher costs.
Switching from one shoe supplier to another for Payless ShoeSource would likely involve significant financial and operational costs. These could include the expense of retooling manufacturing processes, establishing new quality control protocols, and potentially losing volume discounts from the incumbent supplier. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a retail company to onboard a new major supplier, including due diligence and initial setup, can range from $10,000 to $50,000, not including potential production delays.
These switching costs directly bolster the bargaining power of Payless's existing suppliers. If it's costly and disruptive to find and integrate a new supplier, Payless has less leverage to negotiate better terms or prices. This dependence makes it harder for Payless to walk away from current agreements, even if unfavorable, thereby strengthening the supplier's position in pricing and contract negotiations.
Payless Shoes historically sourced a wide variety of materials, from basic synthetic fabrics to more common leather types, which were largely commoditized. This meant that many suppliers could offer similar inputs, diminishing the bargaining power of any single supplier due to the availability of alternatives. For instance, in 2023, the global footwear materials market saw continued production of standard textiles and leathers, with no single Payless-specific material being a significant differentiator.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers might consider opening their own retail stores or selling directly to customers, effectively cutting out intermediaries like Payless. This move would directly challenge Payless's established business model and market presence.
Such forward integration by suppliers would significantly diminish Payless's leverage. It would mean less control over product distribution and availability, potentially leading to higher costs or limited inventory. For instance, if a major shoe component supplier decided to launch its own direct-to-consumer brand, it could siphon off a portion of Payless's customer base and reduce its purchasing power.
- Reduced Control: Payless would lose direct oversight of how its products are presented and sold to the end consumer.
- Increased Competition: Suppliers entering retail directly would create new competitive pressures.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Payless's reliance on suppliers who could become direct competitors makes its supply chain more susceptible to disruption.
Importance of Payless to Suppliers
The significance of Payless ShoeSource's business volume to its suppliers plays a crucial role in determining supplier bargaining power. If Payless constituted a substantial portion of a supplier's overall revenue, that supplier would likely have less leverage. This dependence means suppliers would be more inclined to accept Payless's terms to maintain the business relationship, thereby reducing their bargaining power.
For many suppliers in the footwear industry, Payless was a major customer. This volume meant that losing Payless as a client could have a significant negative impact on a supplier's financial health. For example, during its peak, Payless operated thousands of stores, generating billions in annual sales. This scale naturally made suppliers highly reliant on Payless's orders.
- Payless's substantial order volumes made it a key client for many footwear and accessory manufacturers.
- A significant portion of a supplier's revenue could be tied to Payless, diminishing their ability to dictate terms.
- The sheer scale of Payless's operations meant suppliers were often incentivized to accommodate Payless's demands to secure or maintain their business.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Payless Shoes was influenced by several factors, including supplier concentration and switching costs. In 2024, the footwear manufacturing sector, especially for mass-market retailers, remains concentrated in key Asian countries like Vietnam and China, with a few major factories dominating production. This concentration grants suppliers significant leverage, as disruptions or price hikes from a few key players can directly impact Payless's costs and sourcing flexibility. Furthermore, the costs associated with switching suppliers, estimated between $10,000 and $50,000 in 2024 for onboarding new major suppliers, including due diligence and potential production delays, further solidify the position of existing suppliers.
The commoditized nature of many materials used by Payless, such as standard textiles and leathers, meant that suppliers offered interchangeable inputs, reducing individual supplier power. However, the threat of forward integration, where suppliers might open their own retail stores, posed a significant risk. This move by suppliers could reduce Payless's control over distribution and increase competition, potentially impacting inventory and pricing. The sheer volume of Payless's business also made it a crucial client for many suppliers, potentially reducing their bargaining power as they relied on Payless's orders for a substantial portion of their revenue.
| Factor | Impact on Payless's Supplier Bargaining Power | 2024 Relevance/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier power | Dominance of Asian manufacturers (Vietnam, China) in footwear production. |
| Switching Costs | Increases supplier power | Estimated $10,000-$50,000 to onboard new major suppliers. |
| Material Commoditization | Decreases supplier power | Availability of similar synthetic fabrics and common leathers. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Increases supplier power | Potential for suppliers to open direct-to-consumer channels. |
| Payless's Purchase Volume | Decreases supplier power | Payless's historical scale made it a vital customer for many suppliers. |
What is included in the product
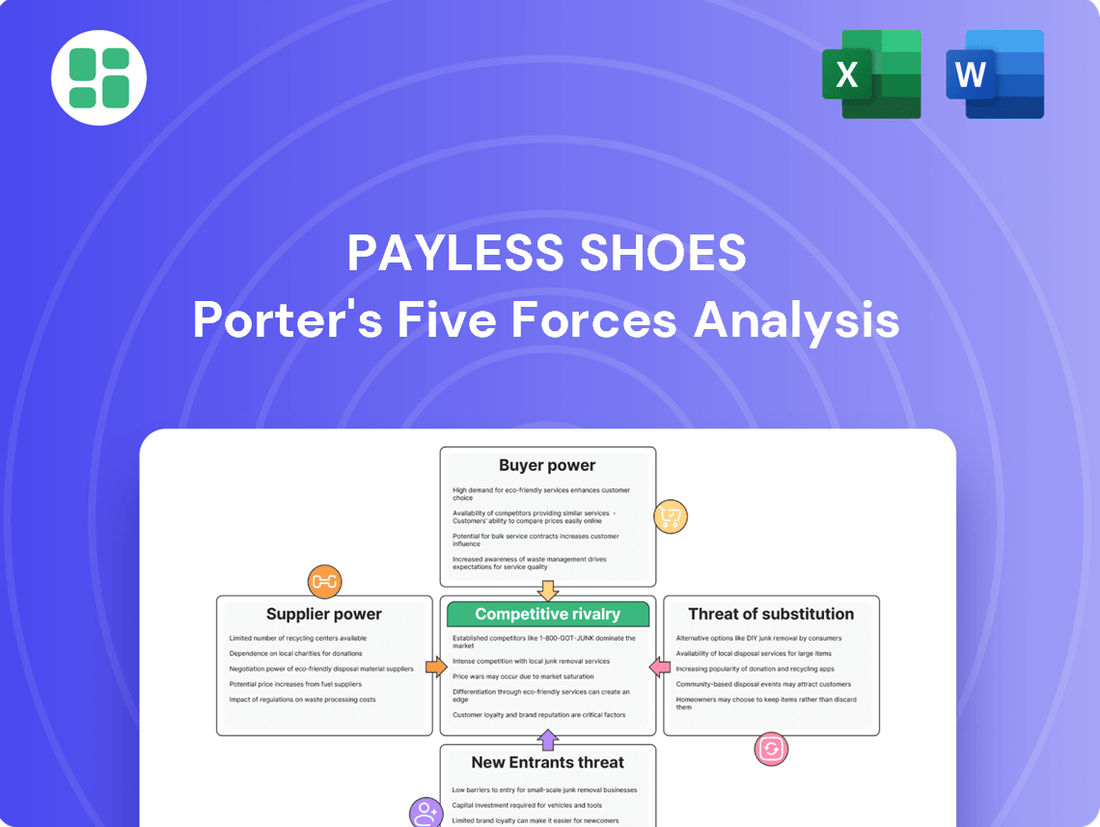
This analysis of Payless Shoes examines the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, all within the context of the footwear retail industry.
Instantly identify and mitigate the intense competitive rivalry that plagued Payless Shoes by visualizing the impact of each Porter's Five Forces.
Effortlessly understand the threat of new entrants and substitute products that eroded Payless Shoes' market share with a clear, actionable framework.
Customers Bargaining Power
Payless ShoeSource's core customer base actively seeks value, indicating a high degree of price sensitivity. This means even minor price increases could prompt customers to explore alternatives, amplifying their bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the average consumer continued to prioritize cost-effectiveness in apparel and footwear purchases, with many actively comparing prices across multiple retailers before making a decision.
Customers have a significant bargaining power due to the vast availability of substitute footwear options. They can easily find similar shoes from numerous online retailers like Amazon and Zappos, as well as brick-and-mortar stores including Walmart, Target, and specialized shoe shops. This abundance of choice means customers can readily compare prices and quality, putting pressure on Payless to offer competitive deals.
Customers switching from Payless ShoeSource generally face very low switching costs. The process of purchasing shoes from a competitor, whether online or in a physical store, is typically straightforward and doesn't involve significant time, effort, or financial investment. This ease of transition directly amplifies customer bargaining power.
Customer Information and Transparency
Payless customers in 2024 are highly informed due to widespread internet access and readily available online reviews and price comparison tools. This transparency significantly amplifies their bargaining power, as they can easily assess product value and competitor pricing.
The ability for consumers to quickly compare Payless's shoe prices and quality against numerous other retailers, both online and brick-and-mortar, puts considerable pressure on the company. For instance, in 2023, a significant portion of consumers, estimated to be over 70%, reported using their smartphones to research products and prices while in a physical store, directly impacting Payless's pricing strategies.
- Informed Consumer Base: Customers can easily access information on product features, durability, and brand reputation through online platforms.
- Price Sensitivity: The availability of price comparison websites and promotional alerts makes customers highly sensitive to price differences.
- Switching Behavior: Well-informed customers are more likely to switch to competitors offering better value or perceived quality for the price.
- Demand for Value: Increased transparency fuels a demand for greater value, pushing Payless to offer competitive pricing and promotions to retain customers.
Volume of Purchases
The volume of purchases by Payless's customers, while often small on an individual basis, becomes a significant factor when considered collectively. This value-seeking customer base, attracted by Payless's often lower price points, purchases in sufficient aggregate volume to influence the company's strategies.
Payless's business model relies on attracting a broad base of consumers who prioritize affordability. For instance, in 2024, Payless continued to target families and budget-conscious shoppers who might purchase multiple pairs of shoes throughout the year, contributing to a substantial overall sales volume.
- Customer Volume: While individual transactions are typically low-value, the sheer number of customers purchasing regularly creates a significant collective volume for Payless.
- Value Proposition: Payless's success hinges on catering to a large segment of the market that prioritizes price, making the volume of these purchases a key driver of its market position.
- Influence on Pricing: The substantial number of customers willing to buy at specific price points gives them considerable leverage in influencing Payless's pricing strategies.
Payless's customers wield considerable bargaining power due to their high price sensitivity and the abundance of readily available, low-cost alternatives. The ease with which consumers can switch to competitors, coupled with their access to price comparison tools and product reviews, forces Payless to maintain competitive pricing. This dynamic is underscored by the fact that in 2024, a substantial portion of consumers continued to prioritize value, actively seeking out the best deals across the footwear market.
| Factor | Impact on Payless | Example (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High | Consumers actively compare prices, leading to pressure on Payless to offer discounts. |
| Availability of Substitutes | High | Numerous online and brick-and-mortar retailers offer similar footwear at competitive prices. |
| Switching Costs | Low | Minimal effort or cost for customers to purchase from competitors. |
| Informed Consumers | High | Online reviews and price comparison tools empower customers with information. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Payless Shoes Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Payless Shoes will equip you with a deep understanding of the competitive landscape, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products, all presented in the exact format you'll receive upon purchase.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Payless ShoeSource faced intense competition from a broad spectrum of retailers. Direct rivals included other discount shoe chains like Famous Footwear and Rack Room Shoes, alongside general merchandise giants such as Walmart and Target, which offered significant footwear selections. The rise of online-only sellers like Zappos and Amazon further fragmented the market, intensifying overall rivalry.
The discount footwear market, while generally projected for growth, faces significant headwinds, indicating a potentially intense competitive landscape. For instance, the global footwear market was valued at approximately $386 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around $500 billion by 2029, suggesting an overall upward trend. However, within this, the discount segment's growth rate can fluctuate based on economic conditions and consumer spending power.
When an industry experiences slower growth or reaches maturity, companies often intensify their efforts to capture existing market share. This can manifest as aggressive pricing strategies, increased marketing spend, and a focus on product differentiation within the value segment. Such conditions naturally amplify competitive rivalry as firms vie for a larger piece of a less expanding pie.
Payless Shoes historically struggled with significant product differentiation compared to its competitors. Many of its offerings were perceived as generic, lacking distinct design innovation or superior quality that could command premium pricing. This undifferentiated product landscape meant that price often became the main competitive lever.
In the highly competitive footwear market, the lack of unique features or strong brand loyalty for Payless meant customers frequently shopped based on price. For instance, in 2018, just before its bankruptcy, Payless was known for its aggressive discounting strategies, often featuring sales of $20 or $30 pairs of shoes, highlighting its reliance on price to attract consumers rather than product appeal.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers in the footwear retail sector, particularly for a company like Payless, are significant. These include substantial investments in physical store locations, which often involve long-term leases and require considerable capital for setup and maintenance. Furthermore, maintaining large inventories of diverse shoe styles and sizes necessitates considerable financial outlay and carries the risk of obsolescence, making it costly to liquidate. Contractual obligations with suppliers and landlords also present hurdles to a swift departure.
These high exit barriers can trap underperforming companies within the footwear market, contributing to sustained competitive rivalry. When it’s difficult and expensive to leave, even unprofitable players tend to persist, intensifying competition for market share and potentially driving down prices and profitability for all involved. This can be seen in the broader retail landscape where store closures, while sometimes necessary, are often preceded by prolonged periods of financial distress due to these exit costs.
Consider these factors contributing to high exit barriers in retail:
- High Fixed Asset Costs: Retailers like Payless invest heavily in store leases, fixtures, and equipment, which have limited resale value outside the industry.
- Inventory Management: Holding vast amounts of seasonal and varied footwear inventory creates significant financial exposure and liquidation challenges.
- Brand and Reputation: A company's established brand, built over years, also represents an asset that is difficult to divest or abandon without significant loss.
- Employee and Supplier Relations: Severing ties with long-term employees and suppliers can involve severance packages and contractual penalties, adding to exit costs.
Market Saturation and Capacity
The discount footwear market, where Payless Shoes historically operated, is characterized by significant saturation. Numerous players, from large department stores to specialized discount chains and online retailers, vie for market share. This intense competition is fueled by relatively low barriers to entry and a broad consumer base seeking value.
Excess production capacity within the global footwear manufacturing sector further exacerbates competitive pressures. Manufacturers often have the ability to produce more shoes than current demand dictates, leading them to seek out any buyer, including discount retailers. This can result in downward pressure on wholesale prices, intensifying the rivalry among discount footwear sellers.
- Market Saturation: The discount footwear segment is highly saturated with a multitude of retailers competing for consumers.
- Excess Capacity: Global footwear manufacturing often operates with excess capacity, providing ample supply to discount channels.
- Price Wars: High saturation and excess capacity frequently trigger price wars, forcing retailers to compete aggressively on cost.
- Marketing Intensity: Retailers in this space often engage in heightened marketing efforts to differentiate themselves and attract price-sensitive customers.
Payless Shoes operated in a highly competitive discount footwear market, facing pressure from both brick-and-mortar rivals like Famous Footwear and mass merchandisers such as Walmart and Target. The rise of online retailers like Zappos and Amazon further intensified this rivalry by offering vast selections and convenient purchasing options. This crowded marketplace meant Payless had to constantly battle for market share, often through aggressive pricing.
The intense competition was exacerbated by a lack of product differentiation; Payless shoes were often perceived as generic, making price the primary decision factor for consumers. For instance, in its final years, Payless heavily relied on deep discounts, with many shoes priced around $20-$30, a strategy that highlighted its struggle to stand out beyond cost. This environment fostered price wars, as retailers fought to attract the price-sensitive customer base prevalent in the discount segment.
The global footwear market, projected to reach around $500 billion by 2029 from approximately $386 billion in 2023, indicates growth, but the discount sector's performance is closely tied to economic conditions and consumer spending power. High exit barriers, including significant investments in physical stores and inventory, meant that even struggling competitors often remained in the market, prolonging intense rivalry and potentially suppressing profitability for all players.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Payless Shoes is significant, particularly concerning the price-performance trade-off. Consumers actively seek footwear that offers adequate protection and style without demanding a premium price. This means looking beyond traditional retail shoe stores for viable alternatives.
In 2024, the market continues to see a rise in direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands and online marketplaces offering footwear at highly competitive price points, often bypassing traditional retail markups. For instance, the average price of a pair of athletic shoes from a major online retailer in early 2024 hovered around $60, directly challenging the value proposition of many mid-range Payless offerings.
Beyond new shoes, consumers also consider used or refurbished footwear as a substitute, especially for less demanding use cases. The burgeoning resale market, including platforms that specialize in pre-owned fashion, provides an even lower-cost entry point for acquiring functional and even stylish shoes, further intensifying the substitute threat.
Customers might consider repairing their existing shoes, especially if economic conditions are tight, or if they are driven by environmental concerns. For instance, a growing number of consumers are embracing sustainability, which could lead them to extend the life of their current footwear rather than purchasing new ones. This trend was gaining momentum even before 2024, with reports indicating increased interest in shoe repair services.
The increasing popularity of the second-hand shoe market, driven by platforms like Depop and ThredUp, presents a significant threat. In 2024, the global secondhand apparel market was projected to reach $350 billion, a substantial portion of which includes footwear. Consumers are increasingly opting for pre-owned or repaired shoes as a more sustainable and budget-friendly alternative to buying new, directly impacting demand for Payless’s new offerings.
Trends Towards Minimalist or Non-Traditional Footwear
Emerging trends like minimalist footwear, or even embracing barefoot walking in certain environments, represent a subtle yet significant challenge to traditional shoe purchases. While currently niche, these movements question the necessity of conventional footwear for everyday activities.
Furthermore, the rise of specialized footwear rental services for specific occasions, like formal events or athletic competitions, offers consumers an alternative to outright purchase. This can reduce the overall demand for new shoes, particularly for items used infrequently.
- Minimalist Footwear Growth: While precise global market share figures for minimalist footwear are still developing, the segment has seen consistent growth, with some reports indicating double-digit percentage increases in specific regions leading up to 2024.
- Barefoot Movement Adoption: The barefoot or "grounding" movement, while not directly a product substitute, influences consumer perception of footwear necessity, potentially impacting casual shoe sales.
- Rental Market Expansion: The global footwear rental market, though nascent, is projected for significant expansion, with estimates suggesting it could reach several billion dollars by the late 2020s, indicating a growing acceptance of non-ownership models.
Alternative Spending for Fashion/Utility
Consumers, particularly those with limited budgets, might choose to allocate their discretionary income towards other fashion items like apparel or bags, or even practical goods such as home furnishings, rather than purchasing new footwear. This represents a significant threat of substitutes, as the decision to buy shoes competes with a wide array of alternative spending options.
For instance, in 2024, the global apparel market was projected to reach over $1.7 trillion, indicating substantial consumer spending on clothing that could divert funds away from shoe purchases. Similarly, the home furnishings sector also commands a significant portion of consumer budgets, further highlighting the competitive landscape for discretionary dollars.
- Broader Discretionary Spending: The threat of substitutes extends beyond direct footwear competitors to encompass all non-essential purchases.
- Budgetary Constraints: Price-sensitive consumers are more likely to compare the value proposition of new shoes against other desired goods.
- Market Diversification: The vastness of the fashion and utility goods markets means consumers have numerous alternatives for expressing style or meeting practical needs.
The threat of substitutes for Payless Shoes is multifaceted, encompassing not only direct footwear competitors but also alternative consumption patterns. Consumers are increasingly looking at value-for-money options, which can include purchasing from direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands that bypass traditional retail markups. For example, in early 2024, many DTC shoe brands offered stylish and durable options priced well below traditional mall retailers, often in the $50-$70 range, directly challenging Payless's mid-tier offerings.
The growing secondhand market is another significant substitute. By 2024, the global secondhand apparel market was projected to exceed $350 billion, with footwear representing a substantial segment. Platforms specializing in pre-owned fashion allow consumers to acquire shoes at a fraction of the original cost, appealing to budget-conscious and environmentally aware shoppers alike.
Furthermore, the rising cost of living and a greater emphasis on sustainability have led some consumers to repair their existing footwear rather than purchase new ones. This trend, gaining traction before 2024, offers a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative that directly reduces demand for new shoe sales.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | 2024 Market Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Brands | Competitive pricing, online-focused, often bypasses retail markups | Average athletic shoe price around $60 from online retailers |
| Secondhand Market | Lower cost, sustainable option, wide variety of brands | Global secondhand apparel market projected over $350 billion |
| Repair Services | Extends product life, cost-effective, environmentally friendly | Increased consumer interest in sustainability and repair options |
| Alternative Spending | Apparel, accessories, home goods competing for discretionary income | Global apparel market projected over $1.7 trillion |
Entrants Threaten
Launching a new footwear retail business, whether brick-and-mortar or online, demands substantial upfront capital. Consider that establishing a physical store involves costs for rent, leasehold improvements, and initial inventory, which can easily run into hundreds of thousands of dollars. For instance, a mid-sized retail space in a decent location could require $100,000 to $300,000 just for the initial setup and stock. E-commerce infrastructure, including website development, digital marketing, and warehousing, adds another significant layer, potentially costing $50,000 to $200,000 or more to compete effectively.
Established players like Payless ShoeSource historically benefited from significant economies of scale, allowing them to negotiate lower prices for raw materials and manufacturing. This scale also enabled them to spread fixed costs over a larger volume of sales, reducing the per-unit cost. For instance, in its prime, Payless operated thousands of stores, creating substantial purchasing power that new entrants would find difficult to replicate quickly.
New footwear retailers face significant hurdles in securing prime physical retail locations and gaining visibility on major e-commerce platforms. Established players often have long-standing relationships with landlords and preferential terms with online marketplaces, making it difficult for newcomers to compete for shelf space or prominent digital placement.
For instance, in 2024, the retail leasing market continued to see high demand for desirable locations, with average commercial rent per square foot remaining elevated in key urban centers. Similarly, online retailers must contend with established brands that benefit from existing customer bases and sophisticated digital marketing strategies, often requiring substantial investment to achieve comparable reach.
Brand Loyalty and Customer Switching Costs
Brand loyalty in the footwear industry can be a significant barrier for new entrants. Consumers often develop preferences for specific brands based on perceived quality, style, comfort, or even emotional connection. For instance, a strong association with athletic performance can keep runners loyal to brands like Nike or Adidas, making it difficult for a newcomer to lure them away.
Switching costs, while not always monetary, can also deter consumers from trying new brands. These costs can include the time and effort required to research alternatives, the potential for dissatisfaction with a new product, or the loss of accumulated loyalty rewards. In 2024, many established footwear retailers continued to invest heavily in loyalty programs, offering points, exclusive discounts, and early access to new products, further solidifying customer retention and increasing the perceived switching costs for consumers.
- Consumer loyalty to established footwear brands can be substantial, driven by factors like perceived quality and style.
- Switching costs for consumers include the effort of research and the risk of product dissatisfaction.
- Loyalty programs, prevalent in 2024, further enhance customer retention and increase barriers to switching.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policies and regulations can significantly raise the barrier to entry for new footwear retailers. For instance, varying state and local sales tax regulations, product safety standards, and environmental compliance requirements add layers of complexity and cost for businesses looking to establish themselves. In 2024, the retail sector, including footwear, continued to navigate evolving consumer protection laws and data privacy regulations, such as potential updates to California's Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), which could impact how new entrants manage customer data and marketing efforts.
Licensing requirements, although generally not overly burdensome for standard retail operations in the U.S., can still present initial hurdles. More impactful are potential trade policies. For example, tariffs on imported footwear components or finished goods, which have been a fluctuating factor in recent years, directly increase the cost of goods sold for any new entrant relying on international supply chains. As of late 2024, discussions around global trade relations and potential shifts in import duties continue to create uncertainty, making it more challenging for new players to accurately forecast their cost structures.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with consumer protection laws, product safety standards, and data privacy regulations (e.g., CCPA) increases operational complexity and cost for new entrants.
- Licensing Requirements: While typically manageable, obtaining necessary business licenses and permits represents an initial administrative step.
- Trade Policies: Tariffs on imported footwear materials or finished products directly inflate the cost of goods, impacting profitability and pricing strategies for new businesses reliant on global sourcing.
- Evolving Legal Landscape: Ongoing changes in regulations, particularly concerning e-commerce and sustainability, demand continuous adaptation and investment from new market participants.
The threat of new entrants into the footwear retail market, including for a company like Payless, is moderate. Significant capital is required for both physical stores and e-commerce operations, with initial setup costs for a retail space easily reaching hundreds of thousands of dollars, and online ventures needing tens to hundreds of thousands for infrastructure and marketing. Established brands benefit from massive economies of scale, allowing them to negotiate better prices and spread fixed costs, a level difficult for newcomers to match quickly. In 2024, securing prime retail locations and visibility on e-commerce platforms remained challenging due to existing relationships and sophisticated digital marketing by incumbents.
Consumer loyalty and switching costs also act as barriers. Brand preference, built on quality, style, or emotional connection, makes it hard to attract customers away from established names. Loyalty programs, heavily utilized in 2024, further lock in customers by offering rewards and exclusive benefits, increasing the perceived effort and risk for consumers to try new brands. For example, many athletic brands continue to dominate their niches due to strong performance associations.
Regulatory and trade policies present additional challenges. Compliance with consumer protection laws, product safety, and data privacy regulations adds complexity and cost. Tariffs on imported materials or finished goods, a fluctuating factor in late 2024, directly increase the cost of goods sold for new entrants relying on international supply chains, making cost forecasting more difficult.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Payless Shoes leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, financial filings of competitors, and consumer spending trend databases to understand the competitive landscape.