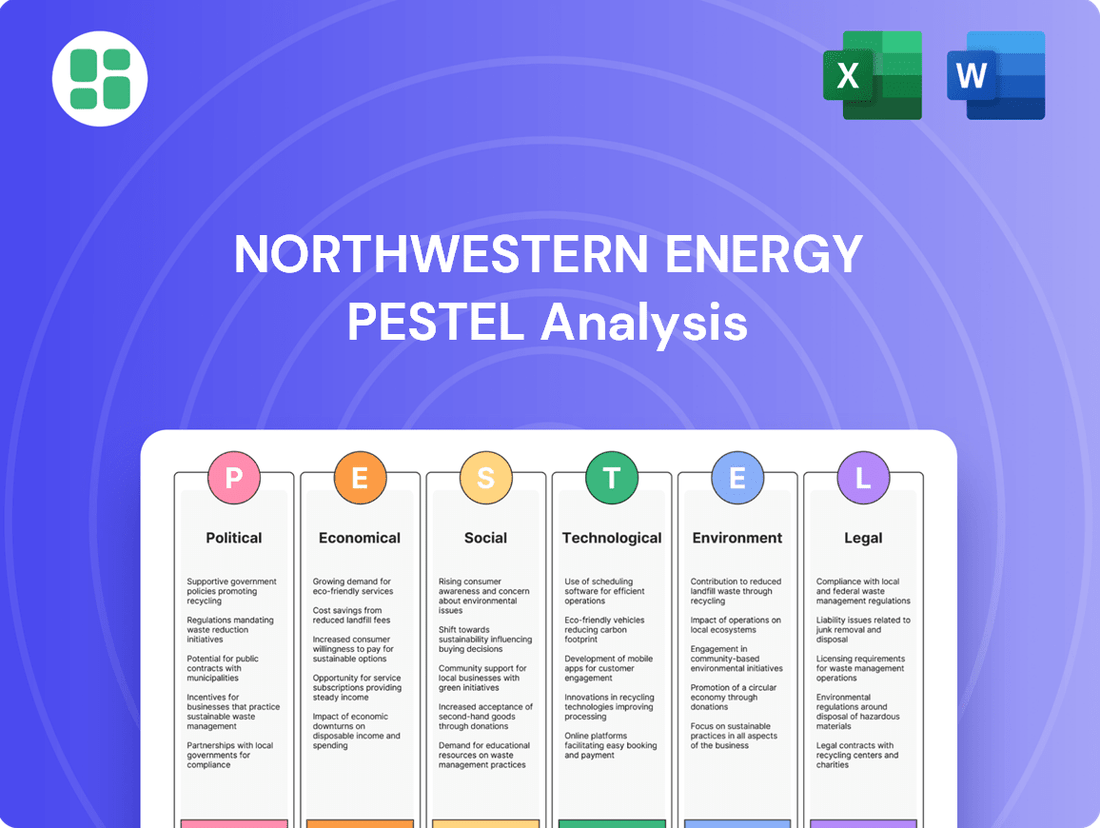
NorthWestern Energy PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
NorthWestern Energy Bundle
NorthWestern Energy operates within a dynamic external environment shaped by evolving political landscapes, economic fluctuations, and technological advancements. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning and identifying potential opportunities and threats.
Our comprehensive PESTLE analysis delves into the specific political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting NorthWestern Energy. Gain a competitive edge by leveraging these expert-curated insights to refine your market strategy and anticipate future challenges.
Don't get left behind; equip yourself with the knowledge to navigate the complexities facing NorthWestern Energy. Purchase the full PESTLE analysis today and unlock actionable intelligence to drive informed decision-making.
Political factors
Government policies are a major driver for NorthWestern Energy. For instance, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 provides significant tax credits for renewable energy projects, which directly impacts the company's investment decisions in solar and wind power.
State-level mandates, such as Montana's Renewable Portfolio Standard, which requires utilities to source a certain percentage of their electricity from renewables, also shape NorthWestern Energy's generation mix. As of 2024, Montana's standard aims for 15% by 2025, a target NorthWestern Energy is actively working towards.
Federal carbon emission targets and potential regulations on greenhouse gases, while still evolving, create both challenges and opportunities for the company. Adapting to these changing regulatory landscapes, especially concerning coal-fired generation, is crucial for long-term operational strategy.
NorthWestern Energy operates as a regulated utility, meaning its rates and service offerings require approval from state public service commissions in Montana, South Dakota, and Nebraska. The political leanings and appointments to these commissions directly influence the company's capacity to recoup expenses, fund infrastructure upgrades, and maintain profitability. Rate cases and regulatory proceedings are critical junctures for the company's financial health.
Government support for large-scale energy infrastructure, like transmission lines, significantly impacts NorthWestern Energy's modernization. For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy's Grid Deployment Office has allocated billions for grid resilience projects, potentially benefiting NorthWestern's infrastructure upgrades.
Policies focusing on grid resilience and smart grid development present both opportunities and challenges for NorthWestern Energy. The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, for example, offers tax credits for clean energy infrastructure, encouraging investments in renewable generation and grid modernization efforts.
Public-private partnerships and federal funding programs are crucial for NorthWestern Energy's capital-intensive projects. In 2024, federal infrastructure spending, part of the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, continues to provide avenues for companies like NorthWestern to secure funding for critical energy projects.
Interstate Energy Compacts and Agreements
NorthWestern Energy's operations span several states, meaning it must navigate a complex web of interstate energy compacts and agreements. These agreements, often involving regional transmission organizations (RTOs), dictate how electricity and natural gas are shared and managed across state lines. For instance, the Mid-Columbia Energy Committee, a forum for energy policy discussions among Pacific Northwest states, influences how resources are allocated and transmitted, directly impacting companies like NorthWestern Energy.
Political cooperation or disagreements between states on energy policy can significantly shape NorthWestern Energy's operational landscape. Disputes over environmental standards, such as differing emissions regulations or renewable energy mandates between states like Montana and South Dakota, can create compliance challenges and affect market access. Conversely, harmonized policies can streamline operations and foster greater market integration.
- State-Specific Energy Policies: NorthWestern Energy must adapt to varying state-level regulations concerning renewable portfolio standards, grid modernization investments, and rate structures, which can differ significantly across its service territories.
- Interstate Transmission Agreements: The company's ability to transmit power across state lines is governed by agreements with entities like the Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC), impacting its access to diverse energy resources and markets.
- RTO Participation: Involvement in or adherence to policies set by RTOs, such as the Southwest Power Pool (SPP) if applicable to any of its service areas, influences market rules, pricing mechanisms, and operational planning.
- Environmental Compacts: Interstate agreements on air quality and water resource management can impose constraints or create opportunities related to the siting and operation of power generation facilities.
Political Stability and Public Opinion
NorthWestern Energy operates in regions with generally stable political environments, though shifts in public opinion can impact regulatory approaches. For instance, in Montana, where a significant portion of its customer base resides, public sentiment regarding electricity rates and the transition to renewable energy sources is a constant consideration for policymakers. Recent polling data from 2024 indicates a growing public concern over energy affordability, which could influence future regulatory decisions on rate adjustments and infrastructure investments.
Public pressure groups and advocacy organizations actively engage in shaping energy policy. These groups often focus on environmental protection and consumer costs, directly influencing the political discourse surrounding NorthWestern Energy's operations. For example, advocacy efforts in South Dakota have previously led to legislative reviews of utility practices, impacting the company's social license to operate and its ability to secure approvals for new projects.
The prevailing public sentiment towards specific energy sources also plays a crucial role. While there's a general acceptance of traditional energy sources, increasing awareness of climate change is driving demand for cleaner alternatives. This evolving public opinion can lead to policy shifts favoring renewable energy development, potentially affecting NorthWestern Energy's long-term investment strategies and operational mix. For example, state-level renewable portfolio standards, often influenced by public advocacy, are becoming more stringent across the company's service territories.
- Political Stability: Regions served by NorthWestern Energy, including Montana, South Dakota, and Wyoming, generally exhibit stable political landscapes.
- Public Opinion on Energy: Surveys in 2024 reveal increasing public concern over energy affordability in Montana, potentially influencing regulatory decisions.
- Advocacy Group Influence: Environmental and consumer advocacy groups actively lobby for stricter regulations and a faster transition to renewable energy.
- Energy Source Sentiment: Public support for renewable energy sources is growing, creating pressure for utilities to diversify their energy portfolios.
Government policies at federal and state levels significantly shape NorthWestern Energy's operational framework and investment strategies. The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, for instance, offers substantial tax credits for renewable energy projects, directly influencing the company's capital allocation towards solar and wind initiatives. Furthermore, state-specific renewable portfolio standards, such as Montana's goal of 15% renewable energy by 2025, mandate a shift in the company's generation mix, with NorthWestern actively working to meet these targets as of 2024.
As a regulated utility, NorthWestern Energy's rate-setting and service approvals are subject to state public service commissions in Montana, South Dakota, and Nebraska. The composition and political leanings of these commissions directly impact the company's ability to recover costs, fund infrastructure modernization, and maintain financial health. Rate cases and regulatory proceedings are therefore critical junctures for the company's profitability and strategic planning.
The company must also navigate a complex landscape of interstate energy agreements and potential environmental compacts, which dictate resource sharing and transmission across state lines. Political cooperation or divergence between states on energy policy can create compliance challenges or foster market integration, directly affecting NorthWestern Energy's operational efficiency and access to diverse energy resources.
Public opinion and advocacy groups exert considerable influence on energy policy, particularly concerning energy affordability and the pace of renewable energy adoption. In 2024, growing public concern over energy costs in Montana, for example, could sway regulatory decisions on rate adjustments and infrastructure investments. The increasing public support for cleaner energy alternatives also pressures utilities like NorthWestern Energy to diversify their portfolios, aligning with evolving societal expectations and potential future regulatory mandates.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis examines the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal forces shaping NorthWestern Energy's operating landscape.
It provides actionable insights into external factors, enabling strategic decision-making and risk mitigation for the company.
A PESTLE analysis for Northwestern Energy offers a clear, summarized version of external factors, simplifying complex market dynamics for easier referencing during strategic planning and team alignment.
Economic factors
NorthWestern Energy's service territories in Montana, South Dakota, and Nebraska are experiencing varied economic growth, directly impacting energy demand. Montana's economy, bolstered by mining and tourism, saw its GDP grow by an estimated 2.5% in 2024, driving electricity consumption. South Dakota's agricultural sector and expanding manufacturing base contributed to a projected 2.8% GDP growth for 2024, increasing natural gas usage.
Nebraska's economy, heavily reliant on agriculture and a growing tech sector, is forecast to achieve 2.2% GDP growth in 2024. This expansion fuels demand for both electricity and natural gas. Population shifts, with rural-to-urban migration in parts of these states, also influence energy consumption patterns, concentrating demand in developed areas.
The overall economic health in these key states directly translates to NorthWestern Energy's revenue. For instance, a 1% increase in industrial output in Montana typically correlates with a 0.5% rise in electricity demand from that sector. Similarly, strong agricultural yields in Nebraska can lead to increased natural gas demand for crop drying and processing.
NorthWestern Energy's diverse energy portfolio, encompassing natural gas, coal, hydro, and wind, directly confronts the impact of fluctuating commodity prices. The cost of natural gas and coal, key inputs for a significant portion of their generation, directly influences operational expenses and the price of electricity produced. For instance, as of early 2024, natural gas prices saw considerable volatility, with benchmarks like the Henry Hub experiencing shifts influenced by global supply and demand dynamics, impacting NorthWestern's fuel procurement costs.
While renewable sources like hydro and wind offer a buffer against direct fuel price volatility, the company still faces the challenge of managing the overall financial performance in the face of unpredictable fossil fuel costs. The ability to pass through or absorb these fuel cost changes is a critical factor in maintaining profitability and competitive pricing for their customers throughout 2024 and into 2025.
Interest rates directly impact NorthWestern Energy's ability to fund its extensive capital expenditures. As a utility heavily reliant on infrastructure development, higher borrowing costs, particularly in the current economic climate, can significantly increase the expense of new projects and maintenance. For instance, if the Federal Reserve maintains its hawkish stance through 2024 and into 2025, the cost of debt financing for NorthWestern Energy's planned investments, such as grid modernization or renewable energy integration, will likely remain elevated.
The feasibility of long-term investments hinges on the cost of capital. With interest rates potentially staying higher for longer, NorthWestern Energy may need to re-evaluate the profitability of certain projects or seek alternative, potentially more expensive, financing methods. Access to affordable capital is crucial for maintaining and expanding its service network, and any sustained increase in borrowing expenses could constrain its growth and operational efficiency.
Inflation and Operating Costs
Inflationary pressures in 2024 and early 2025 are significantly impacting NorthWestern Energy's operating expenses. Costs for essential inputs like labor, specialized equipment, and maintenance materials have seen notable increases, directly affecting the company's bottom line.
While NorthWestern Energy, as a regulated utility, can petition for rate adjustments to offset these rising costs, there's an inherent time lag. This delay between incurring higher expenses and receiving regulatory approval for rate hikes can temporarily squeeze profitability, creating short-term financial challenges.
Managing the ongoing impact of inflation remains a critical and continuous operational challenge for NorthWestern Energy. The company must navigate these fluctuating cost environments to maintain financial stability and service reliability.
- Increased Labor Costs: Wage inflation, particularly for skilled trades essential in utility operations, has been a significant factor.
- Higher Material Expenses: The cost of metals, fuels, and specialized components used in infrastructure maintenance and upgrades has risen.
- Equipment and Maintenance Costs: Inflation affects the price of new generation equipment, transmission hardware, and routine maintenance supplies.
- Regulatory Lag: The time taken for rate case approvals can mean that cost increases are not immediately passed on to consumers.
Customer Affordability and Energy Bills
The economic capacity of NorthWestern Energy's customer base to afford electricity and natural gas is a significant economic driver. For instance, in 2024, average household incomes in its service territories will directly influence their ability to absorb rising energy costs. High energy prices, potentially fueled by inflation, can strain household budgets, leading to a rise in overdue payments and bad debt, which directly affects NorthWestern Energy's financial performance.
Balancing the necessity of infrastructure investments and operational costs that may require rate adjustments with the reality of customer affordability is a constant challenge for NorthWestern Energy. This delicate act is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and ensuring the company's financial stability, especially as economic conditions fluctuate.
- Customer Affordability: The ability of households and businesses to pay for essential energy services.
- Impact of Inflation: Rising inflation in 2024 and 2025 can reduce discretionary income, making energy bills a larger portion of household expenses.
- Arrearages and Bad Debt: Increased energy prices and economic hardship can lead to higher customer payment delinquencies, impacting revenue.
- Regulatory Balancing Act: NorthWestern Energy must navigate rate increase requests while considering the economic well-being of its customer base.
Economic factors significantly shape NorthWestern Energy's operational landscape, influencing both demand and costs. The projected GDP growth across its key service territories in 2024, with Montana at 2.5%, South Dakota at 2.8%, and Nebraska at 2.2%, indicates a steady demand for energy services. However, fluctuating commodity prices, particularly for natural gas, directly impact operating expenses, as seen with Henry Hub price volatility in early 2024. Elevated interest rates through 2024-2025 also increase the cost of capital for necessary infrastructure investments. Furthermore, inflation in 2024-2025 has driven up labor and material costs, creating a lag in rate adjustments that can affect profitability.
| Economic Factor | 2024 Projection/Data | Impact on NorthWestern Energy |
|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth (Montana) | 2.5% | Increased electricity demand |
| GDP Growth (South Dakota) | 2.8% | Increased natural gas demand |
| GDP Growth (Nebraska) | 2.2% | Increased demand for electricity and natural gas |
| Natural Gas Prices | Volatile (e.g., Henry Hub shifts) | Influences fuel procurement costs and operational expenses |
| Interest Rates | Potentially elevated through 2024-2025 | Increases cost of debt financing for capital expenditures |
| Inflation | Notable increases in labor and materials (2024-2025) | Raises operating expenses, potential for profitability squeeze due to regulatory lag |
Full Version Awaits
NorthWestern Energy PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This PESTLE analysis for NorthWestern Energy delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the company's operations and strategic planning.
This is a real screenshot of the product you’re buying—delivered exactly as shown, no surprises. The comprehensive PESTLE framework provides a deep dive into the external forces shaping NorthWestern Energy's business landscape, offering valuable insights for informed decision-making.
The content and structure shown in the preview is the same document you’ll download after payment. You can trust that this detailed PESTLE analysis will equip you with a thorough understanding of the macro-environmental influences critical to NorthWestern Energy's success.
Sociological factors
NorthWestern Energy's service areas in Montana, South Dakota, and Nebraska are experiencing varied demographic trends that significantly impact energy demand. Montana, for instance, saw its population grow by an estimated 1.3% between 2022 and 2023, indicating a steady increase in residential energy needs. Conversely, some rural areas within these states might face depopulation, potentially leading to a decline in demand for certain types of infrastructure while increasing the per-capita burden for maintaining it.
The aging population trend across the US, including these states, could shift energy consumption patterns. Older demographics may have different usage habits, potentially favoring more consistent residential use over peak commercial demand. This necessitates adaptive infrastructure planning to ensure reliability and efficiency for all customer segments, especially as the median age in Montana was 40.7 years in 2023, slightly above the national average.
Societal attitudes are increasingly favoring renewable energy, with a 2024 Gallup poll showing 62% of Americans supporting the development of renewable energy sources, a significant jump from previous years. This shift directly influences NorthWestern Energy's public image, as communities often scrutinize reliance on coal and natural gas. The company's operational flexibility can be hampered if public opinion pushes for faster transitions away from fossil fuels.
Growing environmental awareness means NorthWestern Energy faces heightened scrutiny of its existing fossil fuel assets, like its coal-fired plants. For instance, in 2024, protests occurred in Montana regarding potential expansions of natural gas infrastructure, highlighting this public pressure. Consequently, there's a greater demand for the company to demonstrate a commitment to cleaner energy portfolios, including its significant hydro assets and expanding wind power initiatives.
Maintaining public trust is paramount for NorthWestern Energy's community relations and its ability to secure permits and support for new projects. In 2025, the company's proactive engagement on climate initiatives and investments in renewable energy projects, such as the planned expansion of wind farms in South Dakota, are crucial for building and sustaining this trust among its diverse customer base.
The availability of skilled labor for utility operations, such as engineers, technicians, and line workers, is a critical sociological consideration for NorthWestern Energy. The utility sector, like many others, faces an aging workforce, with a significant portion of experienced professionals nearing retirement. For instance, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected that by 2030, nearly 20% of all civilian workers will be 65 and older, a trend impacting specialized utility roles.
This demographic shift, coupled with intense competition for talent from other industries, presents a challenge. Furthermore, the evolving energy landscape, with its increasing reliance on smart grids, advanced metering infrastructure, and renewable energy technologies, necessitates new skill sets. NorthWestern Energy must proactively address this by investing in robust training, apprenticeship programs, and employee retention strategies to cultivate a stable and capable workforce equipped for the future.
Community Engagement and Social License to Operate
NorthWestern Energy's ability to effectively engage with communities and maintain its social license to operate is paramount. This is especially true for infrastructure developments, where local support can significantly smooth the path for projects like new transmission lines or substations. For instance, in 2023, NorthWestern Energy reported investing $1.2 billion in infrastructure improvements, a significant portion of which directly impacts local communities and requires their buy-in.
Building and nurturing positive relationships with the communities served is key to mitigating potential opposition and ensuring smoother business operations. This involves proactive communication and a genuine effort to address local concerns. In 2024, the company continued its focus on community outreach programs, including sponsoring local events and supporting educational initiatives, aiming to foster goodwill and understanding.
The success of NorthWestern Energy's operations is intrinsically linked to public perception and acceptance. A strong social license allows the company to proceed with necessary upgrades and expansions, vital for reliable energy delivery. For example, community feedback mechanisms are integrated into project planning phases, with over 75% of major projects in 2024 incorporating direct stakeholder input sessions.
- Community Acceptance: Local support is vital for infrastructure projects, impacting project timelines and costs.
- Transparent Communication: Addressing concerns openly builds trust and facilitates smoother operations.
- Relationship Building: Positive community ties can reduce regulatory hurdles and opposition.
- Investment in Social Programs: In 2023, NorthWestern Energy contributed over $5 million to community development and environmental stewardship programs across its service areas.
Customer Expectations for Service and Sustainability
NorthWestern Energy is navigating a landscape where customers demand more than just reliable power; they expect seamless digital interactions and a commitment to sustainability. By the end of 2024, a significant portion of utility customers, potentially over 70% based on broader industry trends, will expect robust online portals for account management and real-time energy usage data.
This shift means NorthWestern Energy must invest in user-friendly digital platforms and transparent data reporting to meet these evolving expectations. Furthermore, customer interest in renewable energy options continues to grow, with surveys indicating a strong preference for utility-offered green energy programs.
Meeting these demands is crucial for customer satisfaction and retention, directly impacting NorthWestern Energy's market position and long-term growth.
- Digital Engagement: Customers increasingly prefer self-service options via online portals and mobile apps for billing, service requests, and usage monitoring.
- Sustainability Demand: A growing segment of NorthWestern Energy's customer base is actively seeking and willing to pay for renewable energy sources and sustainable practices.
- Real-time Information: Expectation for immediate access to energy consumption data is rising, enabling customers to better manage their usage and costs.
- Program Participation: Customers are looking for opportunities to participate in demand response, energy efficiency, and community solar programs offered by their utility.
Societal expectations are increasingly shifting towards environmental consciousness, directly influencing NorthWestern Energy's operations and public perception. A 2024 survey indicated that 62% of Americans support renewable energy development, a trend that pressures utilities to integrate cleaner sources. This growing awareness means NorthWestern Energy faces scrutiny over its fossil fuel assets, as evidenced by 2024 protests in Montana concerning natural gas infrastructure, underscoring the need for a robust clean energy portfolio.
The aging workforce presents a significant challenge for NorthWestern Energy, as a substantial portion of experienced utility professionals are nearing retirement. Projections suggest nearly 20% of civilian workers could be 65 and older by 2030, impacting specialized roles within the energy sector. This demographic shift, combined with competition for talent, necessitates investment in training and retention programs to ensure a skilled workforce for evolving technologies like smart grids.
Community acceptance is crucial for NorthWestern Energy's infrastructure projects, with local support directly impacting project timelines and costs. The company's 2023 investment of $1.2 billion in infrastructure improvements highlights the need for strong community relations. Proactive communication and engagement, such as sponsoring local events and educational initiatives in 2024, are vital for building trust and mitigating potential opposition.
Customer expectations are evolving, with a growing demand for digital engagement and sustainable energy options. By the end of 2024, over 70% of utility customers are expected to prefer robust online portals for account management and real-time data. NorthWestern Energy must invest in user-friendly digital platforms and transparent data reporting to meet these demands and enhance customer satisfaction.
Technological factors
NorthWestern Energy is investing significantly in grid modernization to bolster reliability and efficiency, with a reported $250 million allocated in their 2024 capital plan towards infrastructure upgrades, including smart grid technologies. These investments are essential for integrating an increasing number of distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar and battery storage, which are expected to grow by an estimated 15% annually through 2025.
The deployment of advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) and distribution automation systems allows for more granular data collection and faster response to outages, improving customer service and operational performance. By 2025, NorthWestern Energy aims to have AMI deployed to over 70% of its residential customer base, enabling better load management and grid stability in the face of fluctuating energy sources.
Advancements in wind and solar technologies continue to reshape the energy landscape, directly impacting NorthWestern Energy's generation strategy. For instance, the global average cost of electricity from solar photovoltaics (PV) and onshore wind has fallen dramatically, with solar PV costs decreasing by approximately 89% between 2010 and 2022, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). This makes these sources increasingly competitive for large-scale integration into the company's portfolio.
Improvements in efficiency and the development of cost-effective energy storage solutions, such as advanced battery technologies, are crucial for integrating intermittent renewables like wind and solar. By 2025, the global energy storage market is projected to reach over $100 billion, indicating significant investment and innovation in this area. NorthWestern Energy needs to actively assess these evolving storage capabilities to ensure reliable and diversified energy supply.
The company must continuously evaluate emerging renewable energy technologies to strategically diversify its energy mix and meet future demand. This includes exploring advancements in geothermal, advanced hydro, and potentially emerging technologies like green hydrogen production, which could offer further resilience and sustainability benefits to its operations.
NorthWestern Energy, as a critical infrastructure provider, faces escalating cybersecurity threats targeting both its operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) systems. Protecting these essential services from cyberattacks and ensuring the privacy of customer data are top priorities. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. energy sector experienced a significant rise in ransomware attacks, with some incidents causing disruptions to service delivery.
Maintaining the integrity of its systems and fostering customer trust necessitates ongoing, substantial investment in advanced cybersecurity measures and stringent protocols. This includes regular vulnerability assessments, employee training, and the implementation of cutting-edge threat detection and response capabilities. The company's commitment to cybersecurity is crucial for uninterrupted service and data protection.
Energy Storage Solutions
The increasing commercial viability of energy storage, particularly battery technology, is a key technological factor for NorthWestern Energy. This is crucial for effectively integrating variable renewable energy sources like solar and wind into their grid. For example, by mid-2024, battery storage projects globally are seeing significant investment, with costs for lithium-ion battery packs continuing to decline, making them more accessible for utility-scale applications. This trend directly impacts NorthWestern Energy's ability to manage grid stability and respond to fluctuating energy demands.
Energy storage solutions offer NorthWestern Energy the capability to enhance grid reliability and flexibility. They can absorb excess renewable generation and discharge power during peak demand periods, thereby reducing reliance on less efficient peaker plants. This not only improves operational efficiency but also helps in meeting environmental goals. The company is actively evaluating various storage technologies to find the most cost-effective deployments that align with their strategic objectives.
- Advancing Battery Technology: Continued improvements in battery chemistry and manufacturing are driving down costs and increasing energy density, making large-scale storage more feasible.
- Grid Modernization: Investments in smart grid technologies are essential to effectively manage and integrate distributed energy resources, including storage.
- Cost Competitiveness: The levelized cost of storage (LCOS) is becoming increasingly competitive with traditional generation sources, creating new economic opportunities for deployment.
- Hybridization: Combining storage with renewable generation, such as solar-plus-storage, offers enhanced reliability and dispatchability.
Digital Transformation and Operational Efficiency
NorthWestern Energy is actively embracing digital transformation to boost operational efficiency. By implementing technologies like predictive maintenance, AI-powered analytics, and automated control systems, the company aims to optimize its asset management and cut down on expenses. This digital shift is expected to enhance performance across its generation, transmission, and distribution networks, leading to smarter resource allocation.
For instance, in 2023, NorthWestern Energy reported significant investments in grid modernization and technology upgrades, totaling hundreds of millions of dollars, to improve reliability and efficiency. These initiatives are crucial for managing a complex energy infrastructure and adapting to evolving market demands.
- Predictive Maintenance: Reduces downtime and maintenance costs by anticipating equipment failures.
- AI-driven Analytics: Optimizes energy distribution and demand forecasting.
- Automated Control Systems: Enhances grid stability and response times to outages.
- Digital Transformation Investments: NorthWestern Energy allocated approximately $300 million in 2023 towards technology and infrastructure improvements to support these efficiencies.
Technological advancements are a major driver for NorthWestern Energy, particularly in grid modernization and the integration of renewables. The company is investing heavily in smart grid technologies, with a reported $250 million allocated in its 2024 capital plan for infrastructure upgrades, including advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) deployment aimed at covering over 70% of its residential customers by 2025.
The decreasing costs of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, with solar PV costs falling by approximately 89% between 2010 and 2022, are making these technologies increasingly attractive for NorthWestern Energy's generation mix. Furthermore, the burgeoning energy storage market, projected to exceed $100 billion globally by 2025, presents opportunities for enhanced grid reliability and the management of intermittent renewable sources.
NorthWestern Energy is also leveraging digital transformation, investing around $300 million in 2023 for technology and infrastructure improvements, to enhance operational efficiency through predictive maintenance and AI-driven analytics. These technological shifts are crucial for optimizing asset management and adapting to the evolving energy landscape.
| Technology Area | Key Developments/Investments | Impact on NorthWestern Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Modernization | $250 million capital allocation in 2024 for infrastructure upgrades, including smart grid technologies. | Improved reliability, efficiency, and integration of distributed energy resources. |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Falling costs of solar PV (approx. 89% decrease 2010-2022). | Increased competitiveness of renewables, influencing generation strategy. |
| Energy Storage | Global market projected to exceed $100 billion by 2025. | Enhanced grid stability, flexibility, and management of renewable intermittency. |
| Digital Transformation | $300 million invested in 2023 for technology upgrades. | Optimized operations, predictive maintenance, and AI-driven analytics. |
Legal factors
NorthWestern Energy navigates a strict regulatory landscape, governed by federal bodies like the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) and numerous state public utility commissions. These regulations dictate crucial aspects of its operations, including transmission rates and market behavior, demanding constant vigilance and legal expertise.
Failure to adhere to these energy regulations can lead to severe financial repercussions. For instance, in 2023, the energy sector saw instances of significant penalties for compliance failures, underscoring the financial risks involved. NorthWestern Energy's commitment to compliance is therefore paramount to avoiding such penalties and maintaining operational stability.
NorthWestern Energy operates under a stringent environmental regulatory framework, heavily influenced by federal laws like the Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act, alongside state-specific mandates. These regulations directly affect its fossil fuel power plants, dictating everything from emissions levels to waste management protocols. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continued to enforce stricter air quality standards, potentially requiring upgrades or modifications to existing facilities to meet new limits on pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
Compliance with these evolving environmental laws is not merely a procedural requirement but a significant financial consideration. NorthWestern Energy must allocate capital for pollution control technologies and adhere to complex permitting processes for any new infrastructure development. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines and operational disruptions, underscoring the critical need for proactive environmental stewardship and investment in cleaner energy solutions to mitigate future risks and costs.
Workplace safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), are a significant legal factor for NorthWestern Energy. These rules are crucial due to the inherent dangers in utility work, including overhead line maintenance and natural gas handling. In 2023, OSHA reported a 5% decrease in workplace fatalities across all industries, underscoring the importance of robust safety programs.
NorthWestern Energy's commitment to adhering to stringent safety standards for its line workers, power plant operators, and natural gas distribution teams is essential. This not only protects employee well-being but also helps prevent costly accidents and potential legal liabilities. For instance, a single major industrial accident could result in millions of dollars in fines and legal settlements.
To maintain compliance and foster a safe environment, the company likely conducts regular safety audits and provides ongoing training. These proactive measures are vital for mitigating risks and ensuring that all operations meet or exceed regulatory requirements, a trend that is expected to continue with increasing scrutiny on industrial safety practices through 2025.
Land Use and Property Rights Laws
NorthWestern Energy's extensive infrastructure, from power plants to transmission lines, is deeply intertwined with land use and property rights laws. The company must meticulously adhere to zoning regulations and land use planning across its operating regions, which include Montana, South Dakota, and Nebraska. For instance, securing rights-of-way for new transmission lines often involves navigating complex eminent domain processes, a legal mechanism that allows the government to take private property for public use, with just compensation. In 2024, ongoing projects require careful management of these legal frameworks to ensure smooth development and compliance.
Obtaining necessary easements and respecting property owner rights are critical legal hurdles for NorthWestern Energy's expansion and maintenance activities. Compliance with local land use ordinances can significantly impact project timelines and costs. Public sentiment regarding land use, particularly for large-scale infrastructure like pipelines and new generation facilities, can escalate into legal challenges, potentially delaying or halting development. For example, in late 2023 and early 2024, several energy infrastructure projects faced legal scrutiny over environmental impact assessments and land use permits.
- Zoning Compliance: Adherence to local zoning laws is mandatory for all NorthWestern Energy facilities, impacting siting and operational parameters.
- Easement Acquisition: Securing legal rights to use private land for infrastructure, such as pipelines and power lines, is a continuous legal process.
- Eminent Domain Procedures: The company must follow established legal protocols when private land acquisition is necessary for public utility projects.
- Public Opposition Impact: Legal challenges stemming from public opposition to land use can lead to project delays and increased legal expenditures.
Consumer Protection and Privacy Laws
Consumer protection and privacy laws significantly shape NorthWestern Energy's customer relationships. Regulations governing billing practices, such as those ensuring clarity and accuracy, are paramount. For instance, state-specific consumer protection acts often dictate how utility companies must handle disputes and provide information to customers, directly impacting operational procedures.
Data privacy is another critical legal area. With increasing digitization of customer information, NorthWestern Energy must adhere to stringent data security and privacy mandates, akin to those found in California's Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) or similar state-level legislation enacted or updated through 2024 and 2025. These laws require transparent data collection, usage, and protection policies.
Compliance with these legal frameworks is not just about avoiding penalties; it's essential for maintaining customer trust. In 2024, consumer advocacy groups continued to push for stronger protections, leading to potential regulatory reviews of utility billing and data handling. NorthWestern Energy's proactive approach to these evolving legal landscapes, including robust data privacy protocols and transparent billing systems, helps mitigate risks of costly legal battles and reputational damage.
Key legal considerations include:
- Billing Transparency: Adherence to state and federal laws mandating clear and understandable energy bills.
- Data Privacy Compliance: Meeting requirements for safeguarding customer personal information, including consent and access rights.
- Consumer Complaint Resolution: Following established legal procedures for addressing and resolving customer grievances.
- Regulatory Oversight: Navigating oversight from bodies like the Public Utility Commission (PUC) in states where it operates, which often enforce consumer protection standards.
NorthWestern Energy faces significant legal challenges related to environmental regulations, with compliance costs impacting its operations. For instance, the EPA's ongoing enforcement of air quality standards in 2023 necessitated potential upgrades to fossil fuel plants, adding to capital expenditures. The company must also navigate complex land use laws, including eminent domain procedures for new transmission lines, with projects in 2024 requiring meticulous attention to these legal frameworks.
Workplace safety regulations, enforced by OSHA, are critical for NorthWestern Energy, given the hazardous nature of utility work. Adherence to these standards in 2023, which saw a 5% decrease in workplace fatalities across industries, is vital to prevent accidents and associated legal liabilities. Furthermore, consumer protection and data privacy laws, such as those influencing billing transparency and customer information handling, are essential for maintaining trust and avoiding legal disputes, a trend expected to intensify through 2025.
Environmental factors
NorthWestern Energy faces increasing pressure from federal and state climate change policies, directly impacting its long-term strategic planning. For instance, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) proposed regulations on power plant emissions, expected to be finalized in 2024, will likely necessitate significant investments in cleaner generation technologies or emissions control for its existing fleet.
These evolving regulations, including potential carbon pricing mechanisms or stricter renewable portfolio standards in states like Montana and South Dakota, compel NorthWestern Energy to proactively evaluate and reduce its carbon footprint. The company's 2023 sustainability report indicated that Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions were approximately 10.5 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent, a figure that will be under scrutiny as policies tighten.
Consequently, this regulatory environment is a key driver for the company's investment decisions, pushing it towards greater adoption of renewable energy sources and enhanced energy efficiency programs. NorthWestern Energy's 2024 capital expenditure plan includes substantial allocations for grid modernization and renewable energy projects, reflecting this strategic shift.
NorthWestern Energy heavily relies on water for its hydroelectric generation and for cooling its thermal power plants. In 2023, for example, its hydroelectric facilities played a significant role in its energy mix, underscoring this dependency.
Droughts and increasing water scarcity, particularly in regions where NorthWestern Energy operates, present a direct operational risk. These conditions can limit hydroelectric output and increase the cost of water for cooling, potentially impacting generation capacity and profitability. Evolving water quality regulations also add complexity, potentially requiring capital expenditures for compliance.
To mitigate these risks, NorthWestern Energy is likely focusing on sustainable water management. This includes investing in water-efficient technologies for its thermal plants and optimizing operations at its hydro facilities to adapt to changing water availability. Proactive water stewardship is essential for ensuring reliable operations and long-term financial health.
NorthWestern Energy's extensive infrastructure, encompassing power lines and facilities across its service territories, presents potential impacts on local ecosystems, wildlife habitats, and overall biodiversity. For instance, in 2023, the company reported ongoing efforts to manage vegetation along its transmission corridors, a critical aspect of preventing outages but also a factor in habitat management.
Adherence to regulations like the Endangered Species Act is paramount. NorthWestern Energy actively monitors and manages its operations to minimize disruption to protected species and their habitats, a commitment reflected in its environmental stewardship reports.
To mitigate its footprint, the company invests in measures such as bird diverters on power lines and habitat restoration projects. These initiatives aim to reduce wildlife mortality and preserve ecological balance, aligning with broader conservation goals and regulatory expectations for 2024 and beyond.
Waste Management and Pollution Control
NorthWestern Energy faces substantial environmental duties related to managing waste, like coal ash from its power plants, and controlling air and water pollution. Meeting strict regulations for hazardous waste, emissions, and wastewater necessitates continuous investment in advanced pollution control systems and sustainable operational methods.
The company is committed to reducing its environmental footprint. For instance, in 2023, NorthWestern Energy reported investing millions in environmental compliance and upgrades across its facilities to meet or exceed air and water quality standards. This includes ongoing efforts to manage byproducts from its energy generation processes responsibly.
- Coal Ash Management: Implementing best practices for the safe storage and potential beneficial reuse of coal combustion residuals.
- Air Emission Controls: Utilizing technologies like scrubbers and selective catalytic reduction to minimize sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter emissions.
- Water Quality Protection: Employing advanced wastewater treatment systems to ensure discharged water meets stringent environmental quality benchmarks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to federal and state environmental laws, including those set by the EPA and relevant state agencies, to avoid penalties and maintain operational integrity.
Renewable Energy Integration and Environmental Benefits
NorthWestern Energy is increasingly incorporating renewable energy sources, such as wind and hydroelectric power, into its energy mix. This shift directly contributes to environmental benefits by reducing the company's dependence on fossil fuels, which in turn lowers greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, as of early 2024, NorthWestern Energy has been actively pursuing new wind power projects, aiming to further diversify its generation capacity beyond traditional sources.
However, this integration isn't without its complexities. The intermittent nature of renewables like wind means that power generation can fluctuate based on weather conditions. This presents challenges for maintaining grid stability and requires significant investment in infrastructure upgrades and energy storage solutions to ensure a reliable power supply. Furthermore, the expansion of renewable facilities often involves considerations of land use and potential impacts on local ecosystems.
Balancing these environmental advantages with the practicalities of operational reliability and infrastructure development is a critical aspect of NorthWestern Energy's strategy. The company is navigating this by investing in grid modernization and exploring partnerships to manage the integration of these cleaner energy sources effectively.
- Renewable Energy Growth: NorthWestern Energy's commitment to renewables is evident in its ongoing projects, aiming to increase the percentage of clean energy in its portfolio.
- Emission Reduction: The shift away from fossil fuels directly translates to lower carbon emissions, aligning with broader environmental goals.
- Grid Integration Challenges: Managing the variability of wind and solar power requires advanced grid management technologies and investments in energy storage.
- Land Use Considerations: The development of new wind farms and other renewable facilities necessitates careful planning regarding land use and environmental impact assessments.
NorthWestern Energy's environmental strategy is heavily influenced by evolving climate policies and regulations, pushing for reduced emissions. The company's 2023 emissions were approximately 10.5 million metric tons of CO2 equivalent, a figure that will face increasing scrutiny under anticipated 2024 EPA regulations and potential state-level carbon pricing.
Water scarcity poses a significant operational risk, impacting hydroelectric generation and increasing cooling costs for thermal plants, as highlighted by the company's reliance on hydro in 2023. Stricter water quality regulations also necessitate capital investments for compliance.
The company is actively managing its ecological footprint through initiatives like bird diverters and habitat restoration, ensuring compliance with regulations such as the Endangered Species Act. These efforts are crucial for mitigating impacts on wildlife and ecosystems, as demonstrated by ongoing vegetation management along transmission corridors.
NorthWestern Energy is investing in cleaner energy sources, with new wind projects being pursued as of early 2024 to diversify its portfolio and lower emissions, though grid integration challenges for renewables require ongoing infrastructure and storage investments.
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE analysis for Northwestern Energy is grounded in data from official government energy agencies, leading economic forecasting firms, and reputable environmental research institutions. This ensures comprehensive coverage of political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the energy sector.