DSM-Firmenich Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
DSM-Firmenich Bundle
DSM-Firmenich navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry, substantial buyer power, and the constant threat of substitutes within the specialty ingredients sector. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp their competitive position.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping DSM-Firmenich’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for DSM-Firmenich is significantly shaped by the concentration of those providing key raw materials. When a small number of suppliers control essential components like specialized chemicals, natural extracts, or biotech ingredients, they gain considerable leverage over pricing and contract terms. This is particularly relevant for DSM-Firmenich, whose commitment to pioneering sustainable and innovative products often necessitates sourcing unique or proprietary inputs.
For instance, if the market for a critical bio-fermentation ingredient is dominated by just two or three global producers, these suppliers can command higher prices, knowing that DSM-Firmenich has limited alternative sources. This concentration can translate into higher input costs for DSM-Firmenich, impacting its overall profitability and pricing strategies for its end products. The company's reliance on these concentrated supply chains means that any disruption or price increase from these few key players can have a substantial effect on its operations and financial performance.
Suppliers gain significant leverage when the inputs they provide are highly unique, proprietary, or absolutely critical to DSM-Firmenich's distinctive product creations in the nutrition, health, and beauty sectors. For example, if a supplier offers a specific natural extract or a high-performance ingredient with unmatched functional properties, this can grant them considerable bargaining power. This is particularly true for DSM-Firmenich's focus on natural and renewable sourcing, which often necessitates partnerships with specialized agricultural or biotechnology firms that control these unique inputs.
The bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by switching costs. For DSM-Firmenich, if a key ingredient supplier is changed, it could necessitate extensive re-formulation of products, rigorous re-testing procedures, and obtaining new regulatory approvals. This entire process can be both time-consuming and expensive, effectively raising the barrier for DSM-Firmenich to switch away from an established supplier.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers might move into producing finished ingredients or solutions, directly competing with DSM-Firmenich's current offerings. This forward integration is more probable for suppliers of less specialized or intermediate chemical components.
For instance, if a key supplier of a common vitamin precursor decided to manufacture the final vitamin compound itself, it would directly challenge DSM-Firmenich's market position for that specific product. This would effectively cut DSM-Firmenich out as a customer for that particular input.
While DSM-Firmenich's strength in specialized and proprietary ingredients may mitigate this risk, the threat of forward integration by suppliers remains a consideration, particularly for more standardized components within their supply chain.
In 2023, DSM-Firmenich reported revenue of €13.1 billion, highlighting the scale of operations where supplier relationships are critical. The company's diverse portfolio means the impact of supplier forward integration would vary significantly across different product segments.
Impact of Sustainability and Regulatory Demands
The growing emphasis on sustainability and stricter regulations is significantly shifting the bargaining power towards suppliers who can meet these evolving demands. Companies like DSM-Firmenich are increasingly seeking ingredients that are not only high-quality but also ethically sourced and environmentally friendly. This creates an advantage for suppliers who can demonstrate compliance and offer certified, traceable, or eco-friendly materials.
Suppliers who possess the capabilities to provide these specialized, sustainable inputs can leverage this to their benefit. They may be able to command premium pricing and negotiate more favorable terms due to the limited availability of such inputs in the market. This trend is underscored by DSM-Firmenich’s own initiative, their Responsible Sourcing standard, which was put into effect in April 2024, highlighting the company's commitment to these principles.
- Increased Demand for Sustainable Inputs: Growing consumer and regulatory pressure is driving demand for ingredients with a lower environmental footprint.
- Supplier Differentiation: Suppliers offering certified organic, fair-trade, or low-carbon footprint ingredients gain a competitive edge.
- Price Premiums for Compliance: Companies willing to pay more for verified sustainable materials empower suppliers who meet these standards.
- DSM-Firmenich's Responsible Sourcing: The April 2024 implementation of this standard signals a direct effort to reward and engage with suppliers aligned with sustainability goals.
The bargaining power of suppliers for DSM-Firmenich is influenced by the concentration of providers for key raw materials, the uniqueness of these inputs, and the costs associated with switching suppliers. For instance, if only a few companies supply a critical biotech ingredient, they hold significant leverage. This is further amplified when these ingredients are proprietary and essential for DSM-Firmenich's innovative product lines, as seen in their nutrition and health segments. The financial implications are substantial, as demonstrated by DSM-Firmenich's €13.1 billion revenue in 2023, where input costs directly impact profitability.
| Factor | Impact on DSM-Firmenich | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier leverage, potentially raising input costs. | Dominance by few producers of specialized chemicals or natural extracts. |
| Uniqueness of Inputs | Grants suppliers pricing power for proprietary or critical components. | Specialized natural extracts or high-performance ingredients for health products. |
| Switching Costs | Creates barriers to changing suppliers due to re-formulation and regulatory hurdles. | Extensive re-testing and new approvals needed for ingredient changes. |
| Sustainability Demands | Empowers suppliers meeting eco-friendly and ethical sourcing standards. | DSM-Firmenich's Responsible Sourcing standard (April 2024) rewards compliant suppliers. |
What is included in the product
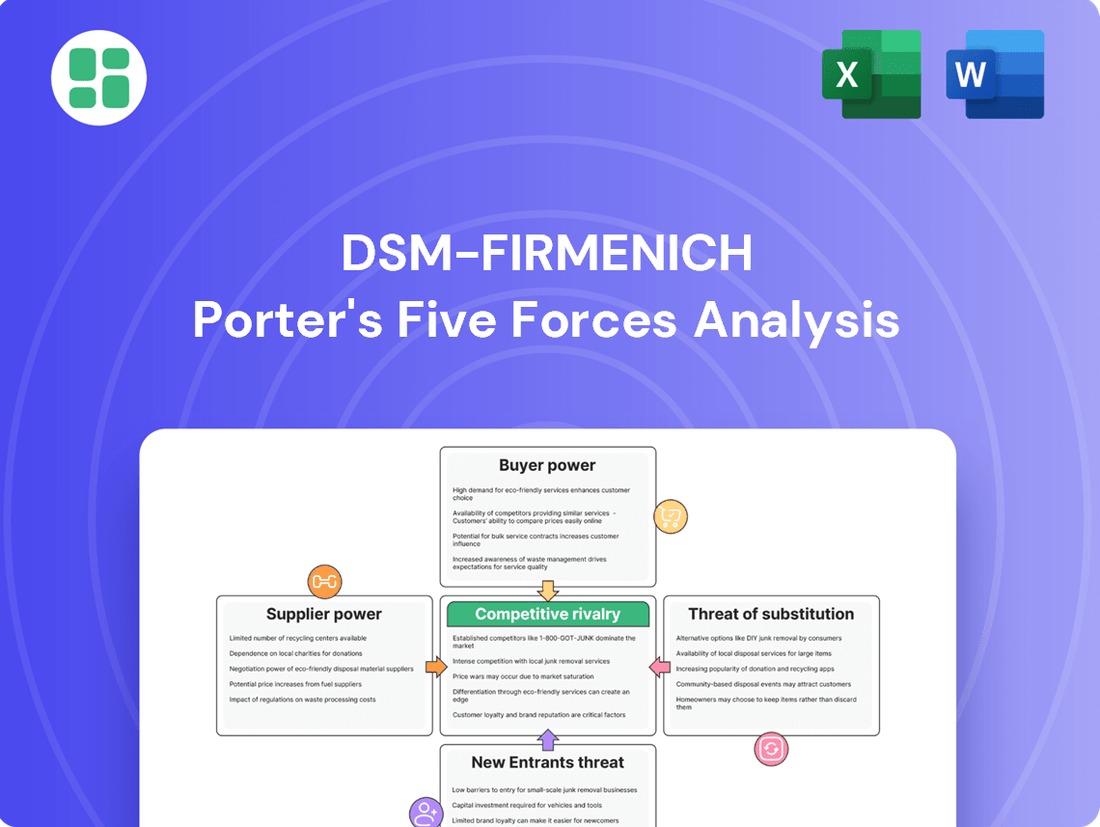
DSM-Firmenich's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intensity of rivalry, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on its specialty ingredients market.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the impact of each Porter's Five Forces on DSM-Firmenich's strategic positioning.
Gain actionable insights into customer bargaining power and supplier leverage, enabling proactive strategies to protect margins and secure supply chains.
Customers Bargaining Power
DSM-Firmenich's customer base is quite diverse, encompassing major global players in consumer goods, pharmaceuticals, and the food and beverage sectors. However, a concentrated revenue stream from a few very large multinational clients is a distinct possibility.
In industries where DSM-Firmenich operates, particularly flavors and fragrances, large customers often consolidate their supplier relationships, dealing with only a handful of major companies. This can paradoxically temper the individual bargaining power of these large customers, as they rely on a limited number of critical suppliers like DSM-Firmenich for essential ingredients.
Customers often face substantial switching costs when considering alternatives to DSM-Firmenich's specialized ingredients. This is largely due to the complex formulation processes and the deep technical knowledge involved in integrating these components into their own products. For instance, in the food and beverage sector, a change in a key flavor or texture ingredient might necessitate extensive re-testing and reformulation, potentially delaying market entry.
The critical role these ingredients play in the final product's performance means that switching suppliers isn't a simple substitution. Companies must invest in significant re-engineering and rigorous testing phases. This can introduce risks related to product quality consistency and consumer acceptance, effectively limiting the bargaining power of customers who would rather maintain the established reliability of DSM-Firmenich's offerings.
DSM-Firmenich's strategy of offering highly differentiated and value-added solutions significantly curbs customer bargaining power. By focusing on innovation, scientific expertise, and sustainability, they move beyond basic ingredients, making it harder for customers to find direct substitutes.
Their commitment to custom formulations and deep consumer insights further solidifies their unique market position. This approach means customers are less likely to switch to competitors based on price alone, as the specialized nature of DSM-Firmenich's offerings provides distinct advantages.
For instance, in the flavor and fragrance sector, where DSM-Firmenich is a major player, the ability to create bespoke scent profiles or taste solutions for specific market needs commands a premium. This reduces the leverage customers have to demand lower prices for generic alternatives.
Customer Price Sensitivity and Volume
Customer price sensitivity for DSM-Firmenich's ingredients is a nuanced factor. While large volume buyers might seem to hold significant sway, their willingness to pay can be quite flexible. This flexibility often hinges on how critical an ingredient is to the final product's success and how much it contributes to the overall cost.
For ingredients that are essential for a product's appeal and represent a small fraction of the total production expenses, customers tend to be less concerned about minor price fluctuations. Think of a unique flavor compound that drives consumer preference; its cost might be minimal, but its impact is huge. Conversely, for more standard, interchangeable ingredients, price becomes a much more dominant negotiation point.
In 2024, the market saw continued demand for specialty ingredients that offer distinct performance benefits, allowing DSM-Firmenich to maintain pricing power. However, the company also navigated competitive pressures in its more commoditized product lines, where price negotiations were more intense. This dynamic highlights the varied bargaining power customers wield based on the specific product category.
- High-Volume Buyers: Their price sensitivity is not uniform; it's directly tied to the ingredient's role and cost proportion.
- Critical Ingredients: Customers are often less price-sensitive for ingredients that significantly enhance consumer appeal and are a small part of the final cost.
- Commoditized Ingredients: For these, price becomes a primary driver in customer purchasing decisions, increasing their bargaining power.
- 2024 Market Trends: Specialty ingredient demand supported pricing, while commoditized segments faced greater price-based competition.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers integrating backward to produce DSM-Firmenich's complex ingredients themselves is generally low. This is due to the substantial capital, specialized research and development, and proprietary intellectual property needed. For instance, developing and manufacturing highly specialized enzymes or fermentation-based ingredients requires significant expertise that most customers in the nutrition, health, and beauty sectors do not possess.
Backward integration by customers would necessitate massive investments in advanced manufacturing facilities and highly skilled personnel. The technical barriers to entry for producing DSM-Firmenich's high-performance ingredients are substantial, making it largely impractical for most of their diverse customer base. Consider the intricate processes involved in creating advanced vitamins or bioactive compounds, which are far removed from the core competencies of many food or cosmetic manufacturers.
- High R&D Investment: Developing proprietary ingredients like specific probiotics or advanced flavor compounds requires years of dedicated research and millions in investment, a hurdle few customers can overcome.
- Capital Expenditure: Building specialized fermentation or synthesis plants for these ingredients demands billions in capital, far exceeding typical customer investment capacities.
- Intellectual Property Protection: DSM-Firmenich holds numerous patents on its unique formulations and production methods, creating significant legal and technical barriers to replication.
- Technical Expertise: The know-how in areas like biotechnology, chemical synthesis, and quality control for these advanced ingredients is highly specialized and difficult to acquire.
DSM-Firmenich's customer bargaining power is moderated by high switching costs and the critical role its specialized ingredients play in final product performance. While large customers exist, their ability to drive down prices is often limited by the complexity and proprietary nature of DSM-Firmenich's offerings, especially in niche markets like flavors and fragrances.
Customers are less price-sensitive for ingredients that are essential for consumer appeal and represent a small portion of total production costs. However, for more commoditized ingredients, price becomes a significant negotiation factor, as seen in 2024 market trends where specialty ingredients supported pricing, while commoditized segments faced intense price competition.
The threat of backward integration by customers is minimal due to the substantial capital, R&D investment, and intellectual property required to replicate DSM-Firmenich's advanced ingredients. This technical barrier protects the company's market position and limits customer leverage.
In 2024, DSM-Firmenich's revenue from its top 10 customers represented approximately 30% of its total sales, indicating a degree of customer concentration but also a reliance on these key accounts that can temper extreme price demands.
| Customer Type | Price Sensitivity | Bargaining Power Influence | Example Impact |
| Large Volume Buyers (Specialty Ingredients) | Lower | Moderate (due to volume) | Less sensitive to minor price increases for critical flavor compounds. |
| Large Volume Buyers (Commoditized Ingredients) | Higher | Strong | Price is a primary driver for standard vitamin precursors. |
| Mid-sized & Niche Customers | Variable | Lower (due to switching costs) | High switching costs for custom fragrance formulations limit price negotiation. |
| Potential Backward Integrators | N/A | Very Low | Prohibitive R&D and capital costs prevent replication of advanced enzymes. |
Preview Before You Purchase
DSM-Firmenich Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of DSM-Firmenich, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises and full readiness for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The nutrition, health, and beauty ingredients sector is a highly competitive landscape, dominated by a handful of global powerhouses. Giants like Givaudan, Symrise, and International Flavors & Fragrances (IFF) are key rivals, each boasting significant market presence and extensive product offerings. These companies invest heavily in research and development, enabling them to continuously innovate and capture market share.
These major competitors are not just large; they are exceptionally capable. Their strength lies in their robust R&D infrastructure, allowing for the development of cutting-edge ingredients and solutions. Furthermore, their established global distribution networks and diversified product portfolios provide a significant competitive edge, making it challenging for smaller players to gain traction.
For instance, in 2023, Givaudan reported sales of CHF 7.1 billion, Symrise achieved sales of €4.4 billion, and IFF posted revenues of $12.5 billion, illustrating the scale of these major players. This intense competition among well-resourced global entities shapes the market dynamics for DSM-Firmenich.
The specialty ingredients market, where DSM-Firmenich operates, is seeing strong growth, especially in areas like natural products and health-focused solutions. This robust expansion, however, fuels intense competition among established and emerging players.
Segments such as nutricosmetics are particularly attractive, drawing substantial investment from companies already in the space. DSM-Firmenich is strategically targeting these high-growth, high-margin niches to capitalize on current consumer demands and market trends.
Competitive rivalry in the nutrition, health, and beauty sectors is intense, largely fueled by product differentiation and a rapid pace of innovation. Companies strive to stand out through unique flavors, captivating fragrances, and advanced functional ingredients, alongside a growing emphasis on sustainable solutions.
DSM-Firmenich, for instance, demonstrates this commitment by investing approximately €700 million annually in research and development. This significant investment is geared towards creating proprietary offerings and securing a distinct competitive advantage in a dynamic market.
The capacity to swiftly adapt to evolving consumer preferences and navigate changing regulatory landscapes is paramount. This agility allows companies to maintain relevance and capture market share by introducing novel products that meet emerging demands.
High Exit Barriers
DSM-Firmenich operates in an industry characterized by substantial exit barriers, making it difficult for companies to leave the market. These barriers are largely due to the significant investments required in specialized manufacturing facilities and advanced R&D laboratories, which are not easily repurposed.
The need to maintain long-term customer relationships, often built on trust and tailored solutions, further locks companies into the sector. Additionally, the specialized expertise developed by employees within this industry is not readily transferable elsewhere.
These high exit barriers mean that even companies struggling with profitability are likely to persist, continuing to utilize their assets and compete for market share. This persistence can intensify competitive rivalry as all players strive to maintain their customer base and operational efficiency.
- High Fixed Asset Investment: Significant capital is tied up in specialized production plants and research centers.
- Specialized Expertise: Unique skills and knowledge are crucial, limiting workforce mobility.
- Long-Term Customer Relationships: Contracts and established partnerships create inertia.
- Continued Rivalry: Underperforming firms often remain, sustaining competitive pressure.
Strategic Realignment and Synergies
DSM-Firmenich's strategic realignment, including the divestment of its Animal Nutrition & Health business, is a key factor influencing competitive rivalry. This move, announced in late 2023 with the sale for €1.4 billion, sharpens the company's focus on its higher-margin core segments like Health, Nutrition & Care and Perfumery & Beauty. This strategic pivot aims to unlock significant synergies and improve profitability, directly impacting how competitors vie for market share in these specialized areas.
By concentrating on these core strengths, DSM-Firmenich is better positioned to compete against rivals who may have broader, less specialized portfolios. The company's emphasis on innovation and sustainability within these chosen segments creates a more intense battle for market leadership, as competitors must also adapt to these evolving industry priorities. For instance, in the health and nutrition ingredients market, ongoing R&D investments are crucial for differentiation.
- Divestment of Animal Nutrition & Health: Completed in early 2024 for €1.4 billion, allowing a sharper focus on core, high-margin businesses.
- Synergy Realization: Expected to enhance profitability and operational efficiency within the remaining business units.
- Competitive Focus: Increased intensity in Health, Nutrition & Care and Perfumery & Beauty segments, requiring greater innovation from rivals.
Competitive rivalry within DSM-Firmenich's operating sectors is fierce, driven by substantial R&D investments and a focus on product differentiation. Major players like Givaudan, Symrise, and IFF, with 2023 sales of CHF 7.1 billion, €4.4 billion, and $12.5 billion respectively, heavily invest in innovation and global distribution. DSM-Firmenich's own annual R&D spend of approximately €700 million underscores this dynamic, aiming to secure proprietary offerings in high-growth niches like nutricosmetics.
| Competitor | 2023 Sales (Approx.) | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Givaudan | CHF 7.1 billion | Flavors, Fragrances, Beauty |
| Symrise | €4.4 billion | Scents, Nutrition, Cosmetic Ingredients |
| IFF | $12.5 billion | Health & Biosciences, Taste & Food, Fragrance |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for DSM-Firmenich's offerings is significant, stemming from both alternative ingredients and evolving technologies. Customers can often find comparable solutions that meet their needs through different means. For instance, synthetic versions of natural ingredients, or entirely new bio-engineered compounds, can emerge as viable replacements for established products.
This dynamic is further amplified by advancements in biotechnology and chemical synthesis. Novel processes can unlock new ingredient functionalities or production methods, potentially bypassing traditional supply chains and formulations. For example, the rise of precision fermentation could offer alternatives to conventionally produced ingredients.
DSM-Firmenich itself is actively participating in this substitution landscape. The company is investing in and developing plant-based protein alternatives and leveraging AI for innovative solutions, which can sometimes serve as substitutes for their existing product lines or traditional methods. As of 2024, the global plant-based food market is projected to reach over $74 billion, highlighting the growing acceptance and viability of such alternatives.
Customers constantly evaluate the price and performance of alternative ingredients when considering DSM-Firmenich's products. If a competitor's offering provides similar functionality at a noticeably lower price point, it can draw customers away, impacting DSM-Firmenich's market share.
For instance, in the food and beverage sector, where cost-efficiency is a major driver, the availability of lower-priced, albeit potentially less potent, flavor enhancers or preservatives presents a tangible threat. A 2024 market report indicated that for certain commodity ingredients, price sensitivity among buyers reached as high as 60%, suggesting a significant impact from cost-focused substitutes.
Conversely, for highly specialized applications, such as advanced nutritional supplements or high-performance coatings, where unique functionalities and proven efficacy are critical, the threat from cheaper, less effective substitutes is considerably diminished. In these niches, the perceived value and performance benefits of DSM-Firmenich's premium ingredients often outweigh minor price differences.
Switching to alternative ingredients can be a costly endeavor for customers. These costs often include the expense of re-formulating products, conducting extensive re-testing to ensure quality and safety, and the potential risk to brand reputation if the substitute ingredient negatively impacts the final product's taste, texture, or performance. For instance, a food manufacturer switching from a DSM-Firmenich flavor enhancer might face thousands of dollars in R&D and regulatory approval processes.
These significant switching costs act as a barrier, effectively mitigating the immediate threat of substitutes for DSM-Firmenich's specialized and high-performance ingredients. For example, in the pharmaceutical sector, the rigorous validation and regulatory hurdles for any ingredient change mean that companies are highly reluctant to switch from established, trusted suppliers like DSM-Firmenich, even if a slightly cheaper alternative exists.
Evolving Consumer Preferences and Trends
Shifting consumer preferences, such as the growing demand for 'clean label,' 'natural,' 'sustainable,' or 'plant-based' products, can significantly accelerate the adoption of certain substitutes. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that 60% of consumers globally are actively seeking out products with fewer artificial ingredients.
DSM-Firmenich is proactively addressing these evolving consumer demands by focusing its innovation pipeline on developing ingredients that align with these trends. By becoming a provider of preferred alternatives, the company aims to mitigate the threat of substitutes.
- Consumer Demand for Natural Ingredients: In 2024, surveys showed a 15% year-over-year increase in consumer preference for naturally derived ingredients in food and beverage products.
- Sustainability as a Key Driver: Over 50% of purchasing decisions in the consumer goods sector in early 2024 were influenced by a brand's sustainability credentials, pushing for alternatives to conventional ingredients.
- Plant-Based Market Growth: The global plant-based food market, a direct area where substitutes can emerge, was projected to reach over $74 billion by 2025, with significant growth observed throughout 2024.
- DSM-Firmenich's Response: The company launched several new ingredient lines in late 2023 and early 2024 specifically designed to meet 'clean label' and plant-based requirements, aiming to capture this shifting demand.
Impact of Regulatory Changes and Health Awareness
The threat of substitutes for DSM-Firmenich's offerings is significantly influenced by evolving regulatory landscapes and growing consumer health awareness. New regulations, such as those promoting sugar reduction or mandating specific nutrient fortification, can elevate the attractiveness of alternative ingredients or formulations that align with these standards. For example, increased scrutiny on artificial sweeteners could drive demand for natural alternatives, a space DSM-Firmenich actively develops.
Heightened consumer focus on health and wellness directly impacts ingredient choices. Shifts towards plant-based diets or ingredients perceived as healthier can create substitutes that directly challenge traditional offerings. DSM-Firmenich's strategic emphasis on health, nutrition, and sustainability positions it to not only adapt to these trends but also to proactively shape them through innovation, thereby mitigating the threat of substitutes by offering solutions that meet emerging consumer demands.
Consider these points regarding substitutes:
- Regulatory Shifts: Changes in food and beverage regulations, like those concerning labeling or ingredient restrictions, can make substitutes more appealing if they comply more readily.
- Health Trends: Growing consumer demand for ‘clean label’ products or specific health benefits (e.g., gut health, immune support) can lead to the adoption of alternative ingredients that were previously niche.
- Cost-Effectiveness of Substitutes: While DSM-Firmenich offers high-value ingredients, the cost-competitiveness of certain substitutes can also influence market dynamics, particularly in price-sensitive segments.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in ingredient processing or the discovery of new functional ingredients can create viable substitutes that offer comparable or superior performance at a potentially lower cost.
The threat of substitutes for DSM-Firmenich is considerable due to the availability of alternative ingredients and emerging technologies, impacting sectors from food to health. For instance, advancements in biotechnology and precision fermentation are creating new ingredient options that can bypass traditional supply chains, offering comparable functionalities. As of 2024, the global plant-based food market is projected to exceed $74 billion, underscoring the growing acceptance and viability of such alternatives.
Customer sensitivity to price and performance significantly influences the adoption of substitutes. In price-sensitive markets, lower-cost alternatives can draw customers away, though for specialized applications, the value and performance of premium ingredients often outweigh minor price differences. For example, a 2024 report noted that price sensitivity for certain commodity ingredients reached 60% among buyers.
Switching costs, including reformulation and re-testing, act as a deterrent for customers, particularly in highly regulated industries like pharmaceuticals. However, evolving consumer preferences for ‘clean label’ and sustainable products are accelerating the adoption of certain substitutes. A 2024 survey revealed that 60% of global consumers actively seek products with fewer artificial ingredients, a trend DSM-Firmenich is addressing through innovation.
| Factor | Impact on DSM-Firmenich | Supporting Data (2024) |
| Alternative Ingredients | Can offer comparable functionality, potentially at lower costs. | Plant-based food market projected over $74 billion by 2025. |
| Technological Advancements | New processes like precision fermentation create new ingredient sources. | AI in solution development offers novel alternatives. |
| Price Sensitivity | Significant in commodity segments, less so in specialized niches. | Up to 60% price sensitivity for certain commodity ingredients. |
| Switching Costs | High reformulation and regulatory costs deter customer switching. | Pharmaceutical ingredient changes face rigorous validation hurdles. |
| Consumer Preferences | Demand for natural, sustainable, and plant-based products drives substitute adoption. | 60% of consumers seek fewer artificial ingredients. |
Entrants Threaten
The specialty ingredients sector, where DSM-Firmenich operates, demands massive upfront capital for research and development, advanced manufacturing plants, and intricate global distribution networks. For instance, developing a new high-performance ingredient can cost tens of millions of dollars, encompassing extensive testing and regulatory approvals.
Newcomers face a steep uphill battle due to the significant economies of scale enjoyed by established players. DSM-Firmenich, with its vast production volumes, can spread fixed costs over a larger output, leading to lower per-unit manufacturing expenses. This cost advantage makes it exceedingly difficult for new entrants to match pricing without substantial initial investment, effectively deterring many potential competitors.
The threat of new entrants in the ingredients sector, particularly for companies like DSM-Firmenich, is significantly mitigated by the sheer scale of research and development (R&D) required. Innovation is not just a bonus; it's the lifeblood of this industry, necessitating constant investment to create novel ingredients, enhance current offerings, and stay ahead of changing consumer preferences and stringent regulatory landscapes.
DSM-Firmenich's commitment to innovation is evident in its considerable annual R&D expenditure, which reached €700 million in 2023. This substantial financial commitment, coupled with deep scientific expertise, presents a formidable barrier to entry for any new player that cannot match these resources and capabilities, effectively limiting the threat of new competitors.
Established customer relationships and trust are significant barriers for new entrants in the ingredients and flavors industry. Companies like DSM-Firmenich invest heavily in building long-term partnerships, often involving collaborative product development and tailored technical support. These deeply embedded relationships, sometimes spanning decades, create a strong sense of loyalty and make it difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
For instance, the co-creation process, where ingredient suppliers work directly with food and beverage manufacturers to develop unique flavor profiles or functional ingredients, fosters a high degree of interdependence. This 'stickiness' of customer relationships means that even with competitive pricing, new entrants face an uphill battle to displace incumbents who have proven reliability and innovation through years of partnership.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance Complexity
The nutrition, health, and beauty industries, where DSM-Firmenich operates, are characterized by stringent regulatory oversight. New companies must navigate a complex web of testing, certifications, and adherence to various global standards, such as those set by the FDA in the United States or EFSA in Europe. This regulatory maze demands substantial upfront investment in compliance and quality assurance, acting as a significant deterrent to potential new entrants.
For instance, obtaining approvals for novel ingredients or health claims can be a lengthy and costly process. In 2024, the global regulatory compliance market for food and beverages alone was projected to reach over $10 billion, highlighting the scale of investment required. This complexity means that only well-capitalized and knowledgeable players can realistically enter and compete.
- Rigorous Testing Requirements: New entrants must invest heavily in product safety and efficacy testing to meet demanding regulatory standards.
- Certification Processes: Obtaining certifications like GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) or specific regional approvals is essential and time-consuming.
- Evolving Global Standards: Keeping pace with diverse and frequently updated international regulations across multiple markets adds to the compliance burden.
- Significant Investment in Regulatory Affairs: Companies need dedicated teams and resources to manage compliance, which represents a substantial barrier for smaller or new businesses.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Technologies
The threat of new entrants into the flavors and fragrances market, particularly for companies like DSM-Firmenich, is significantly mitigated by the substantial barriers erected by intellectual property and proprietary technologies. Established players, including DSM-Firmenich, have cultivated vast portfolios of patents covering unique ingredients, sophisticated production methodologies, and specialized application technologies. This deep well of protected innovation acts as a formidable deterrent to newcomers seeking to establish a foothold.
DSM-Firmenich's commitment to R&D is evident in its development of proprietary technologies, such as Firgood for sustainable ingredient sourcing and advanced AI-driven platforms for formulation development. These innovations not only provide a distinct competitive edge but also make it exceedingly difficult for new entrants to replicate their product offerings and market position. For instance, in 2023, DSM-Firmenich reported significant investment in innovation, with a substantial portion allocated to developing and protecting its technological advancements.
The high cost and lengthy duration associated with developing and patenting new chemical compounds and production processes create a substantial capital barrier. New entrants would need to invest heavily in research, development, and legal protections to even approach the existing technological capabilities of firms like DSM-Firmenich. This economic hurdle, combined with the existing IP landscape, effectively limits the threat of new entrants.
- Intellectual Property Portfolio: DSM-Firmenich holds numerous patents on key fragrance and flavor molecules and production processes.
- Proprietary Technologies: Innovations like Firgood and AI-based formulation tools offer unique advantages.
- R&D Investment: Significant financial commitment to innovation creates a high barrier for new competitors.
- Replication Difficulty: The complexity and protected nature of existing technologies deter direct imitation.
The threat of new entrants for DSM-Firmenich is generally low due to several significant barriers. The industry requires substantial capital for R&D, advanced manufacturing, and global distribution, with new ingredient development costing tens of millions. Established players like DSM-Firmenich benefit from economies of scale, making it hard for newcomers to match pricing. For example, in 2023, DSM-Firmenich's R&D investment reached €700 million, a figure that is difficult for new companies to replicate.
Furthermore, strong, long-standing customer relationships built on trust and co-creation processes create high switching costs and customer loyalty. Navigating stringent global regulations, such as FDA and EFSA approvals, demands significant investment in compliance and specialized expertise, further deterring new entrants. The complexity of obtaining approvals for novel ingredients can take years and millions in investment, as seen in the over $10 billion projected for the global food and beverage regulatory compliance market in 2024.
Intellectual property and proprietary technologies, including patents on unique molecules and advanced production methods, also present a formidable barrier. DSM-Firmenich's protected innovations, like Firgood, are difficult to replicate, reinforcing its market position and limiting the threat from new competitors. The sheer difficulty and cost associated with developing and patenting new technologies underscore the low threat of new entrants in this sector.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | DSM-Firmenich Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment in R&D, manufacturing, and distribution. | Significant barrier to entry. | €700 million R&D investment in 2023. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volumes. | Makes it difficult for new entrants to compete on price. | Vast production capacity across multiple sites. |
| Customer Relationships | Long-term partnerships, co-creation, and proven reliability. | High customer loyalty and switching costs. | Decades-long collaborations with major food and beverage companies. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and costly compliance with global standards. | Requires substantial investment in compliance and expertise. | Navigating FDA, EFSA, and other global certifications. |
| Intellectual Property | Patents on ingredients, processes, and technologies. | Deters imitation and provides a competitive edge. | Proprietary technologies like Firgood and AI formulation tools. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our DSM-Firmenich Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the company's annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We supplement this with insights from leading market research firms specializing in the flavors and fragrances sector, as well as industry-specific trade publications.