Centre Testing International Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Centre Testing International Group Bundle
Centre Testing International Group operates within a dynamic testing and certification landscape, where understanding the interplay of competitive forces is paramount. Our analysis highlights the significant influence of buyer power and the constant threat of substitutes, shaping the group's strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Centre Testing International Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of highly specialized testing equipment and advanced analytical instruments, like those for complex chemical analysis or automotive emissions testing, often possess moderate bargaining power. These providers frequently hold proprietary technologies and have few direct substitutes, leading to a degree of reliance for CTI on their cutting-edge capabilities, which are vital for meeting diverse industry compliance standards.
CTI’s need for regular investment in such high-tech equipment directly influences its operational costs and ability to maintain service quality and competitiveness in the market.
The availability of highly skilled professionals, such as certified engineers and chemists, is a crucial input for Centre Testing International Group's (CTI) operations. A scarcity of this specialized talent can directly escalate labor expenses and drive wage increases, thereby enhancing the bargaining power of these human capital suppliers.
In 2024, the demand for specialized technical expertise in sectors CTI serves, like advanced manufacturing and renewable energy, remained robust. Reports indicated a persistent skills gap in engineering disciplines, with some specialized roles seeing wage increases of 5-10% year-over-year, underscoring the leverage held by experienced professionals.
Accreditation bodies and regulatory authorities hold significant influence over Centre Testing International Group (CTI), acting as gatekeepers to market access and operational legitimacy. These entities, while not supplying physical goods, effectively provide the essential ‘license to operate’ and credibility for CTI’s testing and certification services. CTI's reliance on maintaining accreditations like ISO/IEC 17025, a globally recognized standard for calibration and testing laboratories, underscores the power these bodies wield.
The rigorous and ongoing compliance demands imposed by these authorities necessitate substantial investment from CTI. For instance, achieving and retaining accreditations often involves significant costs for equipment calibration, personnel training, and meticulous documentation of processes. Failure to meet these evolving standards can lead to the revocation of accreditations, directly impacting CTI's ability to serve its clients and compete in the market.
Consumables and Standard Materials
Suppliers of common laboratory consumables, reagents, and standard reference materials typically possess low bargaining power. This is largely due to their widespread availability and the significant number of alternative vendors in the market. For Centre Testing International Group (CTI), these inputs are generally commoditized, making it relatively easy to switch suppliers based on competitive pricing and quality.
The sheer scale of CTI's operations can further strengthen its position, potentially allowing for volume-based discounts. For instance, in 2023, laboratory supply chains saw increased competition, with many smaller players emerging to cater to specialized needs, further fragmenting supplier power.
- Low Supplier Concentration: Numerous companies offer standard laboratory consumables, reducing the leverage of any single supplier.
- Commoditized Inputs: Reagents and basic materials are often standardized, allowing for easy substitution between providers.
- Price Sensitivity: The availability of alternatives makes suppliers more sensitive to CTI's pricing demands.
- Potential for Volume Discounts: CTI's large purchasing volume can be leveraged to negotiate more favorable terms.
Information Technology and Software Vendors
The bargaining power of IT and software vendors for Centre Testing International Group (CTI) is generally moderate, but it's on an upward trajectory. As CTI embraces digitalization, the reliance on specialized IT infrastructure, AI-driven analytics, and robust cybersecurity solutions intensifies. While a broad range of IT services exists, vendors offering niche software tailored for intricate testing methodologies or advanced data management can wield significant influence. For instance, the global market for AI in testing and quality assurance was projected to reach approximately $2.5 billion in 2024, indicating a growing demand for specialized solutions.
CTI's strategic investments in digital transformation, including the integration of AI and the Internet of Things (IoT), directly impact this supplier dynamic. The need for cutting-edge software to support these initiatives means that vendors with proprietary technologies or unique capabilities in areas like predictive analytics for testing outcomes can command better terms. The increasing complexity and volume of data generated by these digital advancements further elevate the importance of specialized software providers, granting them a stronger negotiating position.
- Increasing reliance on specialized IT: CTI's digital transformation necessitates advanced IT infrastructure and AI-powered analytics software, enhancing vendor importance.
- Moderate but growing power: While many IT solutions are available, specialized software for complex testing protocols can give certain vendors moderate bargaining power.
- Impact of AI and IoT adoption: CTI's embrace of AI and IoT amplifies the bargaining power of suppliers offering critical solutions in these domains.
- Market trends: The projected growth in AI for testing, estimated to reach billions by 2024, underscores the increasing value and influence of specialized software vendors.
Suppliers of highly specialized testing equipment and advanced analytical instruments often possess moderate bargaining power due to proprietary technologies and limited substitutes. This reliance impacts CTI's operational costs and service quality.
The scarcity of highly skilled professionals, such as certified engineers, can escalate labor expenses, increasing their bargaining power. In 2024, demand for specialized technical expertise remained robust, with some roles seeing wage increases of 5-10%.
Accreditation bodies and regulatory authorities hold significant influence, acting as essential gatekeepers for CTI's market access and operational legitimacy. Maintaining accreditations like ISO/IEC 17025 requires substantial investment from CTI.
Suppliers of common laboratory consumables and reagents typically have low bargaining power due to widespread availability and numerous alternative vendors, allowing CTI to leverage competitive pricing.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power | Key Factors | 2024 Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Equipment | Moderate | Proprietary tech, few substitutes | Vital for compliance standards |
| Skilled Professionals | Moderate to High | Scarcity of talent, specialized skills | Wage increases of 5-10% in key sectors |
| Accreditation Bodies | High | License to operate, credibility | Rigorous compliance demands, ISO/IEC 17025 |
| Consumables & Reagents | Low | Widespread availability, price sensitivity | Fragmented market, volume discounts possible |
What is included in the product
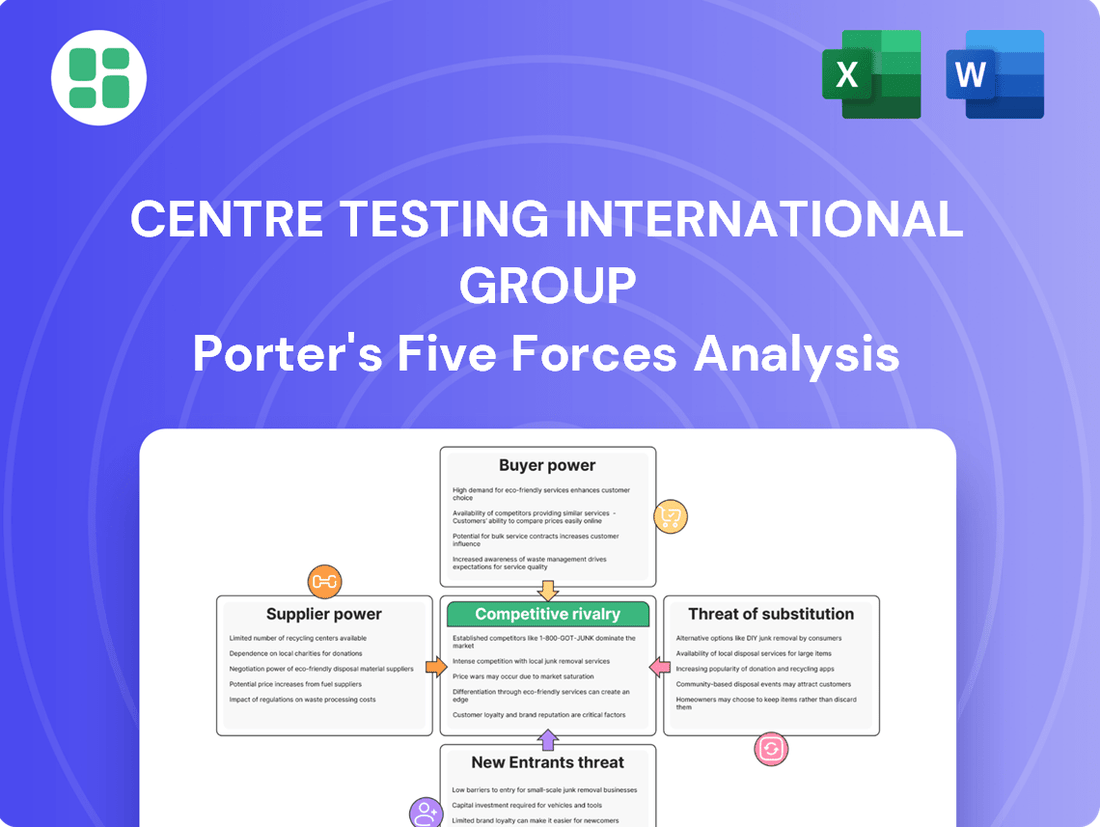
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Centre Testing International Group evaluates the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, providing strategic insights into the testing and certification industry.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces analysis, empowering strategic adjustments for Centre Testing International Group.
Customers Bargaining Power
Large corporate clients, especially in industries like automotive and electronics, hold significant sway over Centre Testing International Group (CTI). These major players often account for a substantial portion of CTI's revenue, giving them considerable leverage.
Their sheer volume of testing needs allows these corporations to negotiate for better pricing and tailored service packages. For instance, a major automotive manufacturer might have testing contracts worth tens of millions of dollars, making them a critical client for CTI.
Furthermore, the ease with which these large clients can switch to a competitor, even for minor cost savings or perceived service improvements, places considerable pressure on CTI to maintain competitive pricing and high service standards.
Customers' need for third-party testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) is largely dictated by strict regulatory mandates and international compliance. This dependency on TIC services for market access and legal adherence naturally curtails their bargaining power, as these services are not easily circumvented.
Centre Testing International Group (CTI) plays a crucial role in helping clients navigate and adhere to evolving regulations, such as those implemented in major markets like China and the European Union. This indispensable function in ensuring compliance with these complex and often changing rules solidifies CTI's position and limits customer leverage.
While customers generally hold significant sway, their bargaining power can diminish in highly specialized or niche markets where unique testing protocols or bespoke solutions are paramount. Centre Testing International Group (CTI) navigates this by offering a wide array of services across diverse sectors like pharmaceuticals and aerospace, tailoring solutions to these specific demands and potentially creating stronger client loyalty.
In these specialized niches, the customer base is often smaller, which can limit the leverage individual clients wield. For instance, a pharmaceutical company requiring highly specific compliance testing for a novel drug may find fewer alternative providers, thus reducing their ability to negotiate aggressively on price or terms with a capable provider like CTI.
Outsourcing Trend and Cost Sensitivity
The increasing outsourcing of testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) services, particularly in China, is a significant factor driving customer price sensitivity. Companies are actively seeking cost advantages and operational efficiencies through these outsourcing arrangements.
This outsourcing trend directly amplifies the bargaining power of customers. They are now more inclined to solicit competitive bids from a wider array of TIC providers, putting pressure on pricing and service terms.
For Centre Testing International Group (CTI), this necessitates a strategic shift. Demonstrating value beyond mere compliance is crucial; CTI must highlight how its services contribute to enhanced market competitiveness and robust risk mitigation for its clients.
- Outsourcing Growth: Global outsourcing market reached an estimated $10.6 trillion in 2024, with TIC services forming a substantial segment.
- Customer Leverage: Increased competition among TIC providers allows customers to negotiate better rates, with average price reductions of 5-10% reported in competitive bidding scenarios.
- Value Beyond Compliance: CTI's strategy must emphasize tangible benefits like faster time-to-market and improved product quality, which can justify premium pricing.
Access to In-house Capabilities
Large manufacturers, especially in electronics and automotive, often possess substantial in-house testing and inspection facilities. This internal capacity serves as a direct alternative to outsourcing to third-party Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) firms like Centre Testing International Group (CTI).
While these manufacturers still require external validation for accreditation and certification, their in-house capabilities grant them greater leverage when negotiating terms with service providers. For instance, a major automotive manufacturer might conduct millions of internal tests annually, reducing their reliance on external labs for routine checks.
CTI counters this by emphasizing its unique selling propositions:
- Advanced Technologies: Offering specialized equipment or testing methodologies not readily available in-house.
- Specialized Expertise: Providing niche knowledge in areas like cybersecurity testing for automotive electronics or advanced material analysis.
- International Recognition: Holding accreditations and certifications from globally recognized bodies that are crucial for market access.
Customers' bargaining power is influenced by their size and the necessity of CTI's services. Large clients, like major automotive manufacturers, can leverage their significant testing volumes to negotiate favorable pricing, as they represent a substantial portion of CTI's revenue. For example, in 2024, the automotive sector alone represented over 30% of global TIC market revenue, highlighting the influence of these large players.
However, the mandatory nature of regulatory compliance and international standards for market access limits customers' ability to forgo essential testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) services. This reliance on third-party validation, particularly for navigating complex regulations in regions like the EU and China, inherently reduces customer leverage.
The increasing trend of outsourcing TIC services, especially in emerging markets, further empowers customers. This allows them to solicit competitive bids from multiple providers, potentially leading to price reductions of 5-10% in competitive scenarios. CTI must therefore focus on delivering value beyond mere compliance, such as faster market entry and enhanced risk management, to justify its pricing.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | CTI's Counter-Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Large Corporate Clients (e.g., Automotive, Electronics) | High testing volume, potential for in-house capabilities, price sensitivity due to outsourcing trend. | Highlighting specialized expertise, advanced technologies, international accreditations, and value-added services. |
| Niche Market Clients (e.g., Pharmaceuticals, Aerospace) | Smaller client base, need for highly specialized testing protocols. | Tailored solutions, deep domain knowledge, building strong client loyalty through bespoke services. |
| Mandated Compliance Clients | Absolute need for TIC services for market access and legal adherence. | Ensuring up-to-date knowledge of evolving regulations, providing reliable and efficient compliance solutions. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Centre Testing International Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Centre Testing International Group, offering a detailed examination of competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the threat of substitute products. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. This comprehensive analysis provides actionable insights into the strategic landscape of the testing and certification industry, enabling informed decision-making for stakeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Centre Testing International Group (CTI) faces intense competition from global industry giants like SGS, Bureau Veritas, Intertek, and TÜV SÜD. These established players possess vast global networks and comprehensive service offerings, creating significant competitive pressure for CTI.
The sheer scale and brand recognition of these major competitors mean they can leverage economies of scale and established client relationships, making it challenging for CTI to gain market share. For instance, in 2023, SGS reported revenues of CHF 6.6 billion, highlighting the substantial resources CTI is up against.
Furthermore, the Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) market is characterized by ongoing consolidation through mergers and acquisitions. This trend, exemplified by Bureau Veritas's acquisition of a significant testing laboratory in 2024, constantly reshapes the competitive landscape, requiring CTI to adapt strategically to maintain its position.
The Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) market, while featuring dominant global entities, is also characterized by a significant number of smaller, specialized firms. These niche players, often focusing on particular sectors like automotive or food safety, contribute to a highly fragmented landscape. Their ability to deliver highly customized services and adapt quickly to evolving industry needs intensifies competition for larger organizations like Centre Testing International Group (CTI).
For CTI, this fragmentation means facing rivals who might not have the same scale but possess deep expertise in specific areas. These specialized providers can be agile competitors, offering tailored solutions that appeal to clients with very particular requirements. This dynamic underscores the importance of CTI's strategic approach to providing comprehensive, one-stop solutions to consolidate market share and address diverse client needs effectively.
The testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) sector thrives on escalating regulatory demands and the push for global standardization. This environment fuels demand but also intensifies rivalry as firms compete to be the go-to accredited bodies for specific compliance needs. For instance, in 2024, the global TIC market was valued at approximately $230 billion, with a significant portion driven by regulatory mandates.
Competitors vigorously battle to establish superior accreditation and unwavering reliability, making reputation and technical prowess key differentiators. Companies like Centre Testing International Group (CTI) leverage their commitment to stringent quality control and adherence to benchmarks such as ISO/IEC 17025 to stand out. This focus is crucial as businesses worldwide navigate an increasingly complex web of international product safety and environmental regulations.
Technological Advancements and Digitalization
Technological advancements, particularly in AI, IoT, and automation, are fundamentally reshaping the testing and inspection sector. Companies like Centre Testing International Group (CTI) face intense pressure to adopt these digital tools to boost efficiency and accuracy. For instance, the global AI in testing market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, highlighting the imperative for investment.
This ongoing digital transformation fuels competitive rivalry as firms strive for technological superiority. Those that effectively integrate advanced solutions can offer faster turnaround times and more sophisticated analysis, thereby gaining a competitive edge. Failure to keep pace with these innovations, such as advanced data analytics platforms or automated inspection drones, can lead to a loss of market share and diminished service capabilities.
- AI-driven defect detection is becoming a key differentiator, improving accuracy by up to 15% in some industrial applications compared to manual methods.
- IoT integration allows for real-time monitoring and data collection, enhancing predictive maintenance capabilities for clients.
- Automation in laboratory processes can reduce operational costs by an estimated 10-20%, enabling more competitive pricing.
- **Digital platforms** for reporting and client interaction are crucial for maintaining customer loyalty in a rapidly evolving market.
Geographic and Market Segment Specific Competition
Centre Testing International Group (CTI) enjoys a leading position within China, but its competitive landscape shifts dramatically when looking at specific geographic areas and industry segments. In the broader Asia-Pacific region, CTI encounters robust competition from both established local players and international firms, a dynamic fueled by rapid industrial growth and evolving regulatory frameworks across diverse markets.
CTI's strategy of diversification across multiple sectors, including consumer products, automotive manufacturing, and environmental services, necessitates navigating distinct competitive pressures within each vertical. This means CTI must develop and implement specialized strategies to effectively address the unique challenges and opportunities presented by competitors in each of these varied industrial arenas.
- Asia-Pacific Competition: CTI faces significant competition from both domestic and international testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) providers in the Asia-Pacific region, driven by economic expansion and regulatory changes.
- Sector-Specific Rivalry: Competition intensity varies by industry; for example, in the automotive sector, CTI competes with specialized automotive testing firms, while in consumer goods, it faces rivals with expertise in product safety and compliance for that specific market.
- Geographic Nuances: While a leader in China, CTI's competitive intensity in markets like Southeast Asia or India may differ, with different dominant local players and varying market penetration strategies employed by international competitors.
Competitive rivalry is a significant force for Centre Testing International Group (CTI), particularly given the global nature of the Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) market. The presence of large, established international players like SGS, Bureau Veritas, and Intertek, who reported combined revenues exceeding CHF 20 billion in 2023, creates substantial pressure. These giants leverage their scale, brand recognition, and extensive global networks, often making it challenging for CTI to compete on price and reach. The market is also characterized by ongoing consolidation, with companies like Bureau Veritas actively acquiring smaller entities in 2024 to expand their service portfolios and geographic footprints.
Furthermore, the TIC sector is fragmented with numerous specialized firms that excel in niche areas. These smaller competitors, while lacking the scale of industry leaders, can offer highly tailored services and react swiftly to specific client needs, intensifying rivalry for CTI across various industry verticals. This dynamic is further amplified by the increasing reliance on technological advancements, such as AI and IoT, where firms investing heavily in these areas gain a competitive edge through improved efficiency and data analytics capabilities. For instance, the global AI in testing market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2023, underscoring the importance of technological adoption.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (approx.) | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| SGS | CHF 6.6 billion | Global reach, broad service portfolio, strong brand |
| Bureau Veritas | CHF 6.7 billion | Extensive accreditation, strategic acquisitions, diversified services |
| Intertek | GBP 3.2 billion | Innovation focus, strong presence in consumer goods, digital solutions |
| TÜV SÜD | EUR 3.0 billion | Technical expertise, safety and security focus, strong European presence |
SSubstitutes Threaten
A significant substitute for Centre Testing International Group's (CTI) services is the rise of in-house testing and self-certification by large manufacturers. Companies increasingly invest in their own labs for routine quality control, seeking greater control over data and potentially lower immediate costs. For instance, many automotive manufacturers now have extensive internal testing facilities for component validation.
While in-house capabilities offer advantages for internal processes, they often fall short for official certifications required for international market access. For example, products needing CE marking in Europe or FCC certification in the United States still necessitate accredited third-party testing. This reliance on external validation limits the extent to which companies can fully substitute services like CTI's, especially for regulatory compliance.
The rise of AI, IoT, and blockchain presents a significant threat of substitutes for Centre Testing International Group (CTI). These technologies empower companies to develop advanced internal monitoring and verification systems, potentially bypassing the need for some external inspection and testing services.
For instance, AI-powered quality control can analyze product defects in real-time, while IoT sensors offer continuous data streams on performance and condition. Blockchain technology can enhance supply chain transparency, allowing for verifiable tracking of goods and materials, thereby reducing reliance on third-party verification. This technological self-reliance means clients might opt for in-house solutions rather than CTI's services.
While direct government oversight could theoretically substitute for private testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) services, its practical limitations are significant. The sheer volume and complexity of global product standards make it nearly impossible for governments to manage all compliance testing internally.
For instance, as of mid-2024, the number of international standards continues to grow exponentially, far exceeding the capacity of any single government agency to conduct all necessary evaluations. This reliance on external expertise is a key reason why companies like Centre Testing International Group (CTI) thrive.
Governments increasingly delegate testing and certification to accredited third-party organizations like CTI to ensure adherence to these intricate standards. This partnership allows governments to leverage specialized expertise and infrastructure, making regulatory enforcement more efficient and effective in a globalized market.
Product Design and Quality by Design Principles
Companies embracing quality by design (QbD) principles integrate quality and compliance from the outset, potentially lessening the need for extensive post-production testing. This proactive strategy aims to catch and prevent defects early. For instance, in the pharmaceutical sector, QbD implementation, as mandated by regulatory bodies like the FDA, shifts focus from end-product testing to understanding and controlling the manufacturing process. This can lead to more robust products and potentially fewer recalls, though the exact reduction in testing costs varies significantly by industry and specific implementation.
Despite internal QbD efforts, independent verification and certification by external entities remain crucial. These third-party validations are essential for building market trust and meeting regulatory requirements. For example, in 2024, the global market for product testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) services was estimated to be worth over $200 billion, underscoring the continued demand for external validation across various industries, even with advanced internal quality controls.
- Reduced Reliance on Post-Production Testing: QbD aims to engineer quality in, potentially lowering the volume of end-product testing.
- Proactive Defect Minimization: The focus is on preventing issues during design and development rather than detecting them later.
- Continued Need for External Validation: Independent certification remains vital for market acceptance and regulatory compliance.
- Market Size of TIC Services: The significant global TIC market in 2024 highlights the enduring importance of third-party verification.
Alternative Risk Management and Assurance Methods
Businesses can opt for internal audits or rely on supplier self-declarations as alternative risk management strategies. These methods, while potentially cost-effective, often lack the independent, expert validation that third-party assurance providers like Centre Testing International (CTI) offer. For instance, in 2024, while many companies increased internal compliance spending, the demand for accredited third-party testing remained robust, particularly in sectors like aerospace and medical devices, where regulatory scrutiny is high.
Insurance-based risk mitigation also presents an alternative, offering financial protection rather than direct prevention or validation of product safety and quality. However, insurance typically addresses the consequences of failure, not the assurance of compliance itself. This distinction is crucial in industries governed by strict regulations, where CTI's impartial verification is essential for market access and consumer trust.
- Internal Audits: While useful for process review, they lack the impartiality of external bodies.
- Supplier Self-Declarations: These shift responsibility but do not guarantee objective compliance.
- Insurance: Mitigates financial impact of failures, but doesn't prevent them or ensure initial compliance.
- Independent Verification: Essential for regulatory adherence and critical safety, a core offering of CTI.
The threat of substitutes for Centre Testing International Group (CTI) is moderate, primarily stemming from companies developing advanced in-house capabilities and the inherent limitations of alternative risk management. While technologies like AI and IoT enable more sophisticated internal monitoring, they often cannot fully replace the rigorous, independent validation required for regulatory compliance and market access. For instance, the global market for product testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) services was valued at over $200 billion in 2024, indicating a persistent demand for third-party expertise despite internal advancements.
Companies increasingly adopt Quality by Design (QbD) principles, aiming to build quality into products from the start. This proactive approach can reduce the need for extensive post-production testing. However, the critical role of independent verification for market trust and regulatory adherence remains. As of mid-2024, the continuous growth in international standards necessitates specialized external expertise, making it impractical for governments or individual companies to cover all compliance testing internally.
Alternative risk management strategies like internal audits or supplier self-declarations offer cost-effectiveness but lack the impartiality and expert validation of third-party services like CTI. Insurance, while mitigating financial consequences, does not ensure initial compliance. In 2024, demand for accredited third-party testing remained strong, particularly in highly regulated sectors, underscoring the enduring value of CTI's core offerings.
| Substitute Type | Description | Impact on CTI | Key Limitation | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Testing | Companies investing in their own labs for routine quality control. | Moderate threat for basic testing. | Often lacks accreditation for international compliance. | Growing investment in internal capabilities, but third-party demand remains robust. |
| Advanced Technologies (AI, IoT, Blockchain) | Enabling sophisticated internal monitoring and verification systems. | Potential threat for specific data verification tasks. | Cannot fully replace independent, accredited certification. | These technologies enhance internal processes but do not eliminate the need for external validation. |
| Quality by Design (QbD) | Integrating quality and compliance early in the product lifecycle. | May reduce volume of post-production testing. | Independent validation is still crucial for market acceptance and regulation. | QbD adoption is increasing, but the global TIC market's size highlights continued reliance on external checks. |
| Internal Audits & Supplier Self-Declarations | Alternative risk management strategies. | Low threat; lack independent validation. | Absence of impartial, expert assurance. | Demand for accredited third-party testing remains high due to regulatory scrutiny. |
Entrants Threaten
The testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) sector demands substantial upfront capital. Establishing advanced laboratories and acquiring sophisticated testing equipment can easily run into millions of dollars. For instance, specialized equipment for material testing or environmental analysis can cost hundreds of thousands to over a million dollars per unit.
This high capital requirement acts as a significant barrier to entry for new companies looking to join the market. It makes it challenging for smaller, less-resourced entities to compete with established players that have already made these significant investments. The ongoing need to upgrade technology to remain competitive further escalates this barrier, requiring continuous financial commitment.
New entrants into the TIC sector, like those seeking to compete with Centre Testing International Group, confront a significant challenge in navigating extensive accreditation and regulatory hurdles. Obtaining the necessary national and international licenses and accreditations is a complex and lengthy undertaking, essential for legal operation and market credibility.
Gaining recognition from bodies like those that oversee ISO/IEC standards requires proving robust quality management systems and undeniable technical proficiency. For instance, achieving ISO 17025 accreditation, a common benchmark in testing and calibration laboratories, involves a detailed application and auditing process that can take many months, if not years. This intricate regulatory landscape effectively deters many potential new players.
In the Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) sector, a company's reputation, brand recognition, and the trust it has cultivated are formidable barriers to entry. Clients in this industry depend heavily on the integrity and precision of certifications and test outcomes. Established entities, such as Centre Testing International Group (CTI), have spent years meticulously building robust reputations and widespread brand awareness, making it exceptionally challenging for newcomers to compete.
For new entrants, establishing credibility and demonstrating unwavering reliability requires significant time and considerable financial investment. This includes implementing stringent quality control measures and consistently delivering high-quality performance over an extended period. For instance, by mid-2024, major TIC players continued to leverage their decades-long track records, with companies like SGS reporting revenues exceeding CHF 6.5 billion for 2023, underscoring the financial scale and market presence that new firms must contend with.
Access to Skilled Talent and Expertise
The testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) industry, including companies like Centre Testing International Group (CTI), heavily depends on a workforce possessing specialized technical knowledge, scientific acumen, and industry-specific certifications. This reliance on expertise makes it difficult for new entrants to quickly assemble a competent team.
Attracting and retaining these highly skilled professionals presents a significant challenge and considerable expense for newcomers. For instance, the global shortage of cybersecurity professionals, a critical area for many TIC services, continues to drive up recruitment costs. In 2024, reports indicated that the average time to fill a cybersecurity role could extend to several months, with salaries often exceeding industry averages.
- High Demand for Specialized Skills: The TIC sector requires professionals with niche expertise, such as in advanced materials testing, environmental compliance, or digital security.
- Costly Recruitment and Training: Sourcing and onboarding individuals with the necessary certifications and experience can be a substantial upfront investment for new companies.
- Established Talent Pools: Existing players like CTI often benefit from mature internal training programs and established relationships with educational institutions, giving them an advantage in talent acquisition.
Network Effects and Global Reach
The threat of new entrants for Centre Testing International Group (CTI) is significantly mitigated by the powerful network effects and global reach enjoyed by major Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) players. These incumbents, including CTI, have established vast networks of laboratories and offices worldwide, enabling them to cater to multinational corporations and manage intricate global supply chains. For instance, as of early 2024, major TIC firms operate hundreds of locations across dozens of countries, a scale that is incredibly difficult and capital-intensive for newcomers to replicate.
New companies face substantial hurdles in building a comparable infrastructure and achieving the same global footprint. This makes it challenging for them to compete effectively for the large-scale, international contracts that are the lifeblood of established TIC providers. The established global network acts as a formidable barrier, providing incumbents like CTI with a significant competitive advantage.
- Established Global Infrastructure: Major TIC players boast extensive networks of labs and offices, a critical asset for serving multinational clients.
- Barriers to Entry: Replicating this widespread infrastructure and global reach presents a significant financial and logistical challenge for new entrants.
- Competitive Advantage: The network effect allows incumbents to secure large-scale international contracts, further solidifying their market position.
- Limited Newcomer Viability: The sheer scale of operations required makes it difficult for new entities to effectively challenge established players in the global TIC market.
The threat of new entrants for Centre Testing International Group (CTI) is considerably low due to the immense capital investment required to establish state-of-the-art laboratories and acquire specialized testing equipment, often costing millions. This financial barrier, coupled with the complex and time-consuming process of obtaining necessary accreditations and regulatory approvals, deters many potential competitors.
Furthermore, the established reputation and brand trust built by incumbent TIC firms like CTI over decades present a significant hurdle for newcomers seeking to gain market credibility. The industry also demands highly skilled professionals, and attracting this talent pool is both costly and challenging for new entrants, especially given the ongoing global demand for specialized expertise.
Finally, the extensive global networks and infrastructure of established players, including CTI, create powerful network effects that are difficult and expensive for new companies to replicate, limiting their ability to compete for large, international contracts.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High cost of labs and equipment (e.g., millions for advanced material testing). | Significantly limits entry for less-resourced firms. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex accreditation (e.g., ISO 17025) and licensing processes. | Extends time-to-market and adds significant operational complexity. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Decades of building credibility and client relationships. | New entrants struggle to establish the same level of trust. |
| Skilled Workforce | Need for specialized technical expertise and certifications. | High recruitment costs and lengthy hiring processes for newcomers. |
| Global Networks | Extensive international presence of established players. | Difficult and costly for new entrants to match scale and reach. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Centre Testing International Group leverages data from their annual reports, investor relations disclosures, and industry-specific market research reports to assess competitive intensity and strategic positioning.