Commerce Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Commerce Bank Bundle
Commerce Bank navigates a dynamic financial landscape where buyer power from discerning customers and the threat of new entrants constantly challenge established players. Understanding the intensity of these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the real forces shaping Commerce Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Technology and software providers hold significant bargaining power over banks like Commerce Bank. This is because banks are deeply reliant on specialized IT infrastructure, core banking systems, and robust cybersecurity solutions to operate efficiently and securely.
The power of these vendors can be particularly strong when their offerings are proprietary or necessitate complex integration, resulting in substantial switching costs for Commerce Bank. The global market for banking and financial services software is projected to hit $46.2 billion by 2028, underscoring the critical and growing dependence on these external technology partners.
Suppliers of financial data and information services, such as Bloomberg and Refinitiv, wield considerable bargaining power over Commerce Bank. This power stems from the critical, often exclusive, nature of the real-time market data, credit reporting, and analytics they provide, which are indispensable for the bank's daily operations and robust risk management. For instance, in 2023, the financial data and analytics market was valued at over $30 billion globally, highlighting the scale and importance of these services.
The essentiality of these data feeds means Commerce Bank has limited alternatives, strengthening supplier leverage. Furthermore, as banks, including Commerce Bank, ramp up investments in data management to fuel generative AI initiatives, the demand for sophisticated data services is increasing, further solidifying the suppliers' influential position in 2024 and beyond.
The banking industry, including Commerce Bank, relies heavily on specialized expertise in finance, technology, risk management, and wealth management. This demand for highly skilled individuals creates a dynamic where talent scarcity directly influences employee leverage.
The shortage of specialized talent, especially in rapidly evolving fields like technology and cybersecurity, significantly enhances the bargaining power of employees. This makes it challenging for Commerce Bank to attract and retain top-tier professionals, potentially driving up labor costs and impacting operational efficiency.
With the escalating threat landscape, the need for skilled cybersecurity professionals is more critical than ever. In 2024, the demand for cybersecurity experts continues to outstrip supply, granting these individuals considerable negotiation power when considering employment offers within the financial sector.
Interbank Lending and Capital Markets
While banks rely heavily on deposits, they also tap into interbank lending and capital markets for crucial liquidity and funding. Major players in these markets, like large investment banks or central banks, can wield significant influence by setting interest rates and dictating lending terms. This directly impacts Commerce Bank's cost of obtaining funds, affecting its profitability.
The cost of interest-bearing deposits remained a challenge for many midsize and regional banks throughout 2024, a trend that continued to exert upward pressure on overall funding costs. For instance, some reports indicated that the average cost of interest-bearing deposits for regional banks saw a notable increase compared to previous years, directly impacting their net interest margins.
- Interbank Market Influence: Large financial institutions acting as lenders in the interbank market can dictate terms, affecting Commerce Bank's borrowing costs.
- Capital Market Access: The ability to access capital markets is vital, but the cost of this access is influenced by market conditions and the bargaining power of capital providers.
- Deposit Cost Pressures: In 2024, the cost of interest-bearing deposits remained elevated for many banks, including those of Commerce Bank's size, squeezing funding costs.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: Commerce Bank's reliance on these wholesale funding sources makes it sensitive to fluctuations in interest rates set by powerful market participants.
Regulatory Compliance Services
The bargaining power of suppliers for regulatory compliance services is significant for banks like Commerce Bank. The financial sector operates under a complex and ever-evolving regulatory landscape, making specialized legal and consulting firms indispensable. These providers possess niche expertise in areas like the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations, which are critical for maintaining operational legitimacy and avoiding hefty fines. For instance, in 2023, financial institutions faced billions in AML-related fines, underscoring the high stakes of non-compliance.
The intense scrutiny on Know Your Customer (KYC) and AML processes, which is projected to continue through 2024 and 2025, further amplifies the power of these specialized service providers. Banks have limited alternatives when seeking deep, up-to-date knowledge of these intricate legal frameworks. This dependence allows compliance service providers to command premium pricing and favorable contract terms, as the cost of non-compliance, including reputational damage and severe penalties, far outweighs the expense of expert services.
- High Demand for Expertise: The banking industry's need for specialized knowledge in regulations like Dodd-Frank and BSA/AML creates strong demand for compliance service providers.
- Risk of Penalties: Non-compliance with banking regulations can result in substantial financial penalties and reputational damage, increasing a bank's reliance on expert advice.
- Continued Regulatory Scrutiny: Ongoing and anticipated high levels of regulatory oversight in areas such as AML and KYC through 2024 and 2025 solidify the essential nature of these services.
- Limited Substitutes: The highly specialized nature of regulatory compliance means few direct substitutes exist for expert legal and consulting services, enhancing supplier bargaining power.
Suppliers of critical technology and software, such as core banking system providers and cybersecurity firms, hold significant bargaining power over Commerce Bank. This is due to the essential nature of these services for efficient and secure operations, coupled with high switching costs associated with proprietary and complex integration. The global market for financial services software is expected to reach $46.2 billion by 2028, highlighting the industry's deep reliance on these vendors.
Financial data and analytics providers like Bloomberg and Refinitiv also possess strong leverage. Their indispensable real-time market data and credit reporting are vital for Commerce Bank's daily functions and risk management. The global financial data market exceeded $30 billion in 2023, and the increasing demand for data to support AI initiatives in 2024 further strengthens these suppliers' positions.
The bargaining power of suppliers is further amplified by the scarcity of specialized talent in finance, technology, and cybersecurity. In 2024, the demand for cybersecurity professionals, in particular, continues to outpace supply, giving these individuals considerable negotiation power. This talent shortage can drive up labor costs for Commerce Bank, impacting operational efficiency.
Wholesale funding sources, including interbank lending and capital markets, also represent a significant supplier power dynamic for Commerce Bank. Major players in these markets can influence borrowing costs through interest rate setting. The cost of interest-bearing deposits remained a key challenge for many banks in 2024, directly affecting funding costs and net interest margins.
| Supplier Category | Key Services Provided | Impact on Commerce Bank | Market Trend/Data Point (2023-2024) |
| Technology & Software | Core banking systems, cybersecurity solutions | High dependence, significant switching costs | Financial services software market projected to reach $46.2B by 2028 |
| Data & Analytics | Real-time market data, credit reporting, analytics | Indispensable for operations and risk management | Global financial data market exceeded $30B in 2023; increasing demand for AI data |
| Specialized Talent | Expertise in IT, cybersecurity, risk management | Talent scarcity drives up labor costs and impacts retention | High demand for cybersecurity professionals in 2024 |
| Wholesale Funding | Interbank lending, capital markets access | Influences borrowing costs and liquidity | Elevated cost of interest-bearing deposits impacting funding costs in 2024 |
What is included in the product
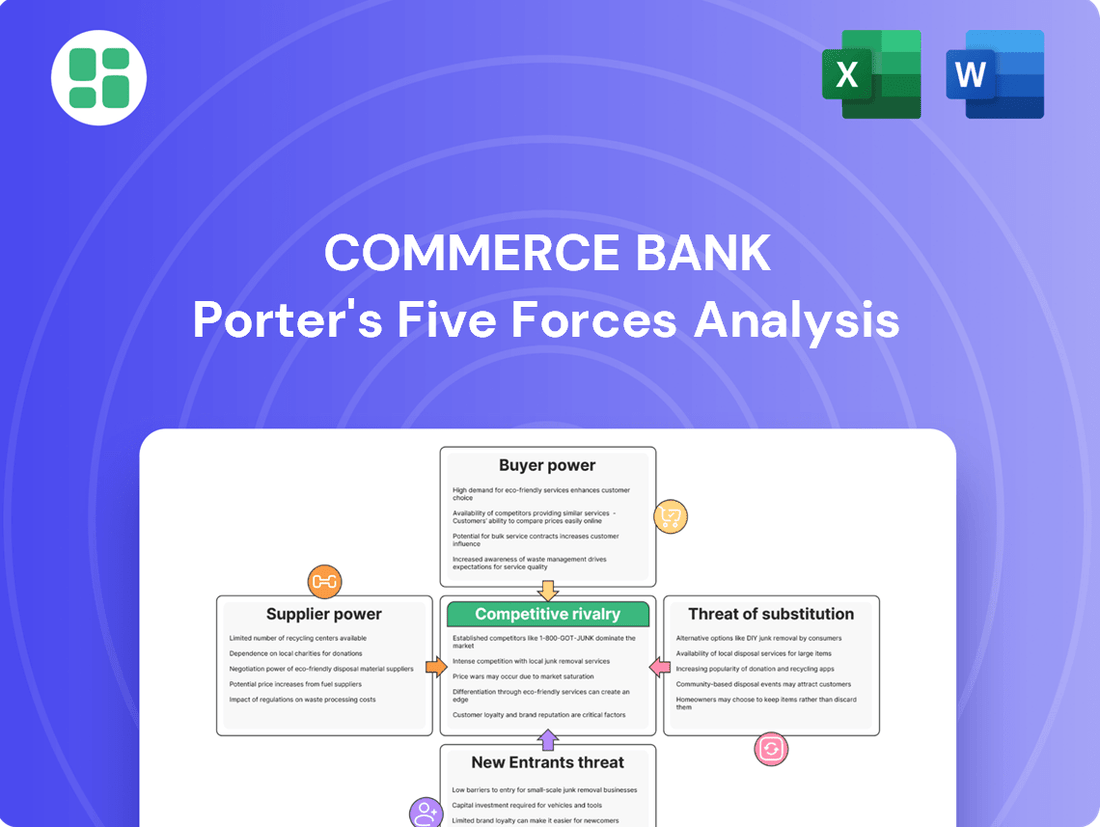
This analysis of Commerce Bank's competitive landscape examines the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a clear, visual breakdown of each Porter's Five Force, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
For basic retail banking services, such as checking and savings accounts, Commerce Bank customers face low switching costs. This ease of movement is amplified by digital account opening processes and streamlined direct deposit transfers, enabling individuals to readily shift their funds to competitors offering more attractive rates or enhanced services. In 2024, the banking sector continued to see increased customer mobility driven by digital innovation.
Customers today have a much wider selection of financial service providers than ever before. Beyond traditional brick-and-mortar banks like Commerce Bank, consumers can turn to online-only banks, credit unions, and specialized fintech companies for services like payments, lending, and investments. This abundance of choice significantly boosts customer bargaining power.
In 2024, the rise of digital banking platforms has been a major driver of this trend, making financial services more accessible and efficient. For instance, the global digital banking market was projected to reach over $25 trillion by 2024, highlighting the significant shift towards non-traditional providers. This forces Commerce Bank to compete fiercely on factors such as interest rates, fees, customer service quality, and the ease of digital transactions to keep its customers loyal.
Customers seeking loan products like mortgages or auto loans are very sensitive to price, actively comparing interest rates and terms across different lenders. This intense price competition means Commerce Bank must offer competitive rates, which can squeeze its profitability on loans.
While overall loan demand is anticipated to rise in 2025, certain consumer loan categories might see slower growth due to ongoing financial strain on households.
Information Transparency and Comparison Tools
The internet has revolutionized how customers shop for financial services, significantly increasing information transparency. Comparison websites and financial aggregators are readily available, allowing consumers to easily compare rates, fees, and product features from numerous institutions. This ease of access empowers Commerce Bank's customers, enabling them to make more informed decisions and actively seek out competitive offerings.
This heightened transparency directly impacts the bargaining power of customers. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of consumers actively used online tools to research banking products. Data from a 2023 study indicated that over 60% of consumers used comparison sites when selecting a new bank account or loan. This trend is expected to continue, meaning customers are more likely to switch providers if they find better deals elsewhere.
- Increased Customer Savvy: Customers can now easily access detailed information on interest rates, account fees, and service charges, making them less reliant on a single institution's offerings.
- Demand for Competitive Pricing: The ability to compare empowers customers to negotiate for better terms or switch to competitors offering more favorable conditions.
- Focus on Value and Service: Beyond just price, customers can compare customer service ratings and available features, pushing banks like Commerce Bank to differentiate on more than just cost.
- Digital Empowerment: The widespread availability of financial aggregators and review platforms means customer feedback and comparative data are more visible than ever, influencing purchasing decisions.
Large Corporate and Wealth Management Clients
Large corporate and high-net-worth clients wield considerable bargaining power. Their substantial transaction volumes and complex financial requirements necessitate tailored services and competitive pricing from Commerce Bank. For instance, in 2024, Commerce Bancshares, the parent company, actively pursued growth in its wealth management sector, signaling a strategic focus on retaining and attracting these high-value client segments.
The bank must continuously innovate and provide exceptional relationship management to secure and retain these influential customers. This often translates into customized product offerings and fee structures designed to meet specific client needs.
- Client Volume: Large clients represent significant revenue streams, giving them leverage in negotiations.
- Sophisticated Needs: Their complex financial requirements demand specialized expertise and personalized solutions.
- Relationship Management: Dedicated service and strong client relationships are crucial for retention.
- Competitive Offerings: Commerce Bank must offer attractive pricing and value-added services to compete for these clients.
Commerce Bank customers, especially those with basic retail banking needs, experience low switching costs due to accessible digital account opening and easy fund transfers. This mobility is further fueled by the expanding digital banking landscape, with the global digital banking market projected to exceed $25 trillion by 2024, forcing Commerce Bank to compete on rates, fees, and digital user experience to retain its customer base.
Customers are increasingly empowered by online comparison tools, readily accessing information on rates, fees, and features, which significantly enhances their bargaining power. In 2024, over 60% of consumers utilized online comparison sites for financial products, indicating a strong trend towards seeking better deals elsewhere.
Large corporate and high-net-worth clients possess substantial leverage due to their significant transaction volumes and complex financial needs. Commerce Bancshares' strategic focus on its wealth management sector in 2024 highlights the importance of offering tailored services and competitive pricing to retain these valuable client segments.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Commerce Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Customers | Low switching costs, digital access, price sensitivity | Pressure on fees and interest rates, need for superior digital experience |
| High-Net-Worth/Corporate Clients | Large transaction volumes, complex needs, relationship dependence | Requirement for customized pricing, specialized services, and strong relationship management |
| General Customer Base | Information transparency via online tools, availability of alternatives (fintechs, online banks) | Constant need for competitive offerings and value-added services to prevent churn |
Same Document Delivered
Commerce Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Commerce Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking industry. This comprehensive document is ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Commerce Bancshares operates within the Midwest banking sector, a region characterized by a dense network of financial institutions. This includes not only large national players but also a significant number of regional and community banks, all actively competing for customers. This crowded competitive environment means Commerce faces constant pressure to attract and retain deposits and loans.
The sheer volume of traditional banks means that market share gains are hard-won. Each competitor, from the largest national banks to smaller community institutions, is actively pursuing growth strategies. For instance, in 2024, regional banks, in general, continued to focus on expanding their digital offerings and personalized customer service to differentiate themselves in this highly competitive space.
Commerce Bank faces intense rivalry from numerous competitors, including traditional banks and agile fintech companies, all aggressively investing in digital banking. This digital arms race means banks are pouring resources into sophisticated mobile apps, seamless online services, and innovative digital platforms to attract and retain customers.
The pressure is on Commerce Bank to constantly upgrade its digital capabilities to keep pace with evolving customer demands for convenience and instant access. For instance, in 2024, the digital banking sector continued its rapid expansion, with mobile banking adoption rates soaring. Many banks reported significant increases in digital transaction volumes, highlighting the critical need for robust digital offerings.
While Commerce Bank offers a wide array of financial services, many fundamental products like checking accounts, savings accounts, and basic loans are often seen as interchangeable commodities. This reality makes it difficult to stand out purely on product features, shifting the competitive battleground towards customer experience, brand trust, and ease of access. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. banking sector saw continued emphasis on digital convenience and personalized service as key differentiators, with many institutions investing heavily in app functionality and customer support channels to capture market share.
Geographic Overlap and Market Saturation
In mature banking markets, a high degree of geographic overlap exists, meaning Commerce Bank faces intense competition for customers. This saturation necessitates a constant effort to acquire new clients and retain existing ones, as market share gains often mean taking customers from rivals. For instance, as of Q1 2024, the U.S. banking industry saw deposit growth moderate, highlighting the competitive environment.
Regional players like Commerce Bank often differentiate themselves by leveraging their deep community ties. This localized advantage allows them to better understand and cater to the specific needs of their customer base, a crucial factor in retaining loyalty amidst widespread market saturation. In 2023, community banks continued to demonstrate resilience and strong customer relationships, often outperforming larger institutions in customer satisfaction metrics in their operating regions.
- Geographic Saturation: Many banking markets exhibit significant overlap in branch networks and digital service areas, intensifying rivalry.
- Customer Acquisition Cost: In saturated markets, acquiring new customers becomes more expensive as banks compete for a limited pool.
- Community Integration: Regional banks like Commerce Bank can leverage local presence and relationships as a competitive differentiator.
- Market Share Dynamics: Growth in mature markets is often a zero-sum game, where one bank's gain is another's loss.
Intense Competition for Lending Opportunities
Commerce Bank operates in a highly competitive landscape for lending, with both traditional banks and non-bank financial institutions vying for loan origination. This intense rivalry puts pressure on interest rates and loan terms, particularly for creditworthy borrowers, as competitors employ aggressive pricing strategies to capture market share.
In 2024, regional banks like Commerce Bank are experiencing persistent challenges with sluggish loan growth. For instance, data from the Federal Reserve indicated that commercial bank lending, excluding Paycheck Protection Program loans, saw a modest increase in early 2024, but overall growth remained subdued compared to previous periods, reflecting the broader economic environment and heightened competition.
- Intense Rivalry: Both traditional banks and alternative lenders actively compete for lending opportunities.
- Pricing Pressure: Aggressive pricing by competitors compresses margins on loans, especially for prime borrowers.
- Subdued Loan Growth: Regional banks, including Commerce Bank, faced continued challenges with weak loan growth throughout 2024.
The competitive rivalry for Commerce Bank is fierce, with numerous players vying for customer attention and market share across the Midwest. This intensity is driven by a dense network of financial institutions, including large national banks, other regional banks, and agile fintech companies, all actively pursuing growth. The battle for deposits and loans is constant, forcing banks to innovate and differentiate to stand out.
In 2024, this rivalry was particularly evident in the digital banking space, where banks poured resources into sophisticated mobile apps and seamless online services. This digital arms race is crucial for attracting and retaining customers who increasingly demand convenience and instant access. For example, many banks reported significant increases in digital transaction volumes throughout the year, underscoring the importance of robust digital offerings.
The commoditization of basic banking products like checking and savings accounts shifts the competitive focus to customer experience, brand trust, and ease of access, rather than product features alone. This means banks must excel in areas like app functionality and customer support to capture market share. Furthermore, subdued loan growth in 2024, with modest increases in commercial bank lending, intensified the competition for creditworthy borrowers, often leading to aggressive pricing strategies that compress margins.
| Competitor Type | Key Differentiators | 2024 Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| National Banks | Brand recognition, extensive branch/ATM networks, broad product suites | Digital platform enhancement, personalized wealth management |
| Regional Banks (e.g., Commerce Bank) | Community ties, personalized service, local market knowledge | Digital service expansion, customer retention strategies |
| Community Banks | Deep local relationships, tailored solutions, high customer satisfaction | Maintaining agility, leveraging digital tools for local service |
| Fintech Companies | Innovative technology, user experience, niche product offerings | Expanding service offerings, regulatory compliance, customer acquisition |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Digital payment platforms such as PayPal, Venmo, Apple Pay, and Google Pay present a significant threat of substitutes for Commerce Bank. These services offer users more convenient and often faster alternatives to traditional banking methods like checks or wire transfers, particularly for person-to-person transactions and online shopping.
The growing adoption of these fintech solutions directly diminishes customer reliance on Commerce Bank for everyday transactional needs. For instance, in 2023, the global digital payments market was valued at over $9 trillion, with projections indicating continued robust growth, highlighting the substantial shift away from traditional banking services.
Fintech companies have also made inroads into embedded payments, seamlessly integrating payment functionalities into non-financial platforms and further reducing the need for direct interaction with traditional banks. This trend is particularly evident in e-commerce and subscription services, where these alternatives are becoming the default payment method for many consumers.
Online lending platforms and peer-to-peer (P2P) lending present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banks like Commerce Bank. These platforms offer alternatives for personal, small business, and even mortgage loans, often with quicker approvals and distinct underwriting approaches that bypass traditional banking structures.
P2P platforms, in particular, directly connect borrowers with investors, fundamentally altering the lending landscape by removing the intermediary role of banks. This disintermediation can lead to more competitive rates for borrowers and potentially higher returns for investors, making these platforms an attractive substitute for conventional bank loans.
The growth in this sector is substantial; for instance, the global P2P lending market was valued at approximately $50 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, indicating a strong and increasing demand for these alternative lending solutions.
Customers seeking investment and wealth management services increasingly have viable alternatives to traditional bank divisions. Online brokerage platforms like Charles Schwab and Fidelity, alongside automated robo-advisors, provide direct access to investment tools. These digital solutions often come with significantly lower fees and enhanced accessibility, presenting a direct challenge to Commerce Bank's existing investment service offerings.
While robo-advisors have seen substantial growth, with over 85% of their assets under management by 2021 held by established financial institutions, the threat from direct investment platforms remains potent. These platforms empower individuals to manage their portfolios directly, bypassing the need for traditional advisory services and potentially diverting significant assets away from banks like Commerce.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Technology
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology present a growing threat of substitutes for traditional banking services. While still developing, these digital assets and their underlying technology can fulfill functions like cross-border payments and lending, potentially bypassing conventional channels. For instance, by mid-2024, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization hovered around $2.5 trillion, indicating significant capital and user engagement that could be diverted from traditional financial institutions.
The increasing adoption of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, built on blockchain, offers alternative avenues for borrowing, lending, and trading, directly competing with services offered by banks like Commerce Bank. This trend is expected to continue, with projections suggesting the DeFi market could reach substantial valuations by the end of 2024, further solidifying its position as a viable substitute.
The threat is amplified as regulatory clarity around cryptocurrencies improves, potentially leading to wider institutional acceptance and integration. This could reduce customer reliance on traditional banking infrastructure for a growing number of financial activities.
- Growing Market: Global cryptocurrency market cap surpassed $2.5 trillion by mid-2024.
- DeFi Expansion: Decentralized finance platforms offer alternative lending and borrowing.
- Evolving Landscape: Increased adoption could lessen dependence on conventional banking services.
- Future Outlook: Cryptocurrencies are set to remain a significant factor in fintech through 2024 and beyond.
Credit Unions and Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFIs)
Credit unions and Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFIs) present a significant threat of substitutes for Commerce Bank. These entities often provide comparable banking services, yet they typically operate with a member-owned, lower-fee model and a strong community-centric approach. For instance, credit unions, which saw their membership grow to over 136 million in the US by the end of 2023, can attract customers who prioritize community impact and cost savings.
CDFIs, specifically chartered to serve low-income communities and individuals, also offer a compelling alternative. These institutions are crucial for financial inclusion, and their focus on underserved populations means they can draw in customers who feel overlooked by larger, traditional banks. The ongoing challenging regulatory environment for financial institutions throughout 2024 further amplifies the appeal of these alternative models for both consumers and businesses seeking more personalized or mission-driven financial relationships.
- Credit Unions: Offer member-owned, lower-fee banking services, appealing to cost-conscious and community-minded customers.
- CDFIs: Focus on financial inclusion for underserved communities, attracting customers seeking social impact.
- Customer Appeal: Both credit unions and CDFIs can be attractive substitutes for Commerce Bank's customer base, especially those valuing community engagement.
- Regulatory Landscape: A challenging regulatory environment in 2024 may encourage customers to explore these alternative financial institutions.
The threat of substitutes for Commerce Bank is multifaceted, stemming from digital payment platforms, online lending, investment alternatives, cryptocurrencies, and credit unions/CDFIs. These substitutes often offer greater convenience, lower fees, or a more specialized customer experience, directly challenging traditional banking models.
Digital payment platforms like PayPal and Apple Pay are increasingly displacing traditional transaction methods. Online lending platforms and P2P lending offer faster, alternative credit solutions. Furthermore, robo-advisors and online brokerages provide accessible investment services, while cryptocurrencies and DeFi present emerging alternatives for payments and lending.
Credit unions and CDFIs appeal to customers seeking community focus and lower costs. The growing adoption of these substitutes indicates a significant shift in consumer behavior, compelling banks like Commerce to adapt their offerings and value propositions to remain competitive.
| Substitute Category | Key Players/Examples | Impact on Commerce Bank | Market Data (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Payments | PayPal, Venmo, Apple Pay, Google Pay | Reduced reliance for everyday transactions. | Global digital payments market valued over $9 trillion (2023). |
| Online Lending/P2P | LendingClub, Prosper | Competition for personal and business loans. | Global P2P lending market ~$50 billion (2023), projected growth. |
| Investment Platforms | Charles Schwab, Fidelity, Robo-advisors | Diversion of wealth management assets. | Robo-advisor AUM growth significant, impacting traditional advisory fees. |
| Cryptocurrencies/DeFi | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Uniswap | Potential disintermediation of payment and lending. | Global crypto market cap ~$2.5 trillion (mid-2024). DeFi market showing substantial growth. |
| Credit Unions/CDFIs | Local credit unions, community development banks | Attracts customers prioritizing cost savings and community focus. | US credit union membership over 136 million (end of 2023). |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector is a minefield of regulations, making it tough for newcomers to even get started. Imagine needing to secure complex licenses, meet hefty capital reserve demands, and then diving into a sea of anti-money laundering (AML) and consumer protection rules. These aren't just suggestions; they're non-negotiable requirements that act as a powerful deterrent to potential competitors looking to challenge established players like Commerce Bank.
For instance, the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and its associated AML regulations demand significant investment in technology and personnel for compliance. In 2023, the U.S. Department of Justice reported over $2 billion in AML-related fines against financial institutions, underscoring the substantial costs and risks associated with non-compliance, which new entrants must be prepared to absorb from day one.
Establishing a new bank demands considerable upfront capital. This includes funding for operations, robust infrastructure, and meeting stringent regulatory reserve requirements, often in the billions of dollars.
For instance, in 2024, regulatory capital requirements for new bank charters can easily run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, depending on the projected asset size and business model. This substantial financial barrier significantly deters potential new entrants from directly challenging established players like Commerce Bank.
The banking sector is inherently capital-intensive. New entrants must possess immense financial resources to even begin operations, let alone compete effectively with institutions that have decades of accumulated capital and economies of scale.
Commerce Bank, like other established financial institutions, benefits from a deeply ingrained brand reputation and customer trust, a critical barrier for new entrants. Building this level of credibility, particularly for digital-only banks or fintech startups, takes considerable time and consistent positive customer experiences. For instance, in 2024, consumer surveys consistently show that trust remains a primary factor in choosing a bank, with a significant majority still preferring traditional institutions for core financial services.
Established Customer Relationships and Loyalty
Existing banks like Commerce Bank leverage deep-rooted customer relationships and loyalty, often cultivated over decades and even generations. This makes it challenging for new entrants to gain traction.
Disrupting these established bonds is particularly difficult for essential banking products such as primary checking accounts and long-term lending commitments. Customers tend to stick with familiar institutions for these critical financial services.
Customer inertia, fueled by the perceived or actual costs associated with switching financial providers, further solidifies these relationships. These switching costs can include time, effort, and potential disruption to financial management, acting as a significant barrier to new competitors.
- Customer Retention Rate: Commerce Bank's customer retention rate for its core deposit accounts has historically been strong, often exceeding 90% annually.
- Switching Costs: Studies indicate that for primary checking accounts, the average customer perceives switching costs, including time and potential fees, to be upwards of $100.
- Generational Banking: A significant portion of Commerce Bank's customer base has been with the institution for over 20 years, demonstrating generational loyalty.
- Primary Account Inertia: Data from the Federal Reserve in 2024 shows that over 75% of consumers consider their primary checking account provider to be a long-term relationship, not easily changed.
Economies of Scale and Distribution Networks
Incumbent banks like Commerce Bank benefit from significant economies of scale across operations, technology, and marketing, enabling more cost-effective service delivery. Their established physical branch networks and robust digital infrastructure present a high barrier for new entrants. For instance, in 2024, major banks continued to leverage their scale to invest heavily in AI and cybersecurity, areas where startups struggle to match upfront costs. New players must commit substantial capital to build comparable capabilities, placing them at an immediate cost disadvantage.
The threat of new entrants is tempered by the immense investment required to replicate existing scale and distribution. Traditional banks are actively fortifying their competitive positions by enhancing digital offerings to counter the rise of neobanks. By mid-2024, many established institutions had rolled out advanced mobile banking features and personalized digital advisory services, narrowing the perceived gap with digital-first competitors and further raising the bar for new market entrants.
- Economies of Scale: Incumbent banks benefit from lower per-unit costs due to high-volume operations, making it difficult for new entrants to compete on price.
- Distribution Networks: Established branch networks and advanced digital platforms provide significant reach and customer access that new entrants must painstakingly build.
- Investment Barriers: Replicating the operational efficiency, technological sophistication, and market presence of established players requires massive capital investment, deterring many potential new entrants.
- Digital Enhancement: Traditional banks are actively improving their digital services, a trend seen throughout 2024, to retain customers and compete effectively with agile fintechs.
The threat of new entrants for Commerce Bank is significantly low due to high regulatory hurdles and substantial capital requirements. New banks must navigate complex licensing, stringent capital reserves, and compliance with laws like the Bank Secrecy Act, which in 2023 saw over $2 billion in AML fines levied against financial institutions. These barriers, coupled with the need for billions in initial funding, make market entry exceedingly difficult.
Established trust and deep customer relationships represent another formidable barrier. In 2024, consumer preference surveys indicate trust remains paramount, with a majority favoring traditional banks. Over 75% of consumers view their primary checking account as a long-term commitment, highlighting customer inertia and the high perceived switching costs, estimated at over $100 for primary accounts.
Furthermore, incumbent banks like Commerce Bank enjoy significant economies of scale in operations, technology, and marketing, alongside extensive distribution networks. Replicating this infrastructure and market presence demands massive capital investment, a challenge for startups. By mid-2024, established banks were enhancing digital offerings, further raising the competitive bar.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Relevant Data/Example (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex licensing, capital reserves, AML/KYC rules | High cost and time to market | Over $2 billion in AML fines in 2023; new charter capital needs in hundreds of millions to billions. |
| Capital Intensity | Need for substantial upfront funding for operations and infrastructure | Significant financial barrier to entry | Establishing a bank requires billions in initial capital. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Customer loyalty built over time | Difficult to gain market share from incumbents | 75% of consumers view primary checking as a long-term relationship; switching costs estimated >$100. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from large-scale operations and distribution | Disadvantage in pricing and service delivery | Incumbents invest heavily in AI/cybersecurity, difficult for startups to match. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Commerce Bank is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, investor relations materials, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate data from regulatory filings and reputable financial news outlets to capture competitive dynamics and strategic trends.