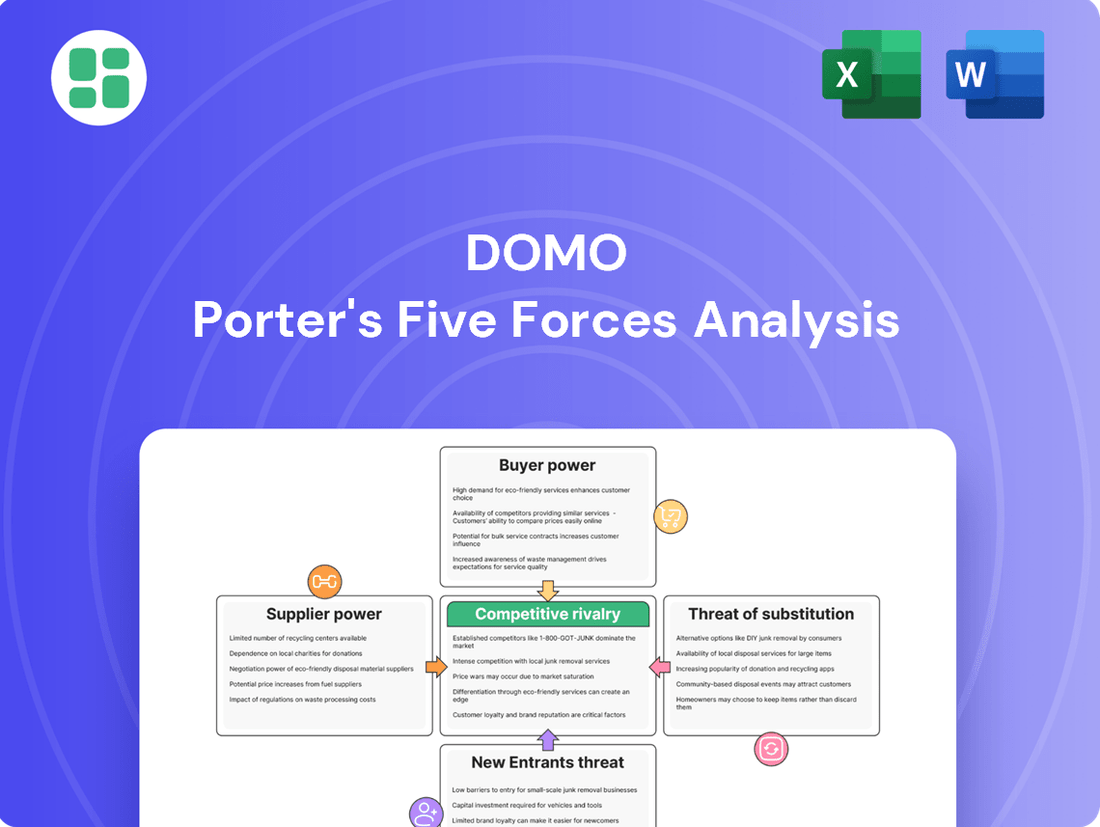
DOMO Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
DOMO Bundle
DOMO's competitive landscape is shaped by several key forces, including the bargaining power of buyers and the threat of substitute products. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any business operating within or looking to enter the data analytics and business intelligence market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping DOMO’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Domo's reliance on a few major cloud infrastructure providers means these suppliers could potentially wield significant power. However, the market for cloud computing is becoming increasingly commoditized, with many providers offering similar basic services. This situation, coupled with Domo's ability to switch providers, even if it involves some effort and cost, helps to temper the individual bargaining power of these infrastructure suppliers over Domo’s core operations.
Specialized technology and software component suppliers hold moderate bargaining power when their offerings are crucial and unique to Domo's platform. If these components are proprietary or lack readily available substitutes, Domo could face increased costs or less favorable contract terms. For instance, if a key AI module or a specialized data connector is only available from a single provider, that supplier gains leverage.
Domo's ability to develop some of these capabilities in-house or its strong relationships with multiple vendors can help to temper this supplier power. In 2023, Domo reported $277.7 million in revenue, indicating a significant scale that allows for negotiation with its suppliers.
The availability of highly skilled engineers and data scientists, especially those with expertise in cloud architecture, data engineering, and AI/ML, significantly impacts supplier power. A limited supply of these professionals can drive up compensation expectations and retention costs for companies like Domo, indirectly increasing operational expenses.
In 2024, the demand for cloud and AI talent remained exceptionally high, with reports indicating a shortage of qualified candidates in specialized areas. For instance, the average salary for a senior data scientist in the US saw an increase, reflecting this competitive landscape and the bargaining power of these skilled individuals.
Data integration and connectivity partners
Domo's core value proposition hinges on its robust data integration capabilities, connecting to a vast array of sources. While many data connections utilize standard APIs, specialized or legacy system integrations often necessitate partnerships with specific connectivity providers. The proprietary nature of some of these integrations can grant these partners a degree of bargaining power.
The bargaining power of data integration and connectivity partners for Domo is generally moderate. Domo's extensive platform and broad market reach mean that while some partners are crucial for specific niche integrations, Domo is not overly reliant on any single provider.
- Domo's extensive partner ecosystem reduces reliance on any single integration provider.
- Specialized or legacy system integrations can grant certain partners moderate bargaining power due to unique technical requirements.
- The cost and complexity of switching integration partners can influence the leverage held by existing partners.
Open-source software and community contributions reduce some supplier power
The rise of open-source software significantly curtails the bargaining power of traditional software suppliers. By leveraging these freely available, robust tools for various functionalities, Domo can decrease its reliance on proprietary solutions. This strategic adoption allows the company to build upon existing, community-driven platforms, thereby diminishing the leverage of commercial software vendors for those particular components.
Community contributions act as a decentralized supply chain, offering an alternative to traditional vendor relationships. This shared development model means that expertise and ongoing improvements are not solely dictated by a single entity. For instance, the widespread adoption and continued development of open-source databases or analytics libraries reduce the need for costly, single-vendor licenses and support contracts, directly impacting supplier pricing power.
- Reduced Vendor Lock-in: Open-source adoption lessens dependence on specific proprietary software providers, giving Domo more flexibility and negotiation leverage.
- Cost Savings: Utilizing free, community-supported software for certain functions can lead to substantial cost reductions compared to licensing commercial alternatives.
- Community as a Resource: The collective expertise and ongoing development within open-source communities provide a distributed form of support and innovation, acting as a counterweight to individual supplier influence.
Domo's bargaining power with suppliers is influenced by the availability of alternatives and the cost of switching. For cloud infrastructure, the market's commoditization and Domo's ability to migrate services temper supplier leverage. However, for specialized software components or unique data integration needs, a lack of substitutes can empower certain suppliers.
The company's scale, as evidenced by its 2023 revenue of $277.7 million, provides a stronger negotiating position. Furthermore, Domo's strategic adoption of open-source software significantly reduces its reliance on proprietary vendors, thereby diminishing their pricing power.
The competitive talent market for skilled engineers and data scientists in 2024 also indirectly impacts supplier dynamics, as higher compensation costs for talent can influence overall operational expenses and procurement decisions.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Influence | Domo's Mitigating Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Infrastructure Providers | Moderate to Low | Market commoditization, ability to switch providers |
| Specialized Software/Component Suppliers | Moderate to High (if unique) | In-house development, multiple vendor relationships |
| Data Integration/Connectivity Partners | Moderate | Extensive partner ecosystem, broad market reach |
| Talent (Engineers, Data Scientists) | High (due to scarcity) | Strategic hiring, retention efforts |
| Open-Source Software | Very Low (for components adopted) | Reduced vendor lock-in, cost savings |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping DOMO's market, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive pressures, allowing for proactive strategy adjustments to mitigate threats.
Customers Bargaining Power
For enterprise clients deeply embedded with Domo, the cost and complexity of migrating data, retraining staff, and rebuilding critical reports and dashboards represent a significant barrier to switching. This integration creates a strong customer stickiness, effectively diminishing their bargaining power.
The business intelligence and data analytics market is quite crowded, meaning customers have plenty of other options. Think of big players like Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, and Qlik, but also smaller, specialized tools or even companies building their own solutions. This abundance of choices gives customers leverage.
Because there are so many alternatives, customers can push back on Domo's pricing or feature set. If Domo isn't seen as competitive, especially when a company is first signing up, customers might threaten to go elsewhere. This pressure is a key reason Domo needs to stay sharp.
For instance, in 2024, the BI and analytics market continued to see robust growth, with many vendors vying for market share. Companies like Microsoft, with its integrated Power BI offering, often provide bundled solutions that can be attractive to large enterprises, intensifying the need for Domo to differentiate itself and offer compelling value propositions.
Enterprise clients increasingly expect sophisticated features and ironclad security from data analytics platforms like Domo. This means Domo needs to deliver not just core functionalities but also advanced analytics, AI capabilities, and robust data protection measures to satisfy these demanding users.
The bargaining power of these customers is significant because their need for comprehensive solutions, scalability, and high security standards directly influences Domo's product development priorities and pricing strategies. Failure to meet these expectations can lead to lost deals and reduced market share.
In 2024, the emphasis on data privacy and regulatory compliance, such as GDPR and CCPA, further amplified customer demands for enhanced security features. Domo's ability to adapt and innovate in these areas is crucial for maintaining its competitive edge and customer loyalty in a market where data breaches can have severe financial and reputational consequences.
Pricing sensitivity varies by customer size and industry
Pricing sensitivity for Domo's offerings can significantly differ based on customer size and the industry they operate in. Smaller businesses, often operating with tighter budgets, tend to be more sensitive to price, seeking cost-effective solutions. In contrast, larger enterprises typically place a higher premium on robust features, seamless integration with existing systems, and comprehensive support services. These larger clients may be willing to incur higher costs to ensure these critical aspects are met.
This segmentation of the customer base directly impacts the bargaining power of customers. Larger clients, due to the substantial volume of their contracts and their strategic importance, often wield more significant leverage in price negotiations. For instance, a Fortune 500 company signing a multi-year, enterprise-wide agreement can command better pricing terms than a small startup. This reality necessitates that Domo maintains flexible pricing models that can accommodate the diverse needs and negotiation strengths of its varied clientele.
For example, in 2023, according to industry reports, the average contract value for enterprise-level business intelligence solutions ranged from $100,000 to over $1 million annually, with larger deals often involving significant discounts. This highlights how volume and customer size directly translate into increased bargaining power. Domo's ability to adapt its pricing strategies, perhaps offering tiered solutions or volume-based discounts, is crucial for capturing and retaining both smaller and larger market segments effectively.
- Customer Segmentation: Smaller businesses are more price-sensitive, while larger enterprises prioritize features, integration, and support, potentially accepting higher costs.
- Bargaining Power Dynamics: Larger customers, due to contract volume, generally possess greater leverage in price negotiations.
- Domo's Strategy: The company needs to implement flexible pricing models to cater to diverse customer needs and negotiation capabilities.
Customers seeking real-time insights and collaboration tools
Customers are increasingly demanding real-time data access and enhanced collaboration features, which are core to Domo's offering. Their need for these capabilities means Domo must consistently deliver on its promise, or customers may seek platforms that offer more immediate value. This drives Domo to maintain its competitive edge in these areas.
- Customer Demand for Real-Time Data: Businesses across sectors are prioritizing instant access to operational and market data to make agile decisions.
- Collaboration Features as a Differentiator: Integrated tools that allow teams to work together on data insights are becoming non-negotiable for many organizations.
- Impact on Domo's Strategy: Domo's success hinges on its ability to continuously innovate and provide superior real-time and collaborative functionalities compared to competitors.
- Potential for Switching: If Domo's platform lags in delivering these critical features, customers have viable alternatives that can fulfill their needs more effectively.
The bargaining power of customers is a significant factor for Domo, influenced by market competition and customer expectations. While Domo's deep integration can create stickiness, the crowded BI market offers many alternatives, allowing customers to negotiate pricing and features. Meeting sophisticated demands for real-time data, collaboration, and security is crucial for retaining these clients.
In 2024, the business intelligence market continued to be highly competitive, with vendors like Microsoft Power BI and Tableau offering compelling integrated solutions. This competitive landscape empowers customers, particularly larger enterprises, to demand more value. For example, reports from 2023 indicated that enterprise BI contracts could range from $100,000 to over $1 million annually, with significant discounts often negotiated by larger clients, demonstrating their leverage.
Customer segmentation also plays a role; smaller businesses are more price-sensitive, while larger clients prioritize features and support, often wielding more power due to contract volume. This necessitates flexible pricing strategies from Domo to cater to diverse needs and negotiation strengths.
| Customer Segment | Key Demands | Bargaining Power Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Smaller Businesses | Price Sensitivity, Cost-Effectiveness | Moderate (due to budget constraints) |
| Larger Enterprises | Advanced Features, Integration, Security, Support | High (due to contract volume and strategic importance) |
Same Document Delivered
DOMO Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The preview you see is the exact DOMO Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive breakdown of competitive forces within the industry. This document is fully formatted and ready for your immediate use, providing actionable insights without any placeholders or surprises. You are looking at the actual, professionally written analysis that will be instantly available to you upon completing your purchase.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Domo operates in a fiercely competitive landscape, facing formidable rivals such as Microsoft Power BI, Salesforce Tableau, and Qlik. These established players boast significant market share, strong brand loyalty, and deep integration capabilities within their respective enterprise software suites, giving them a substantial advantage.
These market leaders often possess considerably larger sales and marketing resources, enabling them to reach a wider audience and exert greater influence. For instance, Microsoft's Power BI benefits from its integration with the vast Microsoft ecosystem, a key differentiator that attracts many businesses. Qlik, another major player, has a long-standing reputation for its in-memory associative engine, a feature that appeals to users seeking advanced analytics.
The sheer scale of these competitors means Domo must continually innovate and clearly articulate its unique value proposition to stand out. In 2024, the business intelligence market is projected to reach over $35 billion, underscoring the immense opportunity but also the intensity of the battle for market share among these giants.
Cloud giants like Amazon Web Services with QuickSight and Google Cloud, through Looker (formerly Data Studio), are increasingly embedding their own business intelligence tools. This trend is particularly impactful for businesses already invested in their cloud ecosystems, as these native BI solutions offer inherent advantages in integration and data accessibility.
This integrated approach presents a bundled offering challenge, making it harder for standalone BI providers to compete on price and convenience. For instance, AWS reported over 100,000 customers using QuickSight as of early 2024, highlighting the growing adoption of these cloud-native solutions.
Domo differentiates itself by prioritizing real-time data delivery and user-friendliness, directly addressing a key competitive pressure. This focus on making complex data accessible to everyday business users, rather than requiring specialized technical skills, allows Domo to stand out against platforms with steeper learning curves.
By enabling quick access to actionable insights, Domo directly counters the rivalry from more developer-centric business intelligence tools. This agility is a significant draw for organizations that need to react swiftly to market changes. For instance, in 2024, businesses increasingly demanded immediate data feedback to inform rapid strategic adjustments.
Pricing strategies and feature parity battles
Competitors in the business intelligence and analytics space frequently employ aggressive pricing tactics, including freemium offerings, which directly challenge Domo's established pricing structure. This pressure forces Domo to continually re-evaluate its own pricing to remain competitive, potentially impacting its revenue streams. For instance, in 2024, many SaaS platforms in related sectors saw pricing adjustments driven by competitive pressures, with some offering tiered discounts or more flexible subscription models to attract and retain customers.
The relentless pursuit of feature parity, coupled with the need to introduce novel functionalities, necessitates substantial and ongoing investment in research and development for Domo. This R&D expenditure is crucial for maintaining and enhancing Domo's value proposition against rivals who are also rapidly evolving their platforms. Companies like Tableau, now part of Salesforce, and Microsoft Power BI have consistently pushed innovation, forcing Domo to match these advancements to avoid falling behind in critical areas like AI-driven insights and data governance.
- Aggressive Pricing: Competitors often use low-cost or free entry points, pressuring Domo's pricing.
- Feature Parity Race: Constant need to match competitor features requires significant R&D spending.
- Innovation Investment: Domo must innovate to justify its value proposition and differentiate itself.
- Strategic Adjustments: The dynamic nature of the market demands continuous strategic adaptation from Domo.
Consolidation and acquisitions in the BI market
Competitive rivalry in the Business Intelligence (BI) market is intensifying due to significant consolidation. Larger vendors are actively acquiring smaller, innovative BI firms to broaden their product suites and gain access to new technologies. This M&A activity, which was particularly active in 2023 and projected to continue through 2024, means that Domo faces rivals with increasingly integrated and comprehensive offerings. For instance, in late 2023, Microsoft continued its push into AI-driven analytics, enhancing its Power BI capabilities, a direct competitor to Domo's core business.
This trend of consolidation directly impacts Domo's competitive landscape. As rivals combine forces and expand their portfolios, the intensity of competition naturally rises. Domo needs to remain highly adaptable, potentially considering its own strategic alliances or acquisitions to bolster its market position and ensure its offerings remain competitive against these larger, more integrated entities. The market's dynamic nature demands continuous innovation and strategic maneuvering.
Key aspects of this rivalry include:
- Increased Market Power: Acquisitions by major players like Microsoft, Salesforce (with Tableau), and SAP lead to concentrated market share, giving these giants greater leverage.
- Broader Feature Sets: Combined entities often offer more extensive BI functionalities, from data preparation to advanced analytics and AI, presenting a more complete solution than standalone offerings.
- Pricing Pressures: Larger, consolidated companies may leverage economies of scale to offer more competitive pricing, putting pressure on smaller vendors like Domo.
- Talent Acquisition: Acquisitions also serve to absorb key talent and intellectual property, further strengthening the acquiring company's competitive edge.
Competitive rivalry in the business intelligence sector is intense, with Domo facing established giants like Microsoft Power BI and Salesforce Tableau, who benefit from extensive ecosystems and marketing resources. The market, projected to exceed $35 billion in 2024, sees cloud providers like AWS QuickSight and Google Looker embedding BI tools, creating bundled offerings that challenge standalone players. Domo differentiates by focusing on real-time data and user-friendliness, a critical advantage in a market demanding quick insights.
| Competitor | Key Strengths | 2024 Market Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Power BI | Deep integration with Microsoft ecosystem, extensive features | AI-driven insights, hybrid cloud solutions |
| Salesforce Tableau | Strong data visualization, large user community | Customer 360 integration, augmented analytics |
| Qlik | Associative Engine technology, in-memory processing | AI/ML integration, cloud-native analytics |
| AWS QuickSight | Cloud-native, pay-per-session pricing, integration with AWS services | Embedded analytics, machine learning integration |
| Google Looker | Cloud-native, data governance, integration with Google Cloud | AI/ML capabilities, real-time analytics |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For many small to medium-sized businesses, manual data analysis using spreadsheets like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets remains a significant substitute for sophisticated business intelligence platforms. These tools are readily available and familiar, offering a low-cost entry point for basic reporting and analysis. This accessibility means that organizations not yet requiring advanced BI capabilities might opt for these simpler, more budget-friendly solutions.
While less efficient and scalable than dedicated BI software, the widespread adoption and low cost of spreadsheet-based analysis pose a threat. In 2024, businesses continue to leverage these tools for departmental reporting and ad-hoc analysis, representing a baseline alternative for many. This threat is particularly relevant for companies in the early stages of digital transformation or those with limited IT budgets.
Large enterprises with substantial IT budgets might develop their own reporting tools or utilize scripting languages like Python and R for data analysis. These in-house solutions offer a high degree of customization, allowing businesses to tailor reporting precisely to their unique needs. However, this approach demands significant upfront investment in development and ongoing resources for maintenance and updates.
While these custom solutions can be powerful, their cost can be a deterrent, especially for smaller or medium-sized businesses. For instance, the average cost for developing a custom business intelligence solution can range from $50,000 to $250,000 or more, depending on complexity, making it a considerable expense. This high cost can limit their adoption as a direct substitute for off-the-shelf reporting platforms, particularly when those platforms meet most of an organization's requirements.
Companies seeking data-driven insights may opt for consulting services or outsourced data analysis instead of investing in a Business Intelligence (BI) platform. These external providers offer expertise and deliver actionable information, effectively bypassing the need for significant upfront software expenditure or the development of in-house analytical capabilities.
While not a direct technological replacement for BI software, these service-based alternatives address the core business requirement of leveraging data for informed decision-making. For instance, the global data analytics market was valued at approximately $27.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong demand for such outsourced solutions.
Generic business intelligence functionalities within ERP/CRM systems
Many ERP and CRM systems now bundle basic business intelligence (BI) features. For instance, Salesforce Einstein Analytics, integrated within their CRM, offers analytics capabilities. SAP's BusinessObjects is another example of an ERP with embedded BI. These built-in tools can satisfy the needs of businesses requiring only fundamental reporting and dashboarding, acting as a readily available substitute for specialized BI solutions.
While these integrated functionalities might not match the depth of dedicated BI platforms, their convenience and cost-effectiveness as part of an existing software suite make them compelling alternatives. Companies can leverage these embedded tools to gain essential insights without the need for separate software purchases or complex integrations. This can significantly lower the barrier to entry for data-driven decision-making.
- Cost Savings: Companies can avoid additional licensing fees for separate BI tools.
- Ease of Integration: Data is already within the ERP/CRM, simplifying access and analysis.
- Basic Functionality: Sufficient for organizations needing fundamental reporting and KPI tracking.
- Vendor Lock-in: Reliance on the ERP/CRM vendor for BI features can limit future flexibility.
Low-code/no-code platforms with integrated analytics capabilities
The increasing sophistication of low-code/no-code platforms, often incorporating robust analytics and reporting features, presents a significant threat of substitution. These platforms empower business users to build custom dashboards and perform analytical tasks without requiring deep technical expertise, potentially bypassing traditional business intelligence (BI) solutions.
For instance, platforms like Microsoft Power BI, which offers low-code capabilities, saw its user base expand significantly, indicating a growing adoption for self-service analytics. This trend democratizes data analysis, allowing departments to generate insights independently. In 2024, the low-code development market was projected to reach over $65 billion, highlighting its rapid growth and potential to absorb demand previously met by dedicated BI tools.
- Democratization of Analytics: Low-code/no-code tools enable non-technical users to create dashboards and reports, reducing reliance on IT or specialized BI teams.
- Agility and Speed: Business units can rapidly develop analytical solutions for specific needs, bypassing longer development cycles of traditional BI implementations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: For simpler analytical requirements, these platforms can offer a more budget-friendly alternative to comprehensive BI suites.
- Integrated Functionality: Many platforms bundle data preparation, visualization, and basic analytics, providing a one-stop shop for certain use cases.
The threat of substitutes for Business Intelligence (BI) platforms is significant, primarily stemming from readily available, lower-cost alternatives. These substitutes range from familiar spreadsheet software to integrated features within existing enterprise systems and the growing capabilities of low-code/no-code platforms.
Manual data analysis using tools like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets remains a prevalent substitute, especially for smaller businesses or those with basic reporting needs. These tools are cost-effective and widely understood, making them an accessible entry point for data analysis. In 2024, businesses continue to rely on these for departmental reporting, representing a baseline alternative for many organizations.
Many ERP and CRM systems now include embedded BI features, such as Salesforce Einstein Analytics or SAP BusinessObjects. These integrated tools can satisfy fundamental reporting and dashboarding requirements, acting as a convenient and cost-effective substitute for specialized BI solutions. The global data analytics market, valued at approximately $27.3 billion in 2023, also highlights the demand for outsourced data analysis services as another substitute.
The rise of low-code/no-code platforms, which increasingly incorporate analytics and reporting, further intensifies this threat. Platforms like Microsoft Power BI enable business users to create custom dashboards, democratizing data analysis and potentially bypassing traditional BI tools. The low-code development market was projected to exceed $65 billion in 2024, underscoring its rapid expansion and impact.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | 2024 Market Relevance | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spreadsheet Software | Low cost, familiar interface, basic functionality | High adoption for departmental reporting | Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets |
| Embedded BI in ERP/CRM | Integrated, convenient, cost-effective as part of existing suite | Sufficient for basic reporting needs | Salesforce Einstein Analytics, SAP BusinessObjects |
| Outsourced Data Analysis Services | Expertise, actionable insights, bypasses software investment | Growing demand, part of a $27.3B market (2023) | Consulting firms, specialized analytics providers |
| Low-Code/No-Code Platforms | Democratizes analytics, agile development, integrated features | Rapid growth, projected $65B market (2024) | Microsoft Power BI, Tableau (with extensions) |
Entrants Threaten
Developing a sophisticated cloud-native Business Intelligence platform, akin to Domo, demands a substantial upfront capital injection. This includes considerable investment in advanced cloud infrastructure, extensive research and development for cutting-edge features, and the recruitment of highly skilled engineering and data science talent. For instance, building a comparable platform could easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars in initial development costs.
The sheer technical intricacy involved in creating such a platform presents another formidable hurdle. Successfully integrating a vast array of disparate data sources, guaranteeing seamless scalability to accommodate growing data volumes, and upholding stringent data security protocols are exceptionally complex challenges. These technical demands significantly elevate the barrier to entry, effectively deterring many aspiring new competitors, particularly smaller startups lacking the necessary resources and expertise.
The threat of new entrants in the business intelligence and data integration space is significantly mitigated by the sheer scale of data connectors Domo offers. Building a comparable ecosystem, which includes integrations with thousands of diverse data sources from cloud platforms to on-premise databases, requires substantial investment in development and ongoing maintenance. For instance, as of early 2024, Domo boasts over 1,000 pre-built connectors, a testament to years of dedicated engineering effort.
A new competitor would face the daunting task of replicating this extensive network. Without a similarly broad range of data integrations, a new platform’s utility is inherently limited, failing to provide the comprehensive, unified view of data that businesses demand. This lack of immediate connectivity creates a significant barrier, as businesses are unlikely to adopt a solution that cannot easily access their existing data infrastructure.
This extensive connectivity fosters a powerful network effect for Domo; the more data sources it connects to, the more valuable it becomes for users. A new entrant would struggle to overcome this established network, as it would take considerable time and resources to build trust and demonstrate equivalent integration capabilities. The high cost and complexity associated with developing and maintaining such a vast array of data connectors act as a formidable barrier to entry.
Domo benefits significantly from its established brand recognition and a deeply entrenched customer base. Years of consistent delivery and marketing have cultivated trust and loyalty among businesses, making it difficult for new entrants to penetrate the market. For instance, in 2024, Domo reported continued growth in its customer base, underscoring the stickiness of its existing relationships.
Newcomers must invest heavily in marketing and sales to even begin chipping away at this established loyalty. The cost of acquiring a new customer in the business intelligence and analytics software space is substantial, often requiring extensive proof-of-concept demonstrations and competitive pricing strategies to lure businesses away from familiar, proven solutions like Domo.
Regulatory compliance and data governance requirements
The escalating complexity of regulatory compliance, particularly concerning data privacy like GDPR and CCPA, significantly elevates the barrier to entry for new players. New entrants must navigate a labyrinth of evolving standards, demanding substantial investment in legal counsel and sophisticated technical infrastructure to ensure adherence. This compliance hurdle is a formidable deterrent, requiring deep expertise and considerable financial resources from any aspiring competitor.
For instance, in 2024, the global spending on cybersecurity and data privacy compliance is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, a figure that will undoubtedly continue to climb. New entrants must factor in these substantial costs for legal reviews, data protection officers, and secure system development.
- High initial investment in legal and technical expertise for compliance.
- Need to adapt to diverse and evolving data privacy regulations globally.
- Significant ongoing costs associated with maintaining regulatory adherence.
- Risk of substantial fines and reputational damage for non-compliance.
Talent acquisition and retention challenges
The threat of new entrants in the Business Intelligence (BI) platform market is significantly amplified by the intense competition for specialized talent. Developing, maintaining, and supporting a sophisticated BI platform requires a deep bench of expertise in areas like data engineering, AI/ML, and cloud architecture. For instance, in 2024, the demand for skilled data scientists and engineers continued to outstrip supply, with reported salary increases of up to 15% for in-demand roles.
New players entering the BI space must contend with established companies that already possess these critical human resources. Startups, in particular, face the daunting task of attracting top-tier engineers and analysts away from more secure, well-funded organizations. This talent acquisition hurdle can translate into substantial recruitment costs and extended development timelines, potentially delaying or even preventing market entry.
The human capital challenge directly impacts a new entrant's ability to innovate and scale. Without the right people, a new BI platform may struggle to deliver the advanced features and reliable performance that customers expect. This can create a significant barrier, as potential customers may be hesitant to adopt solutions from companies perceived as lacking the necessary technical prowess.
- High Demand for Specialized Skills: Expertise in data science, AI/ML, and cloud computing is crucial for BI platform development.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: New entrants face significant expenses to attract skilled professionals in a competitive market.
- Impact on Innovation: Difficulty in securing talent can hinder a new company's ability to develop and launch advanced BI solutions.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Established firms with existing talent pools possess an inherent advantage in attracting and retaining key personnel.
The threat of new entrants into the Business Intelligence (BI) platform market is considerably low due to the immense capital required for development and infrastructure. Building a robust cloud-native BI solution like Domo involves substantial upfront investment in advanced cloud services, extensive research and development for cutting-edge features, and the acquisition of highly skilled engineering and data science talent. For instance, initial development costs for a comparable platform could easily reach hundreds of millions of dollars.
The technical complexity of creating such a platform is another significant barrier. Integrating thousands of diverse data sources, ensuring seamless scalability, and maintaining stringent data security protocols are exceptionally challenging tasks. These technical demands deter many potential competitors, especially smaller startups lacking the necessary resources and expertise.
Domo's extensive network of over 1,000 pre-built data connectors, a result of years of engineering effort, creates a powerful network effect. New entrants would struggle to replicate this breadth of integration, as businesses are unlikely to adopt solutions that cannot easily access their existing data infrastructure. This lack of immediate connectivity significantly limits a new platform's utility and presents a formidable barrier.
Established brand recognition and a loyal customer base further mitigate the threat of new entrants. Domo's consistent delivery and marketing efforts have cultivated trust, making it difficult for newcomers to penetrate the market. In 2024, Domo continued to grow its customer base, highlighting the stickiness of its existing relationships and the substantial investment required in marketing and sales for new players to gain traction.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built on a foundation of robust data, drawing from financial statements, market research reports, and industry expert interviews to accurately assess competitive intensity.