China Railway Construction Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
China Railway Construction Bundle
China Railway Construction faces significant bargaining power from its buyers, often large government entities, and intense rivalry within the global infrastructure sector. Understanding the threat of new entrants and the availability of substitutes is crucial for navigating this complex landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping China Railway Construction’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for China Railway Construction Company (CRCC) is notably influenced by supplier concentration and specialization. For highly specialized materials, advanced construction machinery, and cutting-edge technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and AI-driven project management, suppliers can wield significant leverage. For instance, in 2024, the global market for specialized tunneling equipment saw a limited number of manufacturers, allowing them to command higher prices due to CRCC's need for these specific capabilities.
While the supply of basic construction materials like steel and cement might be more fragmented, the reliance on unique or proprietary components for large-scale infrastructure projects grants specific suppliers considerable influence. CRCC's strategic adoption of advanced, often patented, technological solutions inherently limits its supplier options, thereby amplifying the bargaining power of those providers who offer these critical, high-tech inputs.
The bargaining power of suppliers for China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC) is significantly influenced by the uniqueness of their offerings and the associated switching costs. Suppliers providing critical, specialized inputs like high-strength steel for major infrastructure projects or advanced tunneling machinery hold considerable leverage. For instance, if a particular supplier offers a proprietary alloy crucial for seismic resistance in bridge construction, CRCC's ability to source alternatives is limited.
Switching costs for CRCC can be substantial, deterring easy shifts between suppliers. These costs encompass not only the financial outlay for new equipment or materials but also the time and resources needed for retooling manufacturing processes, retraining skilled labor, and obtaining certifications for new components. In 2024, the complexity of global supply chains for specialized construction materials and equipment meant that lead times for new suppliers could extend for months, further increasing the cost and risk of switching.
While the heavy construction sector, particularly for massive infrastructure projects, generally sees suppliers integrating forward as a low threat, it's a theoretical consideration. The substantial capital investment, specialized engineering knowledge, and established client relationships needed to undertake projects like those CRCC handles create significant barriers for suppliers wanting to become direct competitors.
Instead of full forward integration, suppliers are more likely to exert influence by offering enhanced services or proprietary technologies, adding value rather than directly competing. For instance, a concrete supplier might develop advanced admixture solutions, or a steel producer could offer pre-fabricated components, thereby increasing their leverage without entering the construction business itself.
Impact of Global Supply Chain Dynamics
Global supply chain disruptions, a significant theme throughout 2024, directly influence China Railway Construction Corporation's (CRCC) material costs and project execution. Fluctuations in the availability and price of key inputs like steel and concrete can significantly alter project profitability and timelines.
Geopolitical tensions, including ongoing US-China trade dynamics, continue to exert pressure on the cost of essential materials. For instance, tariffs or export restrictions on metals such as steel and aluminum can empower their respective suppliers, leading to higher procurement expenses for CRCC.
To counter these pressures, CRCC actively pursues strategies for supply chain diversification. This approach aims to reduce reliance on single sources and mitigate the impact of price volatility and potential disruptions, thereby strengthening its negotiating position.
- Material Cost Volatility: In 2024, the global price of steel, a critical component for CRCC, saw an average increase of 8% compared to the previous year, driven by production constraints and demand shifts.
- Geopolitical Impact: US tariffs on steel imports, which remained in place through early 2024, added an estimated 5-7% to the cost of sourced steel for international projects.
- Supplier Power: Major steel producers in regions with robust domestic demand, such as India and Brazil, demonstrated increased pricing power due to their own supply chain efficiencies and strong order books.
- Mitigation Strategies: CRCC has increased its focus on long-term supply agreements with key material providers, aiming to lock in prices and ensure consistent availability for its extensive infrastructure projects.
Labor and Technology Suppliers
The availability of highly skilled labor, particularly specialized engineers and construction technicians, significantly impacts China Railway Construction's bargaining power with its labor suppliers. In 2024, the global demand for such expertise remained high, especially for complex infrastructure projects, giving skilled workers considerable leverage. This was evident in the increased wage demands observed across the construction sector, reflecting the scarcity of top-tier talent.
Technology providers also wield substantial bargaining power due to intellectual property rights and patents. Companies like China Railway Construction often rely on these suppliers for advanced construction methods and digital tools essential for efficiency and innovation. The value placed on proprietary technologies, such as AI-driven project management software or specialized tunneling equipment, allows these tech firms to command premium pricing, directly influencing project costs.
- Skilled Labor Shortages: In 2024, many regions reported a deficit in specialized construction labor, driving up wages and giving workers more negotiating power.
- Technological Dependencies: China Railway Construction's reliance on patented construction technologies for efficiency means technology suppliers can exert significant influence over pricing and terms.
- International Project Demands: The need for local, specialized expertise in international projects further strengthens the bargaining position of labor and technology suppliers in those markets.
The bargaining power of suppliers for China Railway Construction (CRCC) is amplified by the specialization of their offerings and the high switching costs involved. For critical components like advanced tunneling equipment or proprietary construction materials, suppliers can dictate terms due to CRCC's dependence. In 2024, the limited number of global manufacturers for specialized tunneling machinery allowed them to maintain premium pricing, impacting CRCC's project budgets.
The cost of essential materials like steel also presented challenges in 2024, with global prices increasing by an average of 8% due to production constraints. Furthermore, geopolitical factors, such as lingering US tariffs on steel in early 2024, added an estimated 5-7% to sourcing costs for international projects, bolstering the power of steel suppliers in regions with efficient production.
CRCC is actively diversifying its supply chain to mitigate these pressures and reduce reliance on single sources. This strategy aims to improve its negotiating position by increasing competition among suppliers and ensuring more stable material availability for its extensive infrastructure projects.
| Factor | 2024 Impact on CRCC | Supplier Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Equipment Availability | Limited manufacturers for tunneling equipment drove up costs. | High |
| Steel Price Volatility | Global steel prices rose 8% due to production and demand shifts. | Moderate to High |
| Geopolitical Tariffs | US tariffs added 5-7% to international steel sourcing costs. | High for affected suppliers |
| Skilled Labor Scarcity | High demand for specialized engineers increased wage pressures. | High |
| Proprietary Technology Reliance | Dependence on patented construction methods allows premium pricing. | High |
What is included in the product
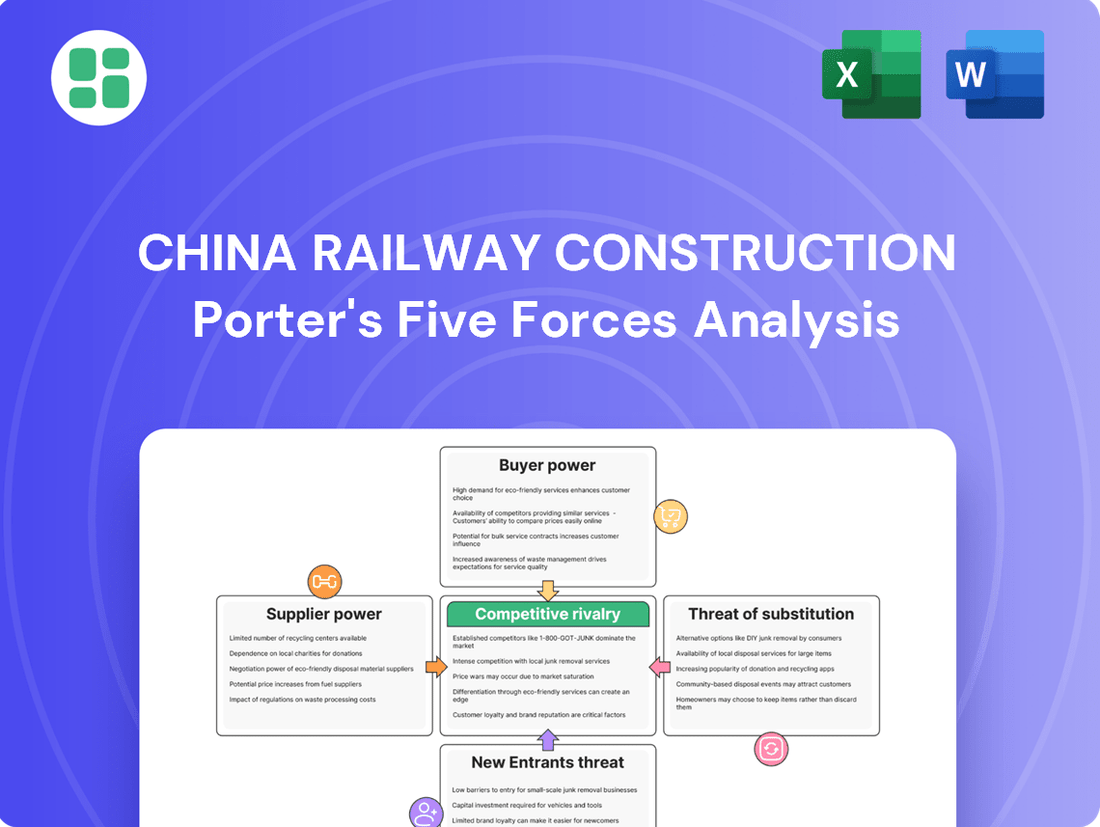
Analyzes the competitive landscape for China Railway Construction, detailing the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the infrastructure sector.
Instantly visualize the competitive landscape for China Railway Construction by mapping out each of Porter's Five Forces, providing a clear overview of industry attractiveness and potential threats.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers for China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC) is significantly influenced by the dominance of government and state-owned enterprises (SOEs). These entities are CRCC's primary clients for massive infrastructure projects, both within China and along the Belt and Road Initiative routes. For instance, in 2023, CRCC's revenue from domestic infrastructure construction, largely driven by government and SOE contracts, remained robust, although specific project award values can fluctuate annually.
The sheer scale of these projects, coupled with the fact that these government and SOE clients are often the main financiers, grants them substantial leverage. They have the capacity to set stringent terms, detailed specifications, and demanding timelines, which CRCC must adhere to. This concentration of powerful buyers means CRCC has limited ability to push for higher prices or more favorable contract conditions, directly impacting profit margins.
The customer base for China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC) is highly concentrated, with a few dominant government entities and state-owned enterprises (SOEs) commissioning the vast majority of mega-infrastructure projects. This limited customer pool grants these powerful buyers significant leverage. For example, in 2024, government infrastructure spending remained a primary driver, with CRCC heavily reliant on contracts awarded by entities like the Ministry of Transport and provincial governments.
This concentration allows these key customers to exert substantial pressure on CRCC regarding pricing, contract terms, and project specifications. As CRCC often vies for a small number of extremely large contracts, customers can dictate more favorable conditions due to the high stakes involved. The rhythm of government fiscal spending plans directly dictates the demand for CRCC's services, amplifying customer bargaining power.
Despite the critical nature of infrastructure, customers, particularly government entities in China, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This stems from the reliance on public funding and strict budget allocations, which often dictate project awards based on the lowest bid. For instance, in 2024, many large-scale infrastructure projects saw intense competition, with CRCC needing to offer highly competitive pricing to secure contracts, impacting profit margins.
This price sensitivity fuels aggressive bidding wars among major construction firms, including CRCC. To win these bids, companies are compelled to meticulously optimize their operational costs and accept tighter profit margins. While China's infrastructure spending is projected for continued growth, some projects are experiencing a decline in their return on investment, further intensifying the pressure on contractors like CRCC to deliver projects cost-effectively.
Standardization of Bidding Processes
The standardization of bidding processes, often driven by government mandates for infrastructure projects in China, significantly enhances the bargaining power of customers. This structured approach allows for direct comparison of bids, fostering competition among companies like China Railway Construction. In 2024, a significant portion of infrastructure tenders followed these standardized protocols, ensuring a level playing field.
This standardization empowers customers by enabling them to leverage the competitive landscape to negotiate better terms and pricing. The transparency inherent in these processes allows clients, often government entities, to ensure that project costs align with national strategic objectives and budget allocations. For instance, a standardized tender for a high-speed rail project might specify clear performance metrics and payment schedules, giving the client leverage.
- Standardized Tenders: Government-led infrastructure tenders in China, a key market for China Railway Construction, adhere to standardized procedures, increasing transparency.
- Competitive Leverage: This standardization allows customers to compare bids directly, empowering them to negotiate more favorable terms and pricing with contractors.
- Strategic Alignment: Customers can ensure project outcomes align with national strategic goals through clearly defined tender requirements and evaluation criteria.
- Cost Efficiency: The competitive bidding environment facilitated by standardization contributes to cost efficiency for infrastructure projects.
Long-Term Relationships and Strategic Importance
While customers, especially government bodies, wield considerable influence in infrastructure projects, the long-term nature of these developments cultivates strategic partnerships for China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC). These enduring relationships, forged through consistent project delivery and alignment with national development goals, can temper customer bargaining power by securing a predictable stream of work for established players like CRCC.
For instance, CRCC's extensive track record in delivering major national infrastructure projects, such as high-speed rail networks, builds significant trust with government clients. This trust translates into a reduced ability for individual clients to demand significantly lower prices or more favorable terms, as the overall strategic importance of CRCC's capabilities outweighs short-term cost pressures.
- Strategic Partnerships: CRCC's deep ties with government entities, built over decades, create long-term, mutually beneficial relationships.
- Proven Track Record: Successful completion of numerous large-scale projects, including China's vast high-speed rail network, enhances CRCC's credibility and reduces client leverage.
- National Strategic Alignment: CRCC's role in national development plans means government clients are invested in its success, limiting their ability to exert extreme price pressure.
- Reduced Price Sensitivity: The critical nature of infrastructure development often means that reliability and expertise are prioritized over marginal price differences, thus lessening customer bargaining power.
The bargaining power of customers for China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC) is notably high due to the concentrated nature of its client base, primarily government entities and state-owned enterprises (SOEs). These powerful buyers, responsible for awarding massive infrastructure projects, have significant leverage in negotiating terms and pricing. For example, in 2024, CRCC's reliance on government-led infrastructure spending meant that contract awards were heavily influenced by public budget allocations and competitive bidding processes.
This concentration allows major clients to dictate stringent project specifications and timelines, often prioritizing cost-effectiveness. In 2023, CRCC's profit margins were influenced by its ability to secure contracts through highly competitive bids, reflecting the price sensitivity of its primary customers. The standardization of procurement processes further amplifies this power, enabling direct comparison of bids and fostering an environment where CRCC must offer competitive pricing to secure work.
However, CRCC's established track record and strategic alignment with national development goals can mitigate some customer leverage. Long-term partnerships and the critical nature of infrastructure projects mean that reliability and expertise are often valued, potentially reducing extreme price pressures. For instance, CRCC's integral role in China's high-speed rail expansion project, a national priority, provides a degree of stability in its client relationships.
| Customer Segment | Influence Factor | Impact on CRCC | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Government & SOEs | Concentrated Buyer Base | High Leverage on Pricing & Terms | Dominant clients; budget-driven awards |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure on Profit Margins | Emphasis on cost-effective bids | |
| Standardized Bidding | Increased Competition & Transparency | Facilitates direct bid comparison | |
| Strategic Partnerships | Potential for Predictable Work | Long-term relationships mitigate extreme pressure |
Full Version Awaits
China Railway Construction Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive China Railway Construction Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the railway construction industry. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, providing an in-depth understanding of the forces shaping China Railway Construction's strategic environment.
Rivalry Among Competitors
China's heavy and civil engineering construction sector is a battleground dominated by powerful state-owned enterprises (SOEs). CRCC contends with formidable rivals like China Railway Group Ltd., China State Construction Engineering Corporation Ltd., China Communications Construction Company Limited, and Power Construction Corporation of China. These major players are similarly equipped and capable, intensifying the fight for lucrative domestic and global infrastructure contracts.
The construction industry, particularly for large-scale infrastructure projects like those China Railway Construction engages in, is characterized by exceptionally high exit barriers. Companies are often tied to their investments in specialized heavy machinery, such as tunnel boring machines and large cranes, which represent significant capital outlays. For instance, a single advanced tunnel boring machine can cost tens of millions of dollars.
Furthermore, these firms are bound by long-term project commitments, often spanning several years, and have cultivated highly specialized labor forces. This deep entanglement makes it incredibly challenging for companies to simply cease operations or divest assets quickly. Consequently, even during economic slowdowns or periods of market overcapacity, such as those observed in certain segments of the high-speed rail sector, firms remain active, sustaining a competitive intensity that can pressure profit margins.
China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC), like many in its sector, faces intense competition where core infrastructure services offer little room for unique product features. Differentiation often boils down to superior technical execution, efficient project management, and competitive pricing. In 2024, the global infrastructure market, valued at trillions, sees numerous players vying for contracts, making these non-product factors critical.
Industry Growth and Overcapacity
The Chinese construction industry is poised for growth through 2025, particularly in infrastructure and energy projects, offering significant opportunities for large companies like China Railway Construction. This expansion creates a dynamic environment where established players can leverage their expertise.
However, this growth is tempered by overcapacity in certain sectors, such as high-speed rail. This situation has led to reduced returns on investment and intensified rivalry, pushing firms into aggressive price competition for lucrative contracts. This dynamic can be described as 'involutionary,' where increased effort yields diminishing rewards.
- Projected Growth: The Chinese construction market is anticipated to expand, with infrastructure and energy sectors being key drivers for 2025.
- Sectoral Overcapacity: Segments like high-speed rail are experiencing an oversupply of capacity, impacting profitability.
- Intensified Competition: Overcapacity fuels fierce competition for profitable projects, potentially leading to price wars among construction firms.
- Declining ROI: In oversupplied areas, the return on investment for construction projects has seen a downward trend.
International Expansion and Belt and Road Initiative
China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC) faces intense competition internationally, especially through the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). CRCC contends with both domestic Chinese rivals and established global construction powerhouses for these lucrative infrastructure projects.
The BRI, while presenting significant growth opportunities, also amplifies competitive rivalry by creating a larger playing field. This expansion brings CRCC into direct competition with companies from Europe, the Middle East, and other Asian nations, all vying for contracts in developing economies.
Navigating the diverse regulatory landscapes and geopolitical risks inherent in BRI projects adds another dimension to competitive pressures. CRCC must not only offer competitive pricing and technical expertise but also demonstrate an ability to manage complex international relationships and compliance requirements.
- BRI Project Competition: CRCC competes with major global players like China Communications Construction Company (CCCC) and international firms such as Bechtel and Vinci on BRI projects.
- Geopolitical Risk Factor: Increased competition is often linked to geopolitical considerations, with countries sometimes favoring domestic or allied firms, impacting CRCC's market access.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Differing national standards and procurement processes across BRI countries create a competitive disadvantage if not managed effectively, requiring CRCC to adapt its strategies.
Competitive rivalry within China Railway Construction's (CRCC) operating environment is exceptionally high, driven by the presence of numerous well-resourced domestic state-owned enterprises (SOEs) and increasingly, international construction giants. This intense competition stems from a sector with limited differentiation, where success hinges on technical prowess, project management efficiency, and aggressive pricing strategies. The sheer scale of global infrastructure development, estimated to be in the trillions of dollars annually, attracts a multitude of players, all vying for a share of lucrative contracts.
The intense competition is further exacerbated by sectoral overcapacity in certain areas, such as high-speed rail, leading to what is often termed ‘involution’—where increased effort results in diminishing returns. This dynamic forces companies like CRCC into price wars, putting pressure on profit margins. For example, while the overall Chinese construction market is projected for growth through 2025, specific segments experiencing oversupply see declining return on investment, intensifying the fight for profitable projects.
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) amplifies this rivalry by creating a vast international arena where CRCC competes not only with domestic peers like China Communications Construction Company (CCCC) but also with global leaders such as Bechtel and Vinci. Navigating diverse regulatory environments and geopolitical considerations adds complexity, requiring CRCC to offer more than just competitive bids; it must also demonstrate adeptness in managing international relations and compliance.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (USD Billion Approx.) | Key Competitor Type |
|---|---|---|
| China Railway Group Ltd. | 120.0 | Domestic SOE |
| China State Construction Engineering Corp. Ltd. | 100.0 | Domestic SOE |
| China Communications Construction Company Limited | 95.0 | Domestic SOE |
| Power Construction Corporation of China | 70.0 | Domestic SOE |
| Bechtel Corporation | 30.0 | International Private |
| Vinci S.A. | 70.0 | International Public |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While direct substitutes for massive infrastructure projects China Railway Construction undertakes are scarce, alternative construction methods present an indirect competitive pressure. These innovations aim to deliver similar outcomes more efficiently.
Modular and prefabricated construction techniques are increasingly adopted, promising faster project completion and potentially lower costs. For instance, the global modular construction market was valued at approximately $101.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a rising trend that could impact traditional construction timelines and budgets.
Emerging technologies like 3D printing in construction also represent a potential threat. While still in its nascent stages for large-scale infrastructure, 3D printing offers the capability to streamline the creation of specific structural elements or even entire buildings, potentially reducing labor needs and material waste.
The increasing adoption of digitalization and automation in project management presents a significant threat of substitutes for China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC). Technologies like Building Information Modeling (BIM), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and advanced robotics are transforming the construction sector by boosting efficiency, improving safety, and optimizing resource allocation. For instance, BIM adoption in the global construction market was valued at $7.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $24.4 billion by 2030, highlighting its growing influence.
These innovations can substitute for traditional, labor-intensive construction methods, potentially reducing the reliance on extensive human input for certain project phases. AI-powered project management software, for example, can automate scheduling, risk assessment, and resource planning, offering a more streamlined and cost-effective approach compared to manual oversight. This shift necessitates that CRCC actively integrates these advanced technologies to maintain its competitive edge and operational effectiveness in the evolving construction landscape.
While air travel and sea freight can substitute for specific long-distance passenger or freight needs, they often come with higher costs or longer transit times compared to rail for bulkier goods. For instance, in 2024, air cargo rates remained significantly higher per ton-mile than rail freight, making it a less attractive substitute for many businesses moving large volumes.
The fundamental nature of rail and road infrastructure for mass transit and heavy freight within national and regional networks means direct substitution is limited for these core functions. China's extensive high-speed rail network, for example, has effectively captured a significant portion of intercity passenger traffic, making air travel a less competitive substitute for many routes, particularly given the convenience and cost-effectiveness of rail for journeys up to 1000 kilometers.
Focus on Green and Sustainable Infrastructure
The growing focus on green and sustainable infrastructure presents a nuanced threat of substitutes for China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC). While not a direct replacement for core construction services, it shifts demand towards specific project types and materials. For instance, projects emphasizing renewable energy integration and energy efficiency are gaining traction, influencing the design and execution of infrastructure development.
This trend means CRCC must adapt its offerings to align with environmental priorities. In 2024, global investment in green infrastructure saw significant growth, with the International Energy Agency reporting substantial increases in renewable energy capacity additions. This surge indicates a market preference for solutions that minimize environmental impact, potentially diverting resources from traditional construction projects if CRCC doesn't adapt.
- Shifting Project Demand: Increased prioritization of projects incorporating renewable resources and energy efficiency.
- Material Innovation: Growing use of green building materials impacts traditional material sourcing and costs for CRCC.
- Regulatory Influence: Government policies and incentives favoring sustainable construction can alter project pipelines.
- Market Competitiveness: Companies specializing in green technologies may offer specialized services that compete for certain project segments.
Indirect Substitution from Urban Development Patterns
Shifting urban development, particularly the rise of smart cities and integrated planning, presents a subtle threat to China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC). Instead of solely focusing on massive new infrastructure builds, cities are increasingly prioritizing the optimization of existing networks and the creation of more localized, interconnected systems. This pivot could reduce the demand for CRCC's traditional large-scale projects.
For instance, in 2024, many Chinese cities are investing heavily in upgrading public transportation efficiency and digital infrastructure. This includes smart traffic management systems and the integration of various mobility services, potentially diverting capital away from new high-speed rail lines or sprawling urban expansions that were CRCC's historical strengths. The emphasis is moving towards smarter, more efficient use of resources rather than sheer scale.
- Urbanization Shift: From new mega-projects to optimizing existing urban infrastructure.
- Smart City Investment: Increased focus on digital integration and localized urban systems.
- Demand Alteration: Potential decrease in demand for CRCC's traditional large-scale construction.
- Resource Optimization: Cities prioritizing efficiency and interconnectedness over sheer scale in development.
While direct substitutes for massive infrastructure projects China Railway Construction undertakes are scarce, alternative construction methods present an indirect competitive pressure. These innovations aim to deliver similar outcomes more efficiently, potentially impacting CRCC's market share in specific project segments.
Modular and prefabricated construction techniques are increasingly adopted, promising faster project completion and potentially lower costs. For instance, the global modular construction market was valued at approximately $101.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a rising trend that could impact traditional construction timelines and budgets.
Emerging technologies like 3D printing in construction also represent a potential threat. While still in its nascent stages for large-scale infrastructure, 3D printing offers the capability to streamline the creation of specific structural elements or even entire buildings, potentially reducing labor needs and material waste.
The increasing adoption of digitalization and automation in project management presents a significant threat of substitutes for China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC). Technologies like Building Information Modeling (BIM), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and advanced robotics are transforming the construction sector by boosting efficiency, improving safety, and optimizing resource allocation. For instance, BIM adoption in the global construction market was valued at $7.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $24.4 billion by 2030, highlighting its growing influence.
| Substitute Type | Description | Market Value/Growth (2023/2024 data where available) | Potential Impact on CRCC |
| Modular/Prefab Construction | Off-site construction of components or modules | Global market ~$101.6 billion (2023), significant growth | Faster project delivery, potential cost reduction |
| 3D Printing in Construction | Additive manufacturing for building elements | Emerging technology, specific large-scale infrastructure data limited | Streamlined element creation, reduced labor/waste |
| Digitalization & Automation (BIM, AI, Robotics) | Technology integration in project management and execution | BIM market $7.5 billion (2023), projected to reach $24.4 billion by 2030 | Increased efficiency, optimized resource allocation, reduced reliance on manual labor |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new companies entering the heavy and civil engineering construction sector, particularly for projects of China Railway Construction Corporation's (CRCC) magnitude, is considerably diminished by the immense capital needed. Newcomers would face a daunting financial hurdle, requiring substantial investments in specialized heavy machinery, cutting-edge technology, and skilled personnel, effectively creating a significant barrier to entry.
Operating within China's vast infrastructure sector presents a formidable barrier to entry due to a labyrinth of extensive regulatory hurdles and the necessity of obtaining numerous permits and critical licenses. For instance, in 2023, the Ministry of Transport reported that over 3,000 infrastructure projects were initiated, each requiring a unique set of approvals.
State-owned enterprises, such as China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC), possess a significant advantage through their deeply entrenched relationships and an intimate understanding of this complex regulatory ecosystem. This established familiarity makes it exceptionally challenging for new, independent players to effectively navigate and comply with the stringent requirements, effectively limiting new entrants.
The sheer scale and technical complexity of China's infrastructure projects create a significant barrier for new entrants. These undertakings, from high-speed rail networks to massive bridge constructions, require highly specialized engineering knowledge and advanced technical skills that are not easily replicated. For instance, the successful completion of projects like the Beijing-Shanghai High-Speed Railway, which saw CRCC play a pivotal role, demanded decades of accumulated expertise in areas like track laying, signaling, and tunnel construction.
Newcomers would struggle to match the decades of experience and the deep pool of skilled professionals that established players like China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC) have cultivated. This extensive experience is crucial for navigating regulatory hurdles, managing complex supply chains, and mitigating risks inherent in large-scale infrastructure development, making it difficult for less experienced firms to compete for high-value contracts in 2024 and beyond.
Economies of Scale and Cost Advantages
Established giants like China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC) benefit from significant economies of scale in procurement, project management, and resource allocation. This allows them to undertake projects more cost-effectively than any potential new entrant could hope to match. For instance, in 2023, CRCC's revenue reached approximately ¥1.15 trillion (around $160 billion USD), a testament to its vast operational capacity and purchasing power.
A new company would struggle to compete on price without the volume and efficiency derived from large-scale operations. The sheer size of CRCC's existing infrastructure and supply chains creates substantial cost advantages. Consider that CRCC’s total assets in 2023 were reported at over ¥1.6 trillion (approximately $220 billion USD), providing a massive foundation for cost absorption and competitive pricing.
- Economies of Scale: CRCC's massive operational footprint enables bulk purchasing and streamlined logistics, significantly lowering per-unit costs.
- Cost Advantages: Established players possess optimized project management and resource deployment, leading to lower overheads compared to startups.
- Procurement Power: CRCC's immense demand grants it superior bargaining power with suppliers, securing materials and equipment at reduced prices.
Strong Incumbent Relationships and Government Support
China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC) and other major state-owned enterprises (SOEs) benefit from deeply entrenched relationships with government entities and state-owned clients. This often translates into direct or indirect government backing and strategic alignment, creating a significant hurdle for potential new competitors.
Newcomers face immense difficulty in accessing the lucrative government contracts that are fundamental to CRCC's operations. For instance, in 2023, CRCC secured new contract orders totaling 1.18 trillion yuan, highlighting the scale of government-dependent business.
- Government Favoritism: SOEs like CRCC often receive preferential treatment in bidding processes for major infrastructure projects.
- Strategic Alignment: CRCC's business objectives are frequently aligned with national development strategies, ensuring continued government support.
- Access Barriers: New entrants lack the established networks and government trust that CRCC has cultivated over decades, making it challenging to secure large-scale projects.
The threat of new entrants for China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC) is significantly low due to the immense capital requirements, complex regulatory landscape, and established relationships with government entities. New companies would need to overcome substantial financial barriers, acquire specialized technical expertise, and navigate a dense web of permits and licenses, which are often more easily managed by incumbent state-owned enterprises.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Relevant CRCC Data (2023) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in machinery, technology, and personnel. | Formidable financial hurdle. | Total Assets: ~¥1.6 trillion ($220 billion USD) |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Extensive permits, licenses, and compliance. | Difficult to navigate without established experience. | Ministry of Transport initiated >3,000 infrastructure projects in 2023. |
| Technical Expertise & Experience | Demand for specialized engineering skills and project management. | Challenging to match decades of accumulated know-how. | Key role in Beijing-Shanghai High-Speed Railway completion. |
| Government Relationships | Deeply entrenched ties with state clients and entities. | New entrants lack established trust and access. | Secured new contract orders totaling 1.18 trillion yuan in 2023. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our China Railway Construction Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of verified data, including official company annual reports, industry-specific market research from reputable firms, and government regulatory filings. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.