Astrana Health Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Astrana Health Bundle
Astrana Health faces a dynamic landscape shaped by intense industry rivalry and the significant bargaining power of buyers. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive environment.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Astrana Health’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Astrana Health's reliance on a robust network of physicians and specialists is significantly influenced by the ongoing national shortage of these critical medical professionals. This scarcity directly amplifies the bargaining power of these suppliers, particularly those in highly specialized or in-demand fields. For instance, the Association of American Medical Colleges projected a shortage of between 37,800 and 124,000 physicians by 2034, a trend that continued to be a concern in 2024.
This limited supply of qualified healthcare providers translates into increased recruitment and retention costs for Astrana Health. As competition for talent intensifies, Astrana may face pressure to offer higher compensation packages, signing bonuses, and other incentives, directly impacting its operational expenses and potentially hindering its capacity for network expansion or service diversification.
Astrana Health relies heavily on specialized medical technologies and pharmaceuticals for its care enablement platform. Suppliers of unique devices, critical software like electronic health record systems from partners such as Elation Health, and essential medications hold considerable sway. This dependence means suppliers can impact Astrana's operational costs and its capacity to offer seamless, coordinated patient care.
The pharmaceutical sector, in particular, can exhibit strong supplier power due to patent protections and complex manufacturing processes. In 2024, prescription drug spending in the U.S. continued its upward trend, with some specialty drugs seeing price increases exceeding 10%, directly impacting healthcare providers’ cost structures.
Beyond physicians, the broader healthcare labor market, encompassing nurses, allied health professionals, and administrative staff, forms a crucial supplier group for Astrana Health. In 2024, the persistent shortage of nurses, with projections indicating a deficit of over 100,000 registered nurses by 2025, significantly bolsters their bargaining power.
Rising wage expectations across the healthcare sector, driven by these shortages, directly translate into higher personnel costs for Astrana Health. For instance, average registered nurse salaries saw an increase of approximately 4-6% in 2023, a trend expected to continue into 2024, impacting Astrana Health's operating expenses and potentially its profit margins.
Consolidation Among Supplier Groups
The healthcare industry is witnessing significant consolidation, not just among providers but also within supplier groups. For instance, large physician practices and specialized service providers are increasingly merging, creating more concentrated supplier bases. This trend directly impacts healthcare management companies like Astrana Health.
When suppliers consolidate, their bargaining power strengthens considerably. This means entities like Astrana Health may face tougher negotiations, potentially leading to less favorable contract terms or higher costs for essential services and supplies. For example, a consolidated group of specialized diagnostic labs might command higher prices than previously when individual labs competed more fiercely.
- Consolidation Impact: Mergers among physician groups and specialized service providers increase supplier leverage.
- Negotiation Power: Concentrated suppliers can demand better terms, potentially raising costs for healthcare management firms.
- Market Dynamics: This shift can reduce Astrana Health's ability to negotiate favorable pricing for its services.
Proprietary Nature of Supplier Offerings
Suppliers offering highly specialized or proprietary services and technologies, which are critical to Astrana's integrated and value-based care model, possess strong bargaining power. If Astrana cannot easily switch to alternative suppliers without significant disruption or cost, these suppliers can demand premium pricing or stricter contractual terms. Astrana's reliance on its proprietary population health management and healthcare delivery platform highlights its need for specific technological inputs.
- Proprietary Technology Dependence: Astrana's integrated care model hinges on its proprietary population health management and healthcare delivery platform. This reliance means suppliers of key technological components or specialized services integrated into this platform hold significant sway.
- Switching Costs and Disruption: If Astrana faces substantial costs or operational disruption in finding and implementing alternative suppliers for these critical proprietary elements, existing suppliers can leverage this to negotiate more favorable terms.
- Limited Alternatives for Specialized Services: For highly niche or custom-developed services that are integral to Astrana's unique value proposition, the pool of alternative suppliers is likely small, further concentrating bargaining power with existing providers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Astrana Health is a significant factor, particularly concerning physicians and specialized medical professionals. The ongoing national shortage of these professionals, projected by the Association of American Medical Colleges to reach between 37,800 and 124,000 by 2034, means Astrana faces increased costs for recruitment and retention. This scarcity directly empowers suppliers in specialized fields, potentially leading to higher compensation demands and impacting Astrana's operational expenses.
Astrana's reliance on critical technologies and pharmaceuticals also grants suppliers considerable leverage. For instance, suppliers of electronic health record systems and essential medications can influence Astrana's costs and its ability to provide seamless patient care. The pharmaceutical sector, in particular, sees suppliers benefiting from patent protections and complex manufacturing, with prescription drug spending continuing its upward trend in 2024, often with specialty drug price increases exceeding 10%.
The consolidation within the healthcare industry, including physician groups and specialized service providers, further concentrates supplier power. This trend means Astrana Health may encounter more challenging negotiations, potentially resulting in less favorable contract terms or higher prices for essential services and supplies. The limited availability of alternative suppliers for proprietary technologies and specialized services integral to Astrana's model also amplifies supplier leverage.
| Supplier Category | 2024 Market Factor | Impact on Astrana Health | Example Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physicians/Specialists | National Shortage | Increased recruitment/retention costs, higher compensation demands | Projected shortage of 37,800-124,000 physicians by 2034 (AAMC) |
| Specialized Technologies (e.g., EHR) | Proprietary Nature, Integration Costs | Leverage for pricing, potential disruption if switching | Reliance on systems like Elation Health |
| Pharmaceuticals | Patent Protection, Manufacturing Complexity | Higher drug costs, impact on operational expenses | U.S. prescription drug spending increasing; specialty drug prices up >10% |
| Healthcare Labor (Nurses, Allied Health) | Persistent Shortages | Rising wage expectations, increased personnel costs | Projected deficit of >100,000 RNs by 2025; RN salaries up 4-6% in 2023 |
What is included in the product
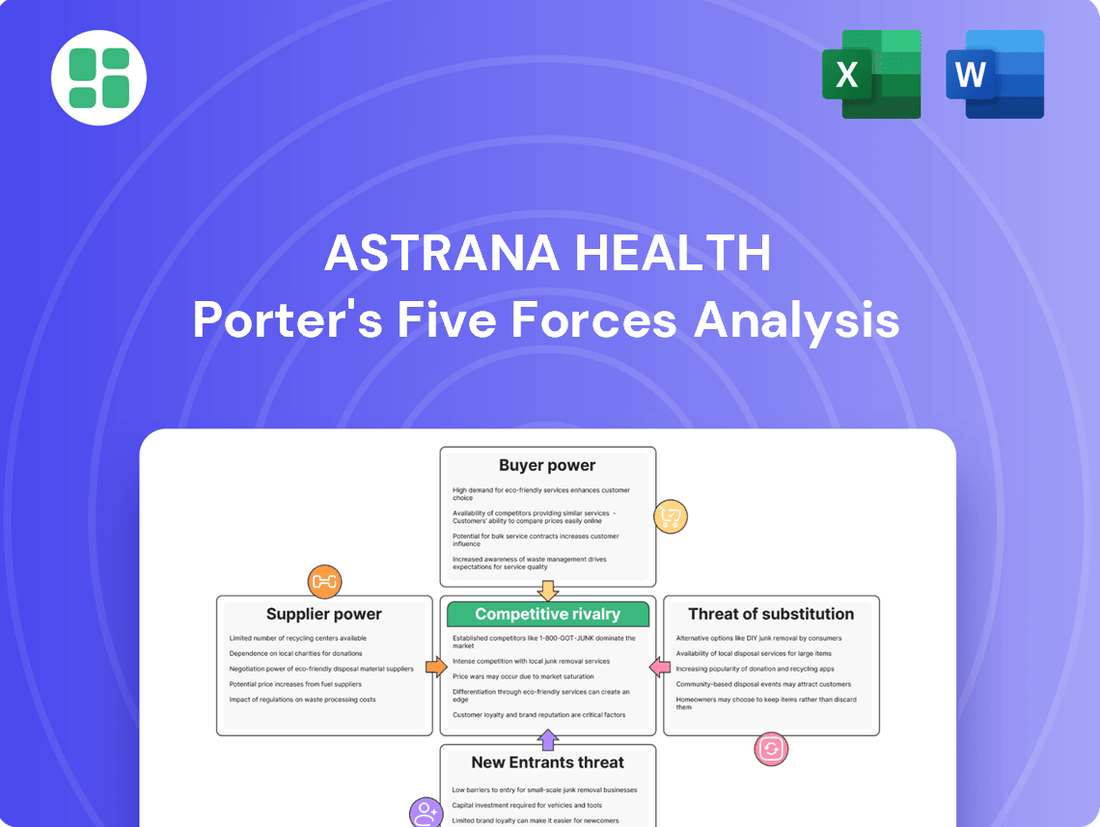
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting Astrana Health, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the healthcare market.
Instantly identify competitive pressures and potential threats with a visually intuitive spider chart, simplifying complex market dynamics for strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Astrana Health's primary customers are large health plans and insurers, like Anthem Blue Cross, with whom they build strategic alliances. These substantial payers hold considerable influence because of their extensive member bases, which allows them to steer patient traffic effectively.
Their ability to negotiate favorable reimbursement rates and contract terms is amplified by the industry's growing emphasis on value-based care. For instance, in 2024, major health insurers continued to leverage their market share, with some reporting billions in revenue, giving them leverage in rate negotiations with providers.
While individual patients may not wield significant direct bargaining power, their collective ability to select from various healthcare providers in competitive markets significantly shapes Astrana Health's strategies for attracting and keeping patients. For instance, in 2024, patient satisfaction scores and provider network breadth were key differentiators cited by consumers when choosing health plans.
Patients today are actively looking for healthcare that is not only high in quality but also convenient and reasonably priced. This trend puts pressure on providers like Astrana to innovate and offer more patient-centric solutions. In 2023, patient surveys indicated a strong preference for telehealth options and transparent pricing, influencing provider selection.
Astrana Health's emphasis on coordinated care pathways and demonstrable positive patient outcomes is a direct response to this evolving consumer demand. By focusing on delivering superior value and experience, Astrana aims to build loyalty and attract a larger patient base, thereby mitigating some of the latent bargaining power of the customer segment.
Large employers, acting as indirect customers for health benefit providers like Astrana Health, wield considerable bargaining power. In 2024, employers continued to prioritize cost containment and value-driven healthcare for their employees, pushing insurers and providers to offer more competitive pricing and demonstrable health improvements.
The ability of these large organizations to choose different health benefit administrators or even engage in direct contracting with healthcare providers significantly strengthens their negotiating position. This flexibility allows them to seek out the most cost-effective and outcome-oriented solutions for their workforce, putting pressure on Astrana to remain competitive.
Government Programs (Medicare, Medicaid)
Government programs like Medicare and Medicaid hold significant sway over Astrana Health. These payers manage a large number of Astrana's patients, giving them considerable leverage in setting reimbursement rates and enforcing regulations. Astrana's increasing focus on Medicare patients directly exposes it to the financial and operational impacts of these government entities.
- Medicare and Medicaid represent a significant portion of managed patient lives for Astrana Health.
- These government payers possess substantial bargaining power, influencing reimbursement rates and regulatory frameworks.
- Astrana's growth in managing Medicare patients increases its reliance on and exposure to the policies of these powerful entities.
Shift to Value-Based Care Models
The healthcare industry's pivot to value-based care (VBC) significantly bolsters customer bargaining power, particularly for payers. By linking payments to patient outcomes, quality indicators, and cost-effectiveness, VBC models allow customers to demand greater accountability and demonstrable value from providers like Astrana Health. For instance, in 2024, many health plans are intensifying their focus on VBC arrangements, with a reported increase in the number of providers participating in risk-based contracts aimed at improving quality and reducing overall healthcare spending.
Astrana Health's strategic embrace of VBC means its revenue and profitability are directly tied to its performance against these customer-defined metrics. This creates a scenario where payers can leverage Astrana's need to meet these targets to negotiate more favorable terms or demand specific service enhancements. The success of VBC initiatives, often measured by metrics such as readmission rates, patient satisfaction scores, and adherence to preventative care guidelines, directly influences Astrana's financial standing, thus amplifying customer influence.
- Increased Leverage for Payers: VBC shifts power to customers by tying reimbursement to performance outcomes, giving them more control.
- Astrana's Performance Dependency: Astrana's financial success is now directly linked to meeting VBC targets set by its customers.
- Demand for Accountability: Customers can more effectively demand higher quality, better patient results, and cost efficiencies under VBC.
- Market Trends: In 2024, a growing percentage of healthcare payments are flowing through VBC models, underscoring the trend's impact on customer power.
Astrana Health faces significant customer bargaining power, primarily from large health plans and government payers like Medicare and Medicaid. These entities, representing millions of lives, can dictate reimbursement rates and contract terms, especially with the industry's shift towards value-based care. In 2024, major health insurers continued to report substantial revenues, reinforcing their negotiating leverage.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | 2024 Impact Example |
|---|---|---|
| Health Plans/Insurers | Large member bases, ability to steer patients, value-based care emphasis | Insurers leverage market share for favorable reimbursement rates. |
| Government Payers (Medicare/Medicaid) | Significant patient volume, regulatory control | Astrana's reliance on Medicare patients exposes it to payment rate changes. |
| Large Employers | Focus on cost containment, direct contracting options | Employers push for competitive pricing and demonstrable health outcomes. |
Same Document Delivered
Astrana Health Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Astrana Health Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing a detailed examination of competitive forces within the healthcare industry. You are viewing the exact document you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring transparency and no hidden surprises. This professionally formatted analysis is ready for immediate download and use, offering actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The U.S. healthcare services market is seeing significant consolidation, with large integrated delivery networks and managed care organizations actively expanding. This trend heightens competition for both patients and healthcare providers, as Astrana Health contends with rivals growing in size and market share, leading to a more concentrated competitive environment.
The competition to provide top-tier value-based care is intense. Companies are constantly innovating to capture market share by offering better patient outcomes and cost efficiencies.
Astrana Health stands out with its unique approach, emphasizing a provider-centric model bolstered by advanced technology and a strong focus on coordinated patient journeys. This strategy aims to streamline care delivery and improve overall patient satisfaction.
Competitors are responding by developing comparable or even more sophisticated solutions. These often include enhanced data analytics platforms, comprehensive care management programs, and tools designed to empower physicians, all aimed at achieving similar value-based care objectives.
Health insurers are increasingly blurring the lines by acquiring or developing their own provider networks. This vertical integration directly challenges Astrana Health by creating new competitors focused on controlling the entire healthcare value chain and managing costs proactively.
For instance, UnitedHealth Group's Optum segment, a major health insurer, has been aggressively expanding its physician group and ambulatory care centers. By 2024, Optum reported serving over 100 million people, demonstrating the scale of this integrated approach and the competitive pressure it exerts on traditional providers like Astrana Health.
Local and Regional Market Dynamics
While Astrana Health operates nationally, its competitive landscape is often defined by intense local and regional rivalries. Established physician groups and smaller community healthcare systems leverage deep community roots and existing patient relationships, presenting significant challenges. For instance, in 2024, Astrana's expansion into markets like Florida and Texas meant confronting well-entrenched regional players who command strong patient loyalty.
These local competitors, including Independent Practice Associations (IPAs), frequently offer specialized services or a more personalized patient experience that can be difficult for larger, more diversified organizations to replicate. Their agility allows them to adapt quickly to local healthcare needs and regulatory changes, a key factor in maintaining market share against national providers.
- Intense Local Competition: Astrana faces significant challenges from established local physician groups and community healthcare systems.
- Community Ties: These local entities benefit from strong community relationships and existing patient bases.
- Regional Expansion Challenges: Astrana's growth into new states, such as Florida and Texas in 2024, involves navigating diverse and often highly competitive regional markets.
- IPA Threat: Independent Practice Associations (IPAs) pose a competitive threat due to their localized focus and patient-centric approach.
Focus on Patient Acquisition and Retention
Competitive rivalry in the healthcare sector, including for Astrana Health, centers heavily on acquiring and keeping patients. This means providers are constantly vying to offer better quality care, easier access to services, and a more positive overall patient experience. For instance, in 2023, patient satisfaction scores became a key differentiator, with leading health systems reporting patient retention rates above 90% based on positive feedback.
Companies compete by focusing on tangible benefits like improved clinical outcomes and the sheer variety of services available within their networks. Astrana's strategic approach, including its recent clinic expansions and key partnerships, directly addresses this rivalry by aiming to broaden patient access and solidify its market position.
- Patient Acquisition: Focus on demonstrating superior quality and accessibility.
- Patient Retention: Driven by patient satisfaction and positive clinical outcomes.
- Competitive Factors: Breadth of services, network strength, and patient experience.
- Astrana's Strategy: Clinic expansions and partnerships enhance patient access and competitive standing.
The competitive landscape for Astrana Health is characterized by intense rivalry, particularly from large, integrated healthcare systems and health insurers expanding into direct care provision. This dynamic is driven by the pursuit of value-based care models, where quality outcomes and cost efficiency are paramount. For example, by the end of 2023, major health insurers were increasingly investing in their own provider networks, aiming to control the entire patient journey and associated costs.
Astrana Health faces significant competition from established regional players and Independent Practice Associations (IPAs) that benefit from strong community ties and patient loyalty. These local competitors often provide a more personalized patient experience, posing a challenge to larger, national organizations. Astrana’s expansion into markets like Florida and Texas in 2024 directly encounters these entrenched regional rivals.
The drive to attract and retain patients fuels much of this rivalry. Providers are differentiating themselves through superior clinical outcomes, enhanced accessibility, and overall patient satisfaction. In 2023, patient satisfaction scores emerged as a critical factor, with leading providers reporting patient retention rates exceeding 90% due to positive patient feedback.
| Competitive Factor | Astrana Health's Response | Key Competitor Example (2024) | Market Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value-Based Care Innovation | Provider-centric model with advanced technology | UnitedHealth Group (Optum) - Expanding physician groups | Increased pressure for outcome-driven solutions |
| Local Market Dominance | National presence with regional expansion | Well-entrenched regional healthcare systems | Challenges patient acquisition and retention |
| Patient Experience & Outcomes | Focus on coordinated patient journeys | IPAs offering personalized care | Drives competition on satisfaction and loyalty |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The burgeoning telehealth and digital health sector poses a substantial threat of substitutes for Astrana Health. These platforms offer convenient virtual consultations and remote monitoring, allowing patients to bypass traditional in-person care for many conditions. For instance, by mid-2024, telehealth utilization remained significantly elevated compared to pre-pandemic levels, with some studies indicating over 30% of patient visits occurring virtually in certain specialties. This accessibility directly competes with Astrana's brick-and-mortar facilities and integrated care approach.
Retail clinics and urgent care centers present a significant threat of substitution for Astrana Health's core services. These accessible, walk-in options, often found in pharmacies or standalone facilities, cater to immediate, non-emergency medical needs. For instance, in 2024, the number of retail clinics in the US was projected to reach over 2,800, offering a convenient alternative for common ailments like flu symptoms or minor injuries.
This convenience and speed can draw patients away from Astrana's primary care physicians, especially for episodic care. The lower overhead and streamlined processes of these substitutes can also translate into more competitive pricing, further incentivizing patients to choose them over traditional healthcare providers for certain services.
The traditional fee-for-service (FFS) healthcare model continues to pose a significant threat of substitution for Astrana Health. Many patients and providers still prefer the familiar FFS structure, where payment is tied to specific services rendered, rather than the newer value-based care arrangements. This preference can slow the adoption of Astrana's integrated or value-driven offerings.
In 2024, the healthcare industry is still navigating this transition. While value-based care models are gaining traction, a substantial portion of healthcare spending, estimated to be around 60-70% in some analyses, still operates under FFS principles. This means a large market segment can easily opt for FFS providers, bypassing Astrana's potentially more complex, outcomes-focused approach.
Self-Care and Wellness Technologies
The rise of self-care and wellness technologies presents a significant threat of substitutes for Astrana Health. Wearable devices, health tracking apps, and readily available online health information empower individuals to manage their well-being proactively. For instance, the global digital health market was valued at approximately $201.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $932.4 billion by 2030, indicating a substantial shift towards self-managed health solutions.
These technologies can serve as direct substitutes for traditional medical interventions, particularly for less severe conditions or routine preventive care. Consumers can monitor vital signs, track fitness, access health advice, and even engage in remote consultations, thereby potentially reducing their reliance on Astrana Health's core services. This trend is further amplified by increasing consumer comfort with technology and a desire for personalized health management.
- Wearable device adoption: In 2024, it's estimated that over 1.1 billion people worldwide will use wearables, a significant portion of whom will utilize them for health monitoring.
- Health app usage: The number of health and fitness apps downloaded globally is expected to exceed 100 billion by the end of 2024, demonstrating widespread engagement with digital health tools.
- Telehealth growth: Telehealth services, often integrated with self-care technologies, saw a surge in usage, with many providers continuing to offer these as convenient alternatives to in-person visits.
- Preventive care focus: A growing consumer emphasis on preventive health means individuals are more likely to adopt technologies that help them avoid illness, potentially bypassing the need for reactive medical care.
Employer-Provided On-Site Health Services
Large employers are increasingly bringing healthcare directly to their workforce. This trend sees companies establishing on-site health clinics or offering direct access to health services, acting as a convenient alternative to traditional external primary care. For instance, in 2024, a significant percentage of Fortune 500 companies either have or are planning to implement on-site health services, aiming to improve employee well-being and manage healthcare costs.
These employer-provided services can directly substitute for the routine health management and primary care services that organizations like Astrana Health offer. By providing convenient, often cost-effective, on-site options, employers can reduce the need for employees to seek care from external providers, potentially impacting patient volume and revenue streams for Astrana Health.
- Growing Adoption: In 2024, an estimated 30% of large US employers offered some form of on-site or near-site health clinic.
- Cost Savings Focus: Employers cite reduced absenteeism and lower overall healthcare expenditures as key drivers for these initiatives.
- Convenience Factor: Employees benefit from immediate access to care, reducing travel time and lost work hours.
- Impact on External Providers: Such services can divert patients away from traditional clinics and coordinated care models.
The accessibility and convenience of telehealth and digital health platforms present a significant threat of substitutes for Astrana Health. These services allow patients to receive care remotely, bypassing traditional in-person visits for many conditions. By mid-2024, telehealth utilization remained substantially higher than pre-pandemic levels, with some estimates suggesting over 30% of patient visits were virtual in certain medical specialties, directly competing with Astrana's established care models.
Retail clinics and urgent care centers offer a strong substitute for Astrana Health's core services by providing quick, walk-in access for non-emergency needs. With over 2,800 retail clinics projected in the US in 2024, these convenient locations cater to common ailments, drawing patients away from traditional primary care for episodic needs. Their lower overhead can also translate to more competitive pricing.
Self-care technologies, including wearables and health apps, empower individuals to manage their wellness proactively, acting as substitutes for traditional medical interventions. The global digital health market, valued at approximately $201.4 billion in 2023, is expected to grow substantially, reflecting a consumer shift towards self-managed health. By the end of 2024, over 1.1 billion people globally are anticipated to use wearables for health monitoring, with more than 100 billion health and fitness app downloads expected.
Large employers increasingly offer on-site or near-site health clinics, directly substituting for external primary care services. In 2024, a considerable percentage of Fortune 500 companies are implementing these services to enhance employee well-being and control costs. This trend means around 30% of large US employers offer such clinics, diverting patients from providers like Astrana Health and impacting their patient volume.
| Substitute Type | 2024 Market/Adoption Data | Impact on Astrana Health |
|---|---|---|
| Telehealth | >30% of visits virtual in some specialties | Bypasses in-person care, reduces reliance on brick-and-mortar facilities |
| Retail/Urgent Care Clinics | >2,800 clinics projected in US | Offers convenient, lower-cost alternatives for episodic care |
| Self-Care Tech (Wearables/Apps) | 1.1 billion+ wearable users globally; >100 billion app downloads | Empowers proactive health management, reduces need for reactive medical care |
| Employer On-site Clinics | ~30% of large US employers offer clinics | Directly substitutes primary care, diverts patient volume |
Entrants Threaten
The integrated healthcare services and management market demands a considerable financial outlay. New players need substantial capital to build out broad networks of healthcare providers, create advanced technology systems for managing patient data and operations, and establish the physical infrastructure for delivering care. Astrana Health's own strategic moves, like its significant investments in partnerships and acquisitions, highlight just how high these entry barriers are.
The U.S. healthcare sector presents a formidable barrier to new entrants due to its exceptionally complex regulatory framework. Navigating the labyrinth of licensing requirements, adhering to stringent privacy mandates like HIPAA, and keeping pace with ever-changing federal and state healthcare policies demands substantial expertise and resources.
For instance, in 2024, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) continued to update reimbursement policies and quality reporting requirements, adding layers of complexity for any new provider seeking to operate. The cost of ensuring full compliance can be prohibitive, effectively deterring many potential competitors from entering the market.
The threat of new entrants for Astrana Health is significantly mitigated by the sheer difficulty in establishing and maintaining an extensive network of primary care physicians, specialists, and ancillary service providers. This network is a foundational asset, requiring substantial time and investment to cultivate. For instance, in 2024, building such a comprehensive web of relationships across diverse healthcare sectors remains a considerable barrier to entry for any new player aiming to compete with Astrana's established provider base.
Need for Established Payer Relationships
New companies entering the healthcare market face a significant hurdle in building relationships with established payers. Securing contracts with major health plans and government entities is absolutely vital for consistent revenue. Astrana Health's success is partly due to its existing, strong ties with insurers like Anthem Blue Cross, which new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly.
These established payer relationships represent a substantial barrier to entry. For instance, in 2024, the average time for a new provider to be credentialed and begin receiving payments from a major payer could extend to several months, impacting cash flow significantly. This process involves extensive vetting and negotiation, making it a time-consuming and resource-intensive undertaking for newcomers.
- Difficulty in Securing Payer Contracts: New entrants must navigate complex credentialing processes and lengthy contract negotiations with health insurance companies.
- Time and Resource Intensive: Establishing trust and obtaining favorable terms from payers requires significant investment in legal, administrative, and sales resources.
- Impact on Revenue: Without established payer relationships, new companies may face delayed or reduced reimbursement, hindering their ability to scale and compete.
- Astrana's Advantage: Astrana Health's existing partnerships provide a critical competitive edge, allowing for more predictable revenue streams and market access.
Proprietary Technology and Data Accumulation
Astrana Health's proprietary population health management and healthcare delivery platform, coupled with its AI-powered solutions, creates a significant hurdle for new entrants. The sheer investment required to replicate this advanced technological infrastructure and gather the extensive patient data needed for effective analytics and value-based care models is substantial.
Developing or acquiring comparable technology and accumulating the vast datasets essential for robust population health analytics and successful value-based care implementation are high barriers. This technological and data-centric advantage makes it challenging for new players to compete effectively.
- Technological Sophistication: Astrana's platform integrates advanced AI, requiring significant R&D investment and expertise to match.
- Data Moat: The accumulation of vast, proprietary patient data is critical for effective population health insights and presents a long-term development challenge for newcomers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex healthcare regulations for data handling and AI implementation adds another layer of difficulty for potential entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Astrana Health is considerably low due to the immense capital required to establish a comprehensive healthcare network and advanced technological infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, the cost of building out integrated care systems and securing robust data analytics capabilities remains a significant deterrent.
Navigating the complex U.S. healthcare regulatory landscape, including stringent privacy laws and evolving reimbursement policies, presents a substantial barrier. In 2024, compliance costs associated with updated CMS regulations alone can be prohibitive for nascent companies.
Astrana Health's established relationships with major health insurers, which can take years and considerable effort to build and maintain, act as a strong moat. Securing favorable payer contracts in 2024 still involves lengthy credentialing processes, often taking months, which new entrants find difficult to overcome quickly.
The technological sophistication of Astrana's population health management platform, powered by AI, and its accumulated proprietary patient data create a high entry barrier. Replicating this data moat and advanced analytical capabilities requires substantial, long-term investment in research and development.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024 Impact Example |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building extensive provider networks and technology systems. | Multi-million dollar investments needed for infrastructure. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Navigating HIPAA, licensing, and evolving healthcare policies. | Increased compliance costs due to updated CMS quality reporting. |
| Payer Relationships | Securing contracts with health insurance companies. | Credentialing and payment cycles averaging 6-9 months for new providers. |
| Technological & Data Assets | Developing advanced AI platforms and accumulating patient data. | Significant R&D spend required to match Astrana's data analytics capabilities. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Astrana Health Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and regulatory filings from healthcare bodies. We also incorporate insights from trade publications and expert commentary to capture the nuances of the healthcare landscape.