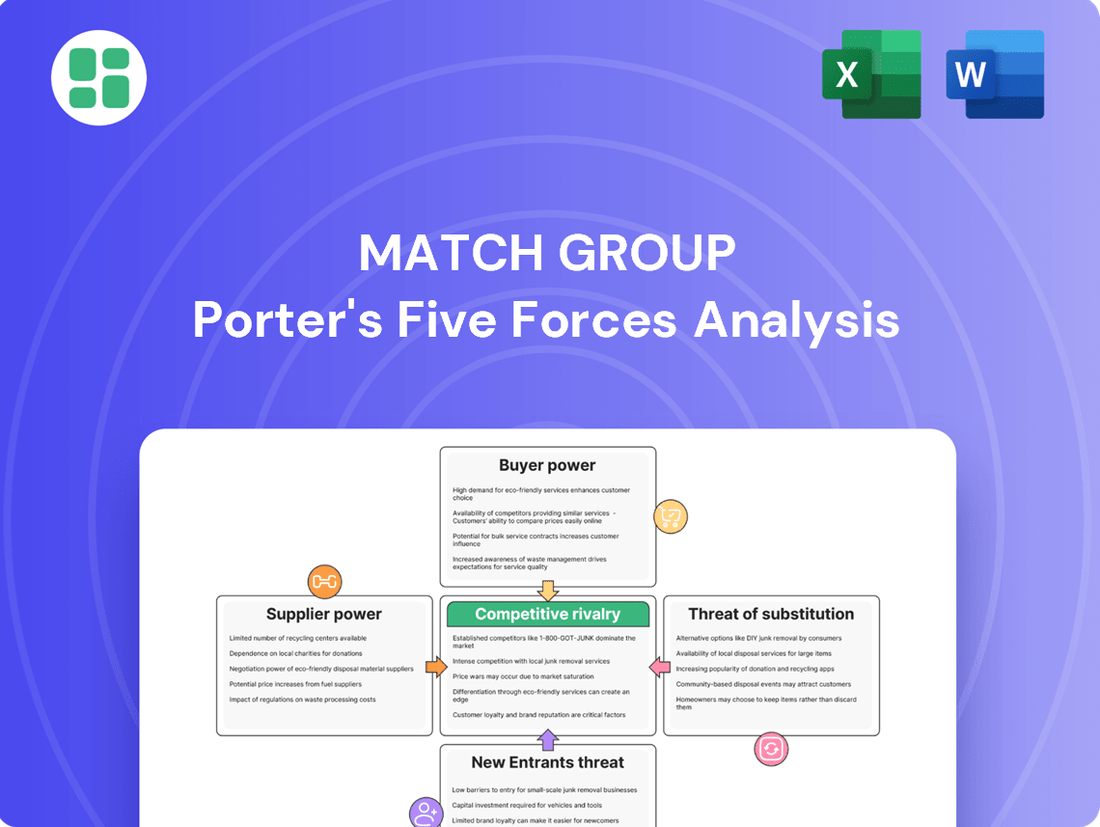
Match Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Match Group Bundle
Match Group, a titan in online dating, faces a dynamic competitive landscape. High buyer switching costs and strong brand loyalty offer some protection, but the threat of new entrants remains a significant factor.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Match Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Match Group's reliance on major cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure for its vast digital operations and data storage is substantial. These providers form the backbone of Match Group's online dating platforms, necessitating robust and scalable infrastructure.
The cloud computing market is highly concentrated, with AWS and Azure holding significant market share. This concentration empowers these suppliers, giving them considerable leverage in negotiating pricing and service level agreements with their customers, including Match Group. For instance, in Q1 2024, AWS reported revenue of $25.0 billion, and Microsoft Azure's commercial cloud revenue grew by 23% in the same period, indicating their market dominance and pricing influence.
While Match Group may explore strategies to diversify its cloud dependencies or optimize its usage, the fundamental reliance on these core infrastructure providers remains a key factor. This dependency can translate into higher operational costs if suppliers increase prices or dictate less favorable terms, directly impacting Match Group's profitability and flexibility.
The Apple App Store and Google Play Store act as crucial gateways for Match Group's dating applications, giving these platforms significant leverage. These app stores are essential for reaching millions of users and they charge substantial fees, often as much as 30%, on transactions made within apps.
Match Group's reliance on these platforms means they must comply with stringent rules and revenue-sharing agreements. In 2023, app store commissions represented a significant cost for many digital businesses, impacting profitability and strategic flexibility.
The specialized skills of software developers, especially those with expertise in AI, machine learning, and secure platform development, form a critical supplier segment for Match Group. The intense demand for these tech professionals drives up labor costs and intensifies competition for top talent.
While Match Group maintains a substantial in-house development team, the ongoing need for cutting-edge innovation means that external talent and specialized agencies can still command significant fees. For instance, in 2024, the average salary for a senior AI engineer in major tech hubs often exceeded $180,000 annually, reflecting this high demand.
Payment Processing Services
Match Group, a leader in online dating, depends on payment processors to manage transactions for its numerous subscription services and in-app purchases. While the payment processing landscape offers several options, the providers of robust, secure, and internationally compliant solutions possess a degree of bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the global payment processing market was valued at over $70 billion, indicating significant scale and specialization among key players.
The leverage these suppliers hold stems from their ability to ensure smooth revenue collection and maintain a positive user experience. Any unfavorable changes in terms or service interruptions could directly affect Match Group's financial performance and customer satisfaction. However, the ability for Match Group to switch providers, while involving some effort, generally presents moderate switching costs compared to reliance on app store payment systems.
- Payment Processor Dependence: Match Group's revenue streams are intricately linked to reliable payment processing.
- Supplier Leverage: Providers of secure, scalable, and compliant payment solutions can exert influence.
- Market Context: The global payment processing market's substantial size in 2024 highlights the importance of key suppliers.
- Switching Costs: While not insignificant, the costs to change payment processors are considered moderate for Match Group.
Intellectual Property and Data Providers
Suppliers of specialized intellectual property, like advanced matching algorithms or data analytics tools, can hold significant sway if their contributions are unique and vital for improving user experience or operational efficiency. Match Group's emphasis on AI-driven matching underscores its dependence on cutting-edge data and analytics solutions, which often originate from a select group of high-value providers.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for sophisticated AI and machine learning expertise within the dating app industry continued to rise. Companies specializing in proprietary algorithms for user behavior prediction and personalized recommendations are in a strong position. These providers can command premium pricing and favorable contract terms due to the difficulty in replicating their specialized knowledge and the direct impact it has on user engagement and retention for platforms like Match Group.
The bargaining power of these intellectual property suppliers is amplified by the increasing complexity and data intensity of modern online dating platforms. Match Group's investment in its AI capabilities, aiming to enhance user matching accuracy and overall platform performance, means that the suppliers of these crucial technologies are essential partners. Their ability to innovate and provide differentiated solutions directly influences Match Group's competitive edge.
- Criticality of AI: Match Group's strategic reliance on AI for matching makes specialized algorithm providers indispensable.
- Limited Providers: The niche nature of advanced AI and data analytics talent means fewer suppliers can offer these critical services.
- Data-Driven Value: Suppliers whose innovations demonstrably improve user engagement and retention possess higher bargaining power.
- 2024 Market Trend: The ongoing demand for sophisticated AI solutions in the tech sector, including online dating, supports higher supplier leverage.
Match Group's reliance on cloud infrastructure providers like AWS and Azure grants these suppliers significant bargaining power due to market concentration. The specialized nature of advanced AI and data analytics talent also empowers suppliers of proprietary algorithms, as their innovations directly impact user engagement and retention.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factor | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Infrastructure (AWS, Azure) | Market concentration, essential service | AWS Q1 2024 revenue: $25.0B; Azure commercial cloud revenue grew 23% |
| App Stores (Apple, Google) | Gatekeepers to user base, transaction fees | App store commissions remain a significant cost for digital businesses |
| Specialized Tech Talent (AI/ML) | High demand, niche skills | Senior AI engineer salaries in tech hubs exceeded $180,000 annually |
| Proprietary Algorithms/IP | Unique, vital for user experience | Demand for AI in dating apps continues to rise, supporting premium pricing |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Match Group's online dating industry.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a clear, visual breakdown of Match Group's Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Users of online dating apps generally face low switching costs. It’s straightforward to download a new application and set up a profile, often with minimal financial outlay or time commitment. This ease of movement allows customers to readily shift to different platforms if they aren't happy with the features, cost, or the caliber of potential matches.
The online dating market is quite crowded, meaning users have a wide array of choices available beyond just the brands owned by Match Group. For instance, in 2024, the global online dating market was valued at over $8 billion, with numerous competitors vying for user attention. This saturation further amplifies the bargaining power of customers.
The online dating market is incredibly saturated, with many direct rivals like Bumble and Grindr, plus niche apps. Social media platforms also serve as indirect alternatives for meeting people. This vast array of options gives users considerable leverage, allowing them to switch to a different service that better suits their needs or relationship aims.
Match Group's broad range of apps, including Tinder, Hinge, and Plenty of Fish, aims to capture various user segments. However, this also highlights the intense competition they face. For instance, in 2023, Tinder, a flagship Match Group product, continued to be a dominant force, but the growth of competitors like Bumble, which reported over 40 million monthly active users in early 2024, underscores the constant pressure for user retention and innovation.
Today's online dating users are looking for more than just a swipe; they want platforms that truly understand them. This means highly personalized recommendations and services are becoming the norm. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of online daters reported that the quality of matching algorithms was a key factor in their platform choice, with many willing to pay a premium for more accurate matches.
This growing demand for personalization is a direct driver of customer bargaining power. Companies like Match Group are compelled to invest heavily in AI and machine learning to refine their matching capabilities. Users can, and do, switch to platforms that offer a more tailored experience, putting pressure on existing providers to constantly innovate and improve their service offerings.
Price Sensitivity and Expectation of Free Tiers
Match Group faces significant customer bargaining power, particularly due to price sensitivity and the expectation of free services. While many users do subscribe to premium features, a substantial segment anticipates basic dating functionalities to remain free. This dynamic pressures Match Group to carefully calibrate pricing for its paid tiers, as customers can readily switch to competitors offering comparable or superior value at a lower cost, or simply utilize free alternatives. For instance, in 2024, the online dating market continued to see a strong presence of freemium models, where users access core services without payment, making the transition to paid subscriptions a conscious decision based on perceived value. This means Match Group needs to constantly demonstrate the tangible benefits of its paid offerings to retain subscribers and attract new ones.
The prevalence of free tiers across the dating app landscape directly fuels customer bargaining power. Users accustomed to accessing basic matching and communication tools without charge are less inclined to pay for incremental features if the perceived value isn't exceptionally high. This forces Match Group to innovate and differentiate its premium services effectively. For example, by Q1 2024, a significant percentage of users on many dating platforms still engaged primarily with free features, highlighting the ongoing challenge of converting these users to paying customers. The ability for customers to easily sample different platforms without significant upfront investment further amplifies their leverage.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers are highly sensitive to the cost of premium dating features, readily comparing prices across platforms.
- Expectation of Free Tiers: A large user base expects core dating functionalities to be available at no cost.
- Competitive Landscape: The availability of numerous free or low-cost alternatives empowers customers to switch easily if they perceive better value elsewhere.
- Monetization Balance: Match Group must strike a delicate balance between generating revenue through subscriptions and maintaining a broad, engaged user base that often starts with free services.
Information Access and User Reviews
Customers today wield significant bargaining power due to readily available information. They can easily access app store ratings, social media discussions, and online forums to compare dating apps and understand their performance. This transparency means users can quickly identify platforms with potential issues, such as fake profiles or safety concerns, influencing their choices.
This ease of access to user reviews and comparative data empowers customers to make informed decisions. For instance, a dating app with a consistently low rating for user experience or a high number of complaints about ghosting or catfishing will likely see a decline in new user acquisition. In 2023, app store ratings and user reviews were frequently cited as key factors influencing download decisions, with many users explicitly stating they check these before committing to a new platform.
- Information Availability: Users can access detailed reviews, performance metrics, and competitor analyses for dating apps.
- Reputation Impact: Negative feedback, amplified through social media and review sites, can rapidly damage a platform's reputation.
- User Acquisition Influence: Transparency regarding issues like fake profiles or safety concerns directly impacts a platform's ability to attract new users.
- Informed Decision-Making: Customers leverage this information to select apps that align with their expectations for safety and user experience.
The bargaining power of customers in the online dating market, including for Match Group, is substantial. This is driven by low switching costs, a highly competitive landscape, and increasing user expectations for personalization and value. For example, by early 2024, the global online dating market was valued at over $8 billion, with numerous competitors like Bumble, which reported over 40 million monthly active users in early 2024, offering users ample alternatives.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Match Group |
|---|---|---|
| Low Switching Costs | Users can easily download new apps and create profiles with minimal effort or expense. | Encourages users to try competing platforms, demanding continuous innovation from Match Group. |
| Market Saturation | A crowded market with many direct and indirect competitors provides users with abundant choices. | Intensifies competition for user acquisition and retention, pressuring pricing and feature development. |
| Expectation of Free Services | Many users expect core dating functionalities to be free, influencing willingness to pay for premium features. | Requires Match Group to carefully balance freemium models with monetization strategies to avoid losing users to free alternatives. |
| Demand for Personalization | Users increasingly seek highly personalized matching algorithms and tailored experiences. | Necessitates significant investment in AI and machine learning to meet user expectations and prevent churn to more personalized platforms. |
Full Version Awaits
Match Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview presents the complete Porter's Five Forces analysis of Match Group, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the online dating industry. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, ready for your business insights.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The online dating arena is incredibly fragmented, boasting thousands of platforms worldwide, from major players to specialized startups, all competing for user engagement.
This intense rivalry compels companies like Match Group to continuously innovate and refine their services to secure and maintain their user base, a trend that remained strong through 2024.
For instance, the global online dating market was valued at approximately $8.0 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating sustained competition and the need for differentiation.
Online dating platforms face substantial fixed costs, including ongoing investment in technology, marketing campaigns, and the crucial effort to acquire new users. These high overheads necessitate a continuous drive for user growth to achieve scalability and profitability.
The intense pressure to build and maintain a large, active user base, which is essential for the network effect in dating apps, fuels aggressive competition for marketing dollars and user attention. This dynamic can significantly impact profitability, as seen in Match Group's Q1 2025 performance where revenue experienced a decline, placing its strategic approach under increased scrutiny.
While the fundamental goal of connecting people remains consistent, dating app companies actively pursue differentiation. This is achieved through innovative features such as AI-driven matchmaking algorithms, integrated video dating capabilities, and robust safety protocols designed to build user trust. Match Group, for instance, has invested heavily in these areas, notably with AI Match and Personality Insights for its popular platforms like Tinder and Hinge.
Network Effects and Brand Loyalty
Match Group thrives on powerful network effects; as more users join Tinder and Hinge, these platforms become more attractive to new users, creating a strong competitive moat. For instance, in Q1 2024, Tinder reported over 10 million paying users globally, underscoring its massive user base advantage. This positive feedback loop makes it difficult for new entrants to gain traction without significant investment.
However, this advantage is tempered by the challenge of 'dating app fatigue,' where users may use multiple apps simultaneously or switch between them. This can dilute brand loyalty, as users seek the best experience across different platforms. In 2023, surveys indicated that a significant percentage of active dating app users were registered on more than one service, highlighting the fluid nature of user engagement.
- Network Effects: Match Group's established brands benefit from a large user base attracting more users, a key advantage in the online dating market.
- Brand Loyalty Challenges: User fatigue and the tendency to use multiple apps can erode loyalty, making it harder to retain users solely on brand name.
- Competitive Response: Competitors actively work to build their own critical mass to counter Match Group's network effect dominance.
Global and Regional Competition
Match Group faces intense competition that spans both global giants and niche regional players. While companies like Bumble offer a significant worldwide presence, numerous localized dating applications cater to specific cultural nuances and demographic preferences in various international markets. This necessitates a dynamic approach from Match Group, requiring constant adaptation of its product offerings and marketing strategies to resonate with diverse user bases across the globe.
The competitive landscape is further shaped by the sheer volume of dating apps available. In 2024, the global online dating market was valued at approximately $9.1 billion, with projections indicating continued growth. This crowded market means Match Group must not only contend with direct competitors but also with the constant emergence of new platforms seeking to capture market share by offering unique features or targeting underserved segments.
- Global Competitors: Bumble, Hinge, and other international dating platforms present a significant competitive threat.
- Regional Players: Localized apps, such as those popular in specific Asian or European markets, cater to distinct cultural preferences and often hold strong user bases.
- Market Saturation: The online dating industry is highly competitive, with a large number of apps vying for user attention.
- Adaptation Challenge: Match Group's success hinges on its ability to tailor its services and marketing to a wide array of international markets and cultural contexts.
The intense rivalry in the online dating sector, characterized by a vast number of platforms, necessitates continuous innovation and user acquisition for companies like Match Group. This competitive pressure is evident in the market's growth, projected to reach approximately $10.1 billion by 2025, up from $9.1 billion in 2024, fueling aggressive marketing spend and feature development.
Match Group's established brands, like Tinder and Hinge, benefit from strong network effects, making them attractive to new users. However, user fatigue and the tendency to use multiple apps challenge brand loyalty, requiring ongoing strategic adaptation to retain users in this dynamic market.
| Key Competitor | 2024 Market Position | Key Differentiators |
| Bumble | Significant Global Presence | Female-first approach, video features |
| Hinge | Focus on serious relationships | Profile prompts, "most compatible" algorithm |
| Localized Apps | Strong regional user bases | Cultural relevance, niche targeting |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Despite the rise of online dating platforms, traditional methods of meeting people, like introductions through friends or attending social events, continue to be strong substitutes for Match Group's services. These methods often involve no direct financial cost and can foster different, sometimes more organic, social connections, posing a challenge to the value proposition of paid dating apps.
Large social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok pose a significant threat of substitutes for Match Group. These platforms, while not exclusively for dating, facilitate user connection and relationship building through direct messaging and group features, allowing individuals to meet and interact outside of dedicated dating apps. For instance, TikTok's user base surpassed 1 billion monthly active users globally by September 2021, highlighting its vast reach for social interaction.
For individuals seeking highly specific connections, niche online communities and interest-based groups can serve as powerful substitutes for broad dating apps. These platforms, often built around shared hobbies or passions, can facilitate deeper initial connections. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 35% of individuals reported meeting partners through shared interest groups, highlighting the appeal of these alternatives.
Offline Matchmaking Services and Events
Professional offline matchmaking services and curated singles' events pose a significant threat of substitutes for Match Group's digital platforms. These offline options offer a more personalized and structured approach, often appealing to individuals experiencing digital dating fatigue or seeking a higher perceived quality of interaction. For instance, while difficult to quantify precise market share shifts, the continued existence and marketing of such services suggest a persistent demand for alternatives. In 2024, the market for in-person dating events and professional matchmaking continues to cater to a segment of the population willing to pay a premium for curated social experiences.
These substitutes, including speed dating and exclusive singles' mixers, attract users who value face-to-face interaction and may find the sheer volume and anonymity of online dating overwhelming. While exact figures for the substitution effect are hard to pinpoint, the ongoing investment in and promotion of these offline avenues by various companies indicates a viable market segment that bypasses traditional dating apps. This segment often prioritizes curated environments and a more traditional courtship process.
- Offline matchmaking services offer a premium, curated experience.
- Speed dating and singles' events cater to those seeking direct, in-person interaction.
- These substitutes address "dating app fatigue" and a desire for higher perceived match quality.
- The continued presence of these services indicates a persistent demand for non-digital dating solutions.
Focus on Self-Improvement or Other Life Priorities
A significant substitute for dating apps is the individual's decision to prioritize self-improvement, career advancement, or other life goals over actively seeking romantic relationships. This can manifest as a deliberate choice to disengage from dating platforms, particularly when users experience burnout or feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of options, often referred to as the 'paradox of choice'.
This trend impacts user acquisition and retention for companies like Match Group. For instance, a 2023 survey indicated that a notable percentage of young adults are delaying major life milestones, including serious relationships, to focus on personal development. This suggests a potential decrease in the addressable market for dating services if these priorities persist.
- Prioritization Shift Individuals may opt for personal growth, career focus, or other life objectives instead of actively pursuing romantic connections via dating apps.
- User Burnout and Choice Overload Excessive options and the effort involved in online dating can lead to user fatigue, prompting a retreat to other life pursuits.
- Market Impact This shift in user priorities can reduce the demand for and engagement with dating services, affecting user base growth and retention.
Beyond dedicated dating apps, social media platforms offer a significant avenue for users to connect and form relationships, acting as powerful substitutes. For instance, TikTok's massive global user base, exceeding 1 billion monthly active users by September 2021, demonstrates its potential for facilitating social interactions outside of traditional dating contexts.
Niche online communities and interest-based groups also present a compelling alternative, allowing individuals to connect over shared passions. A 2024 survey revealed that 35% of people met partners through these interest-focused groups, underscoring their effectiveness in fostering deeper initial connections compared to broader dating platforms.
Traditional methods like introductions through friends or attending social events remain relevant, often involving no direct cost and fostering different, sometimes more organic, social connections. Furthermore, professional offline matchmaking services and curated singles' events cater to those seeking personalized, face-to-face interactions, addressing a segment experiencing dating app fatigue.
In 2024, the market for in-person dating events and professional matchmaking continues to serve individuals willing to pay for curated social experiences, indicating a persistent demand for alternatives to digital dating solutions.
Entrants Threaten
While creating a basic dating app might not demand enormous upfront cash, truly making a splash in the online dating world is another story. Match Group, for instance, has poured considerable resources into its technology and marketing, creating a high bar for newcomers. Think about the sheer expense involved in building out the necessary tech infrastructure to handle millions of users and running widespread advertising campaigns to attract them. This isn't pocket change; it's a significant capital outlay that can easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars to compete effectively.
Established players like Match Group benefit from powerful network effects. For instance, in 2024, Tinder, a key Match Group brand, continued to boast tens of millions of active users, making it far more appealing to new users than a platform with a smaller, less diverse user pool. This self-reinforcing cycle makes it incredibly difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
New entrants face the significant challenge of overcoming this 'cold start' problem. Without a substantial user base, they cannot offer the same breadth of potential connections that users expect, hindering their ability to attract and retain new members. This lack of critical mass directly impacts the value proposition a new dating platform can present.
Match Group's dominance is solidified by its portfolio of deeply ingrained brands like Tinder and Match.com, which have cultivated significant user trust and recognition over many years. Newcomers struggle to replicate this established loyalty, especially when users prioritize safety and authenticity in online dating platforms.
Regulatory and Trust & Safety Hurdles
The threat of new entrants is significantly constrained by stringent regulatory and trust & safety requirements, especially concerning data privacy and user protection. New players must navigate complex legislation like GDPR and CCPA, demanding substantial investment in compliance and robust security infrastructure to combat issues such as scams and fake profiles.
These extensive compliance and safety measures act as a considerable barrier, requiring deep expertise and significant capital outlay that many potential entrants may struggle to meet. For instance, the ongoing efforts to enhance platform safety and combat misinformation require continuous technological development and operational vigilance, adding to the cost of entry.
- Data Privacy Compliance: Adhering to regulations like GDPR and CCPA necessitates significant investment in secure data handling and user consent mechanisms.
- User Safety Investment: Combating scams, fake profiles, and ensuring user well-being requires ongoing development of sophisticated AI and human moderation systems.
- Operational Complexity: Building and maintaining trust and safety protocols is an intensive, resource-heavy undertaking that deters many new market participants.
Access to Distribution Channels and App Store Policies
New entrants in the dating app market face a significant hurdle in gaining access to distribution channels, primarily the Apple App Store and Google Play Store. These platforms control the gateway to the vast majority of smartphone users, making their policies and approval processes critical barriers.
The app stores' stringent review processes, evolving terms of service, and mandated revenue-sharing models, often around 15-30%, can substantially increase costs and limit the operational flexibility of new dating services. For instance, in 2024, developers continue to navigate these complex ecosystems, where visibility and user acquisition are heavily influenced by store algorithms and featured placements.
- App Store Dominance: Apple App Store and Google Play Store are essential for reaching the majority of mobile users.
- Policy Barriers: Strict review processes and changing terms of service create entry challenges.
- Revenue Sharing: Mandatory revenue shares, often 15-30%, impact profitability for new entrants.
- Cost of Acquisition: Navigating app store visibility and user acquisition strategies adds significant costs.
The threat of new entrants into the online dating market, while seemingly low due to high capital requirements and network effects, is subtly influenced by evolving technologies and user preferences. While established players like Match Group, with brands like Tinder and Hinge, command significant market share and brand loyalty, the cost of developing a basic dating app has decreased.
However, achieving critical mass and brand recognition remains a substantial barrier. For example, in 2024, the cost of effective user acquisition through digital marketing and app store optimization can be substantial, often requiring millions in investment to compete with established brands that benefit from strong network effects. The need for continuous innovation in features and safety also adds to the ongoing operational costs for any new entrant aiming to challenge incumbents.
The regulatory landscape, particularly concerning data privacy and user safety, presents another significant hurdle. New entrants must invest heavily in compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA, as well as robust systems to combat fake profiles and ensure user security. This investment in trust and safety, while crucial, adds considerable expense and complexity, making it difficult for smaller players to enter and thrive.
Furthermore, the dominance of app stores like Apple's App Store and Google Play Store creates a duopoly for distribution. New dating apps must navigate their policies, revenue-sharing models (often 15-30%), and algorithms to gain visibility, adding to the cost and complexity of market entry.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Cost/Impact (Illustrative) |
| Capital Requirements | Technology development, marketing, user acquisition | $10M - $100M+ for competitive scale |
| Network Effects | User base size attracting more users | Difficult to quantify, but critical for success |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Established brand recognition and user confidence | Years to build, significant marketing investment |
| Regulatory Compliance | Data privacy (GDPR, CCPA), user safety | Millions in legal, security, and operational investment |
| Distribution Channels | App store policies, revenue share (15-30%) | Impacts profitability and market access |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Match Group Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Statista and IBISWorld, and insights from investor relations sites.