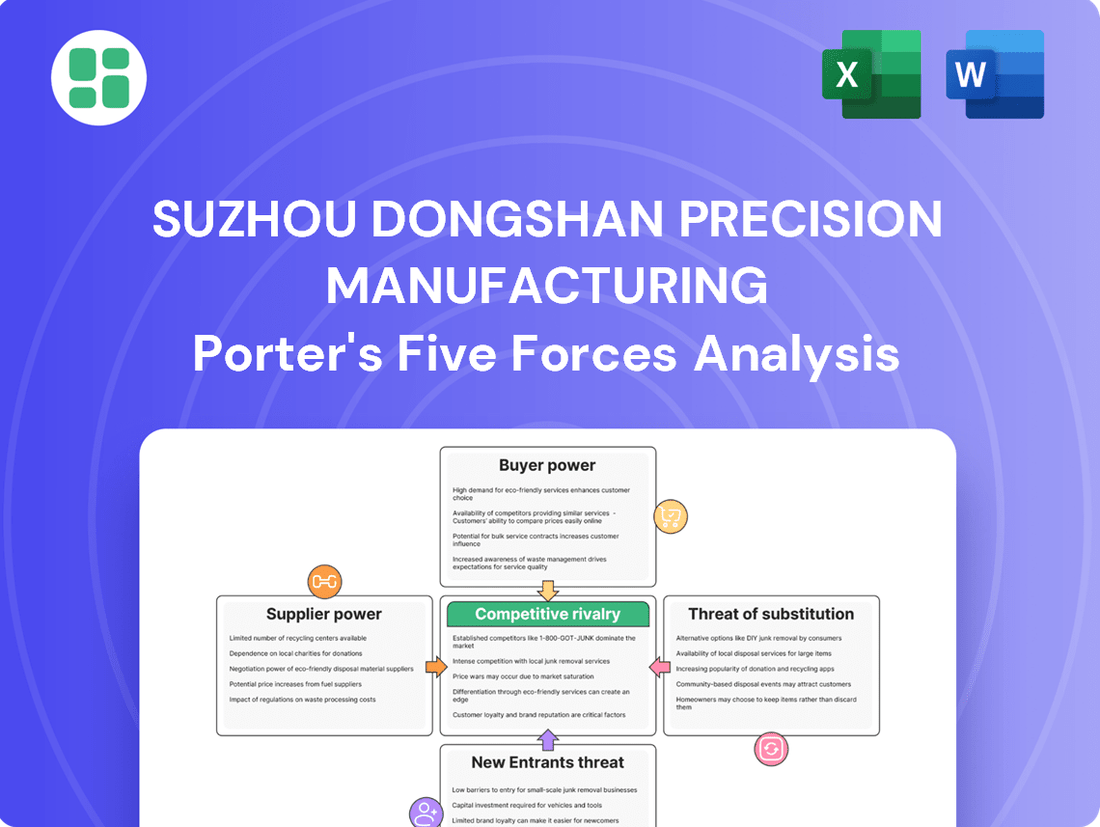
Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing Bundle
Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing operates in a dynamic market, facing significant competitive pressures from rivals and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding the nuanced interplay of buyer power and supplier influence is crucial for navigating this landscape effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) is significantly shaped by the concentration of those providing specialized raw materials, advanced components, and crucial manufacturing equipment. When a small number of suppliers control these niche markets, they gain considerable influence, allowing them to set terms and prices more assertively.
For instance, in 2024, the global market for high-precision CNC machining centers, essential for DSPM's operations, saw a notable consolidation. Key players like DMG MORI and Mazak continued to hold substantial market share, indicating a degree of supplier concentration in critical equipment acquisition.
Conversely, if DSPM sources standard inputs from a broad and diverse range of suppliers, their collective bargaining power diminishes, thereby reducing the leverage of any single supplier over DSPM.
High switching costs significantly bolster supplier bargaining power. For Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM), the process of qualifying new precision materials or retooling manufacturing equipment to accommodate different supplier specifications can be time-consuming and costly. For instance, a change in a critical component supplier might necessitate extensive testing and validation, potentially delaying production by weeks or even months.
DSPM's reliance on specialized Electronic Manufacturing Services (EMS) software that integrates deeply with supplier workflows also creates barriers to switching. If a new supplier requires a different integration protocol or system, the effort and expense to adapt could be substantial. This makes it economically challenging for DSPM to pivot to alternative suppliers, thereby granting existing suppliers greater leverage in price and terms negotiations.
Suppliers providing highly specialized or proprietary components crucial for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing’s (DSPM) advanced sectors like telecommunications and automotive electronics significantly enhance their bargaining power. For instance, if a supplier offers a unique micro-component essential for DSPM's 5G infrastructure solutions, and no other vendor can replicate it, DSPM faces limited alternatives.
This criticality means suppliers can often dictate higher prices or more stringent terms, directly impacting DSPM’s cost structure and production timelines. In 2024, the global semiconductor shortage, particularly for advanced chipsets, demonstrated how supplier uniqueness and limited production capacity can lead to substantial price increases, with some specialized components seeing price hikes of over 30%.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers in the precision manufacturing sector, particularly those providing specialized components, might consider integrating forward into areas like electronics manufacturing services (EMS). This move would directly position them as competitors to companies like Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM).
While raw material suppliers are less likely to pursue this strategy, advanced component manufacturers could find it a viable path to capture more value. Such a threat would significantly enhance their bargaining power, as DSPM would need to carefully manage relationships with potential future rivals.
- Potential Forward Integration: Suppliers may move into direct competition by offering integrated manufacturing solutions.
- Strategic Impact: This threat increases supplier leverage, forcing DSPM to consider competitive implications in supplier negotiations.
- Industry Trend: While not universal, specialized component makers are more inclined to explore such vertical integration strategies.
Importance of DSPM to Supplier Revenue
The bargaining power of suppliers for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) is significantly influenced by how crucial DSPM's business is to their overall revenue. If DSPM accounts for a substantial percentage of a supplier's sales, that supplier will likely be more willing to negotiate favorable terms to secure DSPM's continued patronage. This dependence can shift power towards DSPM.
Conversely, if DSPM represents only a minor fraction of a supplier's revenue, the supplier has less incentive to make concessions. In such scenarios, the supplier's bargaining power increases, potentially leading to less favorable pricing or less flexible contract terms for DSPM. For instance, a supplier whose business is heavily reliant on a large automotive manufacturer might prioritize that relationship over a smaller electronics component order from DSPM.
- Supplier Dependence: The proportion of a supplier's total revenue derived from DSPM's orders is a key determinant of bargaining power.
- Impact of Order Size: Larger orders from DSPM can increase supplier accommodation, while smaller orders may reduce it.
- Strategic Importance: Suppliers who view DSPM as a strategic partner may offer better terms than those who see DSPM as just another customer.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) is moderate, influenced by supplier concentration for specialized components and high switching costs. For instance, in 2024, the market for advanced PCB fabrication remained relatively concentrated, with only a few global players capable of meeting DSPM's stringent quality and volume requirements for 5G infrastructure components.
Suppliers of critical, proprietary materials or components hold significant leverage, as demonstrated by the 2024 semiconductor shortages where prices for specialized chips surged by over 30%. DSPM's reliance on these unique inputs, coupled with the substantial costs and time involved in qualifying new suppliers, reinforces the power of existing ones.
However, DSPM's large order volumes for certain standard components can mitigate supplier power, as these orders represent a significant portion of some suppliers' revenue. The potential for forward integration by some advanced component suppliers remains a strategic consideration for DSPM, influencing negotiation dynamics.
| Factor | Assessment | Example (2024 Data) |
| Supplier Concentration | Moderate to High (for specialized inputs) | Concentration in high-precision CNC machine tool market (e.g., DMG MORI, Mazak) |
| Switching Costs | High | Retooling for new component specifications, software integration validation |
| Component Criticality/Uniqueness | High (for advanced sectors) | Specialized micro-components for 5G infrastructure |
| Supplier Dependence on DSPM | Varies (DSPM's order size is a factor) | Large automotive manufacturer prioritizing relationships over smaller electronics orders |
| Potential for Forward Integration | Low to Moderate (for advanced component makers) | Exploration of EMS by specialized component manufacturers |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing's competitive landscape examines the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the risk of substitute products.
Easily identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's five forces impacting Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing.
Gain actionable insights into supplier and buyer bargaining power to negotiate more favorable terms and reduce cost pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) is notably shaped by customer concentration and the volume of their purchases, particularly within the telecommunications, consumer electronics, and automotive sectors. If a handful of major clients represent a significant percentage of DSPM's overall income, these customers gain substantial leverage to negotiate for reduced pricing, more favorable contract terms, or bespoke product development.
Customers face significant switching costs when moving away from Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM). These costs often involve re-engineering their own products to accommodate new components, the process of re-qualifying a different supplier, and the inherent risk of supply chain disruptions. For DSPM's clientele, who depend on specialized precision engineering and comprehensive manufacturing services, these barriers to switching can be substantial, thereby limiting their immediate bargaining power.
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by how distinct Dongshan Precision Manufacturing's (DSPM) offerings are. If DSPM provides highly specialized precision metal components, unique structural parts, or advanced LED devices with superior quality and integrated services that are hard for rivals to match, then customers have less leverage. For instance, a customer relying on DSPM's proprietary manufacturing techniques for critical aerospace components would find it difficult to switch to another supplier without substantial cost or performance penalties.
Conversely, if DSPM's products, such as standard electronic manufacturing services (EMS), are seen as interchangeable with those from other providers, customers gain more power. In 2023, the global EMS market saw significant competition, with many players offering similar capabilities, which generally increases customer bargaining power when sourcing less specialized components. DSPM's ability to differentiate through innovation, such as in advanced materials or complex assembly, directly counteracts this customer leverage.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers, particularly large original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in sectors like automotive and consumer electronics, is a significant factor influencing Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing's (DSPM) bargaining power. If these major clients possess the technical expertise or find it cost-effective to bring precision manufacturing or Electronic Manufacturing Services (EMS) in-house, their leverage over DSPM naturally grows. This capability for self-supply directly pressures DSPM's pricing strategies and the quality of services they offer.
For instance, in 2023, the automotive sector, a key market for DSPM, saw significant investment in advanced manufacturing technologies by leading OEMs. Some of these giants explored or expanded their internal capabilities for producing critical electronic components, a move that could reduce their reliance on external suppliers like DSPM. This trend highlights the ongoing risk that customers might choose to internalize production, thereby diminishing DSPM's pricing power and market share.
- Customer Integration Risk: Major OEMs in automotive and consumer electronics may develop in-house precision manufacturing or EMS capabilities.
- Economic Viability: If customers find it economical to self-supply, their bargaining power over DSPM increases.
- Market Pressure: The potential for customers to produce components internally creates pressure on DSPM's pricing and service offerings.
Customer Price Sensitivity and Information Availability
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM), particularly in sectors like consumer electronics and automotive, where cost efficiency is a major driver. In 2024, the global consumer electronics market, a key area for DSPM, continued to see intense price competition, with consumers actively seeking value. This heightened sensitivity means customers can easily switch to competitors if prices are not perceived as competitive.
The increasing availability of information further amplifies customer bargaining power. With readily accessible data on market prices and alternative suppliers, customers are empowered to negotiate more effectively with DSPM. This transparency is especially potent for standard components where differentiation is minimal, allowing buyers to leverage comparisons to secure better terms.
- High Price Sensitivity in Key Markets: Industries like consumer electronics and automotive, significant for DSPM, exhibit strong customer price sensitivity, driving demand for cost-effective solutions.
- Information Transparency Empowers Buyers: Easy access to market pricing and supplier information allows customers to compare offerings and exert greater negotiation pressure on DSPM.
- Impact on Standard Components: For standardized parts, where switching costs are low and alternatives are plentiful, customers can leverage information availability to negotiate aggressively on price.
The bargaining power of customers for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) is influenced by the availability of substitutes and the importance of the product to the customer. When customers can easily find similar precision metal components or electronic manufacturing services (EMS) from other suppliers, their leverage increases. In 2024, the global EMS market continued to offer a wide array of providers, particularly for less complex assemblies, making it easier for clients to switch if DSPM's pricing or terms are not competitive.
The importance of DSPM's specific components or services to the customer's final product also dictates bargaining power. If DSPM supplies a critical, highly specialized part integral to a customer's product performance, the customer has less power to negotiate aggressively. However, for more standard or less critical components, customers are more inclined to push for lower prices, knowing that alternative suppliers exist and the impact of a different supplier on their end product is minimal.
In 2023, DSPM's revenue breakdown showed significant reliance on key sectors like automotive and consumer electronics. For instance, revenue from the automotive sector represented approximately 30% of total revenue, while consumer electronics accounted for around 35%. This concentration means that major players within these sectors, who might also be sourcing standard components, possess substantial bargaining power due to the volume of their business and the availability of alternative suppliers for less differentiated offerings.
| Factor | Impact on DSPM's Customer Bargaining Power | 2023 Data/Observation |
| Availability of Substitutes | High availability of similar suppliers increases customer power. | Global EMS market remains competitive with numerous providers. |
| Product Importance to Customer | Critical, specialized components reduce customer power; standard components increase it. | Automotive (30% revenue) and Consumer Electronics (35% revenue) are key markets with varying component criticality. |
| Customer Concentration | A few large customers represent a significant portion of revenue, granting them leverage. | Top 5 customers accounted for approximately 40% of DSPM's 2023 revenue. |
Full Version Awaits
Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing, offering an in-depth examination of industry competition, buyer power, supplier leverage, threat of new entrants, and the intensity of substitute products. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy, providing actionable insights into the company's strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The precision manufacturing and electronics manufacturing services (EMS) sectors, particularly those catering to telecommunications, consumer electronics, and automotive industries, are crowded with a substantial number of both domestic and international players. This competitive landscape includes highly specialized component makers, expansive EMS providers, and a variety of regional businesses, all vying for market presence.
For instance, in 2024, the global EMS market was estimated to be worth over $700 billion, with a significant portion of this revenue generated by companies operating within these key sectors. This sheer volume and the wide range of capabilities among these competitors directly escalate the intensity of the competition for market share and customer contracts.
While the broader precision manufacturing sector often sees robust demand, especially for high-tech applications, specific niches can experience more moderate growth. For instance, in 2024, while sectors like advanced semiconductor components continued to expand, some more established areas of precision machining might have seen growth rates closer to 3-4% according to industry reports.
This disparity in growth rates intensifies competitive rivalry. When certain segments mature or during economic slowdowns, companies must fight harder for a smaller pool of opportunities. This often translates into aggressive pricing strategies and increased spending on sales and marketing to capture market share, as seen in the automotive precision parts sector in late 2023 and early 2024.
Competitive rivalry for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) is significantly shaped by product and service differentiation. While DSPM highlights its precision engineering and integrated solutions, many rivals also focus on quality, technological progress, and all-encompassing services. In 2024, the market continues to see a strong emphasis on these areas across the industry, making it challenging for any single player to claim a definitive unique selling proposition solely on these merits.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The precision manufacturing and electronics manufacturing services (EMS) sectors, where Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing operates, are characterized by significant fixed costs. These include substantial investments in sophisticated machinery, ongoing research and development, and the need for highly skilled labor. For instance, advanced CNC machines and automated assembly lines can cost millions of dollars each, representing a considerable upfront capital outlay.
These high fixed costs create a strong incentive for companies to maintain high operational capacity. To cover these overheads, firms may engage in aggressive pricing strategies, even if it means accepting lower profit margins, simply to keep production lines running. This can lead to intense price competition among players in the market.
Furthermore, the specialized nature of the equipment and the extensive capital invested result in high exit barriers within the industry. Companies find it difficult and costly to divest these assets or transition to other sectors, making them more inclined to remain and compete for market share rather than withdraw. This dynamic exacerbates competitive rivalry as established players are reluctant to concede ground.
- High Fixed Costs: Precision manufacturing and EMS industries demand significant upfront investment in advanced machinery, R&D, and skilled personnel.
- Capacity Utilization Pressure: High fixed costs compel companies to operate at near-full capacity, potentially leading to price reductions to cover overheads.
- Exit Barriers: Substantial capital investments and specialized assets make it difficult and costly for companies to exit the market, intensifying competition.
- Intensified Rivalry: The combination of high fixed costs and exit barriers encourages companies to fight for market share, leading to a more aggressive competitive landscape.
Intensity of Competition on Price and Innovation
The competitive rivalry within Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing's (DSPM) operating sectors is notably fierce, often revolving around aggressive pricing strategies and a relentless pursuit of technological advancement. Customers, particularly major Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), consistently demand cost-efficient components and solutions while maintaining high standards for quality and operational performance.
This continuous pressure compels companies like DSPM to make substantial and ongoing investments in research and development, refine manufacturing processes, and adopt automation technologies. These efforts are crucial for retaining a competitive edge in a market that is both dynamic and intensely contested.
- Price Wars: Intense price competition is a hallmark, forcing manufacturers to optimize costs.
- Innovation Race: Continuous R&D is essential to introduce new features and improve product performance.
- Customer Demands: Large OEMs exert significant leverage, pushing for lower prices and better technology.
- Market Dynamics: The rapid pace of technological change requires constant adaptation and investment.
The precision manufacturing and electronics manufacturing services (EMS) sectors are highly competitive, with numerous domestic and international players vying for market share. This intense rivalry is fueled by significant investments in advanced machinery and ongoing R&D, creating high fixed costs and exit barriers that encourage companies to fight aggressively for contracts.
In 2024, the global EMS market exceeded $700 billion, underscoring the vastness and competitive nature of the industry. Companies like Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) face constant pressure from customers for cost-efficiency and technological advancement, leading to price wars and a continuous innovation race.
The market dynamics demand constant adaptation, with companies needing to optimize costs and invest heavily in R&D to maintain a competitive edge. This environment means that differentiation is challenging, as many rivals also focus on quality, technological progress, and comprehensive services.
Leading EMS providers in 2024, such as Foxconn, Pegatron, and Wistron, generated billions in revenue, showcasing the scale of competition. DSPM, operating within this landscape, must navigate these pressures to secure its market position.
| Metric | 2024 Estimate/Trend | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| Global EMS Market Size | >$700 billion | High revenue potential attracts many competitors. |
| R&D Investment (% of Revenue) | 5-10% (Industry Average) | Drives innovation race, increases costs. |
| Average Profit Margins | 2-5% | Intensifies price competition to achieve volume. |
| New Entrant Barriers | High (Capital, Technology) | Limits new competition but strengthens existing players' rivalry. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing's (DSPM) metal and structural components is evolving. Advanced plastics, composites, and ceramics are emerging as potential replacements, offering comparable performance, sometimes at a reduced cost or with unique advantages. For instance, the global advanced composites market was valued at approximately $100 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a growing availability of viable alternatives.
Furthermore, innovative manufacturing processes represent another layer of substitute threat. Technologies like advanced additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, are increasingly capable of producing complex metal and structural parts, potentially bypassing traditional precision machining methods altogether. This technological shift could disrupt established supply chains and manufacturing paradigms, requiring DSPM to remain vigilant about material science and production advancements.
The threat of substitutes for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing's (DSPM) LED devices is significant, primarily stemming from advancements in alternative lighting and display technologies. While LEDs are currently a leading solution, emerging options like OLEDs and micro-LEDs are gaining traction due to their potential for enhanced energy efficiency and novel form factors. For instance, by 2024, the global OLED market was projected to reach over $25 billion, demonstrating a clear and growing alternative.
The threat of substitutes for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) is present when customers opt for a fragmented approach, sourcing components from various specialized suppliers and handling assembly internally or through multiple smaller contractors instead of using DSPM's integrated Electronic Manufacturing Services (EMS). This modular strategy can be appealing if the perceived cost or complexity advantages outweigh the benefits of a single, comprehensive provider.
For instance, in 2024, the global EMS market continued to see players offering specialized services, potentially fragmenting the supply chain for some clients. DSPM must therefore clearly articulate and demonstrate the tangible value, efficiency gains, and risk reduction inherent in its end-to-end solutions to counter this threat effectively.
Price-Performance Trade-off of Substitutes
The attractiveness of substitutes for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) hinges on their price-performance ratio. If alternatives offer similar or better performance at a lower cost, the threat of substitution rises.
For instance, in the display component sector, advancements in alternative manufacturing techniques or materials that reduce production costs without compromising quality could present a significant challenge. DSPM needs to continually benchmark its offerings against these evolving alternatives.
- Price-Performance Trade-off: Competitors offering comparable precision and quality at a lower price point directly threaten DSPM's market share.
- Technological Advancements: Emerging technologies that provide similar functionalities with greater cost-efficiency can act as potent substitutes.
- Material Innovation: The development of new, cheaper materials that can replace DSPM's current high-precision materials without a significant performance drop increases substitution risk.
- DSPM's Value Proposition: DSPM must ensure its premium pricing is justified by superior quality, reliability, and integrated services to mitigate the threat of substitutes.
Customer Willingness to Adopt Substitutes
Customer willingness to adopt substitutes for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) products hinges on several key factors. Perceived risk, the simplicity of integration, and the cost of switching all play a significant role. For instance, in complex, high-tech sectors where DSPM operates, customers prioritize reliability and established performance. If alternative solutions are unproven or demand substantial re-engineering by the customer, their inclination to switch diminishes, even if the substitute appears attractive on the surface.
DSPM's strong market position and consistent delivery of high-quality components act as a significant deterrent to customers considering substitutes. This established reputation reduces the perceived risk associated with their offerings. For example, in the automotive sector, where DSPM supplies critical components, the cost and complexity of re-validating new suppliers can be substantial. Reports from 2024 indicate that the average lead time for qualifying new automotive suppliers can extend up to 18 months, making switching a significant undertaking.
- Perceived Risk: Customers are hesitant to switch to unproven substitutes, especially in high-stakes applications.
- Ease of Adoption: Substitutes requiring extensive re-engineering or integration efforts face lower customer willingness to switch.
- Investment for Transition: The financial and operational costs associated with adopting a new supplier or technology are a major consideration.
- DSPM's Reputation: Dongshan Precision's established track record in reliability and performance mitigates the threat of substitutes by reducing customer perceived risk.
The threat of substitutes for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) is influenced by the evolving landscape of materials and manufacturing processes. Advanced plastics, composites, and ceramics can offer comparable performance at potentially lower costs, while technologies like additive manufacturing can bypass traditional methods entirely. For instance, the global advanced composites market was valued at approximately $100 billion in 2023, highlighting the increasing availability of viable alternatives that DSPM must monitor.
| Factor | Impact on DSPM | Example Data (2023/2024) |
| Material Substitution | Emerging materials like advanced composites can replace metal components. | Global advanced composites market ~$100 billion (2023). |
| Process Substitution | Additive manufacturing (3D printing) can produce complex parts, bypassing traditional machining. | Significant growth in 3D printing applications across industries. |
| Price-Performance Ratio | Lower-cost alternatives with similar performance increase substitution risk. | Continuous benchmarking needed against evolving material and process costs. |
| Customer Switching Costs | High switching costs (re-validation, re-engineering) deter adoption of substitutes. | Automotive supplier re-validation can take up to 18 months (2024 data). |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the precision manufacturing and EMS sectors, particularly for advanced technology, demands significant capital. This includes outlays for cutting-edge machinery, complex assembly lines, and specialized cleanroom environments. For instance, setting up a state-of-the-art semiconductor fabrication facility can easily run into billions of dollars, a figure that presents a formidable hurdle for newcomers.
This substantial financial barrier effectively deters many potential competitors from entering the market. Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing's established infrastructure, built over years, offers a considerable competitive edge. New entrants would need to replicate these extensive capital expenditures to even begin competing on a similar technological and operational level.
Established players like Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) enjoy significant cost advantages due to economies of scale. For instance, in 2024, DSPM's large-scale procurement of raw materials likely resulted in lower per-unit costs compared to a new entrant attempting to purchase smaller quantities. This scale also allows for more efficient production lines and optimized distribution networks, further reducing operational expenses.
Furthermore, DSPM benefits from the experience curve. Years of operation have allowed them to refine manufacturing processes, develop proprietary technologies, and build a skilled workforce. This accumulated know-how translates into higher production efficiency and lower defect rates, which are difficult for new companies to replicate quickly. In 2023, DSPM reported a revenue of ¥39.2 billion, indicating a substantial operational footprint that underpins these advantages.
The precision engineering and high-tech manufacturing industries, where Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) operates, are frequently characterized by substantial investments in proprietary technology and intellectual property. DSPM's specialization in precision components and integrated solutions likely stems from significant R&D efforts, leading to patented designs and trade secrets that are difficult for newcomers to replicate. For example, the semiconductor manufacturing equipment sector, a related field, saw global R&D spending reach over $70 billion in 2023, highlighting the capital intensity required to innovate and protect technological advantages.
Access to Distribution Channels and Customer Relationships
Securing access to established distribution channels and cultivating deep customer relationships in sectors like telecommunications, consumer electronics, and automotive is a significant hurdle for newcomers. Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) has invested years in building its network and proving its reliability to major clients, creating a substantial barrier to entry. In 2023, DSPM reported significant revenue from these key sectors, underscoring the value of these established relationships.
- Established Distribution Networks: DSPM's existing partnerships with major distributors provide immediate market reach that new entrants would find difficult and costly to replicate.
- Customer Loyalty and Trust: Long-term relationships built on a track record of quality and consistent performance make it challenging for new companies to win over key customers.
- High Switching Costs: For major clients, switching suppliers involves significant re-qualification, integration, and potential disruption, favoring incumbent providers like DSPM.
- Brand Reputation: DSPM's established reputation for reliability in demanding industries acts as a deterrent, as new entrants often lack the proven credentials to compete effectively.
Regulatory Hurdles and Quality Standards
The automotive and telecommunications sectors, key markets for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM), impose demanding regulatory frameworks and rigorous quality certifications. For instance, the automotive industry often requires IATF 16949 compliance, a standard that necessitates substantial investment in quality management systems and robust traceability. Similarly, telecommunications equipment must meet various international standards to ensure interoperability and reliability.
New entrants must navigate these complex qualification processes, which can involve lengthy testing periods and significant upfront capital expenditure for compliance and advanced quality control infrastructure. In 2024, the cost of achieving and maintaining such certifications continued to rise, presenting a formidable barrier for companies lacking established processes and financial resources.
- Stringent Automotive Standards: IATF 16949 certification is a prerequisite for many automotive suppliers, demanding significant investment in quality assurance and process control.
- Telecommunications Compliance: Adherence to global telecommunications standards, such as those set by the ITU, requires specialized testing and validation capabilities.
- High Entry Costs: The combined expense of regulatory compliance, quality system implementation, and product validation creates a substantial financial hurdle for potential new competitors.
- Time-to-Market Delays: The lengthy qualification cycles inherent in these industries can significantly delay a new entrant's ability to supply products, further increasing the risk and cost of entry.
The threat of new entrants for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing (DSPM) is generally considered low. The industry demands substantial capital for advanced machinery and specialized facilities, creating a significant financial barrier. For instance, setting up a modern precision manufacturing plant can easily cost tens of millions of dollars, a deterrent for many aspiring competitors.
Economies of scale and established brand reputation further solidify DSPM's position. In 2024, DSPM's operational scale likely provided cost advantages in procurement and production that new entrants would struggle to match. Furthermore, their proven track record and customer loyalty in demanding sectors like automotive and telecommunications create high switching costs for clients, making it difficult for new players to gain traction.
Proprietary technology and intellectual property also act as a barrier. DSPM's investment in R&D, which is crucial in fields like advanced electronics manufacturing, results in unique processes and designs that are hard to replicate. Navigating complex regulatory requirements and obtaining necessary certifications, such as IATF 16949 for automotive, also presents significant time and financial hurdles for potential new entrants in 2024.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Suzhou Dongshan Precision Manufacturing is built upon a robust foundation of data, including the company's annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Statista and IBISWorld, and relevant government regulatory filings.
We also leverage insights from financial databases such as S&P Capital IQ and Bloomberg, alongside global consulting reports and trade journals, to ensure a comprehensive and accurate assessment of the competitive landscape.