Edgewise Therapeutics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Edgewise Therapeutics Bundle
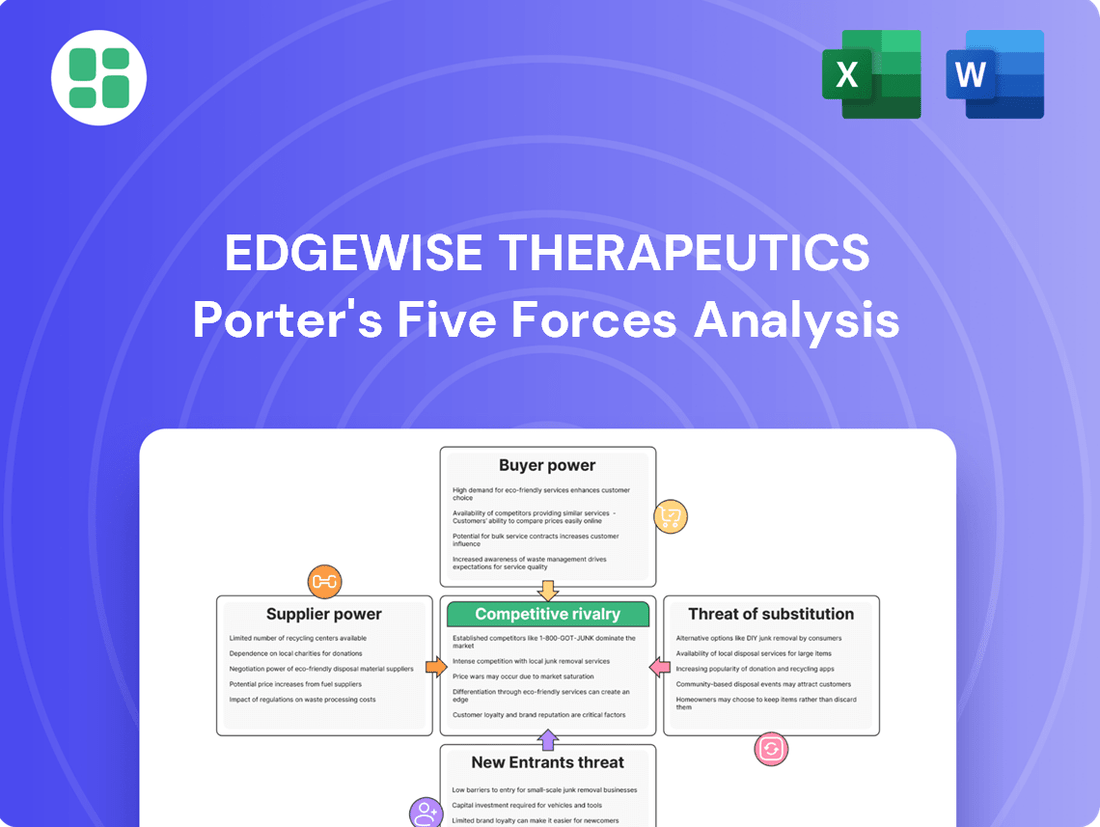
Edgewise Therapeutics faces a dynamic competitive landscape, with the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers significantly influencing its market position. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The full Porter's Five Forces analysis delves deeper, revealing the intensity of each force impacting Edgewise Therapeutics and providing actionable insights for competitive advantage. Unlock the complete strategic breakdown to inform your decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Edgewise Therapeutics, a company in the clinical-stage biopharmaceutical sector, is significantly dependent on specialized Contract Research Organizations (CROs) and Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs). These partners are crucial for executing clinical trials and manufacturing the company's drug candidates.
The market for biopharmaceutical CMOs is substantial and expanding, with projections indicating it will reach USD 19.00 billion by 2025. This growth signifies robust demand for the specialized services these suppliers offer, directly impacting their leverage.
The specialized nature of CRO and CMO services, coupled with the high demand within the biopharmaceutical industry, grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power. Edgewise Therapeutics, like its peers, must navigate this dynamic to secure essential research and manufacturing capabilities.
Suppliers in the biopharmaceutical sector face significant regulatory hurdles, including adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). This compliance requirement narrows the pool of qualified vendors, thereby strengthening the bargaining power of those already meeting these stringent standards. For Edgewise Therapeutics, ensuring its suppliers meet these exacting requirements is critical, especially as its drug candidate sevasemten progresses through late-stage clinical trials for Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies.
Many biopharmaceutical suppliers hold significant bargaining power due to their proprietary technologies and unique expertise. This specialized knowledge, crucial for advanced therapy development and manufacturing, makes it challenging for companies like Edgewise Therapeutics to switch vendors, thereby strengthening the suppliers' position. For instance, the increasing demand for specialized cell and gene therapy manufacturing has led to a surge in demand for highly specialized contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) with unique capabilities.
Limited Raw Material Sources
Edgewise Therapeutics' reliance on specialized raw materials for its novel small molecule therapies, such as sevasemten, could be impacted by a limited supplier base. This scarcity can empower these suppliers, giving them considerable sway over pricing and ensuring consistent availability for Edgewise. For instance, the global API market, while growing, often features concentrated production for niche compounds, a dynamic that could affect companies like Edgewise in 2024 and beyond.
The bargaining power of suppliers is amplified when the availability of critical components is restricted.
- Limited Suppliers: The production of complex pharmaceutical compounds often requires highly specific raw materials or active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) sourced from a small number of specialized manufacturers.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Disruptions in the supply chain, whether due to geopolitical events, regulatory changes, or production issues at a key supplier, can significantly increase the leverage of remaining providers.
- Pricing Power: When demand for these specialized inputs is high and supply is constrained, suppliers can dictate higher prices, directly impacting the cost of goods sold for pharmaceutical companies like Edgewise.
- Impact on Innovation: The dependence on a few suppliers for essential materials can also slow down the development and scaling of new therapies if those suppliers face capacity constraints or prioritize other clients.
Switching Costs
Switching suppliers in the biopharmaceutical industry, particularly for Edgewise Therapeutics, presents significant hurdles. These include the extensive time and resources needed for re-validating manufacturing processes, which can take months or even years and incur substantial costs. For instance, a change in a critical raw material supplier might necessitate repeating preclinical and early-stage clinical studies to ensure product consistency and safety, potentially delaying market entry. In 2024, the average cost for such re-validation processes in the biopharma sector was estimated to be in the millions of dollars.
These high switching costs directly translate into increased bargaining power for Edgewise's existing suppliers. Suppliers are aware that the financial and operational penalties for Edgewise to switch are substantial, allowing them to potentially negotiate more favorable terms, such as higher prices or less flexible payment schedules. This dynamic can impact Edgewise's cost of goods sold and overall profitability, as they may be less able to leverage competitive pricing from alternative vendors.
- Significant Re-validation Costs: Biopharma supplier changes can cost millions due to process re-validation.
- Clinical Trial Delays: New vendors may require additional studies, pushing back trial timelines.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Obtaining approval for new suppliers adds complexity and time.
- Supplier Leverage: High switching costs empower current suppliers to dictate terms.
Edgewise Therapeutics faces considerable supplier bargaining power due to the specialized nature of CROs and CMOs, essential for its drug development. The biopharmaceutical CMO market, projected to reach USD 19.00 billion by 2025, indicates strong demand for these services, enhancing supplier leverage.
Regulatory compliance, such as GMP, further limits the supplier pool, strengthening the position of qualified vendors. Proprietary technologies and unique expertise held by suppliers also make switching difficult and costly for companies like Edgewise, particularly concerning advanced therapies.
The limited availability of specific raw materials and APIs, often produced by a small number of manufacturers, can lead to pricing power for these suppliers. In 2024, the high cost of re-validating processes, potentially millions of dollars, and the risk of clinical trial delays due to vendor changes, solidify the bargaining power of existing suppliers for Edgewise Therapeutics.
| Factor | Impact on Edgewise | Supplier Leverage | 2024 Context |
| Specialized Services | High dependence on CROs/CMOs | Strong | Growing biopharma outsourcing market |
| Regulatory Compliance | Need for qualified vendors | High for compliant suppliers | GMP adherence is critical |
| Proprietary Technology | Difficulty in switching | Significant | Cell/gene therapy demand |
| Limited Raw Materials | Potential supply constraints | High for niche compounds | API market concentration |
| Switching Costs | Millions in re-validation, delays | Very High | Average re-validation cost in millions |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Edgewise Therapeutics' biotech landscape, focusing on its novel therapies.
Effortlessly analyze the competitive landscape of pain management therapies, highlighting Edgewise's unique positioning against rivals.
Gain immediate insight into potential barriers to entry and the bargaining power of suppliers in the lucrative pain relief market.
Customers Bargaining Power
The high cost of rare disease therapies, such as those for Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy, places significant bargaining power in the hands of customers, primarily payers like insurance companies and government health programs. These therapies can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars annually per patient, reflecting substantial R&D investments and limited patient pools. For instance, gene therapies for rare genetic disorders have seen list prices exceeding $2 million per treatment in recent years.
This immense cost naturally invites intense scrutiny from payers. They are increasingly implementing stricter utilization controls and actively pursuing value-based contracts, where payment is tied to the therapy's actual effectiveness and patient outcomes. This shift forces drug manufacturers to demonstrate clear, quantifiable value, thereby empowering customers to negotiate more favorable terms.
Payers are becoming more critical of the cost-effectiveness and added clinical value of expensive treatments for rare diseases, even when they address significant unmet medical needs. This heightened scrutiny on healthcare budgets means Edgewise Therapeutics will likely encounter substantial negotiations and potential obstacles in obtaining favorable reimbursement for its pipeline drugs, such as sevasemten. For instance, in 2024, payers are increasingly demanding robust real-world evidence demonstrating clear patient outcomes and cost savings to justify high drug prices.
Patient advocacy groups, particularly for conditions like Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy, wield significant influence. Their organized efforts are instrumental in shaping drug development pathways and advocating for patient access to treatments. For instance, groups like the Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) actively fund research and engage with regulatory bodies, directly impacting the landscape for companies like Edgewise Therapeutics.
These powerful patient organizations can indirectly affect pricing by highlighting unmet needs and the value of innovative therapies. Their collective voice can sway market perception, influencing demand and potentially setting benchmarks for what patients and payers consider acceptable costs for life-changing treatments. This advocacy underscores a key aspect of customer bargaining power within the rare disease sector.
Availability of Existing and Emerging Therapies
The bargaining power of customers for Edgewise Therapeutics is influenced by the availability of existing and emerging therapies, particularly in the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) market. While Edgewise addresses severe unmet needs, the competitive landscape is evolving. For instance, in 2024, the DMD treatment market includes approved exon-skipping therapies like eteplirsen and golodirsen, along with corticosteroids and early-stage gene therapies. The presence of these diverse treatment modalities, even with varying efficacy and mechanisms, grants patients and their prescribers a degree of choice, which can elevate their negotiating leverage.
This availability of alternatives means that customers can compare different treatment profiles, potential side effects, and cost-effectiveness. For example, while gene therapies offer a novel approach, their long-term data and accessibility are still being established, creating a dynamic where other established or emerging options can be considered. This dynamic directly impacts Edgewise's ability to dictate terms, as customers can weigh the benefits of Edgewise's specific therapy against the existing and pipeline alternatives.
- DMD Market Dynamics: The Duchenne muscular dystrophy treatment landscape in 2024 features multiple approved therapies, including exon-skipping drugs, corticosteroids, and nascent gene therapies, providing patients with a range of options.
- Customer Choice: The existence of various treatment modalities, despite differences in their mechanisms of action, empowers patients and prescribers by offering them choices.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: Increased customer choice translates to a stronger bargaining position for patients and healthcare providers when evaluating and selecting therapies.
- Emerging Pipeline: A robust pipeline of emerging drugs in development further intensifies competition and can potentially increase customer bargaining power as more treatment options become available.
Prescriber and Physician Influence
Physicians and specialists are key influencers in treatment choices for rare diseases like Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD). Their decisions are heavily swayed by robust clinical data, proven long-term effectiveness, safety records, and how easy a treatment is to administer. This collective medical expertise acts as a significant customer force, driving demand for therapies that are both scientifically sound and practical for patient use.
While patients hold the ultimate decision-making power, the prescribing authority of physicians significantly shapes the market landscape for treatments like those from Edgewise Therapeutics. In 2024, the emphasis on real-world evidence and patient-reported outcomes continues to grow, further empowering physicians to advocate for therapies that demonstrate clear benefits and manageable side effects.
- Physician Influence: Specialists in rare diseases are critical gatekeepers for new therapies.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Clinical trial results, efficacy, safety, and administration ease are paramount.
- Patient Advocacy: Physicians often translate patient needs and preferences into treatment demands.
- Market Shaping: Prescribing patterns directly impact a drug's market penetration and success.
The bargaining power of customers for Edgewise Therapeutics is considerable due to the high cost of rare disease treatments, such as those for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Payers, including insurance companies and government programs, scrutinize these high-priced therapies, often exceeding $2 million per treatment for gene therapies. In 2024, payers are increasingly demanding strong real-world evidence of effectiveness and cost savings, pushing manufacturers towards value-based agreements.
Patient advocacy groups, like the Muscular Dystrophy Association, also exert influence by funding research and advocating for patient access, indirectly impacting pricing perceptions. Furthermore, the growing availability of alternative and emerging therapies in the DMD market in 2024, including exon-skipping drugs and early gene therapies, provides patients and physicians with choices, strengthening their negotiating leverage.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Edgewise |
|---|---|---|
| High Therapy Costs | Annual costs for rare disease treatments can reach hundreds of thousands of dollars per patient. | Increases payer scrutiny and demand for cost-effectiveness. |
| Value-Based Contracts | Payment tied to demonstrated patient outcomes and efficacy. | Requires Edgewise to prove clear clinical and economic value for sevasemten. |
| Patient Advocacy Groups | Organized groups influence research and access, impacting market perception. | Can shape demand and acceptable pricing benchmarks. |
| Competitive Landscape (2024) | Presence of approved exon-skipping therapies, corticosteroids, and emerging gene therapies in DMD. | Offers patients and prescribers choice, enhancing their bargaining power. |
Full Version Awaits
Edgewise Therapeutics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Edgewise Therapeutics, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, providing actionable insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes. Rest assured, there are no placeholders or missing sections; you're viewing the complete, ready-to-use document that will be instantly available upon completion of your transaction.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) treatment landscape is intensely competitive, featuring established giants like Sarepta Therapeutics, whose Elevidys (delandistrogene moxeparvovec) has seen significant uptake, and PTC Therapeutics with its exon-skipping therapy Translarna. Edgewise Therapeutics' sevasemten, an orally administered small molecule, faces direct competition not only from these established exon-skipping and gene therapy approaches but also from a growing pipeline of other small molecule candidates aiming for the DMD market.
Competitive rivalry in the rare disease therapeutics space, particularly for conditions like Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), is exceptionally fierce due to significant Research and Development (R&D) investments. Companies are pouring substantial resources into discovering and developing novel treatments, creating a dynamic and competitive landscape.
The depth of R&D pipelines further intensifies this rivalry. Competitors are exploring diverse therapeutic modalities, including gene therapy, exon-skipping biologics, and small molecules, each targeting different aspects of disease progression. This multi-pronged approach means multiple companies are vying for the same patient populations and therapeutic niches.
Leading players such as Pfizer, Dyne Therapeutics, Capricor Therapeutics, and Avidity Biosciences have advanced investigational therapies in their pipelines. For instance, Dyne Therapeutics has candidates like DYNE-251 for DMD, while Avidity Biosciences is developing AOC 444 for DMD. These companies are in direct competition, not only with each other but also with Edgewise Therapeutics, for market share and patient access.
Competitive rivalry in the Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) and Becker Muscular Dystrophy (BMD) space is intense, driven by the varied therapeutic strategies being pursued. These range from gene therapies aiming to reintroduce functional dystrophin to approaches that focus on mitigating inflammation or repairing damaged muscle tissue.
Edgewise Therapeutics' lead candidate, sevasemten, stands out with its unique mechanism of action. As a first-in-class fast skeletal myosin inhibitor, it is designed to protect muscle fibers from damage that occurs during contraction. This differentiated approach sets it apart from many competitors who are focused on other pathways.
For instance, Sarepta Therapeutics' Elevidys, an exon-skipping therapy, targets a different aspect of DMD by aiming to restore dystrophin production. Similarly, other companies are exploring gene replacement or gene editing techniques. Edgewise's focus on protecting against mechanical stress offers a distinct therapeutic angle in this evolving landscape.
Clinical Trial Success and Regulatory Approvals
Success in clinical trials and subsequent regulatory approvals are paramount competitive differentiators within the biopharmaceutical industry. Competitors like Sarepta Therapeutics, with its recent FDA approval for Elevidys, and Italfarmaco, securing approval for Duvyzat, highlight the intense pressure for Edgewise Therapeutics to showcase robust clinical outcomes for its own pipeline programs.
Edgewise has reported encouraging Phase 2 results for sevasemten in patients with Becker muscular dystrophy and is actively collaborating with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on its development path. The company's ability to navigate the regulatory landscape and achieve timely approvals will be a key determinant of its market position.
- Clinical trial success is a primary driver of competitive advantage in biopharmaceuticals.
- Recent competitor approvals, such as Sarepta's Elevidys, set a high bar for efficacy and safety.
- Edgewise's sevasemten has shown positive Phase 2 results for Becker muscular dystrophy, indicating potential.
- Active engagement with the FDA is crucial for Edgewise to achieve its regulatory milestones.
Market Growth and Unmet Needs
Despite existing competition, the market for Duchenne muscular dystrophy treatments is poised for substantial expansion. Projections indicate a growth from approximately USD 4.07 billion in 2025 to USD 9.78 billion by 2030. This upward trend is fueled by an increasing disease burden and significant unmet medical needs within the patient population.
This expanding market landscape presents a dual dynamic: it offers considerable opportunities for innovation and revenue generation, but it also acts as a magnet for new entrants. Consequently, the competitive rivalry intensifies as numerous companies strive to secure a meaningful share of this rapidly growing therapeutic area.
- Projected market growth: USD 4.07 billion (2025) to USD 9.78 billion (2030).
- Key drivers: Rising disease prevalence and persistent unmet patient needs.
- Impact on rivalry: Increased competition as more players target the expanding market.
The competitive landscape for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) treatments is characterized by intense rivalry, with multiple companies pursuing diverse therapeutic strategies. Edgewise Therapeutics' sevasemten, a fast skeletal myosin inhibitor, faces competition from established exon-skipping therapies like Sarepta's Elevidys and PTC's Translarna, as well as a growing pipeline of gene therapies and other small molecules.
The market is attractive due to its projected growth from approximately USD 4.07 billion in 2025 to USD 9.78 billion by 2030, fueling further competition. Companies like Pfizer, Dyne Therapeutics, and Avidity Biosciences are actively developing advanced DMD therapies, intensifying the race for market share and patient access.
Clinical trial success and regulatory approvals are critical differentiators, with recent approvals like Italfarmaco's Duvyzat setting a high benchmark. Edgewise's positive Phase 2 results for sevasemten in Becker muscular dystrophy and its engagement with the FDA are key to its competitive positioning.
| Competitor | Therapeutic Approach | Key Product/Pipeline | Status/Notes |
| Sarepta Therapeutics | Gene Therapy/Exon Skipping | Elevidys (delandistrogene moxeparvovec) | FDA Approved |
| PTC Therapeutics | Exon Skipping | Translarna | Approved in some regions |
| Edgewise Therapeutics | Small Molecule (Myosin Inhibitor) | Sevasemten | Phase 2 data positive for BMD |
| Dyne Therapeutics | Oligonucleotide Therapy | DYNE-251 | Clinical Trials |
| Avidity Biosciences | Antibody Oligonucleotide Conjugates | AOC 444 | Clinical Trials |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Edgewise Therapeutics' potential therapies is significant, given the existing approved pharmacological treatments for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD). These include corticosteroids like deflazacort and vamorolone, which have been standard care for years, and exon-skipping therapies such as eteplirsen, golodirsen, viltolarsen, and casimersen.
Furthermore, the landscape is evolving rapidly with new approvals. For instance, Elevidys, a gene therapy, has been approved, offering a different modality. Italfarmaco's Duvyzat, an HDAC inhibitor, also gained FDA approval in March 2024 for DMD. These diverse treatment options represent direct substitutes that patients and their physicians can readily consider, impacting the market penetration and pricing power of any new entrant.
The threat of substitutes for Edgewise Therapeutics' muscle-targeting therapies is amplified by emerging gene and cell therapies. Beyond currently approved treatments, a strong pipeline of gene therapies, such as Pfizer's fordadistrogene movaparvovec and Regenxbio's RGX-202, are progressing through late-stage clinical trials for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD).
Similarly, cell-based therapies like Capricor Therapeutics' CAP-1002 are also nearing potential approval. These advanced treatment modalities aim to correct the underlying genetic defects or cellular dysfunctions, offering the promise of more definitive and potentially curative long-term solutions for DMD patients.
The potential for these therapies to address the root cause of the disease presents a significant competitive threat, as they could offer superior or complementary benefits compared to Edgewise's current approach, potentially impacting market share and pricing power.
Supportive care, including physical therapy and respiratory management, plays a crucial role in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) and Becker Muscular Dystrophy (BMD) treatment. While these interventions don't replace pharmacological treatments, they significantly improve patient quality of life and can manage symptoms. For instance, in 2024, the global physical therapy market was valued at approximately $65 billion, highlighting the significant investment in non-drug-based care.
These non-pharmacological approaches act as a form of partial substitution by addressing functional limitations and preventing secondary complications, thereby reducing reliance on certain drug classes for symptom management. The effectiveness of physical therapy in maintaining muscle function and mobility is well-documented, offering an alternative pathway to symptom relief for patients.
Alternative Small Molecule Approaches
The threat of substitutes for Edgewise Therapeutics' sevasemten in treating Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) and Becker Muscular Dystrophy (BMD) is present, primarily from other small molecule approaches. While sevasemten targets a specific pathway, ongoing research explores different mechanisms. For instance, tadalafil and metformin have been investigated in pilot studies for BMD, though their efficacy has been less pronounced compared to sevasemten's observed results. The dynamic nature of pharmaceutical research means new small molecule candidates could emerge, potentially offering alternative treatment avenues.
Here's a look at some key considerations regarding these substitutes:
- Emerging Small Molecules: Research continues into other small molecules with distinct mechanisms of action that could address DMD/BMD.
- Tadalafil and Metformin Exploration: Pilot studies have explored tadalafil and metformin for Becker muscular dystrophy, though initial findings have been less compelling than those for sevasemten.
- Continuous Innovation: The ongoing pace of scientific discovery in rare diseases means the landscape of potential substitutes is constantly evolving, with new compounds regularly entering development pipelines.
Patient and Physician Preferences
Patient and physician preferences significantly shape the threat of substitutes for Edgewise Therapeutics' treatments. Factors like the ease of administration, safety, and how well a drug is perceived to work play a crucial role in treatment choices. For instance, Edgewise's sevasemten, a small molecule taken orally, might appeal to patients and doctors who prefer non-intravenous methods. However, the emergence of gene therapies that offer a single, potentially curative treatment could present a strong substitute, influencing decisions away from more traditional, albeit convenient, oral medications.
The perceived advantages of different therapeutic modalities directly impact substitution. While an oral small molecule like sevasemten offers convenience, the long-term benefits and potentially curative nature of gene therapies can be a powerful draw. This creates a dynamic where patients and physicians weigh current ease of use against the promise of more definitive, albeit potentially more complex or novel, treatment approaches.
In 2024, the landscape of therapeutic options is rapidly evolving. Companies are investing heavily in gene therapy research and development, with numerous candidates progressing through clinical trials. This growing pipeline means that the threat of substitution from more advanced or novel modalities will likely increase for existing and emerging small molecule treatments.
- Route of Administration: Oral administration (sevasemten) vs. intravenous or other delivery methods.
- Safety Profile: Perceived long-term safety of small molecules versus newer modalities like gene therapy.
- Perceived Efficacy: Patient and physician belief in the effectiveness and durability of treatment outcomes.
- Novelty and Innovation: The appeal of one-time treatments (gene therapy) versus ongoing oral medication.
The threat of substitutes for Edgewise Therapeutics' treatments remains a significant factor. Established pharmacological options like corticosteroids and existing exon-skipping therapies continue to be utilized, while newer gene therapies, such as Elevidys and those in late-stage development from companies like Pfizer and Regenxbio, offer potentially more definitive solutions. The emergence of treatments like Duvyzat, approved in March 2024, further diversifies the competitive landscape, presenting patients and physicians with a growing array of choices that could impact Edgewise's market position and pricing power.
Emerging gene and cell therapies represent a potent substitute threat. These advanced modalities aim to address the root genetic causes of DMD, potentially offering long-term or curative benefits. As these therapies progress through clinical trials, they could offer a compelling alternative to Edgewise's current approach, influencing patient and physician preferences towards more novel, potentially one-time treatments.
Non-pharmacological interventions, such as physical therapy, also act as partial substitutes by managing symptoms and improving quality of life. With the global physical therapy market valued around $65 billion in 2024, these supportive care measures can reduce reliance on certain drug classes for symptom management, indirectly impacting the perceived need for specific pharmacological treatments.
The evolving therapeutic landscape, driven by continuous innovation, means that Edgewise Therapeutics must contend with a dynamic market. The appeal of different treatment modalities, balancing factors like convenience of administration, safety profiles, and perceived efficacy, will shape patient and physician decisions. The growing pipeline of gene therapies, in particular, poses a substantial threat, potentially shifting preferences away from ongoing oral medications towards more advanced, potentially curative options.
Entrants Threaten
Developing novel biopharmaceutical therapies, particularly for rare diseases, demands substantial capital. This includes extensive preclinical research, multi-phase clinical trials, and navigating complex regulatory pathways. For instance, Edgewise Therapeutics, a company focused on developing therapies for rare genetic diseases, reported R&D expenses that underscore the significant financial hurdle for any new player entering this specialized market.
The lengthy and intricate regulatory approval process presents a formidable barrier to entry for new companies looking to compete in the pharmaceutical space, particularly for treatments targeting rare diseases. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) impose stringent requirements for demonstrating both safety and efficacy, often necessitating extensive and costly clinical trials. In 2024, the average time for a new drug to navigate the FDA approval process remained substantial, with many novel therapies requiring years of development and rigorous testing, making it a significant deterrent for potential entrants.
The threat of new entrants into the rare disease biopharmaceutical space, like that occupied by Edgewise Therapeutics, is significantly constrained by the immense need for specialized expertise. Companies must possess deep knowledge in areas such as muscle physiology for conditions like Duchenne muscular dystrophy, alongside the intricate skills required for rare disease clinical trial design and execution. For instance, navigating the complexities of patient recruitment for ultra-rare conditions demands a unique scientific and medical acumen.
Beyond scientific prowess, establishing the necessary infrastructure presents a formidable barrier. This includes specialized manufacturing capabilities for complex biologics and the development of robust distribution networks capable of handling sensitive therapeutics. The capital investment required for these facilities alone can be prohibitive for many potential new players, effectively limiting the pool of credible entrants.
Strong Intellectual Property Protection
Strong intellectual property (IP) protection acts as a significant deterrent to new entrants in the biopharmaceutical sector. Companies like Edgewise Therapeutics invest substantial resources in securing patents for their novel drug candidates and proprietary technologies. For instance, as of early 2024, Edgewise Therapeutics' pipeline, particularly its EDG-5506 program for Duchenne muscular dystrophy, is protected by a robust patent portfolio, extending exclusivity for years to come.
These patents, coupled with regulatory exclusivities granted by bodies such as the FDA, create formidable barriers. New companies would need to invest heavily in discovering and developing entirely new compounds, a process that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive, or face the complexities and costs of licensing existing IP.
- Patented Drug Candidates: Edgewise's portfolio, including EDG-5506, is shielded by patents that prevent competitors from marketing similar therapies.
- Regulatory Exclusivities: Beyond patents, regulatory bodies grant periods of market exclusivity, further delaying potential new entrants.
- High R&D Investment: The cost and time required to develop new, non-infringing drug candidates are substantial barriers.
Limited Patient Populations and Market Access Challenges
The threat of new entrants into the rare disease therapeutic space, like that for Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy, is tempered by significant hurdles. While these markets are expanding, the patient populations remain relatively small, making patient identification and recruitment for clinical trials a complex undertaking. For instance, Duchenne muscular dystrophy affects an estimated 1 in 3,500 to 6,000 live male births globally, and Becker muscular dystrophy is even rarer.
Furthermore, new companies must navigate the intricate process of securing market access and reimbursement. This is particularly challenging in the current environment where payers are increasingly scrutinizing the high costs associated with treatments for rare diseases. Edgewise Therapeutics, focusing on these areas, must contend with this barrier to entry, which can deter potential competitors by requiring substantial upfront investment and a proven ability to demonstrate significant clinical and economic value.
- Limited Patient Pools: Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy affect a small number of individuals, complicating clinical trial enrollment.
- Market Access Hurdles: Gaining payer approval and reimbursement for high-cost rare disease drugs presents a significant challenge for new entrants.
- Economic Scrutiny: The increasing focus on the cost-effectiveness of treatments for rare conditions acts as a deterrent to new competition.
The threat of new entrants in the rare disease biopharmaceutical sector, where Edgewise Therapeutics operates, is significantly limited by the substantial capital requirements for research and development. Developing novel therapies involves extensive preclinical work, costly multi-phase clinical trials, and navigating stringent regulatory approvals, creating a high financial barrier. For example, the average cost to bring a new drug to market can exceed $2 billion, a figure that deters many potential new players.
Furthermore, the complex regulatory landscape, including requirements from bodies like the FDA and EMA, demands years of rigorous testing and significant investment. In 2024, the lengthy approval timelines for new drugs, often spanning a decade or more, act as a substantial deterrent. This lengthy process, coupled with the need for specialized expertise in areas like rare disease patient recruitment, further constrains new competition.
Strong intellectual property protection, including patents and regulatory exclusivities, shields established companies like Edgewise Therapeutics. For instance, Edgewise's EDG-5506 program benefits from a robust patent portfolio, granting market exclusivity. New entrants would need to invest heavily in developing entirely novel compounds or navigate costly licensing agreements, making entry challenging.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High costs for R&D, clinical trials, and regulatory compliance. | Deters new companies due to substantial upfront investment needs. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Lengthy and complex approval processes by agencies like FDA/EMA. | Extends development timelines and increases costs, acting as a deterrent. |
| Intellectual Property | Patents and regulatory exclusivities protect existing therapies. | Requires new entrants to develop novel, non-infringing products or license IP. |
| Specialized Expertise | Deep knowledge in rare disease biology and clinical trial design. | New entrants must acquire or build specialized scientific and medical acumen. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Edgewise Therapeutics is built upon a foundation of publicly available company filings, including SEC submissions and investor presentations, alongside comprehensive industry reports and market research data to capture the competitive landscape.