Flight Centre Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Flight Centre Bundle
Flight Centre faces significant competitive pressures, with the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers playing crucial roles in shaping its market. Understanding these dynamics is key to navigating the travel industry.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Flight Centre’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The travel industry's reliance on a concentrated group of major airlines and hotel chains grants these suppliers significant leverage. For instance, in 2024, the top three global airlines by passenger revenue controlled a substantial portion of the market, giving them considerable influence over pricing and terms offered to travel agencies like Flight Centre.
These dominant suppliers, with their robust networks and strong brand equity, can dictate terms, including commission structures, to travel retailers. This concentration means that Flight Centre, and similar businesses, have limited alternatives when sourcing core travel inventory, thereby increasing the bargaining power of these key suppliers.
Flight Centre's business model thrives on its extensive network of partnerships with airlines, hotels, and tour operators. These relationships are fundamental to curating diverse travel packages and securing competitive pricing, directly impacting customer value. For instance, in the 2023 financial year, Flight Centre Travel Group reported a significant rebound, with underlying profit before tax reaching AUD 327 million, underscoring the importance of these supplier collaborations in achieving financial success.
Flight Centre's reliance on Global Distribution System (GDS) providers and major airline partners presents a notable supplier bargaining power. While the company cultivates strong relationships, the actual process of switching these critical suppliers would likely incur substantial operational disruptions and considerable financial outlays. This inherent switching cost grants these suppliers significant leverage in price and contract negotiations, impacting Flight Centre's cost structure and operational flexibility.
Impact of Technology and Direct Channels
Airlines are increasingly pushing direct booking channels and New Distribution Capability (NDC) content, which directly impacts intermediaries like Flight Centre by potentially reducing commission payouts. This trend puts pressure on Flight Centre's traditional revenue streams.
To counter this, Flight Centre is making strategic investments in its own technology, notably through its acquisition of TPConnects. This move is designed to lessen dependence on external distribution systems and gain more control over how travel content is offered.
- Direct Booking Trend: Airlines are actively promoting their own websites and NDC content, aiming to capture a larger share of bookings directly from consumers.
- NDC Impact: New Distribution Capability allows airlines to offer richer content and potentially different pricing through direct channels, bypassing traditional Global Distribution Systems (GDS) and travel agencies.
- Flight Centre's Tech Investment: The acquisition of TPConnects, a technology company specializing in NDC integration, signifies Flight Centre's commitment to building its own technological capabilities to compete effectively.
- Mitigating Reliance: By developing in-house technology, Flight Centre aims to reduce its reliance on third-party suppliers and distribution platforms, thereby strengthening its bargaining power in the long run.
Flight Centre's Scale as Countervailing Power
Flight Centre’s immense global footprint as one of the largest travel retailers and corporate travel management companies grants it significant bargaining power. This scale allows Flight Centre to negotiate superior terms, commissions, and pricing with airlines, hotels, and other travel providers. For instance, in the fiscal year 2023, Flight Centre reported total transaction value of AU$17.4 billion, underscoring its substantial purchasing volume.
This considerable buying power acts as a crucial counterweight against supplier influence. By consolidating demand from its vast network of customers and corporate clients, Flight Centre can secure more advantageous arrangements than smaller competitors. This leverage helps to mitigate the impact of suppliers attempting to dictate terms, thereby protecting Flight Centre's profit margins.
The ability to negotiate favorable deals is directly linked to Flight Centre's market share and transaction volume. For example, its corporate travel segment alone managed AU$5.6 billion in travel spending in FY23. This financial clout enables the company to influence supplier behavior and secure benefits that are inaccessible to less dominant players in the travel industry.
- Global Scale: Flight Centre operates in over 20 countries, facilitating substantial purchasing power.
- Negotiating Leverage: The company's large transaction volumes allow for favorable commission rates and terms with suppliers.
- FY23 Performance: A total transaction value of AU$17.4 billion in FY23 highlights Flight Centre's significant buying influence.
- Corporate Travel Dominance: Managing AU$5.6 billion in corporate travel spending in FY23 further strengthens its position with suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Flight Centre is significant, primarily due to the concentrated nature of major airlines and hotel chains. In 2024, the top global airlines by passenger revenue held substantial market share, enabling them to influence pricing and terms for travel agencies like Flight Centre.
These dominant suppliers, with their established networks and brand recognition, can dictate terms, including commission structures, to travel retailers. Flight Centre's reliance on these key suppliers, with limited viable alternatives for core travel inventory, amplifies supplier leverage and impacts the company's cost structure.
Flight Centre's substantial global footprint, evidenced by a total transaction value of AU$17.4 billion in FY23, grants it considerable buying power. This scale allows for negotiation of more favorable terms and commissions with suppliers, acting as a counterweight to supplier influence.
| Supplier Type | Key Players | Estimated Market Concentration (2024) | Impact on Flight Centre |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airlines | Major global carriers (e.g., IAG, Lufthansa Group, United Airlines) | Top 3 control significant passenger revenue | Pricing, commission rates, NDC content access |
| Hotels | Large hotel groups (e.g., Marriott International, Hilton Worldwide) | Concentrated ownership of major brands | Room rates, commission structures, package deals |
| Global Distribution Systems (GDS) | Amadeus, Sabre, Travelport | Dominated by a few providers | Technology access fees, booking fees, data access |
What is included in the product
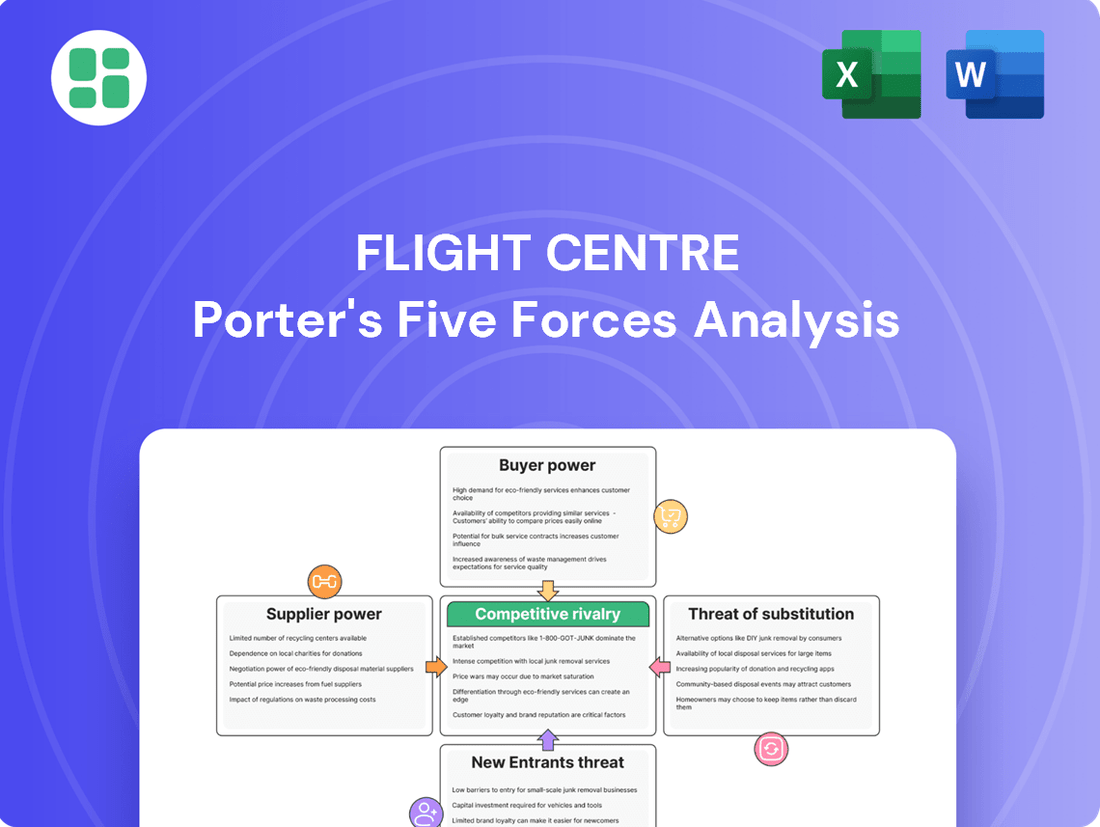
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Flight Centre, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitutes.
Visually identify and address competitive threats with an intuitive Porter's Five Forces dashboard.
Easily pinpoint areas of strategic vulnerability to proactively mitigate risks and improve competitive positioning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers, particularly those booking leisure travel, are highly attuned to price. In 2024, the average leisure traveler spent an estimated $1,500 on domestic trips, making them keen to find the best deals. This price sensitivity is amplified by the ease with which they can compare offerings across numerous online travel agencies, airline websites, and even traditional agents, creating significant downward pressure on margins for companies like Flight Centre.
The rise of online travel agencies and direct booking websites has dramatically increased customer access to information. In 2024, it's estimated that over 80% of travel bookings begin with online research, giving consumers unprecedented power to compare prices and services.
This ease of access to information directly challenges traditional travel agents like Flight Centre. Customers can now easily find and book flights, accommodations, and activities themselves, diminishing the need for intermediaries and thereby increasing their bargaining power.
For many travel services, including those offered by Flight Centre, customers often face low switching costs. This means it's generally easy and inexpensive for travelers to move from one booking platform or travel agent to another if they find a better offer or a more convenient experience elsewhere.
This ease of switching significantly boosts customer bargaining power. For instance, a survey in early 2024 indicated that over 60% of online travel bookers consider price as the primary factor when choosing a provider, highlighting their willingness to switch for cost savings.
Consequently, Flight Centre must remain competitive on pricing and service quality to retain its customer base. The ability for customers to quickly compare and select alternatives puts pressure on the company to deliver value and avoid complacency, as evidenced by the increasing market share of online travel agencies (OTAs) that often compete on price.
Corporate Client Demand and Loyalty
In the corporate travel sector, Flight Centre engages with substantial businesses that represent considerable travel expenditures. These major clients often seek tailored solutions and aggressive pricing. However, Flight Centre's specialized corporate arms, such as FCM Travel and Corporate Traveller, consistently achieve high customer retention, frequently in the high 90s. This demonstrates a strong perceived value and loyalty among these corporate accounts.
This high retention rate suggests that while corporate clients possess bargaining power due to their spending volume, Flight Centre has successfully established sticky relationships. The ability to retain clients at such elevated levels indicates that the company provides services or benefits that outweigh the potential for clients to switch to competitors based solely on price or standard offerings.
- High Retention Rates: Flight Centre's corporate divisions, like FCM Travel and Corporate Traveller, typically boast customer retention rates exceeding 90%.
- Significant Client Spend: The company serves large corporate clients with substantial annual travel budgets, giving these clients leverage.
- Demand for Customization: Corporate clients often require bespoke travel management solutions, influencing service demands.
- Competitive Pricing Pressure: The large volume of business means these clients can negotiate for more competitive pricing structures.
Trends in Travel Spending
The bargaining power of customers within the travel sector, particularly for Flight Centre, is influenced by evolving spending patterns. Recent surveys highlight a notable trend: businesses are increasingly prioritizing travel in fiscal year 2025. A significant portion of global companies intend to boost their travel activities and associated spending.
This upward trend in corporate travel investment suggests a temporary softening of price sensitivity among business clients. For Flight Centre, this translates into a stronger negotiating position within the corporate segment, as companies are more focused on the value and necessity of travel rather than solely on cost reduction.
- Increased Business Travel Investment: Global businesses are planning to expand travel activities and spending in FY2025.
- Reduced Price Sensitivity: This expansion indicates a temporary decrease in customer price sensitivity in the corporate travel market.
- Strengthened Position: The trend enhances Flight Centre's leverage with corporate clients.
While leisure travelers exhibit strong price sensitivity and low switching costs, Flight Centre's corporate clients, despite their volume, show high retention. This suggests that specialized services and tailored solutions offered by Flight Centre's corporate divisions, such as FCM Travel and Corporate Traveller, effectively mitigate the customers' bargaining power.
The increasing emphasis on business travel in FY2025, with companies planning to boost spending, further indicates a potential softening of price sensitivity among these key clients. This trend allows Flight Centre to leverage its established relationships and value proposition.
| Customer Segment | Price Sensitivity | Switching Costs | Bargaining Power Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leisure Travelers | High | Low | Significant downward pressure on pricing |
| Corporate Clients | Moderate (increasingly focused on value in FY2025) | Moderate to High (due to specialized services and retention) | Mitigated by high retention rates and tailored offerings |
Preview Before You Purchase
Flight Centre Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're previewing the final version of the Flight Centre Porter's Five Forces Analysis—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying. This comprehensive analysis delves into the competitive landscape, detailing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the travel industry. What you see here is the complete, ready-to-use file, offering actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global travel market is incredibly fragmented, meaning there are a lot of companies vying for customers. This intense competition is a major factor for Flight Centre. They're up against giants like Expedia Group and Booking Holdings, which dominate online travel bookings.
Beyond the online players, Flight Centre also competes with other established corporate travel management firms such as American Express Global Business Travel and CWT. Even smaller, independent travel agencies contribute to the crowded landscape, offering specialized services or catering to niche markets.
This broad spectrum of competitors, from massive online platforms to local specialists, means Flight Centre must constantly innovate and differentiate itself to capture and retain market share. For instance, in 2023, the global travel market was valued at over $7 trillion, highlighting the sheer scale of the opportunity but also the intensity of the competition within it.
Flight Centre's competitive rivalry is shaped by its multi-channel strategy, blending physical stores with online offerings. This approach aims to stand out against purely digital competitors by providing personalized service and expert advice, a strategy that proved crucial in navigating the travel industry's disruptions. For instance, in the fiscal year 2023, Flight Centre Travel Group reported a significant increase in total transaction value, reaching AUD 22.5 billion, demonstrating the resilience and effectiveness of their blended model in attracting customers across different touchpoints.
The travel industry's competitive landscape necessitates substantial investment in technology and innovation. Flight Centre is demonstrating this commitment through strategic platform rollouts, such as Corporate Traveler's Melon and the FCM Platform. These initiatives are designed to streamline operations and enhance client experiences.
Furthermore, Flight Centre's establishment of an AI Centre of Excellence underscores its dedication to leveraging cutting-edge technology. This move aims to elevate customer service, boost internal productivity, and maintain a competitive edge. In 2024, the company continued to prioritize digital transformation, recognizing its critical role in navigating the evolving market.
Price Wars and Margin Pressure
The travel industry, particularly for leisure, is highly susceptible to price wars. With so many options readily available online, customers can easily compare prices, forcing companies like Flight Centre to compete aggressively on cost. This constant pressure can significantly squeeze profit margins.
Flight Centre has experienced this firsthand. In the fiscal year 2023, the company reported a notable increase in the volume of transactions processed through its lower-margin brands. This shift indicates a strategy to maintain market share by offering more competitive pricing, even if it means accepting thinner profit on each sale.
- Increased Transaction Volume: Flight Centre saw a rise in sales from brands focused on price-sensitive customers.
- Margin Erosion: Aggressive pricing strategies to combat competition can lead to reduced profitability per transaction.
- Online Price Transparency: The ease of online comparison fuels intense price competition in the leisure travel sector.
Corporate Travel Market Share Growth
Flight Centre's corporate travel segment demonstrates robust growth, outperforming the broader market's recovery. This is evidenced by their increasing total transaction value and successful acquisition of new corporate accounts, signaling effective strategies against competitors.
Despite the corporate travel sector still lagging behind pre-pandemic volumes, Flight Centre's corporate division has managed to expand its footprint. For instance, in FY24, their total transaction value (TTV) for the corporate business saw significant uplift, with new wins contributing to this momentum.
- Strong Corporate TTV Growth: Flight Centre's corporate business reported substantial growth in total transaction value for the fiscal year ending June 30, 2024, indicating increased client spending and volume.
- New Account Wins: The company successfully secured several new large corporate accounts throughout 2024, directly challenging established players and expanding its market share in this segment.
- Market Share Gains: These wins and increased TTV suggest Flight Centre is gaining market share within the corporate travel sector, even as overall industry volumes remain subdued compared to 2019 levels.
- Competitive Differentiation: The ability to grow in a challenging environment points to Flight Centre's successful differentiation through service offerings, technology, or pricing strategies compared to rivals.
Flight Centre faces intense competition from online travel agencies, traditional travel management companies, and smaller niche players. This fragmented market forces constant innovation and differentiation, especially in the price-sensitive leisure segment where online transparency fuels aggressive pricing. For example, in fiscal year 2023, Flight Centre's total transaction value reached AUD 22.5 billion, showcasing its ability to compete amidst these pressures.
| Competitor Type | Key Players | Impact on Flight Centre |
|---|---|---|
| Online Travel Agencies (OTAs) | Expedia Group, Booking Holdings | Price competition, need for strong digital presence |
| Corporate Travel Management | Amex GBT, CWT | Competition for large corporate accounts, service differentiation |
| Niche/Independent Agencies | Various smaller firms | Specialized offerings, localized competition |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant substitute for travel agency services, like those offered by Flight Centre, is the ability for consumers to book directly with airlines, hotels, and other travel providers through their own websites or mobile applications. This trend is substantial, with many travelers opting to bypass intermediaries. For instance, in 2023, direct bookings continued to represent a significant portion of the travel market, with many airlines reporting robust direct channel sales, often incentivized by loyalty programs and exclusive offers.
Online travel aggregators and meta-search engines like Google Flights and Skyscanner present a significant threat of substitution for traditional travel agencies. These platforms allow consumers to directly compare prices and options from numerous airlines and hotels, effectively bypassing the need for an intermediary. For instance, in 2024, the global online travel booking market was projected to reach over $900 billion, highlighting the widespread adoption of these self-service tools.
For shorter journeys, Flight Centre's core business of air travel faces competition from alternatives like trains, buses, and private car services. These options can become more attractive, especially as airfares fluctuate.
The increasing popularity of 'slowcations' and land-based travel, partly driven by rising airfare costs, further strengthens the threat of substitutes. For instance, in Europe, rail travel has seen a significant resurgence, with many travelers opting for scenic train journeys over short-haul flights, impacting demand for traditional air booking services.
Do-It-Yourself (DIY) Travel Planning
The rise of DIY travel planning presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional travel agencies like Flight Centre. Travelers increasingly leverage a vast array of online resources, including travel blogs, social media platforms, and user-generated reviews, to research destinations, compare prices, and book flights, accommodations, and activities independently. This accessibility empowers individuals to craft their entire travel experiences without needing professional advice or booking assistance.
This shift directly challenges the core services offered by Flight Centre. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of travelers now prefer to book their trips online, bypassing traditional agents. This trend is fueled by the perceived cost savings and greater control afforded by DIY planning.
The threat is amplified by:
- Abundance of Information: Platforms like TripAdvisor, Google Flights, and countless travel blogs offer detailed itineraries, insider tips, and price comparison tools, readily available to anyone with internet access.
- Direct Booking Channels: Airlines, hotels, and tour operators increasingly offer direct booking options, often with loyalty programs and personalized deals that can be more attractive than those offered through intermediaries.
- Cost Sensitivity: Many travelers, especially younger demographics, are highly price-conscious and view DIY planning as a way to secure the best deals by cutting out agent commissions.
Shift in Travel Preferences and Behaviors
The travel industry is seeing a significant shift in consumer preferences, with a growing demand for sustainable and unique travel experiences. This trend can lead travelers to bypass traditional travel agencies like Flight Centre in favor of specialized niche providers or to plan their own trips, thereby increasing the threat of substitutes.
For example, the rise of platforms offering eco-friendly accommodations and adventure travel experiences directly caters to these evolving desires. In 2024, the global sustainable tourism market was projected to reach $170 billion, indicating a substantial segment of travelers actively seeking alternatives to conventional offerings.
- Evolving Consumer Preferences: A noticeable increase in demand for sustainable travel options and unique, less conventional experiences.
- Niche Provider Growth: The emergence and popularity of specialized travel companies focusing on specific interests like eco-tourism or adventure.
- DIY Travel Planning: Travelers increasingly opting to self-plan and book their trips, bypassing traditional intermediaries.
- Market Data: The sustainable tourism market's significant growth, projected to reach $170 billion in 2024, underscores the shift away from generic travel packages.
The threat of substitutes for Flight Centre is significant, primarily stemming from the ease with which consumers can book travel directly online. This includes booking flights, accommodations, and even complex itineraries through airline websites, hotel portals, and online travel agencies (OTAs). The increasing reliance on digital platforms means travelers can bypass traditional agents entirely, often finding competitive pricing and personalized offers. For instance, in 2024, direct bookings remained a dominant channel, with many airlines actively promoting their own platforms to capture a larger share of the market.
| Substitute Channel | Key Characteristics | Impact on Travel Agencies |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Airline/Hotel Bookings | Loyalty programs, exclusive deals, user-friendly interfaces | Reduces reliance on intermediaries for core travel components |
| Online Travel Aggregators (OTAs) | Price comparison, vast inventory, user reviews | Offers convenient one-stop shopping, potentially at lower prices |
| DIY Travel Planning Platforms | Blogs, social media, review sites for research and booking | Empowers travelers to self-manage and customize trips, bypassing agents |
Entrants Threaten
The digital landscape of the travel sector presents a significant threat of new entrants due to its low barriers to online entry. Establishing an online travel agency or booking platform requires considerably less capital investment than building a traditional brick-and-mortar retail presence, making it easier for new, online-only competitors to emerge and challenge established players like Flight Centre.
New entrants can carve out profitable spaces by focusing on underserved niche markets or specific customer groups. Think about areas like eco-tourism or specialized corporate travel, where tailored services and innovative technology can attract customers away from broader offerings. For instance, Flight Centre's Envoyage initiative aims to cater to a wider array of travel preferences by supporting independent agents, demonstrating a strategic move to capture these specialized segments.
While online travel agencies can launch with relatively low overhead, establishing the kind of brand recognition and trust that Flight Centre has cultivated is a formidable hurdle. Flight Centre's extensive network of physical stores and well-recognized corporate brands like Corporate Traveller and Student Flights represent years of investment and customer engagement, creating a significant barrier for new entrants aiming for comparable market penetration and loyalty.
Access to Supplier Networks and Technology
New entrants can struggle to gain access to crucial supplier networks, particularly with major airlines and hotel groups that often favor long-standing relationships. This can mean less favorable terms and limited inventory for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, established travel agencies often benefit from bulk purchasing agreements and preferred partnerships that are hard for new players to replicate.
However, the landscape is shifting. The increasing availability of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and white-label solutions from technology providers is democratizing access. These tools allow new entrants to integrate with global distribution systems and booking platforms more easily, effectively lowering the barrier to entry by providing ready-made infrastructure.
This technological advancement means that while traditional supplier relationships remain a hurdle, the cost and complexity of building the necessary technological backbone are significantly reduced. This could lead to a more dynamic market where innovation in service delivery, rather than just supplier access, becomes a key differentiator for new entrants.
- Supplier Network Access: Major airlines and hotel chains may restrict access or offer less favorable terms to new entrants compared to established players like Flight Centre.
- Technological Barriers: While historically high, the cost and complexity of accessing booking systems are decreasing due to APIs and white-label solutions.
- Competitive Landscape: In 2024, the travel industry continues to see a mix of legacy players and digitally native disruptors, with technology playing a key role in market entry.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
The travel industry is heavily regulated, with new entrants facing significant challenges in meeting diverse compliance standards. These can include stringent financial protection requirements, such as bonding and insolvency insurance, which are crucial for consumer confidence and are particularly burdensome for startups. For instance, in the UK, the Package Travel and Linked Travel Arrangements Regulations 2018 mandate specific financial safeguards for tour operators.
Navigating these complexities, especially when operating across multiple international markets, acts as a substantial barrier to entry. Each jurisdiction often has unique licensing, consumer protection, and data privacy laws, like GDPR in Europe. The cost and expertise required to ensure full compliance can deter potential competitors from entering the market, thereby protecting established players like Flight Centre.
- Regulatory Complexity: The travel sector is subject to a patchwork of international and national laws governing consumer rights, financial security, and operational standards.
- Licensing and Permits: Obtaining necessary licenses and permits to operate legally, especially for international travel, can be a time-consuming and expensive process for new businesses.
- Financial Protection: Requirements for financial bonding or insurance to protect customer payments, a key compliance area, represent a significant upfront cost.
- Data Privacy Compliance: Adhering to data protection regulations, such as GDPR, adds another layer of complexity and investment for new entrants handling customer information.
The threat of new entrants in the travel sector remains moderate, influenced by both declining and persistent barriers. While digital platforms lower initial investment, building trust and securing supplier networks are still significant challenges.
In 2024, the ease of launching online travel agencies (OTAs) continues to be a factor, with many new players focusing on niche markets. However, the capital required for robust marketing and customer acquisition, alongside the need for established supplier relationships, prevents a complete erosion of barriers.
Flight Centre's established brand and extensive supplier agreements provide a buffer, but the increasing use of APIs and white-label solutions by new entrants is democratizing access to booking systems, thereby lowering technological entry costs.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Platforms | Low initial capital for online presence | Moderate | Many new OTAs launched annually with minimal physical infrastructure. |
| Brand Recognition & Trust | Years of customer engagement and reputation building | High | Flight Centre's established corporate brands like Corporate Traveller provide a significant advantage. |
| Supplier Networks | Access to favorable terms and inventory from airlines/hotels | High | Established players often secure bulk discounts, difficult for newcomers to match in 2024. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating diverse licensing, financial protection, and data privacy laws | Moderate to High | UK's Package Travel Regulations 2018 require significant financial safeguards for tour operators. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Flight Centre leverages data from annual reports, industry-specific market research, and airline financial disclosures. We also incorporate insights from travel industry publications and government aviation statistics to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.