Burke & Herbert Financial Services Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Burke & Herbert Financial Services Bundle
Burke & Herbert Financial Services operates within a dynamic landscape shaped by intense competition and evolving customer expectations. Understanding the underlying forces at play is crucial for navigating this environment effectively.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis dives deep into the specific pressures impacting Burke & Herbert Financial Services, revealing the true competitive intensity and strategic levers available. Unlock actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making and gain a competitive edge.
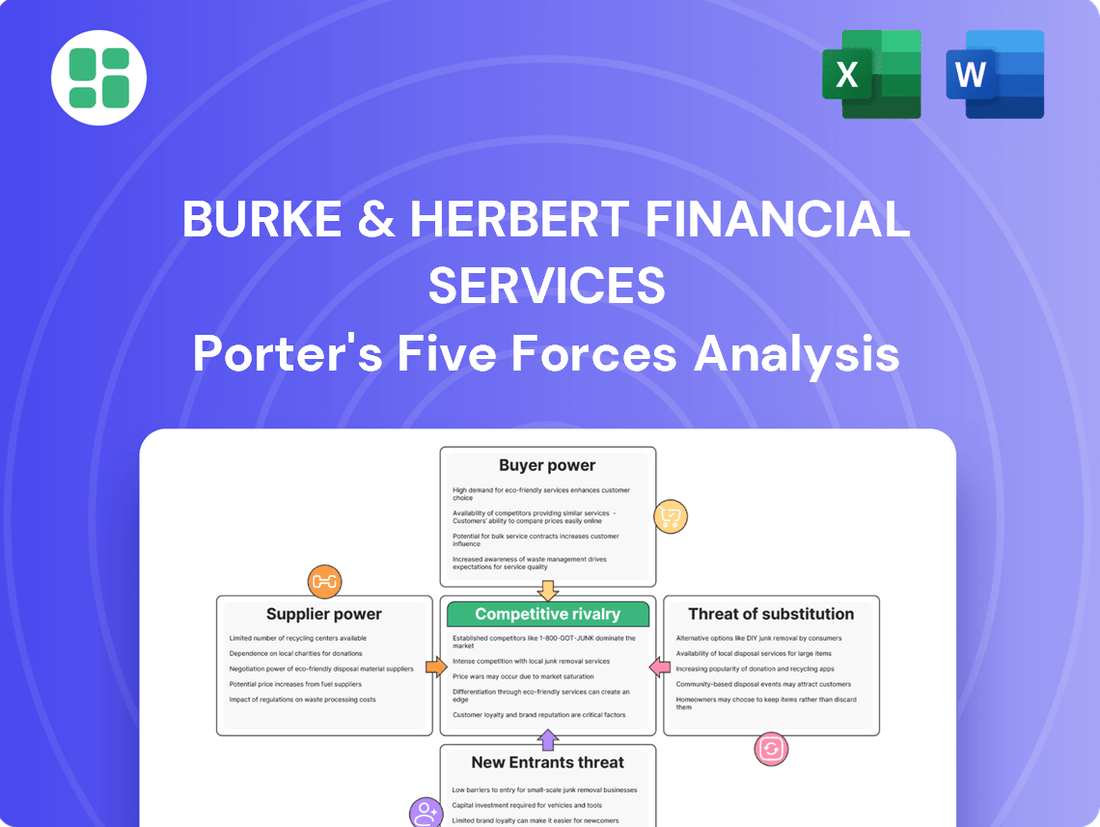
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Depositors are a bank's primary source of loanable funds, making their bargaining power significant. The cost of these deposits directly impacts Burke & Herbert Financial Services' profitability. In 2024, the Federal Reserve maintained a relatively high federal funds rate, pushing up the cost of deposits for many financial institutions as they competed for customer funds.
Burke & Herbert's ability to attract and retain deposits at competitive rates without excessively increasing interest expenses is a key challenge. Factors such as the prevailing interest rate environment and intense competition for deposits from other banks and alternative investment vehicles directly influence how much power depositors wield.
Burke & Herbert Financial Services, like many in the banking sector, relies heavily on third-party technology and software providers for its core operations. This includes everything from the fundamental banking systems that manage accounts and transactions to crucial cybersecurity solutions and the digital platforms customers interact with daily.
The switching costs for these critical systems can be substantial, involving not just the financial outlay for new software and implementation but also the disruption to ongoing operations and the retraining of staff. This inherent stickiness gives established technology vendors significant leverage, especially when their solutions are deeply integrated into Burke & Herbert's existing infrastructure.
Furthermore, the unique features, proprietary integration capabilities, or specialized functionalities offered by certain software providers can further enhance their bargaining power. If a vendor's platform offers a competitive edge or is exceptionally difficult to replicate, Burke & Herbert's ability to negotiate favorable terms may be diminished.
Skilled banking professionals, such as loan officers and wealth managers, wield significant bargaining power, particularly in a competitive labor market like the D.C. metropolitan area. The demand for specialized talent, especially in areas like IT and cybersecurity, drives up compensation packages, directly impacting Burke & Herbert Financial Services' operational costs.
In 2024, the average salary for a banking manager in the D.C. area was approximately $120,000, with specialized roles like IT security analysts commanding even higher figures. This high cost of skilled labor can squeeze profit margins if not managed effectively.
Regulatory and Compliance Services
Burke & Herbert Financial Services, like many in the banking sector, relies heavily on external regulatory and compliance services. This dependence stems from the intricate and ever-changing landscape of financial laws, cybersecurity mandates, and anti-money laundering (AML) requirements. The specialized expertise these legal and consulting firms possess in navigating these complex regulations grants them considerable bargaining power.
The need for specialized knowledge in areas such as data privacy, consumer protection laws, and international banking regulations means that banks often have limited alternatives for obtaining this critical support. For instance, in 2024, the cost of specialized legal counsel for financial institutions saw an upward trend, with some reports indicating an average increase of 5-8% for compliance-related services, reflecting the demand and the specialized nature of the work. This situation allows these service providers to command higher fees.
- Specialized Knowledge: Expertise in banking laws, cybersecurity, and AML regulations is a key driver of supplier power.
- Regulatory Complexity: The constantly evolving nature of financial regulations necessitates ongoing reliance on external experts.
- Limited Alternatives: The scarcity of firms with deep, proven experience in financial compliance narrows a bank's options.
- Increased Costs: In 2024, the demand for these specialized services has led to an estimated 5-8% increase in their associated costs for financial institutions.
Financial Data and Information Providers
Burke & Herbert Financial Services, like many institutions, relies heavily on external entities for critical financial data and information. These providers supply market data, credit ratings, and other essential intelligence that underpins risk assessment and investment strategies. The proprietary nature or established industry standards of these data sources often grant these suppliers significant leverage.
The bargaining power of these financial data and information providers is a key consideration. For instance, the cost of data subscriptions can represent a substantial operational expense for financial services firms. In 2024, the global market for financial data and analytics was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, highlighting the scale and importance of these services.
- Reliance on Proprietary Data: Many providers offer unique datasets or analytical tools that are not readily available elsewhere, creating a dependency for Burke & Herbert.
- Industry Standards and Interoperability: The adoption of certain data formats or rating methodologies as industry standards can limit the number of viable alternative providers.
- Switching Costs: Migrating to a new data provider can involve significant costs related to system integration, data cleansing, and employee retraining.
- Data Quality and Reliability: The perceived quality and reliability of a provider's data can outweigh price considerations, further strengthening the provider's position.
Burke & Herbert Financial Services, like many institutions, relies heavily on external entities for critical financial data and information. These providers supply market data, credit ratings, and other essential intelligence that underpins risk assessment and investment strategies. The proprietary nature or established industry standards of these data sources often grant these suppliers significant leverage.
The bargaining power of these financial data and information providers is a key consideration. For instance, the cost of data subscriptions can represent a substantial operational expense for financial services firms. In 2024, the global market for financial data and analytics was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, highlighting the scale and importance of these services.
Reliance on proprietary data, industry standards, and high switching costs all contribute to the significant leverage held by financial data providers. The perceived quality and reliability of their information often outweigh price, making it difficult for Burke & Herbert to negotiate favorable terms or easily switch providers.
| Data Provider Type | Key Factors Influencing Power | Impact on Burke & Herbert |
|---|---|---|
| Market Data Providers | Proprietary data, real-time access, historical depth | High subscription costs, limited alternatives for comprehensive data |
| Credit Rating Agencies | Industry-wide acceptance, regulatory reliance | Fees for ratings, influence on borrowing costs |
| Financial Analytics Software | Integration complexity, unique algorithms, ongoing support | Significant licensing and implementation costs, vendor lock-in |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Burke & Herbert Financial Services, detailing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a clear, actionable breakdown of Burke & Herbert's Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers can easily switch their basic deposit accounts or secure simple loans from one financial institution to another, particularly with the proliferation of digital banking platforms. This ease of transition is driven by minimal financial or procedural hurdles, allowing consumers to readily seek out more favorable interest rates or superior service offerings.
Customers in the Northern Virginia and D.C. metro area benefit from a wide array of financial service providers. This includes major national banks, local credit unions, and innovative online-only institutions, offering extensive choices.
This abundance of options significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Consumers and businesses can readily compare offerings, fees, and interest rates across different institutions, making it easier to switch for better terms.
For instance, by July 2025, the region's financial landscape features over 100 financial institutions, including 15 large national banks and numerous community banks and credit unions, all competing for customer business.
Customers, especially when looking for loans or competitive deposit rates, are becoming more attuned to interest rate differentials across financial institutions. This heightened price sensitivity means Burke & Herbert faces pressure to offer attractive rates to attract and retain business.
In 2024, for instance, the Federal Reserve's monetary policy decisions significantly influenced market rates. For example, if the Fed maintained higher interest rates, customers actively seeking loans would compare rates from various banks, potentially forcing Burke & Herbert to adjust its lending margins to remain competitive.
Similarly, with the rise of high-yield savings accounts and money market funds, depositors can easily move their funds to institutions offering even a small uptick in yield. This dynamic directly impacts Burke & Herbert's cost of funds and profitability, as they must balance competitive deposit rates with their lending profitability.
Digital Sophistication and Expectation for Convenience
Customers increasingly expect highly convenient and seamless digital banking. This includes user-friendly mobile apps, easy online account management, and instant payment options, pushing financial institutions to prioritize technological advancements. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of banking transactions are conducted digitally, with mobile banking adoption continuing its upward trajectory, forcing firms like Burke & Herbert Financial Services to innovate or risk losing market share to more digitally adept competitors.
The bargaining power of customers is amplified by their ability to easily switch to providers offering superior digital experiences. This pressure compels traditional banks to invest substantially in upgrading their digital infrastructure and services to meet evolving customer demands for speed and accessibility.
- Digital Channel Adoption: In 2024, data shows that over 70% of routine banking tasks are performed via digital channels by a majority of consumers.
- Customer Retention through Digitalization: Banks that offer robust digital platforms report higher customer retention rates, indicating the power of digital convenience.
- Investment in Fintech: Traditional financial institutions are increasingly partnering with or acquiring fintech companies to enhance their digital offerings, a trend that accelerated in 2023-2024.
Customer Loyalty vs. Relationship Banking
Burke & Herbert Financial Services navigates the delicate balance between fostering deep customer loyalty through personalized, relationship-based banking and the increasing customer inclination towards convenience, competitive rates, and advanced digital offerings. This dynamic directly influences the bargaining power of customers.
The effectiveness of Burke & Herbert's personalized service strategy is crucial in mitigating this customer power. By cultivating strong, trust-based relationships, the institution aims to create stickiness that transcends transactional considerations. For instance, in 2024, community banks like Burke & Herbert often report higher customer retention rates when they actively engage with local communities and offer tailored financial advice, a stark contrast to larger, more impersonal institutions.
- Relationship Depth: Burke & Herbert's long-standing presence and focus on personalized interactions, as evidenced by their consistent community involvement, can build a loyal customer base less susceptible to competitor offers.
- Digital Expectations: While relationship banking is a strength, customers increasingly expect seamless digital platforms. Failing to meet these expectations, even with strong personal ties, can empower customers to seek alternatives.
- Rate Sensitivity: Despite loyalty, customers remain sensitive to interest rates and fees. Burke & Herbert must ensure its offerings remain competitive to prevent customers from leveraging rate differences as a bargaining tool.
- Service Differentiation: The bank's ability to differentiate its personalized service from competitors' offerings is key. If competitors can replicate or surpass the personalized experience, customer bargaining power increases significantly.
Customers wield significant bargaining power due to the ease of switching financial providers and the abundance of choices available, especially in the competitive Northern Virginia and D.C. metro area. This power is further amplified by increasing price sensitivity and the demand for seamless digital banking experiences.
In 2024, the financial services sector saw continued digital transformation, with a majority of consumers conducting routine banking tasks via digital channels. For instance, over 70% of such tasks were handled digitally, underscoring the importance of robust online platforms for customer retention and satisfaction.
Burke & Herbert Financial Services must therefore balance its relationship-based approach with competitive rates and advanced digital offerings to effectively manage customer bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Burke & Herbert's Response |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Switching | High; low switching costs for basic accounts and loans | Focus on personalized service and community ties to build loyalty |
| Availability of Alternatives | High; numerous national banks, credit unions, and fintechs | Differentiate through tailored advice and local market understanding |
| Price Sensitivity | Increasing; customers actively compare rates and fees | Monitor market rates and offer competitive deposit and lending terms |
| Digital Expectations | High; demand for user-friendly apps and online management | Invest in digital infrastructure and user experience enhancements |
Same Document Delivered
Burke & Herbert Financial Services Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Burke & Herbert Financial Services Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape, including detailed insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the financial services sector. This professionally formatted document is ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Burke & Herbert Financial Services faces significant competitive pressure from larger national and regional banks operating within its core Northern Virginia and D.C. metropolitan markets. These competitors, such as Capital One and Truist, possess substantial financial resources, enabling them to invest heavily in expansive branch networks and broad marketing campaigns. For instance, as of Q1 2024, Capital One reported total assets exceeding $470 billion, dwarfing Burke & Herbert's asset base, and allowing for aggressive customer acquisition strategies and product development.
Burke & Herbert Financial Services faces significant rivalry from numerous other community banks and credit unions that actively compete within the same local markets. These institutions frequently employ similar relationship-based banking strategies, aiming to attract and retain customers through personalized service and community engagement.
The sheer density of these local financial players intensifies competition for both deposits and loans. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, the U.S. banking industry, including community banks, saw total deposits reach approximately $21.1 trillion, indicating a highly contested market for funding.
Many core banking products, like checking accounts and basic loans, are seen as commodities. This makes it tough for banks like Burke & Herbert Financial Services to stand out just by offering different features. In 2024, this often pushes competition towards price, which can squeeze profit margins for financial institutions.
Geographic Market Concentration
Burke & Herbert Financial Services operates within a concentrated geographic market, primarily serving Northern Virginia and the Washington D.C. metropolitan area. This limited scope means competitors are directly focused on the same pool of customers, significantly intensifying rivalry. For instance, in 2024, the region features a dense network of community banks, credit unions, and larger regional financial institutions all vying for market share.
The intense competition within this specific geographic area forces Burke & Herbert to differentiate itself through customer service and tailored product offerings. This localized competition means that any gains made by one institution are often directly at the expense of another. In 2023, deposits in the Northern Virginia region saw a modest growth of approximately 3.5%, highlighting the competitive landscape where attracting and retaining these deposits is crucial.
- Intensified Local Competition: Burke & Herbert faces direct competition from numerous financial institutions operating within its primary service area.
- Customer Base Overlap: The limited geographic concentration ensures significant overlap in target customer segments, leading to direct contests for business.
- Market Share Dynamics: In 2024, the banking sector in the Washington D.C. region remains highly competitive, with institutions actively seeking to expand their local presence and customer relationships.
- Strategic Focus on Differentiation: To counter this rivalry, Burke & Herbert must continue to emphasize its unique value proposition and customer-centric approach.
Digital Banking and FinTech Competition
Digital-first banks and FinTech innovators are significantly intensifying competition for traditional institutions like Burke & Herbert. These agile players offer streamlined, often cheaper, alternatives for specific services, pushing established banks to enhance their digital offerings and customer experience. For instance, a significant portion of consumers, especially younger demographics, are increasingly adopting digital payment solutions and online lending platforms, directly impacting traditional revenue streams.
This digital onslaught forces incumbent banks to invest heavily in technology to remain competitive. By mid-2024, many traditional banks were allocating substantial portions of their IT budgets to digital transformation initiatives, aiming to match the user-friendliness and speed of FinTech apps. This increased rivalry compels Burke & Herbert to focus on innovation and customer-centric digital solutions to retain market share and attract new customers.
- Increased Digital Adoption: In 2024, the global digital banking user base continued its upward trajectory, with projections indicating further growth as more consumers prefer app-based banking.
- FinTech Investment Surge: Venture capital funding for FinTech companies remained robust in early 2024, fueling innovation in areas like payments, lending, and wealth management.
- Customer Expectation Shift: Consumers now expect seamless, intuitive digital interfaces for all financial transactions, a standard set by FinTech disruptors.
- Pressure on Fees: Digital-only banks often operate with lower overheads, enabling them to offer more competitive pricing and fee structures, putting pressure on traditional banks' profitability.
Burke & Herbert Financial Services contends with intense rivalry from both large national banks and numerous local competitors within its core geographic markets. Larger institutions like Capital One, with over $470 billion in assets as of Q1 2024, leverage significant resources for aggressive marketing and product development, directly challenging Burke & Herbert's market position.
The competitive landscape is further intensified by a dense network of community banks and credit unions that employ similar relationship-based strategies, creating a crowded market for deposits and loans. With total U.S. bank deposits nearing $21.1 trillion in early 2024, securing funding is a constant battle.
Digital-first banks and FinTech innovators are also a major disruptive force, offering streamlined services that pressure traditional institutions to enhance their digital capabilities. The increasing consumer preference for app-based banking, evident in robust FinTech venture capital funding throughout early 2024, necessitates continuous investment in technology for Burke & Herbert to remain competitive.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Burke & Herbert | Example (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large National Banks | Vast resources, broad marketing, extensive networks | Significant pressure on market share and pricing | Capital One (Assets: >$470B, Q1 2024) |
| Local Community Banks/Credit Unions | Relationship-focused, community engagement | Direct competition for local deposits and loans | Dense network in Northern VA/DC metro area |
| FinTech/Digital Banks | Agile, low overhead, user-friendly digital platforms | Drives need for digital innovation, pressure on fees | Robust FinTech VC funding in early 2024 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
FinTech payment and lending platforms present a significant threat by offering streamlined, often digital-first alternatives to traditional banking services. For instance, the global digital payments market was valued at approximately $2.4 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong customer shift towards these new channels.
These platforms, such as PayPal, Square, and various peer-to-peer lending services, can bypass established financial institutions for specific transactions or credit needs. This disintermediation allows them to capture market share by providing convenience and potentially lower costs, directly impacting Burke & Herbert Financial Services' customer base and transaction volumes.
The threat of substitutes for traditional wealth management services is significant, particularly from direct investment and wealth management platforms. These platforms, including online brokerage firms and robo-advisors, empower individuals to manage their own portfolios, often at a lower cost than traditional advisors.
In 2024, the digital wealth management sector continued its robust growth. For instance, assets under management for robo-advisors globally were projected to exceed $2.5 trillion by the end of the year, indicating a strong preference among a growing segment of investors for self-directed, technology-driven solutions. This trend directly challenges the necessity of traditional, human-led wealth management services.
Credit unions present a significant threat of substitution for Burke & Herbert Financial Services. Their member-owned structure often allows them to offer more competitive interest rates on loans and higher yields on deposits, directly siphoning off potential customers. For instance, by the end of 2023, credit unions in the U.S. held over $2.2 trillion in assets, demonstrating their substantial market presence and capacity to serve as a viable alternative to traditional banks.
Furthermore, the rise of non-bank lenders introduces another layer of substitution. These entities, often specializing in niche lending areas like fintech or specific business loans, can provide faster approvals or more flexible terms than established banks. This specialization allows them to capture segments of the market that might otherwise be served by Burke & Herbert, particularly as these lenders continue to expand their product offerings and reach.
Digital Wallets and Alternative Currencies
The rise of digital wallets and alternative currencies presents a growing threat of substitutes for traditional financial services. These platforms, like Apple Pay and Google Pay, offer convenient ways to make payments, bypassing traditional bank accounts and card networks. In 2024, the global digital payment market is projected to reach over $15 trillion, highlighting a significant shift in consumer behavior away from conventional methods.
While cryptocurrencies are still a niche, their increasing adoption for transactions and as a store of value offers another avenue for value transfer outside the established banking system. For instance, by the end of 2023, the number of cryptocurrency users worldwide surpassed 420 million, demonstrating a growing segment of the population comfortable with non-traditional financial instruments.
- Digital Wallets: Offer seamless, often contactless, payment solutions integrated into smartphones and other devices.
- Cryptocurrencies: Provide decentralized alternatives for storing and transferring value, with potential for lower transaction fees and faster cross-border payments.
- Market Growth: The digital payment sector continues its rapid expansion, indicating a sustained consumer preference for alternative financial tools.
Internal Corporate Finance Departments
Large corporations increasingly possess the resources and expertise to manage significant financial functions internally. This trend directly impacts banks like Burke & Herbert Financial Services by reducing the demand for traditional corporate finance services.
For instance, many large enterprises now operate sophisticated treasury departments capable of handling cash management, foreign exchange, and even complex debt issuance without external bank intermediation. In 2024, the trend of in-house treasury management continued to grow, with many Fortune 500 companies reporting increased investment in treasury technology and personnel.
The ability of these corporations to self-fund through capital markets, manage their own payroll processing, and even offer internal lending facilities presents a significant threat of substitution. This can lead to a decline in fee-based revenue for financial institutions that previously relied on these services.
- Reduced Demand for Treasury Services: Large corporations can manage cash, liquidity, and payments internally, bypassing bank treasury solutions.
- In-House Capital Raising: Companies can access capital markets directly for debt and equity, lessening reliance on bank underwriting.
- Internal Payroll and HR Functions: Sophisticated HR systems allow for in-house payroll processing, substituting for bank-provided services.
- Direct Investment and Lending: Some large firms engage in direct lending or investment, acting as their own financial intermediaries.
The threat of substitutes for traditional financial services is multifaceted, encompassing digital payment platforms, alternative lending sources, and even internal corporate capabilities. These substitutes often offer greater convenience, lower costs, or specialized services that can divert customers and revenue from established institutions like Burke & Herbert Financial Services.
Digital wallets and cryptocurrencies are increasingly capturing transaction volume, with the digital payment market projected to exceed $15 trillion globally in 2024. Furthermore, credit unions, with over $2.2 trillion in assets by the end of 2023, provide competitive deposit and loan rates, directly challenging traditional banking models.
Large corporations are also becoming substitutes by managing financial functions internally, reducing their reliance on banks for services like treasury management and capital raising. This trend is evident in the continued investment by Fortune 500 companies in sophisticated treasury technology and personnel throughout 2024.
| Substitute Type | Example | 2023/2024 Data Point | Impact on Traditional Banks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Payment Platforms | PayPal, Apple Pay | Digital payment market projected over $15 trillion in 2024 | Reduced transaction fees and customer base |
| Alternative Lenders | FinTech lenders, Peer-to-peer platforms | Global digital payments market valued at $2.4 trillion in 2023 | Loss of loan origination and interest income |
| Credit Unions | Member-owned financial cooperatives | Over $2.2 trillion in assets held by U.S. credit unions (end of 2023) | Competition for deposits and loans, potentially lower rates |
| Robo-Advisors | Online investment management services | Global AUM for robo-advisors projected to exceed $2.5 trillion by end of 2024 | Reduced demand for traditional wealth management services |
| In-House Corporate Finance | Internal treasury departments | Increased investment in treasury tech by Fortune 500 companies in 2024 | Decreased demand for corporate treasury and advisory services |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a new bank, like Burke & Herbert Financial Services operates within, demands substantial upfront capital. This is largely due to stringent regulatory requirements, such as capital adequacy ratios, which mandate that new entrants must possess a significant financial cushion to absorb potential losses. For instance, in 2024, the Federal Reserve's capital requirements for banks often necessitate a Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio of at least 4.5%, plus additional buffers, meaning a new institution would need to raise hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars before even opening its doors.
The banking sector, including institutions like Burke & Herbert Financial Services, faces significant entry barriers due to a complex web of regulations. These include stringent licensing requirements, adherence to consumer protection laws, and robust anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols. For instance, in 2024, the cost of regulatory compliance for financial institutions continued to be a substantial operational expense, diverting resources from innovation and growth.
New competitors face a significant hurdle in establishing brand recognition and customer trust against established institutions like Burke & Herbert. Many consumers exhibit strong loyalty to their current financial providers, often due to decades of established relationships and a perception of reliability.
For instance, in 2024, the U.S. banking sector saw continued consolidation, with larger banks often leveraging their established brand presence to attract and retain customers. This trend underscores the difficulty for new entrants to carve out market share when consumers prioritize the perceived stability and familiarity offered by incumbents.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Incumbent banks like Burke & Herbert Financial Services benefit significantly from economies of scale. This means their per-unit costs decrease as their output increases, a common advantage in the banking sector. For instance, the substantial investments required for robust IT infrastructure, regulatory compliance, and widespread branch networks are spread across a larger customer base, making it challenging for new entrants to match these cost efficiencies. In 2024, major banks continued to leverage their scale, with many reporting operating expenses that are a smaller percentage of revenue compared to smaller, regional players.
The experience curve also plays a crucial role, allowing established institutions to refine their processes and reduce costs over time. This learning-by-doing effect leads to greater operational efficiency in areas such as loan processing, customer service, and risk management. New entrants must overcome this established expertise, which is often embedded in years of operational history and accumulated knowledge within the workforce.
- Economies of Scale: Large banks can negotiate better terms with technology providers and spread the cost of compliance and marketing over a vast customer base, leading to lower per-customer operating costs.
- Experience Curve Advantages: Decades of experience allow established banks to optimize internal processes, develop sophisticated risk models, and build efficient service delivery channels, which are difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly.
- Capital Investment Barriers: The sheer capital required to build a competitive banking operation, including technology, regulatory capital, and physical presence, creates a high barrier to entry that new firms must surmount.
- Brand Recognition and Trust: Established banks often possess strong brand recognition and a long history of customer trust, which are intangible assets that new entrants must work hard to build.
Niche Market Entry by FinTechs
FinTech companies are increasingly targeting specific, underserved niches within financial services, rather than attempting to replicate full-service banking operations. This focused approach allows them to innovate rapidly and offer specialized solutions, potentially eroding market share in those particular segments for established players like Burke & Herbert.
For instance, in 2024, the global FinTech market size was valued at approximately $2.5 trillion, with significant growth driven by specialized solutions in areas like payments, lending, and wealth management. While a single FinTech might seem small, their collective impact on specific customer bases can be substantial.
- Targeted Niche Focus: FinTechs often excel by concentrating on a narrow segment, such as small business lending or international money transfers, where they can build specialized expertise and technology.
- Agile Innovation: Their leaner structures and tech-centric models enable faster product development and adaptation compared to traditional banks.
- Cumulative Impact: The threat isn't necessarily from a single large competitor, but from the aggregation of many smaller, specialized FinTechs chipping away at different customer touchpoints.
- Customer Experience: Many FinTechs prioritize user-friendly digital interfaces, attracting customers who are dissatisfied with the legacy systems of established institutions.
The threat of new entrants for institutions like Burke & Herbert Financial Services is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements and stringent regulatory landscape. Building a new bank requires substantial upfront investment, often in the hundreds of millions or even billions of dollars, to meet capital adequacy ratios and compliance standards. For example, in 2024, regulatory capital requirements, such as the Common Equity Tier 1 ratio, remained a formidable barrier, demanding a strong financial foundation before operation. This high cost of entry, coupled with the need for extensive licensing and adherence to consumer protection and anti-money laundering laws, deters many potential new players.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront capital needed to meet regulatory standards. | CET1 ratios of at least 4.5% plus buffers, often requiring hundreds of millions. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing, consumer protection, and AML/KYC compliance. | Compliance costs remained a significant operational expense, diverting resources. |
| Brand & Trust | Established customer loyalty and perceived reliability of incumbents. | Continued consolidation favored larger banks with strong brand recognition. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to larger operational scale. | Major banks leveraged scale, reporting lower operating expenses as a percentage of revenue. |
| Experience Curve | Refined processes and cost efficiencies from years of operation. | New entrants must overcome accumulated operational expertise and knowledge. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Burke & Herbert Financial Services is built upon a foundation of robust data, including their annual reports, filings with the SEC, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms. We also incorporate insights from financial news outlets and macroeconomic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.