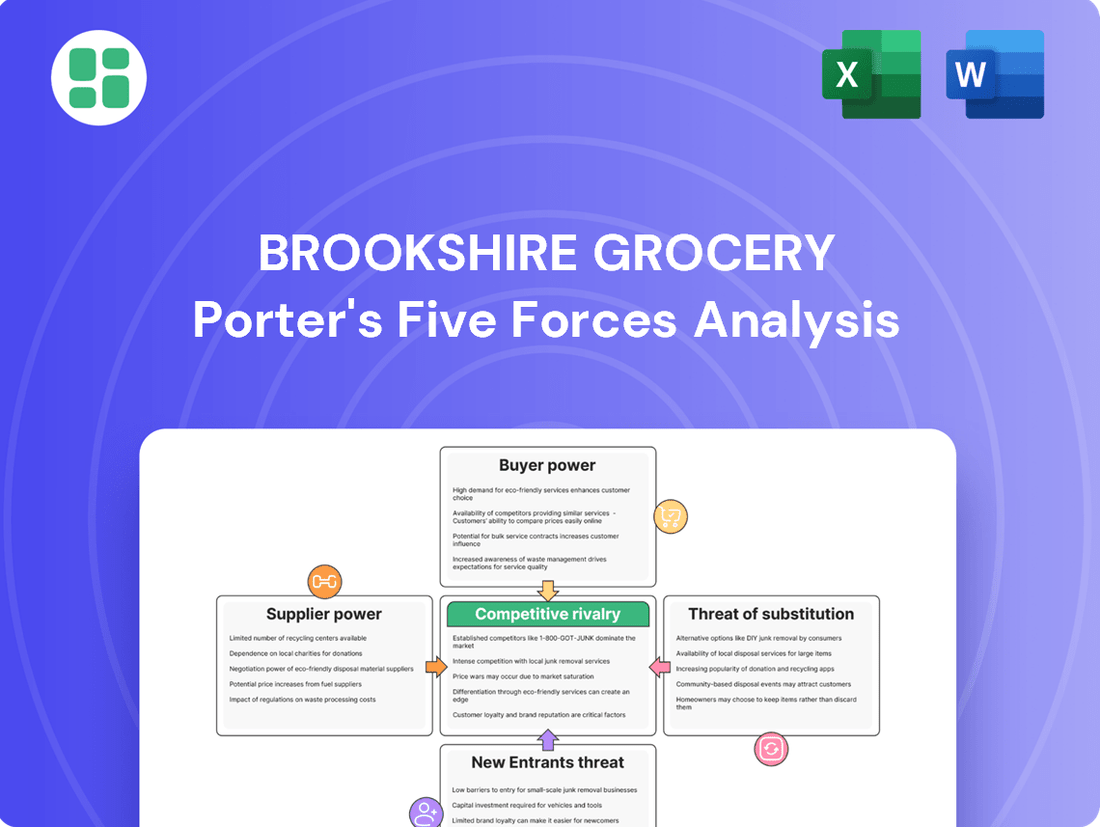
Brookshire Grocery Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Brookshire Grocery Bundle
Brookshire Grocery faces significant competitive pressures, with intense rivalry among existing players and a constant threat from new entrants in the grocery sector. Understanding the bargaining power of both their suppliers and their customers is crucial for navigating this landscape effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Brookshire Grocery’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers significantly impacts Brookshire Grocery Company's bargaining power. For instance, in categories dominated by a few major players, like national beverage brands, these suppliers can command higher prices. In 2024, major CPG (Consumer Packaged Goods) companies continued to hold substantial market share, often exceeding 50% in their respective product segments, giving them considerable leverage over retailers like Brookshire.
When a few large suppliers control a significant portion of a product category, such as dairy or baked goods, Brookshire has fewer viable alternatives. This concentration allows these dominant suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, including pricing and payment schedules, as Brookshire's reliance on them limits its ability to switch. For example, a single large dairy cooperative might supply a substantial percentage of Brookshire's fresh milk needs in certain regions.
Conversely, a fragmented supplier base, common with local produce or specialty items, empowers Brookshire. With numerous small farmers or producers, Brookshire can source from various vendors, fostering competition and allowing them to negotiate better prices and more flexible delivery arrangements. This diversity in sourcing strengthens Brookshire's position, as no single small supplier holds significant sway.
Suppliers offering unique or highly differentiated products wield significant bargaining power. If Brookshire Grocery Company depends on a particular supplier for a sought-after private-label ingredient or a specialty item that is difficult to substitute, that supplier gains leverage in negotiations. For example, a supplier of a proprietary blend for a popular store-brand item could command better terms.
Conversely, when dealing with generic commodities like basic produce or common household goods, where numerous suppliers offer similar products, Brookshire's negotiating position strengthens. The company's recent collaboration with Afresh to enhance fresh operations highlights a strategic move to optimize perishable supply chains, potentially influencing its relationships and leverage with suppliers in that segment.
The costs Brookshire Grocery Company incurs when switching suppliers directly influence the bargaining power of those suppliers. If switching necessitates substantial outlays for new machinery, employee re-training, or complex logistical overhauls, Brookshire will find it more challenging to change suppliers, even if prices rise. This is especially relevant for intricate supply chains or when dealing with suppliers of specialized or proprietary products.
For many standard grocery items, however, the costs to switch suppliers are likely to be minimal. This allows Brookshire to readily pivot to alternative suppliers if more favorable pricing or terms are presented, thereby limiting supplier leverage in these categories.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers can increase their leverage if they have a believable plan to move into the retail grocery sector themselves. For a large grocery chain like Brookshire, this threat is typically minimal. However, certain agricultural producers or food manufacturers might explore direct-to-consumer models or even establish their own stores, potentially creating competition.
While direct forward integration by suppliers into broad-line grocery is uncommon, it's a factor Brookshire must consider, especially in specialized product categories. Maintaining strong supplier relationships is key to mitigating the risk of facing competition from those who supply its shelves. The grocery landscape is evolving, with retailers like Brookshire expanding their private-label offerings, which can reshape dynamics with their suppliers.
- Supplier Integration Risk: Suppliers might gain power by threatening to enter Brookshire's retail space.
- Niche Segment Threat: While generally low, this threat could materialize in specific product areas.
- Private Label Impact: Brookshire's growth in private labels can influence supplier relationships and their integration strategies.
Importance of Brookshire to Suppliers
The significance of Brookshire Grocery Company's business to its suppliers directly influences their bargaining power. If Brookshire constitutes a substantial part of a supplier's revenue stream, that supplier is more likely to concede on pricing, offer discounts, or be flexible with delivery arrangements to secure continued patronage.
Conversely, if Brookshire is a minor client among many for a supplier, the supplier possesses greater leverage. Brookshire Grocery Company's considerable market footprint is evident through its broad store network spanning Texas, Louisiana, and Arkansas.
This network includes various banners such as Brookshire's, Super 1 Foods, Spring Market, and FRESH by Brookshire's, underscoring its importance to suppliers seeking access to a large customer base. For instance, as of early 2024, Brookshire Grocery Company operated over 200 stores, representing a significant volume of sales for its suppliers.
- Brookshire's extensive reach across three states provides a substantial sales channel for its suppliers.
- A supplier's reliance on Brookshire for a significant portion of their income can diminish their bargaining power.
- Conversely, suppliers with diversified client bases may hold stronger negotiating positions with Brookshire.
- The company's multiple store formats cater to different market segments, increasing its appeal to a wider range of suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Brookshire Grocery Company is influenced by several factors, including supplier concentration, the uniqueness of their products, and the cost of switching. In 2024, many key product categories, such as national brands of beverages and packaged foods, remained dominated by a few large suppliers, granting them significant leverage over retailers like Brookshire. This concentration means Brookshire has limited alternatives, allowing these major suppliers to negotiate favorable pricing and terms due to Brookshire's reliance on them.
Conversely, when suppliers offer unique or highly differentiated items, their bargaining power increases. If Brookshire depends on a specific supplier for a sought-after private-label ingredient or a specialty item that's hard to replace, that supplier can negotiate better terms. For instance, a supplier of a proprietary blend for a popular store-brand item could command better conditions.
The cost associated with switching suppliers also plays a crucial role. If changing vendors requires significant investment in new equipment, employee training, or logistical adjustments, Brookshire faces higher switching costs, which strengthens the supplier's position. However, for many standard grocery items, switching costs are minimal, allowing Brookshire to easily find alternative suppliers and thus limiting supplier leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Brookshire | Example (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier power | Dominance of major CPG companies in beverage categories |
| Product Differentiation | Increases supplier power | Proprietary ingredients for private-label goods |
| Switching Costs | Increases supplier power if high | Specialized equipment for unique product lines |
| Brookshire's Importance to Supplier | Decreases supplier power if Brookshire is key | Brookshire's over 200 stores represent significant volume for suppliers |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Brookshire Grocery meticulously examines the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the risk of substitute products. It provides a strategic framework for understanding Brookshire's competitive environment and identifying opportunities for sustainable advantage.
Brookshire Grocery's Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all competitive forces, perfect for quick decision-making and instantly understanding strategic pressure.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer price sensitivity is a major force impacting Brookshire Grocery Company, particularly in 2024. With inflation continuing to affect household budgets, shoppers are more inclined to compare prices and switch to retailers offering lower costs. This makes Brookshire’s pricing strategy critical for customer retention.
In 2024, many consumers are actively seeking out deals and private-label brands to stretch their grocery dollars further. For instance, data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics in early 2024 indicated persistent elevated food prices, reinforcing this trend. This heightened price consciousness directly translates to increased bargaining power for customers, as they have viable alternatives readily available from competitors like Walmart and Kroger.
Customers face remarkably low switching costs when deciding where to buy their groceries. For instance, a shopper can easily shift from Brookshire Grocery Company to a nearby competitor, an online delivery service, or even a different type of food retailer without incurring significant expense or hassle. This ease of movement puts considerable power in the hands of consumers.
This low barrier to switching means customers can readily explore alternatives that offer better pricing, enhanced convenience, or a wider product assortment. In 2024, the proliferation of price comparison apps and loyalty programs from various grocery chains further amplifies this customer power, making it simpler than ever to identify and capitalize on superior value propositions.
While individual shoppers usually have little sway, a large, concentrated customer base in a specific region can wield more influence. Brookshire Grocery Company's broad customer reach across multiple states dilutes the power of any single shopper or small group. For instance, in 2024, Brookshire operated hundreds of stores, serving millions of households, meaning no single customer segment held significant individual bargaining leverage.
However, in local markets where Brookshire is a dominant player, customers might collectively influence decisions through feedback or by shifting their loyalty. Though less common for a retail grocer, institutional buyers could potentially negotiate better pricing, similar to how large corporations secure bulk discounts.
Availability of Information
The internet and a plethora of apps have dramatically increased the availability of information for grocery shoppers. Customers can now effortlessly compare prices, track promotions, and check product availability across various retailers, including Brookshire Grocery Company and its rivals. This transparency directly empowers consumers, allowing them to make well-informed purchasing decisions and seek out the best value for their money.
This heightened access to comparative data significantly bolsters customer bargaining power within the grocery industry. For instance, in 2024, online price comparison tools and grocery apps became even more sophisticated, giving consumers real-time insights into competitor pricing. This means Brookshire Grocery Company must remain highly competitive on price and promotions to retain its customer base.
- Increased Price Transparency: Customers can easily find out if Brookshire Grocery Company's prices are competitive with other local and national chains.
- Promotion Awareness: Shoppers are readily aware of sales and discounts offered by competitors, influencing their loyalty to Brookshire.
- Product Availability Checks: Consumers can confirm if a desired item is in stock at Brookshire or if a competitor has it, impacting their shopping destination.
- Informed Decision-Making: The ease of accessing information allows customers to make more strategic and value-driven choices.
Customer Loyalty and Differentiation
Customer loyalty in the grocery sector is a complex beast, often more about convenience and price than deep brand devotion. While Brookshire Grocery Company strives to cultivate loyalty across its brands, the reality is that many shoppers readily switch for a better deal or a more convenient location. This dynamic means that while loyalty can temper buyer power, it's not an insurmountable barrier.
The grocery market, especially in 2024, is characterized by intense competition and a consumer base highly attuned to value. Private-label brands, for instance, offer a compelling alternative to national brands, directly impacting customer choice and reducing the power a single grocery chain holds over its patrons. Consumers are adept at comparing prices and promotions across different stores, making them less tethered to any one retailer.
- Price Sensitivity: In 2024, grocery inflation continued to be a concern for many households, increasing price sensitivity and the likelihood of switching for savings.
- Promotional Reliance: Many grocery chains, including those in Brookshire's operating regions, rely heavily on sales and loyalty programs to attract and retain customers, indicating that pure brand loyalty is less prevalent.
- Convenience Factor: Proximity and ease of shopping remain significant drivers of customer choice, often outweighing a preference for a specific grocery banner.
- Private Label Growth: The ongoing expansion and improved quality of private-label offerings provide consumers with attractive alternatives, further diluting the bargaining power of individual grocery retailers.
Customers possess significant bargaining power due to low switching costs and increased price transparency, especially in 2024. With grocery inflation persisting, shoppers actively compare prices and promotions, readily switching to competitors offering better value. This makes Brookshire Grocery Company's pricing strategy and promotional efforts crucial for customer retention.
| Factor | Impact on Brookshire Grocery | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Very Low | Consumers can easily switch between grocery stores (e.g., Walmart, Kroger) with no financial penalty. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | U.S. CPI for food at home remained elevated in early 2024, driving consumers to seek discounts. |
| Information Availability | High | Grocery apps and online comparison tools provide real-time pricing and promotion data. |
| Customer Concentration | Low (Individual) | Brookshire's wide customer base across multiple states means no single customer has significant individual leverage. |
What You See Is What You Get
Brookshire Grocery Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Brookshire Grocery Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the grocery retail sector. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately upon purchase, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The grocery retail landscape Brookshire Grocery Company navigates is fiercely competitive, featuring a wide array of players. National giants like Walmart and Kroger, alongside regional grocers and niche specialty shops, all vie for consumer dollars. Brookshire's own diverse portfolio, including banners like Brookshire's, Super 1 Foods, and FRESH by Brookshire's, operates across Texas, Louisiana, and Arkansas, with recent strategic moves like the acquisition of Reasor's in 2022, which added 15 stores, further shaping its competitive position.
This intense rivalry is amplified by the presence of various retail formats, including the growing influence of deep discounters such as Aldi. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. grocery market is projected to reach over $1.1 trillion in sales, underscoring the sheer volume of business available but also the significant competition for market share.
The grocery sector is seeing consistent, though not explosive, expansion. The global grocery market was valued at roughly $3.87 trillion in 2024. This steady growth, projected at a 4.70% compound annual growth rate from 2025 to 2034, fuels intense rivalry as companies like Brookshire vie for every available customer.
While the overall market size is expanding, particularly with the rise of online grocery shopping, this growth doesn't significantly temper the fierce competition. Instead, it reshapes how companies compete, with e-commerce becoming a crucial battleground for market share.
In the grocery sector, truly unique product differentiation for everyday staples is tough, often pushing companies into price wars. Brookshire Grocery Company tries to stand out with high-quality fresh produce, meats, and baked goods, alongside services like in-store pharmacies and fuel centers. However, many rivals offer very similar selections and conveniences.
The increasing prevalence of private-label brands, a strategy Brookshire also employs, highlights a move to offer distinct value propositions and capture price-sensitive shoppers. This trend intensifies the competitive landscape as more companies leverage their own brands to attract and retain customers.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers for grocery retailers like Brookshire Grocery are substantial, primarily driven by significant investments in physical infrastructure. These include extensive real estate holdings, numerous store locations, and complex distribution networks. For example, as of late 2023, Brookshire Grocery operates hundreds of stores across multiple states, representing a considerable fixed asset base that is not easily divested.
Furthermore, contractual commitments with suppliers and labor agreements add to these exit barriers. These ongoing obligations make it challenging and costly for a company to cease operations, even if facing financial difficulties. This situation can result in prolonged competition among even less profitable entities within the sector.
Brookshire's own extensive operational footprint, encompassing a vast network of stores and supporting logistics, solidifies these high exit barriers. This infrastructure commitment means that exiting the market would involve substantial write-downs and unfulfilled contractual liabilities, thereby perpetuating a competitive landscape.
- High Fixed Asset Investment: Grocery chains commit significant capital to real estate, store build-outs, and distribution centers.
- Contractual Obligations: Long-term agreements with suppliers and labor unions create ongoing financial commitments.
- Operational Scale: Brookshire's extensive store count and distribution network represent a significant, difficult-to-exit investment.
- Market Inertia: High exit costs can keep less profitable players in the market, intensifying overall rivalry.
Switching Costs for Customers
Customer switching costs in the grocery industry are generally quite low, which intensifies the rivalry among retailers like Brookshire Grocery Company. This means shoppers can easily move from one store to another based on price, convenience, or product selection.
Because customers can switch so readily, Brookshire Grocery must continuously work to keep them loyal. This often involves offering competitive pricing, superior customer service, or unique product assortments that competitors don't have. For instance, in 2024, grocery retailers are heavily investing in loyalty programs and personalized digital offers to combat churn. The average grocery store in the US might see a customer retention rate that fluctuates significantly based on these efforts. A study by Bain & Company in late 2023 indicated that a 5% increase in customer retention can boost profits by 25% to 95%, highlighting the critical importance of minimizing churn in this low-switching-cost environment.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers can easily switch between grocery stores without significant financial or effort-based penalties.
- Competitive Pressure: This ease of switching forces retailers to constantly compete on price, service, and product variety.
- Retention Strategies: Companies like Brookshire Grocery must invest in loyalty programs, promotions, and enhanced shopping experiences to retain customers.
- Impact on Profitability: High customer churn due to low switching costs can negatively impact profitability, making customer retention a key strategic focus.
The competitive rivalry within the grocery sector is intense, driven by numerous players and low customer switching costs. Brookshire Grocery Company faces competition from national chains, regional grocers, and discounters like Aldi. In 2024, the U.S. grocery market's projected sales exceeding $1.1 trillion highlight the vastness of the market but also the fierce battle for market share, with companies investing heavily in loyalty programs and digital offers to retain customers.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Impact on Brookshire |
|---|---|---|
| National Giants | Walmart, Kroger | Significant price and selection competition. |
| Regional Grocers | Other regional chains | Direct competition in specific geographic markets. |
| Deep Discounters | Aldi, Lidl | Pressure on pricing and value perception. |
| Specialty/Niche | Local markets, organic stores | Competition for specific customer segments. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Brookshire Grocery Company is significant, stemming from a wide array of alternative food acquisition methods. Consumers can turn to convenience stores for quick purchases, farmers' markets for fresh, local produce, and specialty shops for unique items, all of which offer distinct value propositions compared to a traditional supermarket.
Online-only grocery delivery services have also emerged as a powerful substitute. Services like Instacart and Amazon Fresh provide convenience and often competitive pricing, directly challenging the brick-and-mortar model. In 2024, online grocery sales continued their upward trajectory, capturing a larger share of the overall food retail market, further intensifying this competitive pressure.
Furthermore, the widening gap between dining out and grocery shopping costs makes restaurants a strong substitute. As inflation impacts food prices, consumers may opt for prepared meals from restaurants more frequently, viewing it as a viable alternative to preparing meals at home, thereby reducing demand for Brookshire's core offerings.
The price-to-performance ratio of substitutes directly impacts their threat level to Brookshire Grocery. If meal kits, restaurant dining, or online grocers provide superior value, factoring in price, convenience, and quality, customers may be tempted to switch. This is evident as consumers increasingly opt for private-label brands within grocery stores, viewing them as a more budget-friendly substitute for national brands.
Switching costs for customers to move to alternative food solutions are typically quite low. For example, ordering a meal kit or dining out requires minimal effort beyond placing an order, a stark contrast to the time and effort involved in a complete grocery shopping trip. This ease of transition means consumers can readily choose alternatives when convenience, specialized dietary needs, or the desire for prepared meals become more appealing than traditional grocery shopping.
Perceived Value and Convenience of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for traditional grocery stores like Brookshire Grocery is significant, primarily driven by evolving consumer preferences for convenience. Meal delivery services and restaurant-prepared foods offer immediate, ready-to-eat solutions that bypass the need for grocery shopping and home cooking. This is particularly attractive to time-strapped consumers.
The rise of online grocery shopping and home delivery further amplifies this threat. Accelerated by events in recent years, these digital alternatives provide a convenient substitute for the physical store experience. For instance, in 2024, online grocery sales in the U.S. are projected to continue their upward trajectory, capturing a substantial share of the overall grocery market, directly impacting foot traffic for brick-and-mortar retailers.
- Convenience-driven substitutes: Meal kits, prepared meals, and restaurant takeout offer time-saving alternatives to traditional grocery shopping.
- Digital disruption: Online grocery platforms and delivery services provide a seamless substitute for in-store visits.
- Market trends: The increasing adoption of e-commerce in the grocery sector highlights the growing demand for convenient shopping methods.
- Consumer behavior shifts: Busy lifestyles and a desire for immediate gratification are fueling the demand for readily available food options.
Innovation in Substitute Industries
The threat of substitutes for Brookshire Grocery Company is amplified by continuous innovation in sectors like meal kits and online food delivery. These alternatives are becoming more appealing due to new dietary options, personalized meal plans, and increasingly rapid delivery services. For instance, the U.S. meal kit delivery market was valued at approximately $11.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong and expanding substitute market.
This evolving landscape compels Brookshire Grocery Company to adapt and innovate its own product and service offerings. To effectively counter these substitutes, the company may need to expand its prepared foods sections, enhance its online ordering capabilities, or develop more comprehensive meal solutions. Such strategic moves are crucial for retaining customer loyalty and market share in the face of these dynamic alternatives.
- Meal Kit Market Growth: The U.S. meal kit delivery market reached an estimated $11.2 billion in 2023, showcasing the increasing consumer adoption of these substitutes.
- Delivery Speed Improvements: Food delivery services continue to invest in logistics, with many aiming for delivery times under 30 minutes, directly competing with the convenience of in-person grocery shopping.
- Personalization Trends: The rise of personalized nutrition and customized meal plans offered by digital platforms presents a significant challenge to traditional grocery models.
- Brookshire's Response: Potential strategies include expanding ready-to-eat meals, optimizing online shopping experiences, and creating bundled meal solutions to compete with convenience-focused substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Brookshire Grocery is substantial, driven by the increasing appeal of convenient food solutions. Meal kits and prepared meals offer time-saving alternatives, directly competing with the traditional grocery shopping experience. In 2024, the ongoing growth in online grocery sales, projected to capture a larger market share, further intensifies this pressure by providing easy access to a wide range of food options without requiring a physical store visit.
| Substitute Category | Key Value Proposition | 2023/2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Meal Kits | Convenience, portion control, recipe guidance | U.S. market estimated at $11.2 billion in 2023; continued innovation in dietary options. |
| Prepared Meals/Takeout | Immediate consumption, no cooking required | Consumer spending on restaurant meals remains strong, especially as price gaps with home cooking narrow. |
| Online Grocery Delivery | Convenience, broad selection, home delivery | Continued upward trajectory in online grocery sales, increasing market penetration in 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
Opening a new grocery store, particularly a full-service supermarket akin to those run by Brookshire Grocery Company, demands considerable capital. This investment covers real estate acquisition or leasing, construction or significant renovations, and the purchase of essential equipment like refrigeration units, shelving, and point-of-sale systems. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to build a new supermarket can easily exceed $5 million, with some larger formats reaching $10 million or more, not including initial inventory and operational working capital.
Brookshire Grocery Company, like other established grocery retailers, leverages substantial economies of scale. This translates into lower per-unit costs for everything from product sourcing to advertising. For instance, in 2024, major grocery chains often secure discounts of 5-10% or more on high-volume purchases compared to smaller operations.
These scale advantages create a significant barrier for potential new entrants. A newcomer would find it challenging to match the purchasing power and logistical efficiencies that Brookshire Grocery has cultivated over years of operation. This disparity in cost structure makes it difficult for new players to compete on price, a cornerstone of customer acquisition in the grocery sector.
While switching costs for a single grocery trip might be low, building enduring brand loyalty is a significant hurdle for new entrants. Brookshire Grocery Company, with its history dating back to 1928, has cultivated deep customer trust and regional recognition through decades of operation. This established reputation means newcomers must invest heavily in marketing and potentially offer compelling price advantages or novel experiences to persuade shoppers to change their ingrained purchasing habits.
Access to Distribution Channels
New entrants into the grocery sector, like Brookshire Grocery Company, encounter significant hurdles in securing access to established distribution channels. These channels are crucial for efficiently moving goods from suppliers to consumers, ensuring product availability and freshness. Existing companies have invested heavily in building robust logistics and supply chain infrastructure.
Brookshire Grocery Company, for instance, operates its own extensive network of distribution centers and maintains strong, long-standing relationships with a wide array of suppliers. This integrated system allows for optimized inventory management and cost-effective delivery. For a new competitor, replicating this level of logistical sophistication is a formidable challenge.
The cost and time required to establish comparable distribution networks can be prohibitive. Building from scratch means negotiating new supplier agreements, setting up warehousing facilities, and creating transportation fleets. This complexity directly impacts a new entrant's ability to compete on price and product variety, as they may struggle to ensure consistent stock levels of perishable and diverse items.
- Distribution Network Investment: Building a grocery distribution network can cost tens to hundreds of millions of dollars, encompassing warehouses, trucks, and technology.
- Supplier Relationships: Established players often secure preferential terms and guaranteed supply from key vendors due to volume and history.
- Logistical Efficiency: Brookshire's existing infrastructure likely offers economies of scale, reducing per-unit transportation and handling costs compared to a new entrant.
- Market Entry Barriers: The difficulty in accessing efficient distribution is a primary barrier, limiting the number of viable new entrants in the grocery market.
Regulatory and Licensing Requirements
The grocery sector faces significant barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory and licensing requirements. New businesses must navigate a complex web of food safety standards, health permits, and zoning laws. For instance, obtaining necessary licenses for selling controlled substances like alcohol or tobacco adds further layers of complexity and cost.
These compliance hurdles demand substantial investment in legal counsel and operational adjustments, delaying market entry and increasing initial capital outlays. By 2024, the average time to secure all necessary permits for a new food retail establishment could range from several months to over a year, depending on the jurisdiction.
- Food Safety Regulations: Compliance with FDA and local health department guidelines is paramount, impacting product sourcing and handling.
- Licensing for Specific Products: Obtaining permits for alcohol or tobacco sales involves rigorous background checks and fees.
- Zoning and Land Use: Securing appropriate zoning approvals for retail locations can be a lengthy and uncertain process.
- Environmental Regulations: Adherence to waste disposal and energy efficiency standards adds to operational compliance costs.
The threat of new entrants for Brookshire Grocery Company is generally low to moderate. Significant capital investment is required to establish a new grocery store, with costs in 2024 often exceeding $5 million for a full-service supermarket. Established players like Brookshire benefit from substantial economies of scale, securing lower per-unit costs on purchases and advertising, which new entrants struggle to match. Furthermore, building brand loyalty and replicating Brookshire's decades-old reputation presents a considerable marketing challenge for newcomers.
Accessing established distribution channels poses another major barrier. Brookshire's investment in its own distribution centers and supplier relationships creates logistical efficiencies that are costly and time-consuming for new companies to replicate. This difficulty in securing efficient supply chains directly impacts a new entrant's ability to compete on price and product availability. Regulatory hurdles, including food safety standards and licensing, also add significant costs and delays, further deterring new competition.
| Barrier to Entry | Estimated Cost/Time (2024) | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | $5M - $10M+ for supermarket | High barrier due to upfront costs |
| Economies of Scale | 5-10%+ cost advantage for large chains | Difficulty competing on price |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Decades of building trust | Requires significant marketing investment |
| Distribution Network Access | $10sM - $100sM for network build-out | Logistical and cost disadvantages |
| Regulatory Compliance | Months to over a year for permits | Delays market entry and increases costs |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Brookshire Grocery leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and competitive intelligence platforms. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the grocery retail landscape and its influencing factors.