Health Catalyst Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Health Catalyst Bundle
Health Catalyst operates within a dynamic healthcare technology landscape shaped by intense competition and evolving customer needs. Understanding the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of new entrants is crucial for strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Health Catalyst’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Health Catalyst's reliance on cloud infrastructure providers like Microsoft Azure, highlighted by their April 2025 partnership, underscores the significant bargaining power these suppliers hold. The essential nature of cloud services for Health Catalyst's data operating system and analytics means that changes in pricing or service terms from these providers can directly impact Health Catalyst's costs and operational capabilities.
While the scale of providers like Microsoft Azure grants them considerable leverage, Health Catalyst can mitigate this power through strategic actions. Diversifying cloud solutions or securing long-term contracts can provide more favorable terms and predictable costs. The 2025 partnership, for instance, while indicating deeper integration and potential benefits, also signals an increased dependence on Microsoft, a factor that could influence future negotiations.
Suppliers of highly specialized software components or niche data feeds crucial for Health Catalyst's advanced analytics could wield some bargaining power. For instance, if a particular AI framework is essential and has few alternatives, its provider could command higher prices.
However, Health Catalyst's strategic move towards developing its own AI-enabled data toolkits on platforms like Databricks Marketplace, as of July 2025, is designed to mitigate this. This in-house development reduces reliance on external proprietary tools, thereby potentially weakening supplier leverage over time.
The market for highly skilled talent in data science, healthcare expertise, AI/ML engineering, and cybersecurity is exceptionally competitive. These professionals are vital suppliers of critical knowledge, and their limited availability significantly bolsters their negotiating power regarding compensation and benefits.
For Health Catalyst, securing and keeping top-tier talent is paramount to sustaining its innovation momentum and effectively delivering sophisticated solutions. In 2024, the demand for these specialized roles continued to outpace supply, driving up salary expectations across the industry.
Data Sources and Integrators
Health Catalyst's reliance on integrating diverse data sources from healthcare providers means its customers are, in essence, its primary data suppliers. However, third-party data aggregators or specialized interoperability solution providers can also act as crucial suppliers. The bargaining power of these entities hinges on the distinctiveness and indispensability of the data they offer, coupled with the complexity of integrating their services.
For instance, if a particular data aggregator holds a unique dataset vital for advanced analytics that Health Catalyst offers, or if their integration technology is proprietary and difficult to replicate, their bargaining power increases. Conversely, if data sources are abundant and easily integrated through standard protocols, supplier power diminishes. In 2024, the healthcare data integration market saw continued consolidation, potentially increasing the leverage of remaining independent data providers.
- Customer as Data Supplier: Healthcare organizations providing the raw data are the primary suppliers.
- Third-Party Integrators: Companies offering specialized data aggregation or interoperability solutions can also be suppliers.
- Power Determinants: Uniqueness and necessity of data, ease of integration, and proprietary technology influence supplier leverage.
- Market Dynamics: Consolidation in the data integration sector in 2024 may have shifted bargaining power dynamics.
Consulting and Professional Services Partners
Health Catalyst, while possessing internal expertise, may engage external consulting and professional services partners for specialized data strategy, implementation, or market expansion initiatives. The bargaining power of these partners is influenced by their distinct knowledge, industry standing, and the overall demand for their skills within the healthcare IT landscape.
For instance, in 2024, the global IT consulting market was valued at over $300 billion, indicating a robust demand for specialized services. Partners with niche expertise in areas like AI-driven healthcare analytics or specific electronic health record (EHR) integrations could command higher fees and exert greater influence.
- Unique Expertise: Partners offering highly specialized skills in areas like clinical data warehousing or advanced predictive analytics for population health management can wield significant bargaining power.
- Reputation and Track Record: Consulting firms with a proven history of successful healthcare IT implementations and strong client testimonials can negotiate more favorable terms.
- Demand in Healthcare IT: The increasing complexity and digital transformation efforts within healthcare in 2024 mean a high demand for skilled IT consultants, potentially increasing their leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Health Catalyst is notably influenced by cloud infrastructure providers and specialized talent. The essential nature of services from giants like Microsoft Azure, underscored by their April 2025 partnership, grants them considerable leverage over pricing and terms, directly impacting Health Catalyst's operational costs.
Furthermore, the scarcity of highly skilled professionals in data science, AI/ML engineering, and healthcare informatics in 2024 significantly bolsters their negotiating power for compensation. This talent is critical for Health Catalyst's innovation, making retention a key strategic concern.
The bargaining power of data suppliers, including healthcare organizations and third-party aggregators, depends on the uniqueness and indispensability of the data they provide. Consolidation within the data integration market in 2024 could have amplified the leverage of remaining independent providers.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Power | Example Impact on Health Catalyst | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Infrastructure (e.g., Microsoft Azure) | Scale, essential service nature, partnership depth | Potential for price increases, impact on service terms | Continued reliance on major cloud providers |
| Specialized Talent (AI/ML Engineers, Data Scientists) | Scarcity, critical skill demand, industry competition | Higher compensation demands, retention challenges | High demand outpacing supply for specialized roles |
| Data Aggregators/Interoperability Providers | Data uniqueness, integration complexity, proprietary technology | Negotiation leverage for data access and integration costs | Market consolidation potentially increasing power of remaining players |
What is included in the product
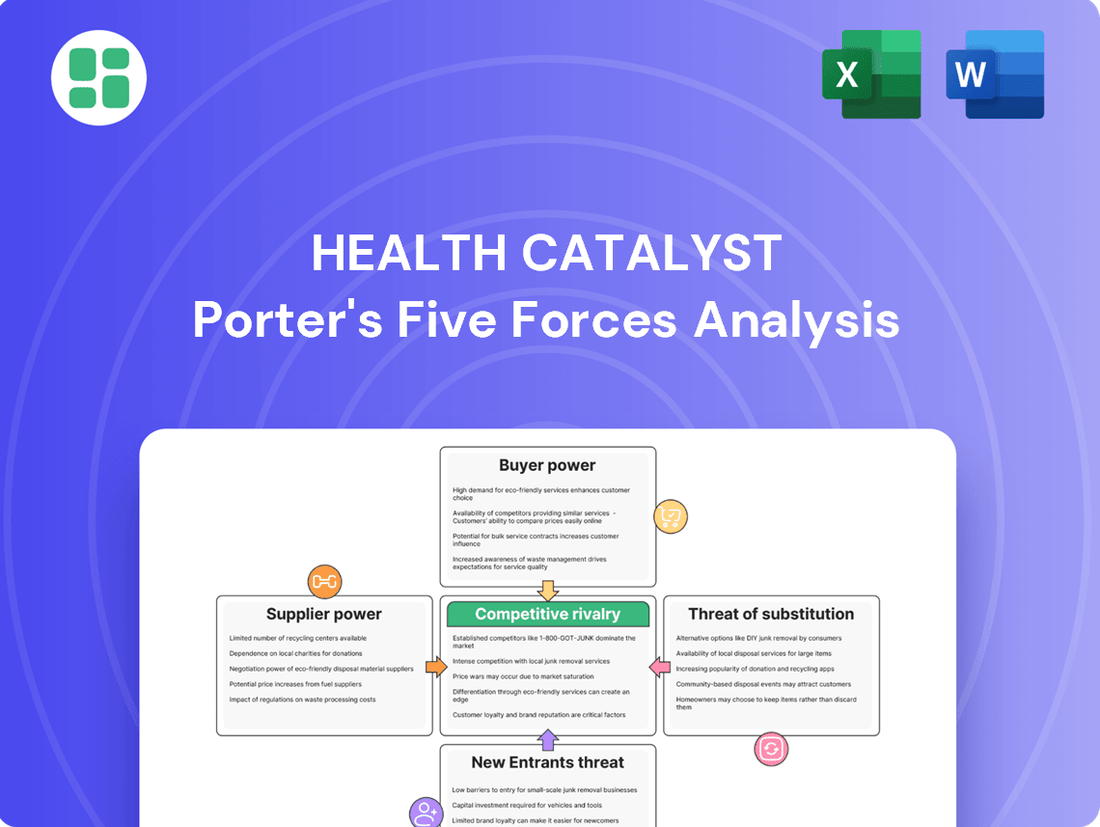
This analysis dissects Health Catalyst's competitive environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the healthcare data analytics market.
Effortlessly analyze competitive pressures by visualizing the five forces in a dynamic, interactive dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
Large healthcare systems, Health Catalyst's primary clientele, wield substantial bargaining power. Their sheer size means they negotiate for significant contract volumes, giving them leverage. For example, in 2024, major hospital networks continued to consolidate, increasing their collective purchasing influence, and many were investing in their own data analytics capabilities, reducing reliance on external vendors.
Once a healthcare organization deeply integrates Health Catalyst's data operating system and analytics applications, the costs to switch become significant. This includes the expense of migrating vast amounts of sensitive patient data, retraining clinical and IT staff on new systems, and the inevitable disruption to critical, ongoing operations. For example, a hospital implementing Health Catalyst's platform might face millions in costs and months of downtime if they were to switch to a competitor.
This high barrier to exit, often referred to as vendor lock-in, effectively diminishes the bargaining power of customers over time. As their reliance on Health Catalyst's specialized infrastructure grows, the financial and operational penalties for changing providers escalate, making them less likely to demand significant concessions or switch to alternatives.
Healthcare organizations are heavily invested in value-based care models, pushing for demonstrable improvements. This focus means customers will demand clear, measurable outcomes from Health Catalyst, directly impacting their willingness to pay and contract terms.
In 2024, the shift towards value-based reimbursement continued to accelerate, with organizations like Medicare increasingly tying payments to quality metrics and patient outcomes. This trend empowers healthcare providers, as they can more effectively negotiate with vendors like Health Catalyst based on the tangible results their solutions deliver, demanding performance-based pricing or risk-sharing agreements.
Budget Constraints and Consolidation in Healthcare
Healthcare providers are notoriously sensitive to price due to significant budget constraints. In 2024, many hospitals and health systems continued to grapple with rising labor costs and inflationary pressures, forcing them to seek the most cost-effective solutions available. This financial reality directly translates into amplified bargaining power for these customers.
The ongoing trend of consolidation within the healthcare industry further concentrates purchasing power. Larger, merged entities can leverage their increased scale to negotiate more favorable terms with vendors like Health Catalyst. For instance, a hospital system formed by multiple mergers can demand significant discounts or customized pricing structures that smaller, independent hospitals might not be able to achieve.
- Budgetary Pressures: In 2023, hospital operating margins saw a slight improvement but remained tight for many, with some reporting negative margins, underscoring the constant need for cost control.
- Consolidation Impact: Major healthcare systems, often formed through mergers and acquisitions, represent a larger, more unified customer base, increasing their leverage in negotiations.
- Demand for Value: Customers are increasingly demanding demonstrable return on investment and cost savings from technology vendors, pushing for solutions that directly address their financial challenges.
Availability of Alternatives
Health Catalyst operates in a market where customers, primarily healthcare organizations, have a variety of data management and analytics options. While Health Catalyst offers a specialized data operating system designed for healthcare, the availability of alternatives significantly impacts customer bargaining power.
Customers can turn to generic business intelligence tools, which, while less specialized, can offer broader functionality. Many Electronic Health Record (EHR) vendors also provide integrated analytics capabilities, presenting a bundled solution that might be attractive. Furthermore, larger healthcare systems may possess the resources and expertise to develop their own internal data teams and solutions, bypassing specialized vendors altogether.
- Generic BI Tools: Solutions like Tableau or Power BI can be adapted for healthcare data, offering flexibility but requiring more customization.
- EHR Integrated Analytics: Vendors such as Epic and Cerner offer analytics modules within their EHR systems, providing a single vendor solution.
- Internal Data Teams: Some health systems invest in building in-house data science and engineering capabilities.
- Perceived Effectiveness: The ability of these alternatives to meet specific healthcare data needs, such as interoperability and regulatory compliance, directly influences how much leverage customers have in negotiations with Health Catalyst.
Customers in the healthcare sector, particularly large hospital systems, hold considerable bargaining power due to their size and purchasing volume. In 2024, continued consolidation among healthcare providers amplified this influence, as larger entities could negotiate more favorable terms. Many organizations also invested in their own data analytics capabilities, reducing their dependency on external vendors like Health Catalyst.
The significant costs and operational disruptions associated with switching data vendors, often running into millions of dollars and months of downtime, create a strong incentive for customers to remain with their current provider. This vendor lock-in, a direct result of deep integration with platforms like Health Catalyst's, effectively limits customers' ability to demand concessions over time.
Healthcare providers are increasingly focused on value-based care, demanding demonstrable improvements and ROI from their technology partners. This trend, accelerated in 2024 by reimbursement models tied to quality metrics, empowers customers to negotiate pricing and contract terms based on the tangible outcomes their solutions deliver.
Financial pressures remain a key driver for healthcare organizations, with many facing tight operating margins and rising costs in 2023 and 2024. This sensitivity to price directly translates into amplified bargaining power, as customers actively seek the most cost-effective solutions available.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | 2024 Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Size & Consolidation | High | Continued healthcare system mergers increased collective purchasing influence. |
| Switching Costs (Vendor Lock-in) | Lowers Customer Power | High integration costs and data migration complexities deter switching. |
| Demand for Value & Outcomes | Increases Customer Power | Shift to value-based care incentivizes negotiation based on demonstrable results. |
| Budgetary Constraints | High | Inflationary pressures and labor costs in 2024 forced cost-conscious negotiations. |
What You See Is What You Get
Health Catalyst Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Health Catalyst provides an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape within the healthcare data analytics industry, detailing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. You're previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying, offering actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The healthcare data analytics landscape is intensely competitive, featuring a broad spectrum of participants. This includes major electronic health record (EHR) providers like Oracle Health (formerly Cerner), alongside dedicated analytics specialists such as Innovaccer and Clarify Health. Furthermore, large consulting firms and even internal IT departments within healthcare organizations contribute to this crowded market.
Health Catalyst contends with a substantial competitive base, facing rivalry from more than 600 active companies. This sheer volume and variety of competitors underscore the dynamic nature of the market and the constant need for innovation and differentiation.
The healthcare analytics market is booming, with forecasts suggesting a substantial expansion from 2024 through 2034. This robust growth, estimated to reach over $100 billion by 2028, can temper direct competition by offering ample room for multiple companies to thrive.
However, this attractive growth rate also acts as a magnet for new entrants and spurs existing players to increase their investments in technology and market share, thereby fueling a dynamic competitive landscape despite the expanding pie.
Health Catalyst's competitive edge hinges on its proprietary data operating system (DOS), which is designed to unlock actionable insights from complex healthcare data. This focus on delivering tangible improvements in clinical quality, financial performance, and operational efficiency allows them to carve out a distinct value proposition.
In 2023, Health Catalyst reported revenue growth, underscoring the market's demand for solutions that demonstrably improve healthcare outcomes. Their ability to quantify these improvements, such as reducing patient readmissions or optimizing supply chain costs, is key to differentiating themselves from competitors offering more generic data analytics platforms.
Switching Costs for Customers
Health Catalyst's high switching costs are a significant factor in its competitive landscape. These costs act as a strong deterrent for clients looking to move to a competitor, thereby safeguarding Health Catalyst's existing market share. This also means that new entrants or existing rivals face considerable hurdles in attracting Health Catalyst's customer base. For instance, the integration of Health Catalyst's data warehousing and analytics solutions into a hospital's IT infrastructure is complex and time-consuming, often involving substantial upfront investment and extensive training. This complexity inherently raises the cost and effort required for a client to switch, reinforcing customer loyalty.
The consequence of these high switching costs is a dynamic where competition intensifies for new client acquisitions and the formation of strategic partnerships. While existing clients are relatively "sticky," companies like Health Catalyst must continually demonstrate value and innovation to win over new business. This can lead to aggressive sales tactics, tailored solution offerings, and potentially price competition for initial contracts. In 2023, the healthcare analytics market saw continued investment, with companies focusing on interoperability and data standardization to potentially lower future switching costs, though significant barriers remain.
- High integration costs for healthcare IT systems create substantial switching barriers for Health Catalyst's clients.
- Competitors face significant challenges in acquiring Health Catalyst's existing customer base due to these entrenched costs.
- The market dynamic encourages intense competition for new client acquisition and strategic alliances.
Mergers and Acquisitions Activity
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are a significant factor shaping competitive rivalry in the healthcare IT and analytics sector. This trend is evident in major deals like Oracle's acquisition of Cerner, a transaction valued at approximately $28.3 billion, which closed in June 2022. Such consolidations lead to the emergence of larger, more powerful entities possessing expanded product suites and significantly wider market penetration.
These larger competitors, armed with integrated technologies and a broader customer base, can exert greater pressure on existing players. This intensifies the competitive landscape as companies strive to match or surpass the expanded capabilities and market reach of these consolidated giants. The ongoing M&A activity, therefore, directly fuels a more aggressive competitive environment.
The impact of these M&A activities includes:
- Increased Market Concentration: Consolidation often leads to fewer, larger players dominating the market, intensifying direct competition among them.
- Enhanced Product Portfolios: Acquired companies bring new technologies and services, allowing acquirers to offer more comprehensive solutions, raising the bar for competitors.
- Greater Financial Muscle: Larger, merged entities often possess greater financial resources for research and development, marketing, and strategic investments, outmaneuvering smaller rivals.
The competitive rivalry for Health Catalyst is fierce, with over 600 companies vying for market share in the booming healthcare analytics space. This intense competition is further amplified by ongoing mergers and acquisitions, such as Oracle's $28.3 billion acquisition of Cerner, which creates larger, more formidable competitors with broader capabilities. Health Catalyst differentiates itself through its proprietary data operating system (DOS) and by demonstrating tangible improvements in clinical quality and financial performance, evidenced by its revenue growth in 2023.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| EHR Providers | Oracle Health (Cerner) | Offer integrated solutions, increasing market concentration. |
| Analytics Specialists | Innovaccer, Clarify Health | Focus on specialized analytics, driving innovation. |
| Consulting Firms | Deloitte, Accenture | Provide broader strategic services, competing on value. |
| Internal IT Departments | In-house solutions | Can offer tailored, cost-effective alternatives. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Generic business intelligence tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik present a significant threat of substitution for specialized healthcare analytics platforms. These general-purpose tools can be adapted to analyze healthcare data, offering a more budget-friendly alternative for organizations with robust in-house data expertise. For instance, Tableau reported a 17% revenue growth in 2023, showcasing its widespread adoption across various industries, including healthcare.
The threat of substitutes for dedicated EHR system analytics is significant, as major EHR vendors like Oracle Health and Epic Systems are embedding sophisticated analytics and AI directly into their core offerings. For instance, Epic Systems continues to enhance its reporting and analytics tools, making it easier for clients to derive insights without external solutions.
Healthcare organizations with substantial investments in these EHR platforms may view their native analytics as a convenient and potentially more cost-effective alternative to specialized third-party analytics providers. This integration reduces the perceived need for separate data analysis tools, thereby lowering the switching costs for adopting internal analytics.
Large healthcare systems, with significant IT budgets, increasingly develop in-house data analytics capabilities. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of major hospital networks have dedicated data science teams, capable of building custom solutions, directly competing with external vendors like Health Catalyst.
This internal development can be a powerful substitute, especially when organizations require highly tailored analytics or have stringent, unique data governance needs that off-the-shelf solutions might not fully address.
The cost-effectiveness and control offered by in-house development present a significant threat, as these systems can adapt their tools rapidly to evolving internal demands without external vendor dependencies.
Traditional Consulting Services
Traditional consulting services present a significant threat of substitution for Health Catalyst's data operating system and analytics applications. Healthcare organizations can opt for these services to gain data strategy, analysis, and improvement recommendations without committing to a new technology platform. This bypasses the need for Health Catalyst's integrated solution, offering a more flexible, albeit potentially less comprehensive, approach to data utilization.
These consulting engagements can provide targeted expertise for specific challenges, making them an attractive alternative for organizations not ready for a full platform adoption. For instance, a hospital struggling with patient readmission rates might hire a consulting firm for a focused analysis and actionable plan, rather than investing in a broad data operating system. In 2024, the healthcare consulting market continued to see strong demand, with firms offering specialized data analytics services as a key differentiator.
- Alternative Approach Healthcare organizations can leverage external consultants for data strategy and analysis, bypassing the need for a dedicated data operating system.
- Flexibility Advantage Consulting services offer tailored solutions to specific problems, providing insights without requiring a complete technology platform overhaul.
- Market Trend The healthcare consulting sector in 2024 remained robust, with many firms specializing in data-driven improvement initiatives.
Manual Data Analysis and Spreadsheets
For smaller healthcare organizations or specific departmental needs, manual data analysis using spreadsheets like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets can act as a substitute for advanced analytics platforms. This approach is appealing due to its low cost and minimal complexity, especially for those with limited budgets or technical expertise.
While less efficient and scalable, these manual methods can still provide basic insights. For instance, a small clinic might track patient wait times or billing accuracy using a spreadsheet, a practice that remains prevalent. In 2024, an estimated 80% of small businesses still rely heavily on spreadsheets for financial tracking and operational analysis, highlighting their continued role as a substitute.
- Low Cost: Spreadsheet software is often already available or inexpensive to acquire.
- Simplicity: Requires less technical training compared to sophisticated analytics software.
- Accessibility: Widely understood and utilized across various business functions.
- Limited Scalability: Becomes cumbersome and error-prone as data volume and complexity increase.
The threat of substitutes for Health Catalyst's offerings is multifaceted, encompassing generic business intelligence tools, integrated EHR analytics, in-house development, traditional consulting, and even basic spreadsheet analysis. These alternatives can fulfill similar data analysis needs, often at a lower cost or with greater flexibility, directly impacting the demand for specialized healthcare analytics platforms.
Generic BI tools like Tableau and Power BI are increasingly adapted for healthcare, offering a cost-effective alternative. For example, Tableau's 17% revenue growth in 2023 demonstrates its broad appeal. Similarly, major EHR vendors like Epic Systems are embedding advanced analytics, reducing the need for external solutions, a trend that continued to strengthen in 2024 as organizations sought integrated workflows.
Furthermore, the rise of in-house data science teams within large healthcare systems, with over 60% of major hospital networks reportedly having such teams in 2024, presents a direct substitute. These internal capabilities offer tailored solutions and greater control. Traditional consulting services also remain a viable substitute, providing focused expertise for specific challenges without requiring a full platform adoption, a market that saw continued strong demand in 2024 for data-driven initiatives.
Even basic spreadsheet analysis, particularly for smaller organizations, continues to serve as a substitute. While less scalable, the low cost and simplicity of tools like Microsoft Excel, still relied upon by an estimated 80% of small businesses for financial tracking in 2024, make them a persistent alternative for rudimentary data needs.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the healthcare data analytics market demands significant upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in developing advanced data platforms, implementing stringent cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive patient information, and recruiting a skilled workforce for sales and implementation. For example, building a comprehensive health data analytics solution can easily cost millions of dollars in research and development alone.
The healthcare sector, particularly for companies like Health Catalyst that handle sensitive patient data, faces significant regulatory and compliance hurdles. Strict laws such as HIPAA in the United States mandate robust data privacy and security measures. For instance, HIPAA violations can result in fines up to $1.5 million per violation category annually, making compliance a costly and complex undertaking for any new entrant.
Navigating these intricate legal frameworks requires substantial investment in legal counsel, compliance officers, and secure technological infrastructure. New companies must also secure various certifications and licenses, a process that can be lengthy and resource-intensive. Building trust with healthcare providers and patients regarding data security is paramount, and a single breach can severely damage a new entrant's reputation, acting as a strong deterrent.
The threat of new entrants concerning access to and integration of healthcare data for companies like Health Catalyst is significantly mitigated by the inherent complexities and existing infrastructure. New players face immense hurdles in acquiring and harmonizing data from disparate sources such as electronic health records (EHRs), which are often fragmented and highly sensitive. For instance, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) imposes stringent regulations on data handling, creating substantial compliance burdens for any new entrant.
Established companies, including Health Catalyst, have invested heavily in developing sophisticated data integration platforms and cultivating long-term relationships with healthcare providers. Health Catalyst, for example, reported in its 2023 annual report that it had integrated data from over 100 million patient records, a testament to its extensive capabilities. This deep well of integrated data and the trust built with existing clients create a formidable barrier, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to match the breadth and depth of data analytics offered by incumbents.
Need for Deep Healthcare Domain Expertise
The threat of new entrants in the healthcare analytics space is significantly dampened by the critical need for deep domain expertise. Success isn't solely about data science; it demands a thorough grasp of clinical workflows, healthcare economics, and the intricate operational challenges faced by hospitals and health systems. New players must invest heavily in acquiring or cultivating this specialized knowledge, a process that is both time-consuming and costly.
This requirement for specialized knowledge acts as a substantial barrier. For instance, understanding regulatory compliance like HIPAA, navigating complex reimbursement models, and interpreting clinical data accurately are not skills easily replicated. A 2024 report indicated that healthcare organizations often prioritize analytics partners with proven experience in specific clinical areas, such as oncology or cardiology, further highlighting the value of established domain knowledge.
- Specialized Knowledge Barrier: Technical skills alone are insufficient; deep understanding of healthcare operations, regulations, and clinical practices is paramount.
- Time and Investment: Acquiring necessary domain expertise requires significant time, resources, and often, partnerships with established healthcare entities.
- Market Preference: Healthcare clients frequently seek analytics providers with demonstrated success in specific clinical or operational domains, favoring experience over novelty.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating intricate healthcare regulations and reimbursement structures demands specialized knowledge that new entrants often lack initially.
Brand Reputation and Customer Trust
Building a strong brand reputation and fostering customer trust in the healthcare industry is a significant hurdle for new entrants. This sector is inherently risk-averse, especially concerning critical IT infrastructure and patient data management. Healthcare organizations often prioritize vendors with a demonstrable history of reliability and success, making it challenging for unproven companies to gain traction.
For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 70% of healthcare IT decision-makers consider a vendor's established reputation and client testimonials as primary factors in their purchasing decisions. This preference for proven solutions acts as a substantial barrier, as new entrants must invest considerable time and resources to establish credibility and demonstrate their capabilities effectively.
- Healthcare's Risk Aversion: Organizations are hesitant to adopt new technologies that could impact patient care or data security, favoring established, trusted vendors.
- Long-Term Trust Building: Establishing a reputation for reliability and data integrity in healthcare takes years of consistent performance and positive client relationships.
- Preference for Proven Track Records: Decision-makers in healthcare often prioritize vendors with a documented history of successful implementations and satisfied clients, creating a barrier for newcomers.
- Data Security Imperative: The sensitive nature of patient data means that trust in a vendor's security protocols is paramount, a trust that is difficult for new entrants to quickly earn.
The threat of new entrants in the healthcare analytics market is considerably low due to the substantial capital requirements for technology development and regulatory compliance. Companies like Health Catalyst have already made significant investments in robust data platforms and cybersecurity, creating a high barrier to entry. For example, building a comprehensive health data analytics solution can easily cost millions of dollars in research and development alone.
Stringent regulations, such as HIPAA, impose complex compliance burdens, demanding significant investment in legal counsel and secure infrastructure. For instance, HIPAA violations can result in fines up to $1.5 million per violation category annually, making compliance a costly undertaking for newcomers. Furthermore, established players like Health Catalyst have integrated vast amounts of patient data, with Health Catalyst reporting over 100 million patient records integrated in its 2023 annual report, making it difficult for new entrants to compete on data breadth.
The need for deep domain expertise in healthcare operations, clinical workflows, and regulatory nuances further deters new entrants. A 2024 report highlighted that healthcare organizations prioritize analytics partners with proven experience in specific clinical areas, underscoring the value of established domain knowledge. Building brand reputation and trust in this risk-averse sector also presents a significant challenge, as over 70% of healthcare IT decision-makers in a 2024 survey prioritized a vendor's established reputation and client testimonials.
| Barrier Category | Description | Example/Data Point |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment in technology, R&D, and cybersecurity. | Developing a comprehensive health data analytics solution can cost millions. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex compliance with laws like HIPAA, requiring legal and infrastructure investment. | HIPAA violations can incur fines up to $1.5 million per violation category annually. |
| Data Integration & Scale | Difficulty in acquiring and harmonizing fragmented, sensitive healthcare data. | Health Catalyst integrated over 100 million patient records by 2023. |
| Domain Expertise | Requirement for specialized knowledge of healthcare operations, regulations, and clinical practices. | Healthcare clients favor partners with proven experience in specific clinical areas (2024 report). |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Need for established credibility and proven reliability in a risk-averse sector. | Over 70% of healthcare IT decision-makers prioritize vendor reputation and testimonials (2024 survey). |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Health Catalyst Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, financial statements of key players, and publicly available regulatory filings. This comprehensive approach ensures an accurate assessment of competitive intensity and strategic positioning.