Credit Agricole Nord de France Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Credit Agricole Nord de France Bundle
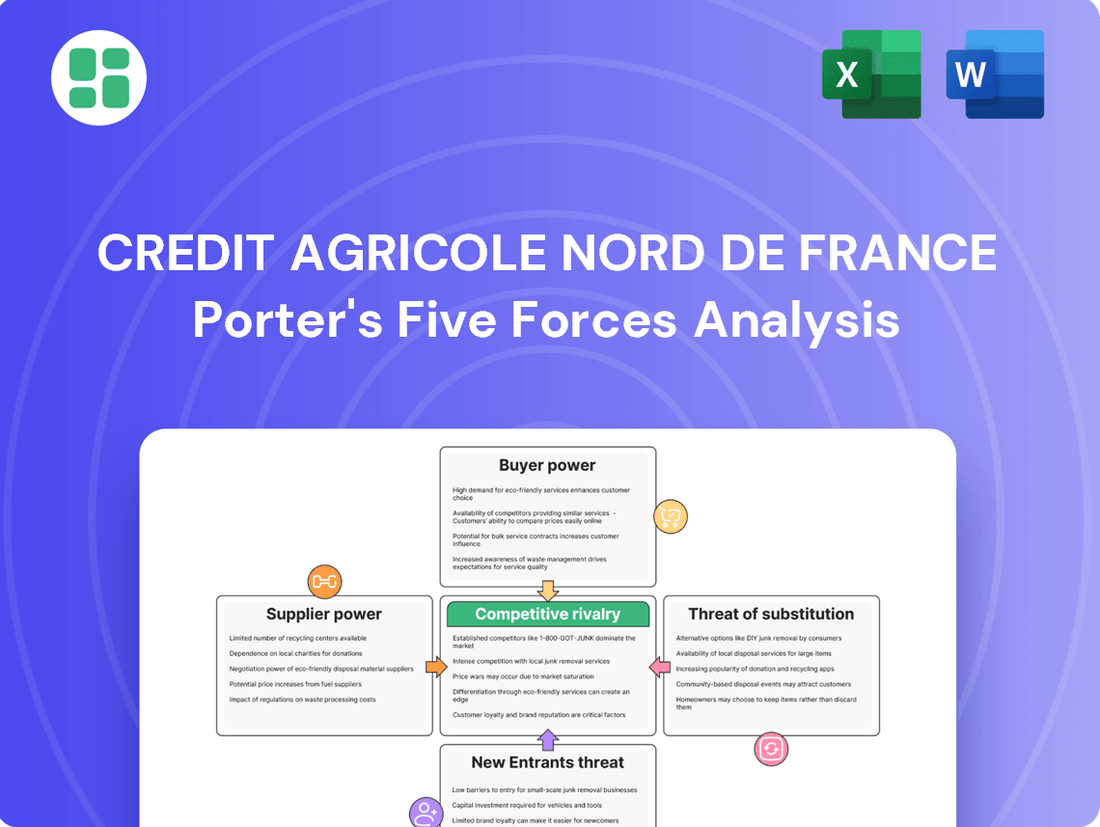
Credit Agricole Nord de France navigates a competitive landscape shaped by moderate buyer power and the ever-present threat of new entrants in the banking sector. Understanding the intensity of these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Credit Agricole Nord de France’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The banking sector's growing dependence on sophisticated IT infrastructure, robust cybersecurity, and tailored financial software significantly boosts the negotiating strength of major technology and software vendors. Crédit Agricole Nord de France's ongoing digital transformation necessitates these providers for essential banking platforms, advanced analytics, and user-facing applications.
The unique characteristics or scarcity of viable substitutes for certain crucial banking technologies can grant these suppliers considerable influence over pricing and contract conditions. For instance, specialized cloud-based core banking solutions, which are becoming increasingly vital for agility, often have a limited number of providers, consolidating their market power.
Global payment network operators like Visa and Mastercard wield substantial bargaining power. Their systems are critical infrastructure for virtually all financial transactions, making them indispensable for banks. For instance, in 2024, Visa reported processing over 230 billion transactions globally, highlighting their vast reach and essentiality.
Crédit Agricole Nord de France, despite its regional focus, relies heavily on these networks to offer payment services to its customers. The bank's operational efficiency and customer satisfaction are directly tied to the terms and accessibility provided by these dominant players. Any changes in fees or service level agreements from these operators can significantly impact the bank's cost structure and competitive offering.
Specialized financial data and analytics firms hold significant bargaining power. Access to accurate, timely data and sophisticated analytical tools is vital for Credit Agricole Nord de France’s risk management and investment strategies. The increasing reliance on data-driven approaches by banks amplifies this supplier power, especially for firms with unique datasets or proprietary algorithms.
Human Capital and Talent Pools
The demand for specialized skills in areas such as cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, data science, and digital banking is exceptionally high within the financial sector. As Crédit Agricole Nord de France aims to bolster its digital offerings, this scarcity of niche talent directly amplifies the bargaining power of both employees and specialized recruitment agencies. This situation can translate into increased labor expenses and significant hurdles in retaining valuable personnel.
The competition for top-tier talent in these crucial fields is fierce, impacting recruitment timelines and compensation packages. For instance, in 2024, the average salary for a data scientist in France saw an upward trend, reflecting this demand. This intensified competition means that suppliers of human capital—namely, skilled professionals and the agencies that source them—hold considerable leverage.
- High Demand for Digital Expertise: Sectors like AI and cybersecurity are experiencing unprecedented growth, driving up the need for qualified professionals.
- Talent Scarcity Drives Costs: The limited supply of individuals with these specific skills leads to higher salary expectations and recruitment fees.
- Impact on Recruitment: Recruitment agencies specializing in financial technology talent can command higher fees due to their access to these sought-after individuals.
- Retention Challenges: Banks face increased pressure to offer competitive compensation and benefits to retain employees with in-demand digital skills.
Regulatory Compliance and Consulting Services
The increasingly intricate web of regulations in France and the broader European Union, including frameworks like DORA and MiCA, demands substantial financial and operational commitment for compliance. For instance, the implementation costs for DORA alone are projected to be significant for financial institutions across the EU.
Specialized consulting firms and external providers offering expertise in regulatory advisory and reporting solutions, such as RUBA or CREDITIMMO, wield considerable bargaining power. These entities are crucial for navigating complex requirements like LCB-FT (Lutte Contre le Blanchiment et le Financement du Terrorisme).
Financial institutions like Crédit Agricole Nord de France rely heavily on these external experts to ensure adherence to stringent compliance mandates, thereby mitigating the risk of substantial fines and reputational damage. The demand for such specialized services is high, granting these suppliers leverage.
- Regulatory Complexity: France and the EU are implementing extensive regulations (e.g., DORA, MiCA, Basel III) requiring significant investment in compliance infrastructure and expertise.
- Consultant Leverage: Specialized firms providing regulatory advisory, reporting solutions, and compliance services (e.g., RUBA, CREDITIMMO) hold strong bargaining power due to their essential role.
- Dependence on Expertise: Banks like Crédit Agricole Nord de France are dependent on these external consultants to successfully navigate strict compliance requirements and avoid penalties.
Suppliers of specialized IT infrastructure and software vendors hold significant power due to banks' increasing reliance on digital transformation. Crédit Agricole Nord de France's need for core banking solutions and advanced analytics, often from a limited pool of providers, amplifies this leverage.
Global payment networks like Visa and Mastercard are indispensable for financial transactions, granting them substantial bargaining power. Their essential role in facilitating payments means banks are highly dependent on their services and terms, as evidenced by Visa processing over 230 billion transactions in 2024.
The scarcity of highly skilled talent in areas like AI and cybersecurity significantly boosts the bargaining power of both employees and recruitment agencies. This demand, reflected in rising data scientist salaries in France in 2024, makes it challenging and costly for banks to attract and retain essential personnel.
Specialized consulting firms offering regulatory compliance expertise are crucial for banks navigating complex French and EU regulations. Crédit Agricole Nord de France's dependence on these firms to ensure adherence to mandates like DORA and LCB-FT gives these suppliers considerable influence over pricing and service delivery.
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting Credit Agricole Nord de France, examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Credit Agricole Nord de France's bargaining power of suppliers and buyers.
Customers Bargaining Power
Crédit Agricole Nord de France caters to a wide array of customers, from individual savers to large agricultural enterprises. This diversity means the bargaining power of customers isn't uniform across the board.
Individual retail customers, while numerous, typically possess limited individual bargaining power. However, their collective strength is amplified by the ease of switching banks and the growing demand for competitive digital offerings and tailored products. In 2024, the digital banking adoption rate continued to climb, putting pressure on banks to offer seamless online experiences.
Conversely, business and agricultural clients, often dealing with substantial financial volumes and playing a crucial role in the regional economy, wield greater negotiation leverage. Their ability to secure more favorable loan terms, investment products, or specialized financial services directly impacts the bank's profitability and market share.
As a cooperative bank, Crédit Agricole Nord de France's ownership by its members significantly shifts customer power. Members directly influence the bank's governance and strategy, impacting decisions on profit allocation and community investment. This cooperative model provides customers with a collective bargaining influence that goes beyond typical banking relationships.
Customers today face remarkably low switching costs for many digital banking services. The proliferation of online-only banks and innovative fintech applications means that opening a new account or transferring funds can often be accomplished in minutes, with minimal paperwork. This ease of transition directly empowers customers, making them less hesitant to explore alternative providers if their current bank falls short on digital experience or pricing. For instance, in 2024, reports indicated a significant increase in new customer acquisition for challenger banks, largely driven by their user-friendly digital platforms.
Access to Information and Price Transparency
Customers in France now have unprecedented access to information about banking products, interest rates, and fees. Online comparison platforms and financial news outlets make it simple for consumers to shop around, directly impacting Crédit Agricole Nord de France's pricing strategies.
This heightened price transparency significantly boosts the bargaining power of customers. They can easily identify and switch to competitors offering better terms, forcing Crédit Agricole Nord de France to remain competitive to retain its client base. In 2024, a significant portion of French consumers actively utilized digital tools for financial research.
- Increased Online Comparison: A substantial percentage of French adults used online comparison sites for financial products in 2024, a trend that continues to grow.
- Demand for Personalization: French consumers are increasingly expecting tailored financial advice and personalized product offers from their banks.
- Price Sensitivity: readily available pricing information makes customers more sensitive to fees and interest rates, driving demand for better deals.
Demand for Personalized and Digital Experiences
French banking customers are increasingly demanding personalized financial product offers and seamless omnichannel experiences. This shift means banks must adapt to meet evolving digital expectations.
Failure to provide convenience and tailored services can lead to customer attrition, with fintechs often leading the charge in this area. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of French consumers expressed a preference for digital banking channels for routine transactions.
- Personalization: Customers expect offers and advice tailored to their specific financial situation.
- Digital Channels: A growing preference for mobile apps and online platforms for banking needs.
- Omnichannel Experience: The ability to seamlessly switch between digital and physical banking touchpoints.
- Competitive Pressure: Fintechs are setting new standards for customer experience, increasing customer leverage.
The bargaining power of customers for Crédit Agricole Nord de France is shaped by both individual client characteristics and broader market trends. While individual retail customers have limited power, their collective influence, amplified by low switching costs and demand for digital services, is significant. Business and agricultural clients, due to higher transaction volumes, possess greater individual leverage, influencing loan terms and specialized services.
| Customer Segment | Individual Bargaining Power | Collective Bargaining Power | Key Influences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail Customers | Low | High | Ease of switching, digital demand, price transparency |
| Business/Agricultural Clients | High | Moderate | Transaction volume, need for specialized services |
| Cooperative Members | High (via governance) | Very High | Direct influence on strategy and profit allocation |
What You See Is What You Get
Credit Agricole Nord de France Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Credit Agricole Nord de France Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive intensity within the regional banking sector. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The French banking sector is highly concentrated, with major national banks like Crédit Agricole Group, BNP Paribas, Société Générale, and BPCE holding significant market share. These large institutions possess vast resources and extensive branch networks, creating a formidable competitive environment for regional players.
In 2024, the combined assets of the top four French banking groups continued to represent a substantial portion of the national financial system, underscoring their dominance. This intense rivalry means Crédit Agricole Nord de France must constantly innovate and offer competitive pricing to retain and attract customers.
French banks, including Crédit Agricole Nord de France, are locked in a fierce pricing battle, especially concerning deposit rates and the margins on retail loans. This intense competition is a significant factor shaping the financial landscape for these institutions.
The French market's specific structure, particularly in lending and savings, contributes to this pressure. It means that banks like Crédit Agricole Nord de France often see slower recovery in their net interest margins when compared to their counterparts in other European countries. This structural characteristic directly impacts profitability.
For instance, in 2023, the average net interest margin for French banks hovered around 1.5%, a figure that reflects the ongoing pricing pressures. This environment forces banks to remain highly competitive on pricing to attract and retain customers, which in turn constrains their ability to boost overall profitability.
Crédit Agricole Nord de France faces significant competition from other regional cooperative and mutual banks, many of which share a similar community-focused ethos and localized operational strategy. These entities often compete directly for the same customer base, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas, by highlighting their deep local roots and commitment to regional development.
The cooperative structure inherently fuels a distinct form of local competition. For instance, in 2024, the French banking sector saw continued consolidation, but many smaller, regional cooperative banks maintained strong market share in their specific territories. These banks often differentiate themselves through personalized service and a tangible connection to the local economy, directly challenging Crédit Agricole Nord de France's market presence.
Digital Transformation and Innovation Race
French banks, including Crédit Agricole Nord de France, are engaged in a fierce digital transformation race. This competition is driven by the need to enhance customer experience, streamline operations, and launch innovative digital products and services. For instance, in 2024, many French banks reported significant increases in their IT and digital spending, with some allocating over 15% of their operating expenses to these areas to stay ahead.
The intensity of this innovation race means that banks must constantly adapt and deploy new technologies. This includes advancements in mobile banking, AI-powered customer service, and personalized financial advice. The pressure to innovate is particularly high for institutions with extensive physical branch networks, as they must strategically integrate digital solutions while managing the costs associated with their brick-and-mortar presence to maintain a competitive edge.
- Intensified Digital Investment: French banks are channeling substantial resources into digital transformation initiatives, with IT and digital budgets seeing double-digit percentage increases year-over-year through 2024.
- Customer Experience Focus: A primary driver of this digital race is the imperative to deliver seamless and personalized customer journeys, pushing banks to adopt cutting-edge technologies.
- Innovation as a Differentiator: Banks are leveraging innovation in areas like AI, big data analytics, and blockchain to create new revenue streams and differentiate their offerings.
- Balancing Physical and Digital: Traditional banks are challenged to optimize their branch networks alongside digital advancements, seeking a cost-efficient model that caters to evolving customer preferences.
Regulatory and Economic Headwinds
The French banking sector is grappling with a noticeable economic slowdown, amplified by political uncertainty and a constantly shifting regulatory landscape. These external forces directly constrain loan growth and squeeze profitability for institutions like Crédit Agricole Nord de France.
Compounding these issues, banks are intensely focused on boosting operational efficiency and proactively managing an uptick in non-performing loans. This internal pressure cooker further intensifies the competitive environment as firms strive to maintain market share amidst these significant headwinds.
- Economic Slowdown Impact: In 2024, France's GDP growth is projected to be modest, around 0.7%, creating a challenging environment for credit expansion.
- Regulatory Burden: Increased capital requirements and compliance costs, driven by Basel III Endgame implementation, add significant operational expenses for banks.
- Profitability Pressures: Net interest margins are under pressure, with the average European bank's net interest income growth expected to moderate in 2024 compared to the strong performance in 2023.
Competitive rivalry within the French banking sector, impacting Crédit Agricole Nord de France, is characterized by intense pricing wars on loans and deposits, driven by a concentrated market dominated by large national players. This rivalry is further intensified by a strong digital transformation race, where banks are heavily investing in technology to enhance customer experience and streamline operations. The average net interest margin for French banks was around 1.5% in 2023, reflecting these pricing pressures.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Strategy | Impact on Crédit Agricole Nord de France |
|---|---|---|
| Large National Banks (e.g., BNP Paribas, Société Générale) | Extensive branch networks, broad product offerings, significant digital investment | Forces Crédit Agricole Nord de France to compete on scale, innovation, and pricing to retain market share. |
| Regional Cooperative Banks | Community focus, personalized service, local economic commitment | Directly challenges Crédit Agricole Nord de France in its core territories, emphasizing local ties. |
| Digital-Only Banks / Fintechs | Agile technology, lower overheads, innovative digital products | Drives the need for rapid digital adaptation and competitive digital offerings from Crédit Agricole Nord de France. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Crédit Agricole Nord de France is significantly amplified by the burgeoning fintech and neobank landscape in France. These agile digital disruptors offer streamlined, specialized financial services that can directly appeal to customers looking for alternatives to traditional banking. For instance, neobanks like Revolut and N26 have seen substantial user growth in France, with Revolut reporting over 8 million European customers by early 2024, many of whom are actively seeking digital-first banking experiences.
These fintech companies, including digital payment providers and alternative lending platforms, present a compelling substitute by often providing lower fees, faster transaction times, and more intuitive user interfaces. This is particularly attractive to younger, tech-savvy demographics who may find traditional banking processes cumbersome. The increasing adoption of digital wallets and peer-to-peer payment systems further erodes the reliance on conventional banking channels for everyday transactions.
Customers are increasingly exploring direct investment avenues, like crowdfunding and peer-to-peer (P2P) lending, as alternatives to traditional banking. These platforms offer a diverse range of investment opportunities and loan options, often with more flexible terms and potentially higher returns than conventional bank products. For instance, the global P2P lending market was valued at approximately $61.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong shift in consumer behavior away from solely relying on established financial institutions.
Bigtech firms like Apple and Google are increasingly offering financial services, particularly in payments and lending. Apple Pay, for instance, saw a significant increase in adoption, with reports indicating over 500 million users globally by early 2024, demonstrating their growing reach into consumer finance.
These tech giants leverage their massive user bases and advanced data analytics to provide seamless, integrated financial experiences, potentially drawing customers away from traditional banking services. Their ability to offer convenient, low-friction payment solutions and accessible credit can disrupt established banking models.
For instance, Google Pay has expanded its offerings to include peer-to-peer payments and even buy-now-pay-later options in select markets, directly competing with bank-offered services. This trend signifies a substantial threat of substitution as consumers may find these integrated digital solutions more appealing than traditional banking channels.
Specialized Non-Bank Lenders and Insurers
For specific financial needs, customers can turn to specialized non-bank lenders and insurers. These providers often focus on niche areas, such as real estate financing or particular types of insurance coverage, offering highly tailored products. For example, in 2024, the alternative lending market continued to expand, with non-bank lenders playing an increasingly significant role in providing credit, particularly for commercial real estate. This specialization allows them to potentially offer more competitive rates or specialized services that directly substitute for parts of Crédit Agricole Nord de France's broader product suite.
These specialized entities can present a significant threat by directly competing with Crédit Agricole Nord de France in specific market segments. By concentrating on particular financial products, they can develop deep expertise and agility, allowing them to respond more quickly to market demands or customer preferences. This focused approach can lead to more attractive offerings for customers seeking specialized solutions, thereby diverting business from traditional, more diversified financial institutions.
- Specialized Lenders: Non-bank lenders focusing on areas like mortgages or business loans can offer tailored solutions.
- Direct Insurers: Insurance companies selling directly to consumers bypass traditional banking channels for protection products.
- Competitive Rates: Niche players may achieve lower overheads, enabling them to offer more aggressive pricing.
- Product Innovation: Focused entities can innovate faster within their specific product categories.
Cryptocurrencies and Digital Wallets
The rise of cryptocurrencies and digital wallets, while still nascent, poses a potential threat of substitution for Credit Agricole Nord de France's traditional banking services. For instance, by the end of 2023, global cryptocurrency adoption reached an estimated 420 million users, indicating a growing segment of the population comfortable with digital asset management and transactions.
These digital currencies offer alternative avenues for value storage and peer-to-peer transactions, bypassing conventional financial intermediaries. As of early 2024, the total market capitalization of cryptocurrencies hovered around $1.6 trillion, demonstrating significant market interest and a growing ecosystem.
- Growing User Base: Global cryptocurrency users surpassed 420 million by the end of 2023.
- Market Capitalization: The crypto market cap approached $1.6 trillion in early 2024, signaling increasing financial activity.
- Transaction Alternatives: Digital wallets facilitate direct peer-to-peer transactions, potentially reducing reliance on traditional payment rails.
The threat of substitutes for Crédit Agricole Nord de France is substantial, driven by a diverse array of non-traditional financial service providers. Fintech companies and neobanks are increasingly offering specialized, digital-first alternatives that appeal to customers seeking convenience and lower costs. For example, neobanks have gained significant traction, with user numbers in Europe reaching tens of millions by early 2024, indicating a clear shift in consumer preference.
These agile players often provide streamlined services, such as digital payments and alternative lending, frequently at lower fees and with faster processing times. This is particularly attractive to younger demographics accustomed to digital interfaces. The growing adoption of digital wallets, with services like Apple Pay boasting over 500 million users globally by early 2024, further highlights the move away from traditional banking channels for everyday transactions.
Beyond digital disruptors, specialized non-bank lenders and insurers are carving out niches, offering tailored solutions for specific financial needs like mortgages or business loans. The alternative lending market, valued at over $61 billion globally in 2023, demonstrates a strong demand for these focused financial products. Furthermore, the burgeoning cryptocurrency sector, with over 420 million users worldwide by late 2023 and a market capitalization nearing $1.6 trillion in early 2024, presents an emerging alternative for value storage and transactions, bypassing traditional financial institutions.
| Substitute Type | Key Offerings | User/Market Data (as of early 2024) | Impact on Traditional Banks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech & Neobanks | Digital payments, alternative lending, streamlined banking | 8M+ European users (Revolut); Significant user growth across platforms | Lower fees, faster transactions, digital-first experience appeal |
| Bigtech Financial Services | Digital wallets, payment solutions, integrated credit | 500M+ global users (Apple Pay) | Convenient, low-friction alternatives, leveraging existing user bases |
| Specialized Lenders/Insurers | Niche mortgages, business loans, direct insurance | Alternative lending market valued at $61.4B (2023) | Tailored products, competitive rates in specific segments |
| Cryptocurrencies & Digital Wallets | Value storage, peer-to-peer transactions | 420M+ global users (late 2023); $1.6T market cap (early 2024) | Potential for disintermediation, alternative transaction methods |
Entrants Threaten
The financial services sector, especially banking, is a heavily regulated arena. This means new players must navigate complex licensing, adhere to strict capital requirements, and maintain ongoing compliance with rules designed to ensure stability and prevent illicit activities. For instance, the implementation of Basel III and upcoming Basel IV (often referred to as CRR3/CRD6) standards in 2024 and beyond significantly increases the capital banks must hold, making it a substantial financial undertaking for any new entrant.
The need for trust and brand reputation presents a substantial barrier for new entrants into the French banking sector, a key consideration for Crédit Agricole Nord de France. Established institutions have cultivated customer trust over many years, a factor that French consumers deeply value when selecting financial partners. In 2024, for instance, surveys consistently show that security and reliability remain top priorities for individuals and businesses alike when choosing a bank.
Crédit Agricole Nord de France's extensive branch network, a cornerstone of its regional cooperative model, presents a significant barrier to new entrants. This dense physical presence, coupled with deeply embedded local relationships, would necessitate enormous capital outlay and considerable time for any competitor to replicate, making it difficult to challenge the bank on its established turf.
Customer Acquisition Costs and Brand Loyalty
The threat of new entrants in the French retail banking sector, particularly for a player like Crédit Agricole Nord de France, is significantly shaped by customer acquisition costs and the enduring strength of brand loyalty. Building a substantial customer base in this mature market requires considerable investment in marketing and advertising, as established players have already cultivated strong relationships and trust.
Despite advancements in digital banking, a notable segment of French consumers still prefers or relies on traditional banking methods, including physical branches. This preference creates a barrier for new entrants, making it both challenging and expensive to attract and retain customers who are accustomed to established institutions.
- High Marketing Spend: Acquiring new customers in French retail banking can cost upwards of €150-€200 per customer, reflecting intense competition and the need for significant outreach.
- Brand Loyalty: Studies in 2024 indicate that over 60% of French banking customers remain with their primary bank for more than 10 years, showcasing deep-rooted loyalty.
- Digital vs. Traditional: While digital adoption is growing, approximately 40% of French adults still visit a bank branch at least once a month, highlighting the continued importance of physical presence.
- Incumbent Advantages: Established banks benefit from economies of scale, existing infrastructure, and regulatory familiarity, which new entrants must overcome.
Fintech Niche Entry and Regulatory Sandboxes
While the traditional banking sector presents significant barriers to entry for new players, particularly in areas like capital requirements and established customer bases, the fintech landscape offers a different dynamic. Fintech firms can strategically target specific, less capital-intensive niches within financial services, such as digital payment solutions or specialized lending platforms. These focused entrants leverage technology to reduce operational overheads, allowing them to compete effectively in these specialized segments.
Regulatory initiatives, including the expansion of regulatory sandboxes, are designed to encourage innovation and can provide a pathway for these agile fintechs to test and refine their offerings. For instance, the UK's Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) sandbox has seen numerous firms successfully navigate the testing phase, with many progressing to full authorization. This environment allows new entrants to gain traction and build a customer base in a controlled manner, potentially challenging incumbent institutions in specific service areas.
- Niche Specialization: Fintechs focus on high-demand, lower-overhead areas like digital payments and peer-to-peer lending.
- Technological Advantage: Leveraging advanced technology reduces operational costs compared to traditional banks.
- Regulatory Support: Initiatives like regulatory sandboxes in jurisdictions such as the UK and Singapore facilitate controlled market entry for innovative financial services.
- Market Penetration: Successful sandbox participants can gain early market share, potentially expanding their services over time.
The threat of new entrants for Crédit Agricole Nord de France remains moderate due to substantial regulatory hurdles and high capital requirements, particularly with Basel IV implementation in 2025. While fintechs can target niches, replicating the extensive branch network and deep customer loyalty of established players like Crédit Agricole requires significant investment and time, making widespread disruption unlikely in the near term.
| Barrier | Impact on New Entrants | Supporting Data (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance & Capital Requirements | High | Basel IV (CRR3/CRD6) increasing capital needs; average cost of obtaining a banking license in France can exceed €5 million. |
| Brand Reputation & Customer Loyalty | High | Over 60% of French customers stay with their primary bank for >10 years; trust remains a top priority. |
| Physical Infrastructure & Network | High | Crédit Agricole's extensive regional branch network requires massive capital to replicate. |
| Customer Acquisition Costs | High | Acquiring a new retail banking customer can cost €150-€200. |
| Fintech Niche Entry | Moderate | Fintechs can enter specific digital payment or lending segments with lower overheads. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Crédit Agricole Nord de France is built upon a foundation of robust data, including the bank's annual reports, regulatory filings from the Autorité de Contrôle Prudentiel et de Résolution (ACPR), and industry-specific market research from firms like S&P Global Market Intelligence.