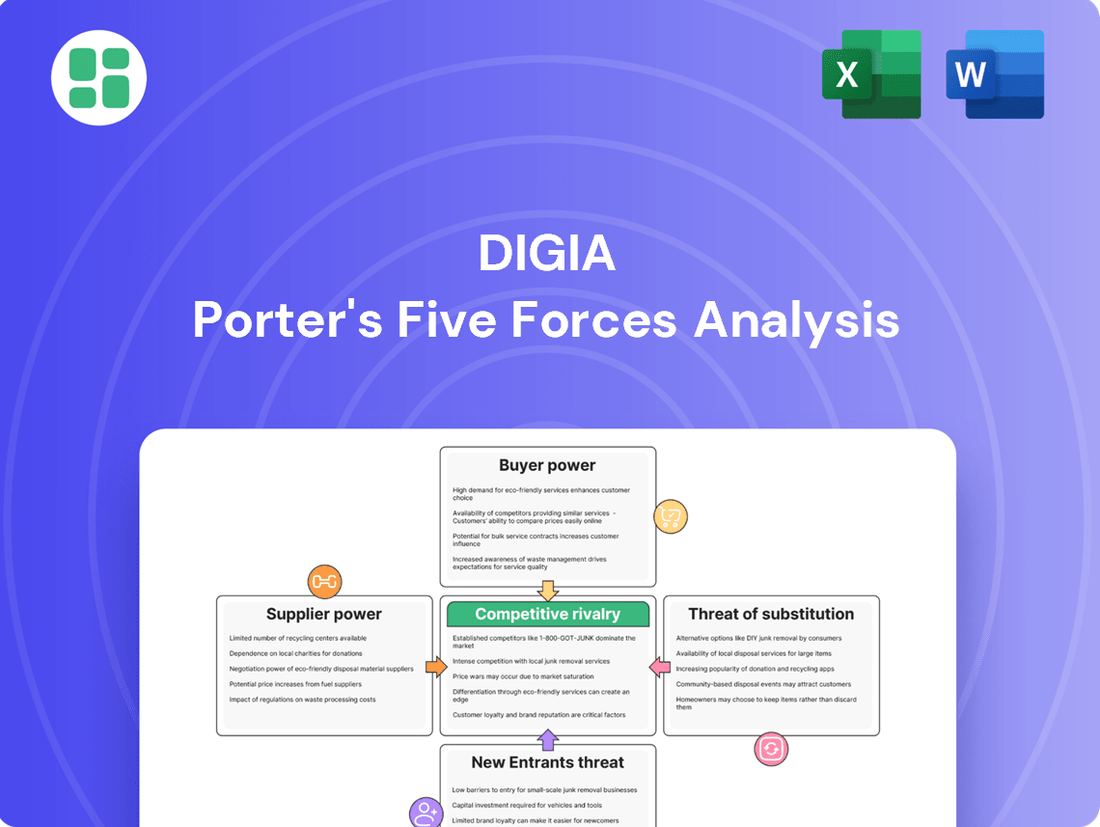
Digia Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Digia Bundle
Digia's competitive landscape is shaped by several key forces, including the bargaining power of its buyers and the intensity of rivalry within the IT services sector. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Digia’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of Digia's suppliers significantly influences their bargaining power. If Digia relies on a limited number of providers for critical software components or specialized IT services, these suppliers can exert greater influence over pricing and terms. For instance, a shortage of skilled cloud engineers from a few key providers could directly impact Digia's project delivery timelines and costs.
In 2024, the IT services sector continued to see consolidation, meaning fewer, larger players in certain specialized areas. This trend can amplify supplier power, as Digia might have fewer alternative sources for essential technologies or expertise. For example, if a major cloud provider increases its pricing, Digia has limited options to switch without incurring substantial costs and disruption.
High switching costs for Digia significantly bolster the bargaining power of its suppliers. If it proves time-consuming and costly for Digia to move from one software platform, cloud service provider, or even a specialized talent pool to another, suppliers can leverage this dependency. For instance, if Digia's core operations are deeply embedded with proprietary technologies from a specific vendor, or if there are substantial integration costs involved in switching, the supplier gains considerable leverage.
The availability of substitute inputs significantly impacts supplier power for companies like Digia. If Digia can readily source its required components, software licenses, or specialized talent from multiple vendors, it reduces the leverage any single supplier holds. For instance, in 2024, the global IT services market saw increased competition among cloud service providers, offering Digia more options for its infrastructure needs.
Uniqueness of supplier offerings
Suppliers offering highly specialized or patented technologies and services possess significant leverage. For Digia, this could manifest through exclusive access to niche AI algorithms or unique cybersecurity solutions that are difficult for competitors to replicate. If these critical inputs are not readily available from alternative sources, suppliers can command higher prices and dictate more favorable terms.
The bargaining power of suppliers is amplified when their offerings are unique and not easily substituted. For instance, if a supplier provides a proprietary software component essential for Digia's core service delivery, and no other vendor offers a comparable solution, that supplier's influence increases substantially. This dependence can lead to higher costs or potential disruptions if the supplier decides to alter their terms.
- Specialized Offerings: Suppliers providing unique AI algorithms or patented cybersecurity solutions gain power.
- Critical Inputs: If these offerings are essential and hard to replace, supplier leverage grows.
- Limited Substitutes: The absence of alternative providers for critical components strengthens supplier bargaining power.
Threat of forward integration by suppliers
The threat of suppliers moving into Digia's business space, known as forward integration, can significantly boost their leverage. Imagine a critical software component provider deciding to offer their own digital transformation consulting services directly to Digia's clients.
This scenario would force Digia to be more accommodating with its suppliers to prevent losing business. For instance, if a major cloud infrastructure provider, which Digia relies on, were to launch its own application development platform, it could directly compete for Digia's customer base.
This potential competition from suppliers is a key factor in assessing their bargaining power.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers can become competitors by offering services directly to Digia's customers.
- Impact on Digia: This forces Digia to maintain favorable terms and relationships with its suppliers.
- Example Scenario: A cloud provider launching its own application development platform could directly challenge Digia's market position.
Digia's suppliers wield significant bargaining power when their offerings are specialized and difficult for Digia to substitute. This is particularly true for providers of niche software components or highly sought-after IT talent. For example, in 2024, the demand for specialized AI and cloud security expertise remained exceptionally high, giving leading providers considerable leverage over pricing and contract terms.
The concentration of suppliers in specific technology areas also amplifies their power. If Digia relies on a few key vendors for critical infrastructure or development tools, these suppliers can dictate terms more effectively. The ongoing consolidation within the IT services sector in 2024 meant that for certain specialized services, Digia had fewer alternative providers to choose from, increasing the bargaining power of those remaining. This can lead to higher costs for Digia, as seen in increased licensing fees for proprietary software or elevated rates for specialized consulting services.
High switching costs further empower Digia's suppliers. When migrating to a new system or provider involves substantial investment in time, resources, and potential operational disruption, Digia is incentivized to maintain existing supplier relationships, even if terms are less favorable. This can be especially pronounced with deeply integrated software solutions or long-term cloud service agreements, where the cost of transition can outweigh the benefits of seeking a new supplier.
| Factor | Impact on Digia's Supplier Bargaining Power | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High if few suppliers for critical inputs | Increased due to IT sector consolidation |
| Switching Costs | High if integration is complex and costly | Significant for proprietary software and cloud platforms |
| Uniqueness of Offering | High if inputs are specialized and non-substitutable | Elevated for AI, cybersecurity, and niche cloud services |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Moderate to High if suppliers can enter Digia's market | Potential concern as tech giants expand service offerings |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape for Digia, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual representation of all five forces, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of Digia's customers is heavily shaped by how concentrated and large they are. If a few major clients, like large public sector entities or significant corporations, account for a big chunk of Digia's income, they can exert considerable influence. For instance, if a single client represented over 10% of Digia's revenue in 2023, their ability to negotiate terms would be substantial.
The availability of numerous alternative software and service providers significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. When clients can readily find comparable digital transformation, business platform, or data and analytics solutions elsewhere, they gain leverage. This ease of switching puts pressure on Digia to maintain competitive pricing and favorable service terms to retain its customer base.
For instance, in 2024, the IT services market is highly fragmented, with many global and regional players offering similar capabilities. A customer seeking cloud migration services, for example, might have dozens of options, from large multinational corporations to specialized boutique firms. This competitive landscape directly impacts Digia's ability to dictate terms and pricing.
Customer switching costs significantly impact their bargaining power. If it's easy and cheap for clients to move their digital services or data analytics projects away from Digia to a competitor, they can push for better pricing or terms. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a business to migrate its cloud infrastructure was estimated to be between $1,000 and $5,000, though this can vary greatly depending on complexity.
Digia's ability to increase these switching costs, perhaps through deeper integration of its proprietary systems or by offering bundled services that are harder to disentangle, would therefore reduce customer bargaining power. Conversely, if Digia's solutions are easily replaceable with minimal effort or expense for the client, customers hold more leverage.
Price sensitivity of customers
The price sensitivity of Digia's customers significantly influences their bargaining power. Public sector clients, often bound by stringent budget limitations, and large enterprises focused on cost optimization, tend to be more responsive to pricing variations. This makes them potent negotiators when seeking to reduce the cost of Digia's services.
When Digia's offerings are viewed as interchangeable or standard solutions rather than distinct, value-added services, customer price sensitivity escalates. This perception can lead to increased pressure on Digia to lower prices, thereby enhancing the bargaining power of these customers.
- Price Sensitivity Drivers: Digia's customer base, particularly public sector entities and large corporations, exhibits a notable sensitivity to price due to budget constraints and cost-optimization initiatives.
- Commoditization Risk: If Digia's services are perceived as commodities, customers will have greater leverage to demand lower prices, directly impacting Digia's pricing power.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the IT services market continued to see intense competition, which generally fuels customer demand for competitive pricing, further amplifying customer bargaining power in segments where Digia's offerings are not highly differentiated.
Threat of backward integration by customers
The threat of customers developing their own in-house digital capabilities, essentially backward integration, significantly enhances their bargaining power against Digia. If a client possesses the necessary resources and technical expertise, they can independently create or manage their digital solutions. This capability allows them to reduce their dependence on external providers like Digia.
This leverage can be directly applied during contract negotiations. For instance, a large enterprise client might possess a strong internal IT department capable of handling custom software development or platform management. In 2024, a trend observed across various industries is the increasing investment by large corporations in building out their internal digital transformation teams, aiming to gain more control over their technology stack and reduce outsourcing costs.
- Increased Customer Leverage: Customers with in-house digital development capabilities can negotiate more favorable terms with Digia.
- Reduced Reliance: The ability to build solutions internally lessens a customer's dependence on Digia's services.
- Industry Trend: Many large organizations are bolstering their internal digital expertise to manage technology more autonomously.
- Cost Control: Backward integration can be a strategy for customers to potentially lower their overall technology expenditure.
The bargaining power of Digia's customers is influenced by the concentration of its client base and the size of individual clients. If a few large clients represent a significant portion of Digia's revenue, they can negotiate more aggressively. For example, if a single client accounted for over 10% of Digia's revenue in 2023, their leverage would be substantial.
The availability of numerous alternative software and service providers significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. When clients can easily find comparable digital transformation, business platform, or data and analytics solutions elsewhere, they gain leverage. This ease of switching puts pressure on Digia to maintain competitive pricing and favorable service terms to retain its customer base.
Customer switching costs also play a crucial role. If it's easy and inexpensive for clients to move their digital services or data analytics projects away from Digia to a competitor, they can push for better pricing or terms. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a business to migrate its cloud infrastructure was estimated to be between $1,000 and $5,000, though this can vary greatly depending on complexity.
The price sensitivity of Digia's customers, particularly public sector entities and large enterprises focused on cost optimization, significantly influences their bargaining power. When Digia's offerings are perceived as interchangeable, customers will have greater leverage to demand lower prices, directly impacting Digia's pricing power.
What You See Is What You Get
Digia Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Digia Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive pressures within its industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive instantly upon purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You can confidently download and utilize this comprehensive analysis immediately, empowering your strategic decision-making without delay.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Finnish software and services market, especially within digital transformation and business solutions, is populated by a substantial number of domestic and international players. This dense competitive landscape means Digia is constantly navigating a crowded field.
The intensity of this rivalry is considerable, driven by companies aggressively pursuing market share. This often translates into price wars, heightened marketing expenditures, and a relentless pace of innovation as firms strive to differentiate themselves and capture customer attention.
Digia contends with a dual threat: specialized niche providers offering focused expertise and larger, more diversified IT service conglomerates that can leverage broader resources and client relationships. For instance, in 2023, the global IT services market was valued at over $1.3 trillion, indicating the sheer scale of competition Digia operates within.
The digital services, business platforms, and data analytics market is experiencing robust growth, which significantly influences competitive rivalry. For instance, the global digital transformation market was projected to reach $1.3 trillion in 2024, up from $1.1 trillion in 2023, indicating a healthy expansion rate. This rapid growth allows companies like Digia to pursue expansion by capturing new opportunities rather than solely focusing on taking market share from existing competitors, thereby tempering the intensity of direct clashes.
In contrast, if this sector were to experience slower growth or enter a mature phase, the competitive landscape would likely intensify. In such scenarios, companies would be compelled to engage in more aggressive strategies, such as price wars or heightened marketing efforts, to gain even marginal increases in their market position. This shift transforms the market into a zero-sum game where one company's gain is another's loss, amplifying competitive pressures.
Digia's competitive rivalry is significantly shaped by the degree to which its digital solutions and services stand out from those offered by competitors. When offerings are perceived as similar or commoditized, the battle often escalates to price, putting pressure on margins.
However, Digia's ability to differentiate through its specialized expertise, unique development methodologies, or a sharp focus on particular industry verticals can effectively lessen this direct price competition. For instance, if Digia can showcase a proven track record in AI-driven customer analytics for the retail sector, this specialized value proposition can command a premium and reduce the impact of rivals offering more generic software development.
Exit barriers for competitors
High exit barriers in the software and services sector, including Digia's operational space, can significantly fuel competitive rivalry. When companies find it costly or challenging to exit the market, perhaps due to substantial investments in specialized technology, long-term customer commitments, or significant employee severance packages, they may persist in competing aggressively even when facing diminished profitability. This scenario often leads to sustained market overcapacity and can result in price wars as companies fight to maintain market share.
For instance, in the broader IT services industry, the cost of retraining or redeploying specialized technical talent, coupled with the sunk costs of proprietary software development or infrastructure, can create substantial hurdles to exiting. This can keep less efficient or unprofitable players in the market longer than they might otherwise remain, intensifying the competitive landscape for companies like Digia.
- High Capital Investment: Significant upfront investment in specialized software development tools, cloud infrastructure, and R&D creates a high cost of exit.
- Long-Term Contracts: Many software and service providers operate on multi-year contracts, making it difficult to disengage from existing customer relationships without incurring penalties or reputational damage.
- Specialized Workforce: The need for highly skilled and specialized personnel in areas like AI, cybersecurity, and cloud computing means that layoffs or redeployments can be costly and complex.
- Brand Reputation and Goodwill: Companies invest heavily in building brand trust; exiting a market can damage this reputation, impacting future ventures.
Diversity of competitors
Digia's competitive landscape is characterized by a wide array of players, from niche local Finnish IT specialists to expansive Nordic IT conglomerates and global consulting powerhouses. This heterogeneity in origins, strategic focuses, and ultimate business objectives means rivalry can manifest in many unpredictable ways. For instance, a local Finnish firm might compete intensely on price for specific services, while a global giant could leverage its broad capabilities and brand recognition for larger, more complex projects.
The varied strategic approaches among these competitors significantly influence the intensity and nature of rivalry. Some may focus on deep specialization in particular technologies or industries, offering highly tailored solutions. Others might pursue a broader, more integrated service model, aiming to be a one-stop shop for clients' digital transformation needs. This strategic divergence means Digia must constantly adapt its own offerings and market positioning to effectively counter different competitive threats.
The diverse goals of these competitors further complicate the competitive dynamic. Local players might prioritize market share within Finland, while Nordic firms may aim for regional dominance, and global entities could be focused on specific high-value contracts or expanding their footprint in key European markets. For example, in 2024, the IT services market in Finland saw continued consolidation, with some smaller firms being acquired by larger Nordic players seeking to expand their service portfolios, while global consultancies continued to bid aggressively on large-scale digital transformation projects.
- Local Specialists: Often possess deep understanding of Finnish market nuances and specific industry needs, leading to highly customized solutions.
- Nordic IT Firms: Benefit from broader regional reach and often a wider range of integrated services, competing on scale and comprehensive offerings.
- Global Consulting Giants: Leverage extensive resources, established methodologies, and global client networks, often targeting large, complex, and high-value projects.
- Strategic Divergence: Competitors may focus on price, specialization, breadth of services, or geographic reach, creating a multi-faceted competitive environment.
Competitive rivalry within Digia's market is intense, fueled by a crowded field of domestic and international players vying for market share. This competition often leads to price wars and increased marketing spend as companies strive to stand out. The global IT services market, valued at over $1.3 trillion in 2023, underscores the sheer scale of this rivalry.
Digia faces competition from both specialized niche providers and large, diversified IT conglomerates. The digital services market's rapid growth, with the global digital transformation market projected to reach $1.3 trillion in 2024, offers opportunities for expansion rather than solely direct market share battles, somewhat tempering immediate rivalry intensity.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Competitive Impact on Digia |
|---|---|---|
| Local Specialists | Deep Finnish market understanding, niche expertise | Targeted competition on specific services, price sensitivity |
| Nordic IT Firms | Broader regional reach, integrated services | Competition on scale, comprehensive offerings, potentially larger projects |
| Global Consulting Giants | Extensive resources, global networks, established methodologies | Competition on large, complex, high-value projects, brand recognition |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Digia's digital services, business platforms, and data analytics solutions is present. Customers can achieve similar outcomes by opting for generic, off-the-shelf software, readily available open-source alternatives, or simpler cloud-based tools. These options can bypass the need for Digia's more comprehensive custom development and integration services.
The attractiveness of substitute offerings hinges on their price-performance trade-off relative to Digia's solutions. If alternatives provide similar functionality at a lower price point, or enhanced performance for a comparable cost, the threat of substitution intensifies.
Customers frequently assess if less complex, more affordable options adequately fulfill their fundamental requirements. For instance, in the software sector, open-source alternatives can present a compelling price-performance advantage for businesses with less intricate needs, potentially diverting market share from premium providers like Digia.
Customer willingness to switch to alternatives for Digia's software solutions is a key factor. If clients are hesitant to adopt new technologies or have deeply integrated existing systems, they are less likely to seek substitutes.
For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of enterprise software users, estimated to be around 60%, expressed concerns about the disruption and costs associated with migrating from established platforms, indicating a lower propensity to substitute.
Conversely, companies actively pursuing digital transformation and cost optimization, which was a prevalent trend in 2024 with many businesses aiming to reduce operational expenses by up to 15%, might be more open to exploring alternative solutions that offer greater efficiency or lower pricing.
Impact of technological advancements
Rapid technological advancements present a significant threat of substitutes for Digia's services. Emerging AI tools and low-code/no-code platforms are increasingly capable of automating development tasks, potentially reducing the demand for Digia's traditional custom software development and integration expertise. For instance, the global low-code development platform market was valued at approximately $15 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a rising availability of faster, often more cost-effective alternatives.
These new technologies can offer functionalities that directly compete with Digia's offerings, blurring the lines between what requires bespoke development and what can be achieved with off-the-shelf or easily configurable solutions. Companies might opt for these advanced platforms to build applications more quickly and with fewer specialized resources, thereby bypassing the need for extensive custom coding and integration services that Digia provides. This shift necessitates that Digia continuously adapts its value proposition to highlight its unique strengths in complex integration, strategic consulting, and highly specialized development needs.
- AI-driven development tools offer faster prototyping and code generation, potentially reducing reliance on traditional development cycles.
- Low-code/no-code platforms empower citizen developers, democratizing application creation and lowering the barrier to entry for digital solutions.
- Integrated SaaS solutions consolidate multiple functionalities, reducing the need for complex, custom-built integrations.
- The market for these alternative solutions is expanding rapidly, with significant investment flowing into AI and automation technologies.
Ease of switching to substitutes
The ease with which customers can switch to alternative solutions significantly influences the threat of substitutes. When transitioning to a substitute involves minimal disruption, straightforward data migration, or little to no additional training, customers are naturally more inclined to explore these alternatives. Digia's strategic focus on building deeply integrated solutions and fostering strong client relationships directly counteracts this ease of switching, making it more challenging for customers to move away.
For instance, in the software industry, high switching costs can stem from proprietary data formats, extensive customization, or the need for specialized user training. Companies that offer integrated ecosystems or provide significant ongoing support often create a 'stickiness' that deters customers from seeking alternatives. Digia's approach aims to embed its services so deeply within a client's operational framework that the cost and effort of replacement become prohibitive.
In 2024, the average cost for a business to migrate its core IT systems was estimated to be in the millions of dollars, with significant downtime and potential data loss being major deterrents. This highlights the importance of high switching costs in maintaining customer loyalty. Digia's ability to demonstrate a clear return on investment and seamless integration into existing workflows is crucial in mitigating the threat of substitutes.
Consider these factors influencing the ease of switching:
- Switching Costs: The financial and non-financial expenses incurred when changing from one supplier or product to another.
- Integration Depth: How extensively a solution is embedded within a client's existing IT infrastructure and business processes.
- Customer Loyalty Programs: Initiatives designed to reward long-term customers and increase the perceived value of staying with a provider.
- Data Portability: The ease with which customer data can be extracted and transferred to a new system or provider.
The threat of substitutes for Digia's digital services is shaped by the availability and attractiveness of alternative solutions. Generic software, open-source options, and simpler cloud tools can fulfill similar needs, potentially bypassing Digia's custom development. The price-performance ratio of these substitutes is a key driver; if they offer comparable functionality at a lower cost, the threat increases.
Emerging technologies like AI-driven development and low-code/no-code platforms are rapidly advancing, automating tasks previously requiring specialized expertise. For instance, the global low-code market was valued at approximately $15 billion in 2023, highlighting the growing accessibility of faster, more cost-effective alternatives that can reduce demand for traditional custom development.
Customer willingness to switch is influenced by switching costs, integration depth, and data portability. In 2024, migrating core IT systems cost businesses millions, with downtime and data loss acting as significant deterrents, underscoring the importance of high switching costs in retaining clients. Digia's focus on deep integration and strong client relationships aims to increase these costs, thereby mitigating the threat of substitutes.
| Factor | Impact on Threat of Substitutes | Example for Digia |
|---|---|---|
| Price-Performance of Substitutes | High price-performance ratio intensifies threat. | Open-source software offering core functionalities at a fraction of the cost. |
| Technological Advancements | New technologies can directly compete with existing services. | AI coding assistants reducing reliance on custom code development. |
| Switching Costs | High switching costs reduce customer inclination to substitute. | Deep integration of Digia's platform into a client's existing ERP system. |
| Ease of Switching | Minimal disruption and training lowers the barrier to adoption of substitutes. | A competitor offering a cloud-based solution with a simple drag-and-drop interface. |
Entrants Threaten
The capital required to launch a competitive software and services firm, particularly one dealing with intricate digital solutions and business platforms like Digia, can be quite significant. This investment covers essential areas such as attracting and retaining top talent, building robust technology infrastructure, and establishing strong marketing and sales operations, all of which serve as considerable deterrents for potential new players.
Digia, like many established software and IT service providers, benefits significantly from economies of scale. This means that as Digia's operations grow, its per-unit costs for development, support, and sales tend to decrease, making it harder for smaller, newer companies to offer competitive pricing. For instance, in 2024, major IT service providers often reported substantial R&D budgets, in the hundreds of millions of euros, which new entrants would struggle to match, impacting their ability to innovate and scale efficiently.
Furthermore, economies of scope allow Digia to leverage its existing infrastructure and expertise across a wider range of services. Offering integrated solutions, from custom software development to cloud migration and maintenance, creates a more comprehensive value proposition for clients. A new entrant focusing on a niche area might find it challenging to replicate this breadth of offering, as building the necessary capabilities and client relationships across multiple service lines requires considerable time and investment.
Digia benefits from deeply ingrained brand loyalty and a robust reputation forged through years of delivering successful digital transformation projects. This established trust is a significant barrier for newcomers aiming to penetrate the market, particularly when clients prioritize reliability in sensitive areas like data security and complex system integrations.
Access to distribution channels and talent
New entrants often face significant hurdles in securing access to critical distribution channels and specialized talent within the digital services sector. Digia, for instance, benefits from established partnerships and a deep network of clients, which are challenging for newcomers to penetrate.
The digital industry demands a highly skilled workforce, particularly in areas like data analytics and platform development. New companies may find it difficult to attract and retain top talent, as established players like Digia often offer competitive compensation and career advancement opportunities. This talent gap can significantly slow down a new entrant's ability to scale and compete effectively.
Consider these specific challenges for new entrants:
- Distribution Channel Access: New companies may struggle to get their digital solutions onto existing platforms or into the hands of target customers who are already loyal to established providers.
- Client Network Replication: Replicating the extensive client relationships and trust that a company like Digia has built over years is a formidable task for any new entrant.
- Talent Acquisition: The competition for skilled professionals in areas such as AI, cloud computing, and cybersecurity is fierce, with established firms often having an advantage in recruitment and retention.
- Brand Recognition and Trust: New entrants must invest heavily in building brand awareness and trust, which are essential for gaining traction in a market where customers often prefer proven solutions.
Government policy and regulatory hurdles
Government policies and regulatory hurdles can significantly impact the threat of new entrants for companies like Digia, especially when they operate in sectors involving public services or sensitive data. Compliance with stringent regulations, obtaining necessary certifications, and navigating complex procurement processes can act as substantial barriers.
For instance, in the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict rules on data handling, requiring new entrants to invest heavily in compliance infrastructure. Similarly, in Finland, where Digia is a prominent player, public sector IT procurement often favors established vendors with proven track records and specific certifications, making it difficult for newcomers to break in. In 2023, the Finnish government continued to emphasize cybersecurity standards for all public sector IT projects, adding another layer of complexity for potential entrants.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants must budget for legal counsel, compliance audits, and system modifications to meet standards like GDPR or national data security laws.
- Certification Requirements: Obtaining certifications such as ISO 27001 for information security or specific government-approved security clearances can be a lengthy and costly process, often favoring larger, established firms.
- Public Sector Procurement Processes: Government tenders can be complex, lengthy, and require extensive documentation and pre-qualification, which can deter smaller or less experienced companies from bidding.
- Impact on Market Entry: These hurdles collectively favor incumbent players who have already invested in and navigated these requirements, thus reducing the immediate threat of new, unproven competitors.
The threat of new entrants into Digia's market is moderately low due to substantial capital requirements for technology, talent, and marketing. Established players benefit from economies of scale and scope, making it difficult for newcomers to match pricing and service breadth. Furthermore, strong brand loyalty and established client networks act as significant barriers.
New entrants face challenges in accessing distribution channels and acquiring specialized talent, as seen in the competitive IT services sector where R&D budgets in 2024 reached hundreds of millions of euros. Replicating Digia's client relationships and brand trust requires considerable time and investment, further deterring potential competitors.
Regulatory compliance, such as GDPR, and specific certifications like ISO 27001, impose significant costs and time delays for new companies. In Finland, public sector IT procurement often favors established vendors with proven track records and security clearances, as emphasized in government standards throughout 2023, thus reducing the immediate threat from unproven competitors.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and reputable financial news outlets. This comprehensive approach ensures a thorough understanding of competitive dynamics.