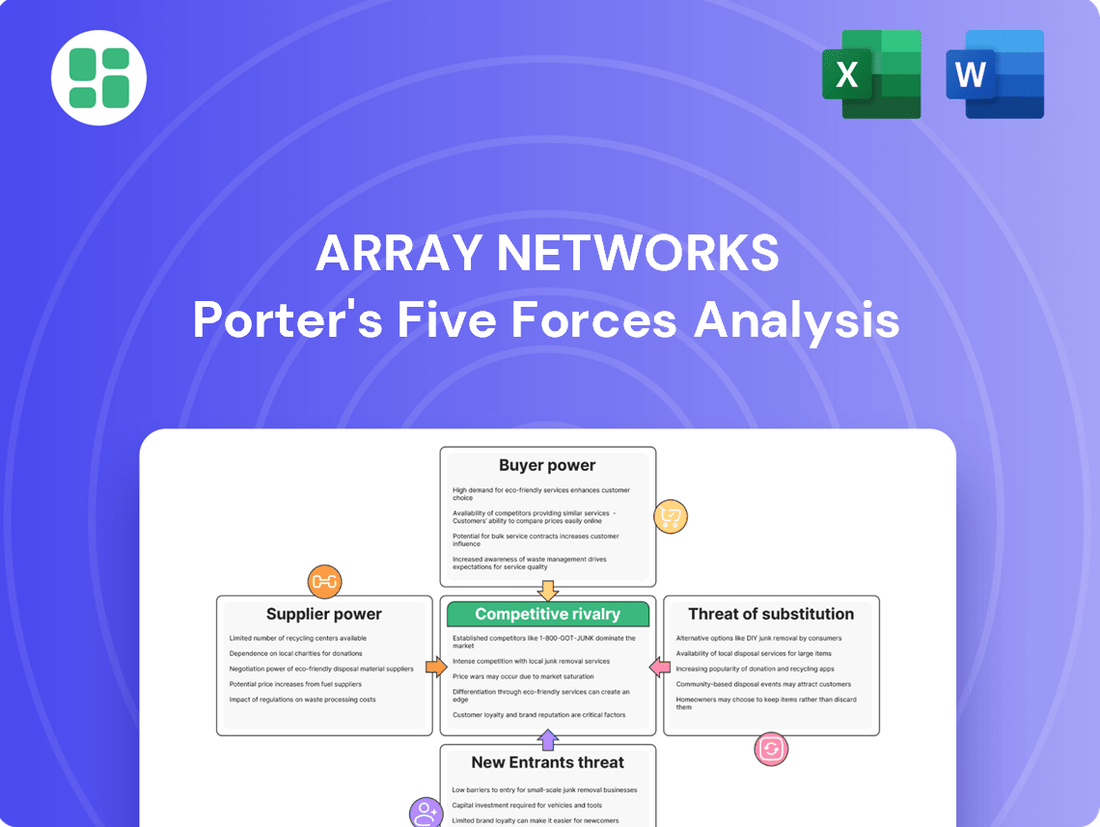
Array Networks Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Array Networks Bundle
Array Networks operates in a dynamic market shaped by intense rivalry and significant buyer power, as customers often have numerous alternatives for application delivery and security solutions. The threat of substitutes is also a key consideration, with evolving technologies constantly presenting new ways to achieve similar business outcomes.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Array Networks’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The specialized nature of networking hardware components, particularly for high-performance application delivery controllers and secure access gateways, means Array Networks likely relies on a limited number of specialized component manufacturers. This concentration can give these suppliers significant leverage over pricing and supply, especially for proprietary chips or critical software modules essential for Array's unique product features.
Any disruption or price increase from these key suppliers could directly impact Array's production costs and profit margins. For instance, in the semiconductor industry, lead times for advanced chips can extend for months, and shortages, like those experienced in 2021-2022 impacting many tech companies, can significantly delay product availability and increase costs.
High switching costs for Array Networks significantly bolster the bargaining power of its suppliers. For instance, the networking hardware industry often sees substantial expenses associated with changing vendors, encompassing product redesign, component re-certification, and manufacturing process re-optimization. These intricate transitions can cost millions in development and testing, making a shift to a new supplier a considerable financial and operational hurdle.
Array Networks might face significant supplier power if key component providers possess proprietary technology. For instance, a supplier with unique ASIC designs for network acceleration or specialized security firmware could command higher prices. This is because replicating such advanced technology would require substantial R&D investment and time for Array Networks, making them reliant on the existing supplier.
Potential for Forward Integration by Suppliers
While not a frequent occurrence, major, diversified technology component suppliers possess the theoretical capability to integrate forward into the application delivery networking sector, thereby directly challenging companies like Array Networks. This potential, even with its significant entry barriers, can subtly bolster a supplier's leverage in price and term negotiations.
The threat of a supplier transitioning into a direct competitor, even if unlikely, grants them increased bargaining power. For instance, if a key semiconductor manufacturer supplying essential components for application delivery controllers (ADCs) were to consider developing its own ADC solutions, it could leverage this potential to negotiate more favorable terms for its existing component sales to companies like Array Networks. This strategic consideration is crucial for Array Networks in managing its supply chain relationships.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: Large, diversified tech component suppliers could potentially enter the ADC market, directly competing with Array Networks.
- Barrier to Entry: Significant capital and expertise are required for such a move, making it a less common threat.
- Increased Bargaining Power: The mere possibility of forward integration empowers suppliers to negotiate better pricing and terms for their components.
- Strategic Consideration for Array Networks: This potential threat necessitates careful management of supplier relationships and supply chain diversification.
Impact of Global Supply Chain Dynamics
The bargaining power of suppliers for Array Networks is significantly influenced by global supply chain dynamics. Geopolitical events, natural disasters, and economic instability can disrupt the availability and price of critical electronic components. For instance, in 2024, ongoing trade tensions and localized conflicts continued to create uncertainty in the semiconductor market, a key input for networking hardware.
This reliance on a global network means suppliers can wield considerable power, especially when resources are scarce or market conditions drive up costs. Array Networks, like many in the industry, must navigate these external factors that can directly impact their cost of goods sold and production schedules. A shortage of specific microchips, for example, could force Array to accept higher prices or face production delays.
- Geopolitical Risks: Trade disputes and regional conflicts in 2024 continued to impact component sourcing, potentially leading to increased costs for Array Networks.
- Natural Disasters: Events like typhoons or earthquakes in manufacturing hubs can halt production, limiting supply and giving suppliers leverage.
- Economic Fluctuations: Inflationary pressures and currency exchange rate volatility in 2024 directly affected the cost of raw materials and manufactured components.
- Component Scarcity: Persistent demand for advanced semiconductors in 2024, driven by AI and other technologies, meant that suppliers of these critical parts held significant pricing power.
The bargaining power of Array Networks' suppliers is heightened by the specialized nature of their components and the significant costs associated with switching vendors. For instance, the reliance on proprietary technology, such as unique ASIC designs for network acceleration, grants suppliers considerable leverage. This dependence means Array Networks faces substantial R&D investment and time if they were to seek alternative solutions, making them vulnerable to price increases or supply disruptions from these key providers.
Global supply chain volatility, particularly in the semiconductor sector, further amplifies supplier power. In 2024, ongoing trade tensions and localized conflicts continued to create uncertainty, impacting component availability and pricing. For example, persistent high demand for advanced semiconductors, fueled by AI advancements, meant that suppliers of these critical parts held significant pricing power, directly affecting Array Networks' cost of goods sold.
| Factor | Impact on Array Networks | Supporting Data/Example (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Component Specialization | Increased reliance on few suppliers | Proprietary ASICs for network acceleration |
| Switching Costs | High barriers to changing vendors | Millions in redesign, re-certification, and re-optimization |
| Supplier Forward Integration Threat | Potential for direct competition | Theoretical capability of large tech component suppliers |
| Global Supply Chain Disruptions | Price volatility and availability issues | Trade tensions and localized conflicts impacting semiconductor markets |
| Component Scarcity | Supplier pricing power | High demand for advanced semiconductors in 2024 |
What is included in the product
This analysis examines Array Networks' competitive environment by dissecting the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, all within the context of the application delivery and security market.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic, visual representation of all five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Array Networks benefits from a wide array of clients, ranging from major corporations in banking and telecommunications to smaller businesses across sectors like BFSI, IT, government, and healthcare. This diversity means no single customer holds significant sway over Array's revenue streams, thereby limiting the bargaining power of individual customers.
For enterprise clients, integrating Array Networks' application delivery controllers and secure access solutions into their complex IT environments often requires substantial upfront investment. This includes costs associated with deployment, intricate configuration processes, and comprehensive staff training to manage these critical systems effectively.
The sheer complexity and vital role of these networking solutions mean that migrating to a rival's offering can trigger significant financial outlays and operational disruptions. These high switching costs effectively diminish a customer's inclination to change vendors, thereby curtailing their bargaining leverage.
Array Networks' solutions are vital for ensuring enterprise applications run smoothly and securely, making them indispensable for businesses. This criticality means customers often prioritize performance and reliability over cost, giving Array a stronger hand in pricing negotiations.
Availability of Competitors and Alternatives
Customers of Array Networks face a competitive market for Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) and secure access solutions. Even with potentially high switching costs, buyers can choose from numerous alternatives. This is a significant factor influencing their bargaining power.
Established vendors like F5 Networks, NetScaler (part of Citrix's portfolio), Fortinet, and A10 Networks offer comparable solutions. Furthermore, the rise of cloud-native alternatives provides even more options for customers seeking to manage their network traffic and security. This broad availability means customers can readily compare features, performance, and pricing across different providers.
- Competitive Landscape: Array Networks operates in a market with strong incumbents and emerging cloud-native players, increasing customer choice.
- Customer Options: Buyers can select from a range of ADCs and secure access solutions, limiting vendor lock-in.
- Pricing Pressure: The availability of alternatives allows customers to negotiate pricing, potentially impacting Array's profit margins if differentiation is weak.
- Feature Comparison: Customers can easily compare Array's offerings against competitors, demanding specific features and performance levels.
Customer Demand for Integrated Solutions
Customers are increasingly looking for all-in-one solutions for application delivery and security, moving away from buying separate tools. This trend is particularly strong as businesses adopt hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, requiring seamless integration.
This demand for unified platforms gives customers more power. They can lean towards vendors like Array Networks if their integrated offerings are seen as more advanced or easier to manage. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that 78% of enterprises consider integrated security and networking solutions a top priority for their cloud migration efforts.
- Integrated Solutions Demand: Businesses prioritize comprehensive platforms over individual products for application delivery and security.
- Cloud Migration Impact: The shift to hybrid and multi-cloud environments amplifies the need for seamless, unified functionalities.
- Customer Leverage: Strong integration capabilities empower customers, allowing them to negotiate better terms with vendors like Array Networks.
- Market Trend: In 2024, a significant majority of enterprises identified integrated solutions as crucial for successful cloud adoption.
While Array Networks benefits from a diverse customer base, the bargaining power of customers is moderated by several factors. High switching costs associated with integrating their complex solutions, coupled with the critical nature of these services for business operations, limit customers' ability to easily change vendors. However, the competitive market for ADCs and secure access solutions, including emerging cloud-native alternatives, provides customers with choices and the ability to negotiate pricing, especially when seeking integrated solutions. A 2024 survey highlighted that 65% of businesses consider vendor lock-in a significant concern when evaluating network infrastructure, underscoring the customer's desire for flexibility.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Array Networks' Position |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Diversity | Lowers individual customer power | Array serves a broad range of clients |
| Switching Costs | Lowers customer power | High integration and training costs deter switching |
| Competitive Alternatives | Increases customer power | Numerous established and cloud-native competitors exist |
| Demand for Integrated Solutions | Increases customer power | Customers seek unified platforms, influencing vendor choice |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Array Networks Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Array Networks Porter's Five Forces analysis, detailing competitive rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. You can trust that this in-depth strategic assessment will equip you with actionable insights into Array Networks' competitive landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The application delivery networking (ADN) and secure access gateway markets are incredibly crowded. Array Networks operates in a space with over 1,000 active competitors worldwide. This intense competition comes from both large, established companies and smaller, specialized firms.
Major rivals such as F5 Networks, NetScaler (Citrix), Fortinet, A10 Networks, and Palo Alto Networks exert significant pressure. This crowded landscape means Array Networks must constantly innovate and find ways to stand out to maintain its market position and attract customers.
The sheer volume of competitors directly fuels price wars. Array Networks and its peers are often compelled to offer competitive pricing to win deals, which can impact profit margins. Differentiation through advanced features, superior performance, or specialized solutions becomes crucial for survival and growth in this environment.
The Application Delivery Controller (ADC) and Secure Web Gateway (SWG) markets are booming, with projections showing CAGRs of 8.98% and 20.5% respectively from 2025. This robust expansion naturally draws in new entrants and spurs existing companies to fight harder for market share. Expect intensified competition through aggressive marketing, accelerated product innovation, and competitive pricing tactics as players vie for dominance.
This dynamic environment, however, also presents a silver lining. The swift shift towards cloud-native and software-defined architectures opens doors for nimble companies like Array Networks. These evolving market demands allow agile players to carve out new niches and capitalize on emerging opportunities, potentially gaining an edge over slower-moving incumbents.
Array Networks carves out its niche by concentrating on application delivery controllers (ADCs), secure access gateways, and virtual application delivery platforms, highlighting performance, security, and uptime. However, the competitive landscape is fierce, with rivals offering robust solutions that often incorporate specialized capabilities like AI-powered threat detection or advanced zero-trust security models.
Maintaining a competitive edge necessitates ongoing innovation and a clear articulation of Array's distinct value proposition. For instance, while Array focuses on core ADC functionalities, competitors might emphasize broader network security suites. In 2023, the global ADC market was valued at approximately $5.5 billion, and sustained differentiation is key to capturing market share in this dynamic sector.
High Exit Barriers
High exit barriers significantly influence competitive rivalry. The substantial capital required for ongoing research and development, coupled with specialized hardware manufacturing processes, makes it difficult for firms to leave the market. For instance, companies heavily invested in proprietary network function virtualization (NFV) infrastructure may find it uneconomical to divest.
Established customer relationships and long-term contracts further cement these barriers. Once a customer integrates a vendor's solutions, switching costs can be prohibitive, encouraging existing players to persevere even during periods of lower profitability. This persistence intensifies competition, as even struggling entities remain active market participants.
These high exit barriers mean that Array Networks faces a market where competitors are less likely to cease operations, contributing to potential oversupply. This sustained competitive pressure can limit Array Networks' ability to raise prices or gain substantial market share, as existing players fight to maintain their positions.
- Significant R&D Investment: Companies in the network infrastructure space, like those Array Networks competes with, often invest heavily in R&D. For example, in 2023, major players in the broader networking equipment market saw R&D expenses ranging from 10% to 20% of their revenue.
- Specialized Manufacturing: The production of advanced networking hardware requires specialized facilities and expertise, representing a sunk cost that discourages exit.
- Customer Lock-in: Long-term contracts and the complexity of integrating network solutions create high switching costs for customers, making it difficult for new entrants and encouraging incumbents to stay.
- Market Persistence: The combination of these factors leads to a situation where even underperforming companies remain in the market, intensifying rivalry and potentially suppressing pricing power for all participants.
Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions
Competitive rivalry is heightened as major players pursue strategic partnerships and acquisitions to broaden their offerings and market presence. A prime example is Hewlett Packard Enterprise's (HPE) acquisition of Juniper Networks, announced in July 2025, a move designed to bolster HPE's AI-native networking capabilities. While Array Networks also engages in partnerships, this trend of consolidation among larger entities can intensify competition.
These larger-scale integrations create more comprehensive solutions and expand the operational scale of competitors. This dynamic can directly impact Array Networks' competitive standing by presenting customers with more integrated and potentially larger-scale alternatives, thereby increasing the pressure on Array to differentiate its own solutions and market approach.
- HPE's acquisition of Juniper Networks in July 2025 aims to enhance AI-native networking.
- Consolidation among larger competitors intensifies rivalry.
- Expanded portfolios and market reach of acquired entities pose a challenge.
- Array Networks must adapt to increased scale and integrated offerings from rivals.
The competitive landscape for Array Networks is extremely intense, with over 1,000 global competitors in the application delivery networking and secure access gateway markets. Major players like F5 Networks and Fortinet drive this rivalry, forcing Array to continuously innovate and differentiate its offerings. The market, projected for robust growth with CAGRs of 8.98% for ADCs and 20.5% for SWGs from 2025, attracts new entrants and intensifies existing competition through aggressive pricing and product development.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (Approx.) | Key Offerings |
|---|---|---|
| F5 Networks | $2.8 billion | Application Delivery Controllers, Security Solutions |
| Fortinet | $5.5 billion | Firewalls, Secure Access Gateways, Network Security |
| A10 Networks | $370 million | Application Delivery Controllers, DDoS Protection |
| Palo Alto Networks | $6.8 billion | Next-Generation Firewalls, Cloud Security |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing adoption of cloud-native application delivery solutions presents a significant threat of substitutes for Array Networks. These solutions, often integrated within cloud platforms, offer functionalities like load balancing and web application firewalls, directly competing with Array's traditional offerings.
Major cloud service providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, provide these integrated services as part of their core offerings. For instance, AWS's Elastic Load Balancing and Azure's Application Gateway offer scalable and managed application delivery, making them attractive alternatives for organizations migrating to or operating within these cloud ecosystems.
This shift towards cloud-native architectures means that businesses increasingly view these CSP-provided services as a viable, and often simpler, substitute for dedicated hardware or virtual appliances from vendors like Array Networks, especially for new deployments or cloud-centric strategies.
The increasing adoption of managed security and networking services presents a significant threat of substitutes for companies like Array Networks. Many businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), are choosing to outsource their application delivery and security infrastructure management to third-party providers.
This shift allows companies to avoid the capital expenditure and operational complexity associated with owning and managing their own solutions. For instance, a 2024 market report indicated that the global managed security services market was projected to reach over $60 billion, highlighting the strong demand for these outsourced solutions.
By entrusting these critical functions to specialists, businesses can reduce their reliance on direct product purchases and in-house deployment of technologies that Array Networks offers, effectively substituting the need for Array's hardware and software solutions.
The rise of powerful open-source solutions for load balancing, proxying, and firewalls presents a significant threat. These software-based alternatives allow organizations to achieve similar functionalities without relying on specialized hardware.
The increasing adoption of software-defined networking (SDN) and network functions virtualization (NFV) further amplifies this threat. While Array Networks provides virtual appliances, the fundamental shift towards software-defined infrastructure means companies can assemble comparable network capabilities using potentially more affordable and less proprietary software components, directly challenging the appeal of hardware-focused offerings.
Built-in Cloud Provider Features
Major cloud providers, including AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, are increasingly offering their own integrated application delivery and security features. These native services, such as AWS Elastic Load Balancing or Azure Application Gateway, can fulfill many of the functions typically provided by third-party Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs). This presents a significant threat of substitutes for companies like Array Networks, especially for organizations heavily reliant on cloud infrastructure.
For cloud-native businesses, these built-in features often represent a more cost-effective and streamlined solution. For instance, in 2024, many enterprises are opting for managed cloud services to simplify their IT operations. The convenience and potential cost savings of using native cloud provider offerings directly compete with the need for specialized, third-party ADCs, thereby diminishing the perceived value of Array Networks' solutions within these environments.
The threat is amplified as cloud providers continuously enhance their native security and performance capabilities. This ongoing development means that the functionality gap between native services and third-party solutions is narrowing. Organizations can leverage these evolving cloud-native tools, such as advanced WAF capabilities or serverless load balancing, reducing their reliance on external vendors and creating a powerful substitute.
Key substitute offerings from major cloud providers include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Elastic Load Balancing (ELB), AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF), AWS Shield.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure Application Gateway, Azure Front Door, Azure Firewall.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Cloud Load Balancing, Cloud Armor, VPC Firewall.
Shift to Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
The cybersecurity landscape is rapidly evolving, with a significant trend towards Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA). This new approach fundamentally alters how secure access is managed, moving away from older VPN and perimeter-focused security models. For instance, Gartner predicted that by 2025, 70% of new remote access VPN purchases would be replaced by ZTNA solutions.
While Array Networks provides SSL VPN solutions and is adapting to zero-trust principles, a widespread enterprise adoption of ZTNA could diminish the demand for their traditional secure access gateways. This shift represents a potent substitute threat, potentially impacting the market share of Array's legacy products as organizations prioritize more granular, identity-centric access controls.
- ZTNA adoption is accelerating across industries.
- Traditional VPNs are increasingly viewed as less secure than ZTNA.
- ZTNA offers granular access control, reducing reliance on network perimeters.
- Array Networks faces a threat if its ZTNA transition lags behind market demand.
The growing prevalence of cloud-native application delivery solutions, often built directly into major cloud platforms like AWS and Azure, presents a substantial threat of substitutes for Array Networks. These integrated services, such as AWS Elastic Load Balancing and Azure Application Gateway, offer comparable functionalities to Array's traditional offerings, especially for businesses prioritizing cloud environments.
Furthermore, the rise of powerful open-source alternatives for load balancing and proxying, coupled with the broader adoption of Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Functions Virtualization (NFV), allows organizations to construct similar capabilities using more flexible and potentially cost-effective software components. This trend directly challenges the necessity of specialized hardware from vendors like Array Networks.
The increasing adoption of Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) solutions also poses a significant substitute threat. As Gartner predicted that by 2025, 70% of new remote access VPN purchases would be replaced by ZTNA, organizations are shifting towards more granular, identity-centric access controls, potentially reducing reliance on traditional secure access gateways offered by Array Networks.
| Substitute Category | Key Players/Technologies | Impact on Array Networks |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud-Native Services | AWS ELB, Azure Application Gateway, GCP Cloud Load Balancing | Direct competition for cloud-centric deployments, offering integrated and potentially lower-cost alternatives. |
| Open-Source Solutions | HAProxy, Nginx, Envoy Proxy | Provides flexible, software-based alternatives that can bypass the need for specialized hardware. |
| ZTNA Solutions | Zscaler, Palo Alto Networks Prisma Access, Netskope | Disrupts traditional secure access gateway markets by offering more granular, identity-aware access. |
Entrants Threaten
The application delivery networking and cybersecurity hardware sectors demand significant upfront capital. Developing sophisticated products like Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) and secure access gateways requires substantial investment in research and development, advanced manufacturing capabilities, and the protection of intellectual property. For instance, the global ADC market was valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating the scale of investment needed to compete.
The high technological complexity of application delivery and security solutions presents a substantial barrier to new entrants. Developing and maintaining these sophisticated systems requires deep expertise in network protocols, cryptography, and distributed systems. For instance, the cybersecurity market, a key area for application delivery, saw significant investment in 2024, with companies actively seeking specialized talent, highlighting the difficulty for newcomers to acquire the necessary skills.
Established players like Array Networks have cultivated significant brand recognition and customer trust over many years. This is especially true with large enterprises that demand unwavering reliability and proven performance for their mission-critical applications. For example, in 2024, Gartner recognized Array Networks for its continued innovation in secure application access, reinforcing its established market position.
New entrants would face a substantial challenge in building credibility and trust within this market. When security and continuous availability are paramount, displacing incumbent vendors requires more than just competitive pricing; it demands a demonstrated history of dependable service and robust solutions.
Strong Network Effects and Ecosystems
The networking industry, including players like Array Networks, thrives on strong network effects. A larger installed base attracts more third-party integrations and developer support, creating a virtuous cycle that benefits incumbents. For instance, by mid-2024, major cloud providers reported billions of connected devices, a testament to these deepening network effects.
Array Networks, like its peers, has cultivated a robust ecosystem of partners, distributors, and service providers. This established network is not easily replicated by newcomers, acting as a significant barrier to entry. Such comprehensive support and distribution channels are critical for efficient market reach and customer acquisition.
- Network Effects: A larger installed base enhances value through increased integrations and community knowledge.
- Ecosystem Development: Established firms possess extensive partner, distribution, and professional service networks.
- Barrier to Entry: Replicating these comprehensive ecosystems is a major challenge for new entrants.
- Market Penetration: Incumbents' established networks are vital for sustained growth and market share.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance Requirements
The cybersecurity and networking sector faces significant regulatory scrutiny, with standards like PCI-DSS and ISO 27001 being critical for sensitive industries such as BFSI and government. New companies entering this space must invest heavily in understanding and adhering to these complex compliance requirements. For instance, in 2024, the global cybersecurity market saw continued emphasis on data privacy regulations, increasing the burden on new entrants to ensure product-level compliance from inception.
Navigating this intricate web of regulations adds substantial cost and operational complexity, acting as a formidable barrier for potential new competitors looking to establish a foothold in the market.
- Regulatory Standards: PCI-DSS, ISO 27001, GDPR are key examples.
- Sensitive Sectors: BFSI and Government are particularly impacted.
- Compliance Burden: New entrants face high costs and complexity.
- Market Entry Barrier: Stringent requirements deter new players.
The threat of new entrants in the application delivery networking space, where Array Networks operates, is generally low. This is due to the substantial capital required for R&D and advanced manufacturing, as highlighted by the global ADC market's significant valuation. Furthermore, the high technological complexity necessitates specialized expertise, a challenge compounded by ongoing investment in cybersecurity talent acquisition in 2024.
Established brand recognition and customer trust, reinforced by recognitions like Gartner's in 2024 for Array Networks, create a significant hurdle for newcomers. Building credibility in a sector where reliability is paramount takes time and a proven track record. Network effects, with billions of connected devices reported by major cloud providers by mid-2024, also solidify the position of incumbents.
The extensive partner and distribution ecosystems cultivated by established firms like Array Networks are difficult and costly to replicate, further limiting new entrants. Additionally, stringent regulatory compliance, particularly in sensitive sectors like BFSI, adds considerable cost and complexity, acting as a major barrier to market entry.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Supporting Data (2024/2023) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in R&D, manufacturing, IP protection | Significant financial hurdle | Global ADC Market ~$3.5B (2023) |
| Technological Complexity | Need for deep expertise in networking, security | Requires specialized talent and knowledge | Increased cybersecurity talent investment in 2024 |
| Brand Recognition & Trust | Years of proven performance and reliability | Difficult to displace incumbents | Gartner recognition for Array Networks (2024) |
| Ecosystem & Network Effects | Established partner networks, large installed base | Challenging to replicate and compete | Billions of connected devices by mid-2024 |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to standards like PCI-DSS, ISO 27001 | Adds cost and operational complexity | Emphasis on data privacy regulations in 2024 |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Array Networks leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, financial filings from Array Networks and its competitors, and cybersecurity trade publications. This combination provides a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape, including threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers.