Ikuyo Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ikuyo Bundle
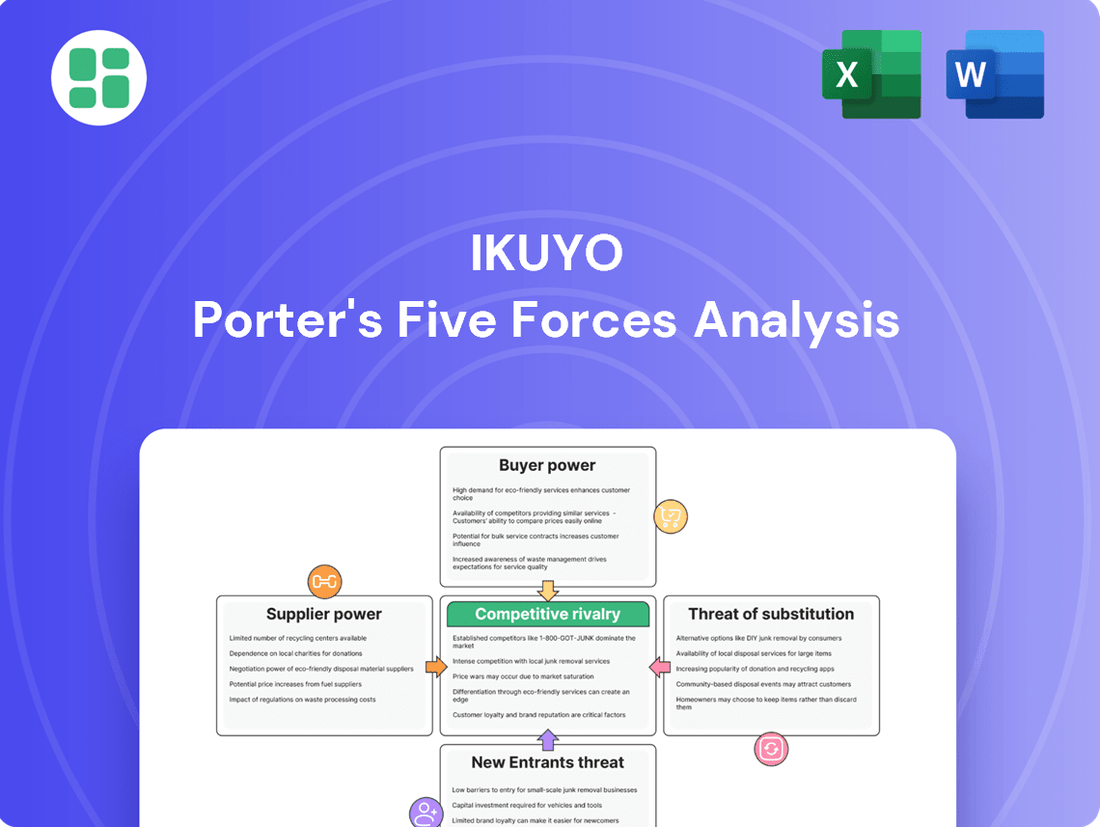
Understanding the five forces shaping Ikuyo's industry is crucial for any strategic decision. This analysis reveals the intense competition, the power of buyers and suppliers, and the potential threats from new entrants and substitutes.
The complete report unlocks a deeper understanding of these dynamics, providing actionable insights into Ikuyo's market position and future opportunities. Gain a competitive edge by exploring the full strategic breakdown.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
In the automotive components sector, particularly for precision-machined parts essential for engines and transmissions, a few specialized suppliers often hold significant sway. These suppliers possess unique, often proprietary, manufacturing capabilities that make their products difficult to replicate or source from alternative providers.
While the automotive industry boasts a vast number of component suppliers overall, the bargaining power of those providing highly specialized or technologically advanced parts can be considerably higher. This leverage stems from the inherent complexity and unique nature of their offerings, making it challenging for automakers to find readily available substitutes.
For instance, in 2024, the market for certain advanced powertrain components saw a concentration of specialized manufacturers. Reports indicate that for critical, high-precision engine blocks, a handful of firms accounted for over 60% of global production, giving them substantial pricing power due to the high barriers to entry and the specialized expertise required.
Switching suppliers for precision automotive components presents substantial hurdles for Ikuyo. The process can involve significant investment in re-tooling existing manufacturing lines, obtaining new certifications for alternative parts, and conducting rigorous testing to ensure compliance with the demanding quality and performance specifications set by Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). This complexity inherently raises the barrier to entry for new suppliers and reinforces the position of current ones.
These high switching costs directly translate into increased bargaining power for Ikuyo's existing suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry saw an average increase of 5-10% in raw material costs for specialized alloys used in critical components, a factor that suppliers can leverage more effectively when Ikuyo faces considerable expense and operational disruption to change its supply base. The financial and temporal implications of such a shift mean Ikuyo is often incentivized to maintain existing relationships, even if pricing becomes less favorable.
The bargaining power of suppliers has significantly increased due to persistent global supply chain issues, especially concerning semiconductors and essential raw materials. This means companies like Ikuyo face greater pressure from their suppliers.
Higher raw material and logistics expenses directly affect suppliers, who naturally pass these increased costs along to manufacturers. For the automotive sector, this has been a major hurdle throughout 2024, and projections suggest it will continue into 2025, solidifying suppliers' leverage.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Ikuyo's business, like taking over assembly or more advanced manufacturing, is generally minimal, especially for highly specialized component makers. While large, diversified suppliers could theoretically make this move, the substantial capital investment and existing strong relationships Ikuyo has with its original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) act as significant deterrents.
Instead of direct forward integration, suppliers might leverage their power through consolidation, acquiring smaller players, or by developing more comprehensive, integrated product offerings that bundle components, thereby increasing their value proposition. For instance, in the automotive sector, a trend towards suppliers offering complete sub-assemblies rather than individual parts has been observed, increasing their leverage.
- Low Likelihood of Direct Forward Integration: High capital requirements and established OEM partnerships typically prevent suppliers from directly entering Ikuyo's assembly or manufacturing processes.
- Supplier Consolidation as a Power Tactic: Suppliers may increase their influence by merging with or acquiring competitors, thereby reducing the number of available suppliers and concentrating market power.
- Development of Integrated Solutions: Suppliers might shift their strategy to offering pre-assembled modules or more complex sub-systems, which indirectly increases their bargaining power by providing a more complete solution to the buyer.
Supplier Importance to Ikuyo's Product Quality
For Ikuyo, a company deeply involved in precision machining for vital automotive components like engines, transmissions, brakes, and fuel systems, the caliber and dependability of its suppliers are absolutely crucial. Any flaw in raw materials or even a single sub-component can lead to significant issues with the final product's performance and, critically, safety. This reality grants suppliers who consistently deliver high quality and reliability considerable leverage.
Ikuyo's commitment to precision and quality is directly tied to the performance of its supply chain. In 2024, the automotive industry continued to grapple with supply chain disruptions, making reliable sourcing even more valuable. For instance, the semiconductor shortage, while easing, still impacted the availability of certain advanced components, demonstrating how dependent automotive manufacturers are on specialized suppliers.
- Criticality of Inputs: Ikuyo's reliance on suppliers for specialized metals, alloys, and pre-fabricated parts means that any compromise in these inputs directly affects the integrity of safety-critical vehicle systems.
- Supplier Dependence: The specialized nature of many automotive components means Ikuyo may have limited alternative suppliers, particularly for niche materials or advanced manufacturing processes.
- Quality Reputation: A single failure traced back to a supplier can severely damage Ikuyo's hard-earned reputation for precision and reliability in the competitive automotive market.
- Cost Implications: While quality is paramount, the cost of these high-spec inputs also plays a role, and suppliers with unique capabilities can often command premium pricing.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Ikuyo is elevated due to the critical nature of specialized automotive components, where quality and reliability are paramount. High switching costs, stemming from re-tooling and certification needs, further solidify supplier leverage. This is exacerbated by ongoing global supply chain disruptions, particularly for semiconductors and raw materials, which have driven up costs and solidified supplier influence throughout 2024.
| Factor | Impact on Ikuyo | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Specialization | Limited alternatives, increased pricing power | Concentration in advanced powertrain components, with a few firms dominating critical parts. |
| Switching Costs | High investment in re-tooling, certification, and testing | Average increase of 5-10% in raw material costs for specialized alloys passed on by suppliers. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Increased dependence on reliable suppliers | Persistent shortages impacting availability of advanced components, reinforcing supplier leverage. |
| Criticality of Inputs | Direct impact on product performance and safety | Reliance on suppliers for safety-critical systems, making quality assurance a key negotiation point. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive intensity within Ikuyo's industry, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Easily identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic, interactive model that visualizes the impact of each force.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ikuyo's customer base is dominated by a few major automotive Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). These large players, both in Japan and worldwide, buy components in massive quantities, giving them considerable leverage. For instance, the top 5 global automotive OEMs, by revenue, often represent a significant portion of any automotive supplier's sales, potentially exceeding 50% in some cases, as of 2024 data. This concentration means these OEMs can strongly influence pricing and demand terms.
While original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) do face some expenses when changing component suppliers, they frequently adopt multi-sourcing strategies. This approach minimizes reliance on any single vendor and cultivates competition among suppliers. In 2024, the automotive sector saw OEMs intensifying their cost-reduction efforts, a trend that significantly amplifies buyer power.
This multi-sourcing practice directly bolsters the bargaining power of customers. OEMs can more readily shift their orders or utilize alternative suppliers if a company like Ikuyo doesn't meet their demands for pricing, quality, or timely delivery. For instance, a major automotive OEM might have contracts with three or four different suppliers for a critical component, giving them substantial leverage.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor impacting Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) in the automotive sector. The market is experiencing heightened price competition, fueled by the emergence of cost-effective electric vehicles and a surge in offerings from Chinese manufacturers. This dynamic directly translates into margin compression for OEMs, forcing them to exert downward price pressure on their suppliers, including companies like Ikuyo. For instance, in 2024, the average transaction price for new vehicles in the US saw a slight decrease compared to its 2023 peak, indicating a shift towards more competitive pricing strategies by automakers.
Information Asymmetry and Standardization
Major automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) hold a significant advantage due to their deep technical expertise and comprehensive market intelligence. This allows them to readily assess and compare the offerings from various suppliers, strengthening their negotiating position. For instance, in 2024, many OEMs reported that their procurement teams utilized sophisticated data analytics to benchmark supplier pricing, with an average of 70% of sourcing decisions influenced by such data.
While Ikuyo's precision components may incorporate unique, proprietary elements, the automotive industry generally sees a high degree of standardization in many parts. This widespread standardization means that buyers can easily compare prices and specifications from a range of suppliers. In 2023, studies indicated that for common automotive components, there were often more than five viable suppliers, increasing buyer options and their leverage.
This inherent transparency in the market, driven by standardization and readily available comparative data, significantly enhances the bargaining power of customers. They can more effectively identify cost-saving opportunities and push for better terms. For example, a 2024 survey of automotive supply chain managers revealed that 85% believed increased component standardization directly led to improved negotiation outcomes with their suppliers.
- Information Asymmetry: Major automotive OEMs possess superior technical and market knowledge compared to many suppliers.
- Standardization Impact: The general standardization of automotive parts allows buyers to easily compare specifications and pricing across different suppliers.
- Negotiation Leverage: Increased transparency and a wider supplier base empower customers to negotiate more favorable terms and prices.
- Data-Driven Benchmarking: In 2024, advanced data analytics were used by 70% of OEMs to benchmark supplier pricing, influencing sourcing decisions.
Backward Integration Threat by Customers
Large automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) possess significant financial resources and technical expertise, enabling them to produce certain components internally. This capability represents a credible, though often unexercised, threat of backward integration. For instance, in 2024, major automotive players continued to invest heavily in advanced manufacturing technologies, signaling their readiness to bring more production in-house if necessary.
This potential for self-sufficiency grants OEMs considerable leverage in negotiations with suppliers like Ikuyo. They can credibly threaten to insource production if pricing or contract terms are deemed unfavorable. This dynamic directly influences supplier behavior, compelling them to maintain competitive pricing and favorable terms to retain business.
- OEMs' Backward Integration Capability: Major automotive manufacturers have the financial clout and technical know-how to manufacture components themselves.
- Negotiation Leverage: The threat of bringing production in-house gives OEMs a strong bargaining position, allowing them to push for better prices and terms from suppliers.
- Supplier Competitiveness: This customer power incentivizes suppliers, such as Ikuyo, to offer competitive pricing and services to avoid losing business to in-house production.
Ikuyo's customers, primarily large automotive OEMs, wield substantial bargaining power due to their significant purchasing volume and the industry's trend towards multi-sourcing. This concentration of buyer power, coupled with increasing price sensitivity among automakers in 2024, forces suppliers to compete aggressively on price and terms. OEMs' technical expertise and market intelligence further amplify their negotiating leverage, allowing them to benchmark and demand favorable conditions.
| Factor | Impact on Ikuyo | Supporting Data (2024 Estimates/Trends) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for major OEMs | Top 5 global automotive OEMs can account for over 50% of a supplier's sales. |
| Multi-Sourcing Strategies | Increased competition among suppliers | OEMs actively use multiple suppliers for critical components to mitigate risk and drive down costs. |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure on supplier margins | Automakers face margin compression due to competitive EV pricing and new market entrants, leading to downward price pressure on suppliers. |
| Technical Expertise & Market Intelligence | Enhanced OEM negotiation position | 70% of OEM sourcing decisions in 2024 were influenced by data analytics for supplier benchmarking. |
| Standardization of Parts | Easier comparison and switching | High standardization for common parts allows buyers to easily compare specifications and prices from numerous suppliers. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Incentive for suppliers to remain competitive | Major OEMs continue investing in advanced manufacturing, retaining the option to insource component production. |
What You See Is What You Get
Ikuyo Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is the complete Ikuyo Porter's Five Forces Analysis, precisely the same comprehensive report you'll receive instantly after purchase. This detailed analysis, covering all five forces impacting Ikuyo, is fully formatted and ready for your immediate use. You can trust that what you preview is exactly what you'll download, offering no surprises and immediate value for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global automotive components market is intensely competitive, featuring a multitude of established manufacturers of varying sizes. Ikuyo, focusing on precision machining, faces this crowded landscape where many firms offer comparable capabilities or finished parts. This broad participation, particularly in specific market niches, escalates competition and exerts downward pressure on both pricing and the pace of technological advancement.
While the automotive components sector anticipates growth, certain traditional segments tied to internal combustion engines are experiencing stagnation or decline as the industry pivots towards electric vehicles. This shift creates a challenging environment for suppliers heavily invested in legacy technologies.
Overcapacity in European production facilities, coupled with a noticeable slowdown in global light vehicle sales growth, is compelling original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to aggressively pursue cost reductions. This pressure trickles down to component suppliers, intensifying competition for available business and often leading to more aggressive pricing strategies.
For instance, in 2024, the global automotive market faced headwinds, with some regions experiencing flat or declining sales. This oversupply and demand imbalance means suppliers are fighting harder for market share, potentially accepting lower margins to secure contracts and maintain production volumes.
In the automotive component manufacturing sector, especially for precision machining, the need for advanced machinery, ongoing research and development, and a highly skilled workforce translates into significant upfront capital investment and thus, high fixed costs. For instance, a state-of-the-art CNC machining center can cost upwards of $500,000, and a full production line easily runs into millions.
These substantial fixed costs create a powerful pressure for manufacturers to maintain high operating capacity to spread the costs and remain profitable. This often results in intense competition among players to secure contracts, as any idle capacity directly impacts the bottom line. In 2024, the global automotive component market, valued at approximately $1.5 trillion, saw fierce bidding for OEM contracts.
Furthermore, the industry is characterized by high exit barriers. Specialized machinery is difficult to repurpose or sell at a reasonable price, and the significant investment in training and retaining a specialized workforce makes leaving the market a costly endeavor. These factors mean companies are more likely to persevere through market downturns, intensifying rivalry even when demand falters.
Product Differentiation and Innovation Pace
Competitive rivalry in the automotive component sector, particularly for Ikuyo, is intense, driven by the need for product differentiation. Companies achieve this through precision engineering, enhanced reliability, the adoption of advanced materials, and the seamless integration of cutting-edge technologies like those for Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) and electric vehicles (EVs).
The pace of innovation is a critical battleground. Ikuyo, like its peers, must pour resources into research and development to stay ahead. Failing to innovate risks commoditization, especially as the automotive industry increasingly demands sophisticated and sustainable solutions. For instance, the global automotive semiconductor market was valued at approximately $52.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $115.5 billion by 2030, highlighting the rapid technological evolution and the premium placed on advanced components.
- Precision and Reliability: Key differentiators in critical automotive components.
- Technological Integration: ADAS and EV technologies are major innovation drivers.
- R&D Investment: Essential for avoiding commoditization and maintaining a competitive edge.
- Industry Shift: The move to EVs fundamentally reshapes demand for traditional automotive parts.
Impact of Electrification and Chinese Competition
The automotive industry's swift pivot to electric vehicles (EVs) profoundly alters competitive dynamics. Suppliers focused on internal combustion engine (ICE) parts face significant disruption, as demand for their core products wanes. For instance, by the end of 2024, a substantial portion of new vehicle sales in key markets like Europe and China are projected to be EVs, directly impacting traditional component suppliers.
Adding to this pressure, Chinese automakers, often possessing cost advantages, are aggressively expanding their global presence. This influx intensifies rivalry, forcing established original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and their suppliers to re-evaluate pricing and innovation strategies. By mid-2024, Chinese EV brands have captured a notable share of their domestic market and are making significant inroads into international markets, a trend that will likely accelerate.
- EV Transition Impact: Suppliers reliant on ICE technology face declining demand as EV adoption accelerates, with projections indicating EVs could represent over 30% of global new car sales by 2025.
- Chinese Competition: Increased market entry by cost-efficient Chinese manufacturers is intensifying price wars and forcing global players to optimize operations and supply chains.
- Strategic Imperative: Ikuyo must proactively adapt its product offerings and manufacturing processes to align with EV technology to mitigate risks and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Competitive rivalry in the automotive components sector is fierce, characterized by numerous players vying for market share. Ikuyo, like its peers, must differentiate through precision, reliability, and technological integration, especially with the industry's rapid shift towards EVs and advanced systems like ADAS.
High fixed costs associated with advanced manufacturing and R&D, coupled with significant exit barriers, compel companies to maintain high capacity utilization, intensifying competition for contracts. The global automotive component market, valued at approximately $1.5 trillion in 2024, reflects this intense bidding environment.
The increasing presence of cost-competitive Chinese manufacturers, particularly in the EV segment, further escalates rivalry, pushing established players to optimize operations and adapt their strategies to remain competitive.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Ikuyo |
| Number of Competitors | Many established and emerging players in precision machining and automotive components. | Intensifies price competition and necessitates strong differentiation. |
| Industry Growth Rate | Overall market growth is steady, but traditional ICE segments face decline while EV segments grow rapidly. | Requires strategic product portfolio adjustment towards EV components. |
| Product Differentiation | Key differentiators include precision, reliability, technological integration (ADAS, EV tech), and R&D capabilities. | Ikuyo must invest in innovation to avoid commoditization and secure premium contracts. |
| Switching Costs for Buyers | OEMs face costs and risks in changing suppliers, but the demand for specialized EV components can drive shifts. | Ikuyo needs to build strong relationships and demonstrate superior technological capabilities to retain and attract OEM business. |
| Exit Barriers | High costs associated with specialized machinery, workforce training, and industry-specific investments. | Companies are likely to remain in the market, sustaining competitive pressure even during downturns. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The accelerating shift to electric vehicles (EVs) presents a significant threat of substitution for Ikuyo. EV powertrains, by design, require substantially fewer components than traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) systems, directly impacting demand for Ikuyo's core offerings in engine, transmission, and fuel/brake systems.
This transition is not a distant prospect; by the end of 2023, global EV sales surpassed 13.6 million units, a substantial increase from previous years. This growing market share means a shrinking addressable market for ICE-specific components, posing an existential risk to suppliers like Ikuyo heavily reliant on this technology.
Beyond fully electric vehicles, hybrid and hydrogen fuel cell technologies pose significant threats to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) components. While hybrids still incorporate some ICE parts, the increasing market share of these alternatives necessitates diversification for suppliers like Ikuyo. Japan's commitment to hydrogen technology, for example, highlights a global trend that could diminish demand for conventional powertrain parts.
The automotive industry's relentless pursuit of lightweighting to boost fuel efficiency and slash emissions presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional metal components. Advanced materials like carbon fiber composites and high-strength aluminum alloys are increasingly replacing steel and iron. This shift directly impacts companies like Ikuyo if they cannot adapt their machining processes to handle these novel materials.
In 2024, the global market for advanced lightweight materials in automotive was valued at approximately $25 billion, with projections indicating substantial growth. Suppliers who master the machining and integration of these materials gain a competitive edge, potentially displacing those relying solely on legacy metalworking techniques. Ikuyo's strategic response to this trend will be critical for maintaining its market position.
Evolving Vehicle Architectures and Software-Defined Vehicles
The automotive industry's rapid shift towards software-defined vehicles presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional mechanical components. As vehicles become more integrated with advanced electronics and software, the need for purely mechanical solutions may diminish. This evolution means that components previously reliant on mechanical engineering could be replaced by mechatronic or entirely electronic systems, forcing companies like Ikuyo to adapt their product development and manufacturing processes to accommodate this increasing complexity.
For instance, advancements in autonomous driving systems are heavily reliant on sensors, processors, and sophisticated algorithms, potentially reducing the demand for certain traditional mechanical parts like steering columns or braking systems as they are replaced by steer-by-wire and brake-by-wire technologies. In 2024, the global market for automotive semiconductors, a key enabler of software-defined vehicles, was projected to reach approximately $100 billion, highlighting the scale of this technological shift and the potential displacement of mechanical alternatives.
- Software-Defined Vehicle Growth: The increasing reliance on software for vehicle functions, from infotainment to powertrain management, directly impacts the demand for traditional mechanical components.
- Mechatronic and Electronic Substitutes: Purely mechanical systems are increasingly being replaced by integrated mechatronic or electronic solutions, such as electric power steering and electronic throttle control.
- Market Data: The automotive semiconductor market, crucial for software-defined vehicles, is expected to continue its robust growth, indicating a strong trend away from purely mechanical architectures.
Alternative Transportation Modes
While Ikuyo is a component manufacturer, shifts towards alternative transportation modes can still impact its business. For instance, increased adoption of public transit, ride-sharing, and micromobility options like electric scooters and advanced e-bikes could lead to fewer new vehicle sales overall. This reduction in car production directly translates to lower demand for the automotive components Ikuyo supplies.
Consider the growing popularity of ride-sharing. In 2024, the global ride-sharing market was projected to reach over $200 billion, indicating a significant shift in how people access transportation. This trend can reduce the need for individual car ownership, thereby decreasing the volume of vehicles manufactured and subsequently, the demand for components like those produced by Ikuyo.
- Reduced Vehicle Production: A rise in alternative transportation usage can lead to a decrease in the number of new cars produced.
- Lower Component Demand: Fewer cars manufactured means less demand for automotive parts, directly affecting companies like Ikuyo.
- Market Size Contraction: The overall market for automotive components could shrink if these societal shifts continue to gain traction.
- Micromobility Growth: The expansion of e-bikes and e-scooters, for example, offers viable alternatives for short-distance travel, potentially impacting car sales in urban areas.
The threat of substitutes for Ikuyo is amplified by the automotive industry's move towards electrification and advanced materials. As EVs gain market share, demand for traditional ICE components, Ikuyo's core business, will decline. Furthermore, the increasing use of lightweight materials like carbon fiber and the rise of software-defined vehicles, which integrate more electronics and fewer mechanical parts, represent significant substitution risks.
| Threat Type | Description | Impact on Ikuyo | 2024 Market Data/Trend |
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | EV powertrains have fewer components than ICE. | Reduced demand for engine, transmission, and fuel/brake systems. | Global EV sales surpassed 13.6 million units by end of 2023. |
| Advanced Materials | Lightweight composites and alloys replace traditional metals. | Potential obsolescence of machining processes for steel/iron. | Global market for automotive lightweight materials valued at ~$25 billion in 2024. |
| Software-Defined Vehicles | Increased reliance on electronics and software. | Mechanical parts replaced by mechatronic/electronic systems (e.g., steer-by-wire). | Automotive semiconductor market projected around $100 billion in 2024. |
| Alternative Transport | Increased use of public transit, ride-sharing, micromobility. | Lower overall new vehicle production, thus lower component demand. | Global ride-sharing market projected over $200 billion in 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the automotive components manufacturing sector, particularly for high-precision parts, necessitates a significant upfront capital outlay. This includes acquiring state-of-the-art machinery, investing heavily in research and development, and establishing robust production facilities. For instance, setting up a new automotive stamping plant in 2024 could easily cost upwards of $50 million to $100 million, depending on scale and automation levels.
Established players like Ikuyo leverage significant economies of scale, enabling them to produce precision-machined components at substantially lower per-unit costs. For instance, in 2024, major players in the automotive supply chain, a key sector for precision machining, reported average production costs that were 15% lower for volumes exceeding 100,000 units compared to those producing under 10,000 units.
New entrants would face immense difficulty matching these cost efficiencies without achieving comparable production volumes, creating a substantial barrier to entry. This cost disadvantage makes it challenging for newcomers to compete on price against established firms like Ikuyo, who have already optimized their operations over years of production.
Furthermore, the experience curve in precision machining offers a distinct advantage to incumbents. Ikuyo's decades of accumulated knowledge translate into refined manufacturing processes, superior quality control, and reduced waste, all contributing to a competitive edge that is hard for new entrants to replicate quickly.
Stringent regulatory standards and certification requirements significantly deter new entrants in the automotive sector. For instance, achieving compliance with safety regulations like those from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the US, or Euro NCAP in Europe, involves substantial investment in testing and development. Furthermore, obtaining certifications such as ISO/TS 16949 (now IATF 16949), a quality management standard for automotive suppliers, is a complex and time-consuming process that can take several years and millions of dollars.
Established Relationships and Supply Chain Integration
Major automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) cultivate enduring, highly integrated relationships with their current component suppliers. These partnerships are founded on mutual trust, demonstrated reliability, and joint development efforts, making it difficult for new entrants to penetrate these established supply chains. For instance, in 2024, the average tenure of a Tier 1 automotive supplier relationship with a major OEM often spans over a decade, reflecting the deep integration and switching costs involved.
Displacing incumbent suppliers who possess strong ties and a proven track record with automotive giants presents a significant hurdle for newcomers. This entrenched loyalty and history of performance create a formidable barrier to market entry, as OEMs prioritize stability and predictability in their sourcing. In 2023, studies indicated that over 70% of automotive component sourcing decisions were made based on existing supplier performance and established relationships, underscoring this barrier.
- Established OEM-Supplier Relationships: Long-standing, trust-based partnerships in the automotive industry are difficult for new entrants to replicate.
- Supply Chain Integration: Deeply embedded suppliers benefit from collaborative development and proven reliability, creating high switching costs for OEMs.
- Incumbent Advantage: Existing suppliers have a track record and established trust, making it challenging for new companies to gain access to major automotive manufacturers.
- Market Access Barrier: The difficulty in breaking into established supply chains significantly limits the threat of new entrants in the automotive sector.
Intellectual Property and Technological Complexity
The precision machining and advanced component manufacturing sector is heavily protected by intellectual property, including patents and proprietary manufacturing processes. This means new companies must either invest substantially in research and development to create their own unique technologies or acquire licenses for existing ones, both of which significantly increase the cost and complexity of entering the market.
The high technical sophistication inherent in this industry naturally restricts the number of potential new competitors. For instance, companies in this space often require specialized certifications and a deep understanding of materials science, as demonstrated by the aerospace sector where suppliers must meet stringent AS9100 quality standards. As of 2024, the global aerospace market, a significant consumer of precision components, was valued at over $800 billion, highlighting the substantial barriers to entry for those without established expertise and IP.
- High R&D Investment: Developing novel machining techniques or advanced materials can cost millions, making it prohibitive for many startups.
- Patent Landscape: A dense web of patents can prevent new entrants from utilizing key technologies without costly licensing agreements.
- Technical Expertise Gap: The need for highly skilled engineers and machinists with specialized knowledge creates a significant human capital barrier.
- Capital Expenditure: Acquiring state-of-the-art CNC machinery and testing equipment can easily run into tens of millions of dollars.
The threat of new entrants into the precision automotive component manufacturing sector, where Ikuyo operates, is significantly mitigated by several formidable barriers. These include the substantial capital required for advanced machinery and R&D, the cost advantages enjoyed by established players due to economies of scale, and the complex regulatory and certification landscape. Furthermore, strong incumbent relationships with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and the protection of intellectual property create additional hurdles for newcomers.
New entrants face immense difficulty matching the cost efficiencies of established firms like Ikuyo, who benefit from economies of scale. For instance, in 2024, major automotive supply chain players reported production costs 15% lower for volumes over 100,000 units compared to those producing under 10,000 units.
The automotive sector's stringent regulatory standards, such as NHTSA and Euro NCAP compliance, along with certifications like IATF 16949, demand significant investment and time, acting as a deterrent. These requirements can take years and millions of dollars to fulfill.
Established OEMs have deep, integrated relationships with current suppliers, often exceeding a decade in tenure as of 2024. These partnerships, built on trust and reliability, make it challenging for new entrants to gain access, as over 70% of sourcing decisions in 2023 were based on existing supplier performance.
| Barrier Category | Specific Barrier | Estimated Cost/Time (2024 Data) | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | State-of-the-art machinery & R&D | $50M - $100M+ for a stamping plant | Prohibitive initial investment |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for high volume | 15% cost advantage for >100K units | Price competitiveness challenge |
| Regulatory & Certification | Safety standards & quality certifications (IATF 16949) | Millions of dollars and several years | Time-consuming and costly compliance |
| Supplier Relationships | OEM integration and trust | Average tenure over a decade | Difficulty in market access and penetration |
| Intellectual Property | Patents and proprietary processes | Significant R&D or licensing costs | Increased complexity and expense |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Ikuyo is built upon a foundation of diverse data sources, including industry-specific market research reports, financial filings from publicly traded competitors, and trade association publications. We also leverage economic indicators and government statistics to understand the broader industry landscape and potential threats.